Biology MCQs With Answers For NEET Population Interaction
Question 1. Interaction between individuals of two different species is called
- Interference interaction
- Apparent interaction
- Intraspecific interaction
- Interspecific interaction
Answer: 4. Interspecific interaction
The interspecific interaction arises from the interaction of a population of two different species. They could be beneficial, detrimental, or neutral to one of the species or both.
Question 2. What sort of results can be observed in an interspecific interaction?
- Beneficial
- Detrimental
- Neutral
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
interactions biology
The interspecific interaction arises from the interaction of a population of two different species. They could be beneficial, detrimental, or neutral to one of the species or both.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. An interaction in which both species are neither harmed nor benefitted is called
- Positive interaction
- Negative interaction
- Antagonistic interaction
- Neutral interaction
Answer: 4. Neutral interaction
Different types of interspecific interactions have different effects on the two participants, which may be positive (+), negative (-) or neutral (0). In neutral interaction, both species are neither benefitted nor harmed from the interaction.

NEET Biology Population Interaction MCQs with answers
Question 4. Different types of interactions and the nature of interactions between species a and b are given in columns 1 and 2, respectively. Choose the correct answer from the answer key where they are matched.
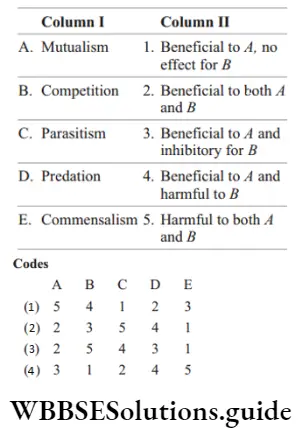
“interactions biology “
Answer: 3. A–2, b–5, c–4, d–3, e–1
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 5. If the ‘+’ sign is assigned to beneficial interaction, the ‘–’ sign to detrimental, and the ‘0’ sign to neutral interaction, then the population interaction represented by ‘+’ ‘–’ refers to
- Mutualism
- Amensalism
- Commensalism
- Parasitism
Answer: 4. Parasitism
- The association of organisms that benefit one of the partners at the expense of the other is called parasitism and is denoted by + −. Commensalism refers to a relationship where one organism benefits, while the other remains unaffected and is denoted by + 0.
- Amensalism refers to the association where one partner is inhibited, while the other remains nearly unaffected and is denoted by – 0. Mutualism is an association of organisms where both are benefitted and is denoted by + +. Thus, the option is correct
Question 6. Predation and parasitism are which type of interactions?
- (+, +)
- (+, 0)
- (–,–)
- (+,–)
Answer: 4. (+,–)
Both predation and parasitism show negative interactions. In negative interaction, one species is harmed (–), while the other is benefitted (+). Predation occurs when members of one species eat those of another species. But not always, this involves the killing of prey. Parasitism is a kind of harmful coaction between two species.

Important MCQs on Population Interaction for NEET
Question 7. An association of two species where both the partners derive mutual benefit from each other is
- Parasitism
- Symbiosis
- Commensalism
- Predation
Answer: 2. Symbiosis
Symbiosis or mutualism is an obligatory positive interspecific interaction strongly beneficial to both species.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 8. An interaction between two organisms of different species, without physically interacting with each other, in which both are benefitted are called
- Commensalism
- Protocooperation
- Scavenging
- Amensalism
Answer: 2. Protocooperation
Protocooperation is a relationship in which organisms in association are mutually beneficial to each other (without physically interacting). This interaction is similar to mutualism, but the relationships between the organisms in protocooperation are not obligatory as in mutualism.
Question 9. Interaction between two organisms of different species in which one organism inhibits the growth of another organism is called
- Commensalism
- Amensalism
- Mutualism
- Protocooperation
Answer: 2. Amensalism
competition interaction
Amensalism is any relationship between organisms of different species in which one organism is inhibited or destroyed while the other organism remains unaffected.
Question 10. In which of the following interactions both partners are adversely affected?
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- Competition
- Predation
Answer: 3. Competition
Competition is the rivalry between two or more organisms to obtain the same resources such as food, light, water, space, shelter, mate, etc. Competitors adversely affect each other.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 11. The relationship between the two organisms where one receives benefit at the host of the other is
- Parasitism
- Amensalism
- Scavenging
- Symbiosis
Answer: 1. Parasitism
Parasitism is the relationship between two organisms of different species in which one organism called a parasite obtains its food directly from another living organism called the host.
Question 12. The mode of nutrition by killing the host is called
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Symbiosis
- Commensalism
Answer: 1. Predation
In predation, the predator kills the prey and consumes it to draw nutrition.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 13. If the stronger partner is benefitted and the weak partner is damaged, it is known as
- Predation
- Allelopathy
- Symbiosis
- Commensalism
Answer: 1. Predation
If the stronger partner is benefitted and the weak partner is damaged, it is known as predation. Predation is an interaction between members of two species in which members of one species capture, kill, and eat up members of other species. The former is called predator, while latter is called prey
“interaction define “
Question 14. Predation is
- An unnatural way of transferring energy to a higher trophic level
- A natural way of obtaining energy from lower trophic level
- A natural way of obtaining nutrition
- All of the above
Answer: 2. A natural way of obtaining energy from a lower trophic level
- Predation is a natural way of transferring energy to a higher trophic level or obtaining energy from a lower trophic level.
- It is an interaction between members of two species in which members of one species capture, kill, and eat up members of other species. The former is called predators, while later are spoken as prey.
Question 15. Predation helps keep a check on
- Prey population
- Biological control of weeds and pests
- Species diversity
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Predators help maintain species diversity in a community by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species. Predators can also be used for biological control of weeds and pests. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 16. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding predators?
- Predators keep prey populations under control
- Predators help in maintaining species diversity in a community
- If a predator is not efficient, then the prey population will become extinct
- Herbivores (predators) have a greater advantage since the plants cannot run away to avoid predation
- Tiger is an example of a predator
Answer: 3. If a predator is not efficient, then the prey population will become extinct
The statement in option (3) is incorrect and can be corrected as if a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct, and following it, the predator will also become extinct for lack of food that is the reason prey species have to evolve various mechanisms to protect themselves so that the balance is maintained. Rest statements are correct regarding predators.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 17. Assertion predation is an interspecific interaction with a feeding strategy. Reason (R) predator and their prey maintain a fairly stable population through time and rarely does one population become abundant or scarce.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 1. Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a. Predation is a natural way of transferring energy to a higher trophic level.
- It is the interaction between members of two species in which members of one species capture, kill, and eat up members of other species, i.e. Interspecific interaction.
- The former are called predators, while the latter are called prey. So, predator and their prey maintain a fairly stable population through time, and rarely does one population become abundant or scarce.
Question 18. Assertion Sometimes one population adversely affects the other by direct attack, but yet depends upon them. Reason (R) in predation, the contact is instant.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is correct, but r is incorrect
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 1. Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a. All living things within an ecosystem are interdependent.
- Any change in the population of one organism affects all other organisms within the ecosystem. Further one population may adversely affect another by a direct attack like predator attacks prey.
- In predation, the predator may or may not kill the prey prior to feeding, during predation the contact is instant on the prey population. Nevertheless, this is unavoidable as the predator population survives on the prey population for its food.
Question 19. Predators also help in …A… Species diversity in a community, by …B… The intensity of competition among competing prey species.
