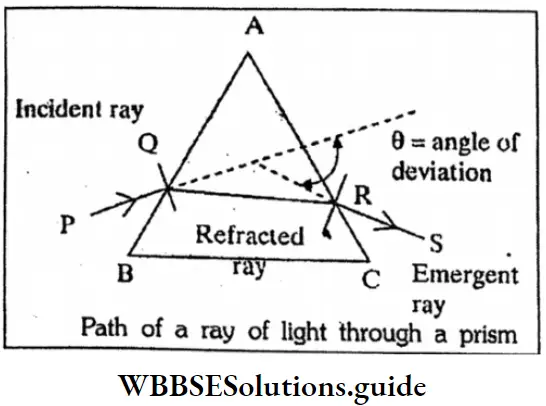
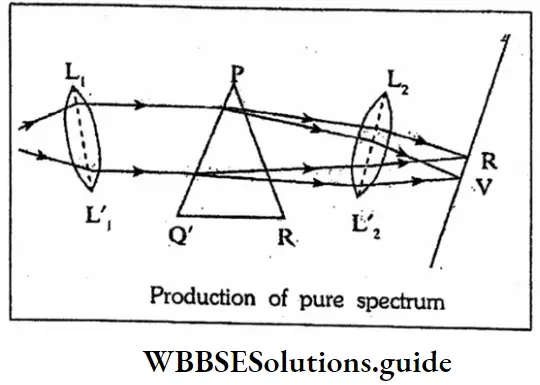
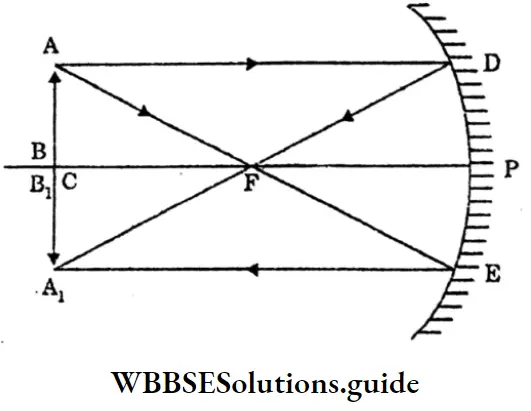
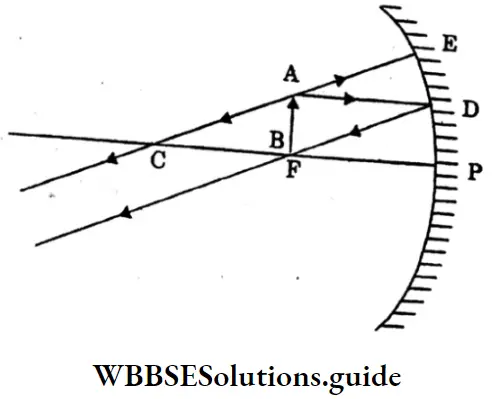
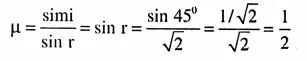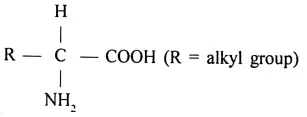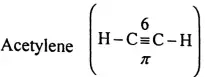Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE Chapter 8 Physical And Chemical Properties Of Matter MCQs
Question 1. The basis of the modern periodic table is
- Atomic volume
- Atomic number
- Atomic size
- Atomic weights
Answer: 2. Atomic volume.
Question 2. Which of the following has the maximum value of electron affinity?
- F
- Cl
- Br
- I
Answer: 2. Cl.
Question 3. Characteristics of transition elements is incomplete
- d-orbitals
- f-orbitals
- p-orbitals
- s-orbitals
Answer: 1. d-orbitals.
Question 4. The element with the highest first ionization potential is
- Boron
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
Answer: 3. Nitrogen.
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE
Question 5. The long form of periodic table based on
- Atomic number
- Atomic mass
- Number of neutrons
- None of these
Answer: 1. Atomic number.
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Physical Science And Environment
Question 6. How many periods are there in the Mendeleev’s periodic table
- 7
- 10
- 6
- 14
Answer: 1. 7
Question 7. The percentage of noble gas present in the air is
- 5%
- 0.01%
- 1%
- 11%
Answer: 3.1%.
Question 8. The shape of the NaCl crystal is
- Tetrahedral
- Octahedral
- Hexagonal
- Icosahedral
Answer: 2. Octahedral.
Question 9. Which has the largest first ionization energy?
- 4
- na
- K
- Rb
Answer: 1. 4.
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE
Question 10. Which one of the following has the largest size?
- Br-1
- I
- I–
Answer: 3. I–
Question 11. Which one of the following is the smallest in size?
- N3-
- O2–
- F–
- Na–
Answer: 4. Na–
Question 12. The element in the third group and third of the periodic table is
- B
- Na
- Al
- Mg
Answer: 3. Al
Question 13. 5f subshell is successively filled up in
- Actinoids
- Lanthanoids
- Tropical metals
- Normal metal
Answer: 1. Actinoids.
Question 14. Which of the following form coloured salts?
- Non-metals
- Metals
- p-block elements
- Transmission elements
Answer: 2. Metals.
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE
Question 15. In the long-form periodic table, the block containing non-metals is
- s
- p
- d
- f
Answer: 2. p
Question 16. Lithium shows a diagonal relationship with
- Ne
- Mg
- Be
- Ce
Answer: 2. Mg.
Question 17. The iso-electronic atom of Ca2+ of Ca2+is
- Mg
- Ne
- Ar
- K
Answer: 3. Ar.
Question 18. Which of the following substances has the highest melting point?
- NaCl
- KCl
- MgO
- BaO
Answer: 3. MgO.
Question 19. The total number of electrons that take part in forming bonds in N2 is
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 10
Answer: 3. 6
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE
Question 20. The compound which contains both ionic and covalent bonds is
- CH4
- H2
- KCN
- KCI
Answer: 3. KCN
Question 21. C-C bond length in the saturated compound is
- 1.47A°
- 1.38A°
- 1.54A°
Answer: 3. 1.54A°.
Question 22. The shortest carbon bond distance is found in the?
- Diamond
- Benzene
- Acetylene
- Ethane
Answer: 3. Acetylene.
Question 23. Which of the following is the most polar?
- CaCl4
- CCI2
- Sncl4
Answer: 3. Sncl4
Question 24. Which of the following exists as monoatomic?
Answer:
- Sulphur
- Helium
- Fluorine
Answer: 2. Helium.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 25. Which class of substance is a common component of all electrovalent compounds?
- Non-Metal
- Metal
- Metalic oxide
Answer: 3. Metal.
Question 26. Which of the following bonds will be non-polar
- N – H
- C – H
- F- F
- O- H
Answer: 3. F – F.
Question 27. Which of the following is more covalent?
- SnCI4
- SnBr4
- Snl4
Answer: 1. SnCl4
Question 28. Which among the following bonds shows the maximum bond strength?
- Sigma bond
- λ bond
- Co-ordinate bond
- Hydrogen bond
Answer: 1. Sigma bond.
Question 29. The element with the atomic number 9 car exhibits an oxidation state of
- +1
- -1
- + 3
- -3
Answer: 2.- 1.
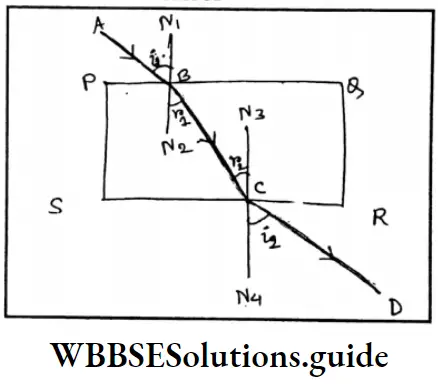
Question 30. Which agent conducts electricity during electrolysis?
- Water
- Ion
- Atom
- Molecule
Answer: 2. Ion.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 31. What is the volume ratio of produced hydrogen and oxygen from the electrolysis of water?
- 1:2
- 2:3
- 2:1
- 1:1
Answer: 3. 2 :1.
Question 32. The flow of current in an electrolyte is due to
- Atoms
- Electrons
- Ions
Answer: 3. Ions.
Question 33. The amount of an ion discharged during electrolysis is not directly proportional to
- Resistance
- Time
- Current
- Non of these
Answer: 1. Resistance
Question 34. On the electrolysis of a q. solution of sodium sulphate, on the cathode, we get
- Na
- H2
- CO
- SO3
Answer: 1. Na.
Question 35. The unit of quantity of electricity is
- Volt
- Coulomb
- Ampere
- Ohm
Answer: 2. Coulomb.
Question 36. For the electroplating of nickel, nickel sulphate is mixed with
- Water
- Nitric acid
- Boric acid
- H2SO4
Answer: 3. Boric acid.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 37. During electrolysis of copper using copper electrodes of copper in solution is
- Increased
- Decreased
- Unaltered
Answer: 3. Unaltered.
