Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface Short Questions With Answers:
Question 1. What is the zenith distance of the sun?
Answer: The sun’s zenith distance is its distance from the vertical.
Question 2. What angle does each meridian make on the Equator?
Answer: 90°.
Question 3. What is the highest meridian of longitude?
Answer: 180°.
Read and Learn all WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
Question 4. How could (by which star) we calculate the latitude in the southern hemisphere?
Answer: The angle that Hadley’s octart makes at any place on Earth in the southern hemisphere is the latitude of the place.
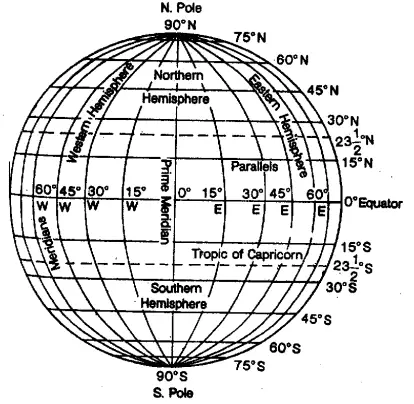
Question 5. What is the latitude of the Arctic Circle?
Answer: 66 (½)°N.
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE
Question 6. From which degree Prime Meridian pass?
Answer: 0°.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Solutions
Question 7. Which longitude is considered to be the International date line?
Answer: 180°.
Question 8. 0° longitude passes through which place?
Answer: Greenwich near London.
Question 9. What is the time difference at 1° interval of longitude?
Answer: 4 minutes.
Question 10. Which parallel is known as great circle?
Answer: Equator.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 11. What is the difference in longitude between a place and its antipode?
Answer: 180°.
Question 12. What is the time difference between a place and its antipode?
Answer: 12 hours.
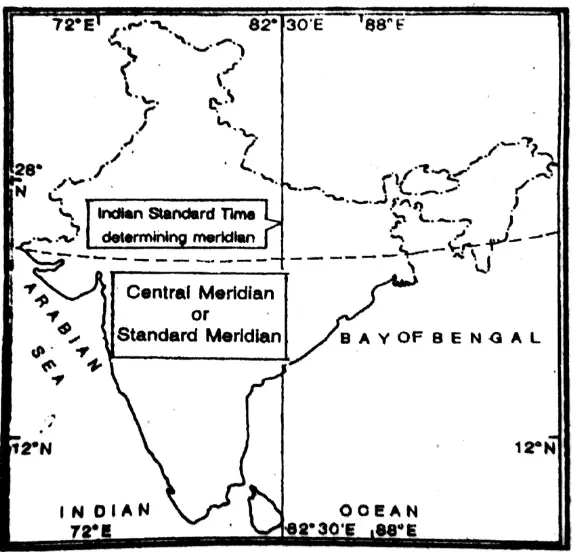
Question 13. Which degree is considered to be the standard meridian in India?
Answer: 82°30°E.
Question 14. How many hours Indian Standard Time is ahead of Greenwich Mean Time?
Answer: 5 ½
Question15. Which instrument is used to measure time at Greenwich?
Answer: Chronometer.
Question 16. Name two great circles in the Earth.
Answer:
(1) Equatorial Great Circle,
(2) Great Circle of Prime Meridian and International Dateline.
Question 17. What is the average distance between latitudes?
Answer: 111 km.
Question 18. What is the latitude of Tropic of Capricorn?
Answer: 23 (½)°s.
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE
Question 19. How many parallels of latitudes are there?
Answer: 181.
Question 20. What is the latitude of Kolkata?
Answer: 22°34’N.
Question 21. What is the antipode of kolkata (22°21″N)?
Answer: 22°34’S.
Question 22. Who invented Sextant?
Answer: John Hadley.

Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Class 9 WBBSE Question Answers
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3 questions and answers True Or False Type
Question 1. The number of Latitude is 180.
Answer: True
Question 2. Number of Longitude is 361.
Answer: False
Question 3. IDL is following 180° meridian of Longitude.
Answer: True
Question 4. Equator is the Great Circle.
Answer: True
Question 5. Standard Meridian of Pakistan is 75°E.
Answer: True
Question 6. Standard Meridian of Bangladesh is 90°E.
Answer: True
Question 7. Prime Meridian is a Full Circle.
Answer: Flase
Question 8. 82°30’ E Longitude is taken as IST.
Answer: True
Question 9. Standard Meridian of Pakistan is 75°E.
Answer: True
Question 10. Standard Meridian of Bangladesh is 90°E.
Answer: True
Question 11. Standard Meridian of India is 82°30°E.
Answer: True
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE
Question 12. Antipodes are two places on the earth’s surface situated just opposite to each other.
Answer: True
Question 13. The highest possible latitude is 360°.
Answer: Flash
Question 14. Longitudes are two places of the earth’s surface located just opposite to each other.
Answer: False
Question 15. Lines of latitudes are purely circular.
Answer: True
west bengal board Class 9 Geography Question 16. The antipode of Kolkata is 22°34°S and 91°30’W.
Answer: True
Question 17. Places lying on the same latitude have the same local time.
Answer: True
Question 18. The biggest possible longitude is 90°.
Answer: False
Question 19. Prime Meridian is the starting line and it is 0°.
Answer: True
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Latitude of the Tropic of Cancer is_______.
Answer: 23 (½)°N.
Question 2. Latitude of the Tropic of Capicorn is __________.
Answer: 23 (½)°S.
Question 3. Modern air routes follow the________.
Answer: Great Circle Route.
Question 4. Number of Latitude is________.
Answer: 181.
Question 5. Number of Longitude is________.
Answer: 360.
Question 6. Value of Prime Meridian is__________.
Answer: 0°.
Question 7. The latitude of Kolkata is ________ North.
Answer: 22°34.
Question 8. The line which lies on the halfway between the north pole and south pole is called____________.
Answer: Equator.
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE
Question 9. The parallels of latitude are___________ circles.
Answer: full.
Question 10. The meridians of longitudes are________.
Answer: semi-circle.
Question 11. The longitude of London is____________.
Answer: 0°.
Question 12. The highest possible latitude is_________.
Answer: 90°.
west bengal board Class 9 Geography Question 13. The International Date Line follows the ___________degree longitude.
Answer: 180°.
Question 14. The line which joins the two poles through the centre of the earth is called_____.
Answer: earth’s axis.
Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface 2 Marks Questions And Answers
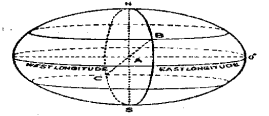
Question 1. What is Prime Meridian?
Answer:
Prime Meridian
The longitude line which passes through Greenwich near London is called prime meridian. Its position is 0°.
Question 2. What are the characteristics of latitude?
Answer:
The characteristics of latitude are:-
(1) All latitudes are whole circles.
(2)They are parallel to each other.
(3) They run in east-west direction.
(4) They gradually become smaller towards the poles from the equator.
Question 3. What is local time?
Answer:
Local time
Local time is apparent at noon time. It is mainly determined by the position of the overhead Sun.
West Bengal board Class 9 Geography
Question 4. What is apparent time?
Answer:
Apparent time
The time of the day indicated by the apparent movement of the sun ona sundial is called apparent time.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 WBBSE
Question 5. What is the time difference between a place and its antipode?
Answer:
12 hrs. is the time difference between a place and its antipode.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Solved Exercises
Question 6. By which instrument GMT can be measured?
Answer: By chronometers, GMT can be measured which is mainly used by the mariners of ships.
Question 7. What is Earth’s Grid?
Answer:
Earth’s Grid
Earth’s Grid is a network of certain imaginary but fixed intersecting lines drawn from the two poles and the equator.
Question 8. What is standard time?
Answer:
Standard time
When the local time of a place is taken as the time for the whole country, it is called the standard time of that country.
Question 9. Why are the lines of longitudes also known as ‘Meridians’?
Answer: The lines of longitude are also known as Meridians of longitude because Meridian is derived from the Greek word ‘Meridianum’ means noon. The sun crosses a meridian at noon so it will be noon at the same time all the places on a particular meridian.
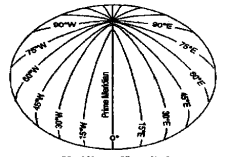
Question 10. Which line of longitude is used to fix the world standard time? State its value in degrees.
Answer: The time at Greenwich has been selected for fixing the world standard time. It is longitude.
Question 11. When it is noon in England, it is 5:30 p.m. in India. Explain.
Answer: The local time of India is B24 =330 mins = 5hrs. 30 mins ahead of Green- which time. This means, when it is noon in England (12:00 hrs) it is 5:30 pm. in India.
west bengal board Class 9 Geography Question 12. Where on earth there is no local time?
Answer: At poles there is no local time.
Question 13. Find the antipode of a place having 10°N (Latitude) and 60°E(longitude).
Answer: The antipode of the place is at 10°S and 120°W (180°-60° = 120°).
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 WBBSE
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 14. What is Great Circle?
Answer:
Great Circle
Equator is known as the Great Circle for its maximum diameter. The line which lies on halfway between the north pole and the south pole, is called the equator (0° latitude). The Great circle route between two points represents the shortest line between two points.
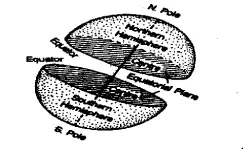
Question 15. What is Latitude?
Answer:
Latitude
Latitudes are the East-West extending imaginary lines, to the north and south of the equator lying parallel to each other on the earth’s surface.
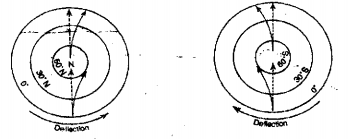
Question 16. What is Sextant?
Answer:
Sextant
Sextant is an instrument that helps to find out the latitude of a place by following the highest elevation of the sun in the sky. Thus, the latitude of a place is determined by this instrument.
Question 17. Mention two ways how the latitude of a place can be determined.
Answer:
(1) With the help of the ascension of the pole star :
Pole star can be seen from anywhere in the Northern hemisphere but not from Southern hemisphere. Its altitude varies with the change in place. At the equator, it can be seen at the horizon. So, moving 1° from the equator to the North pole the pole star also rises by 1°in the sky. In this way, at the North pole, the pole star is seen right overhead making an angle at 90°.
(2) By observing the ascent of the sun :
As the pole star cannot be seen during the daytime, the ascent of the sun is observed to find out the latitude of the place. In this case, also two poles of the sextant instrument is used to observe the ascent of the sun.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 WBBSE
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 18. Give five characteristics of werigierade
Answer:
Characteristics of werigierade
(1) Each longitude or meridian is a half-circle.
(2) The length of each longitude is the same.
(3) The degree of the meridians increase from Prime Meridian (0°) to the East or West up to 180° only.
(4) Meridians are not parallel to each other and all meet at the poles.
(5) The centre of the earth is also the centre of all meridians.
Question 19. Mention three ways how the Longitude of a place can be determined.
Answer:
(1) According to the time difference between two places their longitudes can be determined.
(2) If the longitude at one place is known, the time difference
between the two places will help to determine the longitude of the other place.
(3) The difference between GMT & the local time of any place will help to determine the longitude of the other places.
west bengal board Class 9 Geography Question 20. What are the meridians of Longitude?
Answer:
The semi-circular imaginary lines joining north & south and extending in a north-south direction over the earth’s surface are called meridians of longitude.
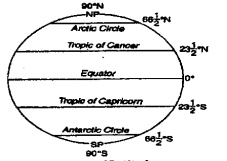
Question 21. How long is 1° Latitude?
Answer: As the earth is slightly flattened at the poles, the linear distance of one degree of latitude at the pole is slightly longer than that at the equator. However, at the equator, 1° of latitude is equal to 40,000 (km)/360 (degree) approx. 111 km.
Question 22. How long is 1° Longitude?
Answer: The linear distance between two longitudes of 1° difference is not the same everywhere. It is the longest at the equator and it decreases towards the poles. At the equator, 1° equals 111 km, but it is zero at the poles. At 30° north or south it s 96.5km., at 60° north or south is 55.4 km and at 80° north or south it is 19.3 km.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 WBBSE
Question 23. What do you mean by A.M. and P.M.?
Answer:
A.M. and P.M
A.M. is abbreviated from ‘Ante Meridian’. It indicates the time of a day before (ante) midday (meridian), i.e., the time from midnight (i.e., 12 O’clock midnight or, 00.00 hours) to midday (i.e. up to 12 noon). P.M. is abbreviated from ‘Post Meridian’, and it indicates the time after (post) midday (meridian), i.e., the time from 12 noon to midnight.
Question 24. Why do we not refer to longitude as distance in km east or west of the 0° meridian ?
Answer: As one approaches from the equator to the poles the distance between a meridian of longitude and the 0° meridian goes on decreasing. It is not possible to state so many varying lengths to identify one longitude. So lines of longitude are always identified by their angular distances.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 WBBSE
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 25. Why do some countries have several time zones?
Answer: Large countries like the U.S.A., Canada, C..S., which have a great east-west stretch adopt several time zones for practical purposes. C.1.S. which extends through 165° to longitude is divided into eleven time zones. When it is 10.00 p.m. on a Monday night in Leningrad, Travelers on the Trans-Siberian Railway adjust their watches a dozen time before they reach their destination.
Question 26. What are the four properties of Great Circle?
Answer:
Properties of Great Circle
(1) Great circles divide a globe into hemispheres.
(2) A plane passing through the centre of a sphere only can produce a great circle.
(3) It is the largest possible circle on a sphere.
(4) An arc of a great circle is the shortest surface distance between any two points on a sphere.
Question 27. Distinguish between the noon meridian and the midnight meridian.
Answer:
Difference between the noon meridian and the midnight meridian
The 0° prime meridian is the noon meridian. Directly opposite of the noon meridian, on the other side of the globe, is the midnight meridian at the |.D.L. The noon meridian separates forenoon and afternoon by a split of second. The midnight meridian separate one calendar day and the next by 24 hours.
Class 9 Geography Determination Of Location WBBSE Notes
Question 28. Is it ever possible for the same day to exist simultaneously on both sides of the International Date Line?
Answer:
Yes, theoretically, at the 0 (zero) hour it is possible for the same day to exist on both sides of the 1.D.L.
At the exact instant when the noon meridian of a particular day (12 hours fast) coincides with the 0° prime meridian the midnight hours meridian of the same day (12 hours slow) must also coincide with the 180 meridians. At this instant, the same
calendar day exists on both sides of the meridian. At all other times the calendar day on the west (Asiatic) of the I.D.L. is a day ahead of that on the east (Pacific American) side.
WBBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer
Question 29. What is a statute mile?
Answer:
Statute mile
A statute mile is a ‘Over-land’ linear measurement of 1760 yds = 5280 ft. = 63.360 ins. = 1609.3 meters. Originally, the miles was the Roman measurement of 1000 paces (Room milia).
Question 30. What is a nautical mile?
Answer:
Nautical mile
A nautical mile is the ‘Over-water’ length of 1 minute of arc or 1,21,600 of a great circle. On any great circle 1 minute = 1 nautical mile. 1 degree = 60 nautical miles. 1 nautical mile = 6,080 feet = 1,1516 statute mile = 1852 m.
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 31. What is a geographical mile?
Answer:
Geographical mile
A geographical mile is strictly the length of 1 minute is measured along the equator = 6,087.2 ft.; in practice, it is, however, taken as 6,080 ft.
Question 32. Where on earth is there no local time? Why?
Answer: At the poles, all the meridians converge to a point at the pole. That is why we cannot refer the time to any local meridian.
Question 33. What are the periods of the sun’s north declination and south declination?
Answer: From 21st March to 23rd September the sun has a north declination and from 23rd September to 21st March, it has a south declination.
WBBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface 2 Marks Questions And Answers (Short Notes)
Question 1. Local Time.
Answer:
Local Time
At any place when the sun is at the zenith (i.e. overhead) it is noon at that time and place. Thus at that place, it is 12 noon and accordingly the time is calculated. This is the local time of that place.
The sun’s position changes according to the change in longitude. Thus the local time of all the places on the same longitude of the meridian will be the same.
Question 2. G.MT.
Answer:
G.MT
It is the local time of the Prime Meridian (0°) at the Royal Astronomical Observatory, Greenwich near London. It is the standard time of U.K. Local time in all meridians to the east of Prime Meridians are ahead to G.M.T. and the local time of the meridians to the west of Prime Meridian are behind G.M.T.
In order to maintain international uniformity, one uniform time, corresponding to the Prime Meridian, is adopted by all countries. This is called Greenwich Mean Time. (G.M.1.) Indian standard time is 5½hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
Question 3. Land of Midnight Sun.
Answer:
Land of Midnight Sun
The Midnight Sun is a phenomenon in which the sun is seen shining above the horizon at midnight in latitudes higher than 66(½)°North or South. Between 21st March to 23rd September for 6 months, there is continuous day at the North Pole.
From Hamerfest port in the Northern border of Norway, even late in the night, the sun can be seen far away in the sky above the North Pole. Thus, the region around the Hammerfest port of Norway is called the land of Midnight Sun.
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 4. Standard time.
Answer:
Standard time
Standard time is an uniform time selected for all places in a country without any regard to their local times. It is generally taken from the central meridian of that country. The local time of that particular meridian is made the standard time of the entire country.
Standard time is taken in order to avoid a host of inconveniences that may occur if every town or village had its own local time. For example-Indian Standard Time is taken from 82°30’E.
Question 5. International Dateline.
Answer:
International Dateline
The International Date Line (IDL) is of great use in traveling around the world, particularly in keeping time of the world in a fixed framework. If there is no IDL and Prime Meridian there would occur an error of a day in other regions to make confusion of time as weil. The fixation of IDL mends this error and confusion. The IDL runs along the 180° meridian. It lies along the Mid-Pacific Ocean which changes where a landmark or a country prevails. On crossing this line, ships and
Question 6. Chronometer.
Answer:
Chronometer
A Chronometer is an accurate time-keeper, which shows the Greenwich Mean Time or the local time of a place and helps us to determine the longitude of a place with reference to the difference in the local time of two places.
Question 7. Great Circles.
Answer:
Great Circles
A great circle is a section of a sphere and the plane of the section passes through the centre of the sphere. The circle that cuts the Earth into two equal halves is called the Great Circle. The equator is about 40,000 Km long and is the largest possible circle on the Earth’s surface hence called Great Circle. it divides the Earth into two equal halves, the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere.
The Prime Meridian (0°) and its antimeridian (180°) together form a full circle that divides the Earth also into two halves (The Eastern and the Western Hemisphere). These two longitudes therefore, together form a Great Circle.
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 8. Antipodes.
Answer:
Antipodes
Antipodes are two places on the Earth’s surface, situated diametrically opposite to each other. If a straight line is drawn through the centre of the Earth, it will reach just the opposite side (the antipodal position).It should be noted that the latitudes of antipodes always interchange their positions in two hemisphere north and south and the difference of longitude between the two places of antipodes will always be 180° and they will be situated on the two hemisphere, viz. eastern and western.
Example: The latitude and longitude of Kolkata are 22°30°N. and 88°30 E respectively. Therefore, the antipodes of Kolkata lies at 22°34°S and 91°30’W (180° — 88°30° = 91°30°). This point is situated in the Pacific Ocean in the west of Chile (South America).
Question 9. Indian Standard Time.
Answer:
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time: In India, the local time of 82°30° East meridian, which passes through the central part of the country (near Allahabad), has been taken as the standard time for the whole country. It is known as Indian Standard Time or I.S.T. It is ahead from Greenwich Mean Time (G.M.T.) by 5 hours and 30
minutes [ 82 1/2° -0°= 82 1/2° x 4÷60=5 hours and 30 minutes.]
Class 9 WBBSE Geography Chapter 3 Important Questions
Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface 3 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. Differentiate between local time & standard time.
Answer:
Differentiate between local time & standard time
| Local Time | Standard Time |
| (1) It is measured by the sun’s mid-day altitude.
(2) A time zone can have many local times. (3) It differs from place to place. |
(1) It is measured by the central longitude’s local time.
(2) A time zone can have only one standard time. (3) It is constant in a particular area. |
Question 2. What is a great circle route? Why do modern air routes follow the great circle routes?
Answer:
Great circle route
Air or sea routes that follow great circle paths are known as great circle routes.
The modern air routes follow great circle routes because –
(1) They represent the shortest distance between any two points on the globe along with its circumference.
(2) On speedy long-distance flights, they save flying time.
(3) Great circle polar routes provide the quickest link between Europe and North America.
wbbse class 9 geography chapter 3
Question 3. What are the uses of latitudes & longitudes?
Answer:
(1) Uses of latitudes :-
(1)The tudes determine the location of a place.
(2) The latitudes determine the heat zones.
(3) It also determines the location of the pressure belt.
(4) The latitude can give an idea about the temperature and natural vegetation of a place.
(2) Uses of longitudes:-
(1) The point of intersection of longitude and latitudes determines the location of a place.
(2) The longitudes determine the local time of a place.
Question 4. What is the standard longitude of India and what is the need of it?
Answer:
Standard longitude of India
82°30′ is the standard longitude of India.
If there is no standard time of India different places have their different local times. India covers an area of 30 longitudes so railway system, airports, T.V., News etc. will have different time if a particular longitude is not followed
consistenly by all. So, to avoid these difficulties Indian standard time is used.
Question 5. Why International Date Line is not Straight?
Answer:
The International Date line passes through Pacific Ocean. It deviates from 180° longitude in some places in order to keep all the islands under one administration on one side of the Dateline.
The Date line goes zigzag in some places to avoid land and to leave island groups wholly. It deviates eastwards in the Bering strait between Alaska and Siberia. The line deviates westwards (7°) of 180° longitude to include the entire Aleutian islands to the east of the line. Further, South the Dateline deviates eastwards (11°) of 180° around Fiji, and Tonga islands.
(iv) In order to exclude Gilibert and phonex the line deviates 35° of 180°.
Question 6. State the differences between parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude.
Answer:
The differences between parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude
| Parallels of Latitude | Meridians of Longitude |
| (1) These are circular lines. | (1) These are semi-circular lines. |
| (2) Their size go on decreasing towards the poles. | (2) Theire size remains the same. |
| (3) The distance between them is uniform. | (3) The distance between them is not uniform. It goes on decreasing towards the poles. |
| (4) There are 179 lines of latitudes. | (4) There are 360 lines of longitudes. |
| (5) Sextant is used to measure latitude. | (5) Chronometer is used to measure longitude. |
| (6) They run in east, west direction. | (6) They run in a north-south direction. |
| (7) Equator is the most important parallel of latitude. | (7) Prime meridian is the most important meridian of longitude. |
| (8) They are located to the north and south of the equator. | (8) They are located to the east and west of the prime meridian. |
Question 7. What do you understand by antipodes?
Answer:
Antipodes
Antipodes are two places on the earth’s surface that are diametrically opposite to one another,in such a manner that a straight line joining them passes through the centre of the earth.
Example :
(1) (for Longitude) the antipode of 40° W is (180°-40°) = 140° E
(2) (for Latitude) = The antipode of 60° N = 60°S.
The antipode of any place on the equator will be on the equator.
Question 8. Distinguish between Greenwich Mean Time and Indian Standard Time.
Answer:
Difference between Greenwich Mean Time and Indian Standard Time
Greenwich Mean Time is the local time of the Prime Meridian (0°) at the Royal Astronomical Observatory, Greenwich near London. It is also known as universal time. On the other hand, Indian standard time is the standard time of India as a whole. ISI is reckoned from the times of the central meridian of the country and it is 82°30’E. It is ahead of GMT by 5 hours and 30 minutes.
Question 9. Explain the Statements:- For Longitudinal difference of 1° time varies for 4 minutes.
Answer:
For Longitudinal difference of 1° time varies for 4 minutes
Earth takes almost 24 hours for a complete rotation. Thus earth completes 360° in 24 hours. So, in one hour the earth moves 15° (360° = 24 hrs. = 15°) and naturally, 1° of longitude will take 4 minutes (60 minutes + 15 = 4 minutes) to rotate. So for a longitude difference of 1° time varies for 4 minutes.
(1) For Longitudinal difference of 1° time varies for 4 seconds. As a difference of 1° longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes or 240 seconds, then for longitudinal difference of 1′ time varies for (240 + 60 seconds) 4 seconds.
Question 10. The variation of time between a place and its antipode is twelve hours — why?
Answer:
The variation of time between a place and its antipode is twelve hours
The difference of the longitudes of a place and its antipode is of 180°. Since 1° longitudinal difference causes 4 minutes time difference. therefore, 180° longitudinal difference causes 180 x 4 mins. or 720 mins. or 12 hrs. time difference. That’s the reason why the variation of time between a place and its antipode is twelve hours.
WBBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer
Question 11. Relation between the line of longitude and time.
Answer:
Relation between the line of longitude and time
There is a definite relation between longitude and time. The earth rotates on its axis and completes one rotation in 24 hours; therefore, 360° meridians of longitude take 24 hours to pass under the sun.
Thus, 15 degrees [360° + 24 = 15°] pass under the sun each hour and 1 degree in 4 minutes [60 minutes = 15° = 4 mins.].
We know that it is noon at a place when the sun is seen just on overhead of the meridian of longitude of that place. Thus, all places on the same meridian have their noon at the same time.
As the earth rotates from West to East, places on the East of the meridian 0° pass under the sun before places which are in the West of this meridian.
