Fundamental Concepts In Organic Reaction Mechanism
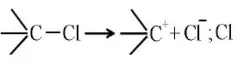
Question 1. Chlorine in vinyl chloride is less reactive because?
- sp2-hybridized carbon has more acidic character than sp3-hybridized carbon
- C—Cl bond develops partial double bond character
- Of resonance
- All of the above are correct
Answer: 3. Of resonance
Solution: CH2=CH−Cl−↔ CH2−CH−Cl+CH2=CH-Cl-↔ CH2-CH-Cl+ is formed between C and Cl. Here it is less reactive due to resonance.
Read And Learn More: NEET General Organic Chemistry Notes, Question And Answers
Question 2. What information is provided by the reaction mechanism?
- The bonds broken and formed
- The reaction intermediates
- The relative rates of discrete steps, especially the slowest one
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: These are characteristics known from the mechanism of reaction.
Question 3. In which of the following ways does the hydride ion tend to function?
- An electrophile
- A nucleophile
- A free radical
- An acid
Answer: 2. A nucleophile
Solution: Hydride ions are formed when hydrogen accepts a proton, so it has a tendency to donate electrons. Since, hydride ion (H¯) has a tendency to donate electrons, it functions as an nucleophile.

NEET General Organic Chemistry Questions and Answers
Question 4. Which of the following is the weakest base?
- Ethyl amine
- Ammonia
- Dimethyl amine
- Methyl amine
Answer: 2. Ammonia
Solution: The Alkyl group (an electron releasing (+I group) increases electron density at N-atom, hence, basic nature is increased. In ammonia, no alkyl group is present, so it is least basic.
Question 5. An SN2 reaction at an asymmetric carbon of a compound always gives
- A mixture of diastereomers
- A single stereoisomer
- An enantiomer of the substrate
- A product with opposite optical rotation
Answer: A single stereoisomer
Solution: In SN2 reactions, the nucleophile attaches itself from the direction opposite to that of the nucleophile already present in the second step, the previous nucleophile is removed and a single stereoisomer is obtained
Question 6. The most common type of reaction in aromatic compounds is
- Elimination reaction
- Addition reaction
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
- Rearrangement reaction
Answer: 3. Electrophilic substitution reaction
Solution: Due to presence of delocalized π-electrons in the aromatic compounds, the electron density is maximum inside the ring. Therefore, aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reaction and resistance to addition reactions.
Question 7. Which behaves both as a nucleophile as well as an electrophile?
- CH3OH
- CH3NH2
- CH3CN
- CH3Cl
Answer: 3. CH3CN
Solution: CH3NH2 and CH3OH are nucleophiles, CH3Cl is an electrophile. But CH3CN is a nucleophile due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on N and is an electrophile due to the presence of a partial positive charge on C.
Question 8. (CH3)4N+ is neither an electrophile nor a nucleophile because it
- Does not have electron pair for donation as well as cannot attract electron pair
- Neither has electron pair available for donation nor can accommodate electrons since all shells of N are fully occupied
- Can act as Lewis’s acid and base
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Neither has electron pair available for donation nor can accommodate electrons since all shells of N are fully occupied
Solution: It’s a fact.
Question 9. If X is halogen the correct order for SN2 reactivity is:
- R2CHX >R3CX > RCH2X
- RCH2X >R3CX > RCH2X
- RCH2X >R2CHX >R3X
- R3CX >R2CHX > RCH2X
Answer: 3. RCH2X >R2CHX >R3X
Solution: Steric hindrance in tertiary halides gives rise to less reactivity for SN2.
Question 10. Which of the following would react most readily with nucleophiles?
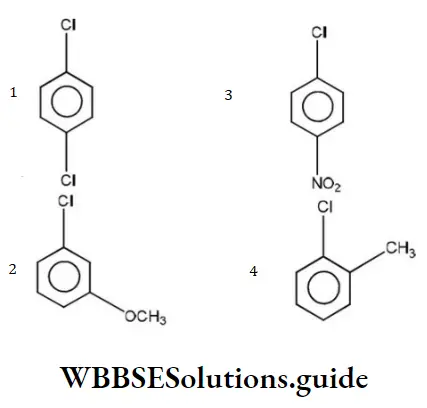
Answer: 3
Solution:
Nucleophiles always attack electron deficient sites. Presence of electron withdrawing groups such as NO2,CHO etc decreases the electron density on the benzene nucleus, hence such groups activate the ring towards nucleophilic attack.
The presence of electron releasing groups such as R or “OR” increases the electron density, thus deactivating the nucleus towards nucleophilic attack. NO2 group activates the ring more than Cl towards nucleophilic attack,hence reacts readily with nucleophile.
Question 11. Which does not have sp2-hybridised carbon atom?
- Acetamide
- Acetic acid
- Acetonitrile
- Acetone
Answer: 3. Acetonitrile
Solution: CH3CN has sp3 and sp-hybridised carbon atoms.
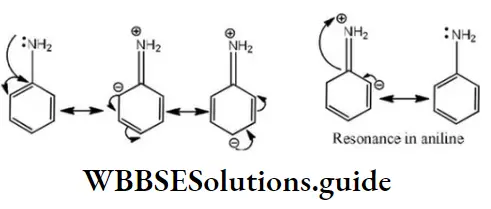
Question 12. The basicity of aniline is less than that of cyclohexylamine. This is due to
- +R effect of – NH2group
- -I effect of – NH2 group
- -R effect of –NH2 group
- Hyperconjugation effect
Answer: 1. +R effect of – NH2 group
Solution: -NH2 has +R effect, it donates electrons to the benzene ring. As a result, the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom gets delocalized over the benzene ring. As a result, the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom gets delocalized over the benzene ring and thus it is less readily available for protonation. Hence, aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 13. Which of the following is an elimination reaction?
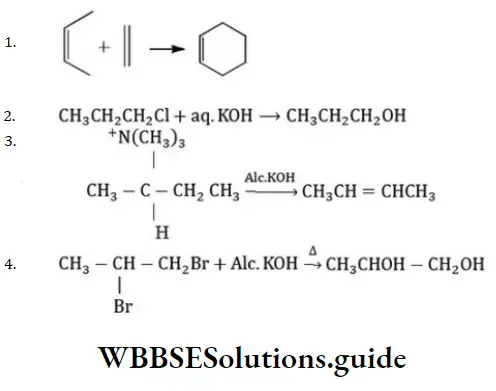
Answer: 3
Solution:
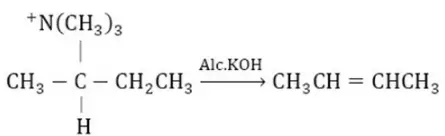
Is an example of an elimination reaction.
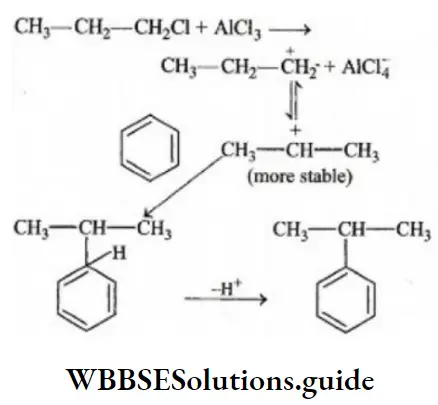
Question 14. The function of AlCl3 in Friedel-Crafts reaction is
- To absorb HCl
- To absorb water
- To produce nucleophile
- To produce electrophile
Answer: 4. To produce electrophile
Solution: The function of AlCl3, in the Friedel-Craft reaction, is to produce electrophile, which later adds to the benzene nucleus
Question 15. The inductive effect
- Implies the atom’s ability to cause bond polarization
- Increases with increase of distance
- Implies the transfer of lone pair of electrons from more electronegative atom to the lesser electronegative atom in a molecule
- Implies the transfer of lone pair of electrons from lesser electronegative atom to the more electronegative atom in a molecule
Answer: 1. Implies the atom’s ability to cause bond polarization
Solution: It’s a fact.
Question 16. Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for
- C6H5OH
- C6H5CH2OH
- CH3-C≡CH
- CH3NH3+ Cl–
Answer: 3. CH3-C≡CH
Solution: Dissociation of a proton from CH3NH3+Cl– is very difficult due to I– effect of Cl–and N+ while in C6H5OH due to the resonance stabilization of phenoxide ion protons are eliminated easily. Similarly, due to H-bonding in C6H5CH2OH, it can be eliminated easily and in CH3C≡CH The proton is acidic in nature hence; it can be dissociated.
Question 17. In the following carbocation, H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is
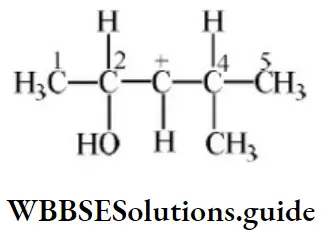
- CH3at C⎼4
- H at C⎼4
- CH3 at C⎼2
- Hat C⎼2
Answer: 4. Hat C⎼2
Solution: Due to the H–shift from C2 to C3 Driving force is conjugation from oxygen. Also, bulky groups hinder the hydride shift.
Question 18. The reaction (Major) The correct statement (s) are
- 2-butene is Saytzeff product
- 1-butene is Hofmann (s) product
- The elimination reaction follows Saytzeff rule
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: The elimination takes place according to the Saytzeff rule. The most substituted alkene (butane-2) is called Saytzeff product whereas less substituted alkene (butane-1) is called Hofmann product
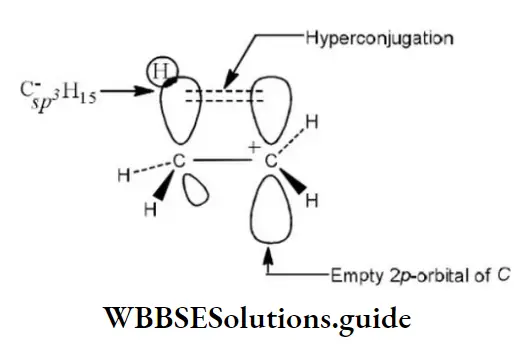
Question 19. Hyperconjugation involves overlap of the following orbitals
- σ- σ
- σ-ρ
- p-p
- π-π
Answer: 2. σ-ρ
Solution: Hyperconjugation arises due to the partial overlap of a sp3-s (a C-H bond) with the empty p-orbital of an adjacent positively charged carbon atom.
Question 20. The compound which reacts with HBr obeying Markownikoff’s rule is
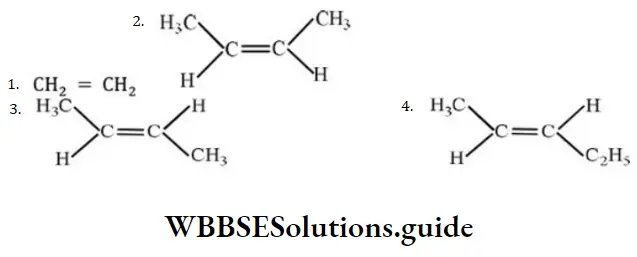
Answer: 4.
Solution: Markownikoff’s rule is obeyed during addition of unsymmetrical addendum on unsymmetrical alkene.
Question 21. The stability of carbanions in the following; is in the order of:
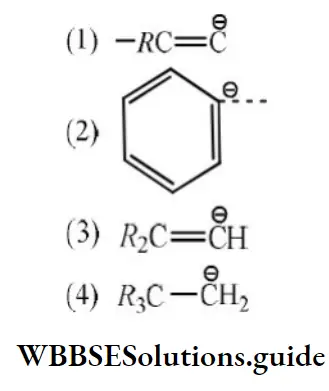
Answer: 4.
Solution: RC≡C- is the most stable because C atom carrying the negative charge is sp hybridized (most electronegative C). Both
2 and 3 have negative charge on sp2 hybridized C atom but 3 is less stable due to electron-releasing alkyl groups. 4 is the least stable as the negative charge is carried by sp3 hybridized C atom.
Question 22. CH3Br + Nu– ⟶CH3-Nu+Br– The decreasing order of the rate of the above reaction with nucleophiles (Nu–) 1 to 4 is [Nu– = (1) PhO–,(2) AcO–,(3) HO–,(4) CH3O–]
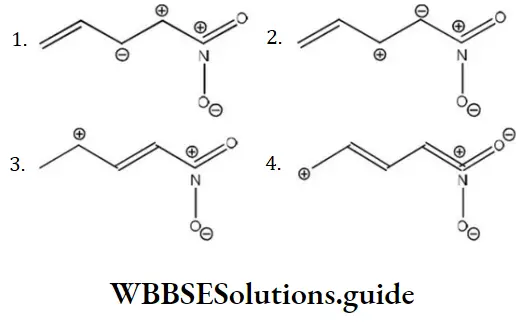
- 4>3>1>2
- 4>3>2>1
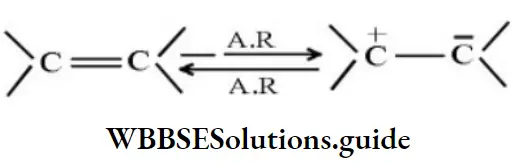
- 1>2>3>4
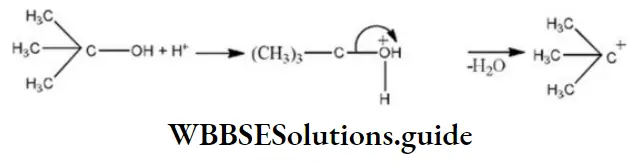
- 2>4>3>1
Answer: 2. 4>3>2>1
Solution: C6H5O– possess less nucleophilicity due to the stabilized nature of phenoxide ions. CH3OH is a weaker acid than CH3COOH and thus CH3O– is a stronger base.
Acidic order: CH3COOH >H2O >CH3OH
Question 23. Which of the following belongs to +I group?
- –OH
- –OCH3
- –COOH
- –CH3
Answer: 4. –COOH
Solution: It is exhibited when an electron releasing group is attached to the carbon chain. Example – Alkyl groups. “The more the number of alkyl groups, more is the +I effect.”
Question 24. The electrophile involved in the reaction is?
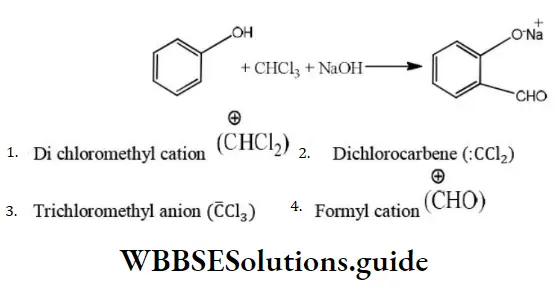
- Di chloromethyl cation
- Dichlorocarbene (:CCl2)
- Trichloromethyl anion (C ̅Cl3)
- Formyl cation
Answer: 2. Dichlorocarbene (:CCl2)
Solution: It is the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. The electrophile formed is: CCl2 (Dichlorocarbene)
Question 25. In the presence of peroxide, hydrogen chloride, and hydrogen iodide do not give anti-Markownikov’s addition to alkenes because
- Both are highly ionic
- One is oxidizing and the other is reducing
- One of the steps are exothermic in both the cases
- All the steps are exothermic in both the cases
Answer: One is oxidizing and the other is reducing
Solution: Follow mechanism of addition of HCl and HI in presence of peroxide. One of the chain propagation steps is endothermic in both cases.
Question 26. According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules, the correct order of priority for the given group is
- –COOH > –CH2OH > –OH > –CHO
- –COOH > –CHO > –CH2OH > –OH
- –OH > –CH2OH > –CHO > –COOH
- –OH > –COOH > –CHO > –CH2OH
Answer: 4. –COOH > –CHO > –CH2OH > –OH
Solution: According to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules, the priority of groups is decided by the atomic number of their atoms. When the atom (which is directly attached to the asymmetric carbon atom) of a group has higher atomic number, then the group gets higher priority. Groups with atoms of comparable atomic number having double or triple bond, have higher priority than those that have single bond. Hence, the order of priority of group is -OH>-COOH>-CHO>-CH2OH
Question 27. Which of the following cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions?
- Chlorobenzene
- Tert-butylchloride
- Isopropyl chloride
- None of these
Answer: 1. Chlorobenzene
Solution: C-Cl bond is aryl chloride is stable due to delocalization of electrons by resonance. Also C-Cl bond possess a double bond character like vinyl chloride, hence SN reactions are not possible in chlorobenzene under ordinary conditions.
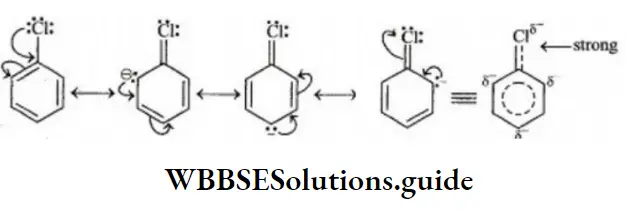
NEET Chemistry Organic Reaction Mechanism Important Questions and Solutions
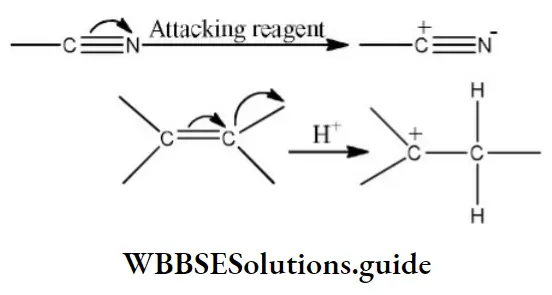
Question 28. Electromeric effect is
- Permanent effect
- Temporary effect
- Resonance effect
- Inductive effect
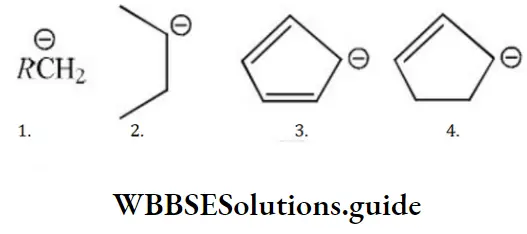
Answer: 2. Temporary effect
Solution: The electromagnetic effect occurs only in the presence of an attacking reagent. It operates in the molecules having multiple bonds. Since it exists only on the demand of attacking reagents, it is a temporary effect. example,
Question 29. The least active electrophile is
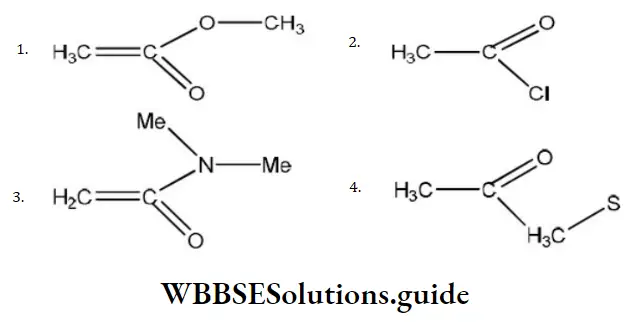
Answer: 3
Solution: In the given electrophile 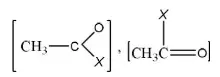
Group is the same. So, only X affects their activity, i.e., we have to discuss activity due to
- –OCH3
- –Cl
- -N<MeMe
- -S – CH3
Since, amines are less active, therefore, electrophile (c) will be least active.
Question 30. Carbanions initiate
- Addition reactions
- Substitution reactions
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: Both (1) and (2)
Solution: It is a fact.
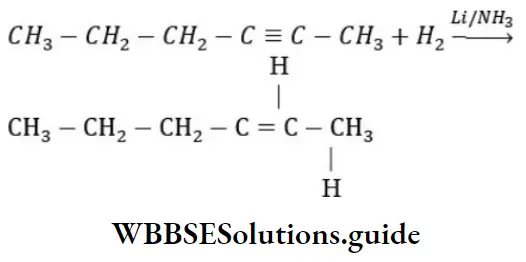
Question 31. 2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment with
- Li/NH3
- Pd/BaSO4
- LiAlH34
- Pt/H2
Answer: 1. Li/NH3
Solution: 2-hexyne gives trans-2-hexene on treatment Li/NH3
Question 32. The chief reaction product of reaction in between n-butane and bromine at 130°C is

Answer: 2
Solution: 2°H is more reactive than 1°.
Question 33. 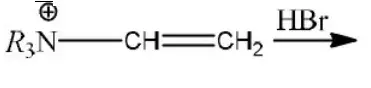 product.
product.
Predominant product is
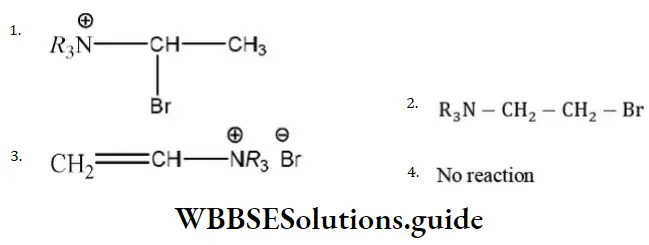
Answer: 2
Solution: Due to \(R_3 \stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{N}}-\) (e– withdrawing tendency) carbocation will appear farther to that (terminal).
Hence, the product is R3N-CH2-CH2Br.
Question 34. Reaction of methyl bromide with aqueous sodium hydroxide involves
- Racemisation
- SN1 mechanism
- Retention of configuration
- SN2 mechanism
Answer: 4. SN2 mechanism
Solution:
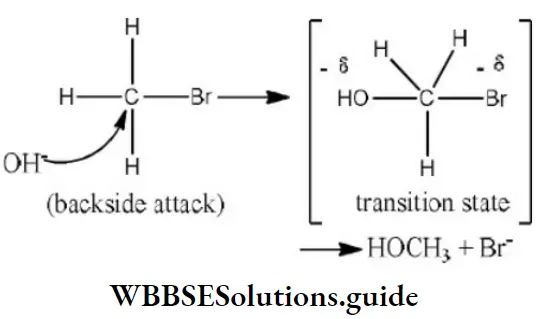
Since, the reaction rate depends upon the concentration of both reactant and nucleophile, it is a SN2 reaction. It involves inversion of configuration.
Question 35. The reaction is fastest when X is
- OCOR
- OC2H5
- NH2
- Cl
Answer: 4. Cl
Solution: The best-leaving group (poorest nucleophile) is Cl⊕, thus the fastest reaction is with Cl.
Question 36. Addition of Br2 on cis-butene-2 gives
- A racemic mixture of 2,3-dibromobutane
- Meso form of 2,3-dibromo butane
- Dextro form of 2,3-dibromobutane
- Laevo form of 2,3-dibromobutane
Answer: 1. A racemic mixture of 2,3-dibromobutane
Solution: Follow mechanism of addition reaction.
