Alekhya puram
Alekhya puram
WBBSE Class 10 Life Science Chapter 3 Heredity And Common Genetic Diseases Multiple Choice Questions
Chapter 3 Heredity And Common Genetic Diseases Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Following the monohybrid cross of Mendel if a hybrid tall (Tt) pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant, what would be the percentage of hybrid tall pea plants in the first filial generation (F,)?
- 25 percent
- 50 percent
- 75 percent
- 100 percent.
Answer. 2. 50 percent
The percentage of hybrid tall pea plants in the first filial generation (F,) will be 50 per cent.
Question 2. What will be the genotype ratio of a cross between hybrid tall pea plants (Tt) and dwarf pea plants (tt)?
- 1TT = 2Tt 1 tt
- 1Tt : 1tt
- Tt = Ite
- All Tt.
Answer: 1 Tt: 1
It will be the genotype ratio of a cross between hybrid tall pea plants (Tt) and dwarf pea plants (tt).
Question 3. If a pure tall (TT) pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant, what would be the percentage of hybrid tall pea plants in the first filial generation (F,) under the rule of mendels monohybrid cross?
- 15 percent
- 50 percent
- 75 percent
- 100 percent.
Answer. 4. 100 percent.
The percentage of hybrid tall pea plants in the first filial generation (F,) by the rule of Mendel monohybrid cross is 100 per cent.
Read and Learn More Class 10 Life Science MCQs
Question 4. The percentage of hybrid tall plants in F, generation produced from crossing two hybrid tall parental stocks is 4
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%.
Answer. 2.50%
The percentage of hybrid tall plants in F, generation produced from crossing two hybrid tall parental stocks is 50%.
Question 5. The father of Genetics is
- Darwin
- Bateson
- Benda
- Mendel.
Answer. 4. Mendel.
The father of Genetics is Mendel.

Question 6. A pair of contrasting characters is called
- Phenotype
- Genotype
- Gene
- Allele.
Answer. 4. Allele
A pair of contrasting characters is called Allele.
Question 7. The character which predominates and is seen in F, generation is said to be ・
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Particular
- Special.
Answer. The character which predominates and is seen in the F, generation is said to be Dominant.
Question 8. The term gene was coined by p
- Morgan
- Weismann
- Lamarck
- Johannsen.
Answer. The term gene was coined by Johannsen.
Question 9. When two individuals are similar in external BRESAUSASE but different in their genetic make-up, they are called as
- Allele
- Pure
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous.
Answer. 4. Heterozygous
When two individuals are similar in external appearance but different in their genetic makeup, they are called Heterozygous.
Question 10. What would be the probable genotype of pure dwarf pea plant a
- Tt
- tt,
- TT,
- None of the above
Answer. 2. tt
The probable genotype of pure dwarf pea plant will be tt
Question 11. Mendel’s choice of contrasting characters from pea plants are
- 8 pairs
- 7 pairs
- 6 pairs
- 5 pairs
Answer. 2. 7 pairs
Mendel choice of contrasting characters from pea plants is 7 pairs.
Question 12. One pure red eyes Drosophila when crossed with pure white eyes Drosophila the offspring in F, generation will be found (when red is dominant over white)
- Both red and white eyes,
- Only red eyes,
- Only white eyes.
- Intermediate type of eyes.
Answer. 2. Only red eyes,
One pure red eyes Drosophila when crossed with pure white eyes Drosophila the offspring in F, generation will found (when red is dominant over white) Only red eyes.
Question 13. When a hybrid black guinea pig is crossed with a pure white Guineapig the offspring of F, will be –
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
- 1:1
- None of them.
Answer. 3.1:1
When a hybrid black guinea pig is crossed with a pure white Guinea pig the offspring of F, will be 1: 1.
Question 14. The phenotype result of Mendel’s dihybrid cross will be
- 1:1:1:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 2:3:3:4:5
- 1:2:3:4
Answer. 2. 9: 3:3:1
The phenotype result of Mendel’s dihybrid cross will be 9: 3:3:1
Question 15. In dihybrid cross types of phenotypic offspring are produced in F, generation ・
- 2
- 5
- 6
- 4
Answer. 4. 4
In dihybrid cross types of phenotypic offspring are produced in F, generation 4.
Question 16. Hereditary component is
- Nucleus
- Chromosome
- DNA
- Protein
Answer. 3. DNA
The hereditary component is DNA.
Question 17. Mendel’s experimental results were published in the year
- 1900
- 1866
- 1865
- 1864
Answer. 2. 1866
Mendel’s experimental results were published in the year 1866.
Question 18. Like begets like is an important and universal phenomenon of life is due
- Genetics
- Eugenesis
- Morphology
- Embryology
Answer. 1. Genetics
Like begets like is an important and universal phenomenon of life due to Genetics.
Question 19. Which one is a hereditary disease?
- Cataract
- Leprosy
- Blindness
- Phenylketonuria
Answer. 4. Phenyl ketonuria
Phenyl ketonuria is a hereditary disease.
Question 20. How many types of genotypes will be obtained in plants of the F, generation when two hybrid tall plants (Tt) are crossed?
- One type
- Two types
- Three types
- Four types
Answer. 3. Three types
Three types of genotypes will be obtained in plants of the F, generation when two hybrid tall plants (Tt) are crossed.
Question 21. The pea plants produced from the seeds obtained from a cross between hybrid tall (Tt) and pure dwarf (tt) pea plants will be
- All tall
- All dwarf
- 50% tall, 50% dwarf
- 75% tall, 25% dwarf.
Answer.
The pea plants produced from the seeds obtained from a cross between hybrid tall (Tt) and pure dwarf (tt) pea plants will be 50% tall, and 50% dwarf.
Question 22. Following the monohybrid cross of Mendel if a hybrid tall (Tt) Pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant, what would be the percentage of
hybrid tall pea plant in the first filial (F,) generation?
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer. The percentage of hybrid tall pea plants in the first filial (F,) generation will be 50%
Question 23. Who is known as the father of Genetics・?
- Lamarck
- Darwin
- Hugo Devries
- Mendel.
Answer. 4. Mendel
Mendel is known as the father of Genetics・
Question 24. The genotypes of F, plants obtained by crossing two hybrids (Aa) plants will be
- One
- Two
- Three
- four.
Answer. 3. Three
The genotypes of F, plants obtained by crossing two hybrids (Aa) plants will be Three types.
Question 25. If hybridization is made between two aye tall pea plants; the hybrid tall pea plants in F, generation will be
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer. 2. 50%
If hybridization is made between two hybrid tall pea plants, the hybrid pea plants in F, generation will be 50%. ゥ
Question 26. The genetic constitution of an organism is
- Phenotype
- Genotype
- Genotype and Phenotype
- None of them.
Answer. 2. Genotype.
The genetic constitution of an organism is genotype.
Question 27. The phenotypic ratio deduced from the Mendel dihybrid cross is
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
- 9: 3:3: 1
- 9:9:1
Answer. 3. 9: 3:3: 1
The phenotypic ratio deduced from the Mendel dihybrid cross is 9: 3:3: 1
Question 28. Inheritance of characters is discussed in a branch of science known as
- Cytology
- Genetics
- Evolution
- Adaptation
Answer. (2) Genetics
Question 29. The term Genetics・has been coined by
- Mendel
- Bateson
- Morgan
- Johansen
Answer. (2) Bateson
Question 30. Mendel did his experiment on a plant known as
- Bean Plant
- Wheat plant
- Paddy plant
- Pea plant
Answer. (4) Pea plant
Question 31. How many laws of inheritance were proposed by Mendel?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer. (2) Two
Question 32. The F, phenotypic ratio of Mendel’s monohybrid cross is
Answer. (2) 3: 1
- 2:1
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
- 9:4:3
Question 33. In the dihybrid cross of Mendel the F, ratio obtained is
- 9:3:3:1
- 9:7
- 1:1:1
- 9:4:3
Answer.(1)9:3:3:1
Question 34. What is the genotypic ratio of F, generation in Mendel’s monohybrid experiment?
- 1:1
- 2:1
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
Answer. (2) 2:1
Question 35. Who proposed the law of independent assortment?
- Darwin
- De Vries
- Mendel
- Lamarck
Answer. (3) Mendel
Question 36. The “tall” trait of the pea plant is
- Dominant
- Semidominant
- Recessive
- Codominant
Answer. (1) Dominant
Question 37. The cross between F, offspring and father or mother is known as
- Test cross
- Reciprocal cross
- Back cross
- None of the above
Answer. (3) Back cross
Question 38. What is meant by the 1: 1 ratio in the monohybrid cross?
- F, organism is homozygote
- F, organism is heterozygote
- F, organism is pure
- The ratio is produced due to back cross
Answer. (2) F, organism is heterozygote
Question 39. Which of the following is a test cross?
- Tt x tt
- tt x tt
- Tt Tt
- TT x TT
Answer. (1) Tt x tt
Question 40. Which of the following is a back cross?
