Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Matter
Matter:
All of us have an idea that we live in an environment full of different kinds of matter having varied properties. Air, water, oil, milk, book, chair, table, gold, silver, pen, pencil, sugar, etc. are all examples of matter.
The matter around us generally exists in three different states-solid, liquid, and gas.
For example:
Ice, iron, salt, etc. are solid; water, mercury, oil, bromine, etc. are liquid; air, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, etc. are gas.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Classification Of Matter
Of the varieties of matter that we see around us some are pure and some are impure. A pure substance is one which contains one kind of material throughout its body.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 General Science and Environment
The substances that contain more than one kind of pure substance are necessarily impure substances or mixtures.
“WBBSE Class 6 General Science Chapter 3 element compound and mixture notes”
Types of pure substances:
The result of elaborate investigations show that pure substances are of two types:
- Element and
- Compound.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Element
An element is a pure substance that can not be broken or decomposed into a new substance by any chemical means.
For example:
Breaking down a piece of iron we get tiny particles which contain all the properties of iron like attraction by a magnet and no new particles having different properties are obtained.
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
This means that iron contains nothing other than iron. Similar results will be found for aluminium or copper.
More examples:
Gold, copper, iron, zinc, silver, mercury, carbon, sulphur, phosphorus, chlorine, bromine, iodine, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.
Do you know that till date 116 elements have been discovered, of which 92 elements are found in nature and they are called natural elements. The rest 24 elements have been discovered by scientists artificially, so they are called artificial elements.

Elements can be solid, liquid or gas:
| Solid elements | Liquid elements | Gaseous elements |
| Gold, copper, iron, zinc, carbon, etc. | Mercury, bromine, etc. | Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, etc. |
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Study Of Metals And Non Metals
Based on physical and chemical properties, the elements are further classified into three groups:
- Metal
- Non-metal and
- Metalloid.
1. Metals:
The elements which are in general hard solids at room temperature with high melting and boiling points, lustrous (shiny), heavy, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, reflect light and produce a characteristic sound when struck (i.e. sonorous) are called metals.
Physical properties are exhibited by a substance externally without any change of its composition.
Chemical properties are exhibited by a substance when it undergoes a complete change of its initial composition due to the action of some other substances or by heat or electricity or sound.
In general, metals are solids. But, mercury is an exception-It is found in a liquid state at room temperature.
More example:
Gold, iron, tin, silver, copper, lead, aluminium, zinc, mercury, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, etc. About 70 metals are found in nature.
Exceptions:
- Mercury is liquid though it is a metal.
- Sodium is soft and light though it is a metal. Sodium can be cut with a knife.
2. Non-metals:
The elements which are in general soft with low melting and boiling points, non-lustrous (non-shiny), brittle, non-conductor of heat and electricity, which do not reflect light and do not produce sound when struck (not sonorous) are called non-metals.
Non-metals can be solid, liquid or gas.
- Solid non-metal: Carbon, sulphur, boron, iodine, phosphorus, silicon, etc.
- Liquid non-metal: Bromine.
- Gaseous non-metal: Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, etc.
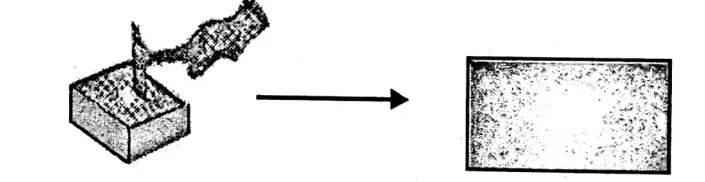
Malleability:
It is the ability of a substance due to which it can be hammered into sheets. Gold and silver are highly malleable. Non-met- als are transformed into powder when hammered hard.
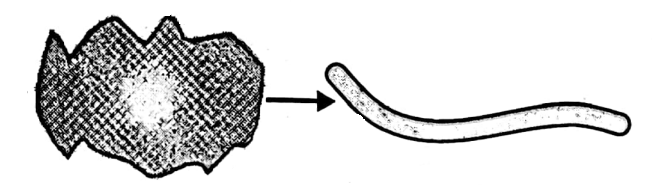
Ductility:
It is the ability of a substance due to which it can be drawn into wires. Gold can be drawn into a very thin wire.
Exceptions:
- Graphite (a form of carbon) is a good conductor of electricity though it is non-metal.
- Diamond (a form of carbon) is a very good conductor of heat though it is a non-metal. Diamond is hard.
- Lodine is solid. It is lustrous though it is a non-metal.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Compound
In ancient times, Indian philosophers thought water, air, and soil are the main constituents of the earth. Scientist Henry Cavendish first proved that water is not the main substance-it can be decomposed into two simpler substances, namely, hydrogen and oxygen.