Question 37. The order of stability of carbanions is
- CH3–>1°>2°>3°
- 3°>2°>1°>CH3–
- –3°>1°>2°>CH3–
- –2°>3°>1°>CH3–
Answer: 1. CH3–>1°>2°>3°
Solution: The positive inductive effect of CH3 group on carbanions intensifies negative charge on C– centre and thus, 3° Carbanion is more reactive.
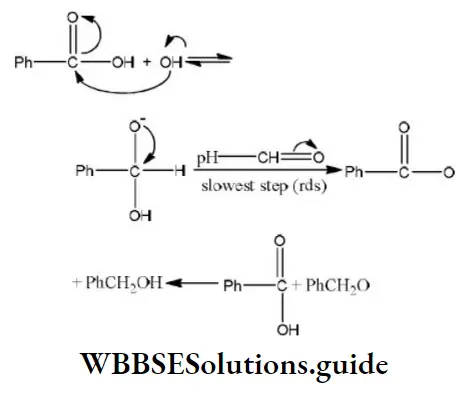
Question 38. In Cannizzaro’s reaction given below \(2 \mathrm{PhCHO} \stackrel{\mathrm{OH}^{\ominus}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{PhCH}_2 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{PhCO}_2^{\ominus}\)
The slowest step is:
- The attack of ::OH⊝ at the carboxyl group
- The transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
- The abstraction of proton from the carboxylic group
- The deprotonation of Ph CH2OH
Answer: 2. The transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
Solution: In Cannizzaro reaction the transfer of H〗 – to another carbonyl group is difficult and the slowest step. (Rate determining step or key step)
Best Practice Questions for NEET General Organic Chemistry (GOC)
Question 39. Which of the following has the highest nucleophilicity?
- F–
- OH–
- CH3–
- NH2–
Answer: 3. CH3–
Solution: Stronger is an acid, weaker is its conjugate base or weaker is the nucleophile. The acidic character order is HF >H2O >NH3>CH4.
Question 40. The following compound will undergo electrophilic substitution more readily than benzene
- Nitrobenzene
- Benzoic acid
- Benzaldehyde
- Phenol
Answer: 4. Phenol
Solution: During electrophilic substitution, electrophile attacks the double bond of the benzene ring. The aromatic compounds having electron donating groups undergo electrophilic substitution more easily due to the favorable effect of the electron donating group.
NO2, COOH, and CHO groups are electron-withdrawing groups so they decrease the reactivity of organic compounds. -OH group is an electron-donating group, so it increases the electron density in the benzene ring and increases the rate of reaction
Question 41. The following reaction is an example of …. reaction. \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{Br}_2 \stackrel{\text { Alc.KOH }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2\)
- Addition
- Dehydrobromination
- Substitution
- Debromination
Answer: 2. Dehydrobromination
Solution:
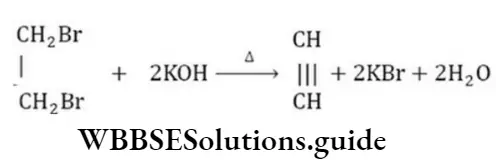
This is a dehydrohalogenation reaction.
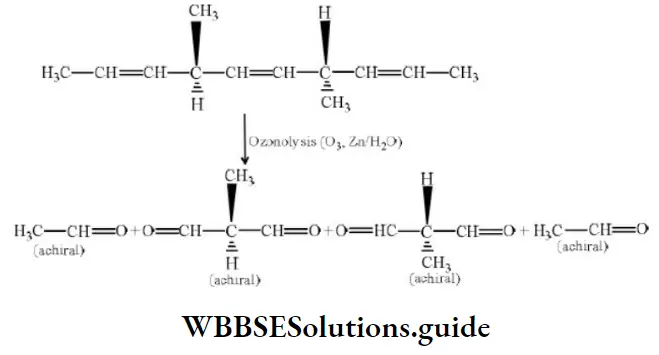
Question 42. The number of optically active products obtained from the complete ozonolysis of the given compound is
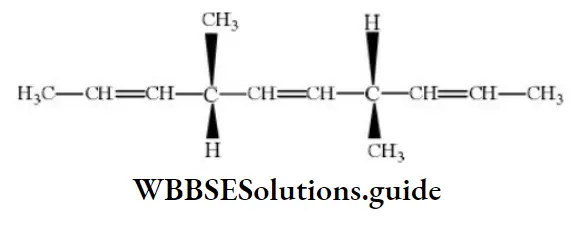
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 4
Answer: 1. 0
Solution: Ozonolysis of the compound may be given as:
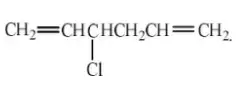
Question 43. The isomeric mono substitution products theoretically possible for the structure, CH2=HC-CH2-CH2 CH=CH2 are∶
- 3
- 2
- 4
- 6
Answer: 1. 3
Solution: CHCl = CHCH2CH2CH = CH2: CH2= CClCH2CH2CH = CH2
Question 44. The most stable carbanion is
- CH⊝3
- RCH2⊝
- R3C⊝
- ⊝CH2CHO
Answer: 4. ⊝CH2CHO
Solution: ⊝CH 2CHO is the most stable carbanion since it is stabilized by resonance
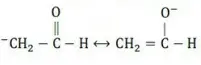
Question 45. Which of the following is the correct order of priority of groups in D-glyceraldehyde?
- OH (1), CHO (2), CH2OH(3) and H (4)
- OH (1), CH2OH (2), CHO (3) and H (4)
- CH2OH (1), CHO (2), OH (3) and H (4)
- CHO (1), OH (2), CH2OH(3) and H (4)
Answer: 1. OH (1), CHO (2), CH2OH(3) and H (4)
Solution: The structure of D-glyceraldehyde is as
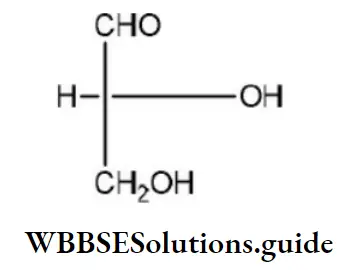
The priority of groups is decided by the following rules
- Atom having higher atomic number gets higher priority
- If the priority cannot be decided by rule 1 then the next atoms are considered for priority assignment.
- Where there is a = bond or=bond both atoms are considered to be duplicated or triplicated ( has higher priority than –CH2OH). Hence, the correct order of priority of groups in
D-glyceraldehyde is as: OH(1),CHO(2),CH2OH (3)and H(4)
Question 46. Which of the following compounds are not arranged in order of decreasing reactivity towards electrophilic substitution?
- Fluorobenzene > chlorobenzene > bromobenzene
- Phenol>n-propyl benzene> benzoic acid>
- Chlorotoluene >para-nitrotoluene>2-chloro-4-nitro toluene
- Benzoic acid> phenol>n-propyl benzene
Answer: 4. Benzoic acid> phenol>n-propyl benzene
Solution: -COOH group is a deactivating group
∴ Benzoic acid is less reactive towards electrophilic substitution.
So, benzoic acid> phenol>n-propyl benzene is not arranged correctly.
Question 47. During the elimination reactions, the hybrid state of carbon atoms involved in change shows:
- sp3 to sp2 nature
- sp2 to sp nature
- No change in hybridized state
- Either of the above
Answer: 4. Either of the above
Solution: CH3CH2X ⟶ CH2= CH2 (sp3 to sp2);
CH2= CHX ⟶ CH ≡ CH (sp2 to sp);
CH2XCH2CH2X⟶∆ (No change).
Question 48. Which of the following is the strongest base?
- Acetamide
- Aniline
- Methylamine
- Dimethylamine
Answer: 4. Dimethylamine
Solution: Presence of methyl group on NH3molecule increases the tendency of the N atom to lose electron pair. However, tertiary amines are less basic due to steric hindrance.
Question 49. One of the stable resonating forms of methyl vinyl ketone is
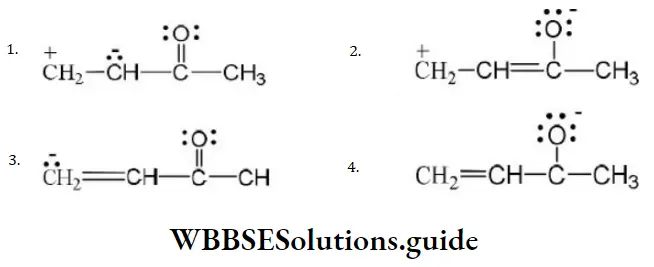
Answer: 2
Solution: The most stable one is that in which the positive and negative charges reside on the most electropositive and most electronegative atoms of the species respectively.
Question 50. The reagent showing addition on alkene against the Markownikoff’s rule
- Br2
- H2S
- HF
- HBr
Answer: 4. HBr
Solution: Kharasch effect involves addition of HBr.
Question 51. Among the following compounds, the most acidic is
- p-nitrophenol
- p-hydroxybenzoic acid
- o-hydroxybenzoic acid
- p-toluic acid
Answer: 3. o-hydroxybenzoic acid
Solution: A monosubstituted benzoic acid is stronger than a monosubstituted phenol as the former being a carboxylic acid. Among the given substituted benzoic acid, ortho-hydroxy acid is the strongest acid although – OH causes electron donation by resonance effect which tends to decrease acid strength. It is due to the very high stabilization of conjugate base by intramolecular
H-bond which outweighs the electron donating resonance effect of – OH.
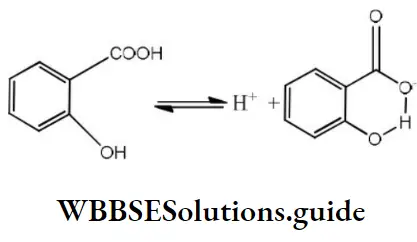
The overall order of acid strength of the given four acids is ortho-hydroxy benzoic acid (pKa =2.98)> Toluic acid pka = 4.37)>p-hydroxybenzoic acid (pka = 4.58)>p-nitrophenol (pka = 7.15).
Question 52. The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for a SN2 reaction is
- RF > RCl > RBr > RI
- RF > RBr > RCl > RI
- RCl > RBr > RF > RI
- RI > RBr > RCl > RF
Answer: 4. RI > RBr > RCl > RF
Solution: The rate of reaction follows the order RI> RBr > RCl> RF; whether it obeys SN1 or SN2 mechanism due to steric hindrance of the alkyl group.
Question 53. Electrophiles are
- Lewis bases
- Lewis’s acids
- Amphoteric
- None of these
Answer: 2. Lewis’s acids
Solution: Electrophiles are electron pair acceptors.
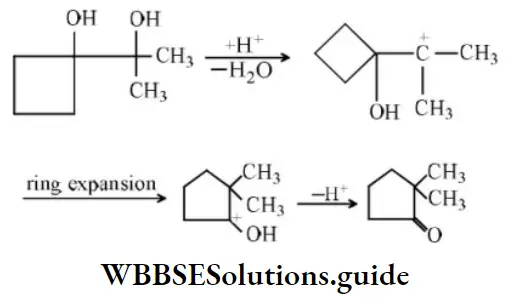
Question 54. Product in the reaction is?
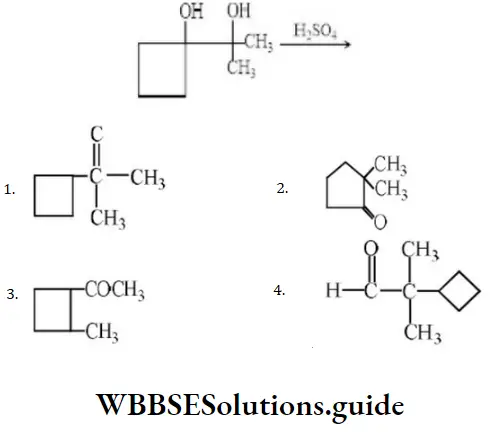
Answer: 2
Solution: In such cases where the migrating group is a cycloalkyl group, ring expansion may occur.
NEET Chemistry Organic Reaction Mechanism Short and Long Answer Questions
Question 55. Which one of the following is an intermediate in the reaction of benzene with CH3Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3?
- Cl+
- CH3–
- CH3+
Answer: 3. CH3+
Solution: CH3+ acts as an intermediate in the given reaction (Friedel Craft’s alkylation). It is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution. In this reaction CH3+is electrophile.
Question 56.+I effect is shown by
- -CH3
- -Br
- -Cl
- -NO2
Answer: 1. -CH3
Solution: +I effect is shown by –CH3 while –I effect is shown by –Br,-Cl and-NO2.
Question 57. Amongst the following which of the above are true for SN2 reaction?
1. The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the nucleophile.
2. The nucleophile attacks the carbon atom on the side of the molecule opposite to the group being displaced.
3. The reaction proceeds with simultaneous bond formation and bond rupture.
- 1,2
- 1,3
- 1,2,3
- 2,3
Answer: 4. 2,3
Solution: Follow the characteristics of SN2 mechanism.
Question 58. In the nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN2 or SN1), the reactivity of alkyl halides follows the sequence
- R-I>R-Br>R-Cl>R-F
- R-Cl>R-F>R-Br>R-I
- R-F>R-Cl>R-Br>R-I
- R-I>R-F>R-Cl>R-Br
Answer: 1. R-I>R-Br>R-Cl>R-F
Solution: The correct order of reactivity is RI>RBr>RCl>RF. It is due to the fact that the weaker the base, the better it will be for the leaving group. Hence, I– is the best-leaving group.
Question 59. Among the following compounds which can be dehydrated very easily is
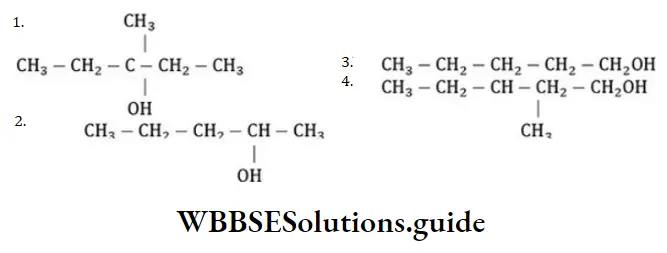
Answer:
Solution: In the above reaction more stable carbocation is generated hence, the compound dehydrates very easily.
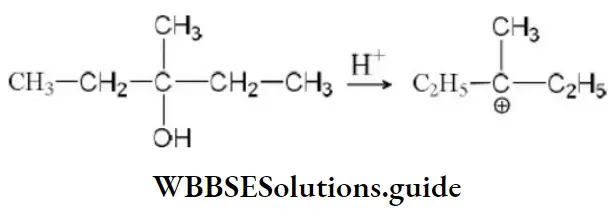
Question 60. Which of the following is not a nucleophile?
- BF3
- CN–
- OH–
- NH3
Answer: 1. BF3
Solution: All neutral covalent compounds in which the central atom has incomplete octet are electrophile. For example, BeCl2,BH3,ZnCl2,AlCl3
Question 61. In the following reactions,
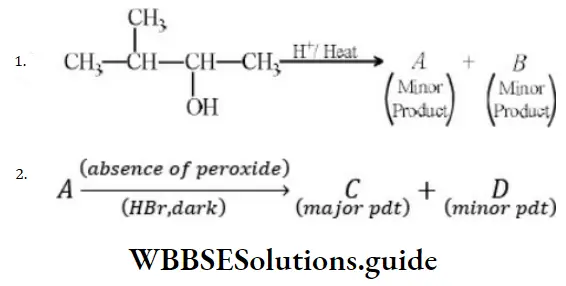
The major products (A) and (C) are respectively
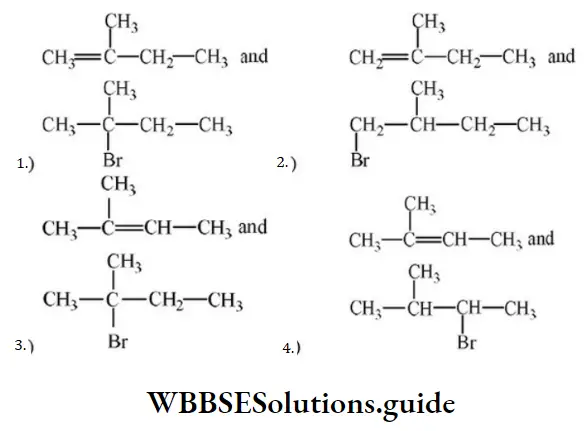
Answer: 3
Solution: In the first reaction, dehydration is governed by the Saytzeff rule which gives a more substituted alkene product. Here, the secondary carbocation formed undergoes 1, 2 hydride shifts and gives more stable tertiary carbocation which further undergoes beta elimination to give the major product (A). Thus, 2- Methyl but-2-ene is the major product.
HBr in the absence of peroxide.
This reaction is governed by the Markovnikov rule according to which when an unsymmetrical alkene undergoes hydrohalogenation, the negative part of the addendum (adding molecule) gets attached to that doubly bonded C which possesses a lesser number of hydrogen atoms. when an unsymmetrical reagent. Thus, in the above case, 2-Methyl 2-bromobutane will be the major product.
Question 62. The rate of the reaction,
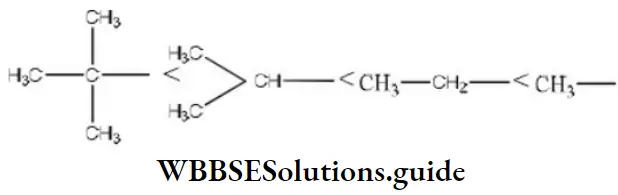
i.e., 4<3<2<1
The increasing order of speed of the above reaction is
- 4,3,2,1
- 1,2,3,4,
- 1,4,3,2
- 3,2,1,4
Answer: 1. 4,3,2,1
Solution: The rate of reaction is influenced by the hyperconjugation effect of group R. It depends on the electron-donating power of the alkyl group (R). The electron-releasing power of the R group depends on the number of hydrogen present in α carbon. The increasing order of speed with R group in the reaction is i.e., 4<3<2<1
General Organic Chemistry NEET Notes with Solved Questions
Question 63. The organic chloro compound, which shows complete stereochemical inversionduring and SN2 reaction, is
- CH3Cl
- (C2H5)2CHCl
- (CH3)3CCl
- (CH3)2CHCl
Answer: 1. CH3Cl
Solution: SN2 order: methyl >1°>2°>3°.
Question 64. Vinyl chloride undergoes
- Only addition reactions
- Only elimination reactions
- Both (1) and (2)
- Substitution reactions
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Solution: Vinyl chloride(CH2=CHCl) undergoes addition and elimination reactions. Substitution’s reaction is shown by compounds having single bonds only.
Question 65. Which of the following is the strongest nucleophile?
- Br–
- :OH–
- :CN–
- C2H5O–
Answer: C2H5O–
Solution: The order of nucleophilicity depends upon the nature of alkyl group ‘R’ on which a nucleophile to attack as well as on the nature of solvent. However, if these are same, then weaker is the acid, stronger is base, i.e., stronger is nucleophilicity. This acidic character is.
HI > HBr > HCl > HCN >H2O > EtOH
Question 66. Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by
- SN1 mechanism
- SN2 mechanisms
- SN1 and SN2 mechanisms
- Neither SN1 nor SN2 mechanism
Answer: 3. SN1 and SN2 mechanisms
Solution: Iso-propyl chloride is a 2° halide and 2° halides can undergo hydrolysis either by SN1
or SN2 mechanism depending upon the nature of the solvent used.
Question 67. Which of the following is not true for carbanions?
- The carbon carrying the charge has eight valence electrons
- They are formed by heterolytic fission
- They are paramagnetic
- The carbon carrying the charge is sp3 hybridised
Answer: 3. They are paramagnetic
Solution: Carbanions contain even number of valence electrons and thus, show diamagnetic behavior.
Question 68. Free radicals can undergo
- Disproportionation to two species
- Rearrangement to a more stable free radical
- Decomposition to give another free radical
- All of the above are correct
Answer: 4. All of the above are correct
Solution: These are the characteristics of free radicals.
Question 69. Due to the presence of an unpaired electron, free radicals are
- Cations
- Anions
- Chemically inactive
- Chemically reactive
Answer: 4. Chemically reactive
Solution: Free radicals have unpaired electrons but are neutrals and are reactive.
![]()
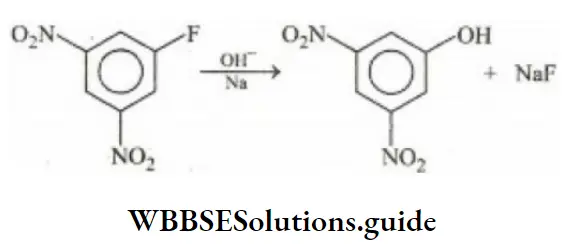
Question 70. Which represents nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction?
- Reaction of benzene with Cl2 in sunlight
- Benzyl bromide hydrolysis
- Reaction of NaOH with dinitrofluorobenzene
- Sulphonation of benzene
Answer: 3. Reaction of NaOH with dinitrofluorobenzene
Solution: Reaction of NaOH with dinitrofluorobenzene represents nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction because the –NO2 group is a deactivating group. They make benzene nucleus electrons deficient and facilitate the nucleophile to attack the ring.
Question 71. The SN1 mechanism for substitution reaction by nucleophile is favored by
- Low concentration of nucleophile
- Weak nature of nucleophile
- Polar solvent
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: These are the characteristics of SN1 mechanism.
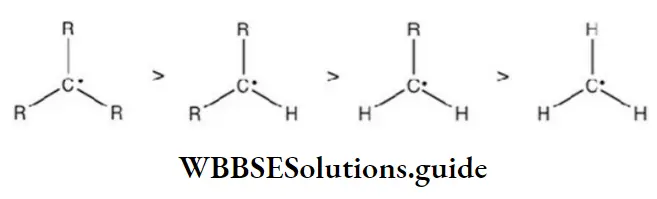
Question 72. Which of the following is the most stable radical?
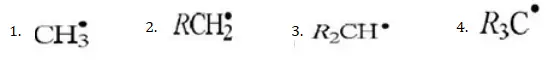
Answer: 4
Solution: The stability of alkyl free radicals can be explained by hyperconjugation and number of resonating structures due to the hyperconjugation.
Question 73. Which of the following types of reaction occurs when a substituent has got a double bond with an evenly distributed π electron cloud?
- Electrophilic addition
- Nucleophilic addition
- Any of the (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Electrophilic addition
Solution: Such a condition is seen when π bond is formed between similar atoms
Question 74. The formation of acetylene from ethylene is an example of
- Addition reaction
- Substitution reaction
- Elimination reaction
- Condensation reaction
Answer: 3. Elimination reaction
Solution: CH2=CH2→-H2CH≡CH Conversion of ethylene into acetylene is an example of an elimination reaction.