- FX,
- F, x recessive
- FE, xP
- F, x any parent
Answer. (4) F, x any parent
Question 41. Which one of the following is the result of a monohybrid cross?
- 1:1:1:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 3:1
- 9:7
Answer: (3)3.: 1
Question 42. What is known as the unit of heredity?
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Gene
- Protein
Answer. (3) Gene
Question 43. When two different alleles of a gene are present the organism is known as ・
- Heterozygote
- Homologous
- Homozygote
- Hemizygote
Answer. (1) Heterozgote
Question 44. When the pure yellow, round pea plant is crossed with a green wrinkled pea plant, the F, pea plant will be
- All yellow wrinkled
- 50% yellow round, 50% green wrinkled
- All yellow round
- 50% yellow wrinkled, 50% green round
Answer. (3) All yellow round
Question 45. When will all children of a couple be found colourblind?
- If the mother is normal and the father is normal
- If the mother is normal and the father is colourblind
- If the mother is homozygous colourblind and the father is normal
- If the mother is homozygous colourblind and the father is colourblind.
Answer. (4) If the mother is homozygous colourblind and the father is colourblind.
Question 46. The separation of linked genes occurs through
- Crossing over
- Segregation
- Mutation
- Linkage
Answer. (1) Crossing over
Question 47. Colourblind is a sex-linked recessive trait. If a mother is colourblind sons will be
- All colourblind
- All normal vision
- 50% colourblind, 50% normal
- None of the above
Answer. (1) All colourblind
Question 48. Which of the following conditions is related to haemophilia?
- A responsible recessive gene present in the X chromosome
- A responsible dominant gene present in the X chromosome
- A responsible dominant gene present in the Y chromosome
- A responsible dominant gene present in the autosomal chromosome
Answer. (1) A responsible recessive gene present in the X chromosome
Question 49. In seven pairs of contrasting characters in the pea plant studied by Mendel, the number of flower-based characters was
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer. (2) 2 :
Question 50. In Mendel’s experiment, how many different kinds of seeds are produced from a short plant with wrinkled seeds (ttrr)?
- 9
- 4
- 2
- 1
Answer.(4) 1
Question 51. A cross between a dominant phenotype with the recessive parent to check its genotype is called
- Test cross
- Back cross
- Monohybrid cross
- Dihybrid cross
Answer. (1) Test cross
Question 52. Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were
- Round seed shape, constricted pod shape and axial flower position
- Ggreen pod colour, inflated pod shape and axial flower position
- Yellow seed colour, violet flower colour and yellow pod colour
- Axial flower position, green pod colour and green seed colour
Answer. (2) Green pod colour, inflated pod shape and axial flower position
Question 53. The colour-based contrasting traits in several contrasting pairs studied by Mendel in pea plants were
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer. (3) 3
Question 54. The mechanism of transmission of characters, resemblances as well as difference, from the parental generation to the offspring is called
- Astrology
- Heredity
- Coincidence
- Nurture
Answer. (2) Heredity
Question 55. One of the scientists who rediscovered Mendelism was
- Bateson
- Darwin
- Tschermak
- Lamarck
Answer. (3) Tschermak
Question 56. is a change in a gene or chromosome.
- Evolution
- Variation
- Heredity
- Mutation
Answer. (4) Mutation
Question 57. The ability of tongue rolling is controlled by–
- Practice
- Gene
- Environment
- Temperature
Answer. (2) Gene
Question 58. An is an alternative form of gene.
- Allele
- Locus
- Genotype
- Phenotype
Answer. (1) Allele
Question 59. The place of location of a gene is called
- House
- Niche
- Locus
- Chromosome
Answer. (3) Locus
Question 60. means that the organism has two copies of the same allele for a gene.
- Hetergogygous
- Hemizygous
- Homozygous
- Hybrid
Answer. (3) Homozygous
Question 61. Genes are present in a sequence on the chromosomes
- Serial
- Linear
- Circular
- Haphazard
Answer. (2) Linear
Question 62. means that an organism has two different alleles of a gene.
- Hemizygous
- Heterozygous
- Homozygous
- Allozygous
Answer. (2) Heterozygous
Question 63. A genetic hybrid would carry two different of the same gene.
- Cocus
- Numbas
- Types
- Allejes
Answer. (4) Alleles
Question 64. The generation is the first set of parents crossed.
- Parental
- Filial
- Hybrid
- Mother
Answer. (1) Parental
Question 65. The Scientific name of the four o’clock plant is mirabilis
- Indicus
- Jalapa
- Domestica
- Bengalensis
Answer, (2) Jalapa
Question 66. The sex chromosomes of human males are
- XX
- AA
- XY
- PQ
Answer. (3) XY
Question 67. Thalassemia is an autosomal trait.
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Sexlinked
- Poisonous
Answer. (2) Recessive
Question 68. Haemophilic persons have problems with blood
- Pigmentation
- Clotting
- Colour
- Temperature
Answer. (2) Clotting
Question 69. Red colour blindness is the most common.
- Green
- Blue
- Black
- Yellow
Answer. (1) Green
Question 70. Genes do not occur in pairs in
- Endosperm
- Zygote
- Gametes
- Somatic cells
Answer. (3) Gametes
Question 71. The phenomenon which defines the independent assortment is
- Segregation
- Dominance
- Crossing over
- Linkage
Answer. (1) Segregation
Question 72. A haploid set of all the genes present in a gametes is called
- Genome
- Linkage group
- Phenotype
- Genotype
Answer. (1) Genome
Question 73. Who first used the termene?
- Mendel
- Johannsen
- Bateson
- Morgan
Answer. (2) Johannsen
Question 74. Incomplete dominance is observed in
- Hibiscus
- Mirabilis
- Sunflower
- Roulfia
Answer. (2) Mirabilis Jalpa (4 0・clock plant)
Question 75. What will be the percentage of hybrid tall plants produced in F, generation due to hybridisation between two hybrid tall pea plants?
- 100%
- 75%
- 50%
- 25%
Answer. (3) 50%
Question 76. The phenotypic ratio of F, generation in Mendel’s dihybrid cross is-
- 1:2:1
- 9:3:3:1
- 1:3
- 1:1
Answer. (6) 9:23:31
Question 77. All the genes present in interbreeding populations are together known as
- Genone
- Gene pool
- Chromosome
- None
Answer. (2) Gene pool
Question 78. The law derived from the dihybrid cross is
- Law of dominance
- Law of segregation
- Law of independent assortment
- All of these
Answer. (3) Law of independent assortment
Question 79. An alternative form of gene is-
- Chromosome
- Allele
- Character
- None
Answer. (2) Allele
Question 80. The combination of genes in an organism is-
- Phenotype
- Genotype
- Variation
- All
Answer. (2) Genotype
Question 81. The total loss of skin pigment in a body is called
- Leukemia
- Colour blindness
- Albinism
- Haemophilia
Answer. (3) Albinism
Question 82. A blood disease caused by gene mutation is-
- Anaemia
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Albinism
- Malaria
Answer. (2) Sickle cell anaemia
Question 83. An X-linked disease is
- Anaemia
- Haemophilia
- Malaria
- All of the above
Answer. (2) Haemophilia
Question 84. Small differences among individuals are called
- Variation
- Mutation
- Evolution
- All of these
Answer. (1) Variation
Question 85. The technique in which the genetic constitution of an organism is altered by introducing a new gene is-
- Genetic counselling
- Genetic engineering
- Heredity
- None of these
Answer. (2) Genetic engineering
Question 86. A genetic disease is
- Haemophilia
- Thalassemia
- Colourblindness
- All of the above
Answer. (4) All of the above
Question 87. The operation of removal of anthers is known as
- Pollination
- Fertilization
- Emasculation
- Selection
Answer. (3) Emasculation
Question 88. The cross between F, hybrid and recessive homozygous parent is called
- Back cross
- Test cross
- Self cross
- Monohybrid cross
Answer. (2) Test cross
Question 89. Sex-linked inheritance was first discovered by
- Mendel
- Punnet
- Johansen
- T.H. Morgan
Answer. (4) T.H. Morgan
Question 90. The functional unit of DNA molecule is called
- Recon
- Cistron
- Muton
- All of these
Answer. (2) Cistron
Question 91. A common hereditary disorder which is carried on by autosomes is-
- Jurner’s syndrome
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Down syndrome
- a and b
Answer. (3) Down syndrome
Question 92. The genotypic ratio of the monohybrid cross is
- 3:1
- 1:2:1
- 2:2
- 1:3
Answer. (2)1:2:1
Question 93. A ‘Y-chromosome-linked character in males is
- Hypertrichosis of ears
- Pattern baldness
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer. (3) Both (1) and (2)
Chapter 3 Heredity And Common Genetic Diseases Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. is one of the discoverers of Mendelism.
Answer. Hugo De vries.
Question 2. The study of heredity is called
Answer. genetics.
