
Class 9 Life Science And Environment
WBBSE For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life MCQS
WBBSE Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life MCQs
Question 1. The biomolecules are —
- Unique to life
- Organic in nature
- The product of biological activity
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 2. The most abundant inorganic compound in living organisms is —
- Sodium chloride
- Water
- Phosphoric acid
- Calcium Carbonate
Answer: 2. Water.
Read And Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Life Science And Environment MCQs
Question 3. Goitre results due to the deficiency of —
- Iron
- Zinc
- Iodine
- Sodium
Answer: 3. Iodine.
Question 4, Which of the following are derived lipids?
- Story! ester
- Steroids
- Neutral fats
- Waxes
Answer: 2. Steroids.

Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Mcq With Answers
Question 5. The sugar present in nucleotides is always —
- Deoxyribose
- Ribose
- Both a and b “
- A pentose sugar
Answer: 4. A pentose sugar.
Question 6. How many types of nitrogenous bases are found in the nucleic acid ?
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 6
Answer: 1. 2.
Question 7. Monosaccharides are —
- Simple sugar –
- Compound sugar
- Derived sugar
- None
Answer: 1. Simple sugar.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 8. Macromolecule is —
- Glucose
- Nucleic acid
- Amino acid
- All
Answer: 2. Nucleic acid.
Question 9. An enzyme activator mineral element is —
- Mg
- Ca
- Mn
- All
Answer: 4. All.
Levels Of Organization Of Life Class 9 Mcq Wbbse
Question 10. A substance used as a heat insulator is —
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Lipid
- Starch
Answer: 3. Lipid.
Question 1. The branch of biology dealing with the study of cells is —
- Histology
- Cytology
- Morphology
- Ecology
Answer: 2. Cytology
Question 2. Which structure of animal cells is characterised by selective permeability?
- Cell wall
- Ribosome
- Chromosome
- Cell membrane
Answer: 4. Cell membrane
Question 3. The cell membrane is mainly composed of —
- Protein and sugar
- Protein and lipid t
- Starch and lipid
- Sugar and minerals
Answer: 2. Protein and lipid
Question 4. The Golgi body originates from —
- Cell membrane
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Cytoplasm
- Nuclear membrane
Answer: 2. Endoplasmic reticulum
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Mcq Questions West Bengal Board
Question 5. The protein factory of the cell is —
- Centrosome
- Chromosome
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
Answer: 3. Ribosome
Question 6. In which one of the following, is DNA absent?
- Mitochondria
- Chloro plast
- Peroxisome
- Nucleus
Answer: 3. Peroxisome
Question 7. The suicidal bag of the cell is —
- Centrosome
- Peroxisome
- Lysosome
- Chromosome
Answer: 3. Lysosome
Question 8. Which of the following is the Lysosome of plant cells?
- Sphaerosome
- Peroxisome
- Glyoxysome
- Microsome
Answer: 1. Sphaero some
Question 9. The chief constituent of the cell wall is —
- Lipid
- Salt
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
Answer: 3. Carbohydrate
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 2 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 10. The true nucleus is not found in —
- Protozoa
- Bacteria
- Funge
- Algae
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Question 11. Covering membrane of vacuole is — e
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Tonoplant
- Chloroplast
Answer: 3. Tonoplast
Question 12. Besides the nucleus, DNA is also found in —
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Chloroplast
- Ribosome
- Golgi body
Answer: 2. Chloroplast.
Question 13. The largest cell is —
- Ramie fibre
- Acetabularia
- Egg of ostrich
- Neuron
Answer: 3. Egg of ostrich
Question 14. Quantasome remains within —
- Chloroplast
- Leucoplast
- Chromoplast
- Tonoplast
Answer: 1. Chloroplast
Levels Of Organization Of Life Mcq For Class 9 Bengali Medium
Question 15. “Powerhouse of the cell” is —
- Golgi body
- Chloroplast
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
Answer: 3. Mitochondria.
Question 16. Who defined protoplasm as a physical basis of life?
- Schwann
- Watson
- Huxley
- Dujardin
Answer: 4. Dujardin
Question 17. Dictyosomes are —
- Type of ribosomes
- Type of flagellalid organelle
- Respiratory particle
- Golgi bodies
Answer: 4. Golgi bodies
Question 18. The organelle found between cell walls of two cells is called —
- Microsome
- Middle lamella
- Lysosome
- Desmosome
Answer: 2. Middle lamella :
Question 19. The “Fluid mosaic model” of the cell membrane is given by —
- Robert Brown
- Singer & Nicholson
- Schleiden & Schwann
- Schimpher
Answer: 2. Singer and Nicholson
Question 20. Hydrolytic enzymes are present in —
- Mitochondria
- Golgi bodies
- Lysosome
- Plastids
Answer: 3. Lysosome
Question 21. Which of the following is the seat of all cell metabolic activities?
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: 1. Cytoplasm
Question 22. The “cell theory” is also known as —
- Cell Biology
- Cytology
- Cell doctrine
- All of these
Answer: 3. Cell doctrine
Question 23. The cell theory was proposed by —
- Singer and Nicholson
- Schleiden and Schwann
- Singer and Schwann
- Schleiden and Nicholson
Answer: 2. Scheliden and Schwann’
Question 24. The term “Plastid” was coined by —.
- Haeckel
- Strasburger
- Virchow
- Flemming
Answer: 1. Haeckel
Question 25. Protoplasmic strands between adjacent plant cells are —
- Ectodesmata
- Desmosome
- Proto plasmic fibrils
- Plasmodesmata
Answer: 4. Plasmodesmata
Question 26. Cristae occurs in —
- Golgi bodies
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- ER
Answer: 3. Mitochondria
Question 27. The endoplasmic reticulum remains attached to —
- Mitochondria
- Golgi bodies
- Nuclear envelope
- Chloroplasts
Answer: 3. Nuclear envelope
Question 28. Robert Brown discovered —
- Cell wall
- Nucleolus
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
Answer: 4. Nucleus
Question 29. Which organelle is present only in plants?
- Glyoxysome
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
- Peroxisome
Answer: 1. Glyoxysome
Question 30. Leucoplast can be —
- Amyloplast
- Elaioplast
- Aleuroneplast
- Any of these
Answer: 4. Any of these
Question 31. Cell theory does not apply to —
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Algael
- Virus
Answer: 4. Virus
Question 32. Which one of these cell organelles lacks a membrane?
- Mesosome
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria
- Liposome
Answer: 2. Ribosome
Question 33. Plant cell normally lacks —
- Ribosome
- Golgi bodies
- Centriole
- Cell membrane
Answer: 3. Centriole
Question 34. Which one of the following structures is an organelle within an organelle?
- Ribosome
- Peroxisome
- ER
- Mesosome
Answer: 2. Peroxisome
Question 35. What is mitoplast?
- Membraneless mitochondria
- Another name for mitochondria
- Mitochondria without outer membrane
- Mitochondria without inner membrane
Answer: 3. Mitochondria without outer membrane
Question 36. The animal cells are interconnected by —
- Plasmodesmata
- Cell wall
- Desmosome
- Plasma membrane
Answer: 3. Desmosome
Question 37. Prokaryotic cells do not have —
- Nucleolus
- Membrane bound organelles
- Centrioles
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these.
Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life Tissue MCQs
Question 1. The basement membrane is associated with —
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Nervous tissue
Answer: 1. Epithelial tissue
Question 2. The nucleus is absent in —
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
- Erythrocytes
Answer: 2. Eosinophil
Question 3. The intercalated disc is present in —
- Striated muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- None of them.
Answer: 3. Cardiac muscle.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Important Mcq With Solutions
Question 4. The outermost covering of the neurone is —
- Analemma
- Neuro lemma
- Myelin sheath
- None of them
Answer: 2. Neuro lemma
Question 5. Scale-like tissue is represented by —
- Squamous epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Ciliated epithelium
Answer: 2. Columnar epithelium
Question 6. The columnar epithelium is found in —
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Sweat gland
Answer: 2. Small intestine
Question 7. Lymphoid tissues are found in —
- Thymus gland
- Sweat gland
- Liver gland
- Stomach
Answer: 1. Thymus gland
Question 8. The tissue forms padding under the skin is —
- Areolar tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Bone
- Cartilage
Answer: 2. Adipose tissue
Question 9. Tendon is an example of —
- Cartilage
- Fibrous connective tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Adipose tissue
Answer: 2. Fibrous connective tissue
Question 10. Connective tissue which joins muscle to bones is —
- Ligament
- Tendon
- Cartilage
- All
Answer: 2. Tendon
Question 11. The tissue concerned with the perception and response of animals is —
- Muscular tissue
- Nerve tissue
- Connective tissue
- Epithelial tissue
Answer: 2. Nerve tissue
Question 12. The tissue present at the joining between two long bones is —
- Tendon
- Ligaments
- Epithelial
- Nerve tissue
Answer: 2. Ligaments
Question 13. A part of the body to perform some specified function is —
- Cell
- Tissue
- Organs
- System
Answer: 3. Organs
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Mcq
Question 14. Tissue is formed by —
- Similar cells with the same metabolic activity
- Similar cells with different metabolic activity
- Dissimilar cells with the same function
- Similar cells with similar origin
Answer: (4) Similar cells with similar origin
Question 15. “Pavement epithelium” refers to —
- Columnar epithelium
- Squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Pseudostratified epithelium
Answer: 2. Squamous epithelium.
Question 16. Ciliated epithelium in our body is found in —
- Vagina
- Trachea
- Bile duct
- Loop of Henley
Answer: 2. Trachea.
Question 17. Who first used the term tissue?
- Myer
- Mapighi
- Xavier
- Linneus
Answer: 3. Xavier.
Question 18. The sensory epithelium is modified into —
- Squamous epithelium
- Columnar cells
- Ciliated cells
- Stratified cells
Answer: 2. Columnar cells.
Question 19. Tearing of ligament is called —
- Sprain
- Dislocation
- Fracture
- Break
Answer: 1. Sprain.
Levels Of Organization Of Life Class 9 Mcq Online Test Wbbse
Question 20. Which of the following stores histamine and serotonin?
- Macrophages
- Mast cells
- Fibroblasts
- Plasma cells
Answer: 2. Mast cells.
Question 21. The haversian system is a feature of —
- Reptilian bone
- Mammalian bone
- Avian bone
- All animals
Answer: 2. Mammalian bone
Question 22. Cells forming cartilage are called —
- Osteoblast
- Fibroblast
- Chondrocytes
- Epiblasts
Answer: 3. Chondrocytes
Question 23. Mast cells are found in —
- Connective tissue
- Muscles
- Epithelial tissue
- Nerve cell
Answer: 1. Connective tissue
Question 24. Adipose tissue is rich in—
- Mast cells
- Fat cells
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
Answer: 2. Fat cells
Question 25. The most abundant protein in the muscle is —
- Actin
- Myosin
- Myoglobin
- Tropomyosin
Answer: 2. Myosin
Question 26. The nerve cells do not have —
- Microtubules
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Centrosome
Answer: 4. Centrosome
Question 27. Nodes of Ranvier are found in —
- Cyton
- Dendron
- Axon
- Dendrites
Answer: 3. Axon
Question 28. The main property of nervous tissue is —
- Contraction
- Irritability
- Excitability
- Both B and C
Answer: 4. Both b and c
Question 29. Areolar connective tissue joins —
- Bone with bones
- Fat body with muscle
- Integument with music
- Bone with muscle
Answer: 3. Integument with muscle
Question 30. Which one of the following is not a connective tissue —
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Blood
- Muscle
Answer: 4. Muscle
Question 31. Bone marrow is absent in —
- Reptilia
- Amphibia
- Mammalia
- Birds
Answer: 4. Birds
Class 9 Life Science Levels Of Organization Mcq In Bengali
Question 32. The science which deals with the study of tissue is called —
- Anatomy
- Histology
- Histogen
- Tissue system
Answer: 2. histology
Question 33. Apical, Intercalary and lateral meristems are differentiated based on —
- Development
- Origin
- Function
- Position
Answer: Origin
Question 34. Intercalary meristem is found in —
- Root
- Stem tip
- Petiole and Internodes
- Latex
Answer: 3. Petiole and Internodes
Question 35. The simple tissue having the thinnest wall in the plant is —
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Aerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 1. Parenchyma.
Question 36. The xylem of the stem is —
- Exarch
- Endarch
- Mesarch
- None of them
Answer: 2. Endarch.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Mcq Questions And Answers
Question 37. The vascular bundle in the dicot stem is —
- Open collateral
- Closed collateral
- Open collateral
- Closed collateral
Answer: 1. open collateral.
Question 38. The living element of the xylem is —
- xylem parenchyma
- xylem fibre
- Tracheid
- Trachea
Answer: 1. xylem parenchyma
Question 39. The photosynthetic parenchyma is —
- Chlorenchyma
- Idioblast
- Aerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 1. Chlorenchyma
Question 40. Meristematic tissue originates from —
- Pro-meristem
- Apical meristem
- Lateral meristem
- Cambium
Answer: 1. Pro-meristem
Question 41. An example of lateral meristem is —
- Cork cambium
- Interfascicular cambium
- Fascicular cambium
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 42. The tissue which consists of dead cells with thickened lignified wall is—
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- None of these
Answer: 3. Sclerenchyma
Question 43. The dead element of phloem tissue is —
- Phloem fibre
- Phloem parenchyma
- Sieve tube
- Companion cells
Answer: 1. Phloem fibre
Question 44. The category of plant tissue that has lost its ability to multiply is—
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 2 Mcq Questions And Answers
Question 45. Air cavity containing parenchyma is called —
- Chlorenchyma
- Aerenchyma
- Prosenchyma
- Mesenchyma
Answer: 2. Aerenchyma
Question 46. Palisade is a type of —
- Parenchyma
- Chlorenchyma
- Photosynthetic tissue
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 47. Science which deals with the study of tissue is called —
- Anatomy
- Histology
- Tissue System
- Histogen
Answer: 2. Histology
Question 48. The cells which can perpetuate themselves are —
- Perpetual cells
- Permanent cells
- Meristematic cell
- Old, inactive cell
Answer: 3. Meristematic cell
Question 49. A simple tissue is always —
- Living
- Thin-walled
- Homogenous
- Storage
Answer: 3. Homogenous
Question 50. Primary growth in plants occurs due to the activity of —
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Cambium
- Both a and b
Answer: (4) both a and b
Question 51. A Cambium is always —
- Primary in origin
- Secondary in origin
- Lateral in position
- Present in the vascular bundle
Answer: 3. Lateral in position
Question 52. Identify the dead plant tissue —
- Phloem
- Xylem
- Sclerenchyma
- Both b and c
Answer: 3. Sclerenchyma
Question 53. Water-conducting elements in angiosperm are —
- Vessels
- Tracheids
- Tracheae
- All of these
Answer: (4) All of these
Question 54. The only living component of xylem tissue is —
- Tracheae
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibre
- Tracheids
Answer: 2. xylem parenchyma
Question 55. The only dead cell of phloem tissue is —
- Phloem fibre
- Phloem parenchyma
- Sieve tube
- Companion cell
Answer: 1. Phloem fibre
Question 56. Chlorophyll: containing parenchyma is called —
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Chlorenchyma
- Aerenchyma
Answer: 3. Chlorenchyma
Question 57. The conducting tissue in plants is —
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Meristematic tissue
- Both a and b
Answer: 4. Both a and b
Question 58. The cells having the capacity to divide are—
- Meristematic cell
- Xylem
- Phloem
- All
Answer: 1. Meristematic cell
Question 59. Parenchyma with large air sacs are called —
- Chlorenchyma
- Aerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Answer: 2. Aerenchyma
Question 60. Cell wall thickened at the corner in—
- Collenchyma
- Parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- None of these
Answer: 1. Collenchyma
Question 61. Stone cells are—
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Sclereids
- Fibres
Answer: 3. Sclereids
Question 62. Meristematic tissue develops from —
- Permanent tissue
- Cambium
- Promeristem
- Phloem
Answer: 3. Promeristem
Question 63. The most efficient conducting element of the xylem is —
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem fibre
- All of these
Answer: 2. Vessels
Chapter 2 Levels Of Organization Of Life Major Organs Of Human Body MCQs
Question 1. The alimentary system is concerned with —
- Circulation
- Digestion
- Respiration
- Excretion
Answer: 2. Digestion
Question 2. The ‘U’ shaped Duodenum is the part of —
- The first part of the small intestine
- The middle part of the small intestine
- The last part of the small intestine
- Large intestine.
Answer: The first part of the small intestine
Question 3. Lungs are the parts of ——
- Alimentary system
- Excretory system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system
Answer: 3. Respiratory system
Question 4. The stomach consists of —
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Five parts
Answer: 1. Two
Question 5. The kidney is a part of —
- Respiratory system
- Excretory system
- Circulatory system
- Alimentary system
Answer: 2. Excretory system
Question 6. The pumping organ of blood is —
- Kidney
- Lungs
- Heart
- Stomach
Answer: 3. Heart
Question 7. One of the functions of the alimentary system is —
- Respiration
- Digestion
- Excretion
- Circulation
Answer: 2. Digestion
Question 8. The human heart is composed of — chambers.