Question 75. Which of the following can act as a nucleophile?
- BF3
- FeCl3
- ZnCl2
- C2H5MgBr
Answer: 4. C2H5MgBr
Solution: Grignard reagents can act as electrophile and nucleophile.
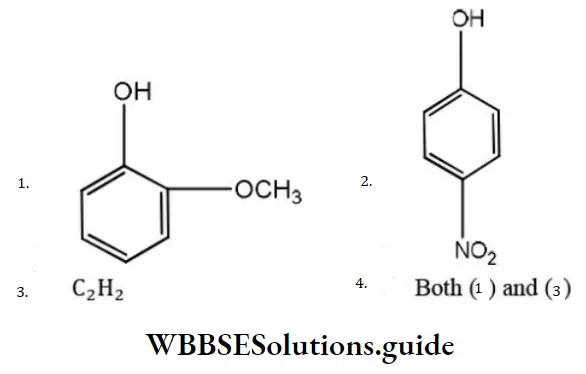
Question 76. Phenol is more acidic than
Answer:
Solution: Methoxy group, due to +I effect, increase electron density on OH- group, thus making it less acidic. Thus, o-methoxy phenol and acetylene are less than phenol. p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Question 77. The formation of ethylene from acetylene is an example of
- Elimination reaction
- Substitutions reaction
- Condensation reaction
- Addition reaction
Answer: 4. Addition reaction
Solution: The formation of ethylene from acetylene is an example of additional reaction
Question 78. Which of the following compounds will be most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction?
- CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3
- CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
- CH2 – CH2– CO- CH- CH3– CH3
Answer: 3. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
Solution:
The case with which a nucleophile attacks the carbonyl groups depends upon the electron-deficiency, i.e, the magnitude of the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon. Since, an alkyl group has an electron-donating inductive effect.
(+I effect),therefore, the greater the number of alkylgroups attached to the carbonyl groups greater is the electron-density on the carbonyl carbon and hence, lower is its reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
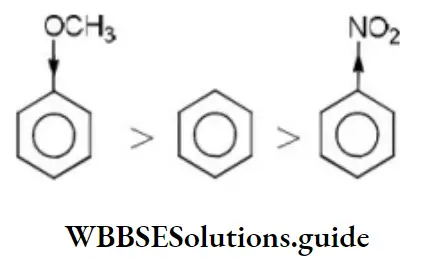
Question 79. Among the following compounds (1-3) the correct order of reaction with electrophilic reagent is
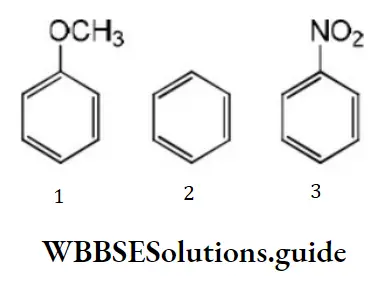
- 2>3>1
- 3<1<2
- 1>2>3
- 1=2>3
Answer: 3. 1>2>3
Solution: Methoxy group is electron releasing group it increases electron density of benzene nucleus –NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group, it decreases the electron density of the benzene nucleus. Thus, the order of reaction with electrophilic regent is
NEET Study Material for Organic Reaction Mechanism with MCQs
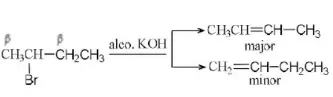
Question 80. Which of the following applies in the reaction CH3CHBrCH2CH3→Alco.KOH?
CH3CH=CHCH3 (Major product)
CH2=CHCH2CH3 (Minor product)
- Hofmann’s rule
- Saytzeff rule
- Kharasch effect
- Markownikoff’s rule
Answer: 2. Saytzeff rule
Solution: This reaction is governed by Saytzeff rule. According to this rule the elimination of β-hydrogen atom take place from the carbon having the lesser number of H-atoms or in other words a stable alkene is formed. (More substituted alkene is more stable)
Question 81. Which of the following is most basic?
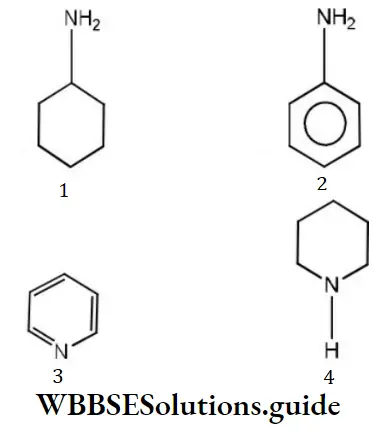
Answer: 4
Solution: Electron donors are bases. (Piperidine), hence, it is most basic.
Question 82. Arrange the following compounds in order of their decreasing reactivity with an electrophile, E⊕.
1. Chlorobenzene,
2. 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene,
3. p-nitrochlorobenzene
- 3>2>1
- 1>3>1
- 1>3>2
- 1>2>3
Answer: 3.1>3>2
Solution: Chlorobenzene has only one deactivating group, .e.,-Cl. In 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene three deactivating group, i.e., two –NO2 and one –Cl are present and p-nitrochlorobenzene two deactivation groups, i.e., one NO2 and one Cl is present. So, the order of reactivity is 1>3>2.
Question 83. Sulfur trioxide is
- An electrophile
- A nucleophile
- A homolytic reagent
- A base
Answer: 1. An electrophile
Solution: SO3 can accept lone pair of electrons in the d-subshell.
Question 84. The chemical name of anisole is
- Ethanoic acid
- Methoxy benzene
- Propanone
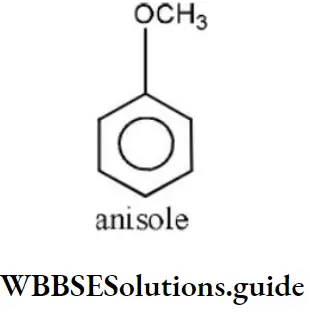
- Acetone
Answer: 2. Methoxy benzene
Solution: It is an ether and the name of ether is given as alkoxy alkane. So, its name is methoxy benzene.
Question 85. Consider the following carbanions
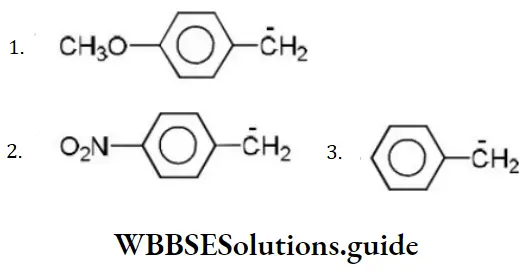
The correct order of stability is
- 1>2>3
- 3>2>1
- 2>3>1
Answer: 3. 2>3>1
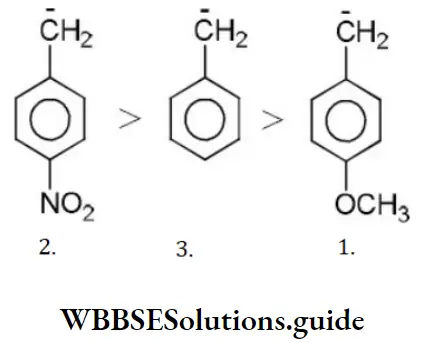
Solution: -NO2 group shows-M effect while CH3O- group shows +M effect. (-Meffect stabilizesan anion). Hence, the order of stability is
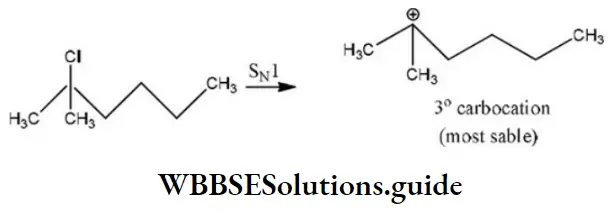
Question 86. Which of the following shows SN1 reaction most readily?
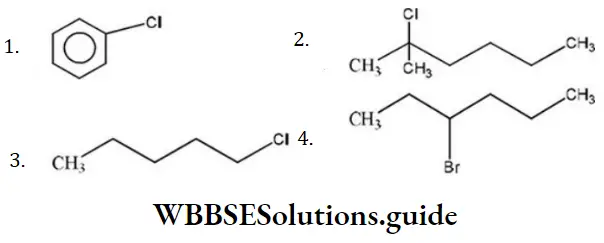
Answer: 2
Solution: SN1 Reaction is most favourable for tertiary substances.
Question 87. Heterolysis of CH3CH2CH3 results in the formation of

Answer: 3.
Solution: In heterolysis, the covalent bond is broken in such a way that one species (less electronegative) is deprived if its own electron, while the other species gain both the electron CH3CH2CH3 → –CH3+ +C2H2
Question 88. The SN1 reactivity of the following halides will be in the order
1 .(CH3)3CBr
2. (C6H5)2CHBr
3. (C6H5)2C(CH3)Br
4. (CH3)2CHBr
5. C2H5Br
- 5>4>1>2>3
- 2>1>3>5>4
- 1>3>5>2>4
- 3>2>1>4>5
Answer: 4. 3>2>1>4>5
Solution: SN1(Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions) Rate∝ (substrate)
Rate determining step in the formation of carbocation depends on the stability of the carbocation formed. The stability of carbocations follows the order
∵ Order of SN1reactivity is
(C6H5)2C(CH3)Br>(C6H5)2CHBr>(CH3)3CBr>(CH3)2CHBr>C2H5Br
i.e., 3>2>1>4>5
Question 89. Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant?
- CH3CHFCOOH
- FCH2CH2COOH
- BrCH2CH2COOH
- CH3CHBrCOOH
Answer: 3. BrCH2CH2COOH
Solution: BrCH2CH2COOH is the weakest acid and has the lowest dissociation constant because.
i.e., of Br is lesser than F and is far away from –the COOH group.
Question 90. The reagent used in the dehydrohalogenation process is
- Alcoholic KOH
- NaNH2
- C2H5ONa
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Solution: All are used as dehydrohalogenating agent.
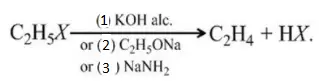
Question 91. Why is light necessary to bring in chlorination r
- The dissociation of Cl2 gives Cl° radical
- The Cl2 molecule absorbs light to show homolytic bond fission
- The formation of Cl° free radical propagates the chain reaction
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: Follow the mechanism of free radical substitution.
Question 92. The structure remaining after one H is removed from hydrocarbon is
- Alkyl group
- Alkenyl group
- Alkynyl group
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Solution: Removal of H from alkane, alkene, and alkyne gives alkyl, alkenyl, and alkynyl groups respectively.
Question 93. Which of the following statements is not correct?
- A >C=C< group is made up of 4 σ -bonds and 2 π-bonds
- A σ-bond is stronger than π-bond
- A σ-bond can exist independently of π-bond
- A double bond is stronger than a single bond
Answer: 1. A group is made up of 4 σ -bonds and 2 π-bonds
Solution:
Question 94. Stability of which intermediate is not governed by hyperconjugation?
- Carbon cation
- Carbon anion
- Carbon-free radical
- None of these
Answer: 2. Carbon anion
Solution: The stability of carbanion is not governed by hyperconjugation. Its stability depends on the +I or -I group.
Question 95. State the hybridization of carbon present in triplet carbene
- Sp3
- Sp2
- Sp
- None of these
Answer: 3. Sp
Solution: The state of hybridization of carbon in triplet carbene is sp.
Question 96. The decreasing order of nucleophilicity among the
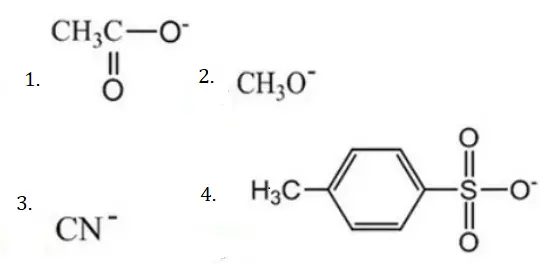
- (3),(2),(1),(4)
- (2),(3),(1),(4)
- (4),(3),(2),(1)
- (1),(2),(3),(4)
Answer: 2. (2),(3),(1),(4)
Solution: If acid is weak, its conjugate base (nucleophile) is strong and vice versa.
Question 97. Following reaction, (CH3)3CBr+H2O→ (CH3)3COH+HBr is an example of
- Elimination reaction
- Free radical substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic substitution
Answer: Nucleophilic substitution
Solution: (CH3)3CBr+H2O→ (CH3)3C-OH+HBr Br is substituted by –OH–(nucleophile)SN1 (Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction)
Question 98. The correct sequence of steps involved in the mechanism of Cannizzaro’s reaction are
- Nucleophilic attack, transfer of H– and transfer of H+
- Transfer of H–, transfer of H+ and nucleophilic attack
- Transfer if H+, nucleophilic attack and transfer of H–
- Electrophilic attack by OH–, transfer of H+ and transfer of H
Answer: 1. Nucleophilic attack, transfer of H– and transfer of H+
Solution: The Cannizzaro reaction is as
Methyl alcohol acetic acid
The mechanism of Cannizzaro reaction is as
Step 1 Attack of nucleophile OH– to the carbonyl carbon
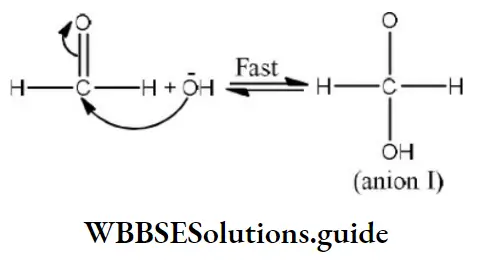
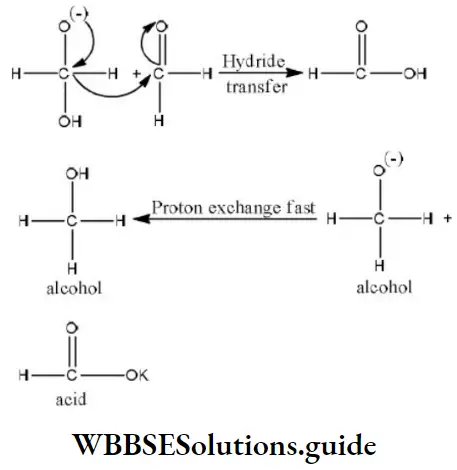
Step 2 The transfer of hydride ions from anion (I) to the second molecule of aldehyde and finally rapid transfer of protons takes place.
Question 99. The arrangement of decreasing order of stability of 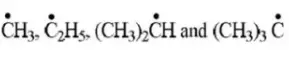
Free radicals is.
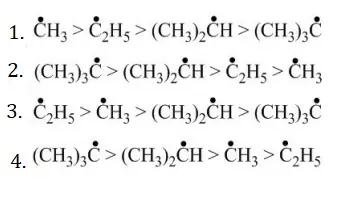
Answer: 2
Solution: Follow the concept of hyperconjugation.
Question 100. Which chlorine atom is more electronegative in the following?

Answer: 4
Solution: More the number of hyper-conjugated structures, more will be electronegative chlorine atoms.

8-hyper conjugative structures
∵ 8-hyperconjugative structures are possible for (d)
∴ Chlorine in this is most electronegative.
Question 101. Arrange the following carbocations in order of stability
1. Benzy – 1
2. Allyl -2
3. Methyl -3
4. Vinyl – 4
- 4>3>2>1
- 1>2>3>4
- 2>4>3>1
- 3>2>1>4
Answer: 2. 1>2>3>4
Solution:
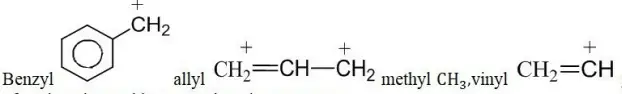 Methyl CH3 CH2= +CH given options can be solved on the basis of conjugative and hyperconjugative structures
Methyl CH3 CH2= +CH given options can be solved on the basis of conjugative and hyperconjugative structures
Question 102. The chain initiating species in the free radical chlorination of methane is?
- Cl free radical
- HCl
- CH3 radical
- Methylene radical
Answer: 1. Cl free radical
Solution: Initiation step involves the splitting of a chlorine molecule which then forms two chlorine atoms; this process is initiated by ultraviolet radiation or sunlight. As we know, chlorine has one unpaired valence electron, which will act as a free radical.
Question 103. Among the following alkenes
1. 1-butene
2. Cis-2-butene,
3. Trans-2-butene the decreasing order of stability is
- 3 > 2 > 1
- 3> 1 > 2
- 1 > 2 > 3
- 2 > 1 > 3
Answer: 1.3 > 2 > 1
Solution: Based on the heat of hydrogenation.
Organic Reaction Mechanism Class 11 NCERT Questions for NEET
Question 104. The substitution reaction among the following is
Answer: 3
Solution:
- It is Diels Alder’s reaction (cyclo addition)
- It is nucleophilic addition reaction
- It is nucleophilic substitution reaction
- It is electrophilic addition reaction
Question 105. Which one of the following compounds will be most readily dehydrated?
Answer: 3
Solution: On the basis of stability of carbocation formed.
Question 106. Consider thiol anion (RS⊝)and alkoxy anion(RS⊝). Which of the following statement(s) is correct?
- RS⊝ is less basic and less nucleophilic than RO⊝
- RS⊝ is less basic but more nucleophilic than RO⊝
- RS⊝ is less basic and more nucleophilic than RO⊝
- RS⊝ is more basic but less nucleophilic than RO⊝
Answer: 2. RS⊝ is less basic but more nucleophilic than RO⊝
Solution: Nucleophilic strength increases down a column of the Periodic Table (in solvents that can have hydrogen bonds, such as water, alcohols, thiol alcohols).
Nucleophilic strength RO–<RS–
Base strength RO⊝ > RS–
Thus, RO⊝ is more nucleophilic but less basic than RO
Question 107. Which of the following alkyl halides is used as a methylating agent?
- C2H5Cl
- C2H5Br
- C2H5I
- CH3I
Answer: 4. CH3I
Solution: Methyl halides are methylating agents.
Question 108. The correct stability order for the following species as
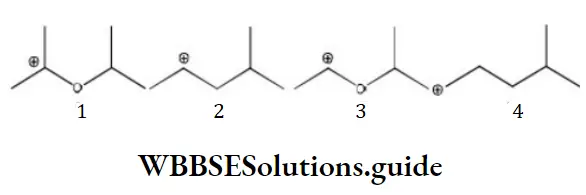
- 2>4>1>3
- 1>2>3>4
- 2>1>4>3
- 1>3>2>4
Answer: 4. 1>3>2>4
Solution: 1>3>2>4
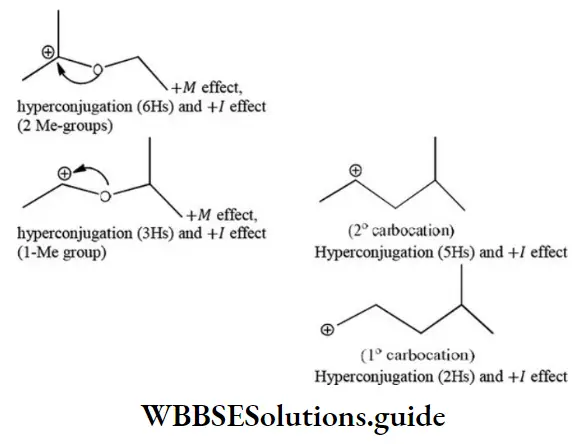
Question 109. Which of the following statement(s) is incorrect?
- The rate of reaction increases with increase in water concentration in the hydrolysis of tertiary butyl bromide in methanol and water
- The relative nucleophilicity in protic solvent is CN–>I–>OH>Br–>CI–>F–>H2O
- In SN2 reactions, the order of reactivity of alkyl halides is in the order methyl > primary > secondary > tertiary
- SN2 reaction involves carbonium ions
Answer: 4. SN2 reaction involves carbonium ions
Solution: SN2 r reaction does not involve ion formation, these in fact involve the formation of transition state.
Question 110. Which of the following is an electrophile?
- Na+
- Li+
- H+
- Ca2+
Answer: 3. H+
Solution: Positively charged species in which central atom has incomplete octet is called an electrophile, H+,X+,R+ are electrophile.
Question 111. The-Ieffect is shown by
- –COOH
- –CH3
- –CH3CH2
- –CHR2
Answer: 1. –COOH
Solution: –COOH is an electron with drawing group.
Question 112. Identify the product in the given reaction: CH3-CH=CH2+NOCl ⟶ Product
- CH3CHCl.CH2.NO
- CH3CH(NO).CH2Cl
- CH3CH2CH(Cl)(NO)
- CH2(NO).CH2.CH2Cl
Answer: CH3CHCl.CH2.NO
Solution: This reaction is an example of electrophilic addition reaction and its addition takes place according to Markownikoff’s rule. Negative part of the additive reagent adds to the less hydrogenated or more substituted carbon atom of the double bond of unsymmetrical alkene.
Question 113. Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
- (CH3)3C-Cl
- CH2=CHCl
- CH3CH2Cl
- CH2=CHCH2Cl
Answer: 2. CH2=CHCl
Solution: Chlorine of vinyl chloride (CH2=CHCl) is non-reactive (less reactive) towards nucleophile in nucleophilic substitution reaction because it shows the following resonating structure due to +M effect of –Cl atom.
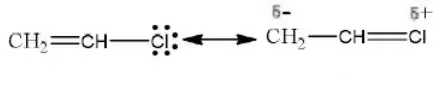
In structure II, Cl-atom have positive charge and partial double bond character with C of vinyl group, so it is more tightly attracted towards the nucleus and it does not get replaced by nucleophile in SN– reaction.
Question 114. The bond that undergoes heterolytic cleavage most easily is
- C–O
- C–C
- C–H
- O–H
Answer: 4. O–H
Solution: Greater the difference in electronegativity of bonded atoms easier will be heterolytic cleavage.
Question 115. Arrange the following in order of increasing dipole moment
1. Toluene
2. m-dichlorobenzene
3. o-dichlorobenzene
4. p-dichlorobenzene
- 1 < 4 < 2 < 3
- 4 < 1 < 2 < 3
- 4 < 1 < 3 < 2
- 4 < 2 < 1 < 3
Answer: 2. 4 < 1 < 2 < 3
Solution: In o-,m-,p- derivatives vectors are at 60°,120° and 180°. Thus, para has zero dipole moment. Alsoortho form has more dipole moment than metaform.
Question 116. Which of the following cannot show electromeric effect?
- Alkenes
- Ketones
- Aldehydes
- Ethers
Answer: 4. Ethers
Solution: Electromeric effect involves complete transfer of π-electron pair to more electronegative atom on the need of attacking reagent.
