Elementary Idea Of Hydroponics And Other Plant Culture Methods
Plants are cultured in artificial culture media, to study mineral requirement and their essentiality. These culture media contain mineral nutrients that are essential for plant growth and development. Three culture media are used to study mineral requirements. These are—
- Solution culture media or hydroponics,
- Sand culture media, and
- Aeroponics.
Concept Of Solution Culture Or Hydroponics
Hydroponics Definition: Hydroponics is the method or technique of growing plants in a nutrient solution without using soil (soilless culture).
The word hydroponics technically means working water in which plants can grow. It has been derived from the Latin words hydro meaning ‘water’, and ponos meaning ‘labor’. Recently hydroponically growing plants have been gaining popularity and are being sold across many different markets.
This process of soilless culture or hydroponics was first described by Francis Bacon (1627) in his book Sylva sylvarum. Later it was described by John Woodward (1699). He experimented on the mint plant.
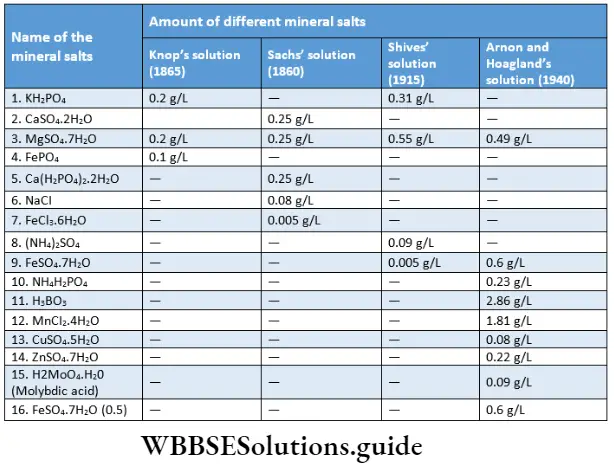
Hydroponics Explanation: During the nineteenth century, there was a practice of growing plants in soil-less conditions. This method was modernized by Sachs (1860) and Knop (1865). They prepared a balanced nutrient solution to grow plants in soil-less conditions.
Sachs’ and Knop’s solutions are mostly used for the process of hydroponics. They included only macronutrients and iron as essential minerals in their solution media. Iron was used as ferrous chloride by Sachs and as ferrous phosphate by Knop.
Later Arnon and Hoagland (1940) included micronutrients in this solution. These scientists found that iron remained soluble as salt of citric acid and tartaric acid. The chemical agent that keeps a metal in the soluble state is called a chelating agent.
The most commonly used chelating agents are EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and DTPA (Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid). They used Fe and Na-EDTA in this solution.
Types of hydroponics systems or techniques
There are two types of hydroponics techniques—passive and active techniques.
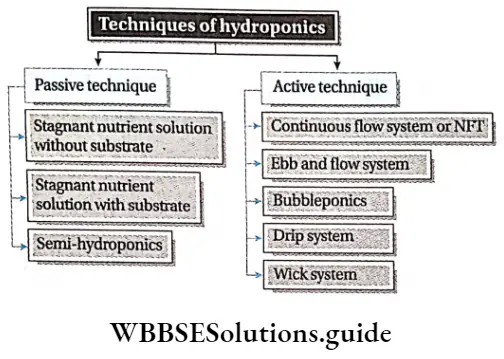
The application of passive or active hydroponics depends on the requirement. Passive techniques are more suitable for growing on a small scale, for example, indoor plants in the living room. However, the active techniques are more suitable for large-scale cultivation. These hydroponics techniques are described below in separate heads.
Passive technique: In this technique, the nutrient solution is stationary and the plant takes what it needs from the solution. Different types of passive techniques are discussed below.
Stagnant nutrient solution without substrate: This is a very simple type of hydroponic system. The system shows the following features—
- A small reservoir of glass or metal is filled with distilled water containing appropriate amounts of essential nutrients.
- The reservoir is covered with a wooden plank with holes or wire gauge, as a plant support system. The plants are kept on the plant support system in such a manner, that their roots directly touch the nutrient solution present in the reservoir.
- This reservoir also has an aeration system through which oxygen is added to water from the environment.
Stagnant nutrient solution with substrate: This technique is suitable for the plants grown inside the rooms.
The system shows the following features—
- One plant or many plants can be kept per pot.
- The roots of the plant are impregnated with an inert and porous substrate. The nutrient solution is brought to the roots of the plant by the capillary activity of the substrate.
- The nutrient solution takes up 1/3 of the height of the pot and the root system occupies the upper 2/3 part (height) of the pot.
Semi-hydroponics: This technique is a combination of hydroponics and irrigation system for growing plants in a soil-free mineral solution.
It shows the following features—
- The plant itself is in a pot with soil and this pot is hung over a nutrient solution.
- The nutrient solution reaches the roots through the capillary activity of clay granules.
Active technique: In this dynamic technique, the nutrient solution is allowed to flow around the roots. The nutrient solution is brought to the roots by the use of a pump of electric vaporizer.