Question 38. Ammonia is :
- Acidic
- Basic
- Neutral
- None of these
Answer: 2. Basic.
Question 39. The high heat of the vaporization of ammonia is due to its
- Basic nature
- Polar nature
- High solubility
- Hydrogen bonding.
Answer: 4. Hydrogen bonding.
Question 40. The reaction N2+3H2, = 2NH3, is
- Exothermic
- Endo thermic
- Neither of the two
- Both the two
Answer: 1. Exothermic
Question 41. Nessler’s reagent is :
- K2Hgl4
- K2 Hgl4+KOH.
- K2Hgl4
- KHgl4+KOH
Answer: 2. K2 Hgl4+KOH.
Question 42. Which is most explosive?
- NCI3
- Pcl3
- AsCl3
- All
Answer: 1. NCI3
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 43. With an excess of Cl2, ammonia gives
- NCI3
- HCI3
- NH4CI
- NO2
Answer: 1. NCI3
Question 44. Non-combustible hydride is
- NH3
- PH3
- AsH3
- SbH3
Answer: 1. NH3
Question 45. An aqueous solution of ammonia consists of
- H+
- OH–
- NH4
- NH+OH–
Answer: 4. NH+OH–
Question 46. The vapour density of ammonia is
- 7
- 8.5
- 7.5
- 17
Answer: 2. 8.5.
Question 47. H2S is
- Smells like fish
- Lighter
- Sightly heavier than air
- None of these
Answer: 1. Smells like fish.
Question 48. The gas which is absorbed by NaOH
- NH3
- H2S
- O2
- None of these
Answer: 2.H2S
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 49. H2 S gas is passed through
- P2O5
- CaCl2
- CaO
- None of the above
Answer: 1. P2O5
Question 50. The molecular weight of H2S is
- 32
- 34.
- 36
- 38
Answer: 2. 34.
Question 51. The percentage of nitrogen in the air by volume is
- 20
- 30
- 78
- 88
Answer: 78.
Question 52. The solubility of nitrogen in water is
- Low high
- Very low
- High
- Very high
Answer: 4. Very high.
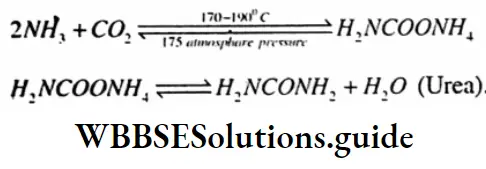
Question 53. Nitrogen-containing organic fertilizer is
- Nitro slim
- Ammonium sulphate
- Urea
- Ammonium nitrate
Answer: 3. Urea.
Question 54. Who discovered nitrogen
- Daniel Rutherford
- Bohr
- Dalton
- Lavoisier
Answer: 3. Daniel Rutherford.
Question 55. In the contract process for the production of H2SO4, on an industrial scale, the impurities of arsenic are removed by :
- Fe2O3
- Al (OH)3
- Fe (OH)3
- Cr (OH)3
Answer: 3. Fe(OH)3
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 56. Oil of vitriol is
- H2SO3
- H2SO4
- H2S2O7
- H2S2O8
Answer: 2. H2SO4
Question 57. Aquafortis is
- HNO3
- HNO2
- H2NO3
- H2N2O2
Answer: 1.HNO3
Question 58. Oleum is
- H2SO5
- H2S2O7
- H2S2O8
- H2SO3
Answer: 2. H2S2O7
Question 59. Most of the plants contain
- Iron
- Zin C
- Sodium
- Potassium
Answer: 4. Potassium.
Question 60. The fluorspar is
- CasO4
- Baso4
- CaCO3
- CaF2
Answer: 4.CaF2
Question 61. Which of the following is not an area of calcium?
- Gypsum
- Limestone
- Dolomite
- Carnalite
Answer: 4. Carnalite
Question 62. Haematite is
- Fe3O4
- Fe2O3
- Fe2O4
Answer: 2. Fe2O3
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 63. Which of the elements is present in haemoglobin?
- Mg
- Fe
- Cu
- Zn
Answer: 2. Fe.
Question 64. Pin iron is also called
- Wrought iron
- Cast iron.
- Steel
- Stainless steel
Answer: 2. Cast iron.
Question 65. The metal present in insulin is
- Copper
- Iron
- Zin C
Answer: Zin C.
Question 66. Which of the following contains nitrogen?
- Fats
- Proteins.
- Carbohydrate
- None
Answer: 2. Proteins
Question 67. Which of the following gases is used in welding?
- C2H4
- C2H2
- CH4
- C2H2
Answer: 2. C2H2
Question 68. Marsh gas mainly contains
- H2S
- CO
- CH4
- C2H2
Answer: 3. CH4
Question 69. The general formula for alkenes is
- CnHzn
- CnH2n+2
- CnHzn-2
- C2nHzn
Answer: 1. CnHzn.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 70. Acidic hydrogen is present in
- Ethyne
- Ethene
- Benzene
Answer: 1. Ethyne.
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE Chapter 8 Physical And Chemical Properties Of Matter Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Periodic changes of what occurs in a periodic table?
Answer: Physical and chemical properties of sets of elements arranged in some manner change periodically.
Question 2. What is the name ‘Oxygen’ group?
Answer: Chalcagens, group.
Question 3. What are ‘d’-block elements called?
Answer: ‘d’-block elements are called transition elements.
Question 4. Is radioactivity a periodic property?
Answer: Radioactivity is not a periodic property.
Question 5. Between Na and Nat which one has greater in size.
Answer: Na has greater in size than Na.
Question 6. Are vander whal’s radii larger than covalent radii?
Answer: Van der Waal’s radii are larger than covalent radii.
Question 7. Have ionisation energies a positive value?
Answer: Ionisation energies have a positive value.
Question 8. What are the elements of the second period called?
Answer: Elements of the second period are called bridge elements.
Question 9. Is the second I.P is always greater than the first I.P. of a given species?
Answer: The second I.P. is always greater than the first I.P. of a given species.
Question 10. What is the valency of an alkali metal?
Answer: The valency of an alkali metal is 1.
Question 11. What is the relation between N3- and O2-?
Answer: N3- and O2- are iso-electronic ions.
Question 12. Between Br and I which one has a metallic character?
Answer: Between Br and I, iodine has a metallic character.
Question 13. What is the valency present in NaH?
Answer: Electrovalency is present in NaH.
Question 14. Which one of NaCl and C6H12O6 will have a higher melting point?
Answer: NaCl.
Question 15. Between MgCl2, and CHCI3, which one is electro-valent in nature?
Answer: MgCl2
Question 16. What do you mean by valence shell?
Answer: The outermost shell of an atom is known as the valence shell.
Question 17. What is the nearest inert element of a chlorine atom?
Answer: The nearest inert element of the chlorine atom is argon (Ar).
Question 18. How many long pair (s) is/are present in XeOF4?
Answer: 1 (one).
Question 19. What is the type of bonding in ferric chloride?
Answer: The type of bonding in ferric chloride is covalent.
Question 20. What is the valency of carbon in CH4, compound?
Answer: The valency of carbon is 4 in the CH4 compound.
Question 21. What is called cryolite?
Answer: AIF3, 3NaF is called cryolite.
Question 22. Is mercury an electrolyte?
Answer: Mercury is a good conductor but not an electrolyte.
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE
Question 23. Which agent conducts electricity through an electrolyte?
Answer: Jons conduct electricity through an electrolyte.
Question 24. What is the function of acid or alkali mixed in water during electrolysis of water?
Answer: Acid or alkali increases the number of ions that help electrolysis.
Question 25. Name two non-electrolytes.
Answer: Sugar solution and glycerine are two non-electrolytes.
Question 26. Name a metal and a non-metal which can be used as electrodes.
Answer: Metal Platinum
Question 27. Between Br– and OH– which ion will be discharged first at the anode?
Answer: Between Br– and OH–,OH– ion will be discharged first at the anode as the position of OH– ion is lower than that of Br– in the electrochemical series.
Question 28. What is called fluorspar?
Answer: CaF, is called fluorspar.
Question 29. What is Nessler’s reagent?
Answer: Nessler’s reagent Nessler’s reagent is an alkaline solution (KOH) of potassium mercuric iodide [K2 Hgl4]
Question 30. Which Particular substance is used to dry ammonia gas?
Answer: Ammonia is dried with calcium oxide (CaO).
Question 31. What is the amount of ammonia present in liquor ammonia?
Answer: 35% (by weight)
Question 32. What is the density of H2S at NTP?
Answer: The density of H2S gas is 1.53 g/L at NTP.
Question 33. Which acid is used to prepare H2S gas in the laboratory?
Answer: Dilute sulphuric acid.
Question 34. Mention one identifying test for H2S.
Answer: head acetate paper turns black when it is held in HS gas.
Question 35. Name the chemicals used in the laboratory method of preparation of nitrogen.