Question 117. Which one is an elimination reaction?
- CH3CH3+ Cl2⟶ CH3CHC2l + HCl
- CH3Cl + KOH(aq.)⟶ CH3OH + KCl
- CH2= CH2 + Br ⟶CH2BrCH2Br
- C2H5Br + KOH(alc.)⟶ C2H4+ KBr + H2O
Answer: 4. C2H5Br + KOH(alc.)⟶ C2H4+ KBr + H2O
Solution: Elimination reactions involves the removal of a molecule (HBr here) from a substrate.
Question 118. In the following reaction sequence, the chain initiation step is?
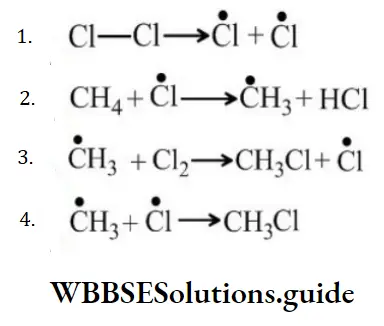
Answer: 1
Solution: Chain initiation step involves the formation of free radicals only.
Question 119. The highest electrical conductivity of the following aqueous solutions is of
- 0.1 M difluoroacetic acid
- 0.1 M fluoroacetic acid
- 0.1 M chloroacetic acid
- 0.1 M acetic acid
Answer: 1. 0.1 M difluoroacetic acid
Solution: Fluoro group causes negative inductive effect increasing ionization, thus 0.1M difluoroacetic acid has highest electrical conductivity.
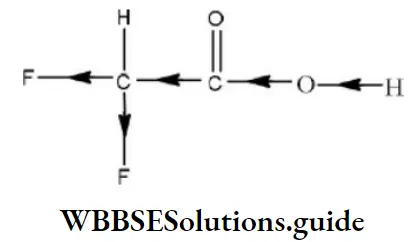
Question 120. The most stable carbocation is
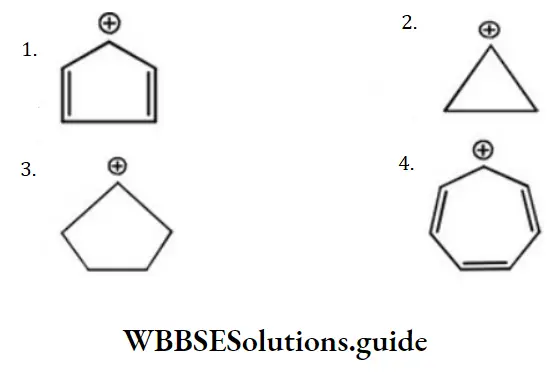
Answer: 4
Solution: 4 is with maximum conjugative structures among them.
Types of Organic Reactions and Reaction Intermediates NEET Questions
Question 121. Most stable carbonium ion is
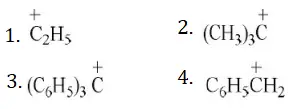
Answer: 3
Solution: In the triphenyl methyl carbonium ion the π-electrons of all the three benzene rings are delocalised with the vacant p-orbitals of the central carbon atom. So, it is resonance stabilized. It is the most stable of all the carbonium ions given is stabilized by hyperconjugation, asecond order resonance.
Question 122. Which of the following resonating structures of 1-methoxy-1, 3-butadiene is least stable?
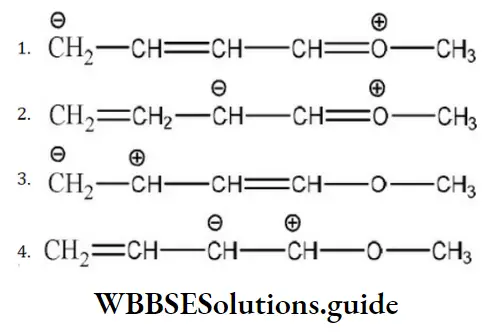
Answer: 3.
Solution: The octet of all atoms is complete in the structures a and b. The molecule in which all the atoms have completed octet is more stable than atoms which have incomplete octet. Larger the number of resonating structures, larger will be the stability, thus structures a and b are stable.
In structure (4), the electron deficient of positive charged carbon is duly compensated by one pair of electrons of adjacent oxygen atoms while such neighbor group support is not available in structure (3). Hence, structure (3) is least stable in comparison to structure (41).
Question 123. The reaction 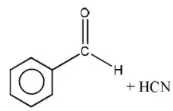 is an example of
is an example of
- Electrophilic addition
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic addition
Answer: 4. Nucleophilic addition
Solution: It is an example of a nucleophilic addition reaction.
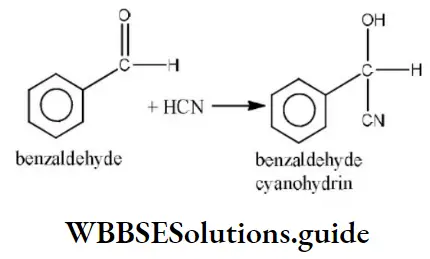
Question 124. The reaction of sodium ethoxide with iodoethane to from diethyl is termed as
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Radical substitution
Answer: 2. Nucleophilic substitution
Solution: When sodium ethoxide reacts with iodoethane, diethyl ether is obtained (Williamson’s synthesis) The mechanism of this reaction is as follows
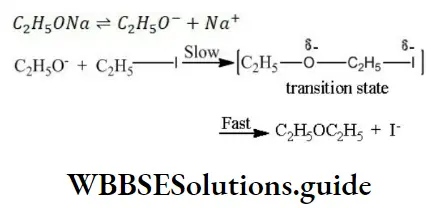
Since, the reaction involves the substitution of a group by a nucleophile, it is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Question 125. Which group has the highest + Inductive effect?
- CH3–
- CH3CH2–
- (CH2)2CH-
- (CH3)3C
Answer: 4. (CH3)3C-
Solution: The increasing order is: -CH3<CH3-CH2– <(CH3)2CH-<(CH3)3C
Question 126. When SCN– is added to an aqueous solution containing Fe(NO3)3,the complex ion produced is
- [Fe(OH2)2(SCN) ]2+
- [Fe(OH2)5(SCN) ]2+
- [Fe(OH2)8(SCN) ]2+
- [Fe(OH2)(SCN)]6+
Answer: 2. [Fe(OH2)5(SCN) ]2+
Solution: On adding SCN– to an aqueous solution of Fe(NO3)3, a blood red colour, due to formation of [Fe(H2O)5(SCN)]+ complex is obtained. This test is used for the detection of Fe3+ ion. SCN– +Fe(NO3)3+ 5H2O→ [Fe(OH2)5(SCN)]2+ + 3NO3– Blood red colour
Question 127. Which shows the easier electrophilic substitution in a ring?
- N-acetyl aniline
- C6H5NH3Cl
- Aniline
- Nitrobenzene
Answer: 3. Aniline
Solution: Ortho and para-directing groups facilitate the ring for electrophilic substitution reaction. –NH2 group increases the electron density in the ring, hence activates electrophilic substitution.
Question 128. Correct gradation of basic character
- NH3CH3NH2>NF3
- CH3NH2>NH3>NF3
- NF3>CH3NH2>NH3
- CH3NH2>NF3>NH3
Answer: 2. CH3NH2>NH3>NF3
Solution: In the gas phase, tertiary amines are more basic than secondary amines which are more basic than ammonia -Group present on the central atom decreases electron density, hence decreases basicity
CH3NH2>NH3>NF3
Question 129. A carbonium ion contains
- A positively charged carbon center
- A negatively charged carbon center
- A carbon with an odd electron on it
- None of the above
Answer: 1. A positively charged carbon center
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 130. In which of the following species the central carbon atom is negatively charged?
- Carbonium ion
- Carbanion
- Carbocation
- Free radicals
Answer: 2. Carbanion
Question 131. Alkaline hydrolysis of an ester (A) gives alcohol and salt
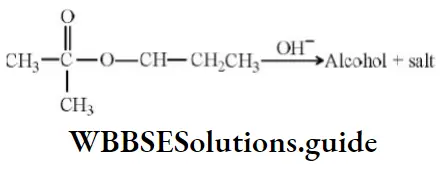
The correct statement about the reaction is
- In alcohol configuration about chiral carbon atom is retained
- In alcohol configuration about chiral carbon atom is inverted
- Alcohol loses optical activity
- All statements are incorrect
Answer: 1. In alcohol configuration about chiral carbon atom is retained
Solution: No bond around chiral carbon is broken and so configuration will be retained.
Question 132. Formic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. This can be explained using
- +Meffect
- -I effect
- +I effect
- -M effect
Answer: 2. -I effect
Solution: Electron withdrawing group has –I effect while electron donating group has +I effect. In CH3COOH, the alkyl group (-CH3) due to its greater +I effect increases the electron density on the oxygen atom of the O-H bond. Due to this the release of H+ ions in acetic acid will be more difficult as compared to the formic acid.
Question 133. Zero inductive effect is shown by?
- C6H5—
- —H
- CH3
- — Cl—
Answer: 4. — Cl—
Solution: Inductive effect of groups is measured with respect to H.
Question 134. The hydrolysis of alkyl halides by aqueous NaOH is best termed as
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
- Electrophilic addition reaction
- Nucleophilic addition reaction
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Answer: 4. Nucleophilic substitution reaction
Solution: \(R-X \stackrel{\mathrm{NaOH}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{NaX} R-X \stackrel{\mathrm{OH}^{-}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{OH}+X^{-}\)This is nucleophilic substitution.
Question 135. The intermediate during the addition of HCl to propene in the presence of peroxide

Answer: 2
Solution: Addition of HCl is not peroxide effect and it occurs via electrophilic addition.
Question 136. The structure which has positive charge on the oxygen atom
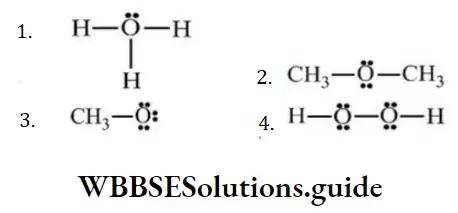
Answer: 1.
Solution:
Question 137. Addition of Br2 on CH2=CH2 in presence of NaCl (aq.) gives?
- CH2Br.CH2Br
- CH2Br.CH2Cl
- CH2Br.CH2OH
- All of these
Answer: All of these
Solution: Once the carbocation is formed as an intermediate, the nucleophile Cl– and OH– present in solution also attach it in addition of Br–
Question 138. The oxygen atom in phenol
- Exhibits only inductive effect
- Exhibits only resonance effect
- Has more dominating resonance effect than inductive effect
- Has more dominating inductive effect than the resonance effect
Answer: 3. Has more dominating resonance effect than inductive effect
Solution: The oxygen atom in phenol has more dominating resonance effect than inductive effect. Increase in charge separation decreases the stability of a resonating structure. Stability of resonating structure in decreasing order will be
1>2 ≡ 4>3
Question 139. The reaction intermediate produced, by homolytic cleavage of a bond is called
- Carbene
- Carbocation
- Carbanion
- Free radical
Answer: 4. Free radical
Solution: In homolytic cleavage, covalent bond is cleaved in such a way that each atom takes its shared electrons with itself and free radicals are formed.

Question 140. Among the following the least stable resonance structure is
Answer: 1
Solution: Two positive charges present at the adjacent place, elevates the energy, thus lowering the stability most.
Question 141. Carbocation can undergo
- Loss of a proton
- Addition to multiple bond
- Combination with anions
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: These are characteristics of carbocations.
Question 142. The electromeric effect in organic compounds is
- Temporary effect
- Permanent effect
- Temporary-permanent effect
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Temporary effect
Solution: It is raised on the need of attacking reagent, example,
Question 143. Dehydration of alcohol usually goes by
- E1 mechanism
- E2 mechanism
- E1 cb mechanism
- SN2 mechanism
Answer:
Solution: Alcohols undergo dehydration usually by E1 mechanism. This is because elimination is preferred in the case of tertiary alcohols, for example,
Question 144. Removal of a hydride ion from a methane molecule will give
- Methyl radical
- Carbonium ion
- Carbanion
- Methyl group
Answer: 2. Carbonium ion
Solution: CH4⟶CH3++ + H–; CH3+ is methyl carbonium.
Question 145. The electrophile involved in the Sulphonation of benzene is
- SO3+
- SO42-
- HSO4–
- SO3
Answer: 4. SO3
Solution: The electrophile involved in the Sulphonation of benzene is SO3 2H2SO4→ SO3+H3O++HSO4–
Question 146. In the following carbocations, the stability order is
1. R-CH2+ CH3
2. 
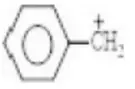
3. 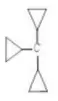
4. 
- 3> 2 >4 > 1
- 2 > 3 >4> 1
- 3 > 2 > 1 > 4
- 3> 4>2> 1
Answer: 1. 3> 2 >4 > 1
Solution: Cyclopropyl methyl carbocations are more stable than benzyl carbocations due to conjugation between bent orbitals of the cyclopropyl group.
Question 147. Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively SN1 mechanism?
- Benzyl chloride
- Isopropyl chloride
- Chlorobenzene
- Ethyl chloride
Answer: 1. Benzyl chloride
Solution: Benzyl carbonium is more stable due to resonance and thus, benzyl chloride is more reactive.
Question 148. Which of the following species is not electrophilic in nature?
- \(\stackrel{\oplus}{C_1}\)
- \(\mathrm{BH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \stackrel{\oplus}{O}\)
- \(\stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{N}} \mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 3.
Solution: H3+O cannot accept electron pairs.
Question 149. Which of the following reactions is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
- RX + Mg ⟶ RMgX
- RX+KOH ⟶ROH+KX
- 2RX + 2Na ⟶ R —R + 2NaX
- RX + H2⟶ RH + HX
Answer: 2. RX+KOH ⟶ROH+KX
Solution: X–is replaced by OH–.
Question 150. Examine the following statements regarding the SN2 reaction
1. The rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of nucleophile
2. The nucleophile attacks the carbon atom on the side of molecule opposite to the group being displaced
3. The reaction proceeds with simultaneous bond formation and rupture
4. Which of the above-written statements is correct?
- 1, 2
- 1, 3
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 3
Answer: 4. 2, 3
Question 151. The number of different substitution products possible when ethane is allowed to react with bromine is sunlight are:
- 9
- 6
- 8
- 5
Answer: 1. 9
Solution: CH3CH2Cl; CH3CHCl2; CH2ClCH2Cl; CH3CCl3; CH2ClCHCl2; CH2ClCCl3; CHCl2CHCl2;CHCl2CCl3; CCl3CCl3
Question 152. Select the strongest bond amongst the following

Answer: 4.
Solution: Triple bond possesses maximum bond energy.
Question 153. Who proposed the concept of hyperconjugation?
- Nathan and Baker
- Mullikan
- Kekule
- Kolbe
Answer: 1. Nathan and Baker
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 154. Among the following compounds nitrobenzene, benzene, aniline and phenol, the strongest basic behavior in acid medium is exhibited by
- Phenol
- Aniline
- Nitrobenzene
- Benzene
Answer: 2. Aniline
Solution: Due to the presence of a lone pair on the “N” atom.
Question 155. Mesomeric effect involves delocalization of
- Pi-electrons
- Sigma electrons
- Protons
- None of these
Answer: 1. Pi-electrons
Solution: Mesomeric effect involves the complete transfer of π or lone pair of electrons to the adjacent atom or covalent bond. Hence, it involves the delocalization of pi (π) electrons.
Question 156. Consider the following reaction, Identify the structure of the major product ‘X’ 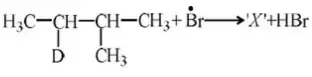

Answer: 2
Solution: Br* is less reactive and more selective and thus formation of 3° free radicals will be the major product.
Question 157. The alkyl halide that undergoes SN1 reaction more readily is
- Ethyl bromide
- Isopropyl bromide
- Vinyl bromide
- n-propyl bromide
Answer: 3. Vinyl bromide
Solution: SN1 mechanism involves the formation of carbocation intermediate. Hence, the species which gives the most stable carbocation readily undergoes SN1 mechanism. t-butyl bromide gives the most stable carbocation, i.e., 3° carbocation, so it readily undergoes SN1 reaction.
Question 158. The homolytic fission of a hydrocarbon results in the formation of:
- Carbonium ions
- Free radicals
- Carbanions
- Carbenes
Answer: 2. Free radicals
Solution: Homolytic bond fission is one in which each entity involved in bond formation retains its electron involved in a shared pair of electrons to form free radicals.
Question 159. Which of the following intermediates have the complete octet around the carbon atom?
- Carbonium ion
- Carbanion
- Free radical
- Carbene
Answer: 2. Carbanion
Solution: Carbanion (CH3⊖) Here, the carbon atom carries a negative charge with a lone pair of electrons has eight electrons in the outermost orbit, and completes its octet.
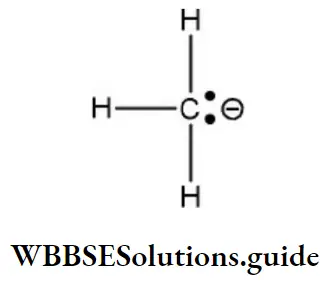
Reactions in which carbanions are formed as intermediate are said to proceed by a “Carbanion mechanism”. Carbanion is sp3 hybridized, three sp3 hybrid orbitals form covalent bonds with three atoms while the fourth sp3 hybrid orbital has a non-bonding pair of electrons. It is pyramidal in shape as similar to NH3.
Question 160. The kind of delocalization involving sigma bond is called
- Inductive effect
- Hyperconjugation effect
- Electromeric effect
- Mesomeric effect
Answer: 1. Inductive effect
Solution: The inductive effect is the permanent effect on σ-electrons. It involves the electron displacement along the chain of saturated carbon atoms due to the presence of a polar covalent bond at one end of the chain.
Question 161. An electrophilic reagent must have
- A vacant orbital
- An orbital containing one electron
- An orbital containing two electrons
- All completely filled atomic orbitals
Answer: 1. A vacant orbital
Solution: The reagent having an affinity for electrons is known as an electrophilic reagent. The electron-deficient species works as an electrophilic reagent. The electrophilic reagent as the name indicates loves the electron because it lacks electrons.
Question 162. The electrophile, E attacks the benzene ring to generate the intermediate σ complex. Of the following, which σ-complex is of lowest energy?
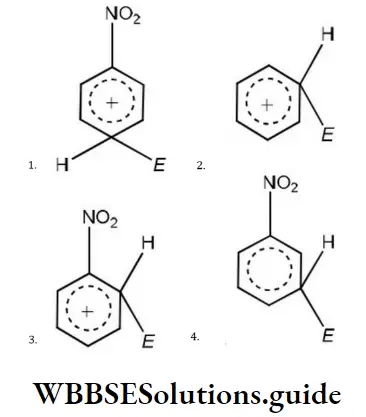
Answer: 2.
Solution: Structure B will be of lowest energy due to resonance stabilization of positive charge.
In all other three structures, the presence of electron-withdrawing NO2 groups will destabilize the positive charge and hence they will have greater energy.
Question 163. Nucleophiles are:
- Electron loving
- Electron hating
- Nucleus loving
- Nucleus hating
Answer: 3. Nucleus loving
Solution: Nucleophiles are electron-rich species and can donate lone pairs of electrons to carbocation or any positive centre.
Question 164. Conversion of CH4 to CH3Cl is an example of which of the following reactions?
- Electrophilic substitution
- Free radical addition
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Free radical substitution
Answer: 4. Free radical substitution
Solution: This is an example of a free radical substitution reaction
Question 165. The SN2 mechanism for, R-X+KOH(aq)⟶R-OH+KX follows with
- 100% inversion
- 50% inversion
- 40% inversion
- 30% inversion
Answer: 1. 100% inversion
Solution: The SN2 mechanism always involves 100% inversion since nucleophile attacks from the back side of the leaving group.
⇒ \(R-X \stackrel{\mathrm{OH}^{-}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{H} \overline{\mathrm{O}}-\cdots \cdot R^{-\cdots-\cdots} X\)
↓
⇒ \(\mathrm{HO}-R+X^{-}:\)
Question 166. The reaction (CH3)3CBr →(H2O) →(CH3)3C.OH is:
- Elimination reaction
- Free radical reaction
- Substitution reaction
- Displacement reaction
Answer: 3. Substitution reaction
Solution: Br is replaced by –OH.
Question 167. The stability of the carbocation decreases in the order
- R2CH+>R3C+>RCH2+>CH+
- R3C+>R2CH+>RCH2+>CH3+
- CH3+>R2CH+>RCH2+>R3C+
- CH3+>RCH2+>R2CH+>R3C+
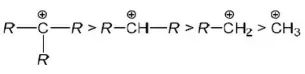
Answer: 2. R3C+>R2CH+>RCH2+>CH3+
Solution: Stability of alkyl carbocations can be explained by inductive effect and hyperconjugation. According to these two affects, the stability order is
Question 168. Most stable carbocation is formed during the heating of which of the following compounds with conc.H2SO4?
- (CH3)3COH
- C6H5CH2OH
- (CH3)2CHOH
- CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
Answer: 2. C6H5CH2OH
Solution: C6H5CH2+ is stabilized by conjugation while intermediates of the rest of the compounds given are stabilized by hyperconjugation.
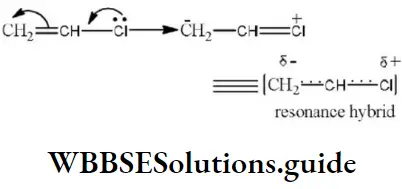
Question 169. Which of the chlorides is less reactive towards hydrolysis?
- Vinyl chloride
- Allyl chloride
- Ethyl chloride
- t-butyl chloride
Answer: 1. Vinyl chloride
Solution: Due to resonance, the partial double bond character is created on vinyl chloride. So, the chlorine atom is not replaced easily
Question 170. The shifting of electrons of a multiple bond under the influence of a reagent is called as
- I-effect
- E-effect
- M-effect
- T-effect
Answer: 2. E-effect
Solution: It is the definition of electromeric effect.
Question 171. Which of the following is an example of a substitution reaction?
4. None of the above
Answer: 1
Solution: Replacement of an atom or group by other atom or group is known as substitution reaction
Question 172. Which of the following aromatic acids is most acidic?