Question 12. Why does International Date Line follow 180° Longitude?
Answer: The reason for the choice of the 180th-degree meridian as the International Date Line, is that it passes through the mid-Pacific Ocean where there are a few landmasses and islands. Hence, there is almost no need for changing the time frequently. In this meridian, there are only few places where bendings are made to maintain the time zones.
Question 13. Find the antipode of a place having 10°N (Latitude) and 60°E(Longitude).
Answer:
10°S latitude and 120° W longitude.
Latitudes in Antipodes interchange the hemispheres. Therefore 10°N latitude becomes 10°S. But, the longitudinal difference between antipodes is 180° and in the opposite hemisphere.
Therefore 180° — 60° E = 120° W.
Question 14. What is meant by local time and standard time?
Answer:
Local Time :
At any place when the sun is at its zenith (i.e. overhead) it is noon at that time and place. Thus at that place, it is 12 noon, and accordingly the time is calculated. This is local time of that place. The sun’s position changes according to the change in longitude. Thus the local time of all the places on the same longitude of the meridian willbe the same.
Standard time :
Standard time is an uniform time selected for all.places in a country without any regard to their local times. It is generally taken from the central meridian of that country. The local time of that particular meridian is made the standard time of the entire country. Standard time is taken in order to avoid a host of inconveniences that may occur if every town or village has its own local time.
Question 15. How can location of a place on the globe be determined?
Answer: With the help of parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude, the location of a place on the globe is determined. But for the exact location, both the parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude are necessary. Either of them cannot determine the exact location. For example, if we say that a place is situated at 30° North latitude. Now, on this latitude so many places are situated. In the same way if we say that place is on 100°E longitude. Again along this longitude many places are located. But when we say that the place is situated on 30° N latitudes and 100°E longitude, that is the intersecting point of a particular parallel of latitude and meridian of longitude, then the exact position of the place is found out. Thus, to locate the exact position of a place on the globe, the meeting point of a parallel of latitude and the meridian of longitude should be must.
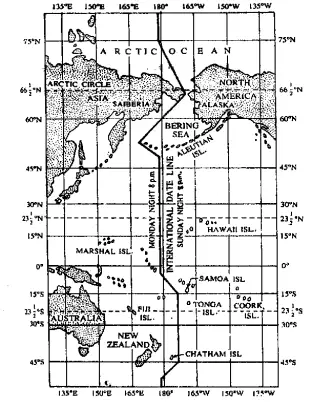
Question 16. What is International Date Line? :
Answer:
International Date Line
The 180° meridian of longitude is regarded as the International Dateline. In the past the circumnavigators always felt the loss or gain of time while traveling around the world. Those travelling towards east always felt that they bad reached anead of their schedule, while thone travelling west felt that they reached their destination late.
If was by an International agreement in 1884, the 1800 meridian of longitude was Relected as the place where circumnavigators would adjost the time of their watches it one crosses this line (180°) from East to west; one day, i.e 24 hrs will be added and one day or 24 hrs will be deducted while crossing from West to East.
This 180° longitude is not drawn as a completely straight line, it turns wherever there is land mass.
Question 17. Define the following: Great circle, Equator, Meridian, Prime meridian.
Answer:
Great circle
A great circle is any circle on the earth’s surface whose centre is the earth’s centre.
Equator
The equator is a great circle midway between the north and south poles.
Meridian
Meridian means ‘mid-day’ The lines of longitude are called meridians as mid- day occurs at the same time at all placer located on the meridian.
Prime meridian
The (0°) meridian which passes through Greenwich, England, is called the prime meridian.
Question 18. How is the time calculated in hours, minutes, and seconds?
Answer:
We specify exact time in the following manner :
(1) It takes 24 hours to make a complete rotation or 360°.
∴In 1 hour the earth rotates 360 ÷ 24 = 15°
(2). 15° longitudinal difference = 1 hour or 60 minutes
∴ 1° longitude difference = 20/15 = 4 minutes
(3) : .. 1° or 60° longitudinal difference
= 4 minutes or 4 x 60 = 240 seconds
∴ 1 longitudinal difference =264/60 on 4 seconds ”
Question 19. What are the Standard Meridians of Pakistan, India and Bangladesh?
Answer: Pakistan = 75°E, India = 82 1/2° E, Bangladesh = 90°E.
Question 20. What are the uses of parallels of latitude?
Answer:
Uses of Parallels :
(1) A place on the earth’s surface cannot be determined only by parallels, it indicates its location either north of the equator or south of it.
(2)The parallel of latitude together with the meridian of longitude yield the exact position of a place.
(3) They enable us to know the distance of a place from the equator and from one latitude to another and they can be used to determine the scale of a map.
(4) They help us to guess what type of climate would prevail in a particular place.
(5)They also give us an idea about the type of natural vegetation in a particular place.
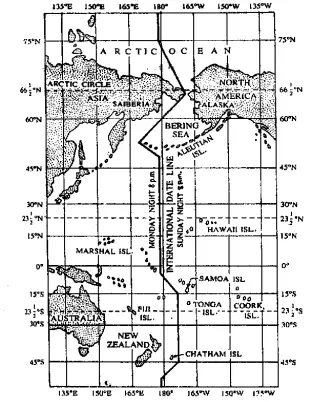
Question 21. What necessitates the International Dateline?
Answer:
Necessitates the International Dateline
International Date Line, generally follows 180° east and west longitude line. It is so located that it is halfway around the world from the Greenwich or Prime Meridian. A peculiar position arises at the meridian 180° east and west.
This meridian is reckoned both as 180°E and 180°W. if the time at any place on the Greenwich Meridian is 8 a.m. on Monday, then calculating eastwards the time at 180°E will be 8 p.m. on Monday, and calculating westward the time at 180°W will be 8 p.m on Sunday.
This means that a man standing west of 180° meridian records his time as Monday, 8 p.m., while his friend standing east of 180° meridian claims Sunday, 8 p.m. Such confusion of one day must be corrected.
Iit was at the initiative of W.M Davis, the 180° meridian was adopted as the International Dateline in 1884 at as International conference. When a man crosses the International Date Line going east, he has to turn his calendar a full day Peak, and going west over tHe State Line, he moves the calendar one day forward.
Thus traveling west from Alaska to Siberia it is 8 p.m. Monday at the International Date Line but it will be 8 p.m. Sunday at the International Date Line when we travel from Siberia to Alaska. In order to avoid dividing nations or islands into two different days the International Date Line is made somewhat irregular.
Question 22. Differentiate between Longitude & Meridians of Longitude.
Answer:
Difference between Longitude & Meridians of Longitude
| Longitude | Meridians of Longitude |
| (1) It is the angular distance on the earth. | (1) It is the linear distance. |
| (2) This is the point of location. | (2) This is the imaginary lines joining all the points on the longitude. |
| (3) This is just a point. | (3) This is a semi-circle. |
| (4) A longitude bisects only one latitude. | (4) There are total 1st latitude bisected by the meridians of longitude. |
Question 23. What are latitudes? What are the characteristics of Latitude?
Answer:
Latitudes:
Latitudes are angular distance lines running in an east-west direction to the north and south of the equator.
Characteristics of latitudes :
(1) All latitudes are whole circles and are parallel to each other
(2) All latitudes are not equal in length and
(3) Latitudes become gradually smaller from the equator to the poles and at the poles, the latitude is only a dot.
Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface 5 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. What is the necessity of determination of the location of a place on the earth’s surface?
Answer:
(1) To know the Concept of Climate :
With the latitudinal location of a place, one can easily derive an idea of the climatic types of the place. For example, if the place is at higher latitude is 60-90°N/S then the place must be in a colder region. Similarly, In the lower latitudes i.e., between 0°-30° N/S the climate is hot summer type.
(2) Concept of time from location :
Time can be early identified by the location of a place. From the longitude, we can find whether the place is in the right or in the left. Eastward location of a place implies its local time advanced and westward location implies its local time behind.
WBBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer
(3) For navigation :
For air and water transport it is easier to reach the exact destination by knowing the accurate location of the place.
(4) Throwing missiles etc :
Pointing out and hitting the object in case of war the exact location of the place must be focussed.
(5) Business transaction :
The perfect location of the place helps in business transactions.
(6) Reading Atlas :
If we know the latitude and longitude of a place it becomes easier to find out the location of a place in the Atlas.
(7) To locate the hemisphere :
Location of a place to helps us to generate an idea about the hemisphere. Where the place is located.
(8) Sunset and Sunrise :
Exact location of the place helps us to generate an idea about the timing of sunrise and sunset.
(9) Season length of day and night :
It is easier to develop the idea of season the length of day and night if we know the exact location.
(10) Reading globe :
To study the globe perfect location help us to mark the area.
Question 2. Give an account of some important parallels of latitude.
Answer:
Important parallels of latitude
Equator, Tropic of Cancer, Tropic of Capricorn, Arctic Circle, Antarctic Circle, Norht Pole and South Pole are the important parallels of latitude. Parallels of latitude are all circles. The Equator forms the great circle and all other circles are small.
(1)Equator (0°) :
Equator is an imaginary great circle, 40,077 km round. Its plane is called Equatorial Plane. Equatorial Plane is at right angles to the earth’s axis of rotation. All points on it are by definition at latitude 0° and equidistant form North Pole as well as from South Pole. Equator divides the earth’s surface into the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere since it is a great circle. Equator is called a great circle because it has the following characteristics :
(1) Its plane passes through the centre of the earth. Circles whose planes do not through the centre of the earth are called small circles.
(2) The Equator is the circumference of the earth. A smail circle is not the circumference of the earth.
(3) The centre of the Equator coincides withthe centre of the Earth.
(4) Equator cuts the earth in halfi.e. in the northern hemisphere and in the southern hemisphere. Every great circle cuts the earth in half and vice-versa. At all places on the Equator, the Sun remains approximately overhead twice a year, once at March Equinox and the other at September Equinox and the Sun of mid-day is never more than 23 4 * from the vertical. It is quite natural that places on or near the Equator are very hot unless they are at high altitudes.
(2)Tropic of Cancer (23 4° N) :
At June solstice occuring on June 21 the subsolar point lies on the tropic of cancer (latitude 234°N). The Tropic of Cancer is the northern extreme parallel of latitude reached by the vertical rays of the Sun.
(3)Tropic of Capricorn (23 4° S):
At December solstice occurring of December 22, the subsolar point lies on the Tropic of Capricorn (latitude 23 4°S.). The Tropic of Capricorn is the southern extreme parallel of latitude reached by the vertical rays of the Sun.
(4)Arctic Circle (664° N) :
At June solstice occurring on June 21 the circle of illumination (or shadow circle) forms tangent to both the Arctic Circles (latitude 66% N) and Antarctic Circle (latitude 66 °S.) having 24 hours sunlight in the entire area inside the Antarctic Circle.
WBBSE Class 9th Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer
(5)North Pole (90°N) :
The North Pole is the smallest parallel of latitude in the northern hemisphere. It is in the form of a point. The shadow circle formed on both the Equinoxes i.e., March and September Equinoxes touch the North Pole.
(6)South Pole (90°S) :
The South Pole is the smallest parallel of latitude in the southern hemisphere. It is in the form of a point. The shadow circle formed on both the Equinoxes i.e., March Equinox and September Equinox touches the South Pole.
Determination Of The Location Of A Place Class 9 WBBSE Short And Long Answers
Question 3. What are the features of parallels of latitude.
Answer:
Features of Parallels of Latitude :
(1) All places on a parallel of latitude in either hemisphere have similar latitude. Although we say Calcutta is at 22°34 north of Equator, there are, however, infinite number of points that are 22°34″ north of the Equator.
(2) Parallels are always parallel to one another.
(3) Parallels except North Pole and South Pole are circular lines.
(4) All parallels except the equator are small circles. Those small circles are getting smaller as they approach both the poles. In fact, at both the a small circles are reduced into points.
(5) As the latitude increases, the circumference of the parallel Becreascl
(6) There cannot be two or more equal parallels in the northern hemisphere or southern hemisphere.
(7) Parallels of two hemispheres may be equal in degree, minute or second.
(8) The linear distance between two parallels of 1° difference is not identical always.
(9) Different places on a parallel are situated east or west of one another.
(10) All places on a parallel do not find sunrise, noon or sunset at a time.
(11) Parallels represent east-west lines.
(12) Every point on the earth, except the North Pole or South Pole, lies on a parallel.
(13) All parallels except North Pole and South Pole intersect Tiere at right angles.
(14) A large number of parallels may by drawn on the earth’s surface.
Ch 3 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Question 4. What do you mean by antisocial? Give its features.
Answer:
Definition Of antisocial: Antipodes are two places on the earth’s surface that are diametrically opposite to one another, in such manner that a straight line joining them passes through the centre of the earth.
Features of Antipodes :
(1) The latitudes of antipodes are always equal [in degree (°) minute (‘), second (“)] and opposite [one north; the other south] hemispheres.
(2) The longitudes of antipodes add up to 180°, one being east, the other west generally. The longitude of Calcutta is 88°24’E. So longitude of its antipodes is 91°36′ W. Because 88°24′ west of Calcutta lies prime meridian (0°) and 91°36’ west of Prime Meridian (0°) will be the antipodes of Calcutta. The difference of longitude between an place and its antipodes will always be 180°.
(3) In case of antipodes,midnight at one place will occur simultaneously with midday at the other or vice versa.
(4) Antipodes of any piace on the equator lie on the equator.
(5) The latitudes of a place and of its antipodes (except on the equator) generally interchange their positions in two hemispheres, north and south. For example, the latitude of Calcutta is 22°34’N. So its antipodes will lie on 22°34’S.
Ch 3 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
(6) Antipodes of any place of the Prime Meridian will lie on 180° longitude or vice versa.
(7) Antipodes of a meridian always lie on its antimeridian Obviously the difference of time between a place and its antipodes will always be 12 hours.
Question 5. If the local time at Haldia (80°E) is 11 a.m. what is the time at its antipode?
Answer:
Local time at
Halidia 11 a.m. i.e 11 hours
Plus 12 hours
∴ Local time at the antipode of Haldia 23 hours i.e. 11 p.m. on the same day. 11 p.m. on the same day.
Question 6. Define Meridian of longitude. What are its features?
Answer:
Definition of Meridian of Longitude: The semi-circular line drawn on a map to link all points on the earth’s surface with the same angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian is defined as Meridian of Longitude.
Ch 3 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Features of Meridians of Longitude :
Meridians of Longitude are halves of great circles, whose ends coincide with the earth’s north and south poles. Although
a meridian and its antimeridian together comprise a complete great circle, a single meridian is only half of a great circle and contains 180° of arc.
Additional features of meridians of longitude are as follows :
(1) All meridians run in a true north-south direction.
(2) An infinite number of meridians may be drawn on a globe. Thus a meridian exists for any point chosen on the globe. For
representation on maps and globes, however, chosen, meridians are spaced at equal distances apart.
(3) All the meridians are equal in length, but not parallel to one another.
(4) The linear distance between two meridians is not uniform
everywhere. It shortens with increasing distance from the equator ranging from 111 kilometers at the equator to nil at the poles per degree.
(5) All places on the same meridian are either at the north or the south of one another
(6) All places on the same meridians have sunrise, noon or sunset at the same time.
(7) All places on the same meridian have the same local time: In the matter of calculation of time, the meridian of longitude plays a significant role.
(8) Each meridian cuts the equator at right angle.
Class 9 Ch 3 Geography WBBSE
Question 7. How you can measure the latitude of Kolkata on Earth?
Answer:
The latitude of a place indicates the angular distance north or south of the Equator. The point that stands for Kolkata on the earth’s surface may be either north or south of the Equator. in order to determine the extent of its northward or southward placement that Calcutta point is connected with the (center) of the earth by an imaginary straight line is drawn from the point of intersection between meridian of the longitude of kolkata and the Equator.
These two imaginary lines (in fact two radii) form an ole angle at the centre of the earth. Such an angle measured in degrees, minutes and seconds is called Latitude. The measurement of such an angle for Kolkata is 22°34’. As kokata stands north of the Equator, the latitude of kolkata is called 22°34’N
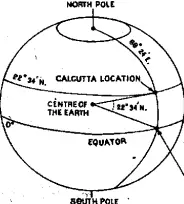
An instrument known as Sextant invented by John Hadley is used to determine the latitude of a place. This instrument measures the angle between the horizon and a celestial body such as at daytime noonday sur or at night the North Star (Polaris) in Northern hemisphere and the Hadley’s Octant in Southern Hemisphere.
However, no matter how accurately we pinpoint the latitude of a place like Calcutta, we have given only half the story. For we have only described the location of Calcutta as being 22°34’ north of the Equator. There are, however, an infinite number of points that are 22°34’ north of the Equator.
Class 9 Ch 3 Geography WBBSE
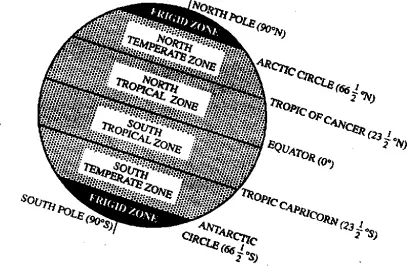
Question 8. Explain the heat zones of the Earth.
Answer:
Heat zones of the Earth
The sun rays fall vertically on the lower latitudes and the Sun never goes overhead beyond23 (½)°N latitude (Tropic of Cancer) and 23 (½)°S (Tropic of Capricorn). So, in between the two Tropics, the temperature remains high throughout the year. This area between the two tropics is known as the Torrid zone of the Earth
The region between the Tropic of Cancer [ 23(½)°N] and the Arctic Circle (66(½)°N] in the Northern Hemisphere and that between the Tropic of Capricorn [ 23(½)°S] and the Antarctic Circle [ 66(½)°S] receive the oblique rays of the Sun. These two regions on either hemisphere have moderate temperatures and are known as the Temperate zones of the Earth.
The region between Arctic Circle (66(½)°N] and the North Pole (90°N) and that between the Antarctic Circle [ 66(½)°S] and the South Pole receive tangential rays of the Sun. These two regions have extremely low temperature and are known asthe Frigid zones of the Earth
The parallels of latitudes; therefore, divide the Earth into different temperature belts or heat zones. Thus we get an idea about the climate of any place lying within these zones.
Question 9. Give a comparison between parallels of latitude & meridians of longitude.
Answer:
Comparison between Parallels of Latitude and Meridians of Longitude :
| Parallels of Latitude_ | _Meridians of Longitude_ |
| 1. The imaginary lines drawn by joining places having the same latitude are called Parallels of latitude. | 1. The imaginary lines drawn by joining places having the same longitude are called Meridian of Longitude. |
| 2. Latitudes encircle the earth in east-west lines. | 2. Longitudes extend in a north-south direction on the earth. |
| 3. Each latitude forms a whole circle and they. But each latitude has different lengths. | 3. Each of them form half-circles but all of them have the same length. |
| 4. The latitudes are nearly equidistant from each other. The earth being an oblate spheroid this distance is more near the polar region than at the equator. | 4. The longitudes are not at equidistance everywhere, as the intervening distance decreases from the equator to the poles where they merge to a point. |
| 5. Except the two poles all other latitudes are whole circles each forming an angle of360°. | 5. Every longitude forms a half-circle, thus each forms an angle of 180°. |
| 6. Because oftheearth’sshapeonlythe equator forms a Great Circle and not the other latitudes. From either side of the equator the length of the latitude gradually diminish towards the poles. | 6. Every longitude forms a great circle with the longitude on the opposite side of the earth. But each longitude is independent or has a certain value so no longitude can be said to be a whole circle or a Great Circle. They are half circles. |
| 7. The latitudes are measured from the Equator. | 7. The longitudes are measured from the Prime Meridian. |
| 8. Latitudes are measured form 0°( Equator) to 90° N and S (North and South Pole). | 8. Longitudes are measured from 0°(Prime Meridian) to 180°E and 180°W longitudes. |
| 9. With latitudes one get an idea about how for a place is located to the north or south of the equator. | 9. In this way it can be understood how far a place is located to the east or west of the Prime Meridian. |
| 10. Except the equator all parallels of latitude have their center on the earth’s axis, the equator and the of the earth are the same. | 10. The center of all longitudes is the same as the center of the earth. |
| 11. The length of all parallels of latitude gradually lessens from the equator to the poles. | 11. All longitudes have the same length. |
| 12. The latitudes are divided into North Latitudes and South Latitudes. | 12. Longitudes are divided into East Longitudes and West Longitudes. |
| 13. In the same parallel of latitude sunrise, noon and sunset occurs at the different times at all places. | 13. In the same meridian of longitude at all places sunrise, noon and sunset occur at the same time. |
| 14. In the same latitude at different regions the local time is different. Thus in determining the local time latitudes have no role to play. | 14. The same meridian has the same local time at all regions along it. Thus longitudes determine the local time of place. |
| 15. The same latitude has very little different places along the latitude. | 15. The same longitude has great differences in climate at variable places along the longitude. |
Class 9 Ch 3 Geography WBBSE
Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface 5 Marks Questions And Answers [Numricals]
Question 1. Calculate the longitude of the position of a ship whose captain observes that it is 7:30 p.m. in the chronometer when the local time in mid-ocean is 1:00 p.m.
Answer:
The difference between the two places is 7.30 p.m. — 1.00 p.m
= 6 hrs. 30 mints. = 390 minutes.
∴ 4 mins. time difference causes the difference of 1° longitude
∴ 390 mins……………………………………………………………..390 ÷ 4
=97°30′ [∴ 1°=60′. ∴ (2/4)°=30°]
We know the time of the place is behind that of Greenwich, the place is 97°30′ West of Greenwich.
∴the longitude of the place = 0° — 97°30′ = 97°30′ W. Answer:
Question 2. An e-mail was sent from Sydney (151°30’E) to Allahabad (82°30’E) on Saturday, the 1st March 2008 at 4 a.m. Find out the time, day, and date of its arrival an Allahabad. op Allahabad
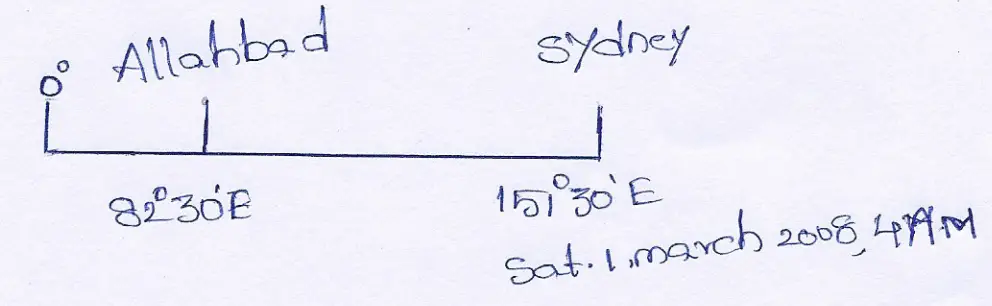
Answer:
The longitudinal difference between Sydney and Allahabad is 151°30” E — 82°30’E = 69°.
We know, 1° longitudinal difference makes a time difference of 4 minutes
∴ 69° ” ” ” ” ” ” 4x 69 = 276 mins
= 4 hrs 36 mins.
As Allahabad is in the West of Sydney, 4 hrs. 36 mins. should be subtracted from the time of Sydney (West-lose-Subtract). Therefore, local time, day, and date of the arrival of e-mail at Allahabad = the Saturday, the ist March 2008 at 4 a.m. — 4 hrs 36 mins = the Friday, the 29th February 2008, 11: 24 p.m
Question 3. The news broadcasted at 8-00 a.m. from Greenwich was heard in a place at 2.30 p.m. What would be the longitude of that place?

