NEET Biology Mcqs Biodiversity and its Different Levels
Question 1. The term ‘biodiversity’ was given by
- WG Rosen
- John Roy
- William Hornaday
- Myers
Answer: 1. WG Rosen
The term biodiversity was coined by WG Rosen in the year 1985 when the plans for National Forum on Biological Diversity to be held in the year 1986 was underway.
Question 2. Biodiversity refers to the totality of
- Genes
- Species
- Ecosystems
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Biodiversity is the totality of different types of ecosystems, different species of organisms with the whole range of their variants (biotypes) and genes adapted to different climates, and environments along with their interaction and process.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 3. The biodiversity of a geographical region represents
- Endangered Species Found In The Region
- The Diversity In The Organisms Living In The Region
- Genetic Diversity Present In The Dominant Species Of The Region
- Species endemic to the region
Answer: 2. The Diversity In The Organisms Living In The Region
“viable material of endangered species can be preserved by “
Biodiversity includes the endangered species, genetic diversity,
endemic species of that region, so diversity in the organisms living in the region mostly represented by the biodiversity of the geographical region.
Question 4. An ecologist uses the term biodiversity for the variety of species of
- All living plants
- All living animals
- Both 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and microbes also living in their natural habitats
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and microbes also living in their natural habitats
An ecologist use the term biodiversity or biological diversity to the variety of life forms and habitats found in defined area. In other words biodiversity can be defined as the variety of species of all living plants and animals and microbes also living in their natural habitats and the ecological complexes of which they are a part.
NEET Biology Biodiversity and Conservation MCQs with Answers
Question 5. The levels of diversity that can be observed in the biosphere are
- Genetic Diversity, Species Diversity And Ecological Diversity
- Species Diversity, Ecological Diversity And Habitat Diversity
- Geographical Diversity, Geological Diversity And Biological Diversity
- Ecological diversity, species diversity and community diversity
Answer: 1. Genetic Diversity, Species Diversity And Ecological Diversity
Immense diversity (heterogeneity) exists in our biosphere, not only at the species level but at all the levels of biological organisation ranging from the macromolecules within cells to biomes. Sociobiologist Edward Wilson described the combined diversity at all levels of biological organisation. These are genetic diversity, species diversity and ecological diversity.
Biodiversity Levels

Important MCQs on Biodiversity and Conservation for NEET
Question 6. Genetic diversity is the measure of
- Varieties Of The Species And Their Relative Abundance Present Within A Region
- Variety In The Genetic Information Contained In The Organisms
- Diversity Of The Genes At Community And Ecosystem Levels
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Variety In The Genetic Information Contained In The Organisms
Genetic diversity is the diversity in number and types of genes as well as the chromosomes present in different species, their variation in the genes and their alleles in the same species. It is mainly the variation in genetic information present in the organisms. These help in speciation or evolution of the new species.
Thus, option 2 is correct.
“biodiversity questions “
Question 7. Genetic diversity is essential for
- Maintenance Of Species
- Prevent Extinction Of Species
- Improvement Of Genetic Code
- Maintenance and improvement of species
Answer: 4. Maintenance and improvement of species
The wide variety of genes in a species is known as its genetic diversity. Genetic diversity helps the organisms to adapt themselves to the changing environmental conditions due to the variations in the alleles of the individuals of the species. The individuals with the alleles more fit to survive in an environment will grow and reproduce thus maintaining themselves and will also lead to continuous survival of species generation after generation.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 8. The medicinal plant, Rauwolfia vomitoria, is an example of ……………………. It grows in the Himalayan ranges and shows variation in terms of the potency and concentration of the chemical (reserpine) that it produces.
- Species Diversity
- Ecological Diversity
- Genetic Diversity
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Genetic Diversity
The medicinal plant, Rauwolfia vomitoria shows variation due to the genetic diversity. Variation in the genes of a species increases with the increase in size and environmental parameters of the habitat. It results in the formation of polymorphs ecotypes, races, varieties and subspecies.
Question 9. Which of the following shows the maximum genetic diversity in India?
- Maize
- Mango
- Groundnut
- Rice
Answer: 4. Rice
The diversity of rice in India is the highest in the world. More than 50,000 genetically different strains of rice has been estimated in India, alone. Basmati rice has 27
Different Levels of Biodiversity MCQs for NEET
Question 10. In India, we find mangoes with different flavours, colours, fibre content, sugar content and even shelf-life. The large variation is on account of
- Species Diversity
- Induced Mutations
- Genetic Diversity
- Hybridisation
Answer: 3. Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity represents the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species whereas, the genetic variability describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary. This diversity lets the population adapt to changing environments. For example, in India, we find mangoes with different flavours, colours, fibre content, sugar content and shelf-life. The great variation is due to the genetic diverisity.
Biodiversity Levels
Question 11. About 1000 different varieties of ………… has been estimated in India.
- Teak
- Mango
- Wheat
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Mango
Mangos has the maximum genetic diversity in India. It has approximately more than 1000 different varieties.
Question 12. The greatest threat to genetic diversity in agricultural crops is Manipal
- Extensive Use Of Insecticides And Pesticides
- Extensive Mixed Cropping
- Introduction Of High Yielding Varieties
- Extensive use of fertilisers
Answer: 2. Introduction Of High Yielding Varieties
Introduction of high yielding varieties is the greatest threat to genetic diversity in agricultural crops. High yielding varieties contain the required traits and therefore are always bred purely. This reduces the genetic diversity within a particular species.
“biodiversity questions and answers pdf “
Question 13. Genetic diversity will be more common in organisms with
- Parthenogenesis
- Sexual Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Parthenocarpy
Answer: 2. Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction provides genetic diversity because progeny produced by the combination of sperm and egg contain different combinations of genes than the parent organisms.
Topic-wise Biodiversity and Conservation MCQs with Explanation
Question 14. Choose the right one which denotes genetic diversity.
- Chromosomes → Nucleotides → Genes → Individuals → Populations
- Populations → Individuals → Chromosomes → Nucleotides → Genes
- Genes → Nucleotides → Chromosomes → Individuals → Populations
- Nucleotides → Genes → Chromosomes → Individuals → Populations
Answer: 4. Nucleotides → Genes → Chromosomes → Individuals → Populations
The genetic hierarchy includes a sequential arrangement of genetic material from simple to complex. Nucleotide is the smallest unit, any genetic variation in nucleotide leads to the change in the population genetics. The correct sequence of genetic diversity is Nucleotides → Genes → Chromosomes → Individuals → Populations
Question 15. The measure of the variety of species and their relative abundance present within a region is referred to as
- Biodiversity
- Genetic Diversity
- Species Diversity
- Geographical diversity
Answer: 3. Species Diversity
The diversity at the species level is measured as species diversity. It is the variety in the number and richness of the species of a region.
Biodiversity Levels
Question 16. Which of the following refers to species diversity?
- Diversity in the amphibians between Western and Eastern ghats
- Genetic variation in the concentration and potency of chemical reserpine
- 1000 varieties of mangoes
- Presence of deserts, rainforests, coral reefs
Answer: 1. Diversity in the amphibians between Western and Eastern ghats
The number of species that live in a certain location is called species diversity. The Western ghats have a greater number of amphibians as compared to Eastern ghats, as the