Answer:
Chemicals required: Ammonium chlorides (NH4CI) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2.)
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE
Question 36. What are the ways of fixation of nitrogen?
Answer:
There are two ways of fixation of nitrogen:
- By electric discharge
- The biochemical reaction through bacteria
Question 37. What is the molecular weight of nitric acid?
Answer: The molecular weight of nitric acid is 63.
Question 38. What is the specific gravity of sulphuric acid?
Answer: 1.84.
Question 39. Which Acid is called the ‘King of chemicals”?
Answer: Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is called the ‘king of chemicals’.
Question 40. What is laughing gas?
Answer: Nitrous oxide (N2O) is called laughing gas.
Question 41. Name a reducing acid.
Answer: Hydrochloric acid (HCI) is an example of a reducing acid.
Question 42. What is royal water?
Answer: Aqua regia is also known as royal water.
Question 43. What is the basic component of chuni (ruby), Panna (emerald) etc.?
Answer: The basic component of chuni and panna is Al2O3
Question 44. What is called Mohr’s salt?
Answer: FeSO4, (NH4)2, SO4, 6H2O is called Mohr’s salt.
Question 45. What is Kipp’s base?
Answer: A mixture of FeS+H2SO4, is called Kipp’s base.
Question 46. What is called Fool’s gold?
Answer: CuFeS2 is called Fool’s god.
Question 47. What is Hydrolith?
Answer: Calcium hydride is known as hydrolith.
Question 48. What is ketose?
Answer: The carbohydrate-containing keto (C = O) group is called ketose.
Question 49. What is amylum?
Answer: Starch is called amylum.
Question 50. What is TEL?
Answer: TEL is commonly used antiknock compound tetraethyl lead, [(C2H5)4, Pb]
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE Chapter 8 Physical And Chemical Properties Of Matter Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom is called ________ the atom.
Answer: Electron affinity
Question 2. There are ________ elements in the fourth period of the periodic table.
Answer: 18
Question 3. Hydrogen belongs to the________ period.
Answer: IA (one)
Question 4. Helium belongs to the ________ group.
Answer: 0 (zero)
Question 5. Na+ ion is ________ in size than no-atom.
Answer: Smaller
Question 6. On Pauling’s electronegativity scale, the element next to F is ________
Answer: Oxygen.
Question 7. Elements of group IA are called ________ metals.
Answer: Alkali
Question 8. The term ‘periodic’ means ________ of anything at regular intervals.
Answer: Recurrence
Question 9. The elements belonging to zero group are chemically________
Answer: Insert
Question 10. 10 strong electro-positive elements are ________ good
Answer: Reducing agent
Question 11. Covalent compounds do not-produce ________ in solution or in fused states, so these are non-electrolytes.
Answer: Ions
Question 12. Almost all the participants in a covalent compound are________
Answer: Non-metals.
Question 13. In an ammonia molecule, each hydrogen atom is related to one pair of shared ________ so the covalency of hydrogen is 1.
Answer: Electrons.
Question 14. Valency of an element in a covalent compound is measured by its relation to the number of shared ________
Answer: Electron-pairs
Question 15. The valency of an element in an electrovalent compound is the number of ________ an atom of it gains or loses in forming the compound.
Answer: Electrons
Question 16. A chemical bond is a strong force of attraction that holds; together ________ in a molecule or crystal.
Answer: Atoms
Question 17. Electrovalency is the type of chemical bonding established by the actual transference of one or more ________ electron (s).
Answer: Valence.
Question 18. In covalency, two or more atoms of the same or different non-metallic elements combine chemically by the process of ________ one or more pairs of valence electrons.
Answer: Sharing.
Question 19. Electrovalent compounds are formed by strong attractive electrostatics between ions of opposite charge.
Answer: Forces.
Question 20. In the formation of all electrovalent compounds, a________ is involved.
Answer: Metal.
Question 21. Formation of NaCl involves ________In energy.
Answer: Decrease.
Question 22. Helium atom contains electron.
Answer: Two (2).
Question 23. Chemical reactions of covalent compounds usually ________
Answer: Slow.
Question 24. Solid NaCl is a ________ conductor of electricity.
Answer: Bad.
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE
Question 25. Covalent compounds are generally soluble in ________ solvents
Answer: Non-polar.
Question 26. ________ Is a vessel in which electrolysis is carried out.is involved.
Answer: Voltameter.
Question 27. In electrolytes, electrical conduction occurs by the migration of________
Answer: Ions.
Question 28. Rubber is________ of electricity.
Answer: Non-conductor.
Question 29. Mercury is a good conductor of electricity but is not an________
answer: Electrolyte.
Question 30. The aqueous solution of sugar is ________
answer: Non-electrolyte.
Question 31. In electrolysis________ conduct electricity.
Answer: Ions.
Question 32. Between H+and Al3+ _______ion is discharged first at the anode.
Answer: H–
Question 33. 2H+ 2e → ________
Answer: 2H
Question 34. In electroplating, the plating metal is used as________
Answer: Cathode.
Question 35. Aluminium is extracted by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of bauxite and ________
Answer: Cryolite.
Question 36. Ammonia has a typical ________ smell
Answer: Pungent.
Question 37.________ reagent is used for the identification of ammonia.
Answer: Nessler’s.
Question 38. Ammonia is dried with ________
Answer: Calcium oxide.
Question 39. Ammonia is ________ for eyes
Answer: Harmful.
Physics Class 10 WBBSE
Question 40. 2NH4Cl+Ca(OH)2 = __________ +CaCl2+ 2H2O
Answer: 2NH3
Question 41. Ammonia gas is collected by __________ the Displacement of air.
Answer: Downward.
Question 42. An aqueous solution of ammonia is __________
Answer: Alkaline.
Question 43. When ammonia l Eakes from the factory we should wash our eyes with __________
Answer: Water.
Question 44. In ammonia, we have nitrogen and __________
Answer: Hydrogen.
Question 45. Ammonia is dried by passing through __________
Answer: Quick line.
Question 46. Ammonia is __________ soluble in water.
Answer: Highly.
Question 47. H2S gas is absorbed in __________ Solution
Answer: Sodium hydroxide.
Question 48. __________ Is used in order to dry H2S
Answer: P2O5
Question 49. H2S is a weak __________ acid.
Answer: Dibasic.
Question 50. Molecular formula of sulphuretted hydrogen is__________
Answer: H2S
Question 51. H2S +H2 SO4 (cons.) = 5 + __________+ 2 H2O
Answer: SO2
Question 53. H2S gas is 1.5 times heavier than __________
Answer: Air.
Question 54. H2S gas turns lead acetate __________
Answer: Black.
Question 55. Solubility of nitrogen in water very __________
Answers: Low.
Question 56. Nitrogen is a __________ gas.
Answer: Colour less.
Question 57. Liquid nitrogen is used as __________
Answer: Condenser.
Question 58. N2 + __________ = 2NH3
Answer: 3H2
Physics Class 10 WBBSE
Question 59. CaC2 + N2 = __________ +C
Answer: CaCN2
Question 60. Natural source of nitrogen is __________
Answer: Air.
Question 61. Nitrogen gas is collected by the __________ displacement of water.
Answer: Downward.
Question 62. The solubility of nitrogen in water is about __________ m/L at NTP.
Answer: 23.5.
Question 63. Nitrolim reacts with steam to form calcium carbonate and
Answer: Ammonia.
Question 64. Nitrogen is a relatively __________ element
Answer: Non-reactive.
Question 65. MnO2+4HCI = MnCI2 +_____ 2H2O
Answer: Cl2
Question 66. 4NH3+ 5O2=_______+6H2O
Answer: 4NO
Question 67.____________ acid is known as aquafortis.
Answer: Nitric.
Question 68. The molecular formula of oleum is __________
Answer: H2S2O7.
Question 69. AgNO3 + HCl = __________ +HNO3
Answer: AgCl.
Question 70. For dehydration
Answer: Sulphuric acid.
Question 71. The boiling point of sulphuric acid is
Answer: 338°C.
Question 72.__________ is also known as chile saltpetre.
Answer: NaNO3
Question 73. NaCl + H2SO4 = ___________HCl (150°C – 200°C)
Answer: NaHSO4
Question 74. At high temperatures, HNO3 decomposes as:
Answer: 4HNO3 = 4NO2 +_________ + 2H2O
Question 75. C12H22O11 (sugar) + cone. H2SO4 = __________(11HO+H2SO4 )
Answer: 12C.
Question 76. The colour of fuming nitric acid is __________
Answer: Yellowish.
Question 77. Concentrated HNO3 is not used to prepare HCl since the former is highly __________
Answer: Volatile.
Question 78. Concentrated sulphuric acid has a great affinity to __________
Answer: Water.
Question 79. 3 HCI + HNO3 (cone) = NOCI + __________ +2H2O (Nitrosyl Chloric)
Answer: 2 (CI).
Physics Class 10 WBBSE
Question 80. Gold is alloyed with copper or silver to make it __________
Answer: Hrder.