Answer: The difference in time between the two places is 2.30 p.m. — 8.00 a.m.
= 6 hrs. 30 min. = 390 minutes.
∴4 minutes time difference causes the difference of 1° longitude
∴ 390° ” ” ” ” ” ” ” “390 ÷ 4 =97°30′
We know, the time of the place is ahead than that of Greenwich.
∴The place is 97°30° East of Greenwich.
∴The longitude of the place is 0° + 97.30 = 97°30′ E.
Question 4. When the local time at Kolkata (88°30’E /22°30’N) was 10.00 am. on Sunday, 1st January 2006, then what would be the local time, day and date of its antipode?
Answer:
Kolkata is 88°30′ E and the longitude of its antipode will be = 180° — 88°30′ = 91°30’W
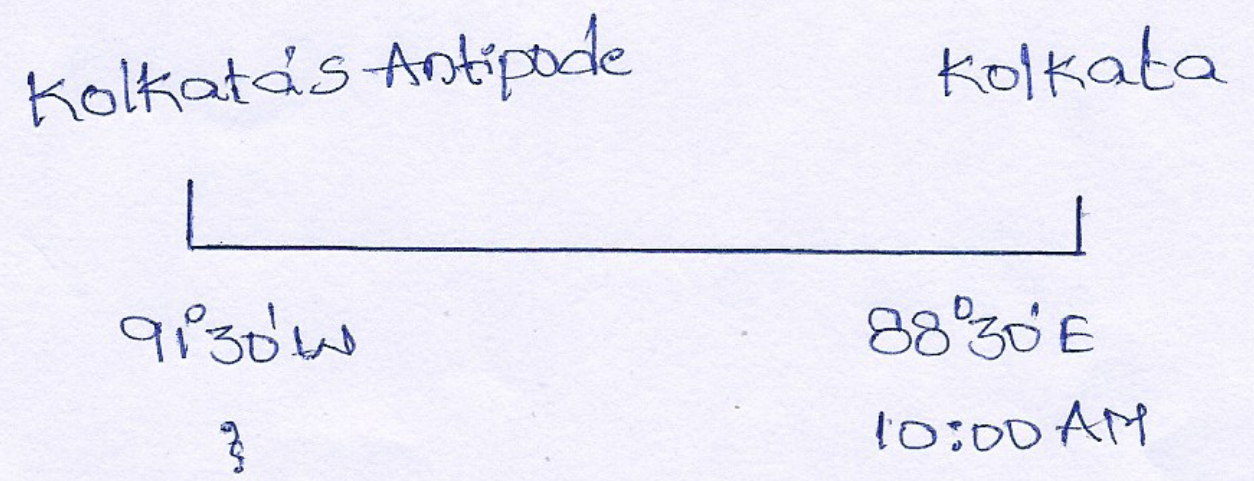