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: 4. Four
WBBSE For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Biology And Human Welfare MCQS
Chapter 4 Biology And Human Welfare MCQs
Question 1. Which one of the following helps in increasing the yield of rice-T
- Pseudomonas
- Azotobactor
- Spirulina
- Azolla
Answer: 4. Azolla.
Question 2. Which one is a symbiotic bacteria?
- Clostridium
- Chlorobium
- Chromatium
- Rhizobium
Answer: 4. Rhizobium
Read And Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Life Science And Environment MCQs
Question 3. The algae spirulina is-
- Biofertiliser
- Single-cell protein
- Antibiotic
- Biopesticide
Answer: 3. Antibiotic.
Question 4. Microbes are very useful in the production of-
- Vaccine
- Antibiotic
- Fuel
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above.

Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Mcq With Answers
Question 5. Which one of the following is not a biofertilizer?
- Agrobacterium
- Rhizobium
- Nostoc
- Mycorrh
Answer: 3. Nostoc.
Question 6. The pathogen of malaria is-
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Nematodes
Answer: 3. Protozoa.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 7. BCG is a vaccine used for the disease-
- Malaria
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Cholera
Answer: 2. Tuberculosis.
Class 9 Life Science Biology And Human Welfare Mcq In Bengali
Question 8. The WASH program was launched by –
- UNESCO
- Russia
- IUCN
- UNICEF
Answer: 4. UNICEF.
Question 9. WBC cells associated with immunity are-
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
- Monocyte
Answer: 1. Neutrophil.
Biology And Human Welfare Class 9 Mcq Wbbse
Question 10. Antibodies are-
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Lipid
- Vitamins
Answer: 2. Protein.
Question 11. The process of developing immunity against infection is called-
- Immunization
- Vaccination
- Sanitation
- Toxication
Answer: 1. Immunization.
Question 12. A sexually transmitted disease is –
- Malaria
- Dengue
- AIDS
- Filaria
Answer: 3. AIDS.
Biology And Human Welfare Class 9 Mcq Online Test Wbbse
Question 13. This germ causes serious diarrhea in humans. It is –
- Salmonella
- Mycobacterium
- Agaricus
- Corynebacterium
Answer: 1. Salmonella
Question 14. This virus is transmitted through blood transfusion. This is –
- Hepatitis A virus
- Hepatitis B virus
- Influenza virus
- None
Answer: 2. Hepatitis B virus
Question 15. Flavivirus causes-
- Hepatitis
- AIDS
- Dengue
- Influenza
Answer: 3. Dengue
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Mcq
Question 16. The cause of tuberculosis is a-
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Bacteria
- Fungi
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 17. Retroviruses cause a disease. This is known as –
- Autoimmune disease
- Immune deficiency disease
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis A
Answer: 3. Immune deficiency disease
Question 18. Mycorrhiza is an association of-
- Bacteria and virus
- Algae and fungi
- Fungi and roots of plants
- Fungi and gymnosperms
Answer: 3. Fungi and roots of plants
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Mcq Questions West Bengal Board
Question 19. Which of the following is not a type of immunoglobulin?
- IgG
- IgE
- IgA
- IgS
Answer: 4. IgS
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Mcq Questions And Answers
Question 20. The foreign substances that on entering our body activate the body’s immune system are-
- Antibodies
- Antigens
- Immunoglobulins
- Lymphocytes
Answer: 2. Antigens
Question 21. Which of the following vaccines contain killed pathogens?
- Killed vaccine
- Toxoid vaccine
- Attenuated vaccine
- Conjugate vaccine
Answer: 1. Killed vaccine
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 4 Important Mcq With Solutions
Question 22. Which of the following is not a type of T-cell?
- Cytotoxic T-cell (T, cell)
- Helper T-cell (T,, cell)
- Suppressor T-cell (T, cell)
- Plasma T-cell (T, cell).
Answer: (4) Plasma T-cell (T, cell)
Question 23. Which of the following is a fungus acting as a bio-control agent?
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- Caudovirales
- Nosema locustae
- Beauveria bassiana
Answer: 4. Beauveria bassiana
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 4 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 24. Tetanus is caused by
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoa
- Fungi
Answer: 1. Bacteria
Question 25. The causative agent of diphtheria is –
- Clostridium tetani
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Answer: 4. Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Question 26. Yellowing of skin and eye is a symptom of –
- Pneumonia
- Tetanus
- Hepatitis
- AIDS
Answer: 3. Hepatitis
Question 27. Dengue is caused by
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium malaria
- Flavivirus
- Plasmodium falciparum
Answer: 3. Flavivirus
Biology And Human Welfare Mcq For Class 9 Bengali
Question 28. Which of the following is an anaerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, acting as a biofertilizer?
- Azotobacter
- Clostridium
- Derxia
- Rhizobium
Answer: 1. Azotobacter
Question 29. Fungi involved in the formation of mycorrhiza are-
- Agaricus
- Amanita
- Saccharomyces
- Ascobolus
Answer: 2. Amanita
WBBSE For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity MCQS
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Life And Its Diversity Plant Kingdom MCQs
Question 1. Bryophytes are — :
- Embryophytes
- Pioneer land plants
- All of these
- Amphibians of the plant kingdom
Answer: 4. Amphibians of the plant kingdom.
Question 2. Which group of plants is known as vascular cryptogams?
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperm
- Algae
Answer: 2. Pteridophyta.
Read And Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Life Science And Environment MCQs
Question 3. Kelps are marine —
- Angiosperm
- Red algae
- Green algae
- Brown algae
Answer: 4. Brown alga.
Question 4. Multicellular rhizoids occur in —
- Liver worts
- Hornworts
- Mosses
- None of these
Answer: 3. Mosses.

Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Mcq With Answers
Question 5. Spirulina belongs to kingdom —
- Monera
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Answer: 1. Monera.
Question 6. An alga which is rich in protein is —
- Ulothrix
- Spirogyra
- Nostoc
- Chlorella
Answer: 4. Chlorella.
Question 7. Which one of the following plants is monoecious?
- Marchantia
- Pinus
- Cycas
- Papaya
Answer: 2. Pinus.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 8. Which one is an edible e-fungus?
- Mucor
- Penicillium
- Rhizopus
- Agaricus
Answer: 4. Agaricus.
Question 9. Component of the cell wall of fungi is —
- Cellulose
- Pectin
- Chitin
- Dextrin
Answer: 3. Chitin.
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Mcq Wbbse
Question 10. A plant with a naked seed is —
- Mango
- Cycas
- Fern
- Neem
Answer: 2. Cycas.
Question 11. Which of the following is a prokaryote?
- Amoeba
- Spirogyra
- Bacteria
- Chlamydomonas
Answer: 3. Bacteria.
Question 12. The lichen represents a symbiotic relationship between —
- Algae and bacteria —
- Fungi and higher plants
- Algae and fungi
- Bacteria and virus :
Answer: 3. Algae and fungi.
Question 13. A thalloid bryophyte is —
- Riccia
- Pogonatum
- Dryopteris
- Lycopodium
Answer: 1. Riccia.
Question 14. Angiosperms are included under —
- Embryophyta
- Trachaeophyta
- Spermatophyta
- Each of them
Answer: 4. Each of them.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 15. In fungi, reserve food is —
- Starch
- Cellulose
- Glycogen
- All of these
Answer: 3. Glycogen.
Question 16. Fern rhizome is —
- Root
- Stem
- Rhizoid
- Rhizophore
Answer: 3. Rhizoid.
Question 17. The smallest flower is of —
- Carica papaya
- Nelumbo nucifera
- Wolfia micro scopia_
- Rafflesia
Answer: 3. Wolfia micro scopia.
Question 18. Which part of the coconut is eaten?
- Entire seed
- Embryo
- Pericarp
- Seed coat
Answer: 1. Entire seed.
Question 19. Which one is a parasitic algae?
- Sargassum
- Ulothrix
- Cephaleuros
- Oedogonium
Answer: 3. Cephaleuros.
Question 20. Which one is not a root vegetable?
- Potato
- Turnip
- Carrot
- Sweet potato
Answer: 1. Potato.
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Animal Kingdom MCQs
Question 1. Which of the following is ectoparasite in other fishes —
- Dogfish
- Lamprey
- Rohu
- Label
Answer: 2. Lamprey.
Question 2. Which of the following is a toad?
- Hyla
- Bufo
- Rana
- Tree frog
Answer: 2. Bufo.
Life And Its Diversity Mcq For Class 9 West Bengal Board
Question 3. Which of the following is a flying lizard?
- Wall lizard
- Varanus
- Draco
- Monitor lizard
Answer: 3. Draco.
Question 4. “Venus flower basket” is the popular name of —
- Spongilla
- Sea lily
- Euplectella
- Obelia
Answer: 3. Euplectella.
Question 5. Leach is —
- Endoparasite
- Ectoparasite
- Vector
- Free-living
Answer: 2. Ectoparasite.
Question 6. The anti-coagulant produced by Leech is —
- Heparin
- Hirudin
- Oxalates
- Citrates
Answer: 2. Hirudin.
Question 7. A characteristic feature of mollusks is —
- Soft body
- Shell
- Foot
- Mantle
Answer: 4. Mantle.
Question 8. The centipedes have —
- 100 legs
- 100-200 legs
- A pair of legs per trunk segment
- Equal to the body segment
Answer: 3. A pair of legs per each trunk segment.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Mcq Questions With Solutions
Question 9. The water vascular system is a characteristic of —
- Sponges
- Motluses
- Coelenterates
- Echinoderm
Answer: 4. Echinoderm.
Question 10. The internal body cavity of coelenterates is —
- Haemocoel
- Coelom
- Enter on
- Pseudocoel
Answer: 3. Enteron.
Question 11. Which one Arthopodes is viviparous?
- Cockroach
- Scorpion
- Prawn
- Centipede
Answer: 2. Scorpion.
Question 12. Which of the following is not a true fish?
- Dogfish
- Jellyfish
- Flying fish
- Goldfish
Answer: 2. Jellyfish.
Question 13. All are cold-blooded animals except
- Crocodile
- Varanus
- Snake
- Pigeon
Answer: Pigeon.
Question 14. The bat is a true —
- Bird
- Flying mammal
- Flying fish
- Flying lizard
Answer: 2. Flying mammal.
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 1 Important Mcqs
Question 15. The scorpion respires through —
- Gills
- Spiracles
- Book lung
- Trachea
Answer: 3. Book lung.
Question 16. The basic unit of classification is —
- Order
- Class
- Species
- Family
Answer: 3. Species.
Question 17. Animals having innumerable pores in their body are grouped under—
- Porifera
- Coelenterata
- Protozoa
- Mollusca
Answer: 1. Porifera.
Question 18. Acoelomate animals fall under the phylum —
- Nemathelminthes _
- Platyhelminthes
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
Answer: 2. Platy helminths.
Question 19. One of the following animals get already digested food and need not digest it again. It is —
- Amoeba
- Cockroach
- Leech
- Taenia
Answer: 4. Taenia.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Mcq Chapter 1
Question 20. The Largest number of animals belong to —
- Mammalia
- Arthropoda
- Reptilia
- Pisces
Answer: 2. Arthropoda.
Question 21. The body of hydra is —
- Monoblastic
- Triploblastic
- Diplomatic
- Polyblastic
Answer: 3. Diploblastic.
Question 22. The ink gland is found in—
- Sepia
- Octopus
- Loligo
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 23. True flight is found in —
- Flying fish
- Flying lizard
- Flying frog
- Bat
Answer: 4. Bat.
Question 24. Mammary glands are modification of —
- Salivary gland
- Sebaceous gland
- Sweat gland
- Lacrymal gland
Answer: 2. Sebaceous gland.
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Mcq In Bengali Medium
Question 25. The phylum of which animals can live on land, in water, and can also fly is—
- Arthropoda
- Protozoa
- Mollusca
- Annelida
Answer: 1. Arthropoda.
Question 26. Which one of we following animals is not a vertebrate?
- Fish
- Pigeon
- Garden lizard
- Amphioxus
Answer: 4. Amphioxus.
Question 27. Stinging cells are found in —
- Frog
- Snake
- Hydra
- Snail
Answer: 3. Hydra. :
Question 28. The bat differs from a bird in having —
- Four chambered heart
- Diaphragm
- Wings
- Small brain
Answer: 2. Diaphragm.
Question 29. The animals of which invertebrate phylum consists kidney-like structure for excretion?
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
- Porifera
- Echinodermata
Answer: 2. Mollusca.
Question 30. The excretory organ of earthworms is —
- Nephirdia
- Kidney
- Trachea
- Gills
Answer: 1. Nephirdia.
Class 9 Life Science Mcq Wbbse Board Chapter 1
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Life and Biology MCQs
Question 1. Who first recognized plants and animals as living objects?
- Linnaeus
- Aristotle
- Pavlov
- Phillipson
Answer: 2. Ristotle
Question 2. In which of the following leaves protoplasmic movement is clearly observed under microscope —
- Vallisneria leaf
- China rose leaf
- Lotus leaf
- Lemna leaf
Answer: 1. Vallisneria leaf
Question 3. The constructive phase in which food materials are built up into more complex substances is called —
- Catabolism
- Metabolism
- Anabolism
- None of these
Answer: 3. Anabolism
Question 4. Movement with the help of flagella is observed in —
- Paramaecium
- Euglena
- Amoeba
- Hydra
Answer: 2. Euglena
Question 5. The characteristic of life is —
- Respiration
- Movement
- Growth
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 6. Life first originated in Earth —
- In the soil
- In air
- In rocks
- In water
Answer: 4. In water
Question 7. The study of the classification of plants and animals based on their relationship, resemblances, and differences is called —
- Ecology
- Taxonomy
- Anatomy
- Genetics
Answer: 2. Taxonomy
Question 8. The term ecology was proposed by —
- Haeckel
- Pavlov
- Simpson
- Tansey
Answer: 1. Haeckel
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Mcq Online Test
Question 9. Biology and Statistics together form a subject called —
- Bionics
- Biometry
- Bioinformatics
- Bio-Geography
Answer: 2. Biometry
Question 10. The subject which deals with the study of cells is called —
- Genetic
- Cytology
- Taxonomy
- Pathology
Answer: 2. Cytology
Question 11. The branch of science which deals with birds is called —
- Apiculture
- Pisciculture
- Ornithology
- None of these
Answer: 3. Ornithology
Question 12. The branch of science which deals with the study of bacteria is called —
- Dendrology
- Agrostology
- Bacteriology
- Helminthology
Answer: 3. Bacteriology
WBBSE For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life MCQS
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Respiration MCQs
Question 1. Who proposed that respiration is a catabolic process?
- Lamark
- Lavoisier
- Priestley
- Barnes
Answer: 2. Lavoisier.
Question 2. Energy currency of the cell is—
- ADP
- Mitochondria
- ATP
- Chloroplast
Answer: 3. ATP.
Read And Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Life Science And Environment MCQs
Question 3. Arespiratory substrate is —
- Glucose
- Protein
- fats
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 4. The starting point of respiration is —
- Amino acid
- Glucose
- Pyruvate
- None
Answer: 2. Glucose.

Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Mcq With Answers
Question 5. The site of glycolysis is —
- Mitochondria
- Cytoplasm
- Golgi bodies
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Cytoplasm.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 6. The final phase of respiration is —
- Glycolysis
- Terminal respiration
- Krebs cycle
- Cytoplasm.
Answer: 2. Terminal respiration.
Question 7. The step common in both aerobic and anaerobic respirations is —
- Krebs cycle
- Terminal respiration
- Glycolysis
- Carbon assimilation
Answer: 3. Glycolysis.
Question 8. In fermentation pyruvic acid is converted into (in animals) —
- Lactic acid
- Ethanol
- Starch
- Glycogen
Answer: 1. lactic acid.
Question 9. In Krebs cycle, the first formed acid is —
- Acetic acid
- Formic acid
- Citric acid
- Carbonic acid
Answer: 3. Citric acid.
Question 10. T.C.A. cycle is also called —
- Glycolysis
- Krebs cycle
- Light phase
- Dark phase
Answer: 2. krebs cycle.
Question 11. The energy produced in aerobic respiration is —
- 646 kcal
- 686 kcal
- 656 kcal
- 486 kcal
Answer: 2. 686 kcal.
Question 12. The number of ATP produced during glycolysis is —
- 4 molecules
- 6 molecules
- 1 molecules
- 2 molecules
Answer: 4. 2 molecules.
Question 13. A bacteria having anaerobic respiration is —
- Clostridium
- Rhizobiun
- Azotobactor
- All
Answer: 4. All.
Question 14. Pneumatophores are found in —
- Halophytes
- Bryophytes
- Epiphytes
- Algael
Answer: 1. Hallophytes.