“WBBSE Class 6 General Science Chapter 3 element compound and mixture notes”
Activity:
Take a beaker and pour a little water in it. Add a little acid in the water. Take a medium-sized rubber cork and two iron nails. Fix the nails on the cork with a little gap between them and dip the cork into the water as shown in inCombining 3-4 electric cells make a battery.
Join two copper wires at two opposite ends of the battery. Join the wires with the nails through a switch. Then, switch on and allow current to pass through the arrangement.
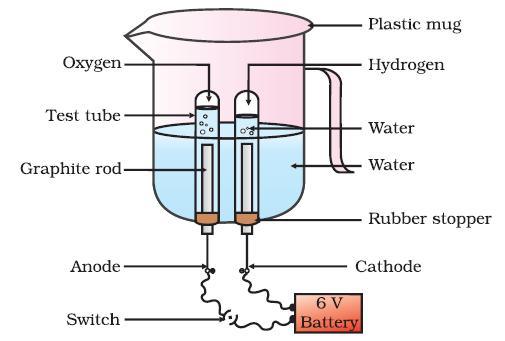
You will observe that gas bubbles are evolving at the two nails. To know the nature of the evolved gases, you are to hold two inverted gas jars filled with water over the nails.
Gases will be collected in the gas jars by downward displacement of water. When the gases become filled completely, the mouth of the gas jars are covered with a glass lid and kept erect.
The two gases are hydrogen and oxygen.
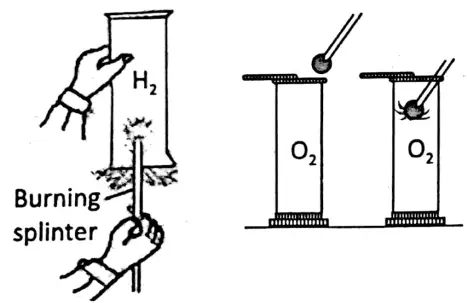
- When a lighted splinter is inserted into the gas jar filled with hydrogen, it is put off but the gas burns with a blue flame.
- On introducing a glowing splinter into the gas jar containing oxygen, the glowing splinter rekindles but the gas does not burn itself.
Also, it can be verified that hydrogen and oxygen are present in water in the ratio of 1: 8 by weight.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Learning Outcome
Water on electrolysis gives hydrogen and oxygen. Water is liquid but hydrogen and oxygen are gases. Hydrogen is combustible and oxygen supports combustion.
Water, on the other hand, is neither combustible nor a supporter of combustion-rather if it is used to put out a fire. So, there is no resemblance in properties between hydrogen and oxygen, each of which differs from water.
“WBBSE notes for Class 6 Science element compound and mixture”
Evidently, water is a complex substance compared to hydrogen and oxygen. Here, the complex substance water is a compound. In a compound, the properties of the constituents are lost and new properties appear instead.
Similarly, ammonia is a compound of two elements-nitrogen and hydrogen, carbon dioxide is a compound containing carbon and oxygen.
More examples of compounds :
| State | Name of compound | Constituent elements |
| Solid | Table salt | Sodium + Chlorine |
| Glucose | Carbon + Hydrogen + Oxygen | |
| Soda | Sodium + Carbon + Oxygen | |
| Liquid | Kerosene | Carbon + Hydrogen |
| Alcohol | Carbon + Hydrogen + Oxygen | |
| Sulphuric acid | Hydrogen + Sulphur + Oxygen. | |
| Gas | Methane | Carbon + Hydrogen |
| Hydrogen chloride | Hydrogen + Chlorine | |
| Hydrogen sulphide | Hydrogen + Sulphur |
Definition:
A compound is a pure substance which can be disintegrated by chemical means into two or more elements.
Alternatively, When two or more elements combine in a definite ratio by weight to produce a substance with new properties then the substance produced is called a compound.
Characteristic properties of compounds :
- A compound is formed by a chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed proportion by weight.
- The composition and properties of all portions of a compound must be the same, i.e., it must be homogeneous.
- The constituents of a compound can not be separated by simple physical means.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Mixture
A mixture is an impure substance.
Two or more elements or compounds may remain blended together in any proportion by weight so that the individual properties of the ingredients are retained.
For example:
On mixing one or two tablespoons of sugar in water taken in a glass and stirred thoroughly by a spoon, the sugar dissolves in the water and a mixture is formed.
Any portion of the mixture tastes equally sweet. The properties of both sugar and water remain unchanged in it, so it is a mixture.
| Mixtures | Name of the constituents |
| Air | Oxygen + Nitrogen + Water vapour + Inert gases |
| Sea water | Water + Salt |
| Smoke | Air + Fine carbon particles |
| Soda water | Water + Carbon dioxide |
| Lemonade | Water + Sugar + Carbon dioxide |
| Beverage | Water + Sugar + Lemon |
Characteristic properties of mixtures:
- The constituents of a mixture remain side by side.
