Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Locomotion And Movement Questions And Answers
Question 1. Name one unicellular organism in which locomotion occurs by protoplasmic streaming. Also, mention the type and organ of locomotion.
Answer:
The unicellular organism is Amoeba sp.
- Type of locomotion—Amoeboid.
- Organ of locomotion—pseudopodia.
Question 2. Which types of cells show amoeboid movement in the human body? Describe with reason.
Answer:
In humans, amoeboid movement is found in macrophages and white blood cells. These cells show amoeboid movement to engulf antigens or microbes and short-distance immigration in circulatory fluid.
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 3. Give two examples of ciliary movement in the human body.
Answer:
Different tubular organs in the human body consist of ciliated epithelial lining. They show ciliary movement.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
Question 4. Ciliated epithelial cells are present in the respiratory tract of human beings.
Answer:
These cilia prevent the entry of pathogens and dust particles inhaled with air, within the body.
Cilia are also found in the fallopian tubes of females. These cilia help in the transportation of ova into the uterus through the fallopian tube.
Locomotion and movement questions and answers PDF
Question 5. What are the special properties of muscles? On the basis of location, how many types of muscles are there in the human body? What are they?
Answer:
Special properties of muscles are—
- Excitability,
- Contractility,
- Reliability,
- Elasticity.
There are three types of muscles, on the basis of location. They are—
- Skeletal muscles,
- Visceral muscles and
- Cardiac muscles.

Question 6. On the basis of origin, what kind of muscle is human muscle? What is the percentage of muscle with respect to total body weight in an adult human being?
Answer:
Muscles in human beings are a special type of animal tissue, originating from the embryonic mesoderm.
In an adult, 40-50% of total body weight is muscles.
NEET locomotion and movement important questions with answers
Question 7. What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum? Mention one of its functions.
Answer:
Sarcoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum, present in the sarcoplasm, is known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).
Function: The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium ions. It acts as the storehouse of calcium. During muscle contraction, SR releases calcium ion which helps in the process
Question 8. Mention the names of two proteins present in myofibrils, which help in muscle contraction and two proteins which prevent muscle contraction.
Answer:
Two proteins which help in muscle contraction are—
- Actin and
- Myosin.
Two proteins which prevent muscle contraction are—
- Troponin and
- Tropomyosin.
Question 9. What are the light and dark bands of muscle fibres called?
Answer:
Light and dark bands of muscle fibres
The light band of muscle fibre is known as the isotropic band or l-band. This band is formed of longitudinal and parallel actin proteins. The dark band is known as the anisotropic band or A-band.
Class 11 biology locomotion and movement Q&A
Question 10. Which is the actin and ATP binding site in myosin? Mention the role of ATPase.
Answer:
- The globular head of myosin is the actin and ATP binding site.
- ATPase dissociates ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate, to release energy. This energy is required for muscle contraction.
Question 11. What is a motor endplate? Mention the name and function of the neurotransmitter secreted from this region.
Answer:
Motor endplate
- Red muscles contain a large amount of myoglobin and also a large number of mitochondria.
- As a result, a huge amount of oxygen is required for the oxidation of glycogen and the synthesis of ATP. This helps in muscle contraction. So, red muscles are known as aerobic muscles.
Question 12. How many pairs of ribs are present in the skeletal system of human beings? Why are ribs called bicephalic?
Answer:
- Twelve pairs of ribs are present in the skeletal system of human beings.
- Each rib has two articulating surfaces or heads. They join with either the sternum or another rib or remain unattached at one end. On their distal ends, they remain attached to the vertebra, so ribs are known as bicephalic.
Question 13. How do the ribs remain attached at the ventral surface of the thoracic region?
Answer:
The ventral ends of the ribs are joined to the sternum through costal cartilages at the ventral surface of the thoracic region.