This technique is more complex than the passive technique but it allows better management of nutrient solution as this is stored in a separate container. This technique may be accomplished in the following ways—
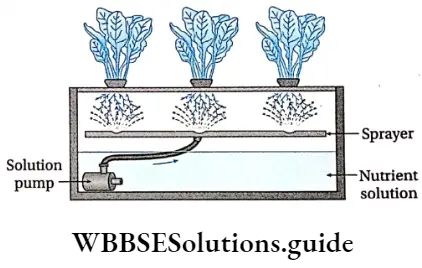
Nutrient-Film hydroponics Technique (NFT) or Continuous Flow System: It is the most commonly used hydroponics system. The system shows the following features—
- A container which is actually a tube is without substrate. The tube has several holes through which plants are attached in such a way that some branches of the root or the main root touch the base of the container. This is slanted over the water reservoir containing an appropriate amount of mineral nutrients.
- Here, the nutrient solution from the water reservoir is pumped into the slanted vessel by using a pump. So, the roots remain in contact with a thin film of nutrient solution. In this system, roots are not submerged in the solution.
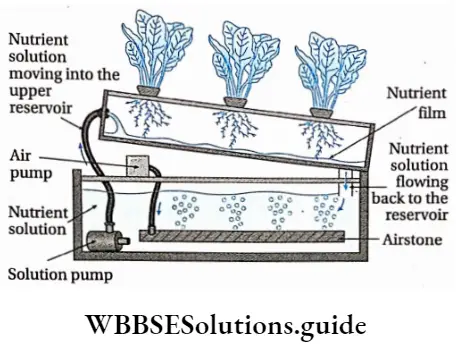
Ebb and Flow hydroponics system: Ebb and flow are the two types of movements of water observed in this system. Ebb is the outgoing and the flow is the incoming phase.
The system shows the following features—
- In this system, a small reservoir is kept over the large reservoir. The large reservoir contains the nutrient solution.
- Plants are kept on the wooden plank at the top of the small reservoir.
- The nutrient solution is moved to the small reservoir through a pump.
- After reaching a certain height, the nutrient solution comes back to the large reservoir through an overflow pipe. This helps maintain the level of solution in the smaller reservoir.
- The nutrient solution in the upper reservoir is aerated by using an electrical air pump. In this way, the roots get an optimum proportion of nutrients, water, and air supply.
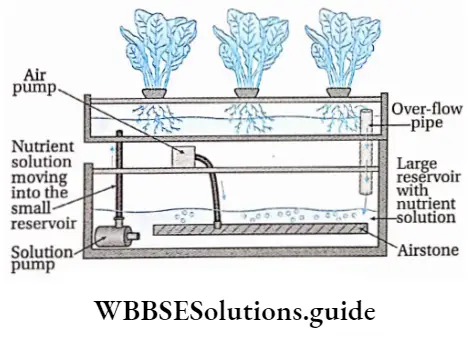
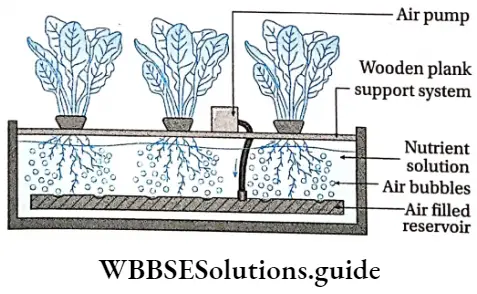
Bubbleponics: The system shows the following features—
- In this system, plants are arranged in the same way as in the stagnant nutrient solution without substrate.
- The nutrient solution is pumped up to the roots to water them from above at regular intervals.
- The advantage is that the plant grows quickly and does not need to develop roots first to reach the nutrient solution.
Drip System:
The system shows the following features—
- It is the most widely used type of hydroponic system. In a drip system, the nutrient solution is pumped to the roots, from the reservoir, with individual drippers at each plant.
- The plants are kept in a nutrient medium. Here a timer controls the pump.
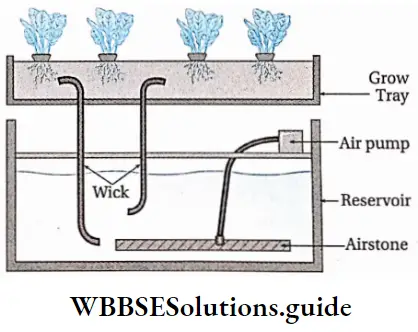
Wick System: A wick is a gauze strip that is made up of porous material. This is used to draw the liquid by its capillary action.
The system shows the following features—
- It is the simplest of all hydroponics systems. Here, the nutrient solution is provided to the plants with the help of a wick.
- A variety of growing mediums, such as perlite, vermiculite coconut fiber, etc., can be used in this system.
Study Of The Mineral Requirements Of Plants Through Hydroponics System
Plants require different minerals for their growth and development.
