Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Body Fluids And Circulation Question And Answers
Question 1. what is the normal range of glucose in human blood? What is the condition known as when glucose in blood exceeds the normal value?
Answer:
The normal range of glucose in human blood is 80-120 mg per 100 mL of blood. When blood glucose exceeds the normal range, the condition is known as hyperglycemia.
Question 2. Where are plasma proteins synthesized in the human body?
Answer:
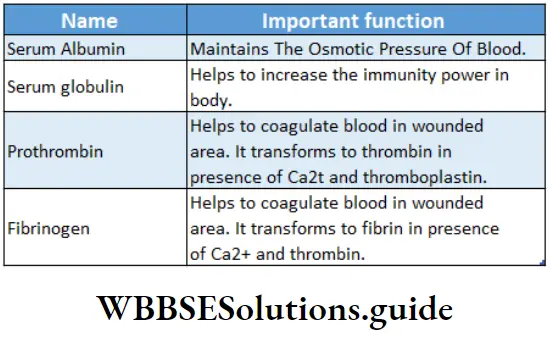
Serum albumin, prothrombin, and fibrinogen are synthesized in the liver but serum globulin is synthesized in the reticuloendothelial (RE) system or lymph nodes.
Body fluids and circulation questions and answers PDF
Question 3. Mention the important functions of plasma proteins.
Answer:
Important functions of plasma proteins
Question 4. Which one is more mature—neutrophils with three-lobed nuclei or neutrophils with seven-lobed nuclei? Name three substances secreted by basophil.
Answer:
Immature neutrophils generally have spherical nuclei and during maturation, they develop lobes. The number of lobes increases with maturity. Therefore, neutrophils with seven-lobed nuclei are more mature than neutrophils with three-lobed nuclei.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
The substances secreted from basophil are—
- Histamine,
- Serotonin And
- Heparin.
Question 5. If your blood group is ‘O’, then from a person of which blood group can you receive blood? If your blood group is ‘AB’, then to a person of which blood group can you donate blood?
Answer:
If my blood group is ‘O’, then I can receive blood from a person of blood group ‘O’ only.
If my blood group is ‘AB’, then I can donate blood to persons having an ‘AB’ blood group only.
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
NEET body fluids and circulation important questions with answers
Question 6. If the father is Rh+ and the mother is Rh-, then which common disease may affect their second child? Write two symptoms of this disease.
Answer:
If the father is Rh+ and the mother is Rh-, then the common disease that may occur in the second child is erythroblastosis foetalis.
Two main symptoms of this disease are—
in the embryonic stage or after birth the child may suffer from chronic anemia, because of the breakdown of a huge number of RBCs i.e., hemolysis,
The amount of bilirubin and biliverdin increases which causes jaundice in the child.

Question 7. Which is the largest lymph gland in the human body? Where is it located in the human body?
Answer:
The largest lymph gland in the human body is the spleen.
The spleen is located in the left hypochondrium (a portion of the abdominal cavity above the naval region) directly beneath the diaphragm, above the left kidney and descending colon.
Question 8. Name one invertebrate which has a closed circulatory system. Where is hemoglobin present in the above-mentioned organism?
Answer:
The earthworm of phylum Annelida has a closed circulatory system.
The blood of earthworms does not contain any RBC but haemoglobin remains dissolved in their blood plasma.
Question 9. Name one vertebrate whose ventricles are separated by a partial septum. Name one reptile whose heart has two auricles and two ventricles.
Answer:
The vertebrate whose ventricles are separated by a partial septum is a lizard Among the reptiles, crocodile’s heart has two auricles and two ventricles.
Class 11 biology body fluids and circulation Q&A
Question 10. Which is known as ‘heart of heart’. Where are Purkinje fibres located?
Answer:
- SAN is known as the ‘heart of heart’.
- In the wall of ventricles and papillary muscles, the branches of the bundle of His are spread as a network of thin fibres. These are known as Purkinje fibres.
Question 11. Which heart sounds are produced when atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves close?
Answer:
When atrioventricular valves in the human heart close, the first heart sound ‘LUBB’ is produced and when semilunar valves close, the second sound ‘DUPP’ is produced.
Question 12. In a normal ECG, what do QRS complex and P wave indicate?
Answer:
In a normal ECG, the QRS complex indicates depolarisation of the ventricles.
P wave indicates depolarisation of atria.
Question 13. In which vertebrate animals, are single and double blood circulation seen? In how many parts can the human circulatory system be divided?