Here A and B can be
- A–exceeding, b–increasing
- A–maintaining, b–reducing
- A–reducing, b–maintaining
- A–maintaining, b–increasing
Answer: 2. A–maintaining, b–reducing.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 20. Pests are organisms that cause harm to plants and/or animals. They show …………………… Which is made use of in creating biological control methods towards it.
- Predator-prey interaction
- Prey feeding habitat
- Prey interaction with other predators
- Predator-predator interaction
Answer: 1. Predator-prey interaction
Biological control method in agriculture pest control based on the predator-prey interaction.
“mention the four aspects of interaction “
Question 21. Many species of fungi, for example. Dactylella, dactylaria, arthrobotrys, and zoophagus capture insects, nematodes, and other worm-like animals. These fungi are
- Parasitic
- Hyperparasites
- Predatory
- Holophytic
Answer: 3. Predatory
Predatory fungi attack nematodes and other microorganisms using a remarkable assay of trapping devices to attract, capture, kill, and digest nematodes for food.
Question 22. Plants have developed various means of protecting themselves from predators. One of the methods is by producing toxic chemicals. Identify such chemicals from the list given below.
- Nicotine
- Caffeine
- Quinine
- Strychnine
- Opium
Choose the correct combination.
- Only 1
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 2, 3, 4 And 5
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3, 4 And 5
A wide variety of chemical substances that we extract from plants on a commercial scale (nicotine, caffeine, quinine, strychnine, opium, etc….) Are produced by them actually as a defense against grazers and browsers. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 23. Monarch butterflies are highly distasteful to predator
- As it can camouflage
- Due to a special chemical present in his body
- Due to a poison secreted by their special glands
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Due to a special chemical present in his body
Monarch butterfly is highly distasteful to their predators because of a special chemical present in their body. Interestingly, the butterfly acquires this chemical during its caterpillar stage by feeding on poisonous weeds.
Question 24. Identify an example of a defense used by plants against herbivores.
- Production of caffeine, tannin quinine.
- Production of non-woody tissues.
- Productions of hair, thorns, and spines.
- Production of hormone-like chemicals that interfere with insect metamorphosis.
“interactions examples “
Select the correct pair.
- 1 And 2
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 3, And 4
Answer: 4. Production of hormone-like chemicals that interfere with insect metamorphosis.
- Production of caffeine, tannin, and quinine are examples of secondary metabolites, that are secreted by plants against herbivores.
- Production of hormones like chemicals, thorns, and spines is also the strategy of plants to avoid grazing by herbivores. Production of non-woody tissues is not the adaptation for plants from predation. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 25. A secondary compound in plants is a result of
- Normal metabolism
- Secondary metabolism
- Evolution
- Genetic difference
Answer: 2. Secondary metabolism
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 26. Prickly pear cactus species was introduced in Australia in
- 1920’S
- 1930’S
- 1960’S
- None of these
Answer: 1. 1920’S
The prickly pear cactus was introduced in Australia in the 1920s’s caused havoc by spreading rapidly into millions of hectares of range land. Finally, invasive cactus was brought under control only after a cactus-feeding predator (a moth) from its natural habitat was introduced into the country.
27. How does an exotic species become invasive?
- Because of natural predators
- Because of competition for natural resources
- Because invaded land does not have native predators
- Because of mutations occurring in their genome
Answer: 3. Because invaded land does not have native predators
When there is no natural predator for a species then it increases in number. Therefore an exotic species becomes invasive when that invaded land does not have any native or natural predator to control its increase.
Question 28. When an organism is ‘cryptically-colored’, it refers to a state where a
- Prey can feed abundantly
- Prey can lessen the impact of predator
- Predator can increase their number
- Predator can increase their reproductive fitness
Answer: 2. Prey can lessen the impact of predator
Prey species have evolved various defenses to lessen the impact of predation. Some species of insects and frogs are cryptically colored, i.e. Camouflage, to avoid being detected easily by the predator
Question 29. Why cannot a predator always have an upper hand over the prey?
- Since prey populations evolve anti-predatory traits
- Since prey populations reproduce at a fast rate
- Since predator populations reproduce at a fast rate
- Since predators are much larger in size than prey communities
Answer: 1. Since prey populations evolve anti-predatory traits
No predator becomes proficient in acquiring prey because prey populations also evolve anti-predatory traits to protect themselves.
NEET quiz on Population Interaction with solutions
Question 30. Animals have the innate ability to escape from predation. Examples for the same are given below. Select the incorrect example.
- Colour change in chameleon
- Enlargement of body size by swallowing air in puffer fish
- Poison fangs in snakes
- Melanism in moths
Answer: 3. Poison fangs in snakes
- Color change in chameleons and melanism in moths are examples of camouflage in animals adapted to prevent predation from prey. As a defense mechanism, puffers have the ability to inflate rapidly, filling their extremely elastic stomach with water or air until they are almost spherical.
- This prevents them from being identified by the predator. But poison fangs in snakes are a method adopted for preying and not escaping predation. Thus, option (3) is correct.
“interaction types “
Question 31. The starfish, disaster is an important predator in intertidal communities of
- American pacific coast
- Indian pacific coast
- Middle pacific coast
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Middle Pacific coast
Predator helps in maintaining species diversity. In the rocky intertidal, communities of the American Pacific coast, starfish pisaster is an important predator.
Question 32. Scavenging is an interaction between two organisms in which
- Certain animals feed on dead organisms
- One is benefitted, while the other is neither benefitted nor harmed
- One organism inhibits the growth of another organism
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Certain animals feed on dead organisms
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation. Thus, scavenging is an interaction between two organisms in which certain animals feed on dead organisms.
Question 33. When both partners/components are affected negatively, the nature of the interaction is
- Commensalism
- Predation
- Competition
- Amensalism
Answer: 3. Competition
Competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 34. Competition is best defined as a process in which the fitness of one species (measured in terms of its ‘r’ the intrinsic rate of increase) is significantly
- Lower in the presence of another superior species
- Higher in the presence of another superior species
- Equal in the presence of another superior species
- Competition exists irrespective of the presence or absence of competing species
Answer: 1. Lower in the presence of another superior species
Competition is best defined by the fitness of one species as compared to the other competitive species. It is lower in the case of other superior competing species.
Question 35. When the value of ‘r’ is significantly low as compared to others it is better known by
- Competition exclusion
- Resource partition
- Interference competition
- Competition release
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 3 And 6
- 6, 5 And 3
- 1, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 2
Answer: 3. 1, 3 And 4
When the value of ‘r’ is significantly low as compared to others it is better known by competition exclusion, interference competition, or competition release. It states that two competing species cannot co-exist in the same habitat at the same time for the same resource. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Question 36. Competition occurs when
- Organisms are at their fittest for reproduction
- Unrelated species compete for the same resources
- Closely related species compete for the same resources
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Competition occurs for the same limited resources between closely related and unrelated species. It is said that competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting. But this is not true, unrelated species also compete for the same resources. Thus, option (4) is correct.
37. Competition for food, light, and space is most severe between the two
- Closely related species growing in different niche
- Distantly related species growing in different niche
- Closely related species growing in the same niche
- Distantly related species growing in the same niche
Answer: 3. Closely related species growing in the same niche
Species that are living close to one another, i.e. In the same habitat and have similar or same requirements, there is maximum competition for food, light, and space between them.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 38. Competition of species leads to
- Extinction
- Mutation
- A greater number of niches are formed
- Symbiosis
Answer: 1. Extinction
- When both partners/components are affected negatively the nature of interaction is known as competition. When two organisms compete for a particular resource in the same niche, both cannot survive.
