Digestion Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 1. The sequential steps of digestion are
- Ingestion, digestion, assimilation, excretion
- Digestion, ingestion, assimilation, excretion
- Ingestion, digestion, excretion, assimilation
- Excretion, assimilation, digestion, ingestion
Answer: 1. Ingestion, digestion, assimilation, excretion
Question 2. The main role of the digestive system is to facilitate the
- Filtration of cellular wastes, toxins and excess water
- Exchange of gases between the blood and the organs
- Relay of chemical signals through the body and brain
- Breakdown and absorption of nutrients essential for growth
Answer: 4. Breakdown and absorption of nutrients essential for growth
“digestive system questions “
Question 3. The mouth, Oesophagus and stomach are organs of the
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Endocrine system
- Excretory system
Answer: 2. Digestive system
NEET Biology Class 7 Digestion MCQs
Question 4. The digestive system begins with the
- Oesophagus
- Intestine
- Stomach
- Mouth
Answer: 2. Intestine
Question 5. What is the role of pre-molars?
- Grinding
- Cutting
- Biting
- Slicing
Answer: 1. Grinding
Digestion NEET MCQs with Answers
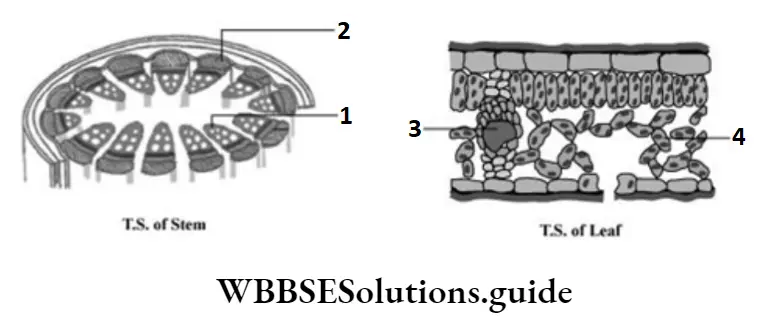
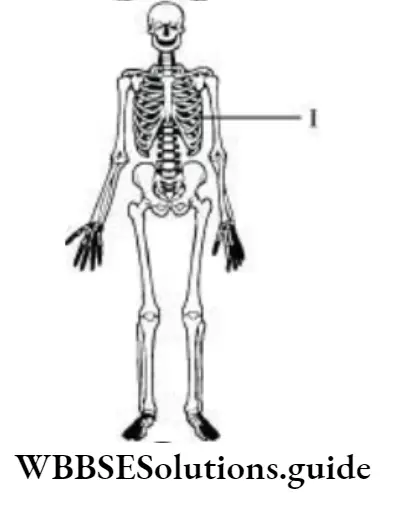
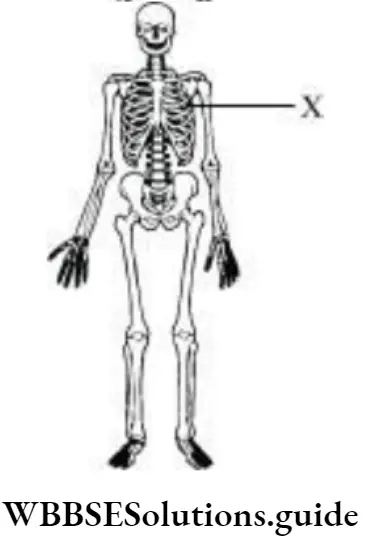
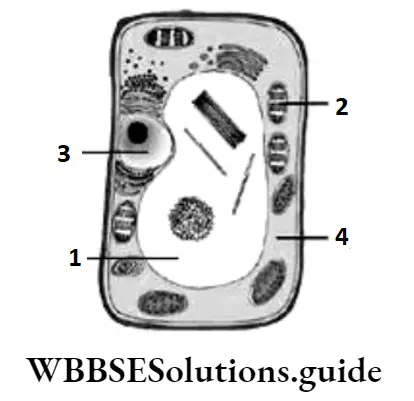
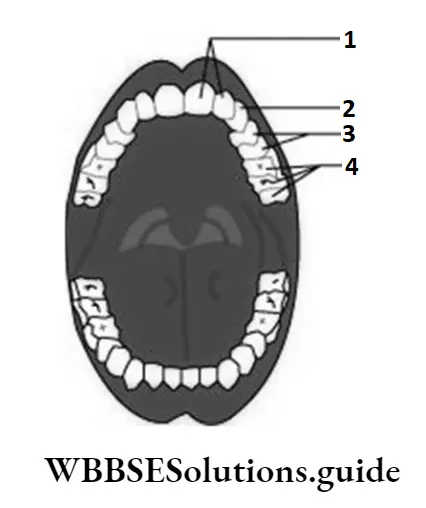
Question 6. Teeth, which are a part of the buccal cavity, help in the mechanical breakdown of food. The given illustration depicts the type of teeth present in the mouth. The teeth that perform the function of piercing and tearing are labelled as
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 2. 2
Question 7. The teeth that help in the biting of food are known as
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Answer: 1. Incisors
Question 8. The respective number of incisors, canines, and pre-molars in a human adult are
- 12, 4, 4
- 8, 4, 8
- 8, 8, 4
- 4, 4, 12
Answer: 2. 8, 4, 8
Question 9. In humans, the total number of piercing and tearing teeth is
- 4
- 8
- 12
- 16
Answer: 1. 4
NEET Biology Digestion Important MCQs
Question 10. What is the role of molars?