Question 3. The pair of contrasting characters are called
Answer. Alleles.
Question 4. is the father of heredity.
Answer. G J. Mendel.
Question 5. The unit of heredity is
Answer. gene.
Question 6. The phenotypic ratio of the monohybrid cross is
Answer. 3:1.
Question 7. The genotypic ratio of the monohybrid cross is
Answer. 1:2:1.
Question 8. The genetic constitution of an individual is called
Answer. genotype.
Question 9. If the pure tall and the pure dwarf plants are crossed, all the plants produced in F, generation would be
Answer. hybrid.
Question 10. The plant on which the monohybrid experiment was conducted by Mendel is:
Answer. Sweet pea.
Question 11. Among the pairs of contrasting characters, Mendel noted smooth seed as against seed.
Answer. rough.
Question 12. The law of segregation is otherwise known as the law of
Answer. purity of gametes.
Question 13. is regarded as the father of genetics
Answer. Mendel.
Question 14. The phenotype that expresses itself in the F, generation is known as
Answer. dominant.
Question 15. The law of independent assortment was the outcome of Mendel’s cross-experiment.
Answer. Dihybrid.
Question 16. In human beings, chromosomes are responsible for maleness.
Answer. Y.
Question 17.9:3:3:1F, the ratio is the outcome of Mendel’s cross.
Answer. dihybrid.
Question 18. In dihybrid F, plants produce types of gametes.
Answer. 4.
Question 19. Genes in a chromosome are arranged in an order.
Answer. linear.
Question 20. Gene is composed of nucleic acid.
Answer. DNA.
Question 21. Scientists first described linkage in Drosophila.
Answer. Morgan
Question 22. The law of Mendel obtained from the monohybrid cross is known as the law of are.
Answer. Segregation
Question 23. From the dihybrid cross, Mendel derived the law of
Answer. Independent Assortment
Question 24. Mendel worked on pairs of contrasting characters.
Answer. 7
Question 25. The dwarf character of the pea plant is a character.
Answer. Recessive
Question 26. is the phenotypic F, ratio obtained from monohybrid cross.
Answer. 3: 1
Question 27. The colourblind gene is located on the chromosome.
Answer. X
Question 28. If the ratio of test cross result is 1: 1, the parental genotype will be 2nA,
Ans. Heterozygous
Question 29. The same genotypic and phenotypic F, ratio is found in the case of gene.
Answer. Semidominant
Question 30. If the mother is colourblind the phenotype of the sons will be
Answer. All colourblind
Question 31. If the mother is a carrier of haemophilia, the sons will be
Answer. 50% normal, 50% haemophilic
Chapter 3 Heredity And Common Genetic Diseases True Or False
Question 1. Mendel worked on principles of classification.
Answer. false
Question 2. Mendel derived his second law as the law of segregation.
Answer. false
Question 3. From the dihybrid cross, Mendel derived his law of independent assortment
Answer. True
Question 4. Colour blindness is an autosomal recessive trait.
Answer. false
Question 5. Thalassemia is an autosomal trait.
Answer. True
Question 6. There is a skip of generations in the case of dominant pedigree.
Answer. false
WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Life Science And Environment Chapter 1 Control And Co-Ordination In Living Organisms Very Short Answer
Chapter 1 Control And Co-Ordination In Living Organisms Very Short Answer
Question 1. What is the function of muscular tissue?
Answer.
Function of muscular tissue
Movement and Locomotion.
Question 2. How many pairs of legs are present in an insect?
Answer.
Three pairs.
Question 3. Name a few animals that cannot locomote.
Answer.
Sponge and Vorticella.
Question 4. Name a few plants that possess the power of locomotion.
Answer.
Chlamydomonas, Volvox and Pandorina.
Question 5. Which unicellular animal moves with the help of pseudopodia?
Answer.
Amoeba.

Question 6. Which plant moves with the help of pseudopodia?
Answer.
Dictyostelium, Slime mold.
Question 7. In which animal setae is present? What is its function?
Answer.
Earthworm; Function: locomotion.
Question 8. Which animal moves with the help of setae?
Answer.
Earthworm.
Question 9. Which type of locomotion is found in WBC?
Answer.
Amoeboid.
“WBBSE Class 10 Life Science Chapter 1 very short answer questions, Control and Co-ordination”
Question 10. In which cells of man is amoeboid movement noticed?
Answer.
WBC.
Question 11. What kind of movement is found in protoplasm?
Answer.
Cyclosis.
Question 12. In which plant we can see the rotation of protoplasm?
Answer.
Vallisnaria & Chara.
Question 13. In which plant we can see the circulation of protoplasm?
Answer.
In the stamens of Spiderwort & Rheo.
Question 14. Name a plant that shows tactic movement.
Answer.
Volvox & Chlamydomonas.
Question 15. In which plant is a chemotactic movement found?
Answer.
In Spermatozoa of Fern.
Question 16. What is the name of the acid which affects the movement of the sperm of a fern?
Answer.
Malic acid.
Question 17. When does the intensity of stimulus control movement? What kind of movement is that?
Answer.
Nastic movement.
Question 18. What is the name of the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Answer.
Neuron(e) / Nerve cell.
“West Bengal Board Class 10 Life Science Chapter 1 solutions, very short answers, with explanations”
Question 19. Cite an example of a nastic movement.
Answer.
Blooming of flower; e.g. blooming of Lotus flower.
Question 20. Name one plant in which nastic movement is seen.
Answer.
Tulip.
Question 21. “Flowers bloom at height” – What type of movement is this?
Answer.
Nastic movement (Epinastic movement).
Question 22. “The leaflets of a sensitive plant become folded when touched.” What type of movement is this?
Answer.
Nastic movement (Seismonastic movement).
Question 23. “Leaves of Mimosa pudica (lajjabati) close down, when touched” – What sort of movement is this?
Answer.
Turgor movement (Seismonastic movement/Nastic movement).
Question 24. Which kind of movement is seen in the trap door or the tentacles of an insectivorous plant when it comes in contact with the body proteins of an insect?
Answer.
Chemonastic.
Question 25. Which type of movement is exhibited by the Indian Telegraph plant?
Answer.
Movement of variation.
Question 26. What are the stimuli which act in nyctinastic movement?
Answer.
Light and temperature.
Question 27. “The shoot system of the plant moves towards the light.” – What type of movement is this?
Answer.
Positive phototropic movement
Question 28. “The root of a plant is going downwards into the earth.” -What type of movement is this?
Answer.
Positively geotropic movement.
Question 29. Name a plant whose roots grow against the *force of gravity.
Answer.
Rhizophora
Question 30. Give an example of hydrotropism.
Answer.
Example of hydrotropism
Movement of root hairs towards water.
Question 31. “Root moves towards water” – What type of movement is this?
Answer.
Hydrotropic movement
Question 32. “Tendrils quickly coiling round a support” – What type of movement is it?
Answer.
thigmotropic movement
Question 33. What is the movement of the plant body affected by touch?
Answer.
Thigmotropism.
Question 34. What type of movement is found in the stomata of a plant?
Answer.
Movement of variation.
Question 35. Name the flight muscles of a bird.
Answer.
Flight muscles of a bird
Pectoralis minor and pectoralis major.
Question 36. Which part of a neuron receives impulses from the preceding neuron and sends them to its cell body?
Answer.
Dendron / Dendrite.
Question 37. Name the junctional region of two consecutive neurons.
Answer.
Synapse.
Question 38. Where does Myelin sheath exist?
Answer.
Axon.
“Class 10 WBBSE Life Science Chapter 1 very short answer questions, solved answers”
Question 39. Which system coordinates the functions of different organs in the animal body?
Answer.
Nervous system.
Question 40. Which part of the neuron helps to reach the nerve impulse to the next neuron from the cell body?
Answer.
Axon.
Question 41. Mention the names of three major parts of the neuron.
Answer.
(1) Axon, (2) Dendron, (3) Cyton.
Question 42. Which systems of the body perform the function of coordination?
Answer.
Nervous System & Endocrine System.
Question 43. Which is the longest cranial nerve?
Answer.
Vagus.
Question 44. Name the largest part of the brain.
Answer.
Largest part of the brain
Cerebrum.
Question 45. Which is the highest center for sensations and activity in the brain?
Answer.
Cerebral cortex.
Question 46. What are the main components (parts) of the central nervous system?
Answer.
Brain and Spinal cord.
Question 47. What is nerve fiber?
Answer.
Nerve fiber
A nerve fiber is a bundle of long axons of neurons enclosed in a sheath.
Question 48. What is nerve?
Ans.
Nerve
The bundle of nerve fibers enclosed in a sheath is called a nerve, e.g. optic nerve.
Question 49. Mention the number of cranial and spinal nerves in man.
Answer.
(1) cranial nerves 12 pairs, (2) spinal nerves 31 pairs.
Question 50. What is a ganglion?
Answer.
Ganglion
The group of cytons (cell bodies) located outside the brain or spinal cord is called a ganglion.
