Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Cell Cycle And Cell Division Questions and Answers
Question 1. Which substances control the cell cycle?
Answer:
Some proteins and enzymes present in the cytoplasm, such as cyclin, and cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdks), control the cell cycle.
Question 2. Which is the longest stage of the cell cycle?
Answer:
The G2 phase of interphase is the longest stage and maximum growth of the cell occurs at this stage.
Cell cycle and cell division questions and answers PDF
Question 3. What is the G0 stage?
Answer:
G0 stage
The point of the G1 phase at which the cell cycle stops is
known as the G0 stage. Although the cells at this stage are metabolically active, they do not divide. Animal nerve cells remain at this stage permanently.
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 4. Why is amitosis called ‘direct division’?
Answer:
In amitosis, cells divide directly without spindle formation and chromosome segregation. Thus, it is also known as direct division.

Question 5. What is the composition of spindle fibres?
Answer:
Composition of spindle fibres
Tubulin protein (95-97%), RNA (3-5%) and a small amount of lipid are constituents of spindle fibres.
Question 6. What are meiocytes and meiospores?
Answer:
Meiocytes and meiospores
The diploid cells which undergo meiosis are called meiocytes, such as spermatocytes, oocytes. The haploid spores that are formed due to meiosis are known as meiospores.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
Question 7. What is a diploid cell?
Answer:
Diploid cell
A cell consisting of two complete sets of chromosomes, receiving one from each parent is called a diploid cell. Human somatic cells are diploid (2n – 46).
Question 8. What is a haploid cell?
Answer:
Haploid cell
The cells which contain half the number of diploid chromosomes or one complete set of chromosomes are called haploid cells. Human gametes are haploid (n=23).
Question 9. What is midbody?
Answer:
Midbody
At the end of anaphase in animal cells, microtubules are arranged at the equatorial plane like a thick plate or string. This structure is known as the midbody.
NEET cell cycle and cell division important questions with answers
Question 10. What is endomitosis?
Answer:
Endomitosis
The type of meiosis in which repeated DNA replication occurs without the occurrence of nuclear division and formation of daughter nuclei by chromosomal segregation is known as endomitosis.
Example polytene chromosome in the salivary gland of order Diptera of insects, etc.
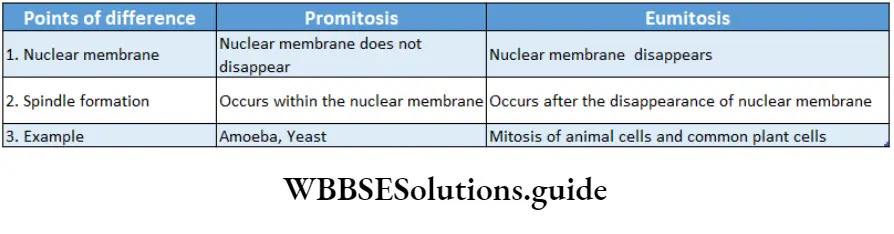
Question 11. What are the differences between pro-mitosis and mitosis?
Answer:
The differences between pro-mitosis and mitosis are as follows—
Question 12. What is synapsis?
Answer:
Synapsis
The phenomenon of pairing of homologous chromosomes at the zygotene subphase of prophase I in meiosis is known as synapsis.
Question 13. What is known as bivalent?
Answer:
Bivalent
The pair of homologous chromosomes formed as a result of synapsis at the zygotene subphase of prophase I in meiosis are called bivalents.
Question 14. How many times does DNA replication occur in meiosis? Why?
Answer:
DNA replication occurs only once. It occurs before meiosis I during S phase of interphase. DNA replication does not occur between meiosis I and meiosis II, i.e., at the interkinesis stage. It is because chromosome division does not take place at meiosis I, DNA remains duplicated.
Question 15. What is interkinesis?
Answer:
Interkinesis
The short period between the telophase of meiosis I and the prophase of meiosis II is known as interkinesis.
DNA replication does not occur at this phase but biochemicals are synthesised.
Question 17. What is metakinesis?
Answer:
Metakinesis
The process by which chromosomes at the prometaphase stage align themselves at the centre of a cell, is known as metakinesis.
Question 18. What is disjunction?
Answer:
Disjunction
The phenomenon of segregation of homologous chromosomes during anaphase I of cell division is known as disjunction.
Class 11 biology cell cycle and cell division Q&A
Question 19. What is non-disjunction?
Answer:
Non-disjunction
When segregation of homologous chromosomes does not occur during cell division, it is known as non-disjunction. So, after division, the daughter cell receives either more or less number of chromosomes than usual.
Question 20. Why amitosis does not occur in advanced organisms?