- Grinding
- Cutting
- Tearing
- Biting
Answer: 1. Grinding
“questions about the digestive system “
Question 11. What is the role of the tongue during the digestion of food?
- Grinding
- Mixing
- Cutting
- Chewing
Answer: 2. Mixing
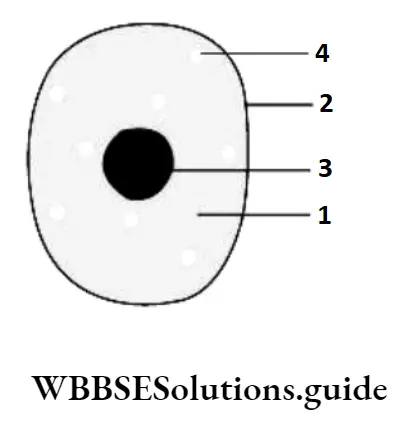
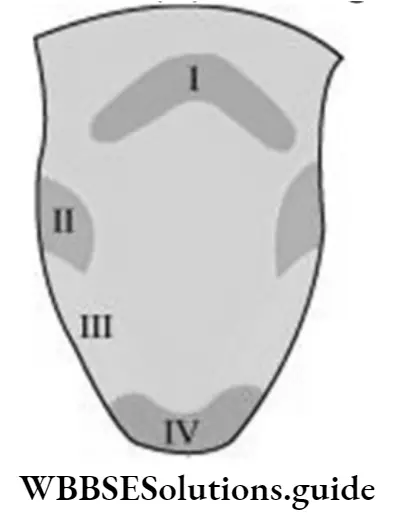
Question 12. The given illustration represents different regions of taste on the tongue. Suppose Radha eats a salty food item Which labelled region on the tongue will detect the salty taste of the food?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 3
Best Multiple Choice Questions for Class 7 Biology Digestion
Question 13. Salivary glands are present in the buccal cavity and secrete saliva that helps in the digestion of food. Which complex food nutrient is broken down by the saliva into simple compounds?
- Fats
- Starch
- Proteins
- Vitamins
Answer: 2. Starch
Question 14. The major organs of the human digestive system are located in the abdominal cavity. Which of the following organs is not a part of the digestive system?
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Intestine
- Trachea
Answer: 4. Trachea
Question 15. What is the function of the oesophagus?
- Churning food
- Absorbing the digested food
- Removing the undigested food from the body
- Transporting food from the mouth to the stomach
Answer: 4. Transporting food from the mouth to the stomach
Question 16. Oesophagus transports food from the _____1_____ to the _____2______. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- buccal cavity 2- stomach
- 1- stomach 2- small intestine
- 1- small intestine 2- anus
- 1- anus 2- buccal cavity
Answer: 1. 1- buccal cavity 2- stomach
Question 17. Which secretion checks the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the stomach?
- Pancreatic juice
- Gastric juice
- Saliva
- Bile
Answer: 2. Gastric juice
Digestion Class 7 NEET Objective Questions
Question 18. Which organ secretes hydrochloric acid to kill the bacteria present in the food?
- Small intestine
- Stomach
- Large intestine
- Oesophagus
Answer: 2. Stomach
“digestive system quiz
Question 19. The gastrointestinal tract between the oesophagus and the large intestine includes the 1 and the 2. The given statement is correctly completed by alternative
- 1- stomach 2- small intestine
- 1- small intestine 2- pancreas
- 1- pancreas 2- liver
- 1-liver 2-stomach
Answer: 1. 1- stomach 2- small intestine
Question 20. If the stomach were not a part of the digestive system, then
- It would not have been possible to consume large quantities of food
- The organs of the excretory system would become highly inefficient
- One would continuously feel hungry
- It would not be necessary to chew food at all
Answer: 1. It would not have been possible to consume large quantities of food
Question 21. Digestion of ____1_____ begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine where it is broken down into ____2_____. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- carbohydrates 2- glucose
- 1-proteins 2-glucose
- 1- carbohydrates 2- amino acids
- 1-proteins 2-amino acids
Answer: 4. 1-proteins 2-amino acids
Question 22. ______1_____ is the part of the alimentary canal that transfers food from the mouth to the _____2_____. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- oesophagus 2-stomach
- 1-oesophagus 2-small intestine
- 1-liver 2-stomach
- 1-liver 2-small intestine
Answer: 1. 1- oesophagus 2-stomach
Question 23. What is the function of the stomach?