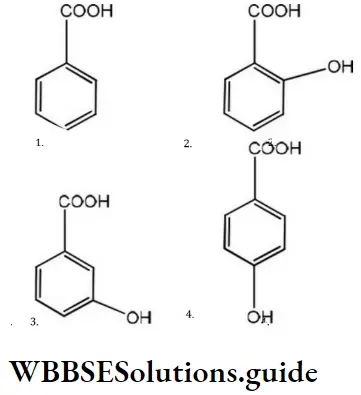
Answer: 2
Solution: Due to resonance; the carbonyl group of benzoic acid is coplanar with the ring. If the electron-withdrawing substituent (i.e.,-I showing) is present at the ortho position, it prevents the) coplanarity and thus, the resonance. Hence, it makes the acid stronger. Thus, among the given acids, ortho hydroxy benzene acid is the most acidic.
Question 173. Which of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic nitration?
- Toluene
- Benzene
- Benzoic acid
- Nitrobenzene
Answer: 1. Toluene
Solution: Due to +I effect of CH3 in toulene, it is more reactive than benzene. Due to electron withdrawing nature of the –COOH group in benzoic acid and –NO2 group in nitrobenzene, both benzoic acid and nitrobenzene are less reactive than benzene.
Question 174. The ion formed by the reaction of HNO2 and H2SO4 is
- Nitronium ion
- Nitrosonium ion
- Nitrite ion
- Nitrate ion
Answer: 2. Nitrosonium ion
Solution: HNO2 +H2SO4⟶NO++HSO4––+H2O
Question 175. Which of the following cannot show SN1 reaction?
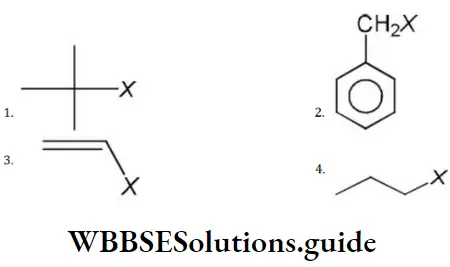
Answer: 4
Solution: Primary and secondary alkyl halides give SN2 reaction
Question 176. Which one of the following has the most nucleophilic nitrogen?
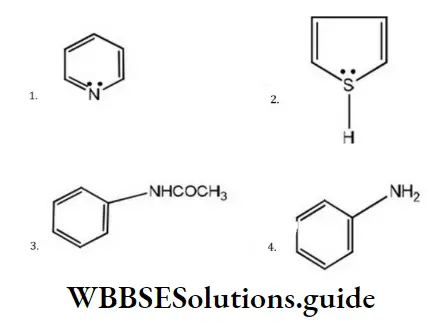
Answer: 1
Solution:
Nucleophiles are the species which have excess electrons. Among the given species, the lone pair of nitrogen of pyrrole is involved in the delocalization of the ring and, thus, are not available for donation. In aniline, the lone pair is involved in conjugation with the π-electrons of the ring while in pyridine, these are relatively free for donation. Thus, the nitrogen of pyridine is most nucleophilic.
(Phenyl and –COCH in toulene, it is more reactive than benzene. Due to electron withdrawing nature of the –CO both are electron withdrawing groups, thus decreasing the nucleophilicity of nitrogen).
Question 177. The most stable carbonium ion among the following is
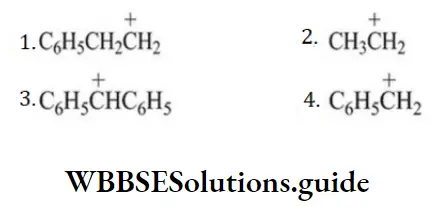
Answer: 3
Solution: \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HC}_6 \mathrm{H}_5\) is the most stable since the positive charge can be delocalized on both phenyl rings
Question 178. Which of the following is an electrophilic reagent?
- RO–
- BF3
- NH3
-
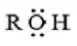
Answer: 2. BF3
Solution: BF3 is an electron-deficient compound.
Question 179. The formation of cyanohydrin from a ketone is an example of
- Electrophilic addition
- Nucleophilic addition
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
Answer: 2. Nucleophilic addition
Solution: Ketone undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction because the nucleophilic end of reagent attack is first followed by the electrophilic end of the reagent.
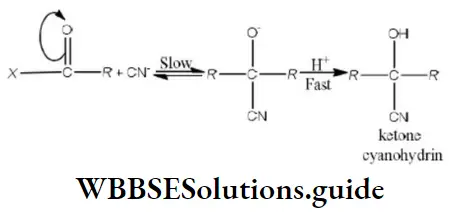
Question 180. Which of the following orders is correct regarding the acidity of the carboxylic group?
- CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH>CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH>ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
- CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH<CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH<ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
- CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH>CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH<ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
- CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH<CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH>ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
Answer: 1. CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH>CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH>ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
Solution: The presence of -I-showing group like Cl increases the acidic character of carboxylic acids and the acidity reduces with increase in the distance between – COOH and – /-showing group.
Question 181. Which step is the chain termination step in the following mechanism?
Answer:
- \(\mathrm{Cl}_2 \stackrel{h v}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}+\mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}+\mathrm{CH}_4 \longrightarrow \stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3+\mathrm{HCl}\)
- \(\stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}\)
- \(\mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}+\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
Answer: \(\mathrm{Cl}^{\bullet}+\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\)
Solution: From the above mechanism it is clear that step 2nd is the chain propagation step because in this step regeneration of species takes place. So, the 3rd & 4th step is the termination step because after these steps no species are available for further reaction.
As two chlorine free radicals reacts together to form chlorine molecule and one chlorine free radical & one methane free radical react together to form chloromethane.
Question 182. Relative stabilities of the following carbocations will be in the order
1. \(\stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3\)
2. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
3. \(\stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{OCH}_3\)
- 3>2>1
- 3<2<1
- 2>3>1
Answer: 1. 3>2>1
Solution: The dispersal of the charge stabilizes the carbocation. More the number of alkyl groups; the greater is the dispersal of positive charge and therefore, more the stability of carbocation, C2H5+>CH3+,O-CH3 is also an electron donating group, thus it will increase the stability of carbocation, hence, the correct order of stability is 3>2>1
Question 183. The addition of HI on double bonds of propene yields isopropyl iodide as a major product. It is because the addition proceeds through:
- More stable carbocation
- More stable carbanion
- More stable free radical
- Homolysis
Answer: 1. More stable carbocation
Solution: Formation of 2° carbocation, i.e.,
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2 \stackrel{\stackrel{+\delta}{\mathrm{H}}-\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{H}}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HCH}_3\)
Question 184.
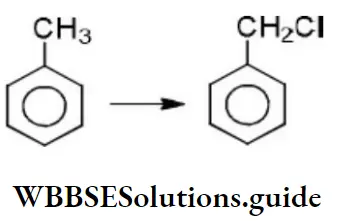
- The above reaction proceeds through
- Free radical substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic substitution
- None of the above
Answer: 1. The above reaction proceeds through
Solution: It is a free-radical substitution reaction, initiated by the formation of chlorine atoms Cl⋅ from Cl2.
The initial step is hydrogen abstraction from toluene, and the most stable free radical is formed, C6H5CH2, the one in which the radical center is in resonance with the aromatic ring.
Question 185. Arrange in order of increasing acidic strength.
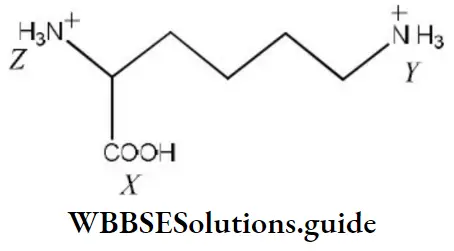
- X>Z>Y
- Z<X>Y
- X>Y>Z
- Z>X>Y
Answer: 1. X>Z>Y
Solution: The pKa value of the carboxylic group is less than pKa of NH3+ in amino acid and —NH3+ will have comparatively less pKa than (Y) due to –I effect of the carboxylic group. We know that acidic strength in inversely proportional to pKa. Hence, the correct order of acidic strength is
Question 186. Heterolysis of the carbon-chlorine bond produces
- Two free radicals
- Two carbonium ions
- Two carbanions
- One cation and one anion
Answer: 4. One cation and one anion
Solution: Heterolysis involves the bond fission in a manner when either of the two atoms involved in bond fission retains the shared pair of electrons, producing positive and negative ions, example,
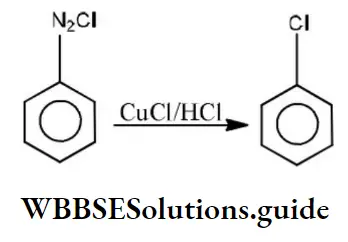
Question 187. Which of the following statements is correct?
- Allyl carbonium ion ismore stable than propyl carbonium ion
- Propyl carbonium ion (CH2=CH–CH3+ ) is more stable than the allyl carbonium ion
- Both are equally stable
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Allyl carbonium ion ismore stable than propyl carbonium ion
Solution: Allyl carbocations are more stable than the alkyl carbocations due to the resonance stabilization.
Question 188. The order of stability of the following carbanion is
- 1>2>3>4
- 1>3>2>4
- 4>3>2>1
- 3>4>1>2
Answer: 4. 3>4>1>2
Solution: I can have a maximum of 3 hyper conjugative structures. 2 has maximum of 5 hyper conjugative structures, 3 has 2 conjugative structures while 4 has 1 conjugative structure.
Question 189. Following reaction is,
- SN
- SE
- El
- EI-CB
Answer: 1. SN
Solution: Diazonium salts are highly reactive. In the Sandmeyer reaction diazo group is replaced by chlorine or bromine in presence of CuCl or CuBr. (Substitution reaction)
⇒\(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{N}_2} \stackrel{\ominus}{\mathrm{Cl}} \stackrel{\mathrm{CuCl}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{N}_2\)
Question 190. Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic attack?
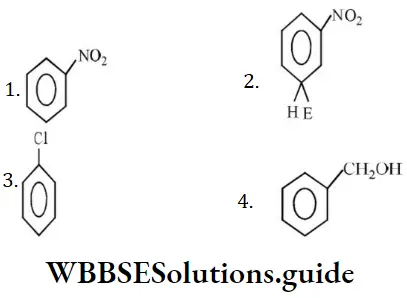
Answer: 2.
Solution: O- and p-directing groups facilitate SE reactions whereas m-directing groups deactivate the benzene ring for SE reactions.
Question 191. Heterolysis of propane gives
- Methyl and ethyl free radicals
- Methylium cation and ethyl anion
- Methyl anion and ethidium cation
- Methylium and ethylium cations
Answer: 3. Methyl anion and ethidium cation
Solution: \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{\text { Hetrolysis }}{\longrightarrow} \overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3+\mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\) due to dispersal of positive charge on ethylium ion on account of positive inductive effect. Thus, propane will not give\(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3 \text { and } \mathrm{CH}_3 \overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Question 192. Which among the following compounds is most acidic?
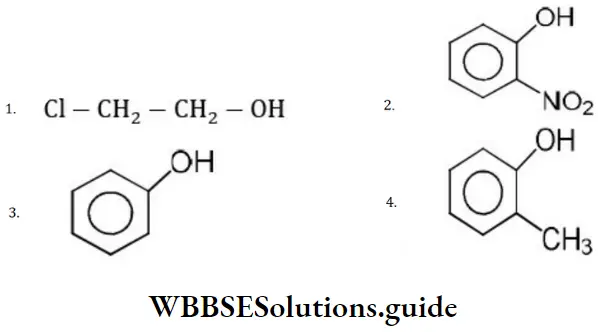
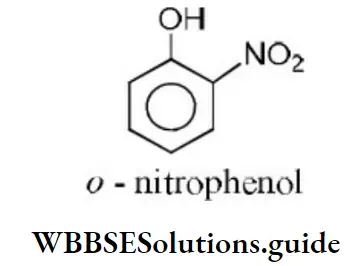
Answer: 2.
Solution: Ortho nitrophenol is the most acidic because the electron withdrawing group increases acidic character due to –I effect of NO2
Question 193. Hyperconjugation is
- σ-π delocalisation
- No bond resonance
- σ-π odd electron
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 194. Identify the reaction.
- Substitution reaction
- Elimination reaction
- Rearrangement reaction
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Rearrangement reaction
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 195. Dehydrogenation of ethanol to give ethanal is known as
- Addition reaction
- α-α elimination reaction
- α-β elimination reaction
- α-― elimination reaction
Answer: 2. α-α elimination reaction
Solution: The reaction in which 2 atoms from a molecule are removed from the same atom is called α – α-elimination. It leads to the formation of an electron deficient reactive intermediate.
Question 196. The stability of a carbonium ion depends upon
- The bond angle of the attached group
- The substrate with which it reacts
- The inductive effect and hyper-conjugative effect of the attached group
- None of the above
Answer: 3. The inductive effect and hyper-conjugative effect of the attached group
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 197. Which of the following is an electrophile?
- : CCl2
- CO2
- H2O
- NH3
Answer: 1. : CCl2
Solution: Electron deficient species or electron acceptor is electrophile. For example
⇒ \(\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3, \ddot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2, \dot{\mathrm{C}} X_2\)
Question 198. The reaction of phenol with chloroforms/sodium hydroxide to give o-hydroxy benzaldehyde involves the formation of
- Dichlorocarbene
- Trichloro carbene
- Chlorine atoms
- Chlorine molecules
Answer: 1. Dichlorocarbene
Solution: Phenol reacts with chloroform and NaOH to give o-hydroxy benzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde. In this reaction dichlorocarbene (∶CCl2) electrophile is generated. This reaction is called the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
⇒\(\mathrm{OH}^{-}+\mathrm{CHCl}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{HOH}+\underset{\text { unstable }}{: \mathrm{CCl}_3^{-}}\)
∶CCl–3 → Cl– +∶CCl2
Question 199. Carbanion can undergo:
- Rearrangement
- Combination with cation
- Addition to a carbonyl group
- All of the above are correct
Answer: 4. All of the above are correct
Solution: These are characteristics of carbanion.
Question 200. During the nitration of benzene, the attacking electrophile is
- NO3–
- NO2–
- NO2+
- HNO3
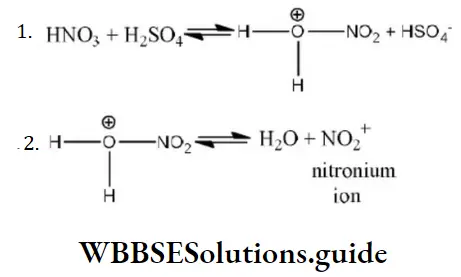
Answer: 3. NO2+
Solution: During nitration of benzene the attacking electrophile is NO2+. It is formed as follows by reaction between HNO3 and H2SO4.
Question 201. The reaction which is not an example of nucleophilic substitution among the following is
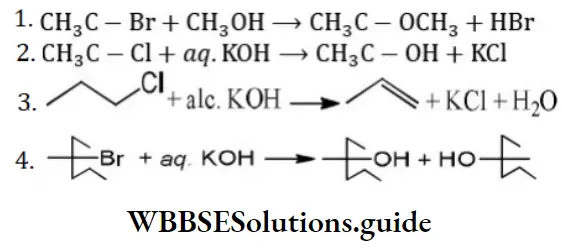
Answer: 3
Solution: CH3 -CH2 -CH2-Cl+alc.KOH⟶CH3-CH=CH2 It is an example of an elimination reaction.
Question 202. The Kolbe’s electrolysis proceeds via
- Nucleophilic substitution mechanism
- Electrophilic addition mechanism
- Free radical mechanism
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
Answer: 3. Free radical mechanism
Solution: The Kolbe’s electrolysis proceeds via free radical mechanism. For example, when sodium propionate is electrolysed, n-butane, ethane and ethylene are obtained. The propionate ion discharges at the anode to form the free radicals.
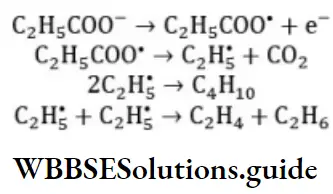
Question 203. In a SN2 substitution reaction of the type, which one of the following has the highest relative rate?
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{Br}+\mathrm{Cl}^{-} \stackrel{\mathrm{DMF}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{Br}^{+}\)
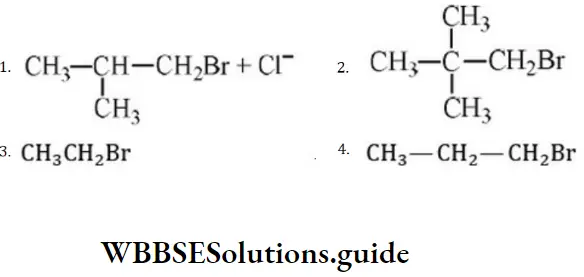
Answer: 3
Solution: For SN2 mechanism, there should be the least steric hindrance.
Question 204. Which of the following sodium compound/compounds are formed when an organic compound containing both nitrogen and sulphur is fused with sodium?
- Cyanide and sulfide
- Thiocyanate
- Sulphite and cyanide
- Nitrate and sulfide
Answer: 2. Thiocyanate
Solution: Na reacts with C, N, and S to form NaCNS (sodium thiocyanate).
Question 205. Which one of the following explain, why propene undergoes electrophilic addition withHBr, but not with HCN?
- Br–is better nucleophile than CN–
- HBr being better source of proton as it is stronger acid than HCN
- HCN attacks preferentially via lone pair of nitrogen
- The C-Br bond being stronger is formed easily as compared to C-CN bond
Answer: 2. HBr being better source of proton as it is stronger acid than HCN
Solution: HBr being a better source of proton. It gives a H+ and a Br– ion
Thus, H+ attack the π bond of propene to form carbonium ion as
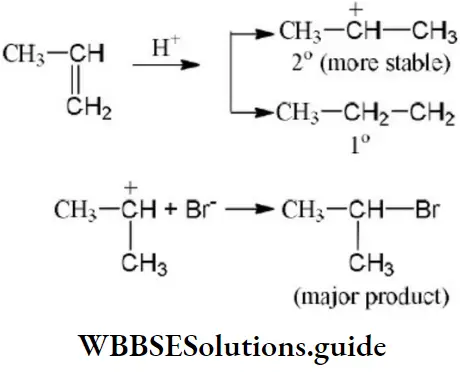
Question 206. Di-chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. This is due to the occurrence of
- Mesomeric effect
- Hyperconjugation
- Inductive effect
- Steric effect
Answer: 3. Inductive effect
Solution: Di-chloro acetic acid due to presence of two electron with drawing chloro groups (-I showing group)is more acidic than acetic acid(+Ishowing-CH3 group).
Question 207. The ease of nitration of the following three hydrocarbons follows the order
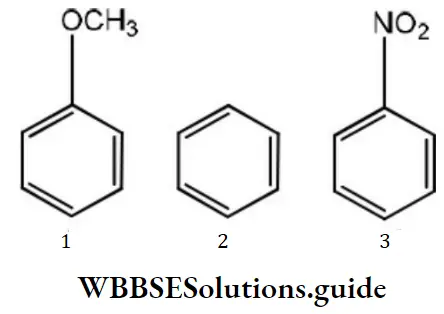
- 2=3≈1
- 2>3>1
- 3>2>1
- 1=3>2
Answer: 2. 2>3>1
Solution: Stability order of arenium ion 2>3>1
Question 208. Consider the following carbanions
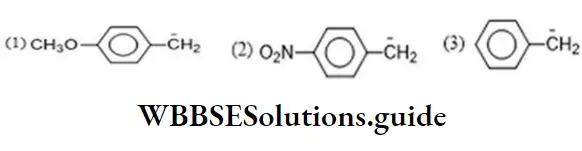
The correct order of stability is
- 1>2>3
- 3>2>1
- 2>3>1
- 1>3>2
Answer: 3. 2>3>1
Solution: – NO2 group shows –Meffect white CH3O-group shows +Meffect (–M effect stabilizes an anion)
Question 209. Williamson’s synthesis involves
- SN1 mechanism
- Nucleophilic addition
- SN2 mechanism
- SE mechanism
Answer: 3. SN2 mechanism
Solution: When sodium or potassium alkoxide is heated with an alkyl halide to give ether, the reaction is known as Williamson’s synthesis.
RONa+R’ X→ R-O-R’+NaX
This is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction and follow SN2 mechanism
Williamson’s synthesis involves SN2 mechanism
Question 210. The reaction is
⇒ \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{Br} \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}}{\longrightarrow}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{COH}\)
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Free radical
- Addition
Answer: 2. Substitution
Solution: The reaction \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{Br} \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}}{\longrightarrow}\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{COH}\) is an example of a substitution reaction
Question 211. The reaction \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{I}+\mathrm{KOH} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{KI}\) is called
- Hydroxylation substitution
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Dehydroiodination
Answer: 3. Nucleophilic substitution
Solution: Nucleophiles may be neutral or negatively charged, whereas substrates undergoing nucleophilic substitution may be neutral or positively charged.
⇒ \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5-\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{OH}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{I}^{-}\)
Question 212. In methanol solution, bromine reacts with ethylene to yield BrCH2CH2OCH3 in addition to 1,2-dibromoethane because:
- The intermediate carbocation may react with Br– or CH3OH
- The methyl alcohol solvates the bromine
- The reaction follows Markownikoff’s rule
- This is a free radical mechanism
Answer: 1. The intermediate carbocation may react with Br– or CH3OH
Solution: In methyl alcohol solution, bromine reacts with ethylene to yield BrCH2CH2OCH3 in addition to 1,2-dibromoethane because the intermediate bromonium ion formed initially may react with Br− or CH3OH.
Question 213. In a compound electrophilic substitution has occurred. The substitute-Eare methyl –CH2Cl,-CCl3 and–CHCl2. The correct increasing order towards electrophilic substitution is
- -CH3<-CH2Cl<-CHCl2<-CCl3
- -CH3<-CHCl2<-CH2Cl<-CCl3
- -CCl3<-CH2Cl<-CHCl2<-CH3
- -CCl3<-CHCl2<-CH2Cl<-CH3
Answer: 4. -CCl3<-CHCl2<-CH2Cl<-CH3
Solution: Chlorine atoms are strongly electronegative (show negative inductive effect i.e., -I effect). They deactivate the ring towards an electrophilic reaction. The increasing order of substituent-E towards electrophilic substitution is -CCl3<-CHCl2<-CH2Cl<-CH3
Question 214. The addition of HBr on butene-2 in presence of peroxide follows the:
- Electrophilic addition
- Free radical addition
- Nucleophilic addition
- None of these
Answer: 2. Free radical addition
Solution: Follow the mechanism of the Kharasch effect.
Question 215. A neutral divalent carbon intermediate produced by the removal of two attached atoms is called
- Free radical
- Carbanion
- Carbocation ion
- Carbene
Answer: 4. Carbene
Solution: Follow carbenes.
Question 216. On exciting Cl2 molecules by UV light, we get
- Cl•
- Cl+-
- Cl–
- All of these
Answer: 1. Cl•
Solution: Covalent bonds are cleaved in a homolytic way in the presence of UV light. It results in the formation of free radicals.