Answer:
Among the vertebrates, fishes have single blood circulation and amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals have double blood circulatory system.
The human body has the following blood circulatory systems—
- Systemic circulation,
- Pulmonary circulation,
- Coronary circulation and
- Portal circulation.
Question 14. How much do SP and DP values indicate high blood pressure or hypertension in humans?
Answer:
When a person’s systolic pressure (SP) is higher than 140 mm Hg and diastolic pressure (DP) is more than 90 mm Hg for a prolonged period, then it is said that the person is suffering from high blood pressure (HBP) or hypertension.
Question 15. What is the full form of CAD? What is its other name? Deposits of which substance causes ‘atheroma’?
Answer:
CAD
- The full form of CAD is coronary artery disease.
- The other name of CAD is atherosclerosis.
- ‘Atheroma’ is caused mainly due to the deposition of Ca2+, fat, cholesterol and fibrous tissues in the inner wall of the artery.
Question 16. Which disease occurs when blood circulation in cardiac muscles of the wall of the heart decreases and chest pain occurs?
Answer:
When blood circulation in cardiac muscles of the wall of the heart decreases and chest pain occurs, then the disease is known as angina pectoris.
Question 17. Except for blood cells, what other cells are produced by the bone marrow?
Answer:
Other than blood cells, bone marrow produces osteoblast, buffer cells, dendritic cells and Langerhans cells.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Body Fluids And Circulation Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is interstitial fluid?
Answer:
Interstitial fluid
Interstitial fluid is the tissue fluid which is present at the intercellular spaces between cells of tissues.
Question 2. What are the formed elements of blood?
Answer:
Blood corpuscles such as RBCs, WBCs and platelets are known as formed elements of blood.
Question 3. What do you mean by universal donor and universal recipient?
Answer:
Universal donor
People with blood group O are universal donors as they can donate blood to people of all blood groups.
Universal recipient
On the other hand people with AB blood group is universal recipient because they can receive blood from people of all the other groups.
Question 4. What is bleeding time?
Answer:
Bleeding time
Bleeding time is the time taken for bleeding to stop from a site of injury. It is measured as the time between the injury and the temporary haemostasis (platelet plug formation).
Question 5. What is clotting time?
Answer:
Clotting time
Clotting time is the time taken by blood to coagulate after it has been shed. It depends on many factors involved in coagulation.
Question 6. What are anticoagulants?
Answer:
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants are substances used to prevent clot formation inside the blood vessels by blocking the action of clotting factors or platelets.
Question 7. What is open circulation?
Answer:
Open circulation
The open circulatory system is the system where, the heart pumps blood (hemolymph) into the hemocoel (body cavity), where the tissues are surrounded by the blood.
Question 8. How many chambers are there in the human heart?
Answer:
The human heart has four chambers—two atria and two ventricles.
Short answer questions on body fluids and circulation
Question 9. What are pericytes?
Answer:
Pericytes
Capillaries and venules, throughout the body, are wrapped by a type of contractile endothelial cells, known as pericytes.
Question 10. Define pulse.
Answer:
Pulse
The term pulse refers to the altering surges of pressure (expansion and then recoil) in an artery that occurs with each cardiac cycle.
Question 1l. Define heart rate.
Answer:
Heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per minute.
Question 12. Define minute volume.
Answer:
Minute volume
Minute volume is the volume of blood pumped by the left ventricle per unit time. It depends on the heartbeat frequency as well as the volume of blood ejected in one contraction.
Question 13. Name two methods for measuring cardiac output.
Answer:
Fick direct method and thermodilution method
Question 14. What do you mean by double circulation?
Answer:
Double circulation
Double circulation is a type of blood circulation where blood flows through the heart twice during its journey around the body—a pulmonary circulation between the heart and the lungs and a systemic circulation between the heart and the rest of the body.
Body fluids and circulation chapter-wise questions with solutions
Question 15. What is PR interval?
Answer:
PR interval
The PR interval starts at the beginning of the P wave and ends at the beginning of the QRS complex. The normal duration of the PR interval is 0.12 to 0.20 secondary.
Question 16. What are cardiopulmonary baroreceptor
Answer:
Cardiopulmonary baroreceptor
Cardiopulmonary Baroreceptors are mechanoreceptors (receptors which are activated by mechanical impulses) located in the atria, ventricles, and pulmonary vessels. These are also referred to as low-pressure baroreceptors. These are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the left ventricle.