- Storing bile juice
- Absorbing the digested food
- Receiving secretions from the liver and pancreas
- Secreting mucous, hydrochloric acid, and digestive juices
Answer: 4. Secreting mucous, hydrochloric acid, and digestive juices
Question 24. The inner lining of the stomach secretes ____1____ that protects the lining of the stomach from the action of ____2___. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- mucous 2- hydrochloric acid
- 1- hydrochloric acid 2- bile juice
- 1- bile juice 2- digestive juices
- 1- digestive juices 2-mucous
Answer: 1. 1- mucous 2- hydrochloric acid
Question 25. The given represents the passage of food through the alimentary canal. At point B, the food is passing through
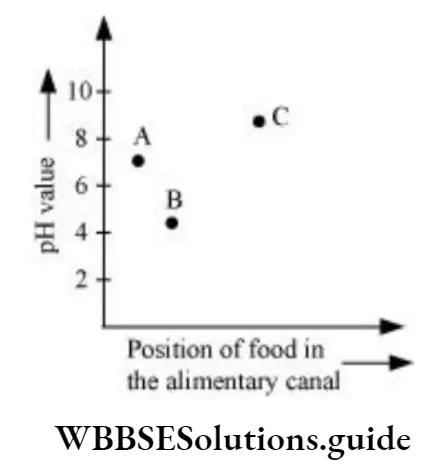
- Mouth
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Answer: 2. Stomach
Question 26. The process of absorption of nutrients takes place in
- Stomach
- Oesophagus
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
Answer: 4. Small intestine
“digestive system quizzes “
Question 27. Which is the longest part of the digestive tract with respect to length?
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Colon
Answer: 2. Small intestine
Question 28. Which of the following statements is correct for villi?
- It helps in swallowing of food.
- It protects the inner lining of the stomach.
- It breaks down proteins into peptides.
- It increases the surface area for food absorption.
Answer: 4. It increases the surface area for food absorption.
Question 29. The information in Which alternative completes the given table?
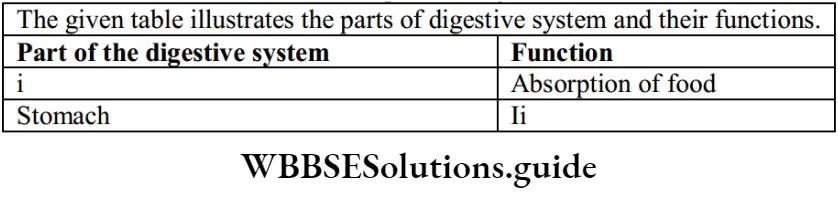
- 1- Large intestine 2- Killing of bacteria
- 1- Large intestine 2- Absorption of water
- 1- Small intestine 2- Killing of bacteria
- 1- Small intestine 2- Absorption of water
Answer: 3. 1- Small intestine 2- Killing of bacteria
Question 30. During the process of _____1_____, the digested food in the small intestine enters the ____2______. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- absorption 2- blood vessels
- 1- absorption 2- food pipe
- 1- assimilation 2-blood vessels
- 1-assimilation 2-food pipe
Answer: 1. 1- absorption 2- blood vessels
Question 31. Which part of the alimentary canal has finger-like projections called villi for the absorption of food?
