Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Questions And Answers
1. Why do waste products not get stored in meristematic tissue?
Answer:
Waste products not get stored in meristematic tissue because
The cells, present in the meristematic tissues are very active, so, they cannot store any waste materials in them.
Question 2. What do you mean by homogeneous and heterogeneous cells?
Answer:
Homogeneous cell: The cells which have the same structure and function are known as homogeneous cells.
Heterogeneous cell: The cells which have different structure and function are known as heterogeneous cells.
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
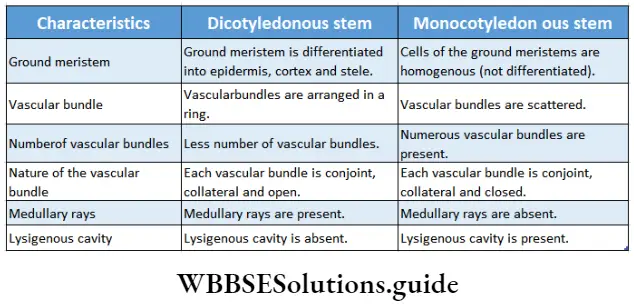
Question 3. How will you identify whether a stem is a dicot or monocot, by observing its cross-section under the microscope?
Answer:
It can be identified by the characteristics given in the following table
Question 4. What is a bundle cap?
Answer:
Bundle cap
In some dicotyledonous plants (for example sunflower), 3 to 4 layers of sclerenchyma cells form cap-like structures on the vascular bundles. This layer of sclerenchyma cells is known as a bundle cap.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
Question 5. Write down the nature of tissue in the cambium. phellogen and ground meristem.
Answer:
Cambium: Secondary meristematic tissue. Phellogen: Secondary meristematic tissue. Ground meristem: Primary meristematic tissue
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 6. Write down the names of the sclereids found in apples, leaves of water lilies and peas.
Answer:
Apple: Brachysclereid.
Leaf of water lily: Trichosclereid. Leaf of pea: Osteosdereid.

Question 7. How will you differentiate metaxylem and protoxylem primarily?
Answer:
The Lumen of the protoxylem is smaller than the metaxylem.
Question 8. Name the dead cells present in the xylem and phloem tissues.
Answer:
Dead cells in xylem tissue: Tracheids, trachea and xylem fibres.
Dead cells in phloem tissue: Phloem fibres.
Question 9. Name the living cells of the xylem and phloem tissues.
Answer:
Xylem: Xylem parenchyma.
Phloem: Companion cell, phloem parenchyma and sieve tube.
Question 10. Define the following fibres—Surface fibre, Extra-xylary fibre, and Perivascular fibre.
Answer:
Surface fibre: The fibres present in any part of the plant are known as surface fibres. example coconut fibre.
Extra-xylary fibre: The fibres found on the outer portion of the xylem tissue, are known as extra-xylary fibre. example surface fibre.
Perivascular fibre: The fibres present near the endodermis, are known as perivascular fibres. example, pericycle fibres.
Question 11. Which cambium is required for the formation of a cambium ring?
Answer:
Interfascicular cambium, as well as intrafascicular (fascicular) cambium, is required for the formation of a cambium ring.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1. Name the cavity of the vascular bundle in the monocot stem.
Answer:
Lysigenous cavity
Question 2. What are the components of cuticles in leaves?
Answer:
Cutin
Question 3. Secondary meristematic tissue develops from which tissue?
Answer:
Permanent tissue
Question 4. In which type of stem vascular bundles are arranged in a ring?
Answer:
Dicotyledonous stem
Question 5. Name the vascular bundle where the phloem surrounds the central strand of the xylem.
Answer:
Hadrocentric or amphicribral vascular bundle
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 6. Name the tissue that gives mechanical support to the plant.
Answer:
Sclerenchyma
Question 7. Which part subterminalises apical meristem of root?
Answer:
Root cap region
Question 8. Give an example of two fruits having sclerite.
Answer:
Guava and pear
Question 9. Name the layer of the root tissue system from which lateral roots emerge.
Answer:
Pericycle
Question 10. From which part of the dicot stem cambium ring forms during its secondary growth?
Answer:
Interfascicular cambium and intrafascicular cambium join to form cambium ring
Question 11. Which tissues form calyptrate?
Answer:
Apical meristematic tissue
Question 12. Write the name of the tissue that is involved with growth in height and width of plants.
Answer:
Lateral growth of plant occurs due to the growth of the cambium and an increase in width occurs due to the division of apical meristematic tissue.
Question 13. Which tissue is called living mechanical tissue? Write its types.
Answer:
Collenchyma. It is of three types—
- Tangential collenchyma,
- Angular collenchyma,
- Lacunar collenchyma.
Question 14. Name the tissue responsible for secondary growth.
Answer:
Secondary meristematic tissue (cambium and cork cambium)
Question 15. Companion cell belongs to which type of permanent tissue?
Answer:
It is a component of phloem.
Question 16. Name the tissue of plants whose cells have thin cell walls and are capable of division even after maturation.
Answer:
Parenchyma cell
Question 17. Name two sieve components found in phloem.
Answer:
Sieve cells and sieve tubes
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 18. The product of photosynthesis is transported from the leaves to various parts of the plant and stored in c some cells before being utilised. What are the I cells/tissues that store them?
Answer:
Parenchyma
Question 19. The protoxylem is the first formed xylem. The protoxylem lies next to the phloem, what kind of arrangement of xylem would you call it?
Answer:
Exarch
Question 20. What is the function of phloem parenchyma?
Answer:
Its function is lateral conduction of food and water from the xylem.
Question 21. What is the epidermal cell modification in plants which prevents water loss?
Answer:
Epidermal hai
Question 22. What is present on the surface of the leaves which helps the plant prevent loss of water but is absent in roots?
Answer:
Cuticle layer and wax
Question 23. What constitutes a cambial ring?
Answer:
Interfascicular and intrafascicular cambium strips
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE
Question 24. The cross-section of a plant material showed the following features when viewed under the microscope—
Answer:
Dicot roo
- Vascular bundles were radially arranged
- Four xylem strands with exarch I conditions of protoxylem. To which organ should it be assigned?
Question 25. What do hardwood and softwood stand for?
Answer:
Hardwood mainly consists of xylem vessels whereas the chief constituent of softwood is tracheids.
Question 26. Write one difference between root hair and stem hair.
Answer:
Root hair absorbs water from soil and stem hair reduces the rate of transpiration