- No two organisms can live in the same niche. One of the two is eliminated. So, in the course of time elimination may lead to extinction as only the fittest will survive.
Question 39. The level of competition between species depends on
- Availability of resources
- Population density
- Climatic condition of an area
- Group interaction of the organism
Choose the option containing
Correct combination.
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 4
- 1, 2 And 4
Answer: 4. Extinction
- The level of competition depends upon many factors like
- Resources availability
- Population density
- Group interaction of organisms.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 40. To avoid the competitive exclusion principle two similar species living in the same area, may evolve to become more different in order to
- Reduce competition
- Increase competition
- Use other species’ resources
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 1. Reduce competition
To avoid the competitive exclusion principle two similar species adapt differently to reduce the competition. So, that two species can live in the same area. Therefore, competition does not always result in the extinction of species.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 41. …A… Being the common food source for migratory flamingos and fishes in lakes of America, need not necessarily be limiting for competition to occur. Here, …B… Will be observed, where the feeding efficiency of any one species …C… Due to the interference of the other species.
- A–zooplankton, b–sharing competition, c–increases
- A–zooplankton, b–interference competition, c–decreases
- A–phytoplankton, b–weak competition, c–reduces
- A–phytoplankton, b–null competition, c–increases
Answer: 2. A–zooplankton, b–interference competition, c–decreases.
Question 42. Competition will be severe in a population with ………………. Distribution.
- Non-random
- Irregular
- Uniform
- Random
Answer: 1. Non-random
- Population dispersion can be defined as the spatial distribution of individuals on the basis of favorable conditions available for their survival non-random distribution is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. In this type of distribution, the distance between neighboring individuals is minimized.
- Animals need certain resources to survive and when the resources become rare during certain parts of the year animals tend to clump together around these crucial resources.
Question 43. Assertion interspecific competition is the only potent force in organic evolution. Reason (R) Unexceptionally two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 4. Both a and r are false
- Population dispersion can be defined as the spatial distribution of individuals on the basis of favorable conditions available for their survival non-random distribution is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. In this type of distribution, the distance between neighboring individuals is minimized.
- Animals need certain resources to survive and when the resources become rare during certain parts of the year animals tend to clump together around these crucial resources.
- The same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually. This may be true if resources are limiting, but not otherwise.
NEET expected MCQs on Population Interaction 2025
Question 44. Hydroxylamine toxins are released by
- All parasites
- Members of actinomycetes
- Blue-green algae
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Blue-green algae
- Blue-green algae (BGA) are cyanobacteria. The toxins produced by cyanobacteria are called cyanotoxins. Hydroxylamine is an inorganic cyanotoxin secreted by the bag.
- This compound is highly toxic to aquatic life. When the bacteria form aquatic blooms they release a lot of cyanotoxins killing aquatic life on a large scale. When these cyanotoxins enter the shells of molluscans they lead to shellfish poisoning.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 45. Interspecific competition between plants may manifest itself in chemical aggression called
- Parasitism
- Predation
- Allelopathy
- Ecological sere
Answer: 3. Allelopathy
Allelopathy is a biological phenomenon by which an organism produces one or more biochemicals that influence the germination, growth, survival, and reproduction of other organisms from the same community. So, interspecific competition between plants may manifest itself by chemical aggression called allelopathy.
Question 46. A high density of elephant population in an area can result in
- Intraspecific competition
- Interspecific competition
- Predation on one another
- Mutualism
Answer: 1. Intraspecific competition
- Competition is rivalry for obtaining the same resource. It is competition between individuals of the same species.
- The intraspecific competition may be very severe because all the members of a species have similar requirements of food, habitat, mate, etc., And they also have similar adaptations to meet their needs. So, if the density of the elephant population in an area increases, it will lead to intraspecific competition.
Question 47. Territoriality occurs as a result of
- Parasitism
- Predation
- Co-operation
- Competition
Answer: 4. Competition
- Territoriality is the separation of competitors. Due to competition between two or more organisms, populations of species that share the same environmental resources (when this is in short supply competition) ultimately result in displacement by one competitor to the others.
- It is to the advantage of the competitors to avoid one another wherever possible. So, territoriality occurs as a result of competition.
Question 48. An indirect competition for shared resources such as a particular nutrient is called
- Mutualism
- Exploitation
- Advantageous
- None of these
Answer: 2. Exploitation
An indirect competition for shared resources such as particular nutrients is called exploitation.
Question49. The principle of competitive exclusion was stated by
- C. Darwin
- Gf gause
- Mac Arthur
- Verhulst and pearl
Answer: 2. Gf gause
The principle of competitive exclusion was given by GF Gause
Question 50. Consider the following statements.
- Two closely related species may not live in the same habitat.
- The more dissimilar the niches of the two species the stronger their competition.
- Two species can occupy the same niche in a geographical area.
- No two species may occupy the same ecosystem.
Choose the option containing
Correct statements.
- Only 1
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
- Only 4
Answer: 4. Only 4
- Only 4 statement is correct. Two or more species with closely niche requirements cannot exist indefinitely in the same area as sooner or later they come into competition for possession of it.
- This is called as Gause’s competitive exclusion principle, which states that an ecological niche cannot be simultaneously and completely occupied by established populations of more than one species.
- Two species can live in the same habitat but not in the same niche more similar the two niches are, severe the competition is so, the correct answer is no two species may occupy the same ecosystem.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 51. ‘Two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely’. This law is also called
- Gause’s law
- Competitive exclusion principle
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
- Gause (1934) found that out of two species of paramecium grown together, one is eliminated. This phenomenon is called Gause’s hypothesis or principle of competitive exclusion.
- This principle operates when the resources are limited and two species compete for the same resources. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Question 52. Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion states that
- More abundant species will exclude the less abundant species through competition
- Competition for the same resources excludes species having different food preferences
- No two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
- Larger organisms exclude smaller ones through competition
Answer: 3. No two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion states that no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
Question 53. Gause’s law is true only when
- Resources are limited
- Resources are unlimited
- Predation is absent
- Prey are unlimited
Answer: 1. Resources are limited
Gause (1934) found that out of two species of paramecium grown together, one is eliminated. This phenomenon is called Gause’s hypothesis or principle of competitive exclusion. This principle operates when the resources are limited and two species compete for the same resources. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Question 54. Carnivorous animals, lions and leopards, occupy the same niche but lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones. This mechanism of competition is referred to as
- Character displacement
- Altruism
- Resource partitioning
- Competitive exclusion
Answer: 3. Resource partitioning
- Carnivorous animals, lions and leopards occupy the same niche but lion predate mostly larger animals and leopard takes smaller ones. This is called resource partitioning.
- It is a mechanism in which there is the division of limited resources by species to avoid competition in an ecological niche and in this way, they find ways to co-exist with one another. That is why lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take small ones.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 55. Resource partitioning includes
- Temporal partitioning
- Spatial partitioning
- Morphological partitioning
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Temporal partitioning
Resource partitioning is the phenomenon where the species are divided on the basis of their food, space, resting sites, etc. They divide a niche for the competition of resources. Thus option (1) is correct.
Question 56. When Darwin spoke of the struggle for existence and survival of the fittest in nature, he was convinced that
- Interspecific competition is a potent force in organic evolution
- Intraspecific competition is a potent force in organic evolution
- Predator-prey interaction is a potent force in organic evolution
- Both and (c)
Answer: 1. Interspecific competition is a potent force in organic evolution
It is generally believed that competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting. But this is not true, unrelated species also compete for the same resources. This is called interspecific competition which proves to be the potent force in organic evolution.