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
- Stomach
- Oesophagus
Answer: 2. Small intestine
Question 32. The breakdown of food is completed in the
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
- Stomach
- Rectum
Answer: 2. small intestine
Question 33. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called ______1______ that take part in the ____2______ of food. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- pseudopodia 2- absorption
- 1-pseudopodia 2-digestion
- 1-villi 2-absorption
- 1-villi 2-digestion
Answer: 3. 1-villi 2-absorption
NEET Biology Class 7 Chapter 6 MCQs with Solutions
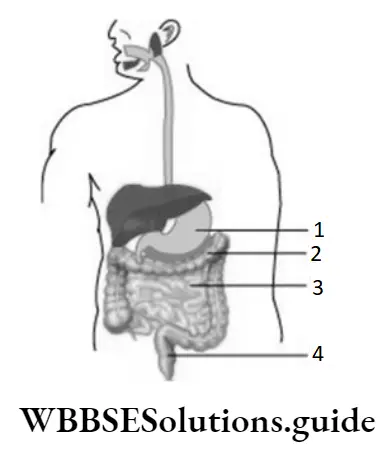
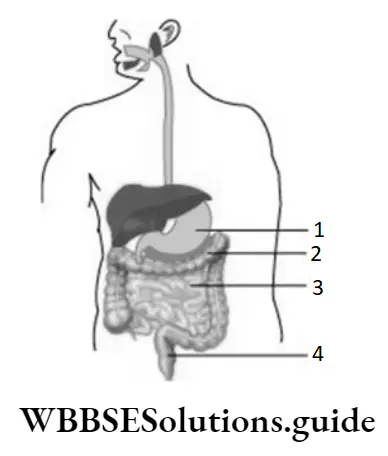
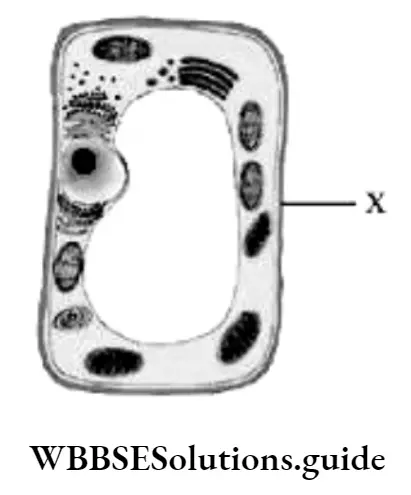
Question 34. The given diagram illustrates the human digestive system. Which part of the human digestive system helps in the absorption of water from undigested food?
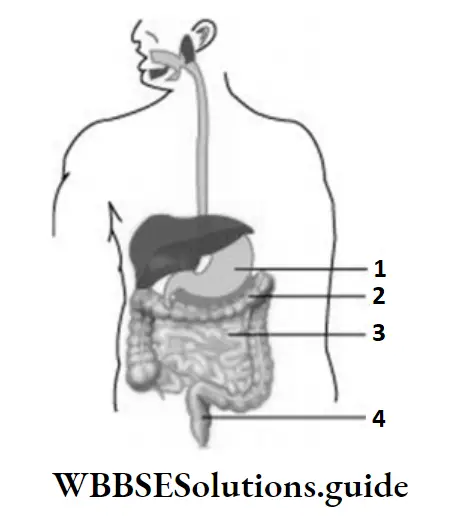
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 4
“digestive system quizzes “
Question 36. Which of the following events takes place in the large intestine?
- Absorption of nutrients
- Absorption of water
- Digestion of starch
- Digestion of fats
Answer: 2. Absorption of water
Question 37. The liver is an important gland of the digestive system. The primary function of the liver is to
- Produce mucous
- Produce hydrochloric acid
- Help in the digestion of fats
- Help in the digestion of proteins
Answer: 3. Help in the digestion of fats
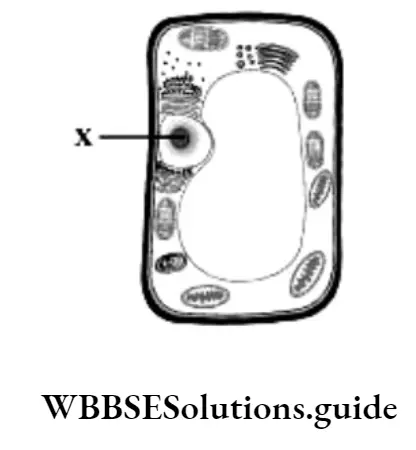
Question 38. The given illustrates the human digestive system. The buccal cavity is marked as 1, the stomach as 2, the gall bladder as 3, and the liver as 4. Which part of the human digestive system produces bile?
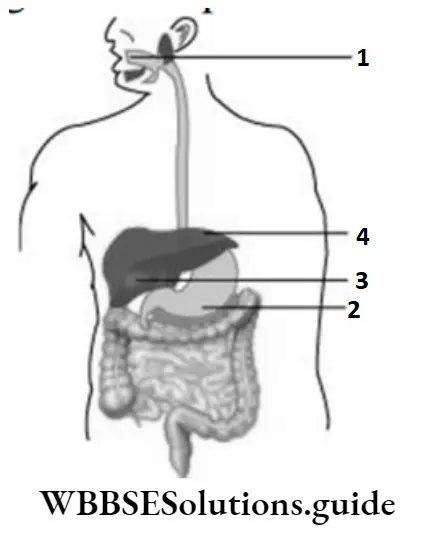
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
NEET Study Material for Digestion with MCQs
Question 39. Jaundice is a disease that affects the liver. A person suffering from jaundice will face maximum difficulty in
- Digesting carbohydrates
- Absorbing proteins
- Absorbing water
- Digesting fats
Answer: 4. Digesting fats
Question 40. Many secretory glands are present in the digestive glands. These glands release digestive juices for the digestion of food. Which organ of the digestive system secretes bile?