- The constituents are blended in any proportion by weight.
- The constituents of a mixture can be separated easily by physical means.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Concept Of Atoms And Molecules
In the 19th century, the famous British scientist John Dalton first developed a scientific theory regarding the structure of matter. He proposed that all matter is made up of very minute, indivisible particles called the ‘atoms’ which can neither be created nor destroyed.
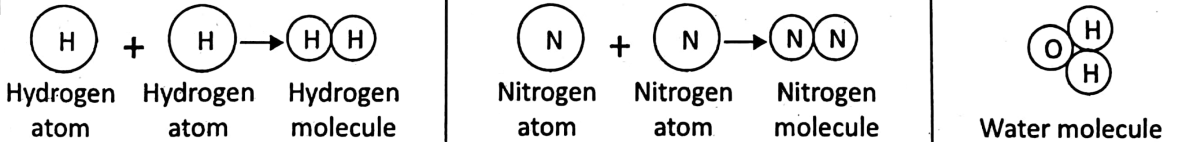
An element is made up of one type of atom only. Later Amedeo Avogadro suggested that the atoms of gaseous elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.
cannot exist in nature freely-rather they are present as particles joining two atoms together. He called these particles as ‘molecules’. Atoms of the same or different elements combine to form a molecule.
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Symbol Formula And Valency
Symbol:
There are so many elements that it is not easy to represent an element by writing its full name. Conveniently it is done by symbols. The symbol is the short form or abbreviated name of an atom of an element.
Scientists follow a different procedure for shortening the names of the elements. John Jacob Berzelius used the first letter (in the capital) of the name of the element as its symbol.
For example:
| Name of element | Symbol |
| Hydrogen | H |
| Oxygen | O |
| Boron | B |
| Fluorine | F |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Sulphur | S |
| Carbon | C |
| Iodine | I |
It has been found out that two or more elements have the same first letter. In those cases, the second letter (in small) is added to the first letter (in the capital).
For example:
| Name of element | Symbol |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Helium | He |
| Aluminium | Al |
| Bromine | Br |
| Cobalt | Co |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Nickel | Ni |
In some cases, second prominent letter (in small) is added to the first letter (in the capital).
For example:
| Name of element | Symbol |
| Chlorine | Cl |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Chromium | Cr |
| Manganese | Mn |
In some cases, symbols are derived by taking a single letter or two letters from the Latin name of some elements.
For example:
| Name of element | Latin name | Symbol |
| Sodium | Natrum | Na |
| Copper | Cuprum | Cu |
| Gold | Aurum | Au |
| Potassium | Kalium | K |
| Iron | Ferrum | Fe |
| Silver | Argentum | Ag |
Formula:
The formula is the shortcut way to express the molecule of a compound. It expresses the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
For example:
One molecule of hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen consists of two atoms and their formula are written as H2, O2, and N2 respectively. Here, the number 2 represents the number of atoms.
So, ‘P’ refers to a molecule of phosphorus which contains 4 atoms, ‘O3 ‘ refers to one molecule of ozone which contains 3 atoms of oxygen, etc. A molecule of water contains 1 atom of hydrogen and 2 atoms of oxygen, so the formula of water is H2 O1 or simply H2 O.
“Class 6 WBBSE General Science Chapter 3 elements compounds and mixtures explained”
Atomicity is the number of atoms present in a molecule. H2 , O2 , N2 have atomicity = 2; atomicity of P4 = 4; atomicity of O3 = 3, atomicity of H2 O = 3, etc.
More Examples
| Name of compound | Formula | Number of atoms | Atomicity | Meanings |
| Carbon monoxide | CO | C = 1, O = 1 | 2 | Mono-1 |
| Nitrogen dioxide | NO2 | N = 1, 0 = 2 | 3 | Di-1 |
| Phosphorus trichloride | PCI3 | P = 1, Cl = 3 | 4 | Tri-1 |
| Carbon tetrachloride | CCI4 | C = 1, Cl = 4 | 5 | Tetra-4 |
| Phosphorus pentachloride | PCI5 | P = 1, Cl = 5 | 6 | Penta-5 |
Valency
In general, the valency of an element is expressed by the number of hydrogen atoms which can combine with one atom of an element to form a compound.
| Name of compound | Formula | Number of atoms | Valency of another element = Number of combined H-atoms |
| Water | H2 O | H = 2, 0 = 1 | Valency of O = 2 |
| Hydrogen chloride | HCI | H = 1, Cl = 1 | Valency of Cl = 1 |
| Ammonia | NH3 | N = 1, H = 3 | Valency of N = 3 |
| Methane | CH4 | C = 1, H = 4 | Valency of C = 4 |
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Various Mixtures Solution
You already got the idea that a mixture contains more than one type of substance mixed in any proportion. Already it is told that solution is a mixture.