Question 57. Diversity in the type of beaks of finches adapted to different feeding habits on the Galapagos islands, as observed by Darwin, provides evidence
- Origin of species by natural selection
- Intraspecific variations
- Intraspecific competition
- Interspecific competition
Answer: 1. Origin of species by natural selection
- Darwin during his famous voyage, observed that finches from various islands of the Galapagos had beaks of different sizes and shapes they observed that this was due to adaptation to different available food types.
- He concluded that the ancestral finches on reaching different islands occupied all empty ecological niches in the absence of competition and evolved into different species. This provides evidence for the origin of species by natural selection.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 58. In laboratory experiments, two species of paramecium were grown alone and in the presence of the other species. The following graphs show the growth of species 1 and species 2, both alone and when in mixed culture.
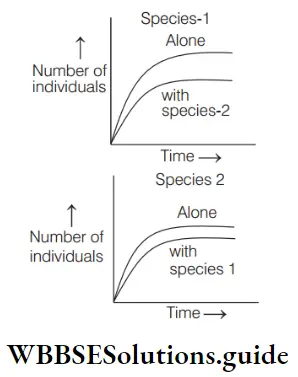
Interpretation of the graphs.
- Competitive exclusion has occurred in these experiments
- Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 1 is less affected
- Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is less affected
- Both species are affected equally by interspecific competition
Answer: 3. Both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is less affected
As we can see from graph I there is more gap between lines of species 1 and 2 than graph. So, it clearly infers that both species are affected by interspecific competition but species 2 is less affected.
NEET Biology Population Interaction MCQs with explanations
Question 59. Relationship between organisms of different species where one organism gets benefits and the other is harmed is called
- Mutualism
- Commensalism
- Parasitism
- Symbiosis
Answer: 3. Parasitism
Parasitism is a negative interaction in which one individual derives benefit at the expense of the other. So, the relationship between organisms of different species where one organism gets benefitted and the other is harmed is called parasitism.
Question 60. A true parasite is one which
- Wholly completes its life cycle in one host
- Completes its life cycle in different host
- Is completely attached to the host
- Is not completely dependent on the host
Answer: 1. Wholly completes its life cycle in one host
A true parasite is one which wholly completes its life cycle in one host. These parasites attach to the host or live and feed on it. The parasites are benefitted, while the host is harmed.
Question 61. Nosema notabilis is an example of
- Commensalism
- Symbiosis
- Parasitism
- Hyperparasitism
Answer: 3. Parasitism
When a parasitic species is parasitized by another parasite species. Such a parasite is called hyperparasite, as in the case of nosema notabilis, which is a hyperparasite on a myxosporidian. So, nosema notabilis is an example of parasitism
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 62. Adaptation of parasites may be
- Loss of unnecessary organs
- Presence of adhesive organs
- Origin of suckers to cling to host
- Development of a digestive system
- High reproductive capacity
Choose the option containing
Correct combination.
- 1, 3 And 4
- 2, 4 And 5
- 1, 4 And 5
- 1, 2, 3 And 5
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 And 5
In accordance with their lifestyle, parasites evolved special adaptations such as loss of digestive systems, loss of unnecessary organs, presence of adhesive organs, origin of suckers, and high reproductive capacity in accordance to their host. So, the development of the digestive system is not an adaptation of parasites. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 63. Which of the following is categorized as a parasite in true sense?
- Koel (cuckoo)
- Housefly
- Head louse
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 3. Head louse
Question 64. Man and Ascaris show
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Commensalism
- Symbiosis
Answer: 2. Parasitism
Scaris is an intestinal parasite of humans. It is the most common human worm infection. The larvae and adult worms live in the small intestine and cause intestinal diseases. So, man and Ascaris show parasitism.
Question 65. During parasitic life, the animal is bound to lose
- All the sense organs
- Most of the nervous system
- Complete gut
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (3)
- A parasite must remain in close contact with its host. It depends on the host for its food and is unable to live a free life for a very long. This is because most parasites have become thoroughly adapted to parasitic existence.
- In doing so they have often lost the power of locomotion, their sense organs are reduced, the gut may be reduced or absent and the reproduction system and nervous system have become greatly developed. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 66. Parasitodism is a case where the larval form
- Lives after host’s death
- Dies with host’s death
- Is a parasite but the adult is free-living
- Is a parasite on another parasite
Answer: 3. Is a parasite but an adult is a free-living
The Ladybird beetle, Cuccinelli is a parasite in its larval stage and is free-living in adults. Other include parasitic hymenopteran and orthopteran.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 67. …A… Is observed in many parasites which have enabled …B… Of host-parasite. …C… Developed by the host and parasite enable them to survive the adaptations that each of them gain over the course of evolution.
- A–parasite-specificity, b–co-evolve, c–counteract
- A–host specificity, b–co-evolution, c–counter mechanisms
- A–enzyme specificity, b–evolve, c–counteract
- A–source-specific, b–extinction, c–counter mechanisms
Answer: 2. A–host specificity, b–co-evolution, c–counter mechanisms
Question 68. Parasite capable of living without a host is called
- Facultative
- Permanent
- Obligate
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Facultative
The facultative parasite is an organism that may survive and dwell in the absence of a host but that occasionally infects a host organism also.
Question 69. Cuscuta is an example of
- Ectoparasitism
- Brood parasitism
- Predation
- Endoparasitism
Answer: 1. Ectoparasitism
- Cuscuta or dodder plant, is a parasitic plant that wraps around other plants for nourishment. Cuscuta is found on the outer side of the host and is a total stem parasite. It is a good example of ectoparasitism. It is commonly found growing on hedge plants. It has lost chlorophyll and leaves in the course of evolution.
- It attaches and wraps itself around the stem of the host plant and produces haustoria that gets inserted into the vascular system of the host. The parasitic plant sucks all the nutrients from the host plant with the help of haustoria.
Question 70. Endoparasites are the parasites which live
- In the intercellular spaces of the host
- Within the cells in the host’s body
- On the surface of the host
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Endoparasites are the parasites that live inside the host’s body. It can live in the intercellular spaces or within the cells in the host’s body. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 71. A phenomenon when a parasite parasitizes another parasite is
- Hyperparasitism
- Parasitoids
- Monoxenous parasitism
- Polyxenous parasitism
Answer: 1. Hyperparasitism
- Hyperparasitism means that a parasite lives in or on another parasite. Common examples are insects that lay their eggs inside or near parasites which are themselves parasitizing the tissue of a host (insect).
- So, indirectly insect is feeding on itself only. Hyperparasitism results in a cycle of energy and nutrients between the host and its parasitoid.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 72. ‘Parasitic castration’ refers to
- Parasites induce their hosts to form antibodies
- Parasites make their hosts form fibrous capsules around them
- Change brought about by the parasite on the host resulting in sexual impotency
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Change brought about by the parasite on the host resulting in sexual impotency
Parasite castration refers to the change brought about by the parasite on the host resulting in sexual impotency. It is a strategy by the parasites. Blocking reproduction is its main target.
Question 73. Which of the following is brood parasitism?
- Snake feeding on rat
- Oxpeckers eat the parasites on rhinoceros
- Jackals and hyenas feeding on dead lions and tigers
- Cuckoo female lay their eggs in the crow’s nest
Answer: 4. Cuckoo females laying their eggs in the crow’s nest
Brood parasites also called social parasites which parasite birds lay eggs in to nests of their host. Thus, the cuckoo female laying their egg in the cow’s nest is brood parasitism.