Question 81. Zinc oxide is an __________ oxide.
Answer: Amphoteric.
Question 82. The chief ore of aluminium is __________
Answer: Bauxite (AI2O3, 2H2O).
Question 83. The formula of malachite is __________
Answer: CuCO3, Cu (OH)2
Question 84. Brass is an alloy of __________
Answer: Copper and zinc.
Question 85. FeSO4 , 7H2O is known as __________
Answer: Green vitriol.
Question 86. MgCl2 on electrolysis gives Mg.
Answer: Molten.
Question 87. Bell metal is an alloy of __________
Answer: Copper and tin.
Question 88. Stainless steel is an alloy of __________
Answer: Chromium, nickel and iron.
Question 89. Generally, the density of iron is __________
Answer: 7.85 g/ml.
Question 90. AlC3 evolves __________ when treated with water.
Answer: Methane.
Question 91. Wurtz reaction is used for the preparation of __________
Answer: Alkanes.
Question 92. _______________ is the abbreviation of polyvinyl chloride.
Answer: PVC.
Question 93. The monomer of____________ is tetrafluoro ethene.
Answer: Teflon.
Question 94. Vitamin C is soluble in____________
Answer: Water.
Question 95. The carbon chains in alkalines are____________
Answer: Zig-Zag.
Question 96. The function group of organic acid is____________
Answer: – COOH.
Question 97. Proteins contain various kinds of acids____________
Answer: Amino.
Question 98._______ and proteins are the polymerisation products of amino____________ acids.
Answer: Polypeptides.
Question 99. Starch is____________saccharide.
Answer: Poly.
Physics Class 10 WBBSE Chapter 8 Physical And Chemical Properties Of Matter Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is atomic volume?
Answer:
Atomic volume: Atomic volume of an element is the volume in cm3 occupied by one gram atom of the element in the solid state hence it is also called gram- atomic volume.
Question 2. What is Mendeleev’s periodic law?
Answer:
Mendeleev’s periodic law (1869): The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Question 3. What is modern periodic law?
Answer:
Modern periodic law (Moseley): It states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Question 4. What is ionic radius?
Answer:
Ionic radius: it is defined as the effective distance from the nucleus of an ion upto which it has an influence in the ionic bond.
Question 5. What is the metallic radius?
Answer: It is defined as one half of inter-nuclear distance between two nearest metal atoms in a metalic lattice is called metallic radius.
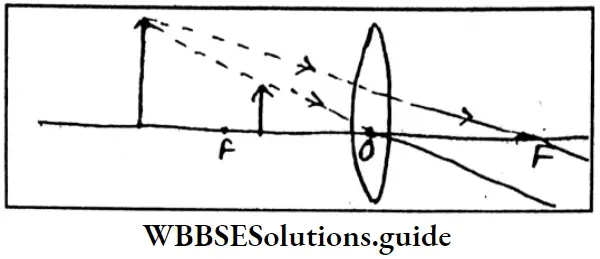
r mettalic \(=\frac{\text { Inter-nuclear distance between two nearest metal atoms in metallic lattice }}{2}\)
Question 6. What is Ionisation energy (IE) or Ionisation potential (IP) ?
Answer:
Ionisation energy or Ionisation potential: First ionisation energy is defined as the amount of energy required to remove one valence electron from an isolated neutral gaseous atom resulting in the formation of a monovalent positive ion.
Question 7. What is electron affinity?
Answer:
Electron affinity (EA): First electron affinity or simply electron affinity is the amount of energy released when one electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form a monovalent negative ion.
Physics Class 10 WBBSE
Question 8. What is the necessity of arranging elements in the periodic table?
Answer:
Necessity of arranging elements in the periodic table: It was observed from the early days that there were few groups of elements each of which had almost identical chemical and physical properties. So, a systematic arrangement of elements is essential since it is difficult to remember the individual properties of elements.
Question 9. What is periodicity?
Answer:
Periodicity: It is the recurrence of elements with similar propertes after certain regular intervals when these are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers.
Question 10. What is the definition of electronegativity?
Answer:
Electronegativity (Pauling’s definition): It is the attractive force which an atom, bonded by a covalent bond exerts on the bond pair of electrons responsible for the covalent bond. The electro-negativity of the elements increases from left to night of the periods in a periodic table.
Question 11. What are s-block elements?
Answer:
S-block elements: These are the elements of IA or 1 group (alkali metals; configuration ns’) and IIA or 2 group (alkaline earth metals; configuration ns3). These are so named because the last electron in them enters S-oribitals.
Question 12. What are p-block elements?
Answer:
P-block elements: These are the elements in which the last electron enters p- orbital of valence shell. The elements with configurations ns2 np’ to ns2 np constitute this block. Thus p-block consists of elements of group IIIA (13), IVA (14), VA (15), VIA (16), VIIA (17) and zero groups (18).
Question 13. What is covalent radius?
Answer:
Covalent radius: It is defined as one-half of the distance between the centres of nuclei of two similar atoms held together by a purely covalent single bond.
Question 14. Explain how the atomic size of the electron change in periodic table?
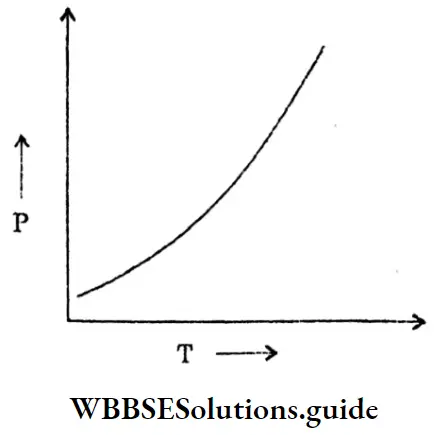
Answer:
Atomic size: The distance of the outermost orbit from the nucleus of a spherically shaped atom is called the atomic size. The atomic size gradually decreases from left to right of the period upto the group VIIB, again increasing in the end element.
Question 15. What is Vander waal’s radius?
Answer:
Vander Waal’s radius: It is defined as one-half of the internuclear distance between two similar, adjacent atoms belonging to two neighbouring molecules of the same substance in the solid state.
r vander waals= \(\frac{\text { (Internuclear distance between two non-bonded nearest neighbouring atoms) }}{2}\)
Question 16. How many periods and groups are pressnt in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
Answer: Mendelev’s periodic table contains seven periods and nine groups.
Question 17. What are the conditions necessary for the formation of Ionic bond?
Answer:
The condition necessary for the formation of Ionic bond:
- Formation of cation from a neutral atom having low ionisation energy.
- Formation of an anion from a neutral atom with high value of electron affinity.
- Formation of crystal lattice from oppositely charged ions involving large release of energy.
Physics Class 10 WBBSE
Question 18. What are the causes of chemical combination?
Answer:
Cause of chemical combination :
- Tendency to acquire nobe gas configuration.
- Tendency to acquire minimum energy.
Question 19. What are the characleristics of ionic compound’s?
Answer:
- All ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids and are composed of ions even in the solid state.
- lonic compounds have low valatility high density and high stability.
- Ionic solid have high melting points and boiling points due to the presence of strong attractive forces between the oppositely charged ions.
- lonic compounds are highly soluble in polar solvents (such as water) having high dielectric constant (80) but insoluble in organic solvents (such as benzene, alcohol, ether etc.)
Question 20. What is Ionic bonding?
Answer.
Ionic bonding: The electrostatic force of attraction which holds the oppositely charged ions together is called ionic bond or electrovalent bond and the compounds which are formed by the transference of electrons from one atom to another are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds. The number of electrons which an atom loses or gains while forming an ionic bond is known as electrovalency.
Question 21. What are the factors on which Lattice energy depends?
Answer:
Lattice energy depends upon the following factors:
- The magnitude of charge of ions: It increases with an increase in charge on cation-anion or both.
- Size of cation: For a common anion, the lattice energy decreases with an increase in size.
- Size of anion: For a common cation, the lattice energy decreases, with the increased size of anion.
Question 22. What are the common types of bonds?
Answer: Depending upon the mode of acquiring the nearest noble gas configuration.
There are three common types of bonds :
- Ionic or Electrovalent bond
- Covalent bond and
- Coordinate or Dative bond.
Question 23. State the common reason behind the phenomena of electron release or electron capture by atoms to form ions.
Answer:
Explanation: An element goes into chemical bondage with another element since it tends to attain the stable state of its nearest inert element in the periodic table. To fulfil this, an atom either gains or loses electrons 70 possess 8 electrons or 2 electrons (for hydrogen atoms) in its outermost orbit. As a result of losing electrons, atoms are transformed to positive ions and on gaining electrons atoms transform to negative ions.
Question 24. What is the electronic theory of bonding?
Answer:
Electronic theory of bonding: Atoms combine by transfer of electrons (ionic bonding) or by sharing of electrons (covalent bonding).
Question 25. What is Lattice energy?