Physiological Processes Of Life Class 9 Mcq Wbbse
Question 15. The respiratory organ in dragonflies is —
- Gills
- External gills
- Tracheal gills
- Moist skin
Answer: 3. Tracheal gills.
Question 16. An example of jelly fish is —
- Koi
- Mangur
- Singhi
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 17. An aquatic mammal respiring with lungs is —
- Sea horse
- Whale
- Shark
- Dolphin
Answer: 2. Whale.
Question 18. The respiratory organ of a crocodile is —
- Gill
- Skin
- Lung
- Trachea
Answer: 3. Lung.
Question 19. Pyruvic acid is the end product of —
- Calvin cycle
- Citric acid cycle
- Glycolysis
- Photolysis
Answer: 3. Glycolysis.
Question 20. Cell organelle which participates in respiration is —
- Goligbodies
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Mitochondria.
Question 21. The percentage of CO, in the air is —
- 0.05%
- 0.06%
- 0.03%
- 0.09%
Answer: 3. 0.03%.
Question 22. RQ of glucose is —
- 2
- Less than one
- 1
- 3
Answer: 3. 1.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Mcq Questions West Bengal Board
Question 23. The covering membrane of lung is —
- Pericardium
- Pleura
- Meninges
- Tonoplast
Answer: 2. Pleura.
Question 24. Spiracles are present in —
- Earthworm
- Cockroach
- Fishes
- Amoeba
Answer: 2. Cockroach.
Question 25. In a plant exchange of gases takes place through —
- Stomata
- Lenticel
- Chloroplast
- Both a and b
Answer: 4. Both a and b.
Question 26. An animal having respiration with mouth cavity and lungs is —
- Fish
- Crocodile
- Frog
- Eathworm
Answer: 3. Frog.
Question 27. In higher plants exchange of gases takes place through —
- Stomata
- Lenticels
- Pneumatophore
- All
Answer: 4. All.
Question 28. Which respiratory pigment is present in pond snails?
- Haemoglobin
- Haemocyanin
- Heparin
- Fibrin
Answer: 2. Haemocyanin.
Question 29. Alveoli are present in —
- Heart
- Brain
- Lungs
- Stomach
Answer: 3. lungs.
Question 30. Lactic acid is found in our body in—
- Lungs
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle.
Answer: 2. Skeletal muscle.
Question 31. Which one of the following organs is the main respiratory organ of a whale?
- Integument
- Lung
- Gill
- Trachea.
Answer: Lung is the main respiratory organ of the whale.
Question 32. The cell organelle which participates in respiration is —
- Golgi bodies
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Chloroplast
Answer: The cell organelle.
Question 33. What is the main respiratory organ of a house lizard?
- Integument
- Nephridia
- External gills s
- Lungs
Answer: Lung is the main respiratory organ of the house lizards.
Question 34. Pyruvic acid is the end product of —
- Citric acid cycle
- Calvin cycle
- Glycolysis
- Photolysis
Answer: Pyruvic acid is the end product of Glycolysis.
Question 35. The respiratory organ of a cockroach is —
- Skin
- Gill
- Trachea
- Lung.
Answer: The respiratory organ of a cockroach is the Trachea.
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 36. In which of the animals, the trachea is the respiratory organ?
- Cockroach
- Fish
- House lizard
- Earthworm.
Answer: The Trachea is the respiratory organ of the Cockroach.
Question 37. The respiratory organ of Crocodile is —
- Gill
- Skin
- Lung
- Trachea
Answer: The respiratory organ of a Crocodile is the Lung.
Question 38. Respiration in the absence of free oxygen is —
- Anaerobic
- Aerobic
- Alcoholic fermentation
Answer: Respiration in the absence of free oxygen is Anaerobic.
Question 39. An animal performing anaerobic respiration is —
- Earthworm
- Tapeworm
- Glow-worm
- None of the above
Answer: An animal performing anaerobic respiration is a Tapeworm.
Question 40. The percentage of oxygen in inspiratory air is —
- 16%
- 12.4%
- 20.60%
- 30%
Answer: The percentage of oxygen in inspiratory air is 20.60%
Question 41. What is the end product of Glycolysis?
- Citric acid
- Malic acid
- Nitric acid
- Pyruvic acid
Answer: Pyruvic acid is the end product of Glycolysis.
Question 42. In the cell of living organisms, the energy is stored in
- NADP
- ADP
- ATP
- PGA
Answer: In the cell of living organisms the energy is stored in ATP.
Question 43. In which animal does skin act as the main respiratory organ?
- Toad
- Prawn
- Cockroach
- Earthworm
Answer: Skin acts as the main respiratory organ in earthworms.
Question 44. The breathing organ of Rohu fish is —
- Green gland
- Trachea
- Gill
- Lung
Answer: The breathing organ of Rohu fish is the Gill.
Question 45. In which of the organs alveolus is seen?
- Liver
- Lung
- Skin
- Kidney
Answer: Alveolus is seen in Lung.
Question 46. Which one of the following is produced in muscle cells during anaerobic respiration?
- Acetic acid
- Lactic acid
- Ethyl alcohol
- Hydrochloric acid
Answer: Lactic acid is produced in muscle cells during anaerobic respiration.
Question 47. Which one of the following is called energy currency?
- NADH2
- ATP
- ADP
- FADH2
Answer: ATP is called energy currency.
Question 48. Cutaneous respiration takes place in
- Cockroach
- Earthworm
- Spider
- Amoeba.
Answer: Cutaneous respiration takes place in Earthworms.
Physiological Processes Of Life Mcq For Class 9 Bengali
Question 49. The respiratory organ of Periplanta Americana is
- Skin
- External gills
- Lung
- Trachea
Answer: The respiratory organ of Periplanta americana is the trachea.
Question 50. The respiratory organ of a shark is
- Lungs
- Trachea
- Internal gills
- External gills
Answer: The respiratory organ of sharks is the internal gills.
Question 51. How many ATP are produced from 1 gm mole glucose by aerobic respiration?
- 8 ATP
- 38 ATP
- 12 ATP
- 7 ATP
Answer: 38 ATP are produced from 1gm mole glucose by aerobic respiration.
Question 52. Glycolysis occurs within the
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Nucleus
Answer: Glycolysis occurs within the cytoplasm.
Question 53. Due to the oxidation of how much glucose about 686 Kcal of energy is generated in aerobic respiration.
- 1 Molecule of glucose
- 1 gm molecule of glucose
- 1. gm of glucose
- 180 kg of glucose
Answer: Due to the oxidation of 1 molecule of glucose about 686 K cal of energy is generated in aerobic respiration.
Question 54. The biochemical pathway which produces pyruvic acid as an end product is —
- Photolysis
- Glycolysis
- Kreb’s cycle
Answer: The biochemical pathway which produces pyruvic acid as an end product is glycolysis.
Question 55. Lactobacillus is used for making
- Acetic acid
- Alcohol
- Lactic acid from Lactose of milk.
Answer: Lactobacillus. is used for making lactic acid from lactose of milk.
Question 56. The labyrinthine organ is an accessory respiratory organ of
- Scorpion
- Koi
- Crocodile
- Frog
Answer: The labyrinthine organ is an accessory respiratory organ of Koi.
Question 57. In which form of energy is the potential energy of the food usually liberated in respiration?
- Light energy
- Heat and kinetic energy
- Electric energy
- Kinetic energy
Answer: The potential energy of food is usually liberated in the form of heat energy and kinetic energy in respiration.
Question 58. What is the respiratory organ of a cockroach?
- Cell Membrane
- Moist skin
- Trachea
- Gills
Answer: The Trachea is the respiratory organ of a cockroach.
Question 59. In anaerobic respiration___ Keal energy is produced.
- 150
- 686
- 574
- 50
Answer: In anaerobic respiration 50 Kcal energy is produced.
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Nutrition MCQs
Question 1. The secretion of which of the following glands does not contain any enzyme necessary for digestion?
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Salivary gland
- Glands of the small intestine
Answer: The secretion of the Liver does not contain any enzyme necessary for digestion.
Question 2. Amongst the following types of food, which one has Nitrogen as an essential component?
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
Answer: Protein has Nitrogen as an essential component
Question 3. An example of a Symbiotic plant is —
- Cuscuta
- Agaricus
- Sundew
- Lichen
Answer: An example of a Symbiotic plant is Lichen.
Question 4. From which part of the human digestive system no carbohydrate-digesting enzyme is secreted?
- Buccal cavity
- Pancreas
- Intestine
- Stomach
Answer: From the Stomach, no carbohydrate-digesting enzyme is secreted.
Question 5. Cuscuta is a –
- Autotroph
- Heterotroph
- Parasite
Answer: Cuscuta is a Parasite.
Question 6. The Vitamin that can be synthesized in the human body is —
- K
- C
- A
- D
Answer: The Vitamin that can be synthesized in the human body is D.
Question 7. Which of the following acts as a source of energy in the body?
- Carbohydrate
- Vitamin
- Water
- Minerals
Answer: Carbohydrates act as a source of energy in the body.
Question 8. Which type of food provides nitrogen to the body?
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Fat
- Vitamin
Answer: Protein type of food provides nitrogen to the body.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Important Mcq With Solutions
Question 9. Which one of the following is the largest digestive gland in vertebrates?
- Salivary glands
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Intestinal gland
Answer: The liver is the largest digestive gland in vertebrates.
Question 10. The proteolytic enzyme in pancreatic juice is —
- Amylase
- Lipase
- Trypsin
- Pepsin
Answer: The proteolytic enzyme in pancreatic juice is Trypsin.
Question 11. The chemical name of Vitamin C is —
- Ascorbic acid
- Retinol
- Phylloquinone
- Nicotinic acid
Answer: The chemical name of Vitamin C is Ascorbic acid.
Question 12. Which of the following parts of the human digestive system does not secrete protein and oil or fat digestive enzyme?
- Mouth
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
- Stomach
Answer: The mouth does not secrete protein and oil or fat digestive enzymes.
Question 13. Due to deficiency of which of the following demented chlorosis occurs in plants?
- Calcium
- Oxygen
- Magnesium
- Sodium
Answer: Due to deficiency Magnesium chlorosis occurs in plants.
Question 14. In which of the following parts of the digestive system of the human body digested food substances are absorbed?
- Oesophagus
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
Answer: Digested food substances are absorbed in the Small intestine.
Question 15. Which of the following organs produces bile?
- Gall bladder
- Pancreas
- Liver
Answer: The liver produces bile.
Question 16. The name of the enzyme which is present in the saliva and which acts upon carbohydrate food is —
- Pepsin
- Ptyalin
- Amylase
- Erepsin
Answer: The name of the enzyme which is present in the saliva and which acts upon carbohydrate food is Ptyalin.
Question 17. The bile duct enters —
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Duodenum
Answer: The bile duct enters Duodenum.
Question 18. Deficiency of which vitamin produces anaemia?
- Vitamin B1
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin B6
- Vitamin B2
Answer: Deficiency of Vitamin B12 produces anaemia.
Question 19. Which vitamin contains cobalt?
- Vit B1
- Vit B2
- Vit B12
- Vit C
Answer: Vit B12contains cobalt.
Question 20. Which of the following diseases results due to deficiency of Vitamin A’?
- Rocket
- Scurvy
- Night blindness
- Beri-Beri
Answer: Night blindness disease results due to a deficiency of Vitamin ‘A’.
Question 21. Where are villi situated?
- In kidney
- In lungs
- Buccal cavity
- Small intestine
Answer: Villi are situated in the Small intestine.
Question 22. What is pepsin?
- Animal hormone
- Enzyme
- Plant hormone
- Panes material
Answer: Pepsin is an Enzyme.
Question 23. Which one of the following vitamins is water soluble?
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
Answer: Vitamin C is water soluble.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Mcq
Question 24. Which one of the following elements is required as a trace element in the plant?
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Boron
- Phosphorus
Answer: Boron is required as a trace element in plants.
Question 25. Which one of the following is hindered due to deficiency of vitamin ‘A’ causing “night blindness” ?
- Rod cell construction
- Retina construction
- Nerve cell construction
Answer: Rod cell construction is hindered due to a deficiency of vitamin ‘A’ causing “night blindness”.
Question 26. The Vitamin synthesized in the human skin is —
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
Answer: The Vitamin synthesized in human skin is Vitamin D.
Question 27. An animal Starch is —
- Glycogen
- Albumin
- Sucrose
- Maltose
Answer: An animal Starch is Glycogen.
Question 28. Blood coagulation does not occur due to the deficiency of which Vitamin?
- Vitamin A,
- Vitamin B12,
- Vitamin C,
- Vitamin K
Answer: Blood coagulation does not occur due to the deficiency of Vitamin K.
Question 29. Mainly from which molecule of the following, energy is released?
- Protein
- Glycerol
- Glucose
- Amino acid
Answer: Energy is released mainly from glucose molecules.
Question 30. A microelement helpful in plant nutrition is.
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
- Zine
- Phosphorus
Answer: A micro element helpful in Plant nutrition is Zinc.
Question 31. Due to the deficiency of which Vitamin the disease Ricket occurs in children?
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin K
Answer: Due to the deficiency of Vitamin D the disease Ricket occurs in children.
Question 32. The component of food which does not yield energy is
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Fat
- Vitamin.
Answer: The component of food which does not yield energy is Vitamin.
Question 33. Pellagra is caused due to the deficiency of 3
- Amino acid
- Nicotinic acid
- Citric acid
- Lactic acid
Answer: Pellagra is caused by to deficiency of Nicotinic acid.
Question 34. The gland from which. three types of digestive enzymes are secreted is —
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Salivary gland
- Gastric gland
Answer: The gland from which three types of digestive enzymes are secreted is the pancreas.
Question 35. Deficiency of which Vitamin causes Scurvy?
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin C
Answer: Deficiency of Vitamin C causes scurvy.
Question 36. Which mineral is present in haemocyanin pigment?
- Fe
- Mg
- Cu
- Co
Answer: Cu mineral is present in haemocyanin pigment.
Question 37. Which animal from the following organisms can prepare its food?
- Toad
- Eugiena
- Mucor
- Mango tree
Answer: Euglena can prepare its food.
Question 38. Proteins contain —
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Nitrogen
Answer: Proteins contain Nitrogen,
Question 39. The substance which is not carbohydrates
- Cane sugar
- Sioumin
- Lactose
- Albumin
Answer: The substance which is not a carbohydrate is Albumin.
Question 40. The antivitamin preventing the action of biotin is
- Carotene
- Avidin
- Pyrimethamine
Answer: The antivitamin preventing the action of biotin is avidin.
Question 41. Protein can be digested by —
- Ptyalin
- Lipase
- Pepsin
- Maltase
Answer: Protein can be digested by Pepsin.
Question 42. Which one of the following diseases is caused by to deficiency of Vitamin E?
- Night blindness
- Infertility
- Rocket
- Scurvy
Answer: Infertility disease is caused by to deficiency of Vitamin E.
Question 43. The metallic ion was essential for blood coagulation—.
- Cat*
- Kt
- Mg**
- Na*
Answer: The metallic ion esser.: al for blood coagulaton is ca**.
Question 44. The major reason for anaemia in the human body is the deficiency of
- Iodine in food
- Calcium in food
- Magnesium in food
- Iron in food
Answer: The major reason for anaemia in the human body is the deficiency of Iron in food.
Question 45. The digestion of carbohydrates occurs in which of the following in man?
- Buccal cavity
- Stomach
- Buccal cavity and stomach
- Buccal cavity and Small intestine
Answer: The digestion of carbohydrates occurs in the buccal cavity and small intestine.
Physiological Processes Of Life Class 9 Mcq Online Test Wbbse
Question 46. The enzyme which is not present in succus entericus is_
- Trypsin
- Maltase
- Sucrase
- Lactase
Answer: The enzyme which is not present in succus entericus is trypsin.
Question 47. Deficiency of Iodine leads to.
- Anaemic
- Pellagra
- Goitre
Answer: Deficiency of iodine leads to goitre.
Question 48. Xeropthalmia is caused by the deficiency of ss.
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
Answer: Xeropthalmia is caused by a deficiency of Vitamin A.
Question 49. A total Parasiteis_
- Mucor
- Spirogyra
- Swarnlata
- Agaricus
Answer: A total Parasite is Swarnlata.
Question 50. Citrus fruits like oranges contain
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
Answer: Citrus fruits like oranges contain Vitamin C.
Question 51. Oxyntic cells are responsible for the secretion of —
- Pepsin
- Ptyalin
- HCI
- None
Answer: Oxyntic cells are responsible for the secretion of HCl.
Question 52. Which element is known as an enzyme activator?
- Zinc
- Copper
- Molybdenum
- Iron
Answer: Zinc is known as an enzyme activator.
Question 53. Osteomalacia is caused by the deficiency of —
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
Answer: Osteomalacia is caused by the deficiency of Vitamin D.
Question 54. The organic substance from which energy is not obtained is —
- Protein
- Carbohydrate
- Fat
- Vitamins
Answer: The organic substance from which energy is not obtained is Vitamins.