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Answer: 1. Liver
Question 41. The given illustrates some labelled parts of the human digestive system. The structures that secrete digestive juices are labelled as
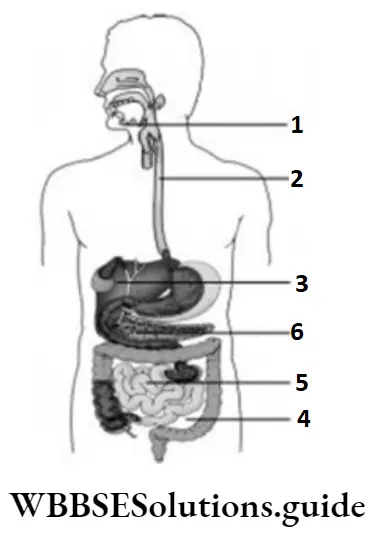
- 1, 2, and 3
- 2, 4, and 6
- 1, 3, and 6
- 4, 5, and 6
Answer: 3. 1, 3, and 6
Question 42. The liver produces bile which helps in fat digestion, which occurs in the duodenum. The bile is secreted into the duodenum and excess bile is stored in the organ present between the liver and the duodenum. Which organ stores excess bile secreted by the liver?
- Stomach
- Gall bladder
- Small intestine
- Urinary bladder
Answer: 2. Gall bladder
“digestive system quizzes “
Question 43. The liver is the largest gland present in the human body. The bile juice secreted by the liver is stored in the
- Salivary glands
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Gall bladder
Answer: 4. Gall bladder
Question 44. Which of the following organs help in digesting sugar?
- Liver
- Rectum
- Stomach
- Pancreas
Answer: 4. Pancreas
Question 45. The liver secretes bile juice that takes part in the digestion of fats. Digestion of fats results in the formation of which substance?
- Glucose
- Glycerol
- Amino acids
- Hydrochloric acid
Answer: 2. Glycerol
Question 46. Salivary glands are present in the
- Mouth
- Throat
- Tongue
- Oesophagus
Answer: 1. Mouth
Question 47. During the process of digestion, starch is broken down into
- Glucose
- Sucrose
- Amino acids
- Fatty acids
Answer: 1. Glucose
Question 48. A person suffers from a disorder in which his stomach is unable to produce gastric acid. What is the result of the given condition?
- Improper digestion of fat
- Improper digestion of lipids
- Improper digestion of glucose
- Improper digestion of proteins
Answer: 4. Improper digestion of proteins
Question 49. The saliva produced in the mouth is responsible for the digestion of
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Proteins
- Fats
Answer: 1. Carbohydrates
Question 50. Shruti took a teaspoonful of boiled rice in test tube 1 and a teaspoonful of chewed rice in test tube 2 She then added 3- 4 mL of water to both the test tubes and then added 2-3 drops of iodine solution to each of the test tubes. The result in terms of changes in colour was observed. Which of the following statements regarding the observation made by Shruti is correct?
- The contents of test tube 1 will show no change in colour while the contents of test tube 2 will show a colour change.
- The contents of test tube 2 will show no change in colour while the contents of test tube 1 will show a colour change.
- The contents of both test tubes 1 and 2 will not show any colour change.
- The contents of both test tubes 1 and 2 will show changes in colour.
Answer: 2. The contents of test tube 2 will show no change in colour while the contents of test tube 1 will show a colour change.
Question 51. The incisors in rabbits are used for
- Cutting
- Biting
- Tearing
- Grinding
Answer: 1. Cutting
Question 52. The gap between incisors and premolars in rabbits is called
- Diasteina
- Diastema
- Triastema
- None
Answer: 2. Diastema
Question 53. Which of the following allows the tongue to manipulate the food
- Diasteina
- Diastema
- Triastema
- None
Answer: 2. Diastema
Question 54. Which of the following is absent in carnivores?
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- None
Answer: 4. None
Question 55. In dogs, which of the following helps in grinding and crushing the bones?
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Answer: 4. Molars
Question 56. Which of the following parts of the tooth is embedded in the jaw?
- Root
- Crown
- Neck
- None
Answer: 1. Root
Question 57. The hardest substance in our body is
- Enamel
- Dentine
- Pulp cavity
- None
Answer: 1. Enamel
Question 58. Which of the following contain blood vessels and nerves?