∴The longitudinal difference between the two places= 88°30′ + 91°30′ = 180°
We know that, 1° longitudinal difference makes a time difference of 4 minutes
∴180° ” ” ” ” =180×4
= 720mins
= 720+ 60 = 12 hrs.
∴The time of the antipodal place of Kolkata will be behind as it is in the West.
Hence time =10-12
= (10+ 12)-12
=10PM
Day = Saturday, and
Date = 31st Dec. 2005
Question 5. The longitudes of P and Q are 100°E and 80°W respectively. Find out the local time of Q when it is 11 p.m. on Sunday at P.
Answer:
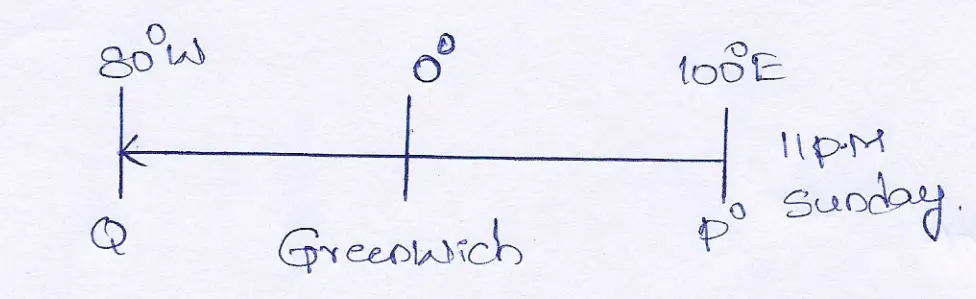
The longitudinal difference between P and Qis (100° + 80) = 180°
For1 longitudinal difference, the time difference is 4 minutes.
∴ For 180 longitudinal difference, the time difference is 4×180 minutes = 720 minutes = 12 hours.
Q is situated to the West of P. Therefore, the time of Q will be backward.
∴ When it is 11 P.M. on Sunday at P then the time at Q will be (11 PM Sunday – 12 hours.)=11A.M. Sunday.
The time of Q will be 11 A. Mon the same day i.e., Sunday.
Question 6. A time alarm has been sent from Greenwich to X at 12 noon and the receiving end i.e. X got the alarm at 4.28 p.m. of the local time of X. The alarm took only 2 minutes to reach the destination. Determine the longitude of X.
Answer:

An alarm has been sent from Greenwich at 12 noon to X. The alarm took 2 minutes to reach X. The alarm reach X at 4.28 P.M. of its local time. Thus the actual time difference between Greenwich and X is {(4.28 P.M. — 2 m) – 12 noon}
= (4.26 P.M. – 12 noon) = 4 hour 26 minutes time difference,
∴For every 4′ time different the longitudinal difference is 1°
∴For every 1 minutes time difference, the longitudinal difference is (¼)°
∴For every 266 minutes time difference the longitudinal difference
¼ x 266 = 66(½)°= 66°30.
As the time of X is ahead of Greenwich, the location of X will be at (0° + 66°30) = 66°30′ E.
Question 7. What would be the local time at New York (75°W) and Mumbai (73°E) when it is noon at Greenwich?
Answer:
| 75° W | 0° | 73° E |
| (New York) | (Greenwich) | (Mumbai) |
| Time? | 12 noon | Time? |
The longitudinal difference between Greenwich and New York is (75°- 0°) = 75°
For 1° longitudinal difference, the time difference is 4 minutes.
∴ 75° longitudinal difference, the time difference 4×75 = 300 min. = 5 hours.
As New York is to the West of Greenwich, so the time of New York will be behind that of Greenwich. When it is 12 noon at 0° (Greenwich), the time of New York will be (12 noon – 5 hrs.) = 7.00 A.M. the same day.
The longitudinal difference between Greenwich and Mumbai is (73°-0°)=73°
For 1° longitudinal difference, the time difference is 4 min.
∴73° longitudinal difference, the time difference 4 x 73
= 292 min.
= 4 hrs. 52 min.
As Mumbai is situated to the East of Greenwich, the time of Mumbai will be ahead of Greenwich. When it is 12 noon at 0° (Greenwich), then the time of Mumbai will be (12 noon +4 hours 52 min.) = 4.52 P.M. the same day.
Question 8. When it is 3 p.m. in Kolkata, it is 10.40 a.m. at X. The longitude of Kolkata is 88°30′ E. What is the longitude of X?
Answer:
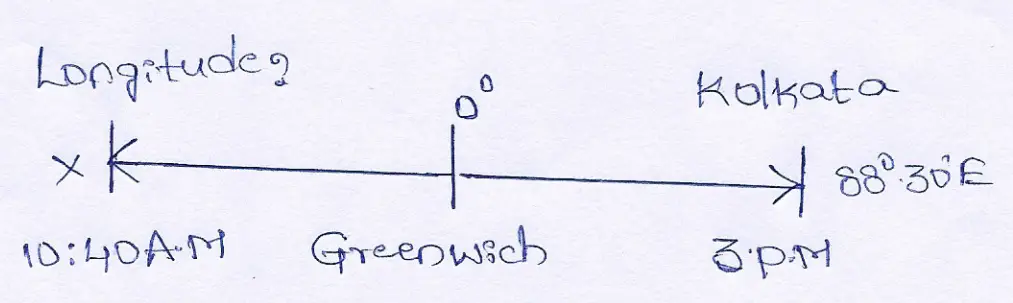
The time difference between Kolkata and X is (3 P.M.—10: 40 A.M) =4 hrs. 20 min. = 260 min.
∴For 4 minutes time difference, the longitudinal difference is 1°
∴ 1 ” ” ” ” (¼)°
∴260 ” ” ” ” =¼ × 260 =65°
As the time of X is behind of Kolkata, so X will be situated to the West of Kolkata.
The longitude of X will be (88° 30′ E – 65°) = 23° 30’E.
Question 9. If the inaugural ceremony of Olympic games at Athens (24°E) commences at 8.30 p.m., when will it be live telecast at Allahabad (82°30’E)?
Answer:
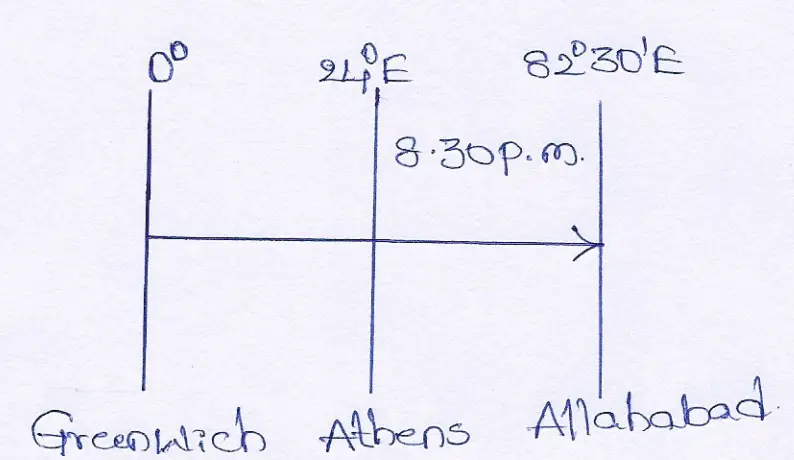
Difference in longitude of the two places = 82°30’— 24° = 58°30’
1° longitudinal difference makes a time difference of 4 minutes
∴ 58° ” ” ” ” ” = 58 x 4 minutes = 232 minutes
Again 1′ longitudinal diffenrence makes a time difference of 4 seonds
∴ 30′ ” ” ” ” 30 x 4 seonds
= 120 seconds or 2 minutes
Total time = 232 minutes + minutes = 234 minutes or 3 hours 54 minutes. Since, Allahabad is situated to the East of Athens, so time of Allahabad will be forward.
∴ required time = 8.30 + 3 hrs. 54 mins. = 12.24 hrs. = 00:24 A.M.
Question 10. A special radio news bulletin was broadcast at 12 noon from New York (74°W) and it was heard at 8 O’ clock at night in a place. What would be the longitude of that place ?
Answer:
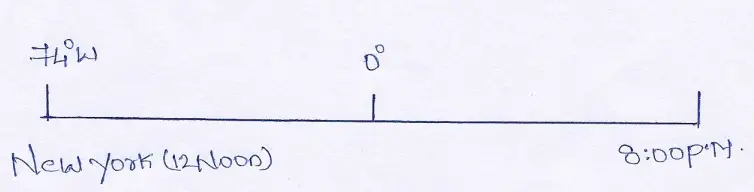
The difference of time between New York and other place is 8 hours or 480 minutes.
∴4 minutes difference occurs in 1° longitude.
∴480 minutes difference will occur in 480 ÷ 4 longitude = 120°
As the time of the place is ahead than that of New York, hence the place is situated East of New York and in Eastern hemisphere.
∴The longitude of the place is 120° — 74° = 46°E.
Question 11. If a cricket match is started at 10.00 a.m. at London (0°) at what Indian Standard Time (I.S.T.) it will be telecast in India ?
Answer:
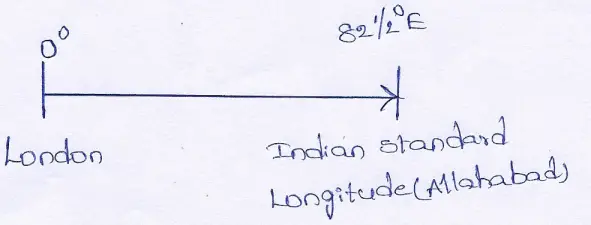
Difference in longitude of the two places = 82 ½°= 165/2°
∴To cross 1° longitude 4 minutes is required
∴ ,, ,, ,, ,, 165/2° ,, ,, ,, ,, 165/2×4=330’minutes=5 hrs. 30 minutes.
India is situated to the east of London, so required Indian standard time will be forward.
∴required time = 10+5 hrs.30 minutes
= 15 hrs.30 minutes.
= 3 hrs. 30 minutes or 3:30 P.M.
Question 12. A hockey match held at Sydney (151°30’ East) Olympic at 6 P.M. was telecast directly when was it visible at Calcutta (88°30’ East) ?
Answer:

Longitudinal difference between Sydney and Calcutta is 151°30’ — 88°30’ = 63°
For 1° longitudinal difference, time difference is 4 minutes.
For 63°” ” ” ” ” 4×63 = 252 minutes.
Total time difference between Sydney, and calcutta = 4hrs 12 minutes.
Since, Calcutta is located to the West of Sydney, therefore, its time will be behind by 4hrs. 12 minutes.
The time, when the match will be visible in India = 6 A.M.—4 hrs 12 minutes = 1.48 A.M.
Question 13. Local time of the two places “A” and “B”‘ are 6.a.m.and6 p.m. respectively, when it is 12 noon at Greenwich. Find out the longitude of the above two places “A” and “B” (mention East or West).
Answer:
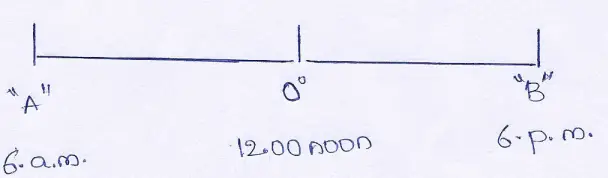
The time difference between Greenwich and place “A” and “B” is (6 a.m. to 12.00 noon and 12.00 to 6 p.m.) or 6 hours or 360 minutes.
4 minutes time difference is for 1° longitude.
360 minutes time difference is for (360 ÷ 4) = 90°
So, the longitudinal difference between Greenwich and the place “A” and”B” is 90°.
We know Greenwich lies on 0° longitude.
As the time of place “A” is behind that of Greenwich therefore it must lie to the West of Greenwich.
So, the longitude of the place “A” is 90° West. Similarly as the time of place ‘B’ is ahead of Greenwich therefore it must lie to the East of Greenwich. So, the longitude of the place “B” is 90° East. Longitude of place “A” and “B” are 90° W and 90° E.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 3 Summary
Question 14. 99, A telegram was sent from Washington (77° W) to Allahabad (82°30′ E) on 31st December 1998 at 8.30 P.M. It took 15 minutes to reach Allahabad. Find out the exact time and date of its arrival there.
Answer:
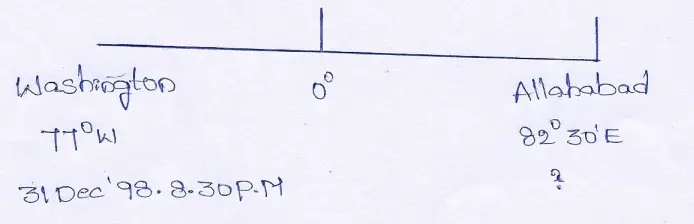
Longitudinal difference between Washington and Allahabad is 77° + 82°30f= 159°30′
For 1° longitudinal difference, time difference is 4 minutes
∴ 159° ……………………………………………… 4×159 minutes
= 636 minutes
= 10 hrs. 36 minutes
Again for 1’ longitudinal Siocneaat time difference is 4 cerns
∴ 30′ …………………………………………………… 4×30 seconds
= 120 seconds
= 2 minutes
∴Total time difference between Washington and Allahabad is 10 hrs. 36 mins. +2 mins. = 10 hrs 38 mins.
∴When it was 20:30 hrs. on 31st December, 1998 at Washington then the local time of Allahabad would be more (as it is located to the East).
i.e., 20:30 + 10 hrs. 38 mins. = 31:08
∴31:08 — 24.00 (31st Dec, 1998)
= 7:08 A.M. ist January, 1999.
As the telegram took 15 minutes to reach Allahabad, so the telegram actually reached Allahabad at 7:08 + 0:15 = 7:23 A.M. on 1st January 1999.
Question 15. A hockey match held at Atlanta (85°W) Olympic at 6 a.m. was telecast directly. When it was visible at Calcutta (88°30’E) ? [M.E.’97]
Answer:
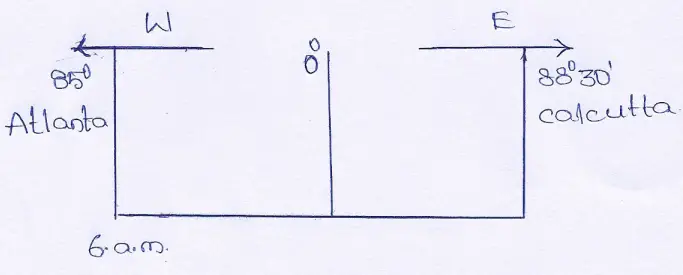
The longitudinal difference between Atlanta and Calcutta = 85°+ 88°30′ =173°30)
For 1° longitudinal difference, time difference is 4 minutes.
∴ 173° ” ” ” ” ” “173 x 4 minutes = 692 minutes
Again for 1′ longitudinal difference, time difference is 4 seconds
∴ 30′ ” ” ” ” ” 30 x 4 seconds
= 120 seconds or 2 minutes
Total time 692 minutes + 2 minutes = 694 minutes or 11 hrs 34 minutes.
As Calcutta is situated East of Atlanta (where it is 6 a.m.), the time of Calcutta will be ahead of Atlanta by 11 hrs. 34 minutes.
Therefore, the time of Calcutta
=6a.m.+ 11 hrs. 34 minutes
= 17 hrs. 34 minutes or 5.34 p.m.
Thus, the telecast will be visible at Calcutta at 5.34 p.m.
Question 16. 96, When it is 6.30 a.m. in Madras, the time in New York is 8.13 p.m. in the previous evening. The longitude of Madras is 80°15′ East. What is the longitude of New York ?
Answer: As time of New York is 8.13 p.m. of the previous day, it is clear, it is situated West of Madras.
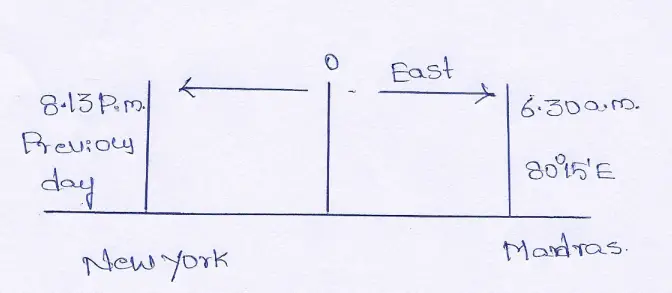
The difference of time between Madras and New York
= 6 hrs. 30 minutes + 3 hrs. 47 minutes (12 — 8 hrs. 13 m.)
= 10 hrs. 17 minutes = 617 minutes
The difference of 4 minutes occur in 1° of longitude.
Therefore, the difference of 617 minutes will be in (*7/,)° = 154° 15′
The longitude of Madras is 80° 15’E
The longitude of New York = 154°15′ — 80° 15′ = 74° W
Question 17. If it is 122 noon at Greenwich what is the local time at Calcutta (88°30’E)?
Answer:
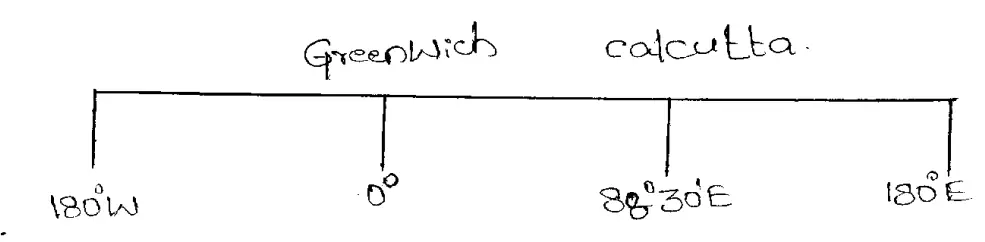
We already know that the longitude of Greenwich is 0°
∴the difference in longitudes between Calcutta and Greenwich is 88°30′ — 0 = 88°30′
∴the time difference between Calcutta and Greenwich will be—
1° longitude difference causes a time difference of 4 minutes
∴for 88°” ” the difference will be 88 x 4 minutes 352 minutes
Again 1′” ” has a time difference of 4 seconds
∴30. ” ” has a time difference of 30′ x 4 sec. = 120 sec. or 2 miunutes
∴the time difference between Calcutta and Greenwhich is (352 + 2 minutes = 354 minutes ÷ 60 minutes) 5 hours 54 minutes.
Since Calcutta lies to the east of Greenwich the time will be ahead compared to Greenwich time. So when it is noon at Greenwich the local time of Calcutta will be (12 noon ÷ 5 hours 54 minutes) 5-54 PM.
Question 18. When the 1.5.7. is 12 noon what is the G.M,T, ? (Central Meridian of
India 82°30′ E*).
Answer:
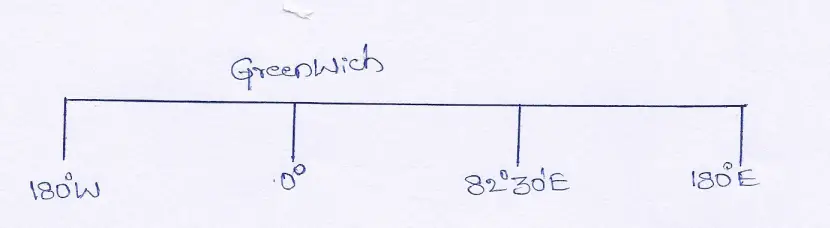
We already know that the standard meridian of India is 82°30′ E and Greenwich’s is O°.
∴the difference in the standard meridian of India and the longitude of Greenwich is 82°30’— 0 = 82°30′
∴ the time difference between them will be —
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
∴for 82°” ” ” the time difference is 82° x 4 minutes = 328 minutes or 5 hours 28 minutes
Again 1′ ” ” longitude has a time difference of 4 seconds
∴30′ ” ” ” has atime difference of 30′ x 4 seconds = 120 seconds or, 2 minutes
Therefore their time difference is (5 hours 28 minutes +2 minutes) 5 hours minutes.
Since Greenwich is located to the west of India their time will be behind or less than that of India.
∴when the 1.S.T. is 12 noon the G.M.1T. is (12 noon÷5 hours 30 minutes) 6-30 AM.
Class 9 Geography Determination Of Location WBBSE MCQs With Answers
Question 19. The longitudes of Calcutta and Seol are 88°30′ E and 127°06′ E respectively. When the local time in Calcutta is 12 noon what is the local time at Seoul.
Answer:
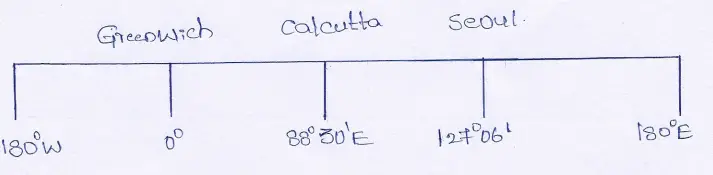
We know, the longitude of Calcutta is 88°30′ E and the longitude of Seoul is 127°06’E∴ their difference in longitude is 127°06′ — 88°30′ = 38°36′
∴their time difference will be—
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
∴for 38°” ” ” the time difference will be 38 x 4 minutes = 152 minutes or, 2 hours 32 minutes
Again 1′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 seconds
∴ for 36′ difference in longitude the time difference will be 36 x 4 = 144 secs.
=2 min. 24sec.
∴the time difference between Seoul and Calcutta is (2 hours 32 minutes + 2 minutes 24 seconds) 2 hours . 34 minutes 24 seconds.
As Seoul lies to the east of Calcutta is 12 noon the local time in Seoul is (12 noon ÷2 hours 34 minutes 24 seconds) 2.34.24 PM.
Question 20. When it is 12 noon by Chronometer what will be the Standard Time of India?
Answer: The Chronometer watch runs according to Greenwich Mean Time so by Chronometer when it is 12 noon, G.M.T. is also 12 noon.
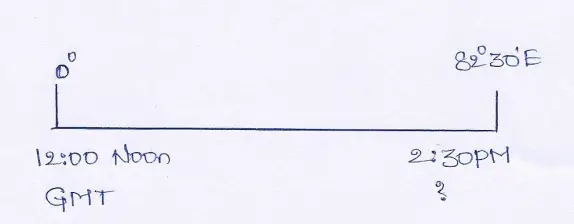
On the other hand, we also know the Standard Meridian of India is 82°30′ E. Therefore the difference in longitude between India and Greenwich is (82°30′ — 0) = 82°30′.
∴ the time difference for 82°30′ is —
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
∴82° difference in longitude has a time difference of = 82° x 4 minutes = 328 minutes or 5 hours 28 minutes.
Again 1′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 secs.
∴30′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 sec.
30′ x 4 sec. = 120 seconds or 2 minutes
Therefore for 82°30! of longitudes, the time difference is (5 hours 28 minutes ÷ 2 minutes) 5 hours 30 minutes. or 5:30 P.M
Question 21. When G.M.1. (0°) is 6-00 AM, what is the local time in the capital of Egypt, (Cairo 31°15′ E)?
Answer:
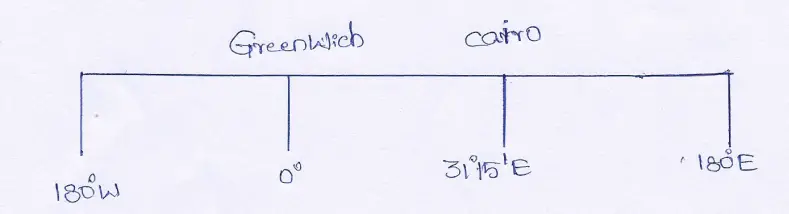
Longitudinal difference between Greenwich and Cairo is 31°15’— 0° = 31°15′
∴their time cirference is—
1° of longitude takes 4 minutes to rotate
∴ 31° of longitude takes 31° x 4 minutes = 124 minutes or, 2 hours 4 minutes to rotate
Again to rotate 1′ of longitudes will taken is 4 seconds
∴15′ of longitudes will take 15′ x 4 seconds = 60 seconds. or, 2 hours 4 minutes to rotate.
Therefore the time difference between Greenwich and Cairo is (2 hours 4 minutes +1 minutes) 2 hours 5 minutes.
Since Cairo is located to the east of Greenwich the local time at Cairo will be (600 AM + 2 hours 5 minutes) 8-05 AM.
Question 22. A place located at 108°15’30’ W longitude has a local time of Wednesday 10-00 PM. Then what is the time at Greenwich ?
Answer:
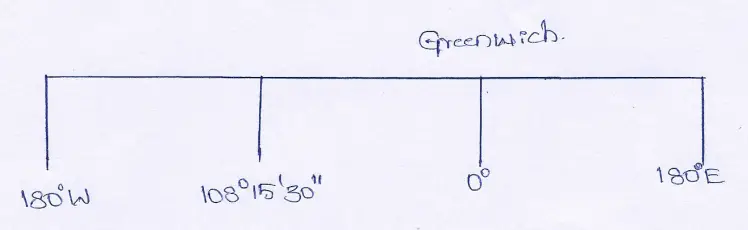
Between Greenwich and the place located at 108°15’30” W the difference in longitude is 108°15’30” — 0° = 108° 15’30”.
1° difference in longitude has a 4 minute difference in time
∴108° difference in longitude has a time difference of 108° x 4 minutes = 432 minutes or 7 hours 12 minutes
Again 1′ difference in longitude has a 4 second difference in time
∴15′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 15′ x 4 sec = 60 sec. or 1 minute
Again 1′ or 60″ or difference in longitude has 4 sec difference in time 30×4
∴30″ difference in longitude has \(\left(\frac{30 \times 4}{60}\right)\) = 2 sec difference in time.
Thus the difference in time of Greenwich and the place located on 108°15’30” Wis (7 hours 12 minutes + 1 minute + 2 seconds) = 7 hours 13 minutes 2 seconds.
Since the place at longitude 108°15’30” W is located to the west of Greenwich the time at Greenwich will be far ahead of the other place.
So when it is Wednesday 10-00 PM at a place on the longitude 108°15’30” W at Greenwich it will be (Wednesday 10-00 PM + 7 hour 13 minutes 2 seconds) 5-13-02 AM the next day i.e. Thursday.
Question 23. When at Greenwich it is 4-00 AM at 80° longitudes what will be the local times.
Answer:
The difference in longitude between Greenwich and 80° longitude is 80° For 80° difference in longitude, the difference in time will be 80° x 4 minutes = 320 minutes or5 hours 20 minutes.
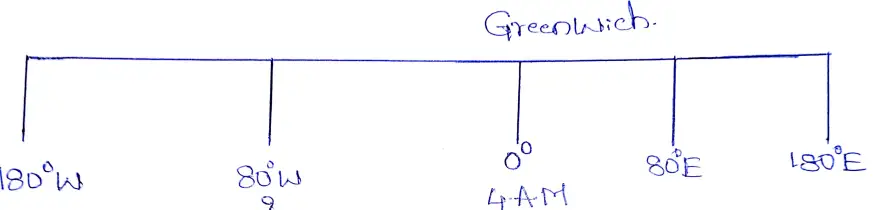
The question does not state in which hemisphere 80° longitude lies, eastern or western.
(1) If the place is located at 80°E, then at Greenwich when it is 4-00 AM, at 80°E it will be more, so (4-00 AM +5 hours 20 minutes / or 9-20 AM.)
(2) If the place is located at 80°W then there the time will be behind Greenwich. At Greenwich when it is 4-00 AM at 80°W it will be (4-00 10-40 PM of the previous day.
Question 24. When in India (Allahabad 82°30’ E) it is 29th June 11.30 PM what will be the time and date in Mexico City (99°05′ W), the capital of Mexico?