Question 74. Obligate parasites are those organisms which
- Live only on living host
- Are essentially parasites, but can also become saprophyte
- Live only on dead and decaying organic matter
- Are essentially saprophytes, but can also parasites
Answer: 1. Live only on living host
Obligate parasites can grow only upon suitable living host tissues. The best examples of obligate parasites are the causal organisms of downy and powdery mildews as perenospora and erysiphe.
Question 75. The parasite that completely depends on the host for its entire requirement is called
- Ectoparasite
- Holoparasite
- Hemiparasite
- Semiparasite
Answer: 2. Holoparasite
The parasite which completely depends on the host for its entire requirement is called holoparasite.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 76. A parasite that lives within plant tissue is called
- Ectophyte
- Epiphyte
- Hydrophyte
- Endophyte
Answer: 4. Endophyte
- An endophyte parasite remains inside the cells of plant tissue. Other options are explained as ectophytes when the parasite remains outside the cells of plant tissue.
- Hydrophytes plants growing in water are called hydrophytes. Epiphytes are those plants that live on another plant for shelter only. They are photosynthetic and do not depend on another plant for nutrition.
Question 77. Which of the following is hemiparasite?
- Rafflesia
- Viscum
- Loranthus
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 3. Loranthus
Rafflesia is a hemiparasite.
Question 78. Newly developed pathogens are more damaging to the host therefore are called
- Distant pathogen
- Chronic pathogen
- Instant pathogen
- Bt pathogens
Answer: 3. Instant pathogen
Newly developed pathogens are more damaging than the host therefore are called instant pathogens, which have not yet developed adaptation to negative interaction, for example. Sars.
Question 79. Human liver fluke (a trematode parasite) depends on which two intermediate hosts.
- Snail
- Fish
- Pig
- Mosquito
Choose the option containing
Correct combination.
- 1 And 2
- 2 And 3
- 3 And 4
- 4 And 5
Answer: 1. 1 And 2
Human liverfluke depends upon two intermediate hosts, i.e. A snail and fish to complete its life cycle. Thus, option (1) is correct.
Question 80. Which one is incorrect regarding parasitism?
- Parasite shows a special adaptation
- Ectoparasite shows a more complex life cycle
- Endoparasite shows a more complex life cycle
- Crow is an example of a brood parasite
Answer: 2. Ectoparasite shows a more complex life cycle
The statement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as ectoparasites show a simple life cycle as compared to endoparasite as their life cycle involve mostly one host, whereas an endoparasite completes its life cycle as more than one host and hence has a complex life cycle. Rest options are correct regarding parasitism.
Question 81. Match the following columns.
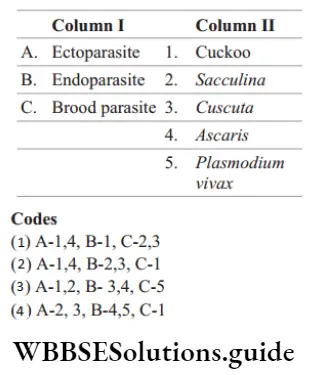
Answer: 4. A–2,3; b–4, 5; c–1
82. Match the following columns.
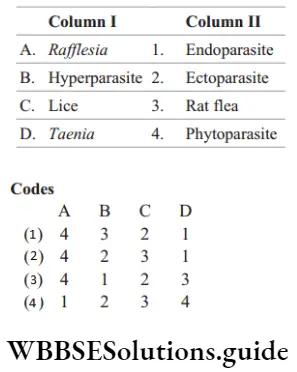
Answer: 1. A–4, b–3, c–2, d–1
Question 83. Choose the incorrect statements.
- Parasites might render the host more vulnerable to predation by making it physically weak
- The majority of the parasites harm the host and reduce their population density
- Ideal parasites should be able to thrive within the host without harming it
- The malarial parasite does not need a vector in order to spread to another host.
Answer: 4. Malarial parasite does not need a vector in order to spread to another host.
The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as the malarial parasite needs a vector female anopheles mosquito to spread to other hosts. Rest options are correct statements.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 84. Consider the following statements.
- The life cycle of a human liver fluke involves only the snail as an intermediate host.
- The malarial parasite needs a vector (mosquito) to spread to other hosts.
- The female mosquito is not considered a parasite, however, it needs our blood for reproduction.
- In case of brood parasitism, the eggs of parasitic birds (e.g. Cuckoo) are not detected and ejected from the nest because of parasite’s eggs resemble the host’s eggs in morphology and colour.
- A population of frogs protected from all predators would increase indefinitely.
Choose the option containing
Correct statements.
- 1 And 2
- 2 And 3
- 3, 4 And 5
- 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 4. 2, 3 And 4
- Statements 2, 3, and iv are correct. Statements I and v are incorrect and can be corrected as the life cycle of a human liver fluke involves the snail and pig as intermediate hosts. A population of frogs protected from all predators would not increase indefinitely because nature’s resources are limited.
- Beyond a carrying capacity, the population would not increase because it is the maximum number of populations that can be sustained by the habitat.
Question 85. The percentage of insects known to be phytophagous is
- Nearly 75%
- Nearly 25%
- Nearly 50%
- Nearly 35%
Answer: 2. Nearly 25%
For plants, herbivores are the predators of nearly 25% of all insects known to be phytophagous (feeding on plant sap and other parts of plants). The problem is severe in the case of plants because they are non-motile.
Question 86. In a biotic community, which one of the following can be called a protective device?
- Symbiosis (commensalism)
- Mimicry
- Competition
- Parasitism
Answer: 3. Competition
Mimicry is the superficial but resemblance of one organism to another or to natural objects to secure its concealment or protection. Thus, mimicry can be called a protective device.
Question 87. In commensalism
- One species is benefitted and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted
- One species is no benefit and the other is harmed
- One species is no benefit and the other is not harmed
- Both species benefit
Answer: 1. One species is benefitted and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted
Commensalism is the interaction in which one species (commensal) benefits and another species (host) is neither harmed nor benefitted, for example. An orchid grows as an epiphyte on a mango branch to absorb sunlight in the tropics.
Question 88. In commensalism
- The population of commensal and host remain unaffected
- The population of commensal increases while that of the host remains unaffected
- The population of both commensal and cost increases
- The population of commensal increases, while the population of the host gradually decreases
Answer: 2. The Population of commensal increases while that of the host remains unaffected
In commensalism, the population of commensals increases while that of the host remains unaffected.
Question 89. The interaction between the organisms of one of the following pairs is an example of commensalism.
- Cattle or sheep and grass
- Wasps and fig tree
- Orchid and mango tree
- Cuckoo and crow
Answer: 1. Cattle or sheep and grass
- Commensalism is the type of interaction in which one of the partners is benefitted, while the other partner is unharmed. This type of interaction takes place in the cattle or other grazing animals and the egrets. The grazing animals, while grazing disturbs the grass come out.
- The egrets are present on the back of the grazing animals. The egrets feed on these insects. There is no harm done to the cattle. So, cattle or sheep and grass is an example of commensalism.
Question 90. Between which of the following, the relationship is not an example of commensalism?
- Orchid and the tree on which it grows
- Cattle egret and grazing cattle
- Sea anemones and clown fish
- Female wasp and fig species
Answer: 4. Female wasp and fig species
- Among the given examples, the relationship between a female wasp and fig species does not show commensalism. In commensalism, one species derives the benefit, and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted.