- Enamel
- Dentine
- Pulp cavity
- None
Answer: 3. Pulp cavity
Question 59. Teeth problems include
- Plaque
- Cavities
- Decay
- All
Answer: 4. All
Question 60. Which of the following should be consumed to prevent plaque formation?
- Foods that contain sufficient calcium
- Foods that contain sufficient phosphorus
- Foods that contain sufficient vitamin D
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Digestion Class 7 NCERT MCQs with Answer Key
Question 61. Plaque formation can be avoided by
- Not eating foods like sweets, chocolates and ice-creams
- Cleaning teeth after eating sweet, sticky food
- Using fluoride toothpaste
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 62. Dental hygiene is very important. It involves keeping the mouth clean and protecting it from dental caries. What causes dental caries?
- Poor nutrition
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Excess nutrition
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Digestion Conceptive Worksheet
Question 1. Which step occurs after ingestion?
- Assimilation
- Absorption
- Digestion
- Egestion
Answer: 3. Digestion
Question 2. Which of the following organs is not a part of the digestive system?
- Kidney
- Stomach
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
Answer: 1. Kidney
Question 3. Which of the following events does not occur inside the mouth?
- Wetting of the ingested food with the help of saliva
- Crushing of the ingested food with the help of teeth
- Breakdown of proteins into simpler compounds
- Breakdown of starch into simple sugar
Answer: 3. Breakdown of proteins into simpler compounds
Question 4. The teeth used to bite an apple are the
- Molars
- Canines
- Incisors
- Premolars
Answer: 3. Incisors
Question 5. How many teeth does a human adult have?
- 26
- 28
- 30
- 32
Answer: 4. 32
Question 6. Teeth are classified according to their shape and function. Incisors are chisel-shaped front teeth. Incisors are specialized for
- Cutting
- Tearing
- Piercing
- Grinding
Answer: 1. Cutting
Question 7. Teeth are structures present in the jaws of human beings and animals. In human beings, teeth help in biting, tearing, and chewing of food. Which of the following functions is performed by incisors?
- Biting
- Tearing
- Chewing
- Grinding
Answer: 1. Biting
Question 8. What is the role of canines?
- Cutting
- Biting
- Tearing
- Grinding
Answer: 3. Tearing
Question 9. The given illustration represents different regions of taste on the tongue. The region on the tongue that detects a sweet taste is labelled as
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
Question 10. The labelled parts in the given illustrate the location of different taste buds on the tongue. The location on the tongue that possesses the taste buds to identify bitter taste is labelled as
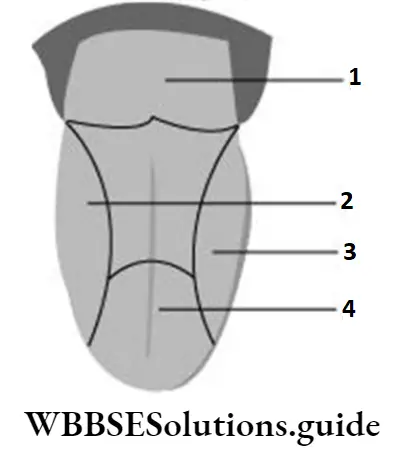
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
Question 11. Oesophagus connects the
- Mouth to the small intestine
- Small intestine to the colon
- Mouth to the stomach
- Stomach to the large intestine
Answer: 3. Mouth to the stomach
Question 12. Which part of the alimentary tract is not involved in digestion?
- Stomach
- Mouth
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
Answer: 3. Oesophagus
Question 13. Which of the following organs does not secrete digestive enzymes?
- Mouth
- Liver
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
Answer: 3. Oesophagus
Question 14. The stomach does not perform the function of
- Storing food
- Absorbing nutrients
- Mixing food with gastric juices
- Mashing food into smaller pieces
Answer: 2. Absorbing nutrients
Question 15. The food from the stomach enters the
- Rectum
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Answer: 3. Small intestine
Question 16. Digestion of food occurs with the help of
- Intestines and kidneys
- Heart and intestines
- Stomach and mouth
- Kidneys and mouth
Answer: 3. Stomach and mouth
Question 17. Which of the following organs aids in the digestion of food?
- Stomach
- Kidneys
- Lungs
- Skin
Answer: 1. Stomach
Question 18. Which of the following functions is not performed by the stomach?
- Storing food for some time
- Absorbing certain chemicals
- Breaking food into smaller particles
- Releasing bile for the digestion of fat
Answer: 4. Releasing bile for the digestion of fat
Multiple Choice Questions on Human Digestive System for NEET Exam
Question 19. Where does the digestion of proteins start in the human body?