Answer:
Amitosis causes unequal distribution of chromatin material in daughter cells. So, the uniformity in chromosome number will not be maintained.
As a result, structural and functional abnormalities would arise in daughter cells which would hamper the normal metabolic functions of the organisms.
Question 21. What is a cell plate?
Answer:
Cell plate
During cytokinesis in plant cells, the thin plate-like structure formed by the fusion of phragmosomes at the equatorial region of the plant cell, is known as cell plate.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Cell Cycle And Cell Division Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1. What is metacentric chromosome?
Answer:
Metacentric chromosome
A chromosome with a centrally placed centromere that divides the chromosome into two arms of approximately equal length, is called a metacentric chromosome.
Question 2. What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Answer:
The average cell cycle span of a mammalian cell is 24 hours.
Question 3. Given that the average duplication time of E.coli is 20 minutes, how much time will E.coli cell take to become 32 cells?
Answer:
Number of cells = 2n, where n is number of divisions.
Total no. of cells = 32 As, 32 = 21 2 3 4 5 n = 5
Hence, time required for five generations is—
5 x 20 = 100 minutes.
Question 4. What is mitosis?
Answer:
Mitosis
The indirect process of division of a somatic cell
which produces two daughter cells that are structurally and genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell is known as mitosis.
Short answer questions on cell cycle and cell division
Question 5. Can there be DNA replication without cell division?
Answer:
Yes, DNA replication can occur without cell division. We can see this situation in two following processes—endomitosis and free nuclear division.
Question 6. What is a cell cycle checkpoint?
Answer:
Cell cycle checkpoint
The particular type of signalling mechanism or regulation that may prevent the cell from continuing to tire the next phase of the cell cycle is called the cell cycle checkpoint.
Question 7. What do you mean by a haploid set of chromosomes?
Answer:
Haploid set of chromosomes
A single set of chromosomes present in cells is known as a haploid set of chromosomes.
Question 8. What is the G1 phase?
Answer:
G1 phase
The stage of the cell cycle that exists from the birth of a new cell till the onset of the S phase during interphase is known as the Gi phase.
Question 9. Can there be mitosis without DNA replication in S
Answer:
No, because DNA is required to be distributed in daughter cells during mitosis.
Cell cycle and cell division chapter-wise questions with solution
Question 10. Why is mitosis called equational division?
Answer:
For the distribution of genetic material in daughter cells equal to that of parent cells, DNA replication is required prior to cell division.
Question 11. What do you mean by homologous chromosomes?
Answer:
Homologous chromosomes
Mitosis is also called equational division because the number of chromosomes in daughter cells, after mitosis remains the same as that of the parent cell.
Question 12. Which of the phases of the cell cycle has the longest duration?
Answer:
A pair of chromosomes in the offspring, obtained one from each parent, that are similar in length, gene position and centromere location, are called homologous chromosomes.
Question 13. What is the function of the spindle apparatus?
Answer:
Function of the spindle apparatus
The spindle apparatus is responsible for chromosome movements first towards the equator and then towards the poles. It helps in the segregation of sister chromatids during cell division.
Question 14. Which part of the human body should one use to demonstrate stages of mitosis?
Answer:
Bone marrow.
Question 15. Two key events take place during the S phase in animal cells: DNA replication and duplication of centriole. In which parts of the cell do these events occur?
Answer:
DNA duplication takes place in the nucleus and centriole divides in the cytoplasm.
Question 16. What do you mean by criminalisation?
Answer:
Criminalisation
The process of the movement of interstitial chiasmata to the terminal ends of bivalent during the diplotene of prophase I in meiosis I is known as terminalisation.
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 17. A cell has 32 chromosomes. It undergoes mitotic division. What will be the chromosome number (N) during metaphase? What would be the DNA content (C) during anaphase?
Answer:
The number of chromosomes is 32 at metaphase. DNA content becomes double that of the parent cell at anaphase.
Question 18. What do you mean by recombination?
Answer:
Recombination
The exchange of genetic materials between homologous chromosomes by the process of crossing over is known as recombination.
Objective questions on cell cycle and cell division with answers
Question 19. If a tissue has at a given time 1024 cells, how many cycles of mitosis had the original parental single cell undergone?
Answer:
Ten generations [210= 1024 cells].
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 20. What is carcinoma?
Answer:
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a type of cancer of epithelial tissue.
Example Lung carcinoma.
Question 21. An anther has 1200 pollen grains. How many pollen mother cells must have been there to produce them?
Answer:
300 pollen mother cells are needed to produce 1200 pollen grains.
Question 22. In which phase of cell division does DNA replication take place?
Answer:
In the cell cycle, DNA synthesis takes place during the S phase (synthesis phase.)