Question 51. What is the nature of an impulse?
Answer.
Nature of an impulse
The impulse is electrical.
Question 52. What is a synapse?
Answer.
Synapse
A junction between the termination of two neurons is the synapse.
Question 53. Name the fluid present between the meninges.
Answer.
This fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Question 54. What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid?
Answer.
It helps in protection and is also nutritive in function.
Question 55. What is the corpus callosum?
Answer.
Corpus callosum
The transverse band of nervous tissue which connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called corpus callosum.
Question 56. What are gyri and sulci ?
Answer.
The brain’s convolutions are called gyri while shallow grooves in the cerebral cortex are called sulci.
Question 57. Which one is the sensory organ of the vertebrates?
Answer.
Eye.
Question 58. Where is the retina situated?
Answer.
Eye.
Question 59. From which part of the eye does the seeing process start?
Answer.
Cornea.
Question 60. Due to which defect eye patients cannot see things near?
Answer.
Longsightedness or hypermetropia.
“Control and Co-ordination in Living Organisms WBBSE Class 10, very short answers, exam-focused”
Question 61. Through which mechanism the dilation & contraction of the pupil is done?
Answer.
Automatic reflex.
Question 62. In which animal are both simple and compound eyes found?
Answer.
Cockroach.
Question 63. What is the unit of compound eye?
Answer.
Ommatiduim; (pi. ommatidia).
Question 64. Name the muscles that make the eye lens thicker and flatter while focusing on an object.
Answer.
Miniature muscles.
Question 65. What is the function of the pupil in the eye of man?
Answer.
Through it, light enters the eye/control of light entry.
Question 66. What performs the function of coordination in a plant body?
Answer.
Hormone.
Question 67. Name one chemical co-ordinator in the plant.
Answer.
Auxin.
Question 68. Name a hormone that is produced in plant leaves.
Answer.
Florigen.
Question 69. What is the function of florigen?
Answer.
Formation (production) and blooming of flowers.
Question 70. Name the hormone responsible for the growth of petiole in the lotus.
Answer.
Auxin.
Question 71. From which gland is the gonadotrophic hormone secreted?
Answer.
Pituitary gland.
Question 72. Which endocrine gland is known as the “third eye”?
Answer.
Pineal gland.
Question 73. Which endocrine gland is called life-watch?
Answer.
Pineal gland.
Question 74. Which gland is known as the ‘pacemaker’ of the endocrine orchestra?
Answer.
Thyroid gland.
Question 75. From which gland thyroxine is secreted in the human body?
Answer.
Thyroid gland.
Question 76. A certain group of cells in the pancreas acts as an endocrine gland. What is the group of cells called?
Answer.
Islets of Langerhans.
Question 77. Name two mixed glands.
Answer.
Pancreas, Gonad.
Question 78. Name the hormone which is secreted from the adrenal gland.
Answer.
Adrenaline / Cortin.
Question 79. Name two trophic hormones.
Answer.
ACTH and GTH.
Question 80. Name two hormones produced by the alimentary canal.
Answer.
(1) Gastrin (2) Secretin.
Question 81. Mention the chemical nature of animal hormones.
Answer.
Protein or peptide; modified amino acid and steroid.
Question 82. What are chemical co-ordinators?
Answer.
The hormones that bring about the co-ordination of the body in association with the nervous system are called chemical co-ordinators.
Question 83. What is the other name of insulin?
Answer.
The other name of insulin is antidiabetic hormone.
Question 84. What is the function of ADH?
Answer.
The ADH is a water-retaining hormone that maintains electrolytic balance in the body.
Question 85. Name the hormone and the endocrine gland that require iodin for their functioning.
Answer.
The thyroxine hormone and thyroid gland require iodine for their functioning.
Question 86. Name the main chemical substance present in thyroxine.
Answer.
The main chemical substance present in thyroxine is iodine.
Question 87. What condition in the human body may result due to prolonged deficiency of iodine in food?
Answer.
The prolonged deficiency of iodine in food may result in goiter.
Question 88. What is diabetes mellitus?
Answer.
Diabetes mellitus
The excretion of glucose along with the urine is called diabetes mellitus. It is caused due to the deficiency of insulin hormone.
Question 89. Name some important sex hormones.
Answer.
Testosterone, oestrogen and progesterone.
Question 90. Which hormones are associated with puberty in males and females?
Answer.
Testosterone hormone is associated with puberty in males while estrogen and progesterone are associated with puberty in females.
Question 91. Where is the pituitary gland located?
Answer.
At the base of the brain in the region of the diencephalon.
Question 92. Where are the cells of Islets of Langerhans located?
Answer.
The cells of Islets of Langerhans are located in the pancreas.
Question 93. What is the main criterion for movement and locomotion?
Answer.
There must be a stimulus. Without the influence of stimulus, displacement of body parts will not be considered a movement
Question 94. Why is the circulation of protoplast, not a locomotion?
Answer.
It is not an example of locomotion because no stimulus is involved here, the locomotion takes place through the Brownian movement of protoplasmic particles.
Question 95. Why is chromosomal movement in the spindle not considered as locomotion?
Answer.
The displacement of chromosomes is not in response to stimulus, but due to the contraction of spindle fibers.
Question 96. Why is the displacement of plants floating in water not an example of locomotion?
Answer.
Displacement takes place due to water current and not due to stimulus, therefore, this is not an example of locomotion.
Question 97. Give an example of locomotion in plants.
Answer.
Movement of Chlamydomonas toward a source of light is an example of phototaxis.
Question 98. What is heliotropism ?
Answer.
Heliotropism
The tropic movement (bending of stem tip) under the influence of the direction of sun rays is heliotropism.
Question 99. What is haptonasty?
Answer.
Haptonasty
Nastic movement in response to touch stimulus is called haptonasty.
Question 100. What type of movement is observed in sunflowers?
Answer:
When the sunflower opens in the morning it is an example of helionastism. When a sunflower moves along the direction of the sun’s path in the sky, it is an example of heliotropism.
Question 101. Do you consider pseudopodia as a locomotory organ of Amoeba?
Answer.
The pseudopodia in amoeba, although help in locomotion, they are not permanent structures of Amoeba. It is, therefore, not proper to consider pseudopo dia as a locomotory organ.
Question 102. What would happen to the locomotion of Earthworm when it is placed on a glass sheet?
Answer.
The earthworm will be unable to locomote as it will not be able to use its setae.
Question 103. What would happen to the locomotion of cockroaches if the middle legs were amputated?
Answer.
The cockroach will not be able to locomote as it will not be able to balance its body.
Question 104. What would happen to a fish if the air bladder is removed?
Answer.
The fish will not be able to float
Question 105. What would happen to a fish if the paired fins were amputated?
Answer.
The fish will not be able to change direction during locomotion.
Question 106. Which animal cannot locomote? Amoeba/Obelia/Earthworm.
Answer.
Obelia.
Question 107. Which plant shows locomotion? Chara/Volvox/Pea.
Answer.
Chara.
Question 108. Which one is not locomotion? Ciliary movement of Chlamydomonas/ Protoplasmic movement / Amoeboid movement.
Answer.
Protoplasmic movement
Question 109. Locomotion in plants is termed as Taxism Tropism/Nastism.
Answer.
Taxism.
Question 110. Movement of curvature in plants due to growth is termed Tropism/ Hyponastism/Epinastism.
Answer.
Tropism.
Question 111. Seismonasty is caused due to Light/Wound/Touch.
Answer.
Touch.
Question 112. Setae are the locomotory organs of cockroaches/Fish/earthworms.
Answer.
Earthworm.
Question 113. Swimbladder is present in Cockroach/Fish/Earthworm.
Answer.
Fish.
Question 114. Number of pairs of walking legs present in cockroaches is 2/3/4.
Answer.
3 pairs.
Question 115. What is the name of the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Answer.
Neurone or Nerve cell.
Question 116. What is the name of the junctional region of two consecutive neurons?
Answer.
Synapse.
Question 117. How many cranial nerves are present in man?
Answer.
12 pairs.
Question 118. The cerebellum is a part of which brain?
Answer.
Hindbrain.
Question 119. Which cell other than neuron is seen in the nervous system?
Answer.
Neuroglea.
Question 120. Where is Schwann’s cell located?
Answer.
In the axon of the neuron.
Question 121. In which part of a neuron are Nissl’s granules found?
Answer.
In the cell body or cyton of neurons.
Question 122. “When we suddenly come across bright light our eyes automatically close up”-What kind of reflex action is this?
Answer.
Simple or unconditioned or Inborn reflex action.
Question 123. Which system coordinates the functions of different organs in the animal body?
Answer.
Nervous system.
Question 124. What are the different parts of the central nervous system?
Answer.
The brain and spinal cord are the two parts of the central nervous system.
Question 125. In which part of the neuron the nodes of Ranvier are found?
Answer.
Nodes of Ranvier are found in the nerve fiber of neurons.