⇒ \(\mathrm{Cl} \stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{Cl}} \stackrel{\mathrm{UV}}{\longrightarrow} \dot{\mathrm{Cl}}+\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{l}\) (Chlorine Free Radicals)
Question 217. For the reaction,
- Chloro benzene and carbon tetrachloride
- Meta chloro benzotrichloride ortho,
- Para chloro benzo trichloride
- None of these
Answer:
Question 218. Which of the following compounds is resistant to nucleophilic attack by hydroxyl ion?
- Methyl acetate
- Acetonitrile
- Acetamide
- Diethyl ether
Answer: 4. Diethyl ether
Solution: Diethyl ether is resistant to nucleophilic attack by hydroxyl ion.
Question 219. Among the following compounds (1-2) the correct order of reaction with the electrophile is
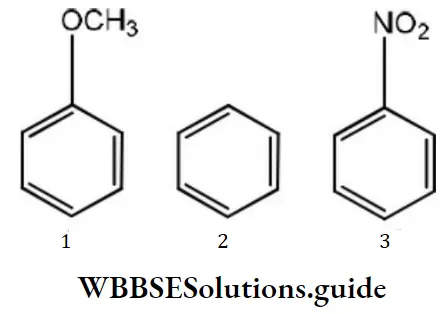
- 2>3>1
- 3<1<2
- 1>2>3
- 1≈2>3
Answer: 3. 1>2>3
Solution: Activating groups like –OCH3,-OH etc activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution while deactivating groups like-NO2,-COOH etc. deactivates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution. Thus, order of reaction towards electrophile (of the given compounds) is as 1>2>3.
Question 220. In the given structure, which carbon atom is most electronegative?
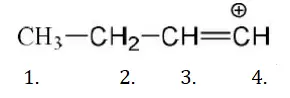
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
Solution: Electronegativity of different hybrid and unhybrid orbitals in decreasing order is as follows s>sp>sp2>sp3>p
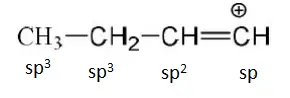
Question 221. SN1 reaction on optically active substrates mainly gives
- Retention in configuration
- Inversion in configuration
- Racemic product
- No product
Answer:
Solution: SN1 mechanism gives rise to 50% inversion as it involves front seat as well as back seat substitution. This leads to racemic products.
Question 222. The stability order for carbocations given below are?
![]()
- 1< 2 < 3
- 3 < 2 < 1
- 3< 1 < 2
- 2 < 1 < 3
Answer: 1. 1< 2 < 3
Solution: Vinyl carbocations are more stable than primary carbocation but less stable than secondary carbocation.
Question 223. Which one of the following reactions is a condensation reaction?
- HCHO ⟶para-formaldehyde
- CH3CHO⟶para-aldehyde
- CH3COCH3⟶ mesityl oxide
- CH2= CH2⟶ polyethylene
Answer: 3. CH3COCH3
Solution: Rest all are polymerization reactions.
Question 224. Inductive effect involves
- Delocalization of σ-electrons
- Displacement of σ-electrons
- Delocalization of π-electrons
- Displacement of π-electrons
Answer: 2. Displacement of σ-electrons
Solution: Inductive effect involves only displacement (and not delocalization) of σ-electrons.
Question 225. The most stable carbocation among the following is?
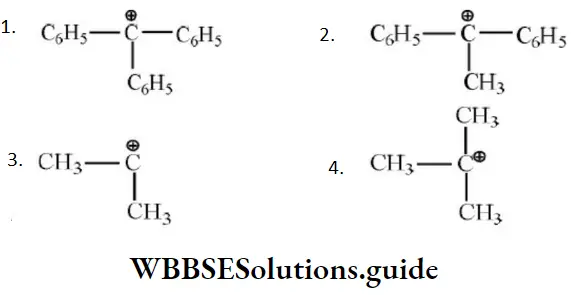
Answer: 1
Solution: Due to the property of resonance, extra stability is seen in 3° carbocation.
Question 226. Which group has the maximum-Inductive effect?
- -NO2
- -CN
- -COOH
- -F
Answer: 1. -NO2
Solution: The increasing order of inductive effect is: -F<-COOH<-CN<-NO2.
Question 227. Which of the following statements is not characteristic of free radical chain reaction?
- It gives a major product derived from most stable free radical
- It is usually sensitive to change in solvent polarity
- It proceeds in three main steps like initiation, propagation and termination
- It may be initiated by UV light
Answer: 2. It is usually sensitive to change in solvent polarity
Solution: Free radical chain reaction is initiated by UV light. It proceeds in three main steps likeinitiation, propagation and termination. It gives major products derived from the most stable free radical.
Question 228. Reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction of
1. HCHO
2. CH3CHO
3. CH3COCH3 is
- 2>3>1
- 3>2>1
- 1>2>3
- 1>3>2
Answer: 3. 1>2>3
Solution: The nucleophilic addition reaction is the characteristic addition of carbonyl compounds. Reactivity order of carbonyl compounds is in the order.
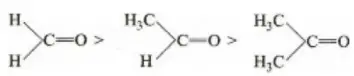
This is due to an increase in the intensity of charge on carbon of the carbonyl group due to +I effect of alkyl groups.
Question 229. Which of the following is a nucleophilic addition reaction?
- Hydrolysis of ethyl chloride by NaOH
- Purification of acetaldehyde by NaHSO3
- Alkylation of anisole
- Decarboxylation of acetic acid
Answer: 2. Purification of acetaldehyde by NaHSO3
Solution: Sodium hydrogen sulphite adds to aldehydes and ketones to form crystalline bisulphite addition products. The product is water soluble and can be converted back to the original carbonyl compound by treating it with dilute mineral acid or alkali. Therefore, these are useful for separation and purification of aldehydes like acetaldehydes.
Question 230. When thiourea is heated with metallic sodium, the compound which can’t be formed is
- NaCNS
- NaCN
- Na2SO4
- Na2S
Answer: 3. Na2SO4
Solution: The chemical formula of thiourea is NH2CSNH2 so here Na2S, NaCN and NaCNS will be formed but not Na2SO4
Question 231. Which of the following statements is correct?
- +Igroup stabilizes a carbocation
- +Igroup stabilizes a carbanion
- -I group stabilizes a carbocation
- -I group stabilizes a free radical
Answer: 1. +Igroup stabilizes a carbocation
Solution: +I group stabilizes carbocation due to the dispersal of positive charge on the + I effect group also.
Question 232. The stability of 2,3-dimethyl but-2-ene is more than 2-butene. This can be explained in terms of?
- Resonance
- Hyperconjugation
- Electromeric effect
- Inductive effect
Answer: 2. Hyperconjugation
Solution: The former possesses 12α-H atoms whereas, later possesses six α-H atoms. More is the no. of α-H atom, more is the delocalization and more is the stability.
Question 233. Which of the following is singlet carbine?

Answer: 2
Solution: An intermediate neutral species having a divalent carbon atom with 6 valence electrons out of which two are present in the same orbital with opposite spins is called singlet carbene.
Question 234. The product of the reaction is
Answer: 2
Solution: When 3-methyl-2-pentene is reacted with hypochlorous acid, the product formed is 2- chloro-3-methyl pentanol-3. The reaction obeys Markovnikov’s addition and the hydroxide and chloro group is added across the double bond of two carbons.
Question 235. Alkyl halide can be converted into alkene by
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- Elimination reaction
- Both nucleophilic substitution and elimination reaction
- Rearrangement
Answer: 2. Elimination reaction
Solution: \(\left.\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{X}+\mathrm{KOH} \text { (alc. }\right) \rightarrow \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2+\mathrm{KX}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Alkyl halide undergo β-elimination to form alkene.
Question 236. Which step is the chain propagation step in the following mechanism?
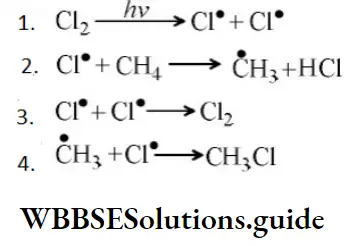
Answer: 2
Solution: The chain propagation step involves the use of free radical and regeneration of another free radical.
Question 237. The addition reaction among the following is
Answer: 2
Solution: It is an example of an addition reaction.
Question 238. In this reaction, an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CHO}+\mathrm{HCN} \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CN} \stackrel{\text { H.OH }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{COOH}\)
- 50%D+50%L-isomer
- 20%D+80%L-isomer
- D-isomer
- L-isomer
Answer: 1. 50%D+50%L-isomer
Solution: Lactic acid obtained in the given reaction is an optically active compound due to the presence of chiral C-atom. It exists as d and l forms whose ratio 1:1.
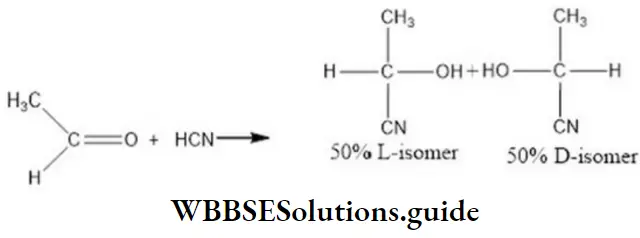
Question 239. The reaction is an example of
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Elimination reaction
- Nucleophilic addition
Answer: 2. Electrophilic addition
Solution: A hydrogen halide containing a highly polar H-Xbond can easily lose to the pi bond of an alkene. The result of the attack of H⊕ is an intermediate carbocation, which quickly undergoesreaction with the negative halide ion (X–) to yield an alkyl halide
Question 240. How many structures of F are possible?
- 2
- 5
- 6
- 3
Answer: 4. 3
Question 241. Which one of the following does not show resonance?
- Carbon dioxide
- Benzene
- Nitromethane
- Propane
Answer: 4. Propane
Solution: Alkanes do not show resonance.
Question 242. The reagent used in dehalogenation process is
- KOH alc.
- Zn dust + alc.
- Na
- KOH(aq)
Answer: 2. Zn dust + alc.
Solution: Zn dust is used for dehalogenation
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_2 X . \mathrm{CH}_2 X \stackrel{\text { Zn dust }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}_2\)
Question 243. Which alkyl halide is preferentially hydrolyzed by SN1 mechanism?
- (CH3)3C.Cl
- CH3CH2CH2Cl
- CH3CH2Cl
- CH3 Cl
Answer: 1. (CH3)3C.Cl
Solution: Tertiary halide always favors SN1 mechanism (as they give comparatively stable carbocation) white primary halide favors SN2 mechanism.
Question 244. Which of the following has the most acidic hydrogen?
- 3-hexanone
- 2, 4-hexanedione
- 2, 4-hexanedione
- 2, 3-hexanedione
Answer: 2. 2, 4-hexanedione
Solution: When methylene group (-CH2) is attached with two electron withdrawing groups (like,- CHO,>C=O,-COOH,-CN,-X,etc), its acidity will increase due to –I effect of the electron withdrawing groups.
Question 245. In the reaction, water is formed by the combination of?
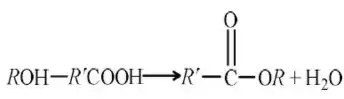
- Hydroxyl of acid with alcoholic hydroxyl hydrogen
- Hydroxyl of alcohol with carboxylic hydrogen
- Both the above changes
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Hydroxyl of acid with alcoholic hydroxyl hydrogen
Solution: Follow the mechanism of esterification.
Question 246. The function of soda lime, a mixture of solid NaOH and solid CaO during the decarboxylation of carboxylic acids is
- To increase the rate of reaction
- To decrease the rate of reaction
- To change the rate of reaction
- None of the above
Answer: 2. To decrease the rate of reaction
Solution: CaO is added to NaOH to retard activity of NaOH, otherwise decarboxylation of acids will occur more violently.
⇒ \(R \mathrm{COONa} \stackrel{\mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{CaO}}{\longrightarrow} R-\mathrm{H}+\mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3\)
Question 247. Example of chlorinolysis among the following is
Answer: 4.
Solution: Chlorinolysis involves the substitution reactions by chlorine.
Question 248. The correct order of nucleophilicity among the following is
- 3, 2, 1, 4
- 1, 2, 3, 4
- 4, 3, 2, 1
- 2, 3, 1, 4
Answer: 4. 2, 3, 1, 4
Solution: The nucleophilicity depends on the strength of the conjugate acid of the nucleophile. If the conjugate acid of the nucleophile is a weak acid, then the corresponding nucleophile will be stronger in nature.
Going by that fact, the conjugate acids of the above nucleophiles are acetic acid, methanol, hydrogen cyanide and toluene para sulphonic acid.
Among the following acids, the weakest acid is methanol. Hence its conjugate base, methoxy group will be the strongest nucleophile, while the weakest one will be the p-toluene sulphonate.
Question 249. The stability of
In the increasing order is
- 3<1<4<2
- 1<2<3<4
- 4<3<2<1
- 2<3<4<1
Answer: 1. 3<1<4<2
Solution: Can be solved on the basis of hyperconjugative structures
Question 250. Dehydrohalogenation of an alkyl halide is a/an
- Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- Elimination reaction
- Both nucleophilic substitution and elimination reaction
- Rearrangement
Answer: 2. Elimination reaction
Solution:
- In nucleophilic substitution reaction more powerful nucleophile replaces weaker nucleophile.
- In rearrangement reaction atoms replace their position within the molecule.
- In elimination reaction small molecules (example, H2O, NH3) are lost.
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{KOH} \text { (alc.) } \stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{RCH}=\mathrm{CH}_2+\mathrm{KCl}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
∵ KCl and H2O molecules are lost during reaction.
∴ It is an elimination reaction.
Question 251. Electrophiles are
- Electron loving species
- Electron hating species
- Nucleus loving reagents
- Nucleus hating reagents
Answer: 1. Electron loving species
Solution: Electrophiles are electron deficient species which can share a lone pair of electrons with carbanion and are thus called Lewis’s acids.
Question 252. Correct order of nucleophilicity is
- I–>Br–>Cl–>F–
- F–>Cl–>Br–>I–
- Cl–>F–>Br–>I–
- I–>Cl–>Br–>F–
Answer: 1. I–>Br–>Cl–>F–
Solution: Nucleophilicity increases on going down in the group of the Periodic Table
⇒ \(\mathrm{I}^{\ominus}>\mathrm{Br}^{\ominus}>\mathrm{Cl}^{\ominus}>\mathrm{F}^{\Theta}\)
Question 253. Polarization of electron in acrolein may be written a
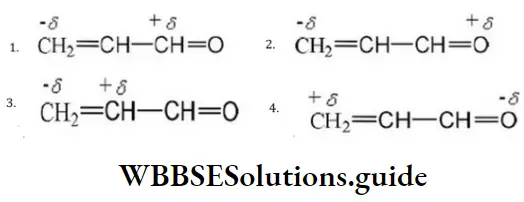
Answer:
Solution: Due to -R effect of –CHO group, oxygen carries –δ charge while the terminal carbon carries + δ,ie,
⇒ \(\begin{aligned}
& +\delta \\
& \mathrm{CH}
\end{aligned}=\mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{O}^{-\delta}\)
Question 254. Which of the following does not show electromeric effect?
- Alkenes
- Ethers
- Aldehyde
- Ketones
Answer: 2. Ethers
Solution: Electromeric effect implies complete transfer of π electrons in presence of a reagent.
Since, simple ethers do not contain a multiple bond, therefore, they do not show electromeric effect
Question 255. The chlorination of methane to give CCl4 is an example of
- Addition
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Chain reaction
Answer: 4. Chain reaction
Solution: Halogenation of methane is a chain reaction and propagate through free radicals.
Question 256. An organic compound C5H11X on dehydrohalogenation gives pentene-2 only. What is the halide?
- CH3CH2CHXCH2CH3
- (CH3)2CHCHXCH3
- CH3CH2CH2CHXCH3
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2X
Answer: 1. CH3CH2CHXCH2CH3
Solution: Follow Saytzeff rule for elimination. 3-halopentane will give only pentene-2.
Question 257. Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing SN2 reactivity? (X=α halogen)
- RCH2X>R3CX>R2CHX
- RCH2X>R2CHX>R3CX
- R3CX>R2CHX>RCH2X
- R2CHX>R3CX>R2CH2X
Answer: 2. RCH2X>R2CHX>R3CX
Solution: SN2 reactions are greatly controlled by steric factors. SN2 reactivity decreases as bulkyness of alkyl group increases.
Question 258. Chloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. This can be explained using
- -M effect
- -I effect
- +Meffect
- +I effect
Answer: 2. -I effect
Solution: Cl is an electron-withdrawin (i.e.,-I showing) group. It withdraws electrons when attached to the carboxylic acid and decreases the electron density on the oxygen atom. This will facilitate the release of H+ by making O-H bond more polar and thus –Cl increases the acidity of acetic acid when attached at, α position because of –I effect.
Question 259. Anti-Markovnikov’s addition of HBr is not observed in
- Propene
- Butene-1
- But-2-ene
- Pent-2-ene
Answer: 3. But-2-ene
Solution: The rule is valid for unsymmetrical alkene.
Question 260. Consider the following carbocations,
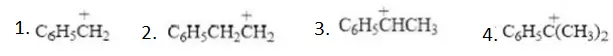
- 2<1<3<4
- 2<3<1<4
- 3<1<2<4
- 4<3<1<2
Answer: 1. 2<1<3<4
Solution: Resonance and inductive effect decide the stability of carbocations.
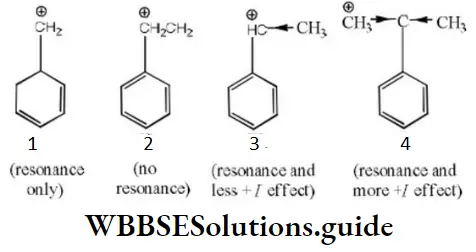
∴ Correct order of stability is 2<1<3<4
Question 261. Which of the following orders is not correct regarding the –I effect of the substituents?
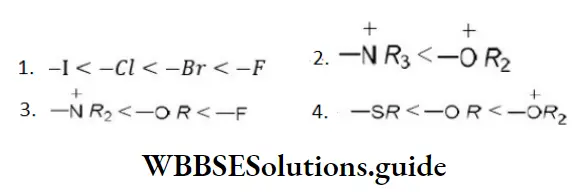
Answer: 3
Solution: -I power of groups in decreasing order with respect to the reference HNO2>CHO>COOR>F>Cl>Br>I>OH>OR>NH2
Question 262. The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with alcoholic KOH is
- 3°<2°<1°
- 3°>2°>1°
- 3°<2°>1°
- 3°>2°<1°
Answer: 2. 3°>2°>1°
Solution: Such dehydrohalogenation follow E2 mechanism. The driving force of such a reaction is the stability of alkene produced. Since, tertiary alkyl halide can give more substituted alkene, it reacts fastest followed by secondary and primary i.e.,3°>2°>1°.
Question 263. Which of the following species is paramagnetic?
- A carbocation
- A free radical
- A carbanion ion
- All of these
Answer: 2. A free radical
Solution: Free radicals have unpaired electrons.
Question 264. The fairly neutral character of CH3OH is changed to which of the following by adding sodium metal?
- Acidic
- Neutral
- An electrophile
- A nucleophile
Answer: 4. A nucleophile
Solution:
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3{ }^{-} \mathrm{O} \text { is nucleophile } ; \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{Na} \rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{O}^{-} \mathrm{Na}^{+}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Question 265. Which of the following order is correct regarding the acidity of carboxylic acids?
- Cl3CCOOH>Cl2CHCOOH>ClCH2COOH
- Cl3CCOOH>Cl2CHCOOH<ClCH2COOH
- Cl3CCOOH<Cl2CHCOOH>ClCH2COOH
- Cl3CCOOH<Cl2CHCOOH<ClCH2COOH
Answer: 1. Cl3CCOOH>Cl2CHCOOH>ClCH2COOH
Solution: As the –Igroup increases at the α-carbon, acidity increases.
Question 266. The total number of contributing structures showing hyperconjugation (Involving – C – H bonds) for the following carbocation is
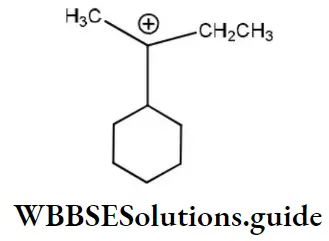
- Three
- Five
- Eight
- Six
Answer: 4. Six
Solution: There are total 6α-H to sp2 carbon and they all can participate in hyperconjugation.
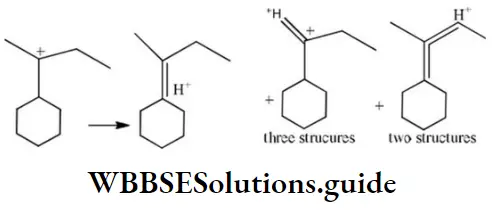
Question 267. RX+I–→ R-I+X– is an example of … reaction.
- Nucleophilic addition
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Elimination
Answer: 2. Nucleophilic substitution
Solution: RX+I–→ R-I+X–
This reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution.
Question 268. The correct order of increasing basicity of the given conjugate bases (R=CH3) is
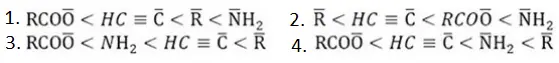
Answer: 4
Solution: In carboxylate ion, the negative charge is present on the oxygen, a most electronegative element here, thus it is resonance stabilized.
HC≡C–: Carbon is sp-hybridized so its electronegativity is increased higher relative to nitrogen. N̅H2: Nitrogen is more electronegative than sp3- hybridized C-atom. From the above discussion, it is clear that the order of the stability of conjugated bases is as RCOO–>HC≡C–>N̅H2>R–and higher is the stability of conjugated bases, lower will be basic character. Hence, the order of basic character is as
RCOO–<HC≡C–<N̅H2<R–
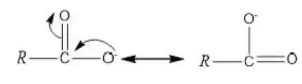
Question 269. The reaction, CH2= CHCHO → HX gives?
- CH3CHXCHO
- CH2XCHCHO
- CH2= CHCHX2
- None of these
Answer: 2.
Solution: The negative inductive effect of –CHO group plays a role to give anti Markownikoff’s addition.
Question 270. A solution of D (+)-2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemizes slowly in the presence of small amount of SbCl5 due to the formation of
- Carbanion
- Carbene
- Free radical
- Carbocation
Answer: 4. Carbocation
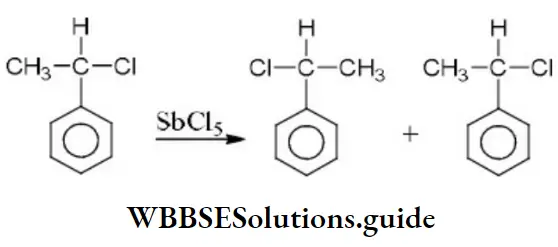
Solution: The solution of D(+)-2-chloro-2-phenyl ethane in toluene racemizes slowly in the presence of SbCl2 due to the formation in carbocation.
Question 271. During the debromination of meso-dibromo-butane, the major compound formed is
- n-butane
- l-butene
- Cis-2-butene
- Trans-2-butene
Answer: 4. Trans-2-butene
Solution: Follow the mechanism of debromination.
Question 272. Reaction
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Nucleophilic addition
Answer: 4. Nucleophilic addition
Solution: Carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition.
Question 273. Which one of the following gives a white precipitate with AgNO3?
Answer: 2
Solution: A chloride linked with alkyl group is replaced with AgNO3 and give white precipitate of AgCl.
Question 274. The + I.E. (inductive effect) is shown by?
- CH3
- —OH
- F
- -C6H5
Answer: 1
Solution: —CH3 is an electron-repelling group.
Question 275. Chlorobenzene is o, p-directed in electrophilic substitution reaction. The directing influence is explained by
- +M of Ph
- +I of Cl
- +M of Cl
- -I of Ph
Answer: 3. +M of Cl
Solution: Chlorobenzene is o, p directing in electrophilic substitution reaction. The directing influence is explained by +M of Cl atom
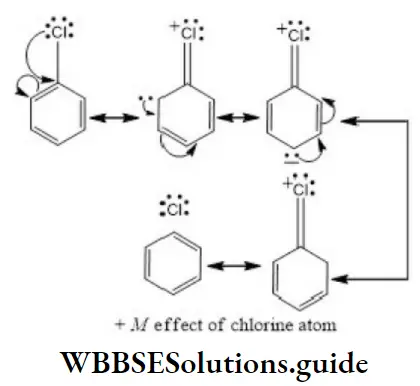
Question 276. List the following alkoxide nucleophile in decreasing order of their SN2 reactivity
1. Me3CO–
2. MaO–
3. MeCH2O–
4. Me2CHO–
- 2>3>5>4>1
- 5>3>2>1>4
- 1>5>2>3>4
- 3>5>1>2>3
Answer: 1. 2>3>5>4>1
Solution: Epoxide is an ambident substrate for nucleophilic substitution reactions. In protonated epoxide carbon-2 and carbon-3 both acquire some positive charge due to the highly electronegative atom.
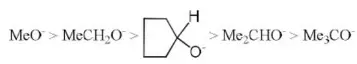
Question 277. Due to the presence of an unpaired electron free radicals are
- Cations
- Anions
- Chemically inactive
- Chemically reactive
Answer: 4. Chemically reactive
Solution: Free radicals have unpaired electrons, but are neutrals and are reactive.
⇒ \(\stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3+\stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3 \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
Question 278. Which one of the following carbanions is the least stable?
- CH3CH2–
- HC≡C–
- (C6H5)3C–
- (CH3)3C–
Answer: 4. (CH3)3C–
Solution: An organic ion with a pair of available electrons and a negative charge on the central carbon atom is called a carbanion. Electron attracting group – CN, >C= Oincreases stability, and electron releasing group (-CH3 etc) decreases the stability of carbanion. In (CH3)3C–, three –CH3 groups (electron releasing group) are present, so it is least stable.
Question 279. The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2OH
- (CH3)3COH
- CH2=CHCH2CH2OH
- CH3CHOHCH2- CH3
Answer: 2. (CH3)3COH
Solution: Increasing order of stability of carbocation. 1°carbocation <2° carbocation<3°carbocation
Question 280. Most stable carbonium ion is
- \(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}_2} \mathrm{H}_5\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5\right)_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)
Solution: is resonance stabilized? In the triphenyl methyl carbonium ion, the π-electrons of all the three benzene rings are delocalised with the vacant p- orbital of central carbon atom. So, it is resonance stabilized. Therefore, it is the most stable of the given carbonium ions.
More the number of resonatic structures, the more will be the stability.
Question 281. Which of the following species does not exert a resonance effect?
- C6H5NH2
- C6H5OH
- C6H5Cl
Answer:
Solution: Among the given species does not exert a resonance effect.
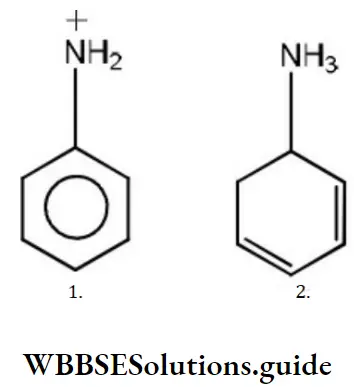
Structure 2 is not possible because in it, nitrogen contains 10 valence electrons.
Question 282. The compound can be distinguished by?
- Chlorinated products
- Products formed by addition of bromine
- Reaction with H2/Ni
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Products formed by addition of bromine
Solution: Addition of Br2 gives altogether different products units cis and trans butene-2.
Question 283. When two halogen atoms are attached to two adjacent carbon atoms, the dihaloalkane is called?
- Alkylidene dihalide
- Alkane dihalide
- Alkylene dihalide
- Alkyl halide
Answer: 3. Alkylene dihalide
Solution: Vicinal or alkylene dihalides.
Question 284. Reactions involving heterolytic fission are said to proceed via :
- Ionic mechanism
- Polar mechanism
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Solution: Heterolytic bond fission gives rise to formation of ions.
Question 285. Select the organic compound which was prepared for the first time in laboratory from its elements
- Urea
- CH3COOH
- C2H5OH
- None of these
Answer: 2.
Solution: Just after few years when Wohler prepared urea from KCNO and (NH4)2SO4, Kolbe prepared acetic acid in the laboratory from its element and gave the final blow to Vital force theory.
Question 286. Which of the following is the most stable cation?
- \(\mathrm{F}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus}\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{CH}^{\oplus}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3^{\oplus}\)
- \(\mathrm{CF}_3^{\oplus}\)
Answer: 2. \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_2 \mathrm{CH}^{\oplus}\)
Solution: Due to the presence of methyl group positive inductive effect increases and the stability of carbocation also increases. The stability order of carbocation is Tertiary > Secondary> Primary
Question 287. Which of the following has the highest degree of coordination bond?
- CH3OH
- AlCl3
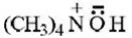
- BF3O(Et)2
Answer: 4. BF3O(Et)2
Solution: Three coordinate bonds on O atom.
Question 288. Which of the following is an electrophile?
- H2O
- SO3
- NH3
- ROR
Answer: 2. SO3
Solution: The species which are electron deficient and accept a pair of electrons are called electrophile. Hence, SO3 is an electrophile as it contains an electron deficient centre. While H2 O,NH3 and R-O-R are nucleophiles.
Question 289. A molecule is R3C—H. If H is replaced by Z(R3C—Z) and on doing so electron density on R3—C part increases, then Z is
- Electron attracting group
- Electron withdrawing group
- Electron repelling group
- Either of the above
Answer: 3. Electron repelling group
Solution: The Z repels electrons and thus, electron density increases on R3C part.
Question 290. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- SN2 reaction proceeds with inversion
- SN1 reaction proceeds with racemisation
- SN2 reaction involves transition state
- In transition state, one end carries δ+, and another end carriesδ–charge
Answer: 4. In transition state, one end carries δ+, and another end carriesδ–charge
Solution: SN2 reaction proceeds with inversion and a transition state is formed which does not carry any charge.
Question 291. Which of the following is an example of an elimination reaction?
- Chlorination of methane
- Dehydration of ethanol
- Nitration of benzene
- Hydroxylation of ethylene
Answer: 2. Dehydration of ethanol
Solution: Chlorination of methane is a free radical substitution reaction.
Dehydration of ethanol is an elimination reaction.
Nitration of benzene is an electrophilic substitution reaction. Hydroxylation of ethylene is a redox reaction.
Question 292. C3H5Cl+aq.NaOH→ C2H5OH+NaCl; this reaction is
- Electrophilic substitution of 1 order
- Electrophilic substitution of 2 order
- Nucleophilic substitution of 1 order
- Nucleophilic substitution of 2 order
Answer: 4. Nucleophilic substitution of 2 order
Solution: The given reaction can be represented as
NaOH→ Na++OH–
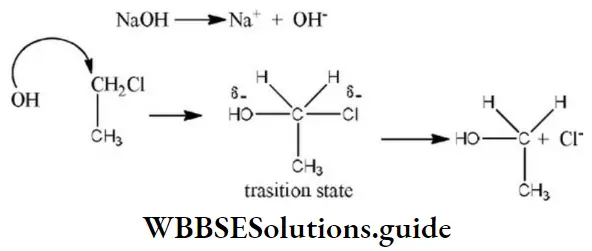
Since in this reaction, a nucleophile replaces the other group, it is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction. The mechanism shows that the rate depends on the concentration of both alkyl halide and nucleophile. So, it is an example of
SN2(nucleophilic substitution of 2 order reaction.
Question 293. Which of the following statements (s) is (are) not true?
- Carbanions and carbonium ions, usually exist in ion pairs or else solvated
- Acidity increases and basicity decreases in going from left to right across a row of Periodic CH4<NH3<H2O<HF(acidity), CH3–>NH2–>OH–>F– (basicity)
- RCOOH like RCOR reacts with H2 NOH to give an oxime
- Decreasing order of ionizing power of solvents is CF3COOH>HCOOH>H2O>CH3COOH>CH3OH>C2H5OH>(CH3)2SO>CH3CN
Answer: 3. RCOOH like RCOR reacts with H2 NOH to give an oxime
Solution: Aldehydes and ketones combine with a variety of compounds of the Z-NH2 to formoxime
Question 294. Which of the following is arranged according to the nature indicated?
- Electrophile
- Electrophile
- Electrophile –CH3OH,N3–. Nucleophile –NO2+,Br+
- Electrophile –Br+,N3–,Nucleophile –CH3OH,
Answer: 1. Electrophile
Solution: Electrophiles are the species having a tendency to accept a pair of electrons, example.,NO2+,Br+ etc. Nucleophiles are the species having a tendency to donate a pair of electrons. example,CH3OH.N3–
Question 295. Which of the following belongs to –I group?
- -C6H5
- -CH3
- -CH2CH3
- -C(CH3)3
Answer: 1. -C6H5
Solution: C6H5 – (phenyl) group has – I effect group
Question 296. Arrange the carbanions, in order of their decreasing stability (CH3)3C̅,C̅Cl3,(CH3)2C̅H,C6H5C̅H2
- C6H5C̅H2>C̅Cl3>(CH3)2C̅>(CH3)2C̅H
- (CH3)2C̅H>C̅Cl3>C6H5CH2>(CH3)3C̅
- C̅Cl3>C6H5C̅H2>(CH3)2C̅H>(CH3)3C̅
- (CH3)3C̅>(CH3)2C̅H>C̅H2>C̅Cl3
Answer:
Solution: −I effect [e− withdrawing] exerting groups stabilize carbanion by the dispersal of their negative charge while +I effect exerting [e− releasing] groups destabilize the carbanion by increasing electron density on them.
On the other hand, resonance stabilized carbanion is stable due to the involvement of their lone pair of electrons with the delocalization of π-electrons of the attached phenyl group
Question 297. Which one of the nitrogen atoms in the below molecule is the most nucleophilic?
- 3
- 1
- 1 A
- 2 three N atoms
Answer: 2.1
Solution: When the nucleophilic site is the same, nucleophilicity parallels basicity. It means more the basic the nucleophile, stronger is the nucleophile. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \ddot{\mathrm{N}}(\mathrm{I})\) is the most nucleophilic
Furthermore the NH2 group is away from the –C-group and is not involved in resonance. Hence, its lone pair is readily available.
Question 298. The increasing order of positive I-effect shown by H,CH3,C2H5 and C3H7 is
- H <CH3<C2H5<C3H7
- H>CH3<C2H5>C3H7
- H <C2H5<CH3<C3H7
- None of the above
Answer: 1. H <CH3<C2H5<C3H7
Solution: Follow inductive effect.
Question 299. Which of the following reactions proceeds via secondary free radical?
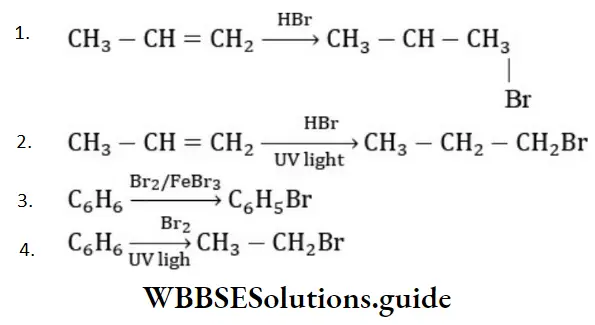
Answer: 2
Solution: 1-Propane undergoes bromination in the presence of UV light through a secondary free radical mechanism as given below.
Question 300. Which of the following will be easily nitrated?
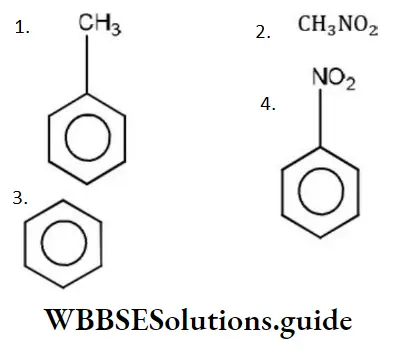
Answer: 1
Solution: Nitration of aromatic compounds takes place by an electrophile. The electrophile will be more attracted towards electron rich positions in the benzene ring. Hence, electron donating groups will be easily nitrated.
Toluene will be most easily nitrated among these compounds due to presence of electron donating group (i.e.,CH3). Nitrobenzene will be most slowly nitrated due to the presence of electron withdrawing group (i.e.,NO2). CH3NO2 will be formed by free radical substitution of CH4
Question 301. In E2 elimination, some compounds follow Hofmann’s rule which means:
- The double bond goes to the most substituted carbon
- The compound is resistant to elimination
- No double bond is formed
- The double bond goes mainly towards the least substituted carbon
Answer: 1. The double bond goes mainly towards the least substituted carbon
Solution: Follow elimination rules.
Question 302. t-butyl chloride reacts with OH– by SN1 mechanism and rate ∝[t-buty1 chloride].
- One of the reasons for this is that
- Stereochemical inversion takes place t- buty1 carbocation is first formed which is more stable
- The product t-butyl alcohol is more stable
- The intermediate t-butyl carbocation is stabilized by solvation
Answer: 2. Stereochemical inversion takes place t- buty1 carbocation is first formed which is more stable
Solution:
Rate ∝[t-butyl chloride]
Tertiary butyl carbocation is first formed which is more stable
Question 303. Resonance in benzene is accompanied by delocalization of π-electrons. Each π- electron is attached with:
- 4 carbon
- 2 carbon
- 3 carbon
- 6 carbons
Answer: 4. 6 carbons
Solution: Each π-electron is delocalized over six carbon atoms in ring.
Question 304. Which of the following is not a nucleophile?
- BF3
- NH3
- CN–
- OH–
Answer: 1. BF3
Solution: Electron donors having lone pair of electrons are nucleophile. BF3 is not nucleophile because it does not have lone pair of electrons. It is in fact Lewis’s acid because it accepts pair of electrons. NH3,CN– and OH– all have lone pair of electrons, so they are nucleophiles.
Question 305. Among the following the strongest nucleophile is
- C2H5SH
- CH3COO–
- CH3NH2
- NCCH2–
Answer: 1. C2H5SH
Solution: Nucleophiles are those substances which can donate a pair of electrons. They can be neutral or negatively charged. The nucleophilic power depends on the tendency of species to donate the electrons. Due to the presence of +Ieffect it increases. Hence, higher the +I effect, higher the nucleophilic power. The +I effect of ethyl is greater than +I effect of methyl group
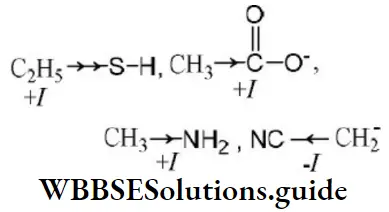
Question 306. Which of the following is the most stable carbocation?
- \(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3\)
- R\(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(R_2 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
- \(R_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)
Answer: 4. \(R_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)
Solution: In case of alkyl carbocations as the number of R group decreases stability decreases. Thus, the correct order of stability of carbocation is \(R_3 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}}\)>\(R_2 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)>R\(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)>\(\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_3\)
Question 307. The appropriate reagent for the following transformation is
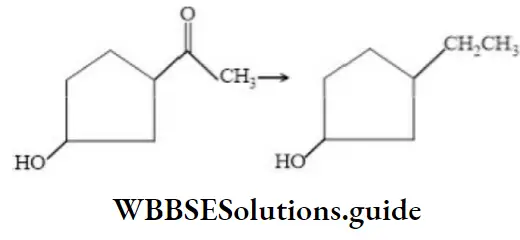
- Zn (Hg),
- HCl
- NH2NH2,OH–H2/Ni
- NaBH4
Answer: 2.
Solution: Both Wolf-Kishner and Clemmensen reduction are used to convert ![]() The latter is not suitable as it will also attack –OH group of rings.
The latter is not suitable as it will also attack –OH group of rings.
Question 308. The correct order for homolytic bond dissociation energies. (∆Hin kcal/mol) for CH4 (1),C2H6 (2) and CH3Br(3), under identical experimental conditions
- 3>2>1
- 2>3>1
- 3>1>2
- 1>2>3
Answer: 2. 2>3>1
Solution: The order of homolytic bond dissociation energies of CH4, C2H6 and CH3Br is as CH4> C2H6> CH3Br ∆H (kcal/mol) 105> 100 > 70
Question 309. Which one is least reactive in a nucleophile substitution reaction?
- CH3CH2Cl
- CH2=CHCH2Cl
- CH2=CHCl
- (CH3)3CCl
Answer: 3. CH2=CHCl
Solution: Vinyl chloride is the least reactive for SN reaction due to resonance
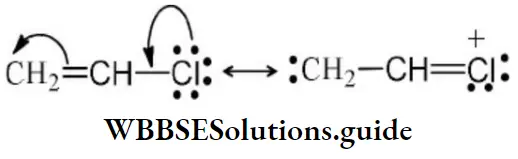
Question 310. Homolytic fission of C—C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon is …. hybridized.
- Sp3
- Sp2
- Sp
- Sp2d
Answer: 2. Sp2
Solution: Homolytic fission of the C-C bond in ethane gives free radicals. In a free radical the central carbon atom is sp2 sp2-hybridised.
Question 311. Which of the following orders regarding relative stability of free radicals is correct?
- 3°<2°<1°
- 3°>2°>1°
- 1°<2°>3°
- 3°>2°<1°
Answer: 2. 3°>2°>1°
Solution: Free radicals are electron-deficient compounds. Alkyl groups are electron donor groups and they increase the stability of free radicals.
∴ The more the number of alkyl groups, the more will be stability of free radicals.
∴ 3°>2°>1° is the correct order of stability of free radicals.
Question 312. Which of the following is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction?
- CH2=CH-Cl
- C6H5Cl
- C6H5CH2Cl
- ClCH2-CH=CH2
Answer: 2. C6H5Cl
Solution: During the nucleophilic substitution weaker nucleophile is replaced by a stronger nucleophile. The compound having a C-Cl bond which can be most easily broken will be the most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. In vinyl chloride CH2=CH-Cl and chlorobenzene C6H5Cl the C-Cl bond has partial double bond character due to resonance.
∴ They do not give nucleophilic substitution reactions easily
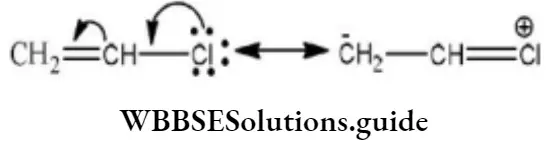
Benzyl chloride,  gives nucleophilic substitution easily because they carbocation formed is stabilized due to resonance.
gives nucleophilic substitution easily because they carbocation formed is stabilized due to resonance.
Question 313. Correct order of stability is
- HC≡C̅>CH2=C̅H>CH3-C̅H2
- CH3-C̅H2>CH2=C̅H>CH ≡C̅
- CH3-C̅H2>CH ≡CH≅CH2=C̅H
- All are equally stable
Answer: 2. CH3-C̅H2>CH2=C̅H>CH ≡C̅
Solution: Stability of alkyl carbanion 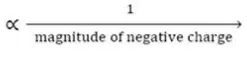 and magnitude of negative charge ∝+I power of the group. Hence, acetylenic carbanion is more stable than vinylic carbanion which is more stable than alkyl carbanion
and magnitude of negative charge ∝+I power of the group. Hence, acetylenic carbanion is more stable than vinylic carbanion which is more stable than alkyl carbanion
Question 314. During the addition of bromine on ethene, the first species formed is

Answer: 1
Solution: Addition of Br2 on ethene follows electrophilic addition Intermediate is cyclic bromonium ion
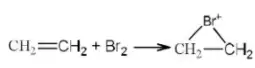
Question 315. For all practical purposes, the influence of the inductive effect is neglected after
- 2nd carbon atom
- 1st carbon atom
- 3rd carbon atom
- None of these
Answer: 1. 2nd carbon atom
Solution: Follow inductive effect.
Question 316. Which of the aldehyde is the most reactive?
- C6H5-CHO
- CH3CHO
- HCHO
- All the equally reactive
Answer: 3. HCHO
Solution: Among carbonyl compounds, reactivity decreases with increase in the alkyl groups as alkyl groups (+I effects) decrease the positive character on the C-atom. Thus, the correct order of reactivity is HCHO>CH3CHO>C6H5CHO
Question 317. The stabilization due to resonance is maximum in:
- Cyclohexane
- Cyclohexene
- 1 ,3-cyclohexadiene
- 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene
Answer: 4. 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene
Solution: C6H6 has more canonical forms.
Question 318. In which of the following molecules, the resonance effect is not present?