Answer:
Lattice energy: The lattice energy of an ionic solid is the amount of energy released when the required number of cations and anions combine to form one mole of an ionic solid.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 26. What are the main types of physical bonds?
Answer:
The main types of physical bonds are:
- Hydrogen bond
- Metallic bond
- Vander Waal’s interactions.
Question 27. What is a covalent bond?
Answer:
Covalent bond (G.N. Lewis, 1916): A covalent bond is formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms, both of which are short electrons. The compound so formed is called covalent compound. The member of electrons contributed by an atom for sharing is known as its covalency.
Depending upon the number of electrons shared between two atoms being one, two or three, we have single covalent bond (: or =), double covalent bond (: : or=) and triple covalent bond (::: or≡).
Question 28. What are the exceptions of the octet rule?
Answer:
Exceptions of octet rule: There are many atoms which do not obey the octet rule and may contain six (as in BF3), or ten (as in PF3) electrons.
Question 29. What are the characteristics of covalent compounds?
Answer:
Characteristics of covalent compounds :
- Covalent compounds exist in solid, liquid and gaseous state.
- These compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- These (except graphite) are bad conductors and react sowly.
- These are soluble in non-polar solvents such as benzene, acetone etc. but are insoluble in polar solvents such as water.
- Due to the directional nature of covalent bonds. These compounds show stereoisomerism.
Question 30. What is octet rule?
Answer:
Octet rule: It states that atoms react because they have a tendency to complete their octet (or duplet) i.e. to have eight electrons in the valence shell (or two electrons if only one shell is present) They can do so by losing, gaining or sharing electrons.
Question 31. Write down the electronic configuration of a chlorine atom, a chlorine ion.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of chlorine atom: 2, 8, 7 electronic configuration of a chlorie ion is: 2, 8
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 32. Water is generally a good solvent for ionic compounds why?
Answer:
Explanation:
The dielectric constant of water is high (80): The electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions gets reduced to (\(\frac{1}{8}\)) of the original force in air. Hence, ions of an electrovalent compound get separated which is then solvated by water.
Question 33. Why does the tendency of sharing electrons grow in many nonmetallic atoms during the formation of covalent compounds?
Answer:
Explanation: During the formation of covalent compounds of non-metallic atoms, each participant involved in the process tends to attain a duplet or octet stable state. To attain such stable state they share electrons.
Question 34. SnCl is a poor conductor of electricity. Why?
Answer:
Explanation: SnCl4, being a covalent compound does not ionise and hence, is a poor conductor of electricity.
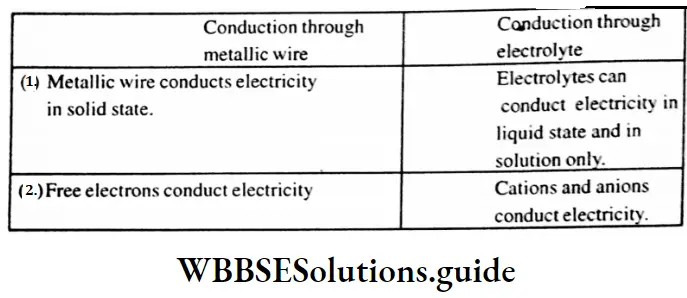
Question 35. What are conductors?
Answer:
Conductors: A substance which allows the electric current to flow through it is called a conductor, for example, Cu, Ag, Al etc.
Question 36. What is Non-conductors?
Answer:
Non-conductors: A substance which does not-conductor. for example, wood, gas, rubber etc.
Question 37. What are electrolytic conductors or electrolytes?
Answer:
Electrolytic conductors or electrolytes: These are compounds which in the fused state on in solution in a suitable. solvent (particulary water) conduct an electric current and undergo distinct chemical Decomposition during the process of conducting current.
For example, Aqueous solution of H2SO4, NaOH, NaCl etc.
Question 38. Why is mercury considered as non-electrolyte?
Answer:
Explanation: Mercury is a liquid metal. It conducts electricity but during the passage of electric current, it is not decomposed. So, it is considered as non- electrocyte.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 39. What is Electrolysis?
Answer:
Electrolysis: The process of chemical decomposition of an electrolyte in solution or in the state by the passage of electric current is called electrolysis.
Question 40. What is electrolytic conduction?
Answer:
Question Electrolytic conduction: The movement of ions towards oppositely charged electrodes is known as electrolytic conduction.
Question 41. What is called Electrodes?
Answer:
Electrodes: The two metallic or graphite strips or rods, placed in a voltameter to pass electrolyte during electrolysis are known as electrodes.
Question 42. What is called Electrolytic dissociation?
Answer:
Electrolytic dissociation: The splitting up of an electrolyte into ions is known as electrolytic dissociation. This is a reversible process. This means that the electrolyte molecules break up partly into ions and the ions in solution constantly reunite to form the undissociated molecules.
Question 43. What are Metallic conductors?
Answer:
Metallic conductors: These are the substances (metals) which allow the current to pass through them but do not undergo any change in themselves. for example,Cu, Ag, An etc.
Question 44. What are Non-metallic conductors?
Answer:
Non-metallic conductors: These are the substances (non-metals) which allow the current to pass through them out and do not undergo any change in themselves, for example, Graphite, gas-carbon etc.
Question 45. What are the applications of electrolysis :
Answer:
Application of electrolysis:
- Electroplating
- Electro-refining of metals.
- Electro-typing
- Extraction of metals.
Question 46. What are the conditions for a good deposit?
Answer:
Conditions for good deposit:
- High current density
- Low temperature
- High metal concentration in the electrolyte
- The electrolyte must be complex salt of the metal to be deposited.
Question 47. Explain the electroplating of Ag.
Answer:
Electroplating of Ag:
Electrolyte: Potassium argento cyanide solution K [Ag (CN)2]
⇒ K [Ag (CN)2]→ K ̄+Ag ̄+2CN ̄
Electrodes:
- Cathode: the article is to be electroplated.
- Anode: Pure Ag plate
- Reaction at cathode: Ag + e → Ag↓
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 48. Explain the electroplating of Ni.
Answer:
1. Electroplating of Ni: Electrolyte Nickel sulphate (NiSO) with Boric acid (H3BO3)
⇒ NiSO4……… Ni2-+ 4SO2-
2. Electrodes:
- Cathode: The article is to be electroplated.
- Anode: Pure Ni-plate.
3. Reaction at the cathode: Ni2-+2e→ Ni↓
Question 49. What is the cathodic reaction? Give one example.
Answer:
Cathodic reduction: The reduction of ions taking place at a cathode of a cell is known as cathode reduction.
Example: Reduction of Cu2- ions to cu at the cathode of Daniell cell is an example of cathodic reduction.
Question 50. Anhydrous HCI is a bad conductor of electricity but aqueous HCI is a good conductor. Why?
Answer:
Explanation: Being covalent in nature, anhydrous HCI is a bad conductor. However, in aqueous solution, it ionsies to give H and Cl- ions which conduct the electricity.
Question 51. State two physical properties of HCI :
Answer:
Physical properties of HCI :
- It is a colourless gas with a choking smell and strongly fuming in moist air, hydrogen chloride is 1.27 times as heavy as air; it neither burns nor supports burning.
- It is highly soluble in water. At 0°C, 450 ml of hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved in 1 ml of water.
Question 52. How is pure hydrogen chloride prepared?
Answer: Preparation of pure hydrogen chloride Pure hydrogen is obtained by the action of water upon silicon tetrachloride.
Equation: SiCI4 + 4H2O= Si (OH)4+ 4 HCI
Question 53. State the reaction of HCI with Na.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride neither burns in the air nor supports combustion. However, burning sodium continues to burn in the gas with a bright yellow flame producing hydrogen and anhydrous sodium chloride.
Equation: 2Na + 2HCl = 2NaCl + H2↓.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 54. What is a reaction between NaCO, and HCI?
Answer:
Reaction of Na2 CO3 with HCI :
HCl reacts with Na2CO3 to liberate carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HCI = 2NaCl + CO2 ↑+ H2O.
Question 55. Why hydrogen chloride is not collected over displacement of water?
Answer:
Reason: Hydrogen chloride is highly soluble in water. It has been found that at 0°C, 450 ml of hydrogen chloride is dissolved in 1 ml of water. So, it is not collected over displacement of water.
Question 56. How copper and silver react with hydrochloric acid?
Answer: Generally, copper and silver are not attacked by hydrochloric acid. In the presence of air, copper and silver react very slowly producing corresponding chlorides and water.
Equations:
2Cu + 4 HCI + O2= 2CuCl2 + 2H2O
4Ag + 4HCI + O2 4AgCl + 2H2O
Question 57. How does ammonia react with hydrogen chloride?
Answer: Reaction of ammonia with hydrogen chloride: Ammonia in contact with hydrogen chloride gives dense white fumes of solid ammonium chloride. This reaction is an example of the formation of a solid product by the interaction of two gases.