Short answer questions on locomotion and movement
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE Locomotion And Movement Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. Out of ‘X’ pairs of ribs in humans only V pairs are true ribs. Select the option that correctly represents values of X and Y and provides their explanation—
- X=12, Y=5 True ribs are attached dorsally to the vertebral column and sternum on the two ends
- X=24, Y=7 True ribs are dorsally attached to the vertebral column but are free on the ventral side
- X=24, Y=12 True ribs are dorsally attached to the vertebral column but are free on the ventral side
- X=12, Y=7 True ribs are attached dorsally to the vertebral column and ventrally to the sternum
Answer: 4. X=12, Y=7 True ribs are attached dorsally to the vertebral column and ventrally to the sternum
Question 2. The pivot joint between the atlas and axis is a type of—
- Cartilaginous joint
- Synovial joint
- Saddle joint
- Fibrous joint
Answer: 2. Synovial joint
Question 3. Smooth muscles are—
- Involuntary, fusiform, non-striated
- Voluntary, multinucleate, cylindrical
- Involuntary, cylindrical, striated
- Voluntary, spindle-shaped, uninucleate
Answer: 1. Involuntary, fusiform, non-striated
Question 4. Osteoporosis, an age-related disease of the skeletal system, may occur due to—
- Immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue
- High concentrations of Ca2+ and Na+
- Decreased level of oestrogen
- Accumulation of uric acid leads to inflammation of joints
Answer: 3. Decreased level of oestrogen
Question 5. Name the ion responsible for unmasking active sites for myosin for cross-bridge activity during muscle contraction:
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Potassium
Answer: 1. Calcium
MCQs on locomotion and movement with answers for NEET
Question 6. Which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system?
- Locomotion
- Production of erythrocytes
- Storage of minerals
- Production of body heat
Answer: 4. Production of body heat
Question 7. Which of the following joints would allow no movement?
- Ball and socket joint
- Fibrous joint
- Cartilaginous joint
- Synovial joint
Answer: 2. Fibrous joint
Question 8. Choose the wrongly matched pair:
- A portion of myofibril—sarcomere between two Z-lines
- Isotropic band— Actin
- Anisotropic band— Myosin
- The central part of the l-band — M-line
Answer: 4. The central part of l-band — M-line
Question 9. Which of the following is not involved in muscular contraction?
- Calcium ion
- Troponin
- Actin
- Magnesium ion
Answer: 4. Magnesium ion
Question 10. Select the correct matching of the type of the joint with the example in the human skeletal system—
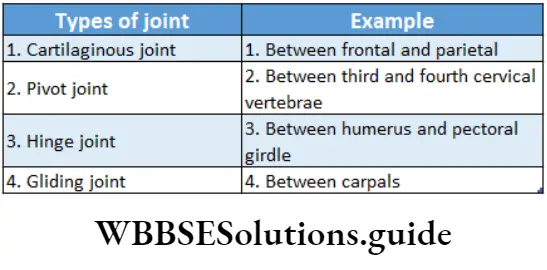
Answer: 4
Question 11. The U-shaped bone present at the base of the buccal cavity is—
- Maleus
- Ethmoid
- Zygomatic
- Hyoid
- Sphenoid
Answer:
Question 12. Match the following columns:
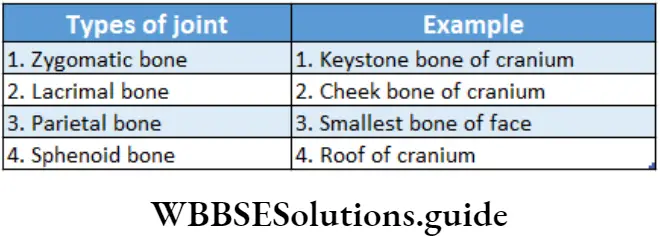
- 1-1,2-3,3-5,4-2
- 1-2,2-4,3-5,4-1
- 1-2,2-4,3-1,4-3
- 1-2,2-3,3-4,4-5
Answer: 4. 1-2,2-3,3-4,4-5
Question 13. Knee Joints is an example of-
- Ball And Socket joint
- Jinge Joint
- Pivot Joint
- Gliding Joint
Answer: 2. Jinge Joint
Difference between locomotion and movement with examples Q&A
Question 14. Which option is correct for the region labelled as A, B, C and D in the given diagram?
- 1-scapula, 2-Clavicle, 3-Humerus, 4-Ulna
- 1-Clavicle, 2-Scapula,C-Humerus,4-Radius
- 1-Clavicle,2-Ulna,3-radius, 4-Humereus
- 1-Clavicle,2-Glenoid Cavity,3-Raidus, 4-Ulna
Answer: 2. 1-Clavicle, 2-Scapula,C-Humerus,4-Radius
Question 15. The pituitary gland is located in A, which is a B of C bone.
- 1-Rathke’s pouch, 2—Depression, 3—Nasal
- 1—Sella turcica, 2—Raised surface, 3— Ethmoid
- 1—Sella turcica,2—Depression, 3—Sphenoid
- 1—Rathke’s pouch, 2—Depression, 3—Sphenoid
Answer: 3. 1—Sella turcica,2—Depression, 3—Sphenoid
Question 16. Select the correct statement regarding the specific disorder of the muscular or skeletal system:
- Muscular dystrophy—age-related shortening of muscles.
- Osteoporosis—decrease in bone mass and higher chances of fractures with advancing age.
- Myasthenia gravis—an autoimmune disorder which inhibits the sliding of myosin filaments.
- Gout—inflammation of joints due to extra deposition of calcium.
Answer: 2. Osteoporosis—decrease in bone mass and higher chances of fractures with advancing age.
Question 17. Pick out the correct match:
- Sternum-14
- Pelvis-3
- Ribs-20
- Face-5
Answer: 2. Pelvis-3
Question 18. Which of the following is not a sesamoid bone?
- Radius
- Patella
- Fibula
- Pisciform
Answer: 2. Patella
Question 19. The main difference between bone and cartilage is Of—
- Mineral salts
- Harversian canals
- Lymph vessels
- Blood vessels
Answer: 2. Harversian canals
Question 20. Chemical ions responsible for muscle contraction are—
- Ca2+ and K+
- Na+ and K+
- Na+ and Ca2+
- Ca2+ and Mg2+
Answer: 4. Ca2+ and Mg2+
Question 21. Acetabulum is a concave surface of—
- Pelvis
- Pectoral
- Foramen magnum
- Foramen manor
Answer:
Question 22. The elbow joint is an example of a—
- Pivot joint
- Hinge joint
- Gliding joint
- Ball and socket joint
Answer: 2. Hinge joint
Question 23. The characteristics and an example of a synovial joint in humans are—
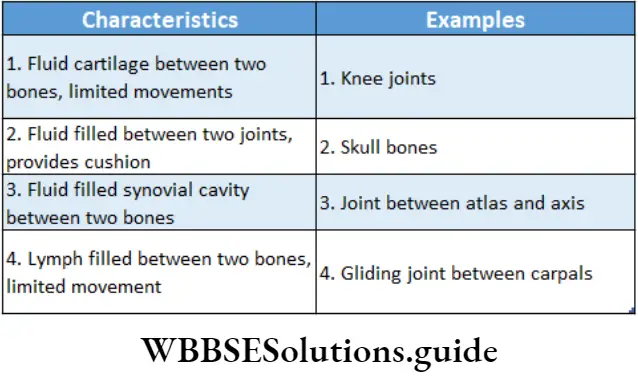
Answer: 3
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE Locomotion And Movement Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is locomotion?
Answer:
Locomotion
Locomotion is the process by which an organism can move from one place to another in response to stimuli.
Question 2. Give two examples of locomotion.
Answer:
Two examples of locomotion
Flying and running are two examples of locomotion.
Question 3. What is movement?
Answer:
Movement
Movement is the process by which an organism is able to move its organs or parts of the body in response to stimuli by remaining in a fixed position.
Question 4. Name the primary germ layer from which muscle tissue arises.
Answer:
Mesoderm is the primary germ layer from which muscle tissue arises.
Question 5. How many bones are present in the human skull?
Answer:
29 bones.
Question 6. Name the proteins present in muscle fibres.
Answer:
Actin, myosin, tropomyosin, troponin, titin.
Question 7. Name the stored food material in muscle cells.
Answer:
Glycogen is the stored food material in muscle.
Question 8. Some of the muscle fibres are red in colour. Explain.
Answer:
A high concentration of myoglobin makes some muscle fibre red in colour.
Question 9. What is the sternum?
Answer:
Sternum
The sternum (breastbone) is a thin, knife-shaped bone located at the anterior side of the thoracic region of the skeleton along the midline of the body.
Muscle contraction and skeletal system-related questions
Question 10. The three tiny bones, present in the middle ear, are called ear ossicles. Write them in the correct sequence beginning from the ear drum.
Answer:
Malleus, incus, stapes.
Question 11. Give the location of the ball and socket joint in a human
Answer:
Hip joint (between pelvic girdle and head of femur) and shoulder joint (between pectoral girdle and head of humerus
Question 12. Give the name of the cells/tissues in the human body
which—
- Exhibit amoeboid movement
- Exhibit ciliary movement.