The solution of sugar or salt in water is a homogeneous mixture as the proportion of sugar or salt and water in every part of the mixture is the same.
In a solution, the substance whose proportion is less than the other is called the solute and whose proportion is comparatively larger. then the other is called solvent.
Generally, in a solution of sugar or salt in water, the solid substance (sugar or salt) is the solute and the liquid substance (water) is the solvent.
Thus, Solution = Solvent + Solute
In general, the colour of a solution is the same as that of the solute.
| Solute | Solvent | Solution | Type of the solution |
| Copper sulphate | Water | Copper sulphate solution | Solid-liquid solution |
| Glycerine | Water | Glycerine solution | Liquid-liquid solution |
| Carbon dioxide | Water | Soda-water | Gas-liquid solution |
Chapter 3 Element Compound And Mixture Process Of Separating Components Of A Mixture
The constituents of a mixture can be separated by a simple physical process. A single particular process can not be applied to all types of mixtures. Any process suitable for a particular mixture may not be applicable in the case of another mixture.
“Step-by-step notes on element compound and mixture Class 6 WBBSE”
Filtration:
Perhaps you know that muddy water (a mixture of water, mud, sand, etc.) looks turbid. If it is kept in a vessel undisturbed for some time you might have noticed that mud, sand, etc.
Settle at the bottom of the vessel and the water above these settled solid matters appears more transparent. The settled solid is called sediment. The clear water (or supernatant liquid) at the top may be poured off without disturbing the sediment.
This process of separating mud from water is called decantation. The supernatant water is apparently clear but still contains tiny particles. So by decantation complete separation is not possible.
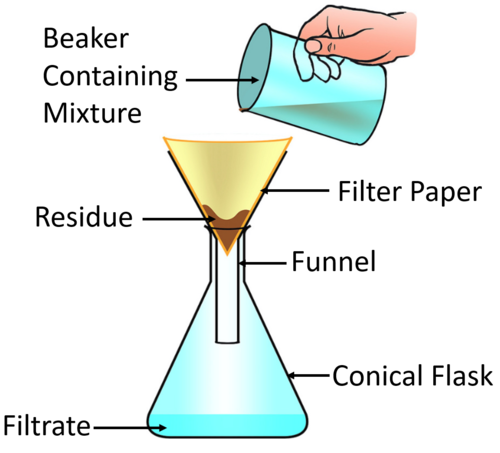
Then, a better process called filtration is employed. A special type of porous paper called filter paper is generally used in laboratories for the separation of an insoluble solid like sand or chalk dust from a liquid (water).
A mixture of sand and water is taken in a beaker. A circular (dry) filter paper is folded two times and opened in the form of a cone such that three folds remain on one side and a single fold on the other.
“WBBSE Class 6 General Science Chapter 3 important questions and answers”
The cone is fitted in a funnel and the filter paper is made wet with a few drops of water so that it sticks to the sides of the funnel. The mixture is then poured slowly into the filter paper down a glass rod.
Water passes through the pores of the filter paper while sand is retained in the filter paper. Water collected in a receiver looks transparent; it contains no suspended solid particles.
This clear water is called filtrate, and the solid left on the filter paper is called the residue. The total process is called filtration.
Crystallization
By filtration, a solution of sugar can not be separated into its constituents, because sugar disappears completely in water. In that case, crystallization is a suitable process.
Take a solution of sugar and water in a beaker. Heat the solution gently and go on heating with constant stirring with a glass rod. The solution will become more and more concentrated. Then allow the solution to cool down at room temperature.
“Solved examples of elements compounds and mixtures WBBSE Class 6 Science”
Some granular crystals of sugar separate out from the mixture. Such little grains have a geometric shape. There are called crystals. The process of separating solid crystals from a solution is called crystallization.
Separation by using a magnet:
You know that a magnet attracts magnetic substances like iron. Take a mixture of iron fillings and sand. Spread the mixture over the clean paper. Place a magnet over the mixture and pull it back and forth through the mixture.
Iron fillings are attracted by the magnet, but the sand particles remain unattracted. Repeat the process several times. The magnet is taken outside and by jerking, iron fillings are separated out from the sand.
WBBSE Notes For Class 6 General Science and Environment
-
- Chapter 1 Interdependence of Organisms and the Environment
- Chapter 2 Phenomena Around Us
- Chapter 3 Element, Compound and Mixture
- Chapter 4 Rocks and Minerals
- Chapter 5 Measurement
- Chapter 6 Primary Concept of Force and Energy
- Chapter 7 Statics and Dynamics of Fluid
- Chapter 8 The Human BodyChapter 9 Common Machines
- Chapter 10 Biodiversity and its Classification
- Chapter 11 Habits and Habitats of Some Important Animals
- Chapter 12 Waste Products