Question 126. Name a mixed cranial nerve.
Answer.
Vagus nerve.
Question 127. Write the name of the 1st cranial nerve.
Answer.
Olfactory nerve.
Question 128. What is the function of Pons in the brain?
Answer.
It controls respiration, secretion of saliva, and micturition.
Question 129. Which part of the brain controls intelligence?
Answer.
Cerebrum.
Question 130. How many spinal nerves are present in a man?
Answer.
31 pairs.
Question 131. Where is corpus callosum found?
Answer.
Corpus callosum is found between two cerebral hemispheres of the Cerebrum of the human brain.
Question 132. What is the function of CSF?
Answer.
It serves as the shock-absorbing medium and maintains constant pressure in and around the brain.
Question 133. Is there any nervous system present in plants?
Answer.
No.
Question 134. Withdrawal of a finger from a hot object is an example of which type of reflex?
Answer.
This is an example of unconditioned reflex action.
“WBBSE Class 10 Life Science Chapter 1 important very short answers, for board exam preparation”
Question 135. What is known as the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Answer.
Neurone is known as the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Question 136. Which plant hormone is responsible for Apical dominance?
Answer.
Auxin hormone is responsible for Apical dominance.
Question 137. Which hormone helps in the tropic movement of plants?
Answer.
Auxine hormone helps in the tropic movement of plants.
Question 138. Which plant hormone causes the growth of apical bud?
Answer.
Auxine hormone causes the growth of the apical bud.
Question 139. In which part of the plant auxin is formed?
Answer.
In meristematic tissue of apical parts of plants such as root apex and stem apex.
Question 140. What is the full name of I.A.A.?
Answer.
I.A.A. : Indole Acetic Acid.
Question 141. Who performs the function of coordination in a plant body?
Answer.
Hormone.
Question 142. Name one chemical co-ordinator in plants.
Answer.
Auxin.
Question 143. Name a hormone that is produced in plant leaves.
Answer.
Florigen.
Question 144. Which hormone plays an important role in the phototropic movement?
Answer.
Auxin
Question 145. Which hormone helps to produce seedless fruits?
Answer.
Auxin and Gibberelline.
Question 146. Which plant hormone is called a “growth inhibitor”?
Answer.
Abscisic acid
Question 147. Your school garden is overgrown with weeds. Which hormone will you apply to kill them?
Answer.
We will apply synthetic Auxin (2, 4 – D) to kill them.
Question 148. What is the full name of IBA?
Answer.
The full name of IBA is Indole Butyric Acid.
Question 149. What are the components of the nervous system of a vertebrate?
Answer.
The components of the Nervous system are :
(1) Neuron(e), (2) Synapse, (3) Brain, (4) Spinal cord.
Question 150. What helps in the coordination of plants?
Answer.
The hormone helps in the coordination of plants.
Question 151. What is the process by which “seedless fruits” can be produced without fertilization by applying plant hormones?
Answer.
Parthenocarpy is the process by which “seedless fruits” can be produced without fertilization by applying plant hormones.
Question 152. Write the full chemical name of an artificial plant hormone.
Answer.
Naphthalene Acetic Acid is an artificial plant hormone.
Question 153. Name one important hormone of a vertebrate.
Answer.
Thyroxine.
Question 154. Name the gland which is situated within the skull of human beings.
Answer.
Pituitary gland.
Question 155. Name a hormone that stimulates the adrenal gland.
Answer.
ACTH.
Question 156. Name the hormone that is secreted from the thyroid gland.
Answer.
Thyroxine.
Question 157. From which gland thyroxine is secreted in the human body?
Answer. T
hyroid gland.
Question 158. What is the full form of STH hormone?
Answer.
Somato Trophic Hormone.
Question 159. Give the full name of a hormone that helps to strengthen the bones of the human body.
Answer.
Somato Trophic Hormone (STH).
Question 160. Name the disease caused due to hypofunction of STH.
Answer.
Dwarfism.
Question 161. Name the hormone which is secreted from the adrenal gland.
Answer.
Adrenaline.
Question 162. What is the cause of tetany?
Answer.
Deficiency of parathormone.
Question 163. Excess secretion of which hormone causes the Exophthalmic goiter?
Answer.
Thyroxine.
Question 164. Name the gland from which ADH is secreted.
Answer.
The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Question 165. Name an organ that performs both exocrine and endocrine functions.
Answer.
Pancreas.
Question 166. Which hormone helps in re-absorption?
Answer.
Aldosterone.
Question 167. Name any two local hormones of a man.
Answer.
(1) Secretin, (2) gastrin.
Question 168. What is acromegaly?
Answer.
Acromegaly is a disease caused by to hyper-action of STH in adults.
Question 169. From which gland is insulin secreted?
Answer.
Insulin is secreted from the Beta cells of Islets of Langerhans.
Question 170. Write the full name of ACTH.
Answer.
The full name of ACTH is Adreno Cortico Trophic Hormone.
Question 171. Which hormone secreted from the pituitary gland controls the secretion of the ovary and testis?
Answer.
Gonado trophic hormone controls the secretion of the ovary and testis.
Question 172. From which gland is testosterone hormone secreted?
Answer.
The testosterone hormone is secreted from the testis.
Question 173. Write the full form of G.T.H.
Answer.
Gonado Trophic Hormone.
Question 174. Which one is ductless between the salivary gland and the thyroid gland?
Answer.
The thyroid gland is a ductless gland.
Question 175. Where is adrenalin secreted?
Answer.
Adrenal gland (Medulla).
Question 176. From where is estrogen secreted?
Answer.
Placenta.
Question 177. Which hormone helps in lowering blood sugar levels in men?
Answer.
Insulin.
Question 178. What is the cause of Diabetes insipedus?
Answer.
Deficiency of ADH.
Question 179. Which hormone is secreted from the corpus luteum of the ovary?
Answer.
Progesterone.
Question 180. From which gland trophic hormones are secreted?
Answer.
Pituitary gland (Anterior lobe).
Question 181. Name the hormone secreted from the Testis in a man.
Answer.
Testosterone hormone is secreted from the Testis in man.
Question 182. Write the full name of T.S.H.
Answer.
The full name of T.S.H is Thyroid Stimulating Hormone.
Question 183. Name the hormone which controls the secondary sexual characteristics of women.
Answer.
The ‘Oestrogen’ hormone controls the secondary sexual characteristics of women.
Question 184. Name the hormone which helps in the production of sperm.
Answer.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone helps in spermatogenesis.
Question 185. Name three types of nervous systems present in mammals.
Answer.
(1) Central nervous system, (2) Peripheral nervous system, (3) Autonomic nervous system.
Question 186. Who discovered the hormone Insulin?
Answer.
Banting and Best.
Question 187. What is Abscisic acid?
Answer.
Abscisic acid is a major hormone in the plant that induces the formation of an abscission zone in the leaf stalk or petiole and will bring about the shedding of leaves.
Question 188. What is the function of ethylene in plants?
Answer.
It suppresses stem and root elongation and hastens the process of ripening in fruits.
Question 189. What is a Postulated hormone?
Answer.
Postulated hormone: Characteristics and mode of action of these hormones are not known, e.g. Florigen, Vernalin, Calines, etc.
Question 190. What are the three layers covering each nerve?
Answer.
Each nerve is covered by three layers, starting with the inner endoneurium, which covers the nerve fibers; the middle layer called the perineurium, and the outer layer over the perineurium, called the epineurium.
Question 191. What is a dendrite?
Answer.
The branch that originated from the dendron is called a dendrite.
Question 192. What are the two main parts of the central nervous system?
Answer.
Brain and Spinal Cord.
Question 193. What is the main function of the nervous system?
Answer.
It controls the different activities of different organ systems of the body.
Question 194. What is the cranial nerve?
Answer.
Cranial nerve: Nerves originating from the brain are called cranial nerves.
Question 195. What is a neuroglia?
Answer.
Neuroglea: The specialized connective tissues of the nervous system other than nerve cells that provide protection and supply nutrients to it, are called neuroglea.
Question 196. Name the natural hormones of plants.
Answer.
(1) Auxin, (2) Gibberellin, (3) Cytokinin and (4) Ethylene.
Question 197. What is endocrine gland?
Answer.
An endocrine gland is a ductless gland that pours its secretion directly into the blood. The secretion is called hormone which has some definite physiological actions.
Question 198. Name the secondary plant organs where transversely geotropic movement is found.
Answer.
Secondary roots.
Question 199. Name the precursor of IAA Synthesis.
Answer.
Tryptophan amino acid.
Question 200. Which hormone is anti auxin?
Answer.
Abscisic acid.
Question 201. What is the scientific name of the Indian Telegraph plant?
Answer.
Desmodium gyrans.
Question 202. What is the other name of long-sightedness?
Answer.
Hyperopia or Hypermetropia.
Question 203. What is another name for the forebrain?
Answer.
Prosencephalon.