- Mouth
- Stomach
- Liver
- Small intestine
Answer: 2. Stomach
Question 20. Which of the following functions is not performed by the stomach?
- Storage of food
- Adsorption of water
- Digestion of protein
- Secretion of bile
Answer: 4. Secretion of bile
Question 21. The process in which the digested food in the small intestine enters the blood vessels is known as
- Ingestion
- Assimilation
- Digestion
- Absorption
Answer: 4. Absorption
Question 22. From the stomach, food passes into the
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Oesophagus
- Rectum
Answer: 1. Small intestine
Question 23. Food is absorbed into the blood in the
- Stomach
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Answer: 3. Small intestine
Question 24. Maximum absorption of nutrients from the digested food takes place in the
- Stomach
- Oesophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Answer: 3. Small intestine
Question 25. The absorption of nutrients from digested food occurs in the
- Rectum
- Oesophagus
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
Answer: 4. Small intestine
Question 26. What is the function of the small intestine?
- Releasing bile juice
- Transferring food to the stomach
- Absorbing water from undigested food
- Absorbing nutrients from the digested food
Answer: 4. Absorbing nutrients from the digested food
Question 27. The given shows the digestive system. In the given, the part that is labelled A is the
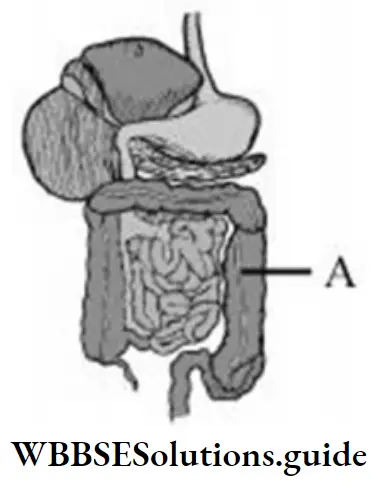
- Rectum
- Oesophagus
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
Answer: 3. Large intestine
Question 28. The absorption of water from undigested food takes place in the
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Stomach
- Liver
Answer: 2. Large intestine
Question 29. Which organ performs the function of absorption of water and minerals?
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
- Stomach
- Rectum
Answer: 1. Large intestine
Question 30. The liver is the largest gland in the human body. What is the main function of the liver?
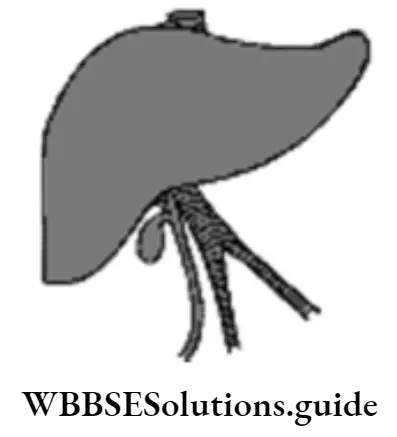
- Secretion of bile
- Digestion of proteins
- Absorption of nutrients
- Transportation of oxygen
Answer: 1. Secretion of bile
Question 31. The liver helps in the digestion of
- Fats
- Sugar
- Protein
- Minerals
Answer: 1. Fats
Question 32. The human digestive system is represented in the given. In the given, the organ that secretes bile is labelled
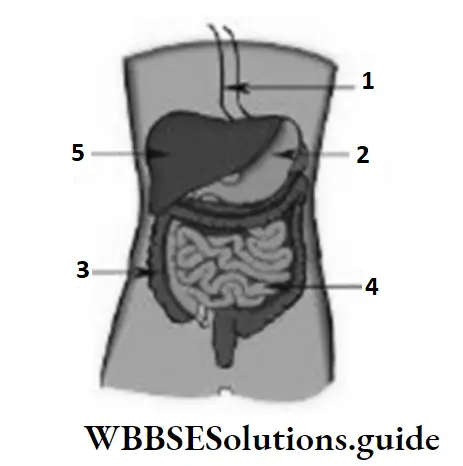
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 1
Answer: 1. 5
Question 33. The liver is situated on the right-hand side of the human body. It plays a major role in digestion by secreting enzymes. Liver secretes
- Bile juice
- Pancreatic juice
- Insulin
- Glycogen
Answer: 1. Bile juice
Question 34. The liver is a very important part of the body and its main function is the secretion of bile. Bile is a digestive fluid. Apart from bile, other secretions control a host of activities. Which of the following statements about the liver is false?
- It aids digestion of lipids
- It aids digestion of fats
- It secretes insulin
- It secretes bile
Answer: 3. It secretes insulin
Question 35. Which arrow diagram correctly represents the sequence of digestion?