Equation: NH3 (g) + HCI (g) NH4CI (S)
Question 58. Show the presence of chloride ions in hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Presence of chloride ion in hydrochloric acid: When hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of silver nitrate, a white precipitate of the chloride of silver is obtained.
Silver chloride is insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
Equation: AgNO3 + HCI + AgCl ↓ + HNO3
Question 59. State the identification of hydrogen chloride gas.
Answer: Identification of hydrogen chloride gas: Dense white fumes are formed when a glass rod, moistened with strong ammonium a solution, is held in the hydrogen chloride gas.
Equation: NH3 (g) + HCI (g) NH4CI (s)
Question 60. Why nitric acid is prepared at a lower temperature (200°C) in the laboratory?
Answer:
Nitric acid is prepared at a lower temperature (200°C) in the laboratory because.
- At high temperatures, nitric acid decomposes.
4 HNO3= 4NO2 +O2 + 2H2O.
- Nitric acid vapour attacks the glass surface of the retort.
- Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) formed at higher temperatures sticks to glass and is difficult to remove from the glass retort.
Question 61. What are the physical properties of nitric acid?
Answer:
Physical properties of nitric acid :
- Pure nitric acid is a colourless, fuming liquid of specific gravity 1.52 at 15°C
- It boils at 86°C and freezes at -42°C into a transparent crystalline substance.
- It is highly soluble in water.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 62. State the reaction of nitric acid with alkalis.
Answer:
Reaction of nitric acid with alkalis: As nitric acid is a strong acid, it rapidly reacts with and neutralises alkalis to form salt and water.
Equations:
1. NaOH + HNO3= NaNO3 + H2O
2. NH4 OH + HNO3 = NH4NO3 + H2O
Question 63. What is aqua regia? What is its use?
Answer:
Aqua regia: A mixture of conc. HNO, (1 vol.) and conc. hydrochloric acid (3 vols.) is known as aqua regia.
Au + 4HCI + HNO3= HAUCI4+NO+ 2H2O
(Soluble chloro auric acid)
Use of aqua regia: It dissolves gold and platinum.
Question 64. What is fuming sulphuric acid or oleum?
Answer:
Fumming sulphuric acid or oleum: Fumming sulphuric acid or oleum is obtained when SO3 is passed over 98% (approximately) sulphuric acid.
Equation: H2SO4+SO3= H2S2O7 (oleum)
Question 65. What is passive iron?
Answer:
- Passive iron: Cold and concentrated nitric acid or fuming nitric acid or fuming nitric acid when comes in contact with iron produces passive iron is chemically inactive.
- Cause of passivity: The nitric acid when comes in contact with iron, an insoluble coating of iron oxide (Fe3O4) forms on iron at initial stage. The coating makes iron chemically inactive.
Question 66. What is acid rain?
Answer:
Acid rain:
- The oxides NO2 and SO2 reacting with moisture and oxygen of air corres ponding produce HNO3 and H2SO4. The acids dissolve in rainwater. The rain coming down on earth carrying these acids is known as acid rain.
- The function of acid rain The acids present in the rainwater damage buildings monuments, and statues by corrosion. Soil also becomes acidic which causes degradation of soil that in turn causes decline in forest area and agricultural productivity.
Question 67. State the effect of SO2 pollution.
Answer:
Effect of SO2 pollution:
- SO2 creates problems in eyes and also in the lungs,
- Many diseases like asthma, bronchitis etc. affect if SO2 is inhaled.
Question 68. What is stone cancer?
Answer:
Stone cancer: In the atmosphere, sulphur dioxide (SO) gas reacts with oxygen and water vapour producing sulphuric acid. The acid being dissolved in rainwater comes down on marble walls. The marble walls thus corrode, the corrosion of the marble is called stone cancer.
Question 69. State physical properties of H2SO4.
Answer:
Physical properties of :
- It is a colourless, odourless heavy oily liquid.
- Its specific gravity is 1.84 and its b.p. (boiling point) is 338°C.
- It is soluble in water and it is a corrosive acid.
Question 70. Water is not added on concentrated sulphuric acid to make it dilute why?
Answer:
Explanation: Huge amount of heat is produced if water is added to concentrated sulphuric acid. As a result, water all on a sudden being volatilised spreads all around and Creates a Problem. So conc H2SO4 acid is slowly added to with constant stirring.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 71. State the reaction of H2SO4 with carbonates and bicarbonates.
.Answer: Reaction of H2SO4 with carbonates and bicarbonates: At ordinary temperature, it liberates carbon dioxide from carbonates and bicarbonates.
Equations:
Na CO3 + H2SO4 = NaSO4+ CO2↑ +H2O
NaHCO3 + H2SO4= NaH2SO4 + CO2↑ +H2O.
Question 72. Explain the following: Concentrated nitric acid turns yellow in sun light. Answer: Explanation:
Nitric acid turns yellow because of its decomposition forming nitrogen dioxide (NO) gas.
Equation: 4HNO3 = 4NO2+ 2H2O +O2
Question 73. Concentrate Nitric acid can be kept is a vessel made of aluminium-Why?
Answer:
Reason: Concentrate Nitric acid does not react with aluminium, so it can be kept in the aluminium vessel.
Question 74. What is thermite? What is its use?
Answer:
Thermite: Thermite is a mixture of aluminium powder and ferric oxide.
Use: It is used for welding purposes.
Question 75. State what happens when? Zn is added to the caustic soda solution.
Answer:
Explanation: Zinc reacting with caustic soda solution produces sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
Equation: Zn + 2NaOH = Na2 ZnO2 + H2↑
Question 76. What is stainless steel? State one use of it.
Answer:
Stainless steel: It is an alloy which composes iron (Fe) = 73%, Chromium (Cr) = 18% Nickel (Ni) = 8% and carbon (C) Uses of stainless steel: It is broadly used to make instruments.
Question 77. Why alumina (Al2O3) cannot be reduced by carbon?
Answer:
Explanation: At high temperatures, Al2O3 reacts with carbon to form aluminium carbide.
Equation: 2Al2O3 + 9C → AI4C3+6CO
Question 78. Why aluminium cannot be obtained by the electrolysis of bused AICI,?
Answer:
Explanation: Aluminium cannot be obtained by the electrolysis of fused AICI3, since it is covalent solid and sublimes at 453K.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
79. Although less conducting than copper, aluminium is used for power transmission. Why?
Answer:
Explantion: Aluminium being lighter and cheaper than copper is used for power transmission.
Question 80. Why did aluminium act as a good reducing agent?
Answer:
Explanation: Reducing the character of a substance depends upon its affinity for oxygen. Aluminium due to its high affinity for oxygen is a good reducing agent. It reduces a large number of oxides of other metals.
For example: 2A1+ Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe + heat.
Question 81. Explain the following: Anode mud in copper refining contains silver and gold.
Answer:
Explanation: Silver and gold being less electro-positive cables because it is a good conductors. Moreover, being a noble metal, it is not affected by the atmosphere.
Question 82. What is organic chemistry?
Answer:
Organic chemistry: All carbon-containing compounds except oxides of carbon, metal carbonate, bicarbonate, hydrogen cyanide and metallic cyanides are organic compounds and the chemistry of organic compounds is called organic chemistry.
Question 83. What are Monosaccharides?
Answer:
Monosaccharides: These are the compounds such as glucose and fructose which do not break into simpler compounds on hydrolysis.
Question 84. What is Moltose?
Answer:
Moltose: It is obtained by the partial hydrolysis of starch by enzyme diastase present in malt.
Question 85. What is Lactose?
Answer:
Lactose: It occurs in the milk of all animals cow’s milk contains about 5% Lactose while human milk contains about 7% lactose.
Question 86. What is Cellulose?
Answer:
Cellulose: It is the main structural material of wood and other plants. Cotton is about 80% cellulose.
Question 87. What are Amino acids?
Answer:
Amino acids: These are organic compounds containing both amino and carboxylic group in their molecules. They are represented by the general formula.
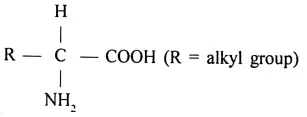
Question 88. What are essential amino acids?
Answer:
Essential amino acids: Human body can synthesise 10 out of 20 a-amino acids found in proteins. The remaining 10 must be present in our diet and are called essential amino acids.
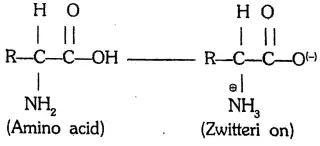
Question 89. What is Zwitter ion?
Answer:
Zwitter ion: In aqueous solution, the acidic carboxyl group donates a proton to the basis amino group to form an internal salt called a dipolar ion or zwitter ion. Although it is neutral overall, it contains both a positive and a negative charge.
Question 90. What are peptides
Answer:
Peptides: These are condensation products of self-amides formed by the reaction of two or more amino acid molecules.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 91. What is peptide linkage?