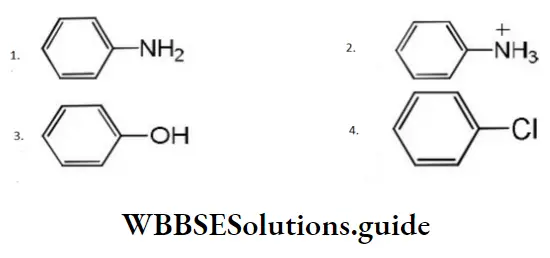
Answer: 2
Solution: If positive charge is present on the nitrogen, then the positive charge will not be in conjugation to the ring because in this case nitrogen will become pentavalent
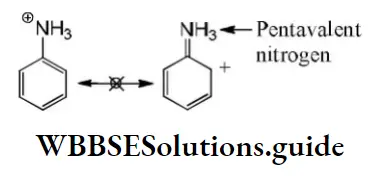
Question 319. Hydride ion transfer takes place in
- Frankland method
- Wurtz reaction
- Cannizzaro’s reaction
- Wolff-Kishner reduction
Answer: 3. Cannizzaro’s reaction
Solution: Cannizzaro reaction involves oxidation as well as reduction of aldehydes having lack of α-H atom. The mechanism of this reaction is as
1. Attack of OH– on carbonyl carbon
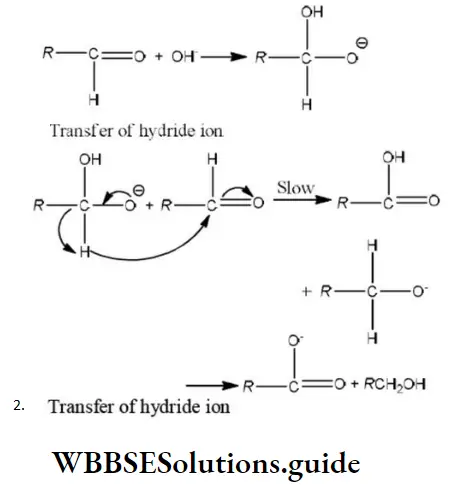
Question 320. The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system of nomenclature is
- -COOH,-SO3H,-CONH2,-CHO
- -SO3H,-COOH,-CONH2,-CHO
- -CHO,-COOH,SO3H,-CONH2
- -CONH2,-CHO,-SO3H,-COOH
Answer: 1. -COOH,-SO3H,-CONH2,-CHO
Solution: The correct decreasing order of priority for the functional groups of organic compounds in the IUPAC system is -COOH>SO3H>-COOR>COCl>-CONH2>-CN>-CH=O
Question 321. Which one is a nucleophilic substitution reaction among the following?
Answer: 4
Solution: Nucleophile (-NH3) replaces other nucleophile (-Br) in the reaction.
Question 322. LiAlH4 is used as
- Oxidizing agent
- Reducing agent
- A mordant
- A water softener
Answer: 2. Reducing agent
Solution: It is a strong reducing agent.
Question 323.
1. \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Br} \stackrel{\text { LAH }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_6\) and LAH
2. (CH3)3CBr → Alkene, the reason for this is
- SN2(2) E1 mechanism
- SN1, (2) E2 mechanism
- SN1, (2) E1 mechanism
- SN2, (2) E2 mechanism
Answer: 1. SN2(2) E1 mechanism
Solution:
Question 324. Which of the following orders is correct regarding the –I effect of the substituents?
- -NR2>-OR>-F
- -NR2<-OR<-F
- -NR2>-OR<-F
- -NH2<-OR>-F
Answer: 2. -NR2<-OR<-F
Solution: Correct order of -I effect is −NR2<−OR<−F.
Question 325. CH3CH2Cl undergoes homolytic fission, produces

Answer: 1
Solution: In homolysis, the covalent bond is broken in such a way that each resulting species known as free radical.
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{Cl} \underset{\text { fission }}{\stackrel{\text { Homolytic }}{\longrightarrow}} \mathrm{CH}_3 \stackrel{\dot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2}{ }+{ }^{\bullet} \mathrm{Cl}\)
Question 326. Nitration of benzene is
- Electrophilic substitution
- Electrophilic addition
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic addition
Answer: Electrophilic substitution
During nitration, benzene ring is attacked by NO2+ and hydrogen of benzene ring is replaced by NO2 group.
∴ Nitration of benzene is an electrophilic substitution because NO2+ is an electrophile.
Question 327. Bromination of alkanes involves
- Carbanions
- Carbocations
- Carbenes
- Free radicals
Answer: 4. Free radicals
Solution: Bromination of alkanes in the presence of sunlight involves the formation of free radical, example,
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_4 \underset{\mathrm{hv}}{\stackrel{\mathrm{Br}_2}{\longrightarrow}} \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Br}\)
Mechanism:
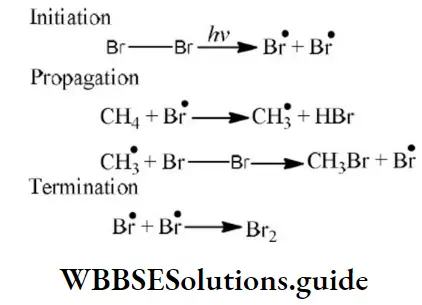
Question 328. Conversion of chlorobenzene to phenol involves
- Electrophilic substitution
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Free radical substitution
- Electrophilic addition
Answer: 2. Nucleophilic substitution
Solution:
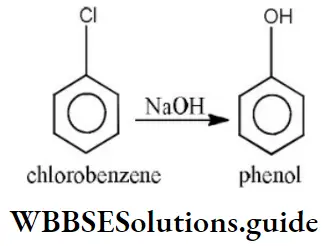
In this process one group is replaced by other, hence, it is a substitution process and both the leaving and attacking groups are nucleophilic, therefore it is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Question 329. Which of the following is most reactive towards elimination reaction?
- RCOO–
- CN–
- NO3–
- RO–
Answer: 4. RO–
Solution: With the increasing basicity of the added base, the rates of the elimination reactions have been found to increase. Thus, RO– is most reactive
Question 330. Dehydrohalogenation in the presence of OH– is correctly represented by
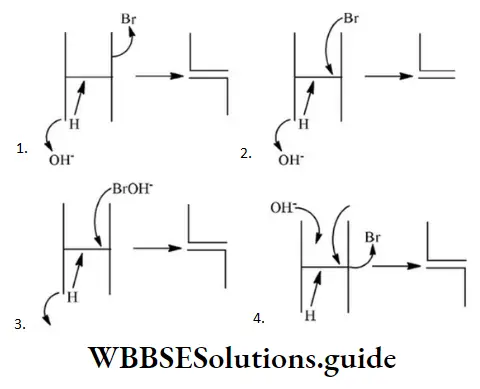
Answer: 2
Solution: The dehydrohalogenation in presence of OH– is correctly represented by In this mechanism the base OH– removes a proton from the β carbon.
Question 331. The most unlikely representation of resonance structures of p-nitro phenoxide ions
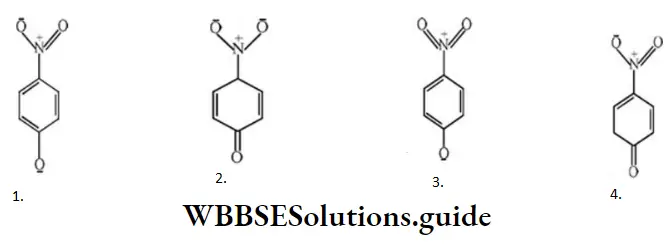
Answer: 2
Solution: “N” is pentavalent which is not possible.
Question 332. The enol form of acetone after treatment with D2O gives
Answer: 2
Solution: The enol form of acetone on treatment with D2O undergoes enolization, deutration (addition of D2O) and dehydration (removal of H2O). The repeated enolization, deutration and dehydration ultimately gives CD3COCD3.
Question 333. Which of the following is free radical?
- Cl+
- Cl–
- Cl
- • NO2
Answer: 3. Cl
Solution: Free radicals are represented by putting a dot on the entity.
Question 334. The effect involving the complete transfer of a shared pair of electrons to one of the atoms joined by a multiple bond at the requirement of attacking reagent is called
- Inductive effect
- Mesomeric effect
- Electromeric effect
- None of these
Answer: 3. Electromeric effect
Solution: The definition of electromeric effect.
Question 335.
In 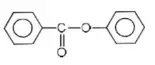 Electrophilic substitution occurs at
Electrophilic substitution occurs at
- Ortho⁄paraat first ring
- Meta at first ring
- Ortho⁄para at second ring
- Meta at second ring
Answer: 3. Ortho⁄para at second ring
Solution: Second ring is in conjugation with lone pair of oxygen
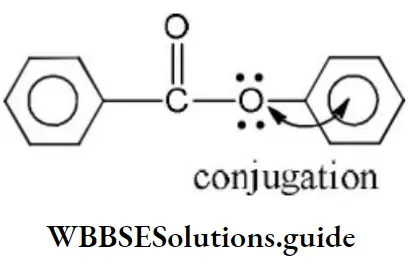
Question 336. The increasing order of stability of the following free radicals are
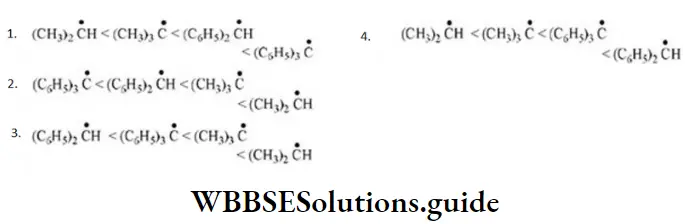
Answer: 1
Solution: Free radicals’ stability
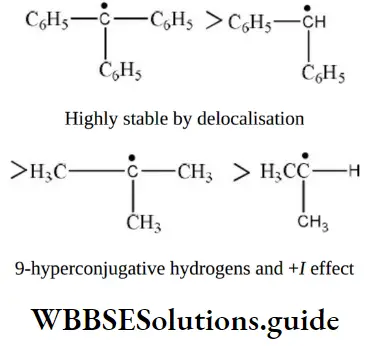
Question 337. Predict the nature of principal product in the reaction,
- BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br+KOH (alc.)⟶Product1,3-butadiene
- Cyclobutane
- BrCH2CH2CH = CH2
- None of these
Answer: 1. BrCH2CH2CH2CH2Br+KOH (alc.)⟶Product1,3-butadiene
Solution: Follow the elimination of HBr from two ends.
Question 338. Which of the following requires radical intermediate?
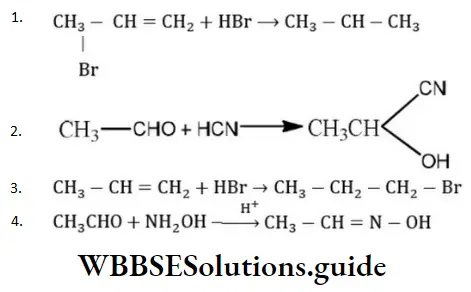
Answer: 3
Solution:
⇒ \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2+\mathrm{HBr} \underset{\text { peroxide }}{\stackrel{\text { Organic }}{\longrightarrow}} \mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{Br}\) Requires radical intermediate.
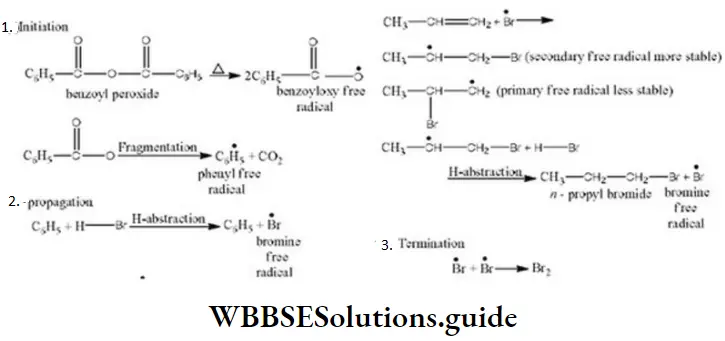
Question 339. The following reaction is an example of \(>\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{NOH} \rightarrow>\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{NOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Addition
- Addition elimination
Answer: 4. Addition elimination
Solution: In the reaction Both addition and elimination take place simultaneously. Thus, the reaction is an addition elimination
Question 340. In the reaction of phenol with chloroform and aqueous solution of NaOH at 70°C, the electrophile attacking the ring is
- CHCl3
- CHCl2
- ∶CCl2
- COCl2
Answer: 3. ∶CCl2
Solution: When phenol reacts with chloroform and aqueous NaOH solution, it gives salicylaldehyde. CHCl3+OH–⇋H2O+CCl3–
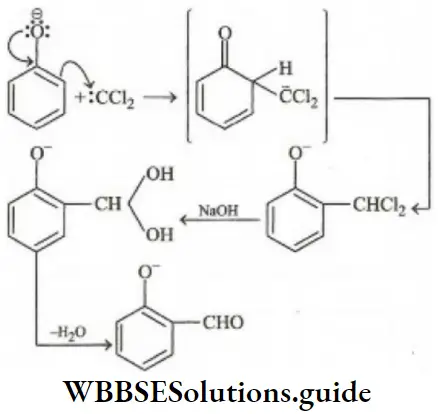
Question 341. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the nitro group is meta-directing because it
- Decreases electron density at ortho and para positions
- Decreases electron density at the meta position
- Increases electron density at meta position
- Increases electron density at ortho and para positions
Answer: 3. Increases electron density at meta position
Solution: When nitro group is present in the benzene nucleus, it withdraws electrons from o and p-positions. Thus, the electron density at the o and p-positions decrease. m-positions become positions of comparatively higher electron density and therefore, electrophilic attack occurs at mpositions.
Question 342. Which of the following compounds yields most stable carbanion after rupture of the bond?
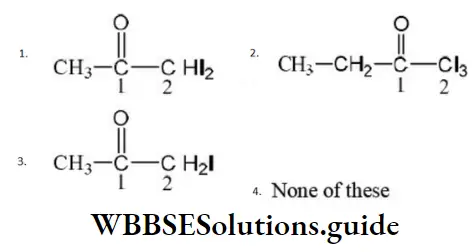
Answer: 2
Question 343. The equation of Benzon
- C2H5OH
- C6 H6
- CH4
- CHO
Answer: 2. C6 H6
Solution:
Question 344. Dehydration of alcohol is an example of which type of reaction?
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Addition
- Rearrangement
Answer: 2. Elimination
Solution: Dehydration of alcohol involves the loss of two atoms or groups from the adjacent carbon atoms; hence it is an example of a β-elimination reaction.
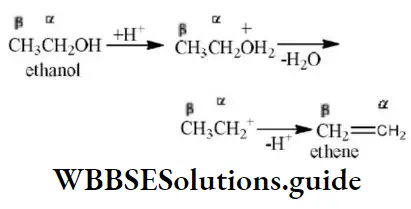
Question 345. The halogen compound which most readily undergoes nucleophilic substitutions is
- CH2=CHCl
- CH3CH=CHCl
- CH2=CHC(Cl)=CH2
- CH2=CHCH2Cl
Answer: 4. CH2=CHCH2Cl
Solution: CH2=CH.CH2Cl compound undergoes nucleophilic substitution most readily.
Question 346. Reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction of is
1. HCHO
2. CH3CHO
3. CH3COCH3
- 2>3>1
- 3>2>1
- 1>2>3
- 1>2<3
Answer: 3. 1>2>3
Solution: Aldehydes and ketones readily undergo nucleophilic addition reaction. The order of reactivity is as the +I effect of alkyl group increases
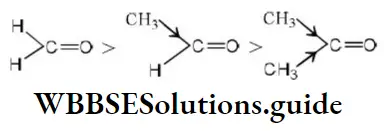
Question 347. H2C=O behaves as:
- Nucleophile
- Electrophile
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Solution: O is more electronegative than C, therefore, C carries a small positive charge and, O carry a small negative charge. In other words, it acts as an electrophile due to the presence of a partial positive charge on C and act as a nucleophile due to the presence of a partial negative charge on O.
Question 348. The strongest base among the following is?
- NH4+
- :NH3
- :NH2–
- :OH–
Answer: 3. :NH2–
Solution: Least stable be the species ion, more basic be the given species. As NH2− (amide ion) is the least stable species ion, it is the most basic species.
Question 349. In hyperconjugation, the atom involved is
- β-H atom
- α-H atom
- γ-H atom
- All of these
Answer: 2. α-H atom
Solution: —do—
Question 350. Addition of Br2 on trans-butene-2 gives:
- A racemic mixture of 2,3-dibromobutane
- Meso form of 2,3-dibromobutane
- Dextro form of 2,3-dibromobutane
- Laevo form of 2,3-dibromobutane
Answer: 2. Meso form of 2,3-dibromobutane
Solution: Follow the mechanism of addition reactions.
Question 351. Which one of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition?
- CH3CHO
- PhCOCH3
- PhCOPh
- CH3COCH3
Answer: 1. CH3CHO
Solution:
Carbonyl compounds undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction.

If group or atom attached with carbonyl carbon shows negative inductive effect, then it decreases electron density on carbonyl carbon and facilitate the attack of nucleophile, hence reactivity of the carbonyl compound increases.
The aromatic aldehydes and ketones are less reactive than their aliphatic analogues due to +R effect of benzene ring. The increasing order of the nucleophilic addition reaction in the following compounds will be.
CH3CHO>CH3COCH3>PhCOCH3>PhCOPh
Question 352. In which of the reactions, addition takes place according to Markownikoff’s rule?
- CH3CH=CHCH3+Br→
- CH2=CH2+HBr→
- CH3CH=CH2+HBr→
- CH3CH=CH2+Br2→
Answer: 3. CH3CH=CH2+HBr→
Solution: Markownikoff’s rule is for the addition of an unsymmetrical additive on an unsymmetrical alkene.
Question 353. SN1 mechanism for the reaction, R-X+KOH ⟶ROH+KX follows \(R-X \rightarrow R^{+}+X^{-} \stackrel{\mathrm{OH}^{-}}{\rightarrow} \quad \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{OH}\)
- Carbocation mechanism
- Carbanion mechanism
- Free radical mechanism
- Either of the above
Answer: 1. Carbocation mechanism
Solution: \(R-X \rightarrow R^{+}+X^{-} \stackrel{\mathrm{OH}^{-}}{\rightarrow} \quad \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{OH}\)
Question 354. “The negative part of the addendum adds on the carbon atom joined to the least number of hydrogen atoms.” This statement is called?
- Markownikoff’s rule
- Peroxide effect
- Baeyer’s strain theory
- Thiele’s theory
Answer: 1. Markownikoff’s rule
Solution: It is Markownikoff’s rule.
Question 355. The following reaction is described as
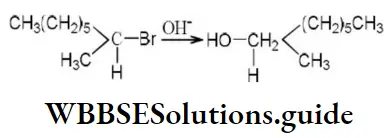
- SE2
- SN2
- SN1
- SN0
Answer: 2. SN2
Solution: In this reaction inversion takes place. Hence, it is an example of SN2 reaction. In this mechanism the attack of OH– ions take place from the back side while the Br– ion leaves from the front side
Question 356. A carbonium ion is formed when a covalent bond between the two atoms in an organic compound undergoes?
- Homolysis
- Heterolysis
- Cracking
- Pyrolysis
Answer: 2. Heterolysis
Solution: Heterolytic bond fission produces positive and negative ions.
Question 357. Grignard reagent adds to
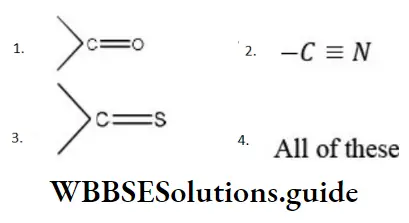
Answer: 2
Solution: Grignard reagent reacts with >C=O, -C≡N,>C=S as follows
Question 358. What will be the compound if two valencies of the carbonyl group are satisfied by two alkyl groups?
- Aldehyde
- Ketone
- Acid
- Acidic anhydride
Answer: 2. Ketone
Solution: – do –
Question 359. Among the following anions
1. CH3–
2. NH2–
3. OH–
4. F– the order of basicity is?
- 1>2>3>4
- 2>2>3>4
- 3>2>1>4
- 3>1>2>4
Answer: 1. 1>2>3>4
Solution: Stronger is the acid, weaker is its conjugate base or weaker is its nucleophilicity. The acidic order HF >H2O >NH3>CH4
Question 360. Intermediate product formed in the acid catalyzed dehydration of n-propyl alcohol is?
- CH-CH2-CH3
- CH3-CH=CH2
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_3\)
Solution: 2° carbocation is more stable.
Question 361. In the compound, electrophilic substitution occurs at
- Ortho/para position at ring
- Meta position at the ring
- Ortho/para position at the ring
- Meta position at ring
Answer: 3. Ortho/para position at ring
Solution: Electrophilic substitution reaction takes place in compounds in which π-electrons are highly delocalised. The electrophile attacks the region of high electron density; therefore, electrophilic substitution occurs at ortho/para position at ring 2.
Assertion – Reasoning Type
Each question contains Statement 1 (Assertion) and Statement 2 (Reason). Each question has the 4 choices (1), (2), (3), and (4) out of which Only one is correct.
- Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is correct explanation for Statement 1
- Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True Statement 2 is not the correct explanation for Statement 1
- Statement 1 is True, Statement 2 is False
- Statement 1 is False, Statement 2 is True
Question 362.
- Statement 1: Electrophiles are electron rich in nature
- Statement 2: H3O+,BF3 and AlCl3 are electrophile and can accept electron pair
Answer: 4. Statement 1 is False, Statement 2 is True
Solution: Electrophiles are electron deficient while nucleophiles are electron rich in nature, ie, electrophile can accept an electron pair while nucleophile donates an electron pair
Question 363.
- Statement 1: Dehydration of alcohol is an example of an elimination reaction
- Statement 2: When H2SO4or H3PO4(concentrated) are used as dehydrating agent, the mechanism is E1
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True Statement 2 is not the correct explanation for Statement 1
Solution: Alcohols leading to conjugated alkenes are more easily dehydrated than the alcohols leading to non-conjugated alkenes
Question 364.
- Statement 1: The order of stability of carbocation are \(R_3 \mathrm{C}^{+}>R_2 \stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}>R_{\mathrm{R}}^{+} \mathrm{H}_2>\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}^{-}} \mathrm{H}_3\)
- Statement 2: The stability of carbocations is influenced by both resonance and inductive effects
Answer: 3. Statement 1 is True, Statement 2 is False
Solution: The stability of carbocation is explained on the basis of hyperconjugation and inductive effect hence the stability order of carbocation is 3°>2°>1°>Methyl carbocation
Question 365.
- Statement 1:
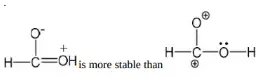
- Statement 2: A compound in which the positive and negative charges reside on the most electropositive and most electronegative atoms of the species respectively is more stable
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is the correct explanation for Statement 1
Solution: Both structures are resonating structures of formic acid In negative charge is on oxygen but in negative charge is on carbon therefore (I) will be more stable than the FQ