- Wasp and fig trees show mutualism. Here, the fig flower is pollinated by the wasp and the female wasp uses the fig fruit for oviposition. In this way, both organisms are benefitted. Other options show examples of commensalism.
Question 91. Pencillium does not allow the growth of the bacterium, staphylococcus. This sort of relationship is called
- Commensalism
- Antagonism
- Amensalism
- Mutualism
Answer: 3. Amensalism
Amensalism is an interaction between two living individuals of different species in which an organism does not allow another organism to grow or live near it. So, penicillium does not allow the growth of the bacterium staphylococcus.
Question 92. If the strong partner is benefitted and the weak partner is damaged, the relationship is known as
- Amensalism
- Symbiosis
- Commensalism
- Allotropy
Answer: 1. Amensalism
If the strong partner benefits and the weak partner is damaged, the relationship is known as amensalism.
Question 93. Which one of the following population interactions is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics?
- Commensalism
- Amensalism
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
Answer: 2. Amensalism
- Amensalism/antibiosis (0, –) is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics as
- Antibiotics are chemicals secreted by one microbial group (for example. Penicillium) that harm other microbes (for example. Staphylococcus).
- It has no effect on the penicillium or the organism that produces it
Question 94. A plant that grows inside a plant of another species symbiotically is called
- A semiparasite
- A parasite
- An endophyte
- A saprophyte
Answer: 3. An endophyte
- Endophyte is a plant growing inside a plant of another species symbiotically. Other options are explained as semiparasite depends upon other organisms for its practical requirements.
- A parasite is an organism that obtains some benefit from other organisms at its (other organisms) expense. Saprophyte finds its food from dead material.
Question 95. A praying mantis is a good example of
- Warning coloration
- Social insects
- Camouflage
- Mullerian mimicry
Answer: 3. Camouflage
A praying mantis is a good example of camouflage. Camouflage is the natural colouring of an animal which enables it to blend in with its surroundings. A praying mantis is the common name for an insect of the order–Mantodea.
Question 96. The pilot fish always accompanies …………… For feeding on falling pieces of food.
- Shark
- Hermit crab
- Labeo
- Golden fish
Answer: 1. Shark
The pilot fish always accompanies the shark to feed on falling pieces of food. This association between pilot fish and sharks is called commensalism.
Question 97. Which one is true?
- Commensalism–when none of the interacting populations affect each other
- Symbiosis–when the interaction is useful to both populations
- Symbiosis–when neither population affects the other
- Commensalism–when the interaction is useful to both populations
Answer: 2. Symbiosis–when the interaction is useful to both the populations
(2) Option (2) is true as when the interaction is useful to both populations it is called symbiosis. Symbiosis means living together. It is a beneficial co-action between two or more different species in which both species are benefitted. Rest options are false.
Question 98.
- The concept of mimicry was given by …A…
- …B… Is known as the father of Indian plant ecology.
- The term ‘ecology’ was coined by …C….
Choose the option containing
- A–Haeckel, B–Ramdeo Misra, C–reiter
- A–Hw bates, B–ramdeo misra, C–ernst haeckel
- A– Ramdeo Misra, B–birbal sahani, C– reiter
- A–Hw bates, B–birbal sahani, C– ernst haeckel
Answer: 2. A–hw bates, B–ramdeo misra, C–ernst haeckel
- The concept of mimicry was first given by HW Bates (1) in 1862.
- The Father of Indian plant ecology is Ramdeo Misra (2).
- The term ‘ecology’ was coined by Ernst Haeckel (3) in 1861.
Question 99. An interesting modification of flower shape for insect pollination occurs in some orchids, in which a male insect mistakes the pattern on the orchid flower for the female of his species and tries to copulate with it, thereby pollinating the flower. This phenomenon is called
- Mimicry
- Pseudopollination
- Pseudocopulation
- Pseudoparthenocarpy
Answer: 1. Mimicry
- Mimicry is a resemblance of an organism to its natural surroundings, a non-living object or another organism to conceal itself from its enemies.
- Flowers of Ophrys muscifera resemble the female wasps of Colpa aurea so that the male wasp tries to copulate with the flowers and pollinate them.
Question 100. A type of mimicry where the mimic closely resembles the model and both are harmful to the predator is
- Mullerian mimicry
- Batesian mimicry
- Webrian mimicry
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Batesian mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of biological resemblance in which a noxious or dangerous, organism (the model), equipped with a warning system such as conspicuous coloration, is mimicked by a harmless organism (the mimic). The mimic gains protection because predators mistake it for the model and leave it alone.
Question 101. Which type of association is found between entomophilous flower and pollinating agent?
- Mutualism
- Commensalism
- Cooperation
- Co-evolution
Answer: 4. Co-evolution
Co-evolution can occur in any interspecific relationship like symbiosis or mutualism. The relation between an entomophilous flower and a pollinating insect shows co-evolved mutualism. In this, the plant depends exclusively on the insect for pollination and the insect relies on the plant for food.
Question 102. Assertion in mutualism, both the population benefit and neither can survive under natural conditions without the other. Reason (R) Both populations benefit from the association, but their relationships are not obligatory.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but r is false
A is true, but r is false. Reason can be corrected as in mutualism, both populations benefit by the association, but their relationships are obligatory, i.e. The species are in close proximity and interdependent with one another in a way that one cannot survive without the other.
Question 103. Mutualism is a kind of …………………. Interaction.
- Positive interspecific
- Negative interspecific
- Positive intraspecific
- Negative intraspecific
Answer: 1. Positive interspecific
Mutualism is defined as an interaction between individuals of different species that results in positive (beneficial) effects on per capita reproduction or survival of the interacting population. Thus, option (1) is correct.
Question 104. Mutualism is found in
- Hermit crab and sea anemone
- Butterfly and flower
- Zoochlorella and hydra
- E. Coli and man
Answer: 3. Zoochlorella and hydra
Mutualism is an obligatory positive interspecific interaction strongly beneficial to both species. Hydra can form a symbiotic relationship with algae such as zoochlorella which is green algae, zoxantheal which is referred to as brown algae. The relationship will assist in the benefits to both organisms.
Question 105. Which of the following associations shows mutualism?
- Fig and wasp
- Barnacles on whale
- Roundworms in the human intestine
- Orchids on mango tree
Answer: 1. Fig and wasp
- Mutualism is an interaction between two organisms of different species in which both partners benefit, with none of the two capable of living separately. In many species of fig trees there is a relationship with the pollinator species of wasp.
- The female wasp uses the fruit not only as an oviposition site but also uses the developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae.
- The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg-laying sites. So, fig and wasp associations show mutualism.
Question 106. Flagellate protozoan living in the gut of termites is a case of
- Mutualism
- Parasitism
- Amensalism
- Commensalism
Answer: 1. Mutualism
Termites feed on wood though they do not possess enzymes for digesting the same. Termites harbor cellulose-digesting flagellates (trichonympha campanula) for this purpose. Flagellates are unable and live independently. Termites would die of starvation in the absence of flagellates. Thus, flagellate protozoan living in the gut of termites is a case of mutualism.
Question 107. Orchids can be found associated with
- Oryza sativa
- Brassica crucifer
- Nerium oleander
- Shorea robusta
Answer: 4. Shorea robusta
Orchids can be found associated with Shorea robusta.