Question 204. What is the other name for the tail fin?
Answer.
Caudal fin.
Question 205. Name the wing feathers of a bird.
Answer.
Remiges.
Question 206. Name the tail feathers of a bird.
Answer.
Rectrices.
Question 207. What is the other name for the study of joints?
Answer.
Arthrology.
“WBBSE Class 10 Life Science Control and Co-ordination, very short Q&A, solved questions”
Question 208. Name the fluid present in diarthroses.
Answer.
Synovial fluid.
Question 209. Which gland is called the master of the master gland?
Answer.
Hypothalamus.
Question 210. Name the fluid that is present inside and outside the brain.
Answer.
Cerebro spinal fluid.
Question 211. Name the junction between two nerve cells.
Answer.
Synapse.
Question 212. Name the part of the brain which is concerned with memory.
Answer.
Cerebrum.
Question 213. Name the part of the human brain that controls body temperature.
Answer.
Hypothalamus.
Question 214. Name a bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath.
Answer.
Nerve.
Question 215. Name the kind of nerve-carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle.
Answer.
Motor Nerve.
Question 216. Name a Neurotransmitter.
Answer.
Acetylcholine.
Question 217. Name the outer covering of the Neurone.
Answer.
Neurolemma.
Question 218. Mention the gap between the axon terminal and dendrites of another cell.
Answer.
Synaptic cleft.
Question 219. Where is located association neuron?
Answer.
Brain and spinal cord.
Question 220. Name the place of best vision in the retina of the eye.
Answer.
Yellow spot
Question 221. Name the term for the capacity of the eye to focus at different distances.
Answer.
Accommodation of eye.
Question 222. Mention the fiber that collectively holds the lens in position.
Answer.
Suspensory ligaments.
Question 223. Mention the place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
Answer.
Blind spot
Question 224. Name the circular window enclosed by the iris.
Answer.
Pupil.
Question 225. Name the blind retinal cells sensitive to dim light.
Answer.
Rod cells.
Question 226. Name the part that equalizes the air pressure in the middle and external ear.
Answer.
Eustachian tube.
Question 227. Name the ear ossicle attached to the tympanum.
Answer.
Hammer.
Question 228. Name the tube which connects the cavity of the middle ear with the throat.
Answer.
Eustachian tube.
Question 229. Which part of the eye is responsible for its shape?
Answer.
Ciliary body.
Question 230. Name the enzyme secreted by the tear gland.
Answer.
Lysozyme.
Question 231. Name the condition in which the eye lens turns opaque and the vision is cut down.
Answer.
Cataract.
Question 232. A potted plant having a long straight shoot is laid parallel to the ground for a week. It would be observed that the -shoot bends vertically upwards at the end of the week. Mention its reason.
Answer.
Due to the positively phototropic movement, the shoot bends vertically upwards. The auxin hormone controls it.
Question 233. What will happen to a seedling if it is kept horizontally on moist soil?
Answer.
The plumule (stem) will go towards light while the radicle (root) will go towards the soil.
Question 234. Name an animal and a plant that moves with cilia.
Answer.
Animal : Paramoecium, Plant : Volvox.
Question 235. Give one example of a locomotory organ one from a unicellular and one from a multicellular organism.
Answer.
(1) Unicellular : Pseudopodia of Amoeba,
(2) Multicellular: Tentacles of Hydra.
“Best very short answer questions for WBBSE Class 10 Life Science Chapter 1, with answers”
Question 236. The pollen tube moves towards embryosac through the style in flower. Why and what sort (type) of movement is it?
Answer.
In response to the chemical substances pollen tube moves towards embryosac. It is a chemotropic movement
Question 237. Name the two muscles that help in locomotion in man.
Answer.
(1) Gluteus medius, (2) Bicep femoris.
Question 238. Name an animal that cannot move from one place to another and a plant that can.
Answer.
Animal: Sponge, Plant: Volvox.
Question 239. Define and exemplify movement.
Answer.
Movement: A change in the place or position of the organs of an organism in response to stimuli is known as movement In plants it is seen in the growth of the different parts of the plants and blooming and closing of the flowers. In animals, it can be seen in movements of legs, wings, fins, head, trunk, tail, eyelids, eyeball, pinna, and in almost all the internal organs like lungs, heart, alimentary canal, etc.
Question 240. What is locomotion?
Answer.
The process by which an organism entirely changes its position from one place to the other is known as locomotion. In the act of walking, running, crawling, hopping, swimming, or flying freely either on land in water, or in the air.
Question 241. What is a neuron? Mention its functions.
Answer.
(1) The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
(2) The function of neurons is the transmission of nerve impulses from various parts of the body to the brain and from the brain to the various parts.
Question 242. What is the weight of the human brain and the length of the spinal cord?
Answer.
(1) Weight of Brain: 1350 gm. (2) Length of Spinal cord: 45 cm.
Question 243. How does an impulse travel across a synapse?
Answer.
The impulse travels across a synapse in one direction only, always from the axons to the dendrites and the cell body of the next neuron. Acetylcholine prevents its backflow.
Question 244. What are the functions of the cerebral cortex?
Answer.
The cerebral cortex is related to intelligence. It is also concerned with thinking, perception of smell, sight; hearing ability of speech, and movement
Question 245. Define reflex action with an example.
Answer.
Any involuntary response to stimuli at an unconscious level that passes along a reflex arc is called reflex action, e.g. winking of eyes when an insect or a dust particle approaches the eyes.
Question 246. Define the reflex arc and state its components.
Answer.
The path through which nerves perform the reflex action is called the reflex arc. Its components are sensory organ, spinal nerve, sensory nerve, spinal cord, motor, and effector organ.
Question 247. What are unconditioned reflexes?
Answer.
Reflexes that can be evoked immediately after birth without any previous encounter with stimulus are called unconditioned reflexes.
Question 248. What is a conditioned or acquired reflex?
Answer.
A conditioned reflex is acquired after birth by applying an indifferent stimulus before or along with an inborn reflex.
Question 249. Name two types of reflexes.
Answer.
The two types of reflexes are –
(1) Unconditioned
(2) Conditioned
Question 250. What happens when accidentally our hand touches hot objects?
Answer.
When our hand accidentally touches any hot object, we withdraw our hand very quickly. This act is governed by the reflex action.
Question 251. Who used the word hormone and when?
Answer.
Animal Hormone: Starling in 1905, Plant Hormone: Fitting in 1910.
Question 252. Why are hormones called “Chemical messengers”?
Answer.
The hormones are carried to all the parts of the body through blood circulation to bring about the harmonious working of the body. Since they act as messengers to regulate physiological processes, they are often called chemical messengers.
Question 253. Which hormone is called emergency hormone and why?
Answer.
The adrenal medullary hormones or catecholamines (ex. adrenalin) are called emergency hormones because they help the body fight against or adjust to emergency conditions by increasing the circulation and respiration along with the activity of skeletal muscles, eyes, etc.
Question 254. Why is the pituitary known as the master gland of the body?
Answer.
The pituitary is known as the master gland of the body because it secretes several hormones that control the activities of other endocrine glands.
Question 255. What are trophic hormones? Give two examples.
Answer.
Hormones of the anterior pituitary are called trophins or trophic hormones because they govern the activities of other endocrine glands.
Ex: Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
Question 256. What is a local hormone? Give two examples of it.
Answer.
Hormones that act at sites very close to the places of their origin are called local hormones. Ex: Gastrin and secretin.
Question 257. What are neurohormones? Give two examples.
Answer.
Neurohormones or neurosecretions are chemical substances produced and liberated by nerve cells, which are carried by blood to various tissues to regulate their functions.
Ex: Oxytocin, vasopressin (or ADH).
Question 258. Define and exemplify neurotransmitters.
Answer.
Neurotransmitters are chemical substances produced and liberated by nerve cells, that act locally and are not carried by blood to distant organs.
Ex: Acetylcholine, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA).
Question 259. What are pheromones ?
Answer.
Pheromones:
Pheromones (gaseous animal hormones) are chemical agents released by one animal into the environment, which produce some behavioral developmental, or reproductive effects in other animals of the same species. Ex: Bombykol of female moth and other sex attractants of animeriÿ. These chemicals are liberated from one animal and attract their opposite sexes for reproduction.
Question 260. How is iodine important to our body?
Answer.
Iodine is the main component of thyroxine hormone which regulates the basal metabolic rate of the body. In this way, iodine is very important to our body.
Question 361. What is a goiter? Why does one suffer from goiter?
Answer. The enlargement of the thyroid gland is called goiter. The person suffers from goiter due to the absence of iodine in the food for a long time.
Question 362. What is parahormone? Give two examples.
Answer.
Parahormones are hormone-like chemical substances that are not true hormones. These are blood-borne chemical substances that are not produced from specialized endocrine tissues. Ex: Erythropoietin, angiotensin.
Question 363. What is the function of a neuron?
Answer.
It helps in the formation of nervous tissue and finally nervous organs such as the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Question 364. What are the functions of the dendron and axon (state only one function of each)?
Answer.
Function of Dendron It carries -impulses from the sense organ to the cell body. The function of the Axon It carry impulses away from the cell body to the motor organ of the body.
Question 365. What is Synapse?
Answer.
Synapse: The physiological junction between the terminal axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron is called a synapse.
Question 366. What is ganglion or nerve ganglion? State one function of it.
Answer.
The fused form of cell bodies of neurons located outside the Central Nervous System is called ganglion or nerve ganglion. Function It helps in the formation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Nerves are originated from these ganglions.
Question 367. Mention one similarity and one dissimilarity between the functions of the nervous system and hormones in the animal body.
Answer.
Similarity Both help in the control and coordination of the functions of different body organ systems. Dissimilarity The Nervous system acts as a physical co-ordinator while hormones
act as a chemical co-ordinator.
Question 368. Mention one characteristic of each of the afferent nerve and efferent nerve.
Answer.
(1) Afferent nerve is made up of sensory neurons and it carries impulses from the sense organ to the central organ. Example Optic nerve.
(2) Efferent nerve is made up of motor neurons and it carries impulses from the central organ to the motor organ. Example:- Occulomotor.
Question 369. What do you mean by the term ‘reflex action’? Give an example.
Answer.
The involuntary action that is automatically controlled by the central nervous system is called ‘reflex action’.
Example:- Withdrawal of hand after touching a hot object.
“Class 10 WBBSE Life Science Chapter 1 very short answers, Control and Co-ordination, study guide”
Question 370. Give one example of a simple reflex action and another example of a compound one.
Answer.
(1) Simple reflex action Withdrawal of hand after touching a hot object.
(2) Compound reflex action Salivation to remember a sour thing.
Question 371. What are the components of the nervous system of a vertebrate?
Answer.
(1) Brain, (2) Spinal Cord, (3) Neves.
Question 372. What is the nervous system?
Answer.
Nervous system: The organ system that is only present in a higher group of animals and whose main function is to control and coordinate the functions of other organ systems of the body, is called the nervous system.
Question 373. Mention the names of three major parts of a neuron.
Answer.
(a) Dendron, (b) Cyton or Cell body, (c) Axon.
Question 374. What is a motor neuron?
Answer.
The neurons that take part in the formation of motor nerves (efferent nerves) originate from the central nervous system (brain or spinal cord) and carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to the muscle organs are called motor neuron.
Question 375. What is a neurotransmitter?
Answer.
Neurotransmitter: The chemical substance produced between two neurons and which helps in the transmission of impulses, is called a neurotransmitter. Example Acetyl choline.
Question 376. What is meninges?
Answer.
Meninges: The membranes (Piamater, Arachnoid, and Duramater) that cover the brain are collectively called meninges.
Question 377. Where are meninges situated and what are their functions?
Answer.
Meninges are located around the brain. Function (1) It protects the brain from injury or jerking, (2) It also supplies nutrients to the brain.
Question 378. What is cerebral circulation?
Answer.
Cerebral circulation: The distribution of nutrients and collection of toxic substances from the cerebrum is called cerebral circulation.
Question 379. Write the full form of CNS. Mention the different parts of CNS.
Answer.
(1) Central Nervous System.
(2) Brain and Spinal cord.
Question 378. What are the hollow spaces of the brain and spinal cord called and what are they filled up with?
Answer.
(1) Hollow spaces of the brain are called ventricles.
(2) The hollow space of the spinal cord is called neurocoel.
(3) The ventricles and neurocoel are filled with Cerebro Spinal Fluid.
Question 379. What do you mean by ventricles of the brain? How many ventricles are there in the brain?
Answer.
(1) Ventricles – The hollow, irregularly shaped cavities of the brain are called ventricles.
(2) There are four ventricles in the brain.
(1) Two lateral ventricles – These lie within the cerebral hemispheres.
(2) Third ventricle – It lies between two Thalami.
(3) Fourth ventricle – It lies between the cerebellum.
Question 380. What is the foramen of Monroe?
Answer.
Foramen of Monroe
The Foramen of Monroe is an opening connected with the third ventricle of the brain.
Question 381. What is a reflex arc?
Answer.
Reflex arc
The path traveled by impulse during reflex action is called a reflex arc.
Question 382. What is auxin?
Answer.
Auxin:
Auxin is a plant hormone produced by the meristematic tissue of the root apex and stem apex.
Question 383. Name three plant hormones.
Answer.
(1) Auxin, (2) Gibberellin, (3) Cytokinin.
Question 384. Mention the sources of Gibberellins and Kinins.
Answer.
(1) Sources of Gibberellins – Germinating seeds, leaves.
(2) Sources of Kinins – Coconut milk, fruits of banana, apple, and tomato.
Question 385. What is Gibberellin?
Answer.
Gibberellin:
Gibberellin: It is a non-nitrogenous organic acid produced mainly within matured cells and germinating seedlings.
Question 386. What is 2, 4-D?
Answer.
2, 4-D
It is an artificial (synthesized in the laboratory) plant hormone whose full form is 2, 4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid.
Question 387. Mention one function of each of any two natural hormones of plants.
Answer.
The function of Gibberellin (1) It checks and minimizes the dormancy period of seeds.
(2) It helps in parthenocarpy.
Function of kinin (1) It influences the dormancy period of seeds.
(2) It helps in the blooming of flowers.
Question 388. Name a non-acidic plant hormone and mention one important function of it.
Answer.
(1) Gibberellin
(2) It is involved in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds.
Question 389. What is the name of the hormone regulating tropic movements in plants? From which part is it secreted?
Answer.
(1) The name of the hormone regulating tropic movement in plants is ‘Auxin’.
(2) Site — It is synthesized in the meristematic tissue of the growing apices of
stem, coleoptyle, root, and young leaves.
Question 390. On which other hormones does the secretion of hormones from the testes and ovaries depend?
Answer.
On Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinising Hormone, their secretion depends.
Question 391. Write one structural and one functional difference between Axon and Dendron.
Answer.
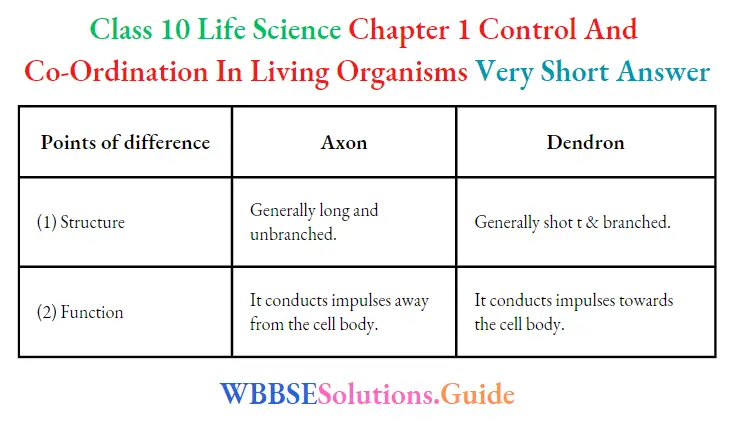
Question 392. What is sensitivity?
Answer.
Sensitivity
Sensitivity is the ability of organisms to detect change and respond to it
Question 393. What are the uses of synthetic hormones?
Answer.
(1) Rooting of cutting (2) Delay of pre-harvest fruit crop (3) Developing parthenocarpic fruits (4) Artificial auxin acts as a herbicide.
Question 394. What happens when hormones are not secreted at the requisite level?
Answer.
When hormones are not secreted at the requisite level some disorders occur in the human body. Such as :
(1) Dwarfism – Due to less secretion of STH in childhood.
(2) Diabetes insipedus – Due to deficiency of ADH.
(3) Goitre or Grave’s disease – Due to Hypersecretion of thyroxine.
(4) Diabetes Mellitus – Due to less secretion of insulin.
Question 395. How do animals respond to stimuli?
Answer.
Irritability or sensitivity is a characteristic feature of all living organisms. It refers to their ability to respond to a stimulus. The stimulus is received by a receptor. It is transmitted using nerves. Finally, an effector (muscle and gland) brings about a response.
Question 396. Illustrate the Nervous Pathway.
Answer.
Stimuli → Receptor → Nerve centre → Effector
Question 397. Why do animals move from one place to another?
Answer.
Animals move from one place to another for to following reasons :
(1) When they hunt for food (2) Escape when under attack (3) Coordinate breeding activity with season when food is plentiful for them and their young.
Plentiful for them and their young.
Question 398. What are the motivations behind locomotion?
Answer.
(1) Finding food (2) Avoiding capture by predators, (3) Dispersal, (4) Finding new favorable habitats, (5) Bringing together individuals for reproductive activity.
Question 399. What is the hypothalamus? Where is it located? Mention its function.
Answer.
Hypothalamus
(1) The hypothalamus is an endocrine gland.