Answer:
Peptide linkage:
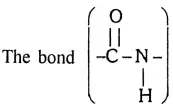
The bond Between the Carboxyl group of an acid molecule and nitrogen of the other amino acid molecule is known as the peptide bond or peptide linkage.
Question 92. What is Denaturation?
Answer:
Denaturation: After coagulation, proteins lose their physiological activity and certain other properties. This phenomenon is known as denaturation.
Question 93. What are Enzymes?
Answer:
Enzymes: These are also proteins which acts as catalyst in many biochemical reactions. Enzymes are specific in action due to their specific structural arrangement.
Question 94. What is the biuret test?
Answer:
Biuret test: To alkaline solution of proteins add a dilute solution of CuSO Formation of violet colour confirms proteins.
Question 95. What are vitamins?
Answer:
Vitamins: These are the biomolecules needed in small quantities, that regulates many biochemical function and prevent the development of many deficiency diseases.
Question 96. What are fats?
Answer:
Fats: These are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They are made of glycerol and fatty (organic) acids. Fats may be of animal or vegetable origin.
Question 97. State examples of conjugated proteins and derived proteins.
Answer:
Conjugated proteins:
- Phosphoproteins
- Glycoproteins.
Derived proteins: This type of protein is obtained after the partial hydrolysis of protein of very high molecular weight by acid, base or enzyme to simplier proteins.
Question 98. What are the types of simple proteins?
Answer:
Types of simple proteins :
Albumins → Example, milk, serum etc.
Globumins → Example, egg, yolk, tissues etc.
Glutemins→ Example, wheat, rice etc.
Prolomins → Example, barley, wheat etc.
Scleroproteins →Example, Keratin, fibroin etc.
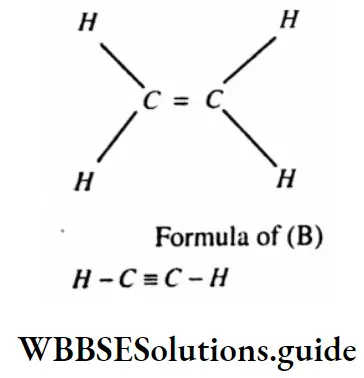
Question 99. What are Alkynes?
Answer:
Alkynes: Those unsaturated hydrocarbons containing triple bonds (S) between two adjacent carbon atoms in their molecules are called as alkynes.
For example, Acetylene
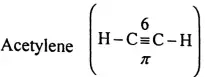
Question 100. What is Isomerism?
Answer:
Isomerism: In organic chemistry when the same molecular formula represents two or more compounds which differ in their physical and chemical properties, then such compounds are called isomers and the phenomenon is called isomerism.
Question 101. What is catenation?
Answer:
Catenation: The property by virtue of which carbon forms covalent linkage chains is called catenation.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 102. What are the types of structural isomers?
Answer:
Types of structural isom:
Chain isomerism; For example,
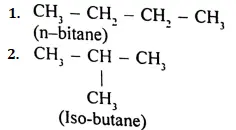
Chapter 8 Physical And Chemical Properties Of Matter Broad Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are groups and sub-groups?
Answer:
Groups Mendeleev’s periodic table shows that the elements with related chemical properties fall in one below the other forming vertical columns called groups. There are nine group from group I to group VIII and O (zero).
Sub-groups Each of the groups from I to VII has been divided into two. Sub-groups A and B.
Question 2. What are halogen elements? In which do they belong?
Answer:
Halogen elements: The four strongly electro-negative non-metals fluorine (F), chlorine (CI), bromine (Br) and iodine (1) form a family of closely allied elements known as the halogens meaning literally sea self-producer as these elements react with most metals to form compounds similar to sea-salt, sodium chloride.
Position in periodic table: Habzen elements placed in group VII B of the periodic table. The electro-negative character of the elements increases from left to right in a period. So, the strongly electro-negative elements are in the most extreme right group i.e. in group VII B of the period table.
Question 3. What are called alkali metals? In which group do they belong? State the similarity of their chemical properties.
Answer:
Alkali metals: Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Rubidium (Rb) and Caesium (Cs). These five metals are generally known as alkali metals.
Position in the periodic table: The alkali metals are included in the A subgroup of the first group
Similarity:
- Alkali metals are strong electropositive.
- The oxides of these metals are strongly basic.
- Each has valency 1.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 4. Discuss the position of hydrogen in the periodic table. Answer: Position of hydrogen in the periodic table :
Reasons for placing in group IA :
- Like the alkali metals, hydrogen is electropositive.
- The valence of hydrogen is I, alkali metals are also non-valent.
- During the electrolysis of a fused chloride of an alkali metal, deposits at the cathode; in the electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, hydrogen collects at the cathode.
- Like alkali metals, hydrogen has a reducing property and forms stable oxides like water (H2O).
- Like hydrogen, each of the alkali metals. Li, Na, K, Rb Cs, Fr possesses one valence-lectron.
Reasons for placing in group VIIB:
- Like halogens, hydrogen is a non-metatallic element.
- The valency of hydrogen and that of each halogen is 1.
- Halogen molecules are diatomic, a hydrogen molecule is also diatomic.
- The halogens from metallic halides like, NaCl, KBr, Kl etc. Hydrogen also produces salt-like hydrides like L, H, NaH, CaH, etc with the strongly electropositive element and hydrogen here acts as an electro-negative element.
- Atoms of halogen elements may transform to negative halide ions by taking one electron each.
- For example, x+eX; X = F, Cl, Br, I and hydrogen atom also may transform to a negative hydride ion by capturing one electron: H+e→ H.
- Like the halogens hydrogen also can produce covalent compounds reacting with electro-negative elements like S, O etc.
Due to such varied tendencies for occupying a seat in the periodic table, hydrogen is often called a naughty element or rogue element.
Question 5. Where are the inert gas elements placed and why?
Answer:
Position of inert gas elements in the periodic table:
- He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn. These are inert elements. They are each gaseous and monoatomic. These are chemically non-reactive. As these elements do not react, they have zero valency.
- So they are included in the O (zero) group of the periodic table. Besides Helium, all the inert gases have eight (8) electrons in their outermost orbit. There are only 2 electrons in the outermost orbit of Helium.
Question 6. How is copper purified by the electrolysis method?
Answer:
Purification of copper by electrolysis method :
1. Electrolyte: 15% of CuSO4, solution (aqueous) containing (5-10) % sulphuric acid at 50°C is taken in a voltameter.
2. Electrodes:
- Cathode: Pure thin copper plate.
- Anode: Thick impure copper plate.
3. Electrolysis:
- On electrolysis, copper dissolves from the anode and deposits on the cathode. Thus gradually the anode plate wears out and the cathode plate thickens.
- The copper obtained in the way 99.99% purity.
4. Reaction: \(\mathrm{CuSO}_4 \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{Cu}^{2-}+\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\)
- At cathode: Cathode : Cu2-+2e →Cu↓
- At anode: Cu – 2e → Cu2-
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 7. How is aluminium extracted from the electrolysis method?
Answer:
Extraction of aluminium by electrolysis method :
1. Electrolytes:
- Alumina (Al2O3) 20%
- Fused Cryolite (AIF3, 2NaF 60%)
- CaF2, 20%.
2. Electrodes:
- Cathode: Inner lining of carbon of the steel tank.
- Anode: Thick carbon rod suspended into a fused electrolyte
Reaction:
At cathode: Al3 + 3e → Al↓
At anode : 3F – 3e→ 3F
⇒ Al2O3 +6F → 2 AIF3+3O
⇒ 6O →3O2
Question 8. Draw the diagram of the covalent radius of hydrogen.
Answer:
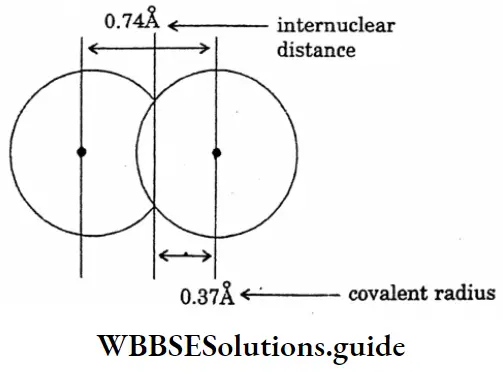
Question 9. Draw the diagram of the showering comparison of Vanderwaal’s radius and covalent radius.
Answer:
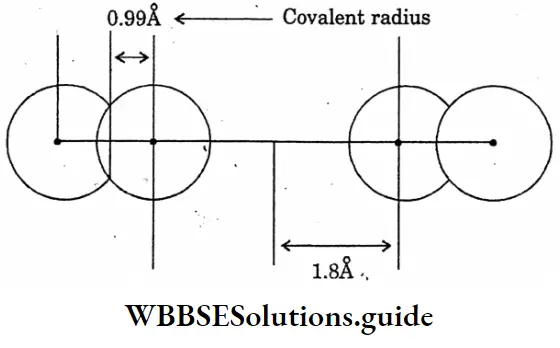
Question 10. State the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
Answer:
Contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid :
Principle:
1. Formation of SO2: SO2 is prepared by burning sulphur or iron pyrites in excess of air.
Equation: S+ O2 = SO↑ Or,
4 Fes,+ || O2 = 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2 ↑
(Iron pyrities)
2. Formation of sulphur trioxide (SO3): SO3 is prepared by the oxidation of sulphur dioxide with oxygen (from air) in the presence of platinised asbestos or, V2 O5 as catalyst at 450°C.