Class 9 Life Science Physiological Processes Mcq In Bengali
Question 55. The metallic element which is required for the formation of haemoglobin is —
- Iron (Fe)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Potassium (K)
Answer: The metallic element which is required for the formation of haemoglobin is Iron (Fe).
Question 56. Which digestive juice in your body would turn a blue litmus paper red?
- Salivary juice
- Bile juice
- Pancreatic juice
- Gastric juice
Answer: Gastric Juice turns a blue litmus paper red.
Question 57. Of the following, is a protective food.
- Carbohydrate
- Vitamin
- Protein
- Fat
Answer: Of the following, vitamin is a protective food.
Question 58. A child has swollen and bleeding gums. Which food could he be given to reduce the symptoms?
- Germinating gram seeds
- Carrot
- Egg
- Lemon
Answer: Lemon should be given to him to reduce the symptoms.
Question 60. Deficiency of which mineral causes chlorosis in plants?
- Mg
- Ca
- Na
- Al
Answer: A deficiency of Magnesium causes chlorosis in plants.
Question 61. An enzyme which is secreted from the stomach is —
- Trypsin
- Pepsin
- Ptyalin
- Erepsin
Answer: An enzyme which is secreted from the stomach is Pepsin.
Question 62. Which one of the following is a fat-soluble vitamin?
- Vitamin ‘B1’
- Vitamin ‘D’.
- Vitamin ‘C’
- Vitamin ‘B12‘
Answer: Vitamin ‘D’ is a fat-soluble vitamin.
Question 63. The nutrients are —
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Water
- All these
Answer: (4) all these.
Question 64. Fats provide more energy than carbohydrates because —
- Fat contains more hydrogen
- Fat contains more oxygen
- Fat contains more useful substances
- Fat contains more carbon.
Answer: 1. Fat contains more hydrogen.
Question 65. Monosaccharides are linked together by —
- Hydrogen bond
- Glucoside bond
- Linkage bond
- None of these
Answer: 1. Hydrogen bond.
Question 66. The chief stored form of carbohydrate in animals is —
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Sucrose
- Maltose
Answer: 2. Glycogen.
Question 67. A derived lipid is —
- Sterols
- Phospholipid
- Glycolipids
- Fatty acids
Answer: 1. Sterols.
Question 68. Cod liver oil is a rich source of —
- Vit Band C
- Vit A and D
- Vit A and C
- Vit D and K
Answer: 2. Vit A and D.
Question 69. The calorific value of fat is —
- 4.3 kcal
- 9.7 kcal
- 9.3 kcal
- 4.1 kcal
Answer: 3. 9.3 kcal.
Question 70. The simplest form of protein is —
- Glucose
- Glycerol
- Amino acid
- Ester
Answer: 3. Amino acid.
Question 71. The essential amino acid is —
- Valine
- Histidine
- Methionine
- All
Answer: 4. All.
Question 72. A derived protein is —
- Glycine
- Polypeptides
- Serine
- All
Answer: 2. Polypeptides.
Question 73. An element acts as a growth promoter and is present in vitamin B-12. What is it?
- Chlorine
- Copper
- Cobalt
- Calcium
Answer: 3. Cobalt.
Question 74. Vitamine acts as —
- Enzyme
- Co-enzyme
- Solvent
- Promoter
Answer: 2. Co-enzyme.
Question 75. Caroten is the provitamin of —
- VitA
- Vit D
- Vit C
- Vit K
Answer: 1. Vit A.
Question 76. An example of antivitamin is —
- Ergosterol
- Avidin
- Carotene
- None of these
Answer: 2. Avidin.
Question 77. Nyctalopia is caused due to the deficiency of —
- VitC
- Vit D
- VitK
- VitA
Answer: 4. Vit A.
Question 78. A bone disease due to the deficiency of Vit D is —
- Xeropthalmia
- Osteomalacia
- Beriberi
- Night blindness
Answer: 2. Osteomalacia.
Question 79. The symptoms of 3D disease for
- Anaemia
- Scurvy
- Pellagra
- Rickets
Answer: 3. Pellagra.
Question 80. The chemical name of Vit E is —
- Calciferol
- Thiamine
- Tocopherol
- Riboflavin
Answer: 3. Tocopherol.
Question 81. A total stem parasite is
- Cuscuta
- Dodder
- Swarnlata
- All
Answer: 4. All.
Question 82. A partial saprophytic plant is
- Mucor
- Agaricus
- Montropa
- Pinus
Answer: 4. Pinus
Question 83. An insectivorous plant is
- Nepenthes
- Calcutta
- Orchid
- Cycas
Answer: 1. Nepenthes.
Question 84. The optimum temperature for enzyme activity is —
- 20-25°C
- 30-40°C
- 35-40°C
- 30-55°C
Answer: 3. 35—40°C
Question 85. The bile juice is stored in—
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Spleen
- Gall bladder
Answer: 4. Gall bladder.
Question 86. The proteolytic enzyme present in intestinal juice is —
- Pepsin
- Trypsin
- Erepsin
- Ptyalin
Answer: 3. Erepsin.
Question 87. Lacteals are present in—
- Villi
- Alveoli
- Stomach
- Mouth
Answer: 1. Villi.
Question 88. Milk does not contain ~
- Vit C
- Iron
- Calcium
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Vit C.
Question 89. Which of the following supplies nitrogen to the body?
- Carbohydrate
- Fat
- Protein
- Vitamin
Answer: 3. Protein.
Question 90. Which one of the following vitamins is water soluble?
- VitA
- Vit C
- Vit D
- VitE
Answer: 3. Vit C.
Question 91. The major reason for anaemia in the human body is the deficiency of
- Iodine in food
- Calcium in food
- Magnesium in food
- Iron in food
Answer: 4. Iron in food.
Question 92. The partly digested food in the stomach is called —
- Cite
- Chyme
- Mastication
- Chewing
Answer: 2. Chyme.
Question 93. Which one is non-functional in humans?
- Caecum
- Colon
- Gall bladder
- Rectum
Answer: 1. Caecum.
Question 94. The largest digestive gland in the human body is =
- Pancreas
- Gastric gland
- Liver
- Salivary gland
Answer: 3. Liver.
Question 95. Asymbiontic association between plants and animals is —
- Algae and fungi
- Zoochlorella and hydra
- Bacteria and fungi
- None of these
Answer: 2. Zoochlorella and hydra.
Question 96. Which one is the heterotrophs from —
- Mango
- Neem
- Mucor
- Hibiscus
Answer: 3. Mucor.
Question 97. An organism that breaks up the food before ingestion is —
- Tapeworm
- Roundworm
- Bacteria
- Cat
Answer: 3. Bacteria.
Question 98. Which one is the example of roughage?
- Pulses
- Rice
- Dalia
- Mango
Answer: 3. Dalia.
Question 99. The process of formation of glycogen from glucose takes place in —
- Muscle
- Liver
- Stomach
- Both muscle and liver
Answer: 4. Both muscle and liver
Question 100. The process by which glycogen is broken down to glucose is called—
- Glycogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Glucogenesis
- All of these
Answer: 2. Glycogenolysis.
Question 101. Simplest Carbohydrate is —
- Polysaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Monosaccharides
- Amino acids
Answer: 3. Monosaccharides.
Question 102. The protein part of an enzyme is —
- Co-enzyme
- Apoenzyme
- Prosthetic group
- None of these
Answer: 1. Co-enzyme.
Question 103. The scientist who first introduced the term enzyme is —
- Munch
- Lindeman
- Kuhn
- Loandsteiner
Answer: 3. Kuhn.
Question 104. The digestive juice that does not contain enzymes is —
- Saliva
- Gastric juice
- Bile juice
- Pancreatic juice
Answer: 3. Bile juice.
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Circulation MCQs
Question 1. Blood of which of the following animals does not contain RBC?
- Earthworm
- Toad
- Man
- Fish
Answer: The blood of Earthworm does not contain RBC.
Question 2. Which one of the following three is not seen in the open type of circulatory system?
- Artery
- Haemocoel
- Capillary
Answer: Capillary is not seen in the open type of circulatory system.
Question 3. In the blood of which of the following animals, haemocyanin is present?
- Earthworm
- Prawn
- Cockroach
- Toad
Answer: In the blood of Prawn haemocyanin is present.
Question 4. In which of the chambers of the human heart, oxygenated blood is received?
- Right ventricle
- Left auricle
- Right auricle
- Left ventricle
Answer: In the Left, auricle of the human heart oxygenated blood is received.
Question 5. The main function of white blood corpuscles (WBC) is to —
- Produce Red Blood Corpuscles (RBC)
- Destroy bacteria
- Distribute heat
- Clotting of blood
Answer: The main function of white blood corpuscles (WBC) is to destroy bacteria.
Question 6. Lymph returns to blood through —
- Capillary
- Artery
- Vein
- Lymph vessel
Answer: Lymph returns to blood through Lymph vessels.
Question 7. The function of the right ventricle is
- To transmit oxygenated blood
- To transmit blood rich in CO2
- To receive blood rich in CO2
- To receive oxygenated blood
Answer: The function of the right ventricle is to transmit blood rich in CO2.
Question 8. Which one of the following in excessive numbers is responsible for Leukemia (Blood cancer)?
- Microbes
- Blood platelets
- W.B.C
- R.B.C
Answer: W.B.C. in excessive numbers is responsible for Leukemia (Blood cancer).
Question 9. Respiratory pigment present in the blood of man is
- Haemocyanin
- Haemolymph
- Haemocyte
- Haemoglobin
Answer: The respiratory pigment present in the blood of man is haemoglobin.
Question 10. Open blood circulation is seen in—
- Earthworm
- Human
- Toad
- Cockroach
Answer: Open blood circulation is seen in Cockroach.
Question 11. What are the veins having capillaries at both ends called?
- Systemic veins
- Pulmonary veins
- Portal veins
- Vena cava
Answer: Veins having capillaries at both ends are called Portal veins.
Question 12. Which one of the following metallic elements is needed in the formation of a haemoglobin molecule? [MP-2002]
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Potassium
- Calcium
Answer: Iron is needed in the formation of haemoglobin molecules.
Question 13. Lacteal contains —
- Deoxygenated blood
- Lymph
- Plasma
Answer: Lacteal contains lymph.
Question 14. Which vein of man carries oxygenated blood?
- Portal vein
- Renal vein
- Pulmonary vein
- Facial vein
Answer: The pulmonary vein of a man carries oxygenated blood.
Question 15. The mitral valve is present at the —
- Junction of right atrium and right ventricle
- Junction of left atrium and left ventricle
- Ventricle and aorta
- Ventricle and pulmonary artery
Answer: The mitral valve is present at the junction of the left atrium and left ventricle.
Question 16. An animal whose blood does not carry oxygen is
- Prawn
- Fish
- Amoeba
- Cockroach
Answer: Cockroach blood does not carry oxygen.
Question 17. In which of the following animals is an open circulatory system found?
- Prawn
- Earthworm
- Toad
- Man
Answer: The open circulatory system is found in Prawn.
Question 18. The largest cell of the blood is —
- Monocyte
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
- Lymphocyte
Answer: The largest cell of the blood is Monocyte.
Question 19. What is the name of the element that helps in blood coagulation?
- Sodium
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
Answer: The element that helps in blood coagulation is Calcium.
Question 20. Which one is related to the other three?
- Lymphocyte
- Monocyte
- Leucocyte
- Eosinophil
Answer: Leucocyte is related to the other three.
Question 21. Which protein is absent in serum?
- Fibrinogen
- Globulin
- Albumin
- Bilirubin
Answer: Fibrinogen protein is absent in serum.
Question 22. The function of the left auricle in the human heart is—
- To transmit oxygenated blood
- To transmit blood rich in CO2
- To receive blood rich in CO2,
- To receive oxygenated blood
Answer: The function of the left auricle in the human heart is to receive oxygenated blood.
Question 23. In the plasma of which of the following animals is haemoglobin present?
- Earthworm
- Prawn
- Cockroach
- Toad
Answer: Hemoglobin is present in the plasma of Earthworms.
Question 24. From which of the chambers of the human heart is oxygenated blood transmitted to different parts of the body?
- Right auricle
- Left ventricle
- Right ventricle
- Left auricle
Answer: From the Left ventricle of the human heart oxygenated blood is transmitted to different parts of the body.
Question 25.____ in the blood of group ‘O’.
- Agglutiongen is not present —_
- Agglutinin is not present
- Agglutinogen ‘A’, is present
- Agglutinogen ‘AB’ is present
Answer: Agglutinogen is not present in the blood of group ‘O’.
Question 26. In which pair of the following animal’s haemoglobin is found?
- Man and cockroach
- Cockroach and Earthworm
- Man and Earthworm
- Prawn and cockroach
Answer: Haemoglobin is found in the blood of man and Earthworm.
Question 27. Heparin is secreted from —
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
Answer: Heparin is secreted from basophil.
Question 28. Cardiac muscle is
- Voluntary striated
- Non-voluntary striated muscle
- Voluntary smooth muscle
- Non-voluntary smooth muscle
Answer: The cardiac muscle is a non-voluntary striated muscle.
Question 29, Lecuocytes which help in antibody formation is
- Eosinophil
- Neutrophil
- Monocyte
- Lymphocyte
Answer: Leucocytes which help in antibody formation lymphocytes.
Question 30. Lymph is a tissue fluid which contains ~
- Leucocytes
- Serum
- Erythrocytes
- None of the above
Answer: Lymph is a tissue fluid which contains leucocytes.
Question 31. Which one is the organic part of blood?
- Albumin
- Fibrinogen
- Calcium
- Urea
Answer: Fibrinogen is the organic part of blood.
Question 32. The life of RBC in man is
- 90 days
- 120 days
- 60 days
- 220 days
Answer: The life span of RBC in men is 120 days.
Question 33. Suppose your blood group is ‘0’ you can receive blood from a person 1aving blood group —
- Group ‘A’
- Group ‘B’
- Group ‘AB’
- Group ‘O’
Answer: Suppose your blood group is ‘0’, You can receive blood from a person having blood group ‘0’.
Question 34. The plasma protein that helps in clotting of blood is—
- Prothrombin
- Albumin
- Fibrin
Answer: The plasma protein that helps in the clotting of blood is prothrombin.
Question 35. The kind of cell absent in lymph is —
- Monocyte
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
Answer: The kind of cell absent in lymph is Basophil.
Question 36. The agglutinin present in Blood Group B is —
- Alpha
- Beta
- Both Alpha and Beta
- No agglulitinin at all
Answer: The agglutinin present in Blood Group Bis is Alpha.
Question 37. Haemoglobin is dissolved in Plasma in —
- Toad
- Earthworm
- Man
- Camel
Answer: Haemoglobin is dissolved in Plasma in earthworms.
Question 38. A person with ‘A’ blood group can take blood from ___ blood group
- A
- O
- B
- A and O
Answer: A person with an ‘A’ blood group can take blood from ‘A’ and ‘O’ blood groups.
Question 39. Blood coagulation is hampered due to the absence of ___.
- Vitamin A and Vitamin K
- Vitamin D.and Magnesium
- Vitamin K and Calcium
- Vitamin A and Calcium
Answer: Blood coagulation is hampered due to the absence of Vitamin K and Calcium.
Question 40. Which component of the blood carries O2 & CO2?
- Red blood corpuscles
- White blood corpuscles
- Red and white blood corpuscles
- Platelets
Answer: Red blood corpuscles of blood carry O2 & CO2.
Question 41. The blood corpuscle that causes phagocytosis is
- RBC
- Platelets
- Lymphocyte
- Neutrophil
Answer: The blood corpuscle that causes phagocytosis is Neutrophil.
Question 42. In which pair of the following animal’s haemoglobin is found?
- Man and cockroach
- Mosquito and earthworm
- Man and earthworm
- Prawn and cockroach
Answer: Haemoglobin is found in the blood of man and earthworms.