(2) It is located in the forebrain, below the thalamus.
(3) It controls hormonal secretions of the anterior pituitary gland and produces the hormones of the posterior pituitary gland (ADH and oxytocin) which are stored in the Pstelir pituitary and released later.
“WBBSE Life Science Class 10 Chapter 1 solutions, very short answer questions, exam preparation”
Chapter 1 Control And Co-Ordination In Living Organisms Diagrammatic Type Questions
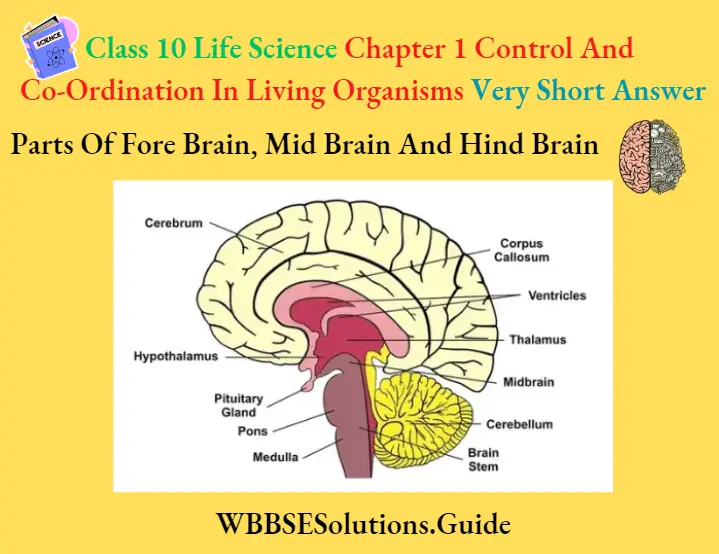
Questions 1. Draw a neat diagram of the human brain and label the following : [Cerebral cortex, Cerebrum, Corpus callosum, Thalamus, Midbrain, Pons, Spinal cord]
Answer.
Question.2. Draw a neat diagram of the structural and functional unit of the nervous system and label the following parts : [Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Dendron, Myelin sheath, Neurilemma, Membrane, Dendrite Cell]
Answer.
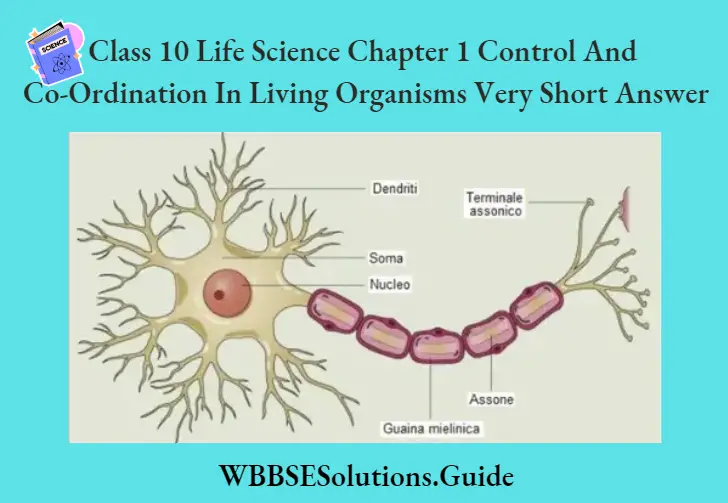
Question 3. Draw a neat and label the following parts of the diagram to show the path of nerve impulses during reflex action. (Sensory neurone, Receptor, Adjustor neurone, Spinal cord, Synapse, Motor neurone)
Answer.
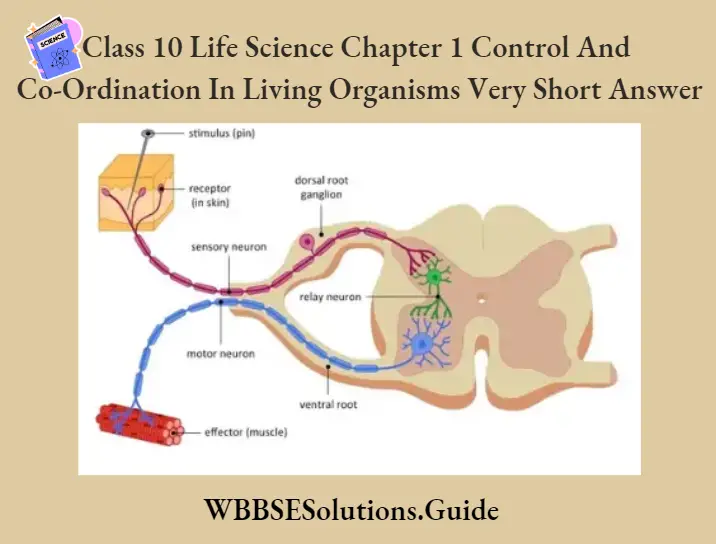
Question 5. Draw a diagram of the human eye and label the following parts: Lens, Retina, Cornea, Sclera, Blindspot, and Aqueous humor.
Answer
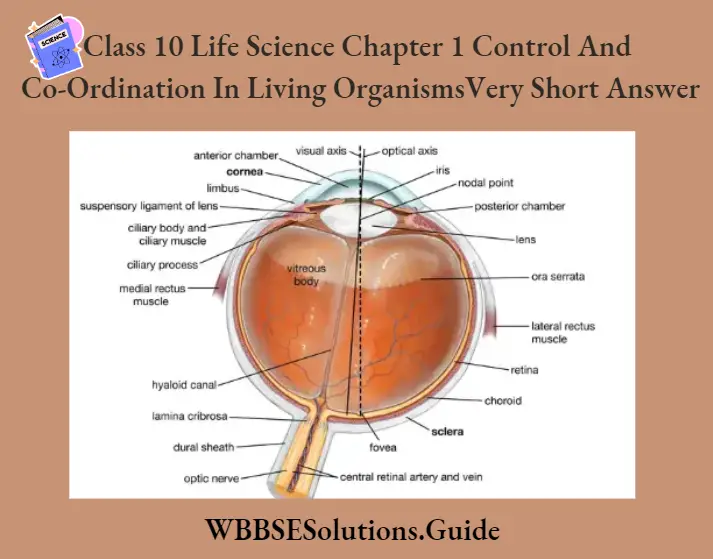
Question 6. Draw a diagram to show different parts of the human ear.
Answer.
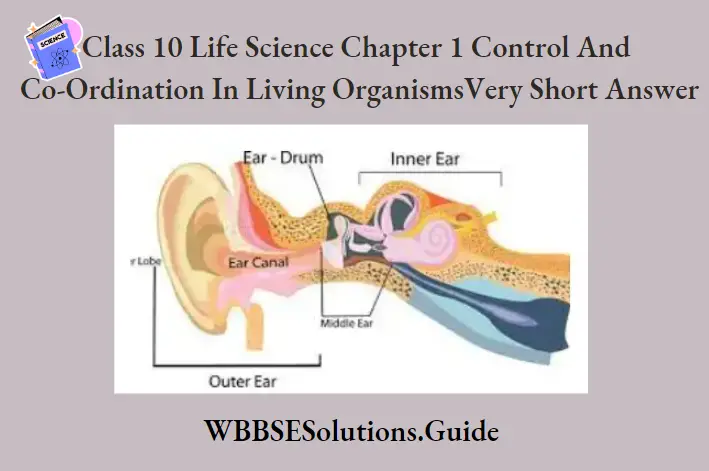
Question 7. Draw a diagram to show the location of endocrine glands in the human body.
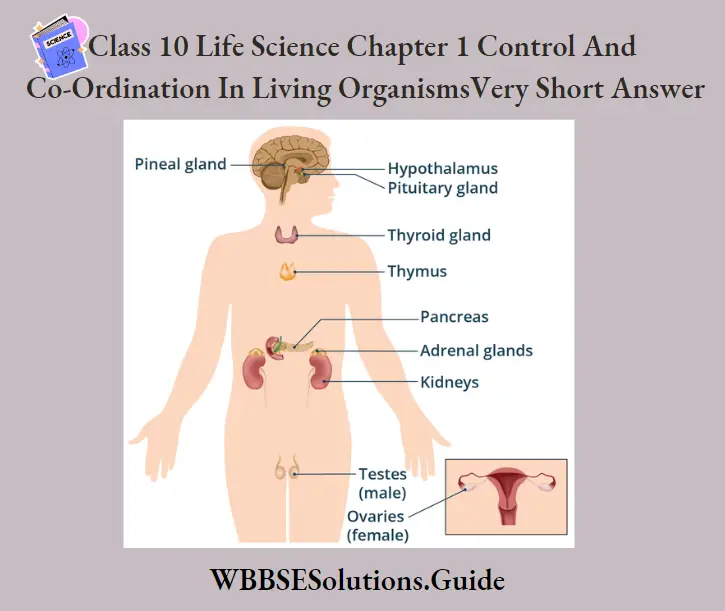
Answer.