Equation: \(2 \mathrm{SO}_2+\mathrm{O}_2 \rightleftharpoons 2 \mathrm{SO}_3+192.5 \mathrm{Kj}\)
3. Formation of oleum:
Now sulphur trioxide thus produced is not allowed to react with water directly sulphur trioxide absorbs concentrated sulphuric acid 98% turning it as fuming sulphuric acid or oleum.
Equation: SO3+ H2SO4= H2S2O7 (Oleum)
4. Dilution of oleum to sulphuric acid: Pure and concentrated sulphuric acid is produced by adding slowly a requisite amount of water in fuming sulphuric acid.
Equation:
H2S2O7 >+ H2O = 2 H2SO4
Question 11.
- Write down the electronic arrangement of the element 17X 35 What is the valency of the element?
- Will the element form an onion or cation?
- What type of valency will be exhibited when the element combines with sodium?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of the element X is: 2, 8, 7,
- As an atom of the element tends to capture or share one electron to attain stable of the octet, its valency is 1.
- It will form an anion by capturing electrons.
- The element will exhibit electro-valency when it combines with sodium since sodium is a metal, an atom which tends to release one electron.
Question 12. The atomic number of element A is 20 and that of another element B is 17. Write down their electronic configuration. Will they produce on electrova- lent compound or a covalent compound? What will be their valencies in that case?
Answer:
- The electronic configuration of A is: 2, 8, 8, 2.
- The electronic configuration of B is: 2, 8, 7.
They will produce an electrovalent compound.
Explanation:
An atom A will give up two (2) valence electrons. Each of the two atoms of B will capture one electron. In the process atoms of A and B attain a stable octet state and atoms of A will be positive ions and those of B will be negative ions.
- A and B thus form an electrovalent compound.
- As an atom of A loses two electrons.
- So A has valency 2 (two) and since each atom of B captures one electron, The valency of B will be one (1).
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 13. What is the difference between ionic compounds and covalant compounds?
Answer:
Difference between ionic and covalent compounds:

Question 14. How ammonia is prepared in the laboratory?
Answer:
Laboratory preparation of Ammonia:
- Chemicals required: Ammonium chloride (NH4, CI) and quick lime (CaO) or dry slaked lime (Ca (OH2)–
- Condition: Normally ammonia gas is obtained in the laboratory by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride with slaked lime. Instead of using slaked lime quick lime may also be used.
- Collection: Ammonia is lighter than air, it may be collected by the downward displacement of air.
Ammonia is not collected through the downward displacement of water because it is highly soluble in water.
Equation of the reaction:
2NH4 CI + Ca (OH)2 = 2NH3 ↑ + CaCl2+ 2H2O
↑
2NH4CH+CaO = 2NH3↑ + CaCl2+H2O
- Precautions: The ingredients, the test tube, the delivery pipes and the gas jar should be absolutely dry. All the connections in the apparatus should be leak-proof.
- Drying of ammonia: As ammonia is a basic substance, it cannot be dried by acidic drying agents like cones. H2SO, or P2O5,
- The gas is absorbed by fused CaCl2, with the formation of an addition compound CaCl2, 8NH3. SO, fused CaCl2, cannot be used to dry ammonia. It is best dried with the basic drying agent, quick lime (CaO).
Question 15. Prove by experiment that ammonia is dissolved in water and produces an alkaline solution.
Answer:
Fountain experiment:
Arrangement of the experiment: A flask is filled with dry ammonia gas and its mouth is corked. The flask is kept inverted position and is clamped to a stand.
Through a hole in the cork one end of a glass tube is introduced inside the flask. This end of the tube inside the flask is shaped into a jet. The other end of the tube dips in some red litmus solution taken in a beaker.
- Operation: Now ice or ether is poured upon the flask.
- Observation: A blue fountain produces inside the flask.
Explanation:
- Due to the evaporation of ether, the flask is cooled. Ammonia gas inside the flask contracts, as a result, there is a partial vacuum inside the flask.
- At this stage, if the stop cock is opened the red litmus solution rushes inside the flask and ammonia is dissolved in it.
- Due to vacuum created inside there is a formation of the fountain and the solution becomes blue.
Conclusion: This experiment proves that ammonia is highly soluble in water and the aqueous solution is alkaline.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
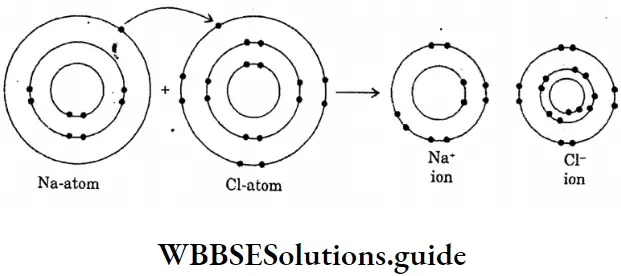
Question 16. Draw the diagram of the formation of sodium chloride.
Answer:
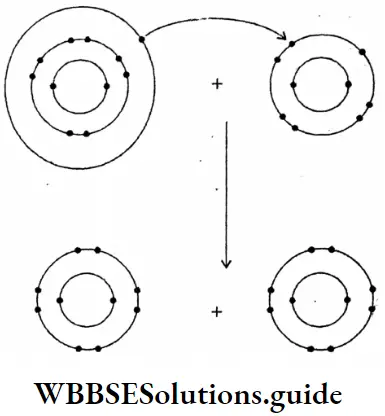
Question 17. Draw the diagram of sodium fluoride :
Answer:
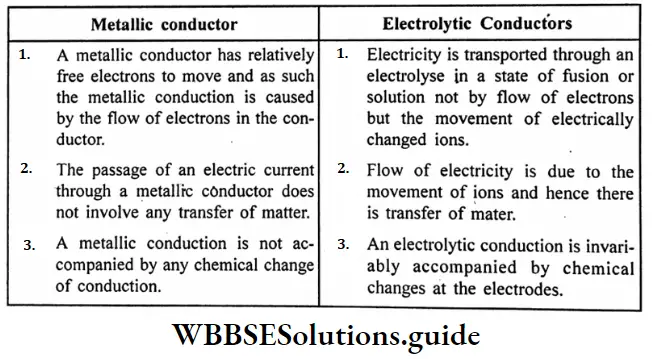
Question 18. What are the main points of difference between metallic conductors on electrolytic conductors?
Answer:
Difference between metallic conductors and electrolytic conductors :
Question 19. What changes are taking place during the electrolysis of an electrolyte?
Answer:
Changes take place during the electrolysis of an electrolyte:
- When fused or dissolved in water, electrolyte splits up into oppositely charged particles called ions.
- On passing an electric current, the cations migrate towards the cathode while the anions migrate towards the anode.
- The cations on reaching the cathode gain electrons from it and from neutral atoms which get deposited on the cathode.
- The anions on reaching the anode lose electrons and get converted into neutral atoms which may be collected as such or they may undergo some secondary change to from some other products.
Question 20. What are Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable materials?
Answer:
- Biodegradable materials: Materials of vegetable and animal origin invariable decay and decompose into CO2, H2O, N2 or NH3 by the combined action of sometimes natural agencies like air, water, subshene etc. These are called biodegradable materials.
- Non-biodegradable materials: Synthetic materials like plastics, polythene, Teflon, PVC etc. are not decomposed by these natural agencies even for a long time. These are called non-biodegradable materials.
Question 21. Briefly explains thermite welding of iron and steel.
Answer:
A mixture of 3 parts of ferric oxide and I part of aluminium powder is called a thermite mixture. When the mixture is ignited ferric oxide is reduced to metallic iron by aluminium. Because of the evolution of large amounts of heat, the temperature rises to Magnesium tape
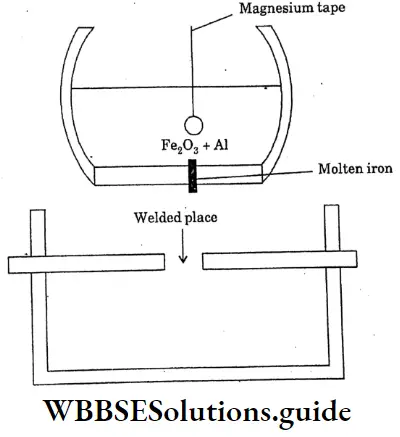
2500c The molten iron thus produced is allowed to fall on the red hot broken rails broken machine parts ect can be welded without removing them from their original sites.