Question 43. The existence of solvent molecules in the cell is called-
- Endosmosis
- Exosmosis
- Diffusion
- Turgidity
Answer: 2. Exosmosis
Question 44. The transport of food from the leaf to different parts of the plant is called-
- Transpiration
- Translocation
- Guttation
- Circulation
Answer: 2. Translocation
Question 45. The instrument used to measure the rate of transpiration is —
- Sphygmomanometer
- Ganong’s photometer
- Spirometer
- Speedometer
Answer: 2. Ganong’s photometer
Question 46. In hydra and starfish, the medium of circulation is —
- Blood
- Lymph
- Water
- Salt
Answer: 3. Water
Question 47. Non-protein nitrogenous substance (NPN) is —
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
- All
Answer: 4. All
Question 48. The life span of platelets is —
- 1-5 days
- 15-20 days
- 5-9 days
- 100-150 days
Answer: 3. 5-9 days
Question 49. Bile pigments are —
- Haemoglobin and haemocyanin
- Bilirubin and biliverdin
- Plasma and Serum
- Platelets
Answer: 2. Bilirubin and biliverdin
Question 50. The ratio of WBC and RBC in our body is roughly —
- 1: 20
- 1: 100
- 1: 500
- 1: 700
Answer: 4. 1: 700
Question 51. The WBC cells which are phagocytic are —
- Neutrophil
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both a and b
Question 52. Serotonin is secreted from —
- Platelets
- Basophils
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
Answer: 1. Platelets
Question 53. Heparin, an anticoagulant, is secreted from —
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
- None of these
Answer: 2. Basophil
Question 54. Haemocyanin is a copper-containing pigment of blood found in —
- Earthworm
- Crab
- Tapeworm
- All of these
Answer: 2. Crab
Question 55. Blood circulation is described by —
- William Harvey
- Karl Landsteiner
- August Weisman
- Lindemann
Answer: 1. William Harvey
Question 56. The breaking down of RBC is called —
- Phagocytosis
- Pinocytosis
- Haemolysis
- Blood clotting
Answer: 3. Haemolysis
Question 57. The elements used in blood clotting are—
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Carbon
Answer: 3. Calcium
Question 58. The open circulatory system is found in—
- Cockroach
- Grasshopper
- Snail
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 59. The mitral valve is located
- Between the left auricle and left ventricle
- Between the right auricle and right ventricle
- Between the left ventricle and Aorta
- None of these
Answer: Between left auricle and left ventricle
Question 60. Haemophilia is a –
- Bacterial disease
- Protozoan disease
- Genetic disorder
- Viral disease
Answer: 3. Genetic disorder
Question 61. The canal system as the circulatory system is found in —
- Hydra
- Earthworm
- Sponges
- Tapeworm
Answer: 3. Sponges
Question 62. In cockroaches, the heart is made up of —
- Four pairs of Pulsatile tubes
- A small sac-like
- Thirteen funnel-shaped chamber
- Three chambered.
Answer: 3. Thirteen funnel-shaped chamber
Question 63. The covering membrane of the heart is —
- Meninges
- Pleura
- Pericardium
- Peristome
Answer: 3. Pericardium
Question 64. The wall of capillaries is formed by —
- Endothelium
- Exothelium
- Mesodirm
- All of these
Answer: 1. Endothelium
Question 65. The circulating medium of insects is called —
- Haemoglobin
- Haemocyanin
- Haemolymph
- None of these
Answer: 3. Haemolymph
Question 66. The ascent of sap in plants takes place through —
- Sieve tube
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem vessels
- Companion cells
Answer: 3. Xylem vessels
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 3 Mcq Questions And Answers
Question 67. Cohesive–adhesive force theory was proposed by —
- Stephan and Hales
- Curtis
- Dixon and jolly
- Munch
Answer: 3. Dixon and Jolly
Question 68. Non-nucleated corpuscles present in human blood is —
- Leucocytes
- Erythrocytes
- Lymphocytes
- 1 and 3
Answer: 2. Erythrocytes
Question 69. The smallest blood corpuscles are —
- Thrombocytes
- Erythrocytes
- Phagocytes
- Monocytes
Answer: 1. Thrombocytes
Question 70. The universal donor is —
- Group ‘O’ individual
- Group ‘AB’ individual
- Group ‘B’ individual
- Group ‘A’ individual
Answer: 1. group ‘O’ individual
Question 71. The largest artery is —
- Vena cava
- Aorta
- Capillaries
- Veins
Answer: 2. Aorta
Question 72. In the absence of which vitamin, blood coagulation does not take place?
- vital
- Vit-B12
- Vit-C
- Vit-K
Answer: 4. Vit-K
Question 73. Which of the following animals has haemoglobin in its plasma?
- Earthworm
- Prawn
- Cockroach
- Toad
Answer: 1. Earthworm
Question 74. Which two animals have haemoglobin in their blood?
- Human and cockroach
- Cockroach and earthworm
- Prawn and cockroach
- Human and earthworm.
Answer: Human and earthworm.
Question 75. Which of the following metallic elements is required for the synthesis of haemoglobin molecule?
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Iron
- Potassium
Answer: 3. Iron
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Excretion MCQs
Question 1. Which of the following alkaloids is found in Rauvolfia?
- Morphine
- Nicotine
- Reserpine
- Quinine
Answer: 3. Reserpine.
Question 2. Which one is not a nitrogenous waste product?
- Quinine
- Creatin
- Daturine
- Tanin
Answer: 4. Tanin.
Question 3. The sweat gland is present in —
- Kidney
- Lungs
- Skin
- Liver
Answer: 3. Skin.
Question 4. Latex is the excretory product of —
- Arjuna
- Rubber
- Sajina
- Apple
Answer: 2. Rubber.
Question 5. The hormone produced in the kidney is —
- Erythropoietin
- ADH
- Vasopressin
- None of these
Answer: 1. Erythropoietin.
Question 6. Cystolith contain —
- Oxalate
- Calcium Carbonate
- Potassium nitrate
- All of these
Answer: 2. Calcium Carbonate.
Question 7. Which of the following alkaloids is found in Cinchona?
- Nicotine
- Reserpine
- Morphine
- Quinine
Answer: 4. Quinine.
Question 8. Raphide is found in —
- Banyan
- Arum
- Guava
- Apple
Answer: 2. Arum.
Question 9. Where does the ornithine cycle operate?
- In stomach
- In liver
- In kidney
- In spleen
Answer: 2. In liver.
Question 10. Which material makes urine faintly yellowish?
- Blood
- Bilirubin
- Haemoglobin
- Bile pigment
Answer: 2. Bilirubin.
Question 11. Which animal has nephridia as an excretory organ?
- Cockroach
- Leech
- Toad
- Tapeworm
Answer: 2. Leech.
Question 12. Which of the following alkaloids is used to decrease blood pressure in humans?
- Nicotine
- Reserpine
- Quinine
- Morphine
Answer: 2. Reserpine.
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Transpiration
Question 1. The loss of unused water of the plant body liberated into the atmosphere in the form of vapour is called —
- Evaporation
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- None of these
Answer: 2. Transpiration
Question 2. Transpiration is least in —
- High wind velocity
- High atmospheric humidity
- Dry soil moisture
- Dry environment
Answer: 3. Dry soil moisture
Question 3. Which one is an internal factor of transpiration?
- Light
- Temperature
- Wind velocity
- Structure of leaf
Answer: 4. Structure of leaf
Chapter 3 Physiological Processes Of Life Movement Of Water, Minerals, Food And Gases
Question 1. Movement of water in the cortex of root outside to inside is due to —
- The gradient of chemical potential
- The gradient of water potential
- Accumulation of inorganic salts
- Accumulation of organic solutes
Answer: 2. The Gradient of water potential
Question 2. The extracellular solutions which contain less concentration of the solutes and have higher solvent concentration than the cytoplasm are known as—
- Isotonic solution
- Hypertonic solution
- Hypotonic solution
- None of these
Answer: 3. Hypotonic solution
Question 3. The active hydrostatic pressure created in the parenchymatous cortical cells of the roots is called —
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Suction pressure
- Root pressure
Answer: 1. Turgor pressure
Question 4. Membrane which allows all the molecules or ions of a solution (both solute and solvent molecules) to pass through is called —
- Impermeable membrane
- Permeable membrane
- Semi-permeable membrane
- Selectively permeable membrane
Answer: 2. Permeable membrane
Question 5. Which one is largely responsible for the ascent of sap?
- Capillary theory
- Pulsation theory
- Root pressure theory
- Cohesion force and transpiration pull theory
Answer: 2. Pulsation theory
Question 6. Which one of the following helps in the ascent of sap?
- Capillarity
- Root pressure
- Transpiration
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Very Short Type Questions And Answers
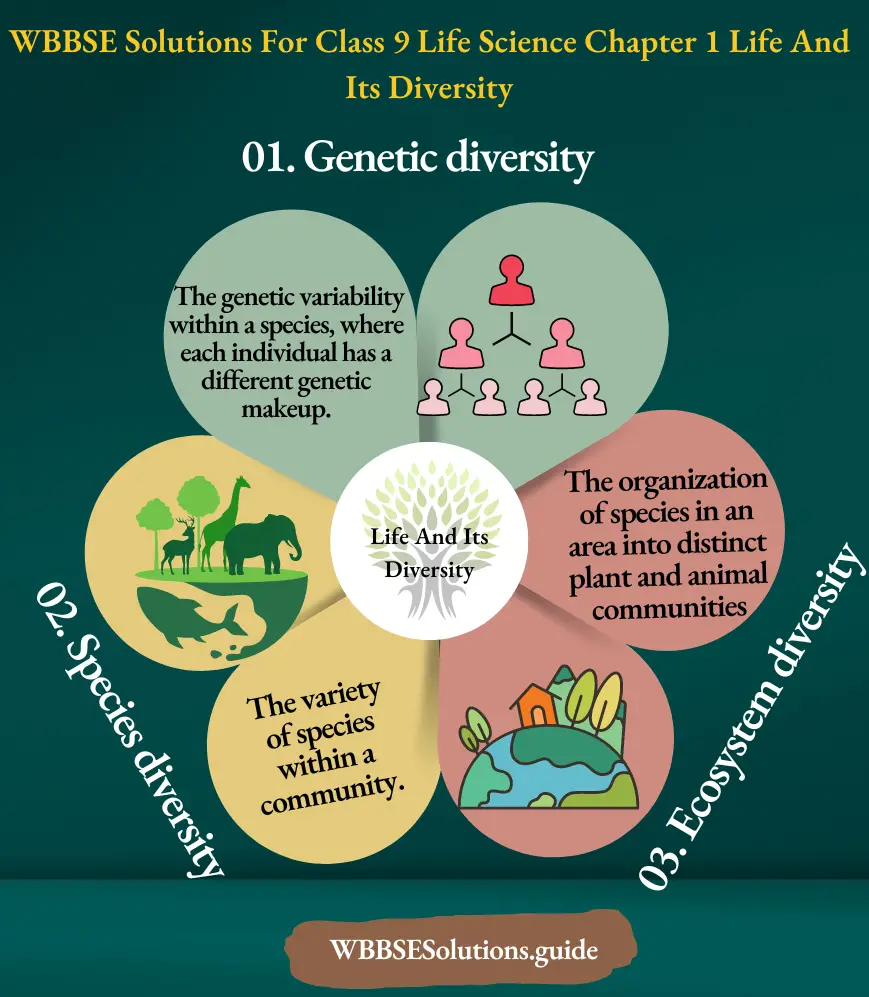
Wbbse Solutions For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity
Question 1. What is the life span of tortoise?
Answer: About 200 years.
Question 2. What is the function of pneumatic bones in birds?
Answer: To reduce the body weight for flying.
Question 3. Define genetic drift.
Answer: The random changes in the allele frequency which is caused by chnce above.
Question 4. How many types of biodiversity are there?
Answer:
(1) Geneticdiversity
(2) species diversity
(3) Community and Ecosystem diversity.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science
Question 5. Who first proposed the term biology?
Answer: Lamarek and Treviranus in 1801
Question 6. Who is the “Father of Biology”?
Answer: Aristotle
Question 7. Who is the “Father of Botany”?
Answer: Theophrastus
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 8. Who is the “Father of Medicine”?
Answer: Hippocrates
Question 9. What is the basic material of life?
Answer: Protoplasm.
Wbbse Solutions For Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity
Question 10. What is cybernetics?
Answer: The branch of science has been formed in Collaboration of biology with technology.
Question 11. What is palaentology?
Answer: Study of fossils.
Question 12. What is biogeography?
Answer: Branch of science that deals with the global distribution of plants and animals.
Question 13. What is space biology?
Answer: The study of survival problems of living things in outer space.
Question 14. Bacteria beiongs to which kingdom ?
Answer: Bacteria belongs to kingdom prokaryotae.
Question 15. Who proposed five kingdom classification of plants ?
Answer: R. Whittaker in 1969 proposed the five kingdom classification.
Question 16. Name one protista.
Answer: One Protista is Paramaecium.
Question 17. Who proposed binomial nomenclature ?
Answer: In the year 1753, the Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus formulated the method of Binomial (bi, two; nomen, name) nomenclature.
Question 18. Which type of leaf venations is noted in monocotyledonous plants ?
Answer: Leaves are provided with parallel venation.
Exception-Arum.
Question 19. Unicellular, eukaryotic and autotrophic plants are included in which kingdom ?
Answer: They are included in Protista.
Question 20. Name the lowest unit of taxonomy.
Answer: The lowest unit of taxonomy is species.
Question 21. Mention two groups under Thallophyta.
Answer: Plants under Thallophyta are again divided into two groups, e.g. — Algae and Fungi.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science
Question 22. What is the name of body cavity in sponges ?
Answer: The body cavity in sponges is called spongocoel.
Question 23. Which cell helps in canal system of sponges ?
Answer: The canal system is helped by Choanocytes / Collar cell / flagellate cell.
Question 24. In which group of animals gastrovascular cavity is found ?
Answer: It is found in group Cnidaria.
Question 25. Which group of animals are commonly called ‘sea walnut’ ?
Answer: Ctenophores are commonly known as ‘sea walnut’.
Read and Learn more about WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Life Science And Environment
Question 26. What is the function of nephridia in earthworm ?
Answer: Nephridia is the excretory organ of earthworm.
Question 27. Name a bird that can not fly.
Answer: Penguin is a bird of Antarctica, which can not fly.
Question 28. Name the mammal that lays eggs.
Answer: Platypus is a mammal that lays eggs.
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Short Type Questions And Answers
Question 1. What is life?
Answer:
Life
Life is defined as the external manifestation of the action and interaction between the living organism and its environment. :
Question 2. What are five basic mechanism which causes Variation?
Answer: Mutation, Recombination, Gene migration, genetic drift and natural selection.
Question 3. What is divergent evolution?
Answer:
Divergent evolution
Formation of different strueture from a common ancestral form is called divergent evolution.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Solutions Wbbse
Question 4. What is convergent evolution ?
Answer:
Convergent evolution
Formation of similar characters among the unrelated group of organism is regarded as convergent evolution.
Question 5. What is the role of gene flow or gene migration in evolution?
Answer: Genetic variation like gene flow is the pre-requisite of evolution. Then the naturalSelection act on this genetic variation.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science
Question 6. What is speciation?
Answer:
Speciation
The process by which one or more species are formed from an existing specis is called speciation.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Solutions Wbbse
Question 7. What is organic evolution?
Answer:
OOrganic evolution
The gradual process of change of one form of life into another and development of new type of living organism from pre-existing type over a long period of time.
Question 8. What is Eugenics?
Answer:
Eugenics
Branch of science which deals with the improvement of human race genetically by Selective control of reproduction.
Question 9. What is chemical evolution?
Answer:
Chemical evolution
The process of development of complex organic molecule such as protein, Nueleic acid from simple inorganic molecule like methane, ammonia, hydrogen etc is called chemical evolution.
Question 10. Name the following branches of biology :
(a) Application of biological processes in technology
(b) Seience of growing fruits and vegetables
(c) Study of pre-historic form of life
(d) Study of causes of immunity
(e) Study of fishes.
Answer: (a) Biotechnology
(b) Horticulture
(c) Palaentology
(d) Immunology
(e) Pisciculture
Question 11. Define taxonomy.
Answer:
Taxonomy
Taxonomy is defined as the science dealing with identification, nomenclature and classification of organism. The term taxonomy was coined by De Condolle in 1813. Carolus Linnaeus is considered as the father of taxonomy.
Question 12. What are coacervates ?
Answer:
Coacervates
According to scientists, the first sign of life was noticed in some larger organic molecules. Oparin (1924) first suggested such a structure and named it coacervate. It is a minute (1 — 100 in diameter), spherical, bubble-like structure composed of a thin layer of organic molecules rich in lipids.
Question 13. What is Immunology ?
Answer:
Immunology :
It involves the study of the defense system in animals and the mechanism by which it is achieved.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science
Question 14. What is biostatistics ?
Answer:
Biostatistics :
The application of statistics in solving biological problems is called Biostatistics. :
Question 15. What are Hemichordates ?
Answer:
Hemichordates
Hemichordates are a small group of marine animals having gill slits, a structure sometimes regarded as notochord in the anterior region only and mostly solid nerve cord. Examples of hemichordates are—Balanoglossus sp. Saccoglossus sp. etc.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Questions And Answers
Question 16. Write two characteristic feature of amphibia.
Answer:
Class—Amphibia :
Characters: 1. Adults are terrestrial and lung—breathing, while larvae are aquatic and gill-breathing.
2. Skin is moist, glandular and naked (i.e., not provided with any exoskeleton).
Question 17. Write any two examples, each of phylum Mollusca and Phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
Phylum — Mollusca :
Example: Garden snail, Octopus (Octopus vulgaris)
Phylum — Echinodermata :
Example: Sea cucumber, Starfish (Asterias rubens)
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Questions Answers
Question 18. Which group of animals are diploblastic and why ?
Answer:
Diploblastic :
When the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, the animal is called a diploblastic animal. The two layers are ectoderm and endoderm.
Example : CnidariAnswer:
Question 19. Write two distinctive features of phylum Porifera.
Answer:
Phylum—Porifera :
(1) Body is multicellular, without well developed tissue system. Exoskeleton is hard and rigid, made up of calcium or silicon-rich cells, called spongin fibres or spicules.
(2) One large aperture, called osculum is present at the upper end of the body. There are numerous tiny pores, called ostia, spread all over their body.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science
Question 20. Mention two characters of phylum Anthropoda.
Answer:
Characters :
(1) Presence of externally jointed appendages is the reason for name arthropoda.
(2) Arthropoda is the largest phylum of kingdom Animalia and over two thirds of all known species on the earth are arthropods.
Question 21. How is porifera different to other animals ?
Answer: Prorifera is multicellular like other animals but porifera does not form any tissue hence all the cells are almost independent and living together like a colony of cells. In other multicellular animals, number of cells together form a tissue having specific structure and function.
Question 22. “All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates” —justifies the statement.
Answer:
“All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates”
In all vertebrates, chordate features are present in early embryonic life. Thus, there is notochord which is gradually replaced by vertebral column in course of development. They have pharyngeal gill slits which may be persistent or replaced by lungs— so all vertebrates are basically chordates.
But all chordates are not vertebrates — for example, in Urochordata and Cephalochordata, notochord is persistent throughout life and is never replaced by vertebrate column. Hence urochordates and cephalochordates are chordates but not vertebrates.
Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Life And Its Diversity Descriptive Type Questions And Answers :
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 1. Define life. Write some characteristics of living beings.
Answer:
Life :
Life is unique, complex cellular organisation of molecules and the cells themselves that shows various types of chemical reactions which lead to availability of energy, growth development, responsiveness, adaptation and reproduction.
Characteristics of Living Beings :
(1) Protoplasm :
All living organisms contain a special type of viscous fluid called protoplasm. Huxley called it the “physical basis of life” because it has capability of performing vital functions. This is composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
(2) Cellular Organisation :
All living beings are composed of cell. Some are unicellular but some are multicellular. Cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
(3) Nutrition :
All organisms obtain food from environment material required for the metabolism and energy. Some are autotrophs but some are heterotrophs.
(4) Respiration :
Life is an energy-consuming process. This energy is obtained by breaking down energy-rich food substances through oxidation and it is called respiration.
(5) Metabolism :
The chemical changes through which living organisms acquire and utilize energy constitute metabolism. The process envolves anabolism and catabolism.
(6) Growth :
Young individuals grow in size. The growth is due to internal addition of protoplasmic materials by which cell enlarge and devide. Growth occures when anabolism exceeds catabolism.
(7) Definite shape and size :
Every living being has definite shape and size by which we can recognise it. A dog never looks like a monkey. A peepal tree differs from a mango tree.
(8) Execretion :
Metabolism produces a number of by-products which are useless to the body. The same are either expelled out of the body (in animals) or are stored inside ageing tissue (in plants)
(9) Movement and locomotion :
All living beings can shift either the whole of their body or a part of it from one place to another. It is called movement. When the whole of the body is displaced, it is called locomotion. Some movement occures due to purely internal forces and called autonomic movement. Others occur in response to external stimuli called paratonic movement.
(10) Irritability :
All the living beings respond to external stimuli such as cold, heat, wind, light, pinprick, etc. This is called irritability. Example – if a pin is pricked in a part ofour body, the part is immediately withdrawn. The plant bend in the direction of the light.
(11) Adaptability :
They are variations which help organisms to modify themselves according to changes in environment and specific requirements of their surroundings. Eg. birds have pneumatic bones and wings for flight and fishes have streamlined body to reduce water friction.
(12) Reproduction :
For the continued existence of the species, all living beings try to produce their own kind. The higher animal may produce young ones or may lay eggs from which hatch the young ones. :
(13) Ageing and death :
Every living being survives for a limited time and ultimately it dies. It has a definite lifespan.
(14) Life cycle :
Each individual passes through a definite life cycle of birth, growth, maturation, reproduction, ageing and death (80-100 years in humans, 200 years in Tortoise, more than 200 years in peepal trees).
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 2. How does the origin of life take place through non living objects?
Answer:
Chemical Origin of Life from non-living objects :
The formation of complex organic molecules from simpler inorganic molecules through chemical reactions in the ocean during the early history of the earth is known as chemical evolution.
The first theory of chemical evolution is given by Oparin and Haldane. According to them, the first formed molecules were small carbon-containing compounds like formal- dehyde and hydrogen cyanide. The small molecules reacted to form sugar, amino acid and nitrogen bases. Small molecules linked together to form nucleic acid and protein. They had ability of self-replication to form first living entity. Oparin suggested that organic compounds could have undergone a series of reactions leading to more complex molecules and forming ‘Coacervates’. It absorb and assimilate organic compounds from environment and became the first life form. The theory of abiogenesis has been proved experimentally by Stanley Miller. He created electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH,, H,, NH, and water vapour at 800°C. He observed formation of Amino Acid. In similar experiments, others observed formation of sugar, nitrogen bases, pigment and fats. For the emergence of life the presence of small organic molecules is not sufficient. There must be assortment of macro molecules including enzymes, proteins and nucleic acid having the self-replicating property. Synthesis of RNA monomers that can be formed from simpler precursor molecules.
Reproduction and energy processing are the two important properties of life forms. Protocells are vesicles fluid-filled compartments can be produced spontaneously when lipid and other organic molecules are added to water. It may be said that the protein coacervates are believed to have given rise to the first living organism.
Photosynthetic organisms are believed to have evolved near about 3500 million years ago. These primitive organisms released oxygen to the atmosphere as a byproduct of photosynthesis. The free oxygen in the atmosphere prevented the abiotic origin of life. So, it can be concluded that life did not evolve from the inorganic substances rather it arose from the pre-existing living organisms.
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Wbbse Solutions In Bengali
Question 3. What are the sources of variation of life? Explain.
Answer:
Sources of Variation in life :
Generally, no.two members of a population are exactly alike. The differences of characteristics between members of the same species are called variation. It is the raw material for evolution. Variation is observed both at the phenotypic level and at the genotypic level.
There are five basic mechanisms which cause variation at the genetic level. These are mutation, recombination, gene migration, genetic drift and natural selection.
Mutation :
A sudden heritable change in the characteristics of the organism. Mutation not only creates variation but also helps in maintaining variations within population. It also introduces new genes and alleles into the gene pool. The variability of genes in a gene pool becomes the raw material for evolutionary change.
Recombination :
Combining of two different genes which in future provide new genes. It takes place due to independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis, crossing over and fertilization. Recombination acts as an agent of evolution.
Genetic drift :
The random changes in the allele frequency which is caused by chance alone are called genetic drift.
Natural Selection :
Selection is the consistent differences in the contribution of various genotypes to the next generation. It favours adaptation as a product of evolution.
Gene migration :
Sometimes few populations are completely isolated from the other population of the same species. If the migrating organisms breed within the new population, then the immigrants will transfer new alleles to the local gene pool of the host population. This is called gene migration.
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Wbbse Solutions In Bengali
Question 4. What are the different branches of Biology ? Define them.
Answer:
Biology :
Biology is mainly divided into two major branches, Botany and Zoology. In addition to these two broad categories, biology is divided into many other branches of study.
 Biochemistry :
Biochemistry :
It is a complementary branch of biology. Chemical combination and their reaction in the protoplasm are guided by the principles of chemistry. Synthesis and functions of enzymes, hormones, etc. can be explained from the knowledge of chemistry.
Histology :
Deals with the structure and composition of tissue.
Genetics :
Branch of biology deals with the heredity and variation of living organisms.
Anatomy :
Deals with the gross structure of internal organs which can be seen with the naked eye.
Physiology :
Study of various life procecses in the living organism.
Ecology :
Study of reciprocal relationship between the organism and their environment.
Evolution :
The study of the descent of recent, more complex, advanced type of organism from simpler, earlier and primitive type, over a period of time.
Immunology :
The science that deals with the phenomena and causes of immunity(defence against diseases)
Molecular Biology :
Study of shape, organization.and orientation of molecules that make the cellular system as a unit.
Question 5. Write the application of physics, chemistry, mathematics, computer in biology.
Answer:
Biophysics :
A new branch of science developed with the-collaboration of physics with biology. Physiological proceses like osmosis, diffusion occuring in the living body can be explained with the help of physical science. Microscope is a very important instrument for the biologist in the contribution of physicist.
Biometrics :
This new branch has been developed from the knowledge of mathematics. Problems of growth, size of population and other various concepts of biology can be explained with the principles of mathematics.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Cybernetics :
This branch has been formed in collaboration of biology with that of technology. The cyber-world provides the information regarding the gene and protein sequence that can be utilised by genetic engineers in developing transgenic organisms.
Question 6. Write the application of Biology in Agriculture, Medicine, Space Science and in other fields.
Answer:
The application of Biology in Agriculture, Medicine, Space science and in other fields: In agriculture :
Agricultural production gradually increased by the application of modern tools and techniques. The expansion of land for cultivation, increase of irrigation facilities, improved varieties of seed, crop rotation, using fertilizers, the productivity of crop increased. Improvement of crops in quality and quantity has been done by hybridization technique. It caused green revolution in India. New breeds are also developed by mutation method. Micropropagation method is also applied for the improvement of crops. Production of seedless fruits is the gift of biology.
In medicine :
Experimentation and research in biological field help us to know about different types of diseases, their pathogen, symptoms, mode of transmission and control methods. Serums, vaccines, hormones which are used in many of the diseases of man, are produced from animal body. Discovery of antibiotics and vaccines are not possible without the knowledge. Primary knowledge and the progress of the surgery largely depend on the animals. Cloning of organs, organ transplantation, Bypass surgery are possible only with the help of biology.
In Space Science :
During exploration of the planet, Cosmonauts keep the green alga chlorella in the space craft for oxygen and food. Space biology is very useful in the field of space research. It deals with the behaviour of living organism in outer space.
Forensic Science :
Scientific knowledge about DNA finger prints, blood typing are applied to deal with criminal activities, civil and criminal laws, solving the issue of paternity problem, can be used to detect a person killed in plane crash by analyzing DNA recovered from the ash.
Biotechnology :
Biotechnology is an integrated application of knowledge and technique of biochemistry, microbiology and genetics to derive benefit in the technological level involving microorganism.
It has area of recombinant DNA technology in gene cloning , producing vaccine, enzyme, interferon waste treatment, producing fuels, producing vitamins antibiotics, producing transgenic plants and animals.
Question 6. Write very brief history regarding the birth of modern taxonomy.
Answer:
History regarding the birth of modern taxonomy
Vedic literature mentions 740 plants and 250 animals. Susruta Samhita has classified animals into oviparous, viviparous, herbivores, carnivores, while plants have been divided into herbs, shrubs, trees, creepers. Hippocrates divided animals into groups like insect, bird, fishes and whales. Aristotle (384-322 BC) divided living being into animals, plants and human being. He is the father of “zoology”. Theophrastus (370-285 BC) is considered as the “Father of Botany”. He classified 480 plants is Historia plantarum, in herb, undershrub, shrub and trees. John Ray (1627-1705) proposed the concept of species as basic unit. Carolus Linnoaeus (1707-1778) is known as the “Father of taxonomy” and “Father of Nomenclature”. He introduced the system of binomial nomenclature.
Modern taxonomy considers a species to be product of evolution. It takes into consideration traits and evidences from all types of studies like morphology, anatomy, cytology, physiology, genetics, biochemistry, etc. The concept was developed by Julian Huxley (1940)
Question 7. Explain the 7 steps of taxonomic hierarchy.
Answer:
7 steps of taxonomic hierarchy
Arranging various taxonomic units in their proper descending order on the basis of their taxonomic ranks, is called taxonomic hierarchy.
In this hierarchy, the kingdom represent the category of the highest rank, while the species represent the category of basic rank. It consists of
(1) species — basic unit of classification
(2) genus — a group of closely related species
(3) family — it is an assemblage of closely related genera
(4) order — itis a taxonomic unit formed by grouping together the closely related families.
(5) class — the order of plants and animals constitute class.
(6) divison — the class together constitute Division in plants and Phylum in animals.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Important Questions With Answers Wbbse
Question 8. Write the systemic position of Human and Mango.
Answer:
systemic position of Human:
Kingdom — Animalia
Phylum — Chordata
Class — Mammalia
Order — Primate
Family — Hominidae
Genus — Homo
Species — Sapiens
Systemic position of Mango:
Kingdom — Plantae
Division — Spermatophyta
Subdivision — Angiospermae
Class — Dicotyledonae
Ordar — Sapindales
Family — Anacardiaceae
Genus — Mangifera
Species — indica
Question 9. Explain briefly binomial nomenclature with an example.
Answer:
B inomial nomenclature with an example
A system of nomenclature in which the scientific name of an organism consists of two parts, first part is the generic name and the second part is the specific name.
Eg : Gossypium herbaceum (cotton). Here Gossypium is the generic name and herbaceum is the specific name.
This system of nomenclature was introduced by Carolus Linnaeus in 1753 in his book “Species Plantarum”.
Generic name should come first and must begin with capital alphabet. Specific name should begin with small alphabet. The scientific name must be either underlined or written in italics. The name of the author who first decribed the species should be written in specific name.
eg. Homo – spiens linnaeus
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 10. Write the significance of Binomial Nomenclature.
Answer:
Significance of Binomial Nomenclature :
(1) The system proved to be so convenient that it was universally accepted by the Biologist and approved by the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN).
(2) It has avoided the confusion usually created by the usage of local name.
Question 11. Name five kingdoms of life.
Answer:
Five kingdoms of classification were proposed by R.H. Whittakar (1969).
There are three main criteria for this classification :
(1) Complexity of cell structure
(2) Complexity oforganism
(3) Mode of nutrition DNA strand Plasmid
The five kingdom of life are :-
(1) Monera
(2) Protista
(3) Plantae
(4) Fungi
(5) Animalia
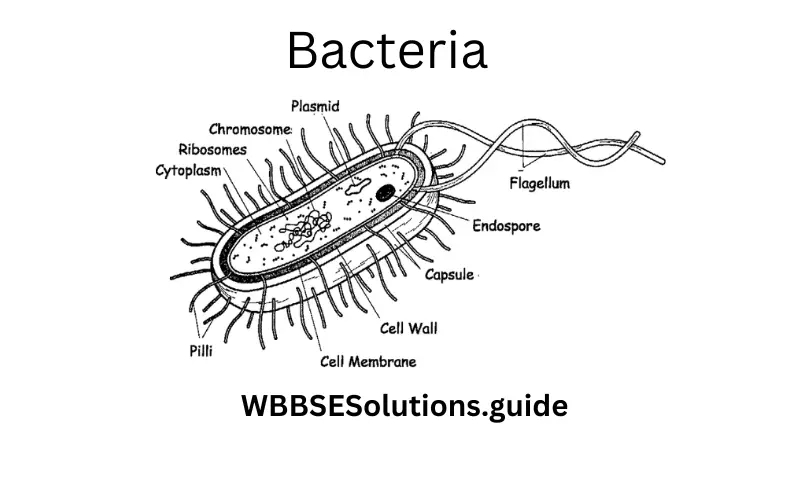
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Important Questions With Answers Wbbse
Question 12. Write three salient features of Monera.
Answer:
Three salient features of Monera
(1) Prokaryotes with incipient unorganised Nucleus
(2) Absence of membrane-bound cell organelles
(3) Rigid cell wall composed of polysaccharide units eae eal
(4) They are useful as well as harmful.
Example — Bacteria and Cyanobacteria. Baden
Question 13. Write three salient features of Protista.
Answer:
Three salient features of Protista
(1) Unicellular organism.
(2) Cell organization — Eukaryotic
(3) Presence of membrane-bound cell organelles
(4) Presence of Mitosis, Meiosis and Sexual reproduction in life cycle.
Example — Amoeba, Paramoceium, Diatoms.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Life And Its Diversity Mcq With Answers
Question 14. Write three salient features of Fungi.
Answer:
Three salient features of Fungi
(1) Multicellular organism (yeast is unicellular)
(2) Eukaryotic heterotrophs
(3) Cell wall of fungal cellulose (Chitin)
(4) Reserve food is glycogen
(5) Nutrition by absorption
(6) They are useful as well as harmful and Cause diseases in plants, animals and humans.
Example — Yeast, Mushrooms, Puccinia.
 Question 15. Write the features of kingdom – Plantae and Animalia
Question 15. Write the features of kingdom – Plantae and Animalia
Answer:
(1) Multicellular
(2) Eukaryotes with Cellulose walls
(3) Photosynthetic organism. (Producers)
(4) Main source of oxygen, organic food and food energy for all organisms.
Example :- Algae, Bryophyta, Angiosperms
Features of kingdom-Animalia
(1) Multicellular, Eukaryotic organism.