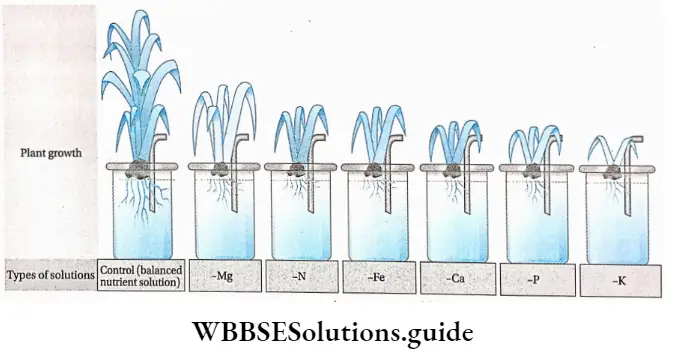
An experiment for studying the essentiality of different minerals is given as follows—
- During this study, a normal balanced nutrient solution is prepared which contains all the essential elements in an appropriate amount. This is taken as control.
- Then a series of nutrient solutions are also prepared. Each of these nutrient solutions has any one of the nutrient elements missing.
- Now, the seedlings of the same size are reared in the nutrient solutions.
- The glass bottles are covered with black paper so that direct sunlight can not reach the roots. It will also prevent the growth of algae.
- The bottles are kept in a place where they can get the appropriate amount of sunlight and air.
- The growth of all the seedlings is observed carefully and regularly.
- The growth of each seedling is compared with that of the seedling in the normal balanced nutrient solution. From the comparison, it has been found that all the seedlings planted in deficient nutrient solutions have stunted growth.
- The deficiency symptoms for each element can be observed clearly. The observations are given below in a tabular manner.
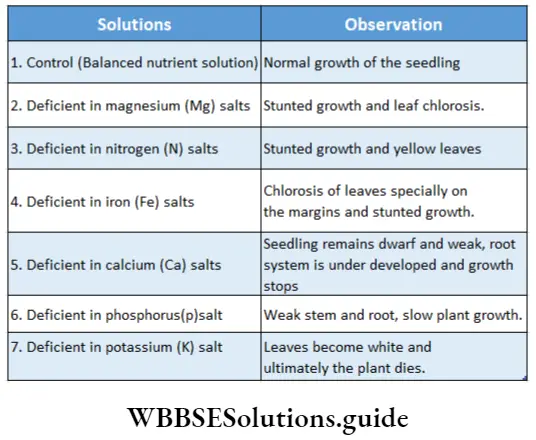
From this experiment, it can be concluded that all the nutrients in their appropriate proportions are important and essential for the proper growth of a plant.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of hydroponics techniques are discussed separately below.
Hydroponics Technique Advantages:
- Hydroponics helps to study the nutrient requirements of the plants. We can find out—
- The essentiality of different nutrients for the growth and development of a plant,
- Deficiency symptoms of any element,
- Harmful effects caused by toxic concentration of any element,
- Role of essential elements in. metabolism of plants.
- Hydroponics is used for growing off-season commercial flowers and vegetables such as lettuce, seedless cucumber, and tomatoes.
- As this method does not require soil, plants be grown irrespective of soil type.
- Plants can be grown without any contamination by soil pathogens and pollutants.
- It is environment-friendly as it does not require any chemical fertilizer.
- Generally, the plants grown by this method give better yields.
Hydroponics Technique Disadvantages:
- The infrastructural cost for this technique is very high.
- The chances of water-borne plant diseases are high, so, maintaining a sterile environment is necessary.
- Chemicals used in the preparation of nutrient solutions may contain toxic impurities. Toxins may affect the normal plant growth.
- Technical expertise is required.
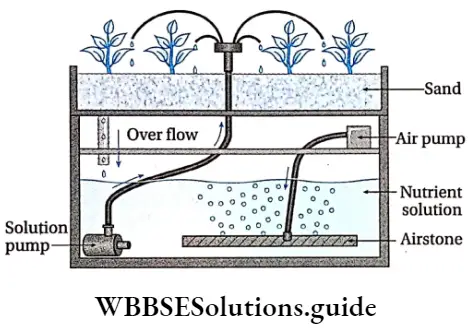
Concept Of Sand Culture
The cultivation of plants in the sand medium is called sand culture. Here acid acid-washed quartz is used as a substrate. Perlite or vermiculite is used along with quartz to enhance root growth. Cultivation is done in a clay vessel.
It is divided into two tiers. The upper tier is filled with sand and the lower tier with nutrient solution. This solution is pumped to the sand layer, continuously or at regular intervals. It is an easy method. It provides a natural environment for plants. However, in this method, it is difficult to maintain proper aeration and pH.
Concept Of Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a type of soil-less plant culture. In this process, the plants are kept suspended in a growth chamber. The nutrient solution is sprayed on the roots of the plants. This spraying may be done continuously or at regular intervals. This method was first discovered by Weathers and Zobel (1992).
The nutrient solution used in this method is more concentrated than that used in hydroponics. In this system, the roots have an excellent aeration. For long-term aeroponic cultivation, the root systems must be free from surrounding constraints. Generally, citrus fruits and olives are grown by this method.