Question 108. The association of fungus and alga is an example of
- Ammensalism
- Commensalism
- Competition
- Symbiosis
- predation
Answer: 4. Symbiosis
- The association of a fungus and an alga in the lichens is considered an example of symbiosis, in which each partner of the association derives something essential for its survival.
Question 109. A female fig wasp enters the syconium of a fig to lay her eggs in the process of which she pollinates the flower. The young larvae feed on some of the seeds and complete their life cycle. The fig is completely dependent on the wasps to pollinate its flowers and the fig wasp requires figs to complete their life cycle. The interaction between figs and fig wasps has aspects of
- Mutualism
- Host-parasite interaction
- Competition
- Ammensalism
- Proto-cooperation
Select the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 5 And 6
- 3 And 4
Answer: 1. 1 And 2
- The given examples show two types of interaction
- Mutualism – the fig plant is completely dependent on the fig wasp to pollinate its flower and the fig wasp requires figs to complete its life cycle.
- Host-parasite interaction– fig wasps are completely dependent on the fig plant for their food shelter, development, etc. Fig wasp acts as a parasite and fig plant acts as a host. Thus, option (1) is correct
Question 110. A free-living nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium that can also form a symbiotic association with the water fern Azolla is
- Chlorella
- Nostoc
- Anabaena
- Tolypothrix
Answer: 3. Anabaena
Anabaena is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria that exist as plankton. They are known for nitrogen-fixing abilities and they form symbiotic relationships with certain plants, such as the mosquito fern, azolla.
Question 111. The association between ants and petioles of certain plants is called
- Interaction
- Mutualism
- Myrmecophily
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The association between ants and petioles of certain plants is called interaction mutualism or myrmecophily.
Question 112. The relationship between leguminous plants and the rhizobium present in their root nodules is
- Synergism
- Commensalism
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
Answer: 4. Mutualism
Root nodule symbiosis is a mutualistic interaction observed between mainly leguminous plants and nitrogen-fixing soil rhizobia, in which plants can obtain fixed atmospheric nitrogen and provide rhizobia with photosynthate as a carbon source.
Question 113. Besides paddy fields, cyanobacteria are also found inside the vegetative part of
- Equisetum
- Psilotum
- Pinus
- Cycas
Answer: 4. Cycas
Coralloid roots of cycas have symbiotic associations with blue-green algae like nostoc and anabaena. Coralloid roots are irregular, negatively geotropic, dichotomously branched coral-like roots that do not possess root hairs and root caps.
Question 114. Lichens are seen growing in areas with low pollution. They represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between
- Fungus and bacteria
- Fungus and photosynthetic algae
- Fungus and archaebacteria
- Fungus and roots of higher plants
Answer: 2. Fungus and photosynthetic algae
Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relation between a fungus and photosynthetic algae or cyanobacteria. It is the interaction conferring benefit to both the interacting species, called mutualism.
Question 115. Mycobiont and phycobiont association is
- Symbiotic
- Commensal
- Parasitic
- Helotism
Answer: 4. Helotism
In lichens, there is the association of mycobiont and phycobiont called helotism because, in this relationship, algae act as slaves, prepare food for fungi and fungi act as masters. The reproduction in algae is inhibited by the influence of fungi.
Question 116. Pollination is an example of
- Mutualism
- Proto-cooperation
- Synergism
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Mutualism
Pollination is an example of mutualism in which the pollinator obtains nectar, pollen grain, etc., And in turn, the flower gets pollinated.
Mock test on Population Interaction for NEET preparation
Question 117. Mycorrhiza, a relationship between fungi and roots of higher plants is
- Parasitic relationship
- Saprophytic relationship
- Symbiotic relationship
- Epiphytic relationship
Answer: 3. Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungi and roots of higher plants, which grow in mineral-deficient soil. It helps to absorb water and minerals like phosphorus from soil for the benefit of plants and in turn gets nutrition from the plant, as fungi cannot synthesize its own food.
Question 118. Which of the following is an example of symbiosis?
- Sea anemone and hermit crab
- Mycorrhiza
- Lichens
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Symbiosis is a term given to any type of interspecific interaction. Thus, all options are correct.
Question 119. One of them shows a symbiotic relationship with man.
- Paramecium
- Trypanosoma
- Leishmania
- Entamoeba coli
Answer: 4. Entamoeba coli
Entamoeba coli is a non-pathogenic species of entamoeba that frequently exists in the human gastrointestinal tract and shows a symbiotic relationship. It relies on intestinal contents for nutrients and humans derive certain vitamins from e. Coli, particularly vitamin-k
Question 120. Mutualism observed in plants is a special kind of interaction involving …a… And …b… .the former obtains nutrition and the latter plays a role in its life cycle.
Whereas the latter gets pollinated in return.
- A–insect, b–plants
- A–plants, b–insect
- A–prey, b–plants
- A–predator, b–plants
Answer: 1. A–insect, b–plants.
Question 121. Which one of the following microbes forms a symbiotic association with plants and helps them in their nutrition?
- Azotobacter
- Aspergillus
- Glomus
- Trichoderma
Answer: 3. Glomus
Azotobacter, Aspergillus, and Trichoderma all are free-living microbes that help plants in their nutrition. Glomus is a fungus that symbiotically forms endomycorrhiza that helps in the absorption of nutrition especially phosphorus from soil.
Question 122. Roots of higher plants show symbiosis with mycorrhiza for obtaining
- Sulfates
- Nitrogen
- Phosphates
- All of these
Answer: 3. Phosphates
Mycorrhiza is an association of a soil fungus, e.g. Boletus, and with the roots of higher plants such as conifers, for example. Pinus. The fungus absorbs water and minerals (mainly phosphates) from the soil and passes them to the plant. The carbohydrate synthesized by the plant is absorbed by the fungus.
Question 123. The association between hermit crabs and sea anemones is
- Symbiosis
- Commensalism
- Parasitism
- Protocooperation
Answer: 4. Protocooperation
- In protocooperation, the two organisms are mutually benefitted by each other. But the association is non-obligatory, i.e. Not necessary for their existence, for example.
- Association between a hermit crab and sea anemone. Hermit crab takes sea anemone on their back to other feeding zone and in turn, gets protection from his enemies.
Question 124. A bird enters the mouth of a crocodile and feeds on parasitic leeches. The bird gets food and the crocodile gets rid of blood-sucking leeches. Both the partners can live independently. Such an association is called
- Mutualism
- Amensalism
- Commensalism
- Protocooperation
- Answer:
Question 125. Which one of the following is a matching pair of certain organism(s) and the kind of association?
- Shark and sucker fish–commensalism
- Algae and fungi in lichens–mutualism
- Orchids growing on trees–parasitism
- Cuscuta (dodder) growing on other flowering plants–epiphytes
Answer: 2. Algae and fungi in lichens–mutualism
Mutualism is a type of symbiotic association between two organisms in which both are benefitted. Lichen is a symbiotic association of an alga and fungus in which an algal partner provides food to the fungal partner by photosynthesis and a fungal partner helps in the absorption of water and minerals.
Question 126. Consider the following statements.
- The mutualistic relationship evolves when the benefit of both species outweighs the loss.
- Mutualism evolves when the benefits of both species outweigh the loss.
- Humans cause an ecological imbalance by eradicating common predators.
- Humans bring about an alteration in competition between species.
Choose the option containing incorrect statements.
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1 And 4
- 2 And 4
Answer: 2. 2 And 3
Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect and can be corrected as mutualistic relationships evolve when the benefit is more than the cost. Human causes ecological imbalance by eradicating common parasite and anthropogenic pollution is causing the extinction of many species. Rest all statements are correct.