Answer: Longitudinal difference between Allahabad and Mexico city is 82°30′ + 99°05′ = 181°35′. .°. their time difference will be—
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
181° difference in longitude has a time difference of 181° x 4 minutes = 724 minutes or 12 hours 4 minutes.
Again, 1′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 seconds.
∴ 35′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 35′ x 4 seconds = 140 seconds = 2 minutes 20 seconds.
Therefore, the time difference of Allahabad and Mexico city is (12 hours 4 minutes + minutes 20 seconds) 12 hours 6 minutes 20 seconds.
As Mexico city is located to the west of Allahabad .”. their time will lie behind that of Allahabad.
∴When on 29th June the 1.5.7 is 11-30 PM at Mexico city it is (11-30 PM — 12 hours 6 minutes 20 seconds) 11-23-40 AM on 29th June.
Question 25. In 1998 World Football Competition (FIFA Cup) will take place in different towns of France. If the final match (between France—Brazil or Argentina—Germany) takes place in the capital, Paris (2°20’E) at 7-00 PM Friday, when can ve see it live on the Indian Television ?

Answer: We know the Standard Meridian of India is 82°30’ E.
∴the difference in longitudes is 82°30′ -2°20′ = 80°10′
The time difference for 80°10′ will be—
1° longitude takes to rotate 4 minutes
∴ 80° of longitudes take to rotate 80° x 4 minutes = 320 minutes or 5 hours 20 minutes.
Again 1′ longitude takes to rotate 4 seconds
∴ 10′ of longitudes take 10 x 4 = 40 seconds
So the time difference between India and Paris is (5 hours 20 minutes + 40 seconds) 5 hours 20 minutes 40 seconds.
Paris and India are located in the eastern hemisphere but India lies further east
∴ Their time will be ahead of Paris.
So in 1998 if the finals of the World Football Competition is held in Paris on Friday at 7-00 PM local time, In India it can be seen at 7-00 PM + 5 hours 20 minutes 40 second = next day i.e. Saturday at 00 hours 20 minutes 40 seconds or 00-20-40 AM.
Question 26. To the South-west of Baghdad, (44°30′ E) at 1-00 AM on 11th February 1991, 2 Scud Missiles were launched. They were launched from two unknown moving missile launching stations to the capital of Israel, Jerusalem (35°13′ E) and capital of Saudi Arabia, Riyadh (46°50′ E) Then what was the local time at Jerusalem and Riyadh.
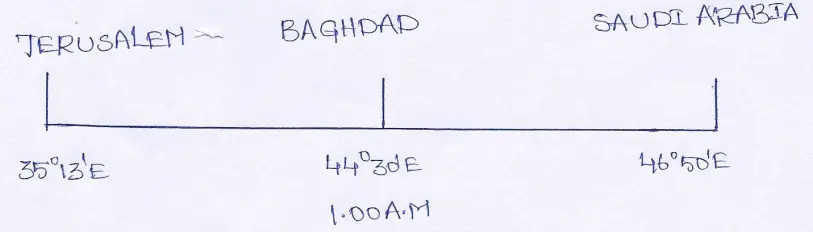
Answer:
(1) Difference in longitudes between Baghdad and Jerusalem is (44°30′ — 35°13′)9°17′. ∴their time difference is—
1° longitude takes to rotate 4 minutes
∴ 9° longitude takes to rotate 9° x 4 minutes = 36 minutes
Again 1° longitude takes to rotate 4 seconds
∴ 17° longitude takes to rotate 17 x 4 = 68 seconds or 1 min 8 sec.
∴Tthe time difference between Baghdad and Jerusalem is (36 min + 1 min 8 sec) 37 min 8 sec
As Jerusalem is located further west their time will be behind Baghbad, or less.
So when it is 1-00 AM local time at Baghdad when the Scud missiles were launched, at Jerusalem the local time was (1-00 AM — 37 Min 8 secs) 00-22-52 HRS or 12.22.52 A.M.
(2) The difference in longitude between Baghdad and Riyadh is (46°50′ — 44°30′) 2°20′. Therefore their time difference is—
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
∴ 2° difference in longitudes has a time difference 2° x 4 minutes = 8 minutes
Again 1′ in longitudinal has a time difference of 4 seconds
∴ 20′ in longitudinal has a time difference of 20′ x 4 seconds = 80 seconds or 1 minute 20 seconds
∴ The time difference between Baghdad and Riyadh is (8 min + 1 min 20 sec) 9 min 20 sec.
Since Riyadh is located further east of Baghdad
∴ The time at Riyadh will be ahead of Baghdad
So at 1.00 AM local time when the Scud missiles were launched from Baghdad at Riyadh the local time was (1-00 AM + 9 min 20 sec) 01-09-20 AM.
Question 27. India launched a space vehicle from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, to land at Mars in the year 2008 on 1st March at 10-00 AM 1.S.T. What will be the time and date then at Washington DC (74°04′ W), capital of U.S.A. ?

Answer: We know the Standard Meridian of India is 82°30′ E.
∴ The difference in longitudes between India and Washington is 74°04′ + 82°30′ = 156°34′. Their time difference will be—
1° difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes
∴ 156° difference in longitude has a time difference of 156° x 4 = 624 min or 10 hours 24 minutes.
Again 1′ difference in longitude has a time difference of 4 seconds
∴ 34′ difference in longitude has a time of 34′ x 4 sec = 136 sec or 2 minutes 16 sec.
∴ 154°34′ difference in longitude has of (10 hrs 24 min + 2 min 16 sec) = 10 hrs 26 min 16 sec.
As Washington is located to the west of India’s central meridian, .’. their time will lie behind the time of India.
Thus in the year 2008 on ist March when a space vehicle is to land in Mars, in Washington D.C. the local time will be— 10-00 AM — 10 hours 26 min 16 seconds = the day before 11-33-44 PM.
As 2008 is a leap year the day before 1st March 2008, will be 29th February 11-33-44 PM 2008.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
Question 28. When it is 6-30 AM in Chennai (80°15′ E), it is 8-15 PM the day before at New York. What is the longitude of New York.
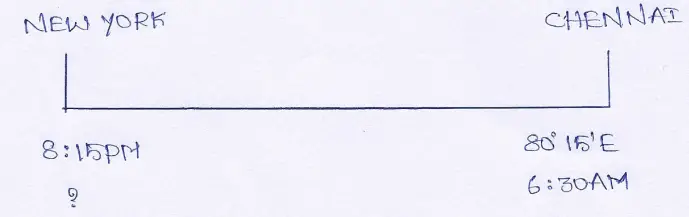
Answer: If the local time at Chennai is 6-30 AM and at New York it is 8-15 PM, of the previous day.
Their time difference is (previous day 8-15 PM—6-30 AM) 10 hours 15 minutes or 615 minutes.
4 minutes time is taken to rotate 1°
∴ 615 minutes time is taken to rotate \(\frac{615}{4}\) = 615 min ÷ 4′ = 153°45′
Thus the difference in longitude between Chennai and New is 153°45′
∴ The time at New York lies behind Chennai, it lies to the west of Chennai.
∴ The longitude of New York is (153°45′ — 80°15′) = 73°30’ W
Question 29. According to 4-30 PM G.M.T. if it is 12 noon at any place, what is the longitude of the place?

Answer: The time difference between G.MT. and the time of the other place is 12 noon — 4-30 = PM = 4 hours 30 minutes or 270 minutes.
If 4 minutes is taken to rotate 1° of longitude
∴ 270 minutes is taken to rotate 240 ÷ 4 = 67°30′
So their longitudinal difference is 67°30′
We know longitudinal difference is 0°.
Since the time of the other place is behind of G.M.T. So it lies to the west of Greenwich. So the longitude of the place is 0° — 67°30′ = 67°30′ W.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
Question 30. When it is 9-00 AM at Greenwich and 5-00 PM at another place, what is the longitude of that place?

Answer: The time difference between Greenwich and the other place is (9-00 AM —5 PM) 8 hours or 480 minutes.
If 4 minutes is taken to rotate 1° of longitude
480 minutes is taken to rotate 480 ÷ 4 = 120° of longitude
∴The difference in longitudes between Greenwich and the other place 120°.
As the longitude of Greenwich is 0° and the time of the other place lies ahead of G.M.T., ∴ its longitude is 120° E.
Question 31. The time difference between 2 places is 2 hours 15 minutes 40 seconds. The longitude of one place is 20°15’ E, so what is the longitude of the other place?
 Answer: The time difference between the 2 places is 2 hours 15 minutes 40 seconds or 135 minutes 40 seconds
Answer: The time difference between the 2 places is 2 hours 15 minutes 40 seconds or 135 minutes 40 seconds
4 minutes is taken to rotate 1° of longitude
∴ 135 minutes is taken to rotate 135 ÷ 4 = 33°45′
Again 4 seconds is taken to rotate 1′ of longitude
∴ 40 seconds taken to rotate 40 = 4 = 10′ of longitude
Thus for 135 minutes 40 seconds the difference in longitudes (33°45′ + 10′) 33°55′
(1) If the time of the place is more than the time of the place whose longitude is known, the former place will lie to the east of the known longitude. .. its longitude will be (33°55′ — 20°15′) or 13°40′ W.
(2) If the time of the place is less than the time of the place whose longitude is known, then the former place will lie to the west of the place, whose longitude is known.So its longitude will be (33°55′ — 20°15′) or 13°40′ W.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
Question 32. At Karachi (67° E) a Pakistan-Srilanka cricket match started at 10-30 AM, The live telecast was heard in the capital of Srilanka, Colombo at 11-21-44 AM. What is the longitude of Colombo ?

Answer: The time difference between Karachi and Colombo is (11-21-44 AM — 10-30 AM) 51 minutes 44 seconds
4 minutes is taken for the earth to rotate 1° of longitude
∴ 51 minutes is taken for the earth to rotate 51 ÷ 4 =12°45′
Again 4 seconds is taken by the earth to rotate 1′ of longitude
∴ 44 seconds is taken by the earth to rotate 44 ÷ 4 =11′
So for a time difference of 51 minutes 44 seconds, the difference in longitude is (12°45 + 11′) 12°56′
As the time of Colombo is ahead of Karachi it lies to the east of Karachi.
∴ The longitude Colombo lies on is (67° + 12°56′) 79°56′ E
Question 33. A jumbo 747 airbus of Pan American Airways Corporation, was hijacked over the Atlantic Ocean while flying from New York to London. While being hijacked the pilot saw the local time was 5-30 PM and the G.M.T. was 6-30 PM. At which longitude was the airbus hijacked?
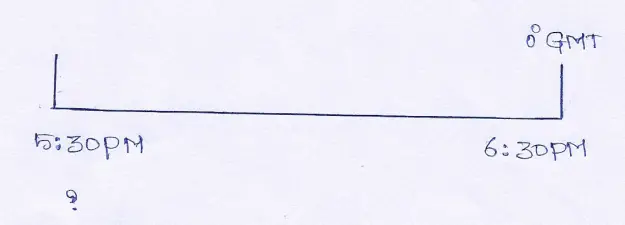
Answer: The time difference between that place and GMT is (6-30 PM — 5-30 PM) 1 hour or 60 minutes
4 minutes is taken by the earth to rotate 1° of longitude
∴ 60 minutes is taken by the earth to rotate 60 ÷ 4 = 15° longitude
Compared to Greenwich as the time is less in this place, it will lie to the west of Greenwich. At the time of hijack, the airbus was flying above 15° W longitude.
WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
- Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet
- Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation & Revolution
- Chapter 4 Geomorphic Processes And Land Forms Of The Earth
- Chapter 5 Weathering
- Chapter 6 Hazards And Disasters
- Chapter 7 Resources Of India
- Chapter 8 West Bengal
- Chapter 9 Map & Scale


 (3) Flow Resource :
(3) Flow Resource :





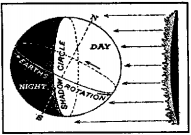

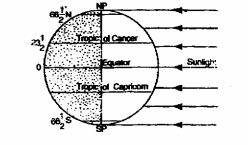

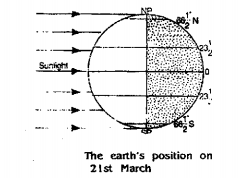
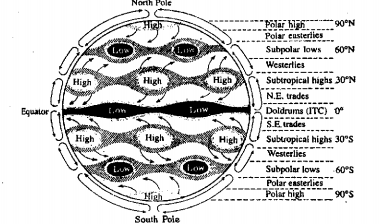

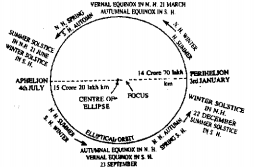

 .
.