- Mouth →oesophagus→ large intestine → small intestine → stomach → rectum
- Mouth → stomach →small intestine → large intestine → oesophagus → rectum
- Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum
- Mouth→ oesophagus →rectum → large intestine → stomach → small intestine
Answer: 3. Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum
Question 36. The process of enzymatic breakdown of food is known as
- Absorption
- Digestion
- Excretion
- Assimilation
Answer: 2. Digestion
Question 37. At the end of digestion, the carbohydrates are broken down into
- Glucose
- Glycerol
- Fatty acids
- Amino acids
Answer: 1. Glucose
Question 38. The inner lining of the stomach secretes various substances like mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The digestive juices secreted by the stomach take part in the digestion of which of the following substances?
- Starch
- Proteins
- Glucose
- Vitamins
Answer: 2. Proteins
Question 39. During the process of digestion, fats are broken down into ____1_____ and ____2______. The information in which alternative completes the given statement?
- 1- fatty acids 2- glycerol
- 1- glycerol 2- amino acids
- 1- amino acids 2-glucose
- 1- glucose 2-fatty acids
Answer: 1. 1- fatty acids 2- glycerol
Question 40. Bile juice is secreted by the liver and is stored in the gall bladder. Bile juice is chiefly involved in the digestion of
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Glucose
Answer: 3. Fats
Question 41. Which of the following is absent in herbivores?
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Answer: 2. Canines
Question 42. The molars and premolars in herbivores help in
- Cutting
- Biting
- Chewing
- Frinding
Answer: 3. Chewing
Question 43. Which of the following in carnivores, helps to grip the food and strip off small pieces of flesh?
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Answer: 1. Incisors
Question 44. In humans, each tooth has
- Root
- Crown
- Neck
- All
Answer: 1. Root
Question 45. Internally, a tooth has
- Enamel
- Dentine
- Pulp cavity
- All
Answer: 4. All
Question 46. Which of the following should be taken to prevent plaque formation?
- Sweets
- Chocolates
- Ice-creams
- None
Answer: 4. None
Question 47. Which of the following are adopted for eating flesh, in a dog?
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars
Answer: 2. Canines
Question 48. Which of the following parts of the tooth is projected above the jaw?
- Root
- Crown
- Neck
- None
Answer: 2. Crown
Digestion Summative Worksheet MCQs
Question 1. Which of the following helps in the digestion of food?
- Nutrients
- Hormones
- Enzymes
- Saliva
Answer: 3. Enzymes
Question 2. Saliva contains an enzyme called
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Pepsin
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Amylase
Question 3. The teeth adapted for flash eating are
- Incisors
- Premolars
- Canines
- Molars
Answer: 3. Canines
Question 4. Finger-like projections called villi are present in
- Stomach
- Large intestine
- Small intestine
- Liver
Answer: 3. Small intestine
Question 5. Most of the digestion takes place in
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Rectum
Answer: 2. Small intestine
Question 6. Absorption of food takes place in
- Small intestine
- Pancreas
- Large intestine
- Liver
Answer: 2. Pancreas
Question 7. A tooth consists of the following parts:
- Gum and crown
- Root, crown and neck
- Enamel and dentine
- Only crown
Answer: 3. Enamel and dentine
Question 8. Absorption of water takes place in
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Rectum
- Large intestine and rectum
Answer: 2. Large intestine
Digestion Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. Saliva is secreted by the ____________ in the mouth cavity.
Answer: salivary glands
Question 2. Number of molar teeth present in a human adult is ________________.
Answer: 12
Question 3. The teeth which help in biting the food in humans are the ________________.
Answer: Incisors
Question 4. Food is digested by chemicals called ________________
Answer: Enzymes
Question 5. Changing food to a usable form is called ________________
Answer: Digestion
Question 6. The liver and ________________ are found near the stomach.
Answer: Spleen
Question 7. The five steps in the process of nutrition are ________________,
________________, ________________, ________________ and ________________.
Answer: Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Assimilation and Egestion
Question 8. The white part of the tooth is called the ________________
Answer: Enamel
Question 9. The part of the tooth embedded in the jaw is called the ________________
Answer: Root
Question 10. In the teeth of a rabbit, ________________ are absent.
Answer: Cannes
Digestion Write True Or False
Question 1. Canines are meant for tearing flesh.
Answer: True
Question 2. Molar teeth are present in a human baby.
Answer: False
Question 3. The mouth cavity is also known as the food pipe.
Answer: True
Question 4. Gastric juice is secreted by the small intestine.
Answer: False
Question 5. Food is mostly digested in the stomach.
Answer: False
Question 6. In humans, there are 14 teeth in each jaw
Answer: False