Question 127. Which of the following can only reproduce only once in their lifetime?
- Pacific salmon fish
- Bamboo
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
The organism that breeds only once in its lifetime are called monocapric, for example. Pacific salmon fish, bamboo.
Question 128. …A… Are organisms that obtain their nutrition only from plants. This mode of nutrition is also a kind of … B…
Choose the correct option A and B.
- A–herbivores, b–predation
- A–herbivores, b–mutualism
- A–omnivores, b–commensalism
- A–omnivores, b–predation
Answer: 1. A–herbivores, b–predation
NEET practice test on Population Interaction
Question 129. Herbivores do not prefer calotropis
- Due to its appearance
- Due to the production of foul odor
- Due to the formation of cardiac glycosides
- Due to its distasteful leaves
Answer: 3. Due to the formation of cardiac glycosides
Question 130. Find the incorrect match.
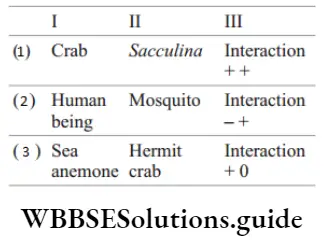
Answer: 1. Only (1) is an incorrect match and can be corrected as crab and sacculina do not show positive interaction. They show negative or parasitic interaction. Parasitic sacculina destroys a crab’s gonads, rendering the crab permanently infertile. The rest matches are correct.
Question 131. Which of the following is inappropriately defined?
- The parasite is an organism that only lives inside the body of other organisms and is detrimental to it.
- A host is an organism that only provides food and shelter to another organism.
- Amensalism is a relationship in which one species is benefitted, whereas the other is unaffected. 4. A predator is an organism that catches and kills other organisms of the same species for food.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 4
- 3 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 3 And 4
Answer: 1. 1 And 4
- Statements I and iv are correct, while ii and iii are incorrect because a host is an animal or plant in which a parasite lives. Amensalim is a relationship between two organisms in which one is inhibited or destroyed and the other is unaffected.
- Predators are those that obtain food by the killing and consuming of other organisms. A parasite is an organism that lives in another organism called the host and harms it.
Question 132. Match the following columns.
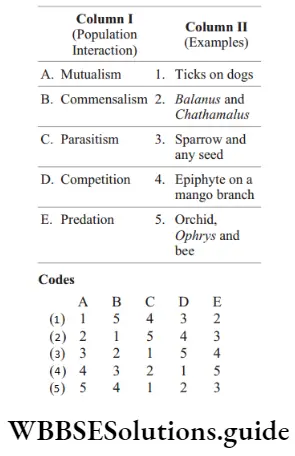
Answer: 3. A–3, b–2, c–1, d–5, e–4
Question 133. Consider the following statements.
- Some species of insects and frogs show critical coloration.
- Some animals are poisonous.
Monarch butterflies are distasteful.
- The above adaptations are against
- Predation
- Mimicry
- Symbiosis
- Protection
Answer: 1. Predation
Given statement are the adaptations through which prey can avoid their predators. Mimicry, camouflage, and poisonous chemicals are the different strategies to avoid predators.
Question 134. Match the items in column I with

Answer: 2. A–3, b–2, c–4, d–1
Question 135. Interactions observed in the ecosystem.
- Fig: wasp:: sea anemone: …A…
- …B… : Barnacle :: plants: grasshopper
- Sacculina : crab:: …C… : Human
- Cat: mouse:: grizzly bear: …d… Identify the option
With the correct set of answers.
- A–shark, b–whale, c–plasmodia, d–sea lion
- A–clown fish, b–dolphin, c–gut flora, d–salmon
- A–clown fish, b–whale, c–plasmodia, d–salmon
- A–crab, b–whale, c–plasmodia; d–elephant seal
Answer: 3. A–clown fish, b–whale, c–plasmodia, d–salmon
Question 136. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Lichen, an association of fungus and algae is an example of mutualism
- Those epiphytes which use other plants only for support and not for nutrition supply are examples of commensalism
- Sea anemone on hermit crab is an example of protocooperation
- Mutualism, protocooperation, and commensalism cannot be included under symbiosis
Answer: 4. Mutualism, protocooperation, and commensalism cannot be included under symbiosis
- The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as symbiosis means ‘living together’. It is a beneficial co-action between two (or more) different species in which one or both the species are benefitted and neither species is harmed.
- Symbiotic relationships are manifested through commensalism, protocooperation, and mutualism and are widespread in nature.
- Commensalism is an association or relationship between two different organisms in which one is always benefitted, while the other is neither benefitted nor harmed.
137. Match the following columns.
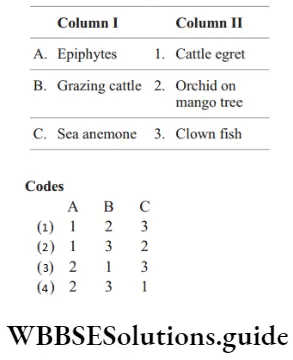
Answer: 3. A–2, b–1, c–3
Question 138. In the case of the peppered moth (Biston betularia), the black-coloured form became dominant over the light-coloured form in England during the Industrial Revolution. This is an example of
- The appearance of the darker-colored individuals due to very poor sunlight
- Protective mimicry
- Inheritance of darker color character acquired due to the darker environment
- Natural selection whereby the darker forms were selected
Answer: 4. Natural selection whereby the darker forms were selected
- In the case of the peppered moth (Biston betularia), the black-coloured form became dominant over the light-coloured form in England during the Industrial Revolution.
- This is an example of natural selection. This group is about species that gain protection from predators due to selection caused by nature.
Question 139.
- Bears go into …A… During winters.
- Conical age pyramid with a broad base …B… Human population.
- Pollination of fig by wasp …C…
- An area with a high level of species richness is known as …D…
Choose the correct combination.
- A–hibernation, B–expanding, C–mutualism, D–hotspot
- A–hibernation, B–expanding, C–mutualism, D–hotspot
- A–hibernation, B–expanding, C–hotspot, D–mutualism
- A–aestivation, B–hotspot, C–expanding, D–mutualism
Answer: 2. A–hibernation, b–expanding, c–mutualism, d–hotspot
Question 140. Match the column 1 with column 2 and select the correct option.
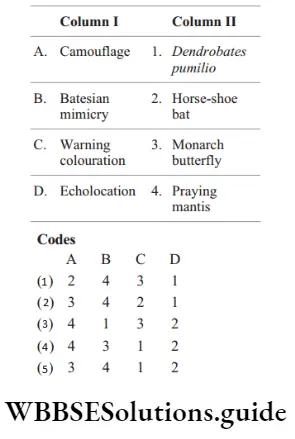
Answer: 4. A–4, b–3, c–1, d–2
Question 141. Which of the following statements regarding species interdependence are true?
- An association of two species where one is benefitted and the other remains unaffected is called mutualism.
- An interspecific association where both partners derive benefit from each other is called commensalism.
- A direct food relation between two species of animals in which one animal kills and feeds on another is referred to as predation.
- A relationship between two species of organisms where both the partners are benefitted from each other is called symbiosis.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 3 And 4
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 2 and 4
Answer: 2. 3 And 4
Statements 3 and 4 are correct as predation is the direct food relation between two species of animals in which one animal (predator) captures and feeds on another (the prey). In symbiosis (mutualism) two organisms live together in close physical association in which both derive benefits, for example. Lichen.