(2) Consumers with heterotrophic, holozoic nutrition
(3) Presence of locomotory organs
(4) Tissue system – such as muscular, nervous, etc.
Example — worms, insects, birds, mammals.
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 16. What are the characteristics of Algae ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Algae
(1) Simplest multicellular green plants
(2) Mostly aquatic-fresh as well as marine water
(3) Having chlorophyll, so main aquatic producer
(4) Mostly filamentous, branched or unbranched
(5) Thallus like body, not differentiated into root, stem and leaf.
(6) Based on photosynthetic pigment, classified as-
Chlorophyceae (green alge)
Phaeophyceae (Brown alge)
Rhodophyceae (Red alge)
Question 17. Write the main features of Bryophyta.
Answer:
Characteristics of Bryophyta :
(1) First group of land plants
(2) Non-vascular and non-flowering plants
(3) known as amphibians of plant kingdom.
(4) Plant body small, green, delicate.
(5) Plant body differentiated into leaf and stem
(6) Rhizoides on lower surface for fixation and absorption. True roots are absent.
(7) Reproductive organs are Antheridium (male) and Archegonium (female organ)
(8) Alternation of generation takes place.
Example — Riccia, Marchantia, Mosses, etc.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Mcq With Answers
Question 18. Write the characteristics of Pteriolophyta.
Answer:
Characteristics of Pteriolophyta
(1) First group of vascular land plants
(2) Non-flowering vascular embryophytes
(3) Presence of True roots, stem and leaves.
(4) Small, herbaceous or shrub like independent plant body.
(5) Xylem without vessels and phloem without sieve tube.
(6) Reproduction by vegetative, asexual and sexual method.
(7) Presnce of alternation of generation.
Example — Lycopodium, Selaginella
Question 19. What are the characteristics of Gymnosperm ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Gymnosperm
(1) Flowering plants (Phanerogams)
(2) Plants with naked seed.
(3) Plant body is adult sporophyte, mostly trees.
(4) Well-developed vascular tissue, xylem without vessel and phloem without Sieve tube and companion cell.
(5) Leaves mostly dimorphic —green photosynthetic foliage and non-green small scaly leaves.
(6) Stem woody and branched (except cycas).
(7) Presence of Cones, male and female separate.
(8) Alternation of generations present.
Example — Cycas, Pinus, Ephedra.
Question 20. What are the characteristics of angiosperm ?
Answer:
Characteristics of Angiosperm—
(1) Most evolved and specialized group of plant kingdom.
(2) Flowering plants, bears fruits.
(3) Flower as reproductive organs with closed carpel.
(4) Double fertilization and triple fusion.
(5) Well-developed conducting tissue-xylem & phloem.
(6) More complex and better adapted for terrestrial condition.
(7) Distinct alternation of generations.
(8) Classified into Dicotyledones and Monocotyledons.
Question 21. Write the differences in Monocot and Dicot plants.
Answer:
Differences in Monocot and Dicot plants
| Monocots | Dicots |
| 1. Adventitious root system. | 1. Tap root system. |
| 2. Parallel venation in leaf. | 2. Reticulate venation. |
| 3. Always alternate Phyllotaxi. | 3. Alternate , opposite or whorled. |
| 4. One cotyledon. | 4. Two cotyledones. |
| 5. Trimerous flower. | 5. Tetra or pentamerous flower. |
| Eg : maize, wheat, rice, coconut. | Eg : chinarose, mango, neem. |
Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Question Answer WBBSE
Q.22. Write down the characteristics of Phylum Protozoa.
Answer:
Phylum — Protozoa:
Characteristics —
(1) There are minute, mieroscopic in size and can not be seen with the naked eyes.
(2) These are unicellular or acellular or non – cellular,
(3) They may be free-living or parasite.
(4) Protoplasm is distinguished into outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm.
(5) Nucleus may be one, two-or many in different protozoans.
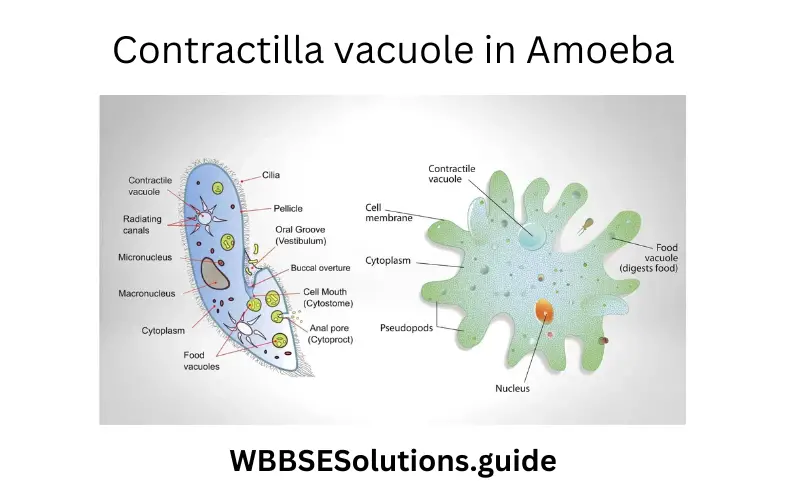 (6) Locomotory organs are pseudopodia, flagella and cilia.
(6) Locomotory organs are pseudopodia, flagella and cilia.
(7) Nutrition may be holozoic.
(8) Respiration takes place through the general surface of the body.
(9) Excretion takes place either through general surface of the body or through contractile vacuole.
(10). Respiration may be asexual or sexual or both.
Example — Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Plasmodium.
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Wbbse Notes
Question 23. Classify animal kingdom.
Answer:
Classification of Kingdom Animalia :
The animal kingdom is divided into two subkingdoms : Non-chordata and Chordata
| Nonchordata | Chordata |
| 1. Notochord is absent. | 1. Notochord is present. |
| 2. Visceral cleft is absent. | 2. Visceral cleft present in pharynx. |
| 3. Central nervous system ventral solid,double. | 3. Central nervous system dorsal, hollow, tubular. |
| 4. Heart is dorsal. | 4. Heart is ventral. |
| 5. Tail is unsegmented. | 5. Post anal, metamerically segmented tail. |
Question 24. Write down the characteristics of Porifera.
Answer:
Phylum — Porifera :
1. These are sedentary. found in water. f Outgoin
2. These are multicellular animals but cellular level of organisation.
3. Body bears numerous minute pores, the ostia.
4. Skeleton is made up of calcareous spicules and of sponge in fibres.
5. Respiration, excretion, nutrition takes place with the help of water current.
6. sexual reproduction takes place by budding or gemmules.
7. Sexual reproduction by gamets, i.e., sperm and ova.
8. They have the power of regeneration.
Example — Spongilla, Scypha, Euplictella.
Question 25. Write down the characteristics of Cnidaria.
Answer:
Phylum—Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
1. Multicellular animals with tissue grade of organisation.
2. They are radially symenetrical and diploblastic.
3. Organs are entirely absent.
4. Digestion is partly intracellular, partly extracellular.
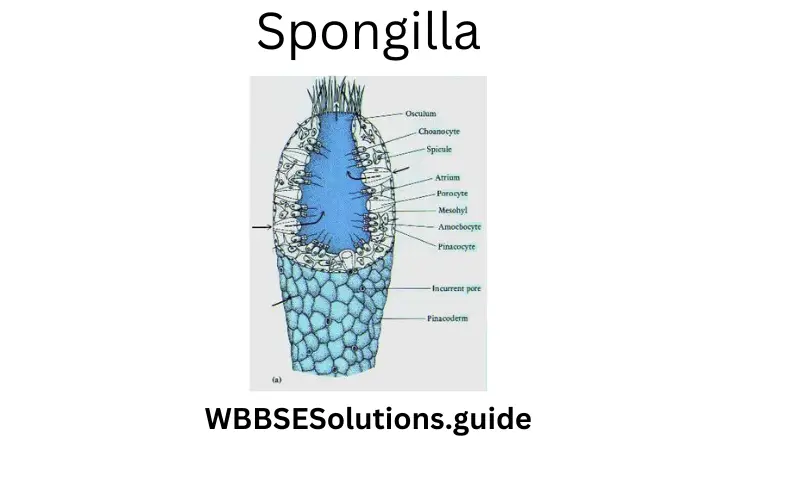 5. Coclenteron represents the digestive tube.
5. Coclenteron represents the digestive tube.
6. Nervous system is primitive.
7. Their skeleton forms corals and coral reefs. :
8. Special stinging cells called Nematoblasts or Cnedoblist are present in groups in tentacles. These are used for food capture and defence.
9. Reproduction takes place by budding and games.
Example — Hydra, Sea anemone, Physalia, Aurelia,
Life And Its Diversity Class 9 Wbbse Notes
Question 26. Write down the characteristics of Platyhelminthes.
Answer:
Phylum — Platyhelminthes :
1. Acoelomate (true body cavity absent).
2. Organ level of organisation.
3. Bilateral symmetry, dorsoventrally flattened.
4. Excretory organs are flame cells.
5. Skeletal, criculatory or respiratory organs are absent.
 6. Hermaphrodite animals.
6. Hermaphrodite animals.
7. Nervous system is represented by a pair of anterior ganglia and 1-3 pairs of longitudinal nerve cords.
Example — Liver fluke, Tapeworm.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Question and Answers
Question 27. Write down the characteristics of Aschelminthes.
Answer:
Phylum — Aschelminthes:
1. Multicellular, long, cylindrical, unsegmented worms.
2. Bilateral symmetry and Triploblastic.
3. They are Pseudocoelomate i.e. a coelom without lining of mesoderm.
4. Circulatory and respiratory organs are absent.
 5. Excretory organs are protonephridia.
5. Excretory organs are protonephridia.
6. Sexes are separate, i.e., dioecious.
7. Digestive system are mouth, pharynx and intestine.
8. Most of them are parasites. “Ascaris
Example — Ascaris, Filaria worm.
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 1 Long Questions With Answers
Question 28. Write down the characteristics of Annelida.
Answer:
Phylum — Annelida:
1. These are elongated, cylindrical, triploblastic and metamerically segmented worms.
2. Organ system level of organization.
3. Locomotory organs are Setae.
4. True coelom present (coelomate).
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Question and Answers

5. Circulatory and nervous system are present.
6. Excretory organs are Nephridia.
7. May be unisexual or bisexual. Earthworm
Example — Earthworm, Neries, Leech.
Question 29. Write down the characteristics of Arthropoda.
Answer:
Phylum — Arthropoda-
1. It is the largest and comprises of about 80% of the total species of the animals.
2. These are multicellular, triploblastic, bilateral symmetry.
3. Coelom is filled with blood (haemocoel).
4. Jointed legs.
5. Exoskeleton is in the form of chitin.
6. Body vascular system is open type.
7. Excretion takes place through green gland and malpighian tubules.
8. Well developed nervous system.
9. Usually dioecious.
10. Body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
Example — Cockroach, Grasshopper, Dragonfly.
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Question and Answers
Question 30. Write down the characteristics of Mollusca.
Answer:
Phylum — Mollusca
1. Body is soft with variable shapes.
2. Triploblastic, bilateral symmetry and Coelomate.
3. Mantle, a thin fold of integument, serves respiration and protection.
4. Alimentary canal is complete.

5. Open type of circulatory system
6. Respiratory organs are ctenidia, gills, mantle and air sacs.
7. Excretion takes place by kidneys.
8. Well-developed Nervous system with a pair of ganglia and nerves.
Exampie — Octopus, Snail, Oysters, Cuttlefish.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Solutions
Question 31. Write down the characteristics of Echinodermata.
Answer:
Phylum — Echinodermata
1. It includes the animals which bear spine-like structures on their integuments.
2. Triploblastic and coelomate.
3. Organ system level of organisation.
4. Integument with calcareous spines.
 5. Simple nervous system.
5. Simple nervous system.
6. Respiration through tube feet, respiratory tree and brutal.
7. Sexes separate and possess power of regeneration.
Example — Starfish, Sea cucumber, Sea urchin
Class 9 Life Science Life And Its Diversity Short Questions And Answers Wbbse
Question 32. Write down the characteristics of Phylum Chordata and their classes with example.
Answer:
Phylum — Chordata :
1. Presence of notochord.
2. Paired gill slits are present at any stage of life.
3. Dorsal tubular nerve cord is always present.,
Phylum chordata has been divided into five classes :
West Bengal Board Class 9 Life Science Question and Answers
 1. Class — Pisces
1. Class — Pisces
(1) Aquatic animals, fresh water as well as marine
(2) Cold blooded or Poikilo thermic
(3) Gills for respiration
(4) Exoskeleton in the form of scales or bony plates
(5) Paired and unpaired fins for locomotion
(6) Two chambered heart, oviparous
 (7) lateral line sence organ present.
(7) lateral line sence organ present.
Example — Scoliodon, Shark, Labeo, etc.
2. Class — Amphibia
(1) Cold blooded animals, skin is soft, moist and glandular
(2) Eyelids are movable and nictitating membrane is present
(3) RBC are nucleated
(4) Respiration takes place through skin, buccal cavity and lungs
(5) External ear is absent. Oviparous animals.
Example — Frog, Toad, Salamander. 3. Class — Reptilia
3. Class — Reptilia
1. Cold blooded animals, body is covered with Cornified skin.
2. These are tetrapods (having four legs) and Pentadactyle (having five fingers).
3. Lungs for respiration but in certain turtles cloacal respiration.
4, Internal fertilisation, mostly oviparous.
Example — Lizard, Snake, Turtle, Tortoise.
4. Class — Aves.
1. Warm blooded vertebrates
2. Arboreal habitat
3. Fore limbs modified for flying and hind limbs for walking.
4. Four chambered heart
5. Hollow bones, one ovary absent.
 Example — Duck, Pigeon.
Example — Duck, Pigeon.
Class 9th Life Science WBBSE
5. Class — Mammalia
1. Constant body temperature
2. Hair, ear pinna, mammary glands are present
3. RBC non-nucleated except camel
4. Four-chambered, well-developed heart
5. Viviparous — give birth to young ones
6. Internal fertilization.
7. The mother suckles her young ones on milk secreted by special glands called mammary glands.

Example — Cat, Dog, Monkey, Man, Tiger.
Wbbse Life Science Class 9 Chapter 1 Long Questions With Answers
Question 33. Discuss about the metabolism property of living organisms. What is irritability ?
Answer:
Metabolism :
The sum total of the biochemical changes involved in a two-fold process of waste and repair of the protoplasm is known as metabolism. The constructive anabolic phase is the one in which complex substances are formed and the destructive, catabolic phase is the one where substances are broken down and discharged. These processes occur constantly within the protoplasm of living organisms, where uptake and use of energy occurred.
The constructive (repair) phase is one in which food materials are built up into more complex substances and the process is known as anabolism, (GK, Ana = upper, balls = throw), while the other phase (waste) is destructive and is known as catabolism (cata =below, balls = throw). For instance, photosynthesis is an anabolic process in which sugar is formed in the cell and potential energy is captivated within the sugar molecule. Respiration is a catabolic process in which the captivated potential energy is released from the sugar molecule as kinetic energy with the oxidation of the sugar molecule.
Irritabillity :
The capacity to respond through internal changes to various exciting agents is commonly known as irritability. The changed environmental condition which excites responds to the living organism is known as stimulus, during which a living body reacts called as response. Thus the ability of living body in responding is known as irritability.
Question 34. What are the applied branches of biology ?
Answer:
Emergence of new branches of Biology :
Biology has enormous applications in other branches of science. It forms an important part of —
(1) Veterinary science — It deals with treatment and surgery of animals.
(2) Marine biology — It deals with the study of life in the sea.
(3) Horticulture — It deals with science of growing flowers, fruits, vegetables, ornamental plants.
(4) Sericulture — It is the technique of producing silk by rearing silkworms.
(5) Pisciculture — It deals with technique of growing fish.
(6) Cloning — It is the rapidly advancing branch of biotechnology introducing a body cell for producing an individual.
(7) Molecular biology — It is the science which deals with interpreting biological events in terms of the molecules in the cell.
(8) Biotechnology — It deals with the application of biological processes in technology such as biogas production from organic wastes; production of insulin through bacteria.
(9) Space biology — It the study of problems of living things in outer space.
(10) Nuclear biology — It is the study of effects of radioactivity on living things.
(11) Bioengineering — It include techniques like making of artificial limb, joints and other parts of from metals or plastic.
Question 35. Discuss the application of biology in genetics.
Answer:
In genetic engineering programmes, mapping of the whole genome of an organism has been possible. Synthesis of many products was possible through genetically engineered cells. Recombinant DNA technology aided in detecting genetic diseases and its cure. Production of vaccines of malarial and viral diseases; production of hybrid plants using protoplast fusion techniques through intergeneric crosses, production of encapsulated seeds, disease-resistant plants, herbicides, stress-resistant plants, essential oils, alkaloids, pigments are possible now. Use of biofertilizers resulted in greater yield of agricultural crops. Bacterial plasmids are being used to abate pollution, treat sewage and domestic wastes.
These plasmids are capable of degrading complex polymers into non-toxic forms. Technologies have been developed to seek an alternative source of energy from biomaterials generated from agricultural, industrial, forestry and municipal sources. Plant weeds are being used for production of biogas used for cooking and lighting purposes.
Tissue culture techniques help in culture of micro-organisms or plant or animal cells or tissues and organs in artificial media. Gene technology is used in the production of recombinant DNA and gene cloning. The use of insulin for diabetes and interferon for treatment against some tumour viruses has been possible. Monoclonal antibodies are used for diagnosis of various diseases. DNA fingerprinting and auto-antibody finger printing are used in the identification of criminals in murder and rape cases. Biotechnologists are producing organic compounds the ethanol, acetone, butanol, gluconic acid, enzymes, antibiotics like penicillin, streptomucin. Microbes are developed to be used as biopesticides and biofertilisers.
Application of gene therapy, anmniocentesis, genetic counselling cloning have gained importance in the present millennium. Using transgenic technique a genetic disease may be cured. Amniocentesis technique may be applied to understand the chromosomal abnormality of the foetus.
Class 9th Life Science WBBSE
Question 36. Mention the rules of writing scientific name of an organism.
Answer:
Rules of Nomenclature :
The following conventions of nomenclature may be noteworthy :
(1) Names given to plants or animals prior to publication of ‘systema nature! (10th edition) are not acceptable.
(2) Names should be written in Latin or its derivative.
(3) Both the genetic and specific names must be written in Italics, the genus starts with a capital letter and the species begins with a small letter, e.g., Solanum tuberosum (Potato).
(4) The specific name is usually a descriptive one, e.g., Hygrophilia spinosa (a plant with spines).
(5) Only a single valid name for each kind of organism is permitted. When two or more names are given correctly to a plant or animal, then the name used by the first author (the author who described the plant or animal first) is approved and the others would be treated as synonyms. This is known as the Law of Priority.
(6) The species must be mentioned for a newly established genus.
(7) The name of the author who first described a species is also added to an abbreviated from after the name of the species, e.g. Mangifera indica Linn. Here Linn. refers to the author Linnaeus who first described the species.
(8) In case of animals the suffix-idea must be added to the family name and suffix-inae to the sub-family name.
Question 37. Discuss the salient features and examples of the subphylums cephalochor data (Acraniata) and Vertebrata (Craniata).
Answer:
Subphylum Cephalochordata (Acranita) :
Salient features :
1. Notochord extends from head to tail.region and is persistent throughout life.
2. Fish like marine animals.
3. ‘V’ shaped myotome muscles are present.
Example : Amphioxus sp, Asymmetron sp.
Subphylum Vertebrata (Craniata) :
Salient features :
1. Presence of endoskeleton made of bones and cartilages.
2. Presence of cranium or brain box that accommodates brain.
3. Presence of dorsal vertebral column formed of vertebrae.
Example : Shark, Rohu, Frog, Lizard, Birds, Guineapig, etc.
Wbbse Class 9 Life Science Chapter 1 Solutions
Question 38. Compare any three features of all the five kingdoms of life.
Answer:
Comparing features of all the five kingdoms of life
| Monera | Protista | Fungi | Plantae | Animalia | |
| 1. Nature of | Prokaryotic | Eukaryotic, | Plant body | Multicelluar, | Multicellular. |
| of Cell and | unicellular, | unicellular | of fungi called | most of them | heterotrophic, |
| cellular orga- | may be | may be | mycelium made | are chlorophyll | eukaryotes. |
| nization | filamentous | colonial | up of fine thre- | containing | cell wall |
| Membrane | cell wall | ads called hyp- | autotrophic | absent. | |
| bound cell | present, | hae, cell wall | eukaryotic | ||
| organelles | some | made up of fu- | cell wall | ||
| absent,e.g. | protists, | ngal cellulose | composed of | ||
| Mitochondria | or chitin | cellulose, | |||
| Golgi bodies, | Multicellular | single central | |||
| etc. | achlorophyllous | vacuole | |||
| In case of | present, | ||||
| Mycoplasma | cell organelles | ||||
| Cell well absent | present, are | ||||
| Instead of cell- | all double | ||||
| ulose cell wall | membraned. | ||||
| is made up of | |||||
| Peptidoglycan | |||||
| or murein | |||||
| 2. Metabolic process | Both | In unicellular | Heterotrophic, may be | Autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
| autotrophic | algae photosynthetic | may be | organisms, | Mode of | |
| and hetero- | nutrition occurs, | decomposers | can able to | nutritiond | |
| trophic mode | e.g. Dinoflagell | or saprophytes | photosynth- | generally | |
| of nutrition | ate. In Amoeba | a few may be | esize | holozoic. | |
| noted. | holozoic and in | parasite. | |||
| Entamoeba | |||||
| absorptive | |||||
| nutrition are noted | |||||
| 3. Ecological role | Some of | Dual nutrition | Live their lives | Lot of diveris- | Include large |
| them are | noted called | as saprophytes | ity noted grows | variety of | |
| nitrogen | mixotrophic | or parasites, | on different | animals, living in | |
| fixing; some | nutrition, | saprophytic | habitats act | different | |
| Monerians | they are | fungi derive | as producers | environments act | |
| perform the | called as | their food | as consumers. | ||
| functions of | plant animal. | matter from | |||
| ammonifica- | dead, decaying | ||||
| tions, | organic matters | ||||
| nitrification | |||||
| and denitrifi- | |||||
| cation. | |||||
| Two common | Bacterium | Paramaecium | Penicillium | Pinus, Hibiscus | Earthworm Human |
| examples | Anabaena | Euglena | Aspergillus | (China rose) | (Homo sapiens) |
Question 39. Discuss the salient features and examples of divisions Agnatha and Gnathos tomala.
Answer:
Division Agnatha :
(A = without; ganathos = Jaw)
(Jawless animal)
Salient features :
1. Mouth is circular (Cyclostomata : Cyclos = circular; stoma = mouth).
2. Absence of jaws surrounding mouth.
3. No paired fins and fins are without fin rays.
Example : Lamprey (Petromyzon marinus )
Hag fish (Myxine glutinosa)
Division Gnathostomata :
(Gnathos = Jaw; stoma = mouth)
(Animals with jaw)
Class 9th Life Science WBBSE
Salient features :
1. Mouth is guarded by upper and lower jaw.
2. Skeleton is mostly made of bones.
3. Respiration occurs by gills or lungs.
Example: Fish, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia.
Class 1. Chondrichthyes (Gr. chondros = Cartilage; icthyes = Fish)
(Fishes having cartilaginous skeleton)
Salient features :
1. Endoskeleton completely cartilaginous; bone absent.
2. Gill slits are without aperculum; mouth ventrally placed.
3. Marine animals where body is covered with placoid scales; no air bladder.
Example : Dogfish/shark (Scoliodon sp.)
Sting ray (Trygon sp.)
Electric ray fish can cause electric shock for defence.
Class 9 Life Science Life And Its Diversity Short Questions And Answers Wbbse
Question 40. Explain the basis of classification of animals.
Answer:
Basis of Classification of Animals : A few fundamental bases of classifying animals are given below.
I. Levels of Organization :
(1) Cellular level :
In case of cellular-level organization, a single cell is responsible for all the metabolic activities. Cellular level organization is present in some of the animals like sponges.
(2) Tissue level :
In case of tissue-level organization, a group of cells is responsible
for all the metabolic activities, e.g. cnidarians.
(3) Organ level :
In case of organ-level organization, some specialized organs are
present for some specific functions, e.g. platyhelminthes.
(4) Organ System level :
In organ system level organization, complex organ systems are present for various functions, e.g. mollusca, chordate.
II. Symmetry :
(1) Asymmetrical :
Some of the animals are almost asymmetrical. Their body cannot
be divided into two equal halves from any plane, e.g. sponges.
(2) Radial Symmetry :
In case of radial symmetry, any plane passing through the
central axis divides the body into two identical halves, e.g. cnidarians, oo sae echinoderms, etc.
(3) Bilateral Symmetry :
In case of bilateral symmetry, the body can be divided into two identical halves only through a single plane, e.g. annelida, arthropoda, etc.
III. Body Organization :
1. Diploblastic :
When the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, the animal is called a diploblastic animal. The two layers are——ectoderm and endoderm.
Example : cnidarians :
Class 9th Life Science WBBSE
2. Triploblastic :
When the cells are arranged in three embryonic layers, the animal is called triploblastic animal. The three layers are——ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Examples : platyhelminthes to chordates.
IV. Coelom :
The body cavity which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals may be-
(1) Coelomates :
If coelom is present, the animal is called coelomate, e.g. annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates.
(2) Pseudocoelomates :
If the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm but the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ect oderm and endoderm, the animal is called pseudocoelomate, e.g. aschelminthes.
(3) Acoelomates :
When the body cavity i is absent, the animal is called acoelomate, e.g. platyheminthes.
V. Notochord :
Notochord is a mesodermally derived rod-like structure. It is formed on the dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals.
(1) Chordates :
If notochord is present then the animal comes under chordates.
(2) Non-Chordates :
An animal without notochord is called non-chordate, e.g. porifera to echinoderms.
Question 41. Distinguish between Algae and Fungi.
Answer:
Difference between Algae and Fungi
| Alagae | Fungi |
| 1. Mostly aquatic, some are terrestrial. | 1. Mostly terrestrial, some are aquatic. |
| 2. Light is necessary for their growth. | 2. They can grow either in presence |
| or absence of light. | |
| 3. Algae possess chlorophyll in addition | 3. Fungi do not possess chlorophyll |
| to other pigments. | and other pigments. |
| 4. Algae are autophytes. | 4. Fungi are heterophytes. They may |
| be either parasite or saprophyte. | |
| 5. Body is composed of parenchymatous | 5. Body composed of pseudoparenc- |
| tissue. | hymatous tissue, made up of fine tub- |
| ular hyphal cells. | |
| 6. The principal cell wall material is cellul-ose. | 6. The principal cel wall material is ctutin. |
| 7. Algal body may be unicellular or mul- | 7. Fungal body may be unicellular or |
| ticellular. In case of multicellular algae, the | multicellular. In case of miriticellular |
| filamentous body may be unbranched | fungi, the body is composed of myceli- |
| or branched. | um. Hyphae collectively forms mycel- |
| ium. | |
| 8. Starch is the main storage food. | 8. Glycogen is the main storage food. |
Question 42. Distinguish between Bryophta and Pteridophyta.
Answer:
Difference between Bryophta and Pteridophyta
| Bryophyta | Pteridophyta |
| 1. Non- vascular cryptogamic plants. | 1. Vascular cryptogamic plants. |
| 2. Plant body is the ha plod (n) garn- | 2. Plant body is the diploid (2n) sporo- |
| et ophyte. | phyte. |
| 3. Gametophytic plants possess rhizoids. | 3. Gametophtic plant does not possess |
| rhizokJs, except certain Ptendophytes | |
| (eg- Dryoptens). | |
| 4. Sporophytic plants are not differen- | 4. Sporophytic plants differentiated into |
| tiated into root, stem and leaves. | root, stem and leaves. |
| 5. Sporophytcs are always dependent | 5. Sporophytcs are always independent. |
| upon the gametophyte. |
Question 43. Distinguish between Angiosperms and Gymnosperms.
Answer:
Difference between Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
| Angiosperm | Gymnosperm |
| 1.The reproductive organ of angiosperm | 1. The reproductive organ of gymnosperm is cone |
| is flower; it is composed of calyx, corolla, | or stroWus. Flowers are unisexual and naked, |
| ardroeoum and gynoedum. Rowers are | calyx and corolla absent. Perianth generally |
| unisexual or bisexual. Perianth may be present. | absent, exception – Gnetum. |
| 2. In case of unisexual flower, calyx, co- | 2. The male flower (mate cone) of gymnosperm |
| rolla and androedum or gynoedum and | is composed of only microsporophyll equivalent |
| in case of txsexual flower calyx, coroia, | to stamen and the female flower 6 composed of |
| andrcedum and gyncecium are present. | only megasporophyll equivalent to carpel. |
| The microsporophyils are compactly arranged | |
| spra&y over a central axis formrg a cone like | |
| structure- the male cone and the megaspocoph- | |
| ylls in most cases are compactly arranged to | |
| form the female cone (exception-Cycas). | |
| 3. In case of angiosperms, except wind, | 3. In case of gymnosperms, poinabon occurs |
| pohnabon also occurs by means of other | only by means of wind. |
| agents. | |
| 4. The carpel s composed of ovary, style | 4. The structure of the carpel is very simple. |
| and sigma. Ovules lies within the ovary. | The carpel is not composed of ovary, style and |
| Herce seeds remain covered by fruit | stgmsa (a so called style present in Gnetum). |
| (closed seeded). One or many carpels take | The megasporangium or ovule rot formed within |
| part m the formation of fruit. | the ovary, reman exposed. Hence seeds remain |
| exposed (naked seeded). The naked seeds lies | |
| over the megasporophylls. | |
| 5. The pollen grains are transferred to the bp | 5. Due to poltnaton the mcrospores (polien grai- |
| of the stigma by help of different agents but | ns) are directly transferred into the ovule. |
| never falls over the ovules directly. The pollen | |
| tube formed from the pollen grans gradually | |
| penetrates the style and ovary and ultimately | |
| reaches the ovule. | |
| 6. The endosperm tissue formed during double | 6. Ther endosperm is haptetd (n) in gymnosperms |
| fertilization is tnploid (3n), because a hapDid | because endosperm s a part of the female |
| male gamete (n) unties with a dpkod defintve | gametophyte formed before fertilization. But |
| nucleus (2n) to form finally the endosperm. | endosperm s partly formed after fertilization m |
| case of Gnetum. |
Class 9th Life Science WBBSE Question 44.
Compare between Cnidaria and Ctenophora.
Answer:
Comparison between Cnidaria and Ctenophora :
Similarities:
1. Both of them are diploblasitc
2. Almost all of them are marine animals.
Dissimilarities:
| Cnidaria | Ctenophora |
| 1. Presence of Cnidobtast cell | 1. Presence of colloblastcetl. |
| 2. Presence of namatocyst. | 2. Presence of comb plates. |
Question 45. Compare between Platyhelminthes and Aschelminthes.
Answer:
Comparison between Platyhelminthes and Aschelminthes
Similarities:
1. Almost all of them are parasitic.
Differences :
| Platyhelminthes | Aschelminthes |
| 1. Bodytape like, Flat, | 1. Body cylindrical,elongated. |
| 2. Alimentary canal is eittar absent | 2. Alimentary canal is complete. |
| Or incomplete. | |
| 3. Mostly hermapbrotfits (bisexu&l). | 3. AH a re unisexual (sexes are separate). |
Question 46. Compare between Annelida and Arthropoda.
Answer:
Comparing between Annelida and Arthropod
| Platyhelminthes | Aschelminthes |
| 1. Body segments ring like and separated | 1. Body segments are not separated by |
| by septum. | septum. |
| 2. Body is not covered by hard exoskel- | 2. Body is covered by hard chitinous |
| eton. | exoskeleton. |
| 3. No jointed appendages. | 3. Appendages are joined with the body by arthrodial membrane. |
| Haemocoel absent, | 4. Haemocoel is present, |
| g. Earthworm, Leech. | e.g. Prawn, Cockroach. |
Question 47 Distinguish between — (a) Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes, (b) Amphibia and Reptilia.
Answer:
Difference between Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes :
| Angiosperm | Gymn-osperm |
| 1. Endoskeleton cartilaginous. | 1. Endoskeleton mostly bony, |
| 2. Mouth ventrally placed in the head. | 2. Mouth at the bp of the head. |
| 3. Air hladded abseht. | 3. Air bladder present. |
| 4. Gills not cohered by operculum. | 4. Gills covered by operculum. |
Difference between Amphibia and Reptilia :
| Amphibia | Reptilia |
| 1 Fore limb with four digits and hind limbwith five digits—digits are without claws. |
1. Both fore limbs and hind limbs are provided with five clawed digits. |
| 2 Skin glandular, naked and moist. | 2. Skin dry, with homy epidermal scales. |
| 3 Heart three chambered. | 3. Heart three and half chambered(ventricle incompletely divided); |
| only incrocodile heart is four chambered (ventricle completely divided). |
Question 48. Distinguish between Cryptogamae and Phanerogamae.
Answer:
Difference between Cryptogamae and Phanerogamae
| Features | Cryptogamae | Phanerogamae |
| 1. Seeds | Do not produce seeds. | Produce seeds. |
| 2. Vascular system | May or nwy not be present. | Always present, |
| . 3. Fertilization | Externa: water serve as metfum. | Do not wed external water. |
| 4. Evolutionary status | Primitive. | Advanced |
| S Example | Algae, muss, fern. | Fine, mango. |
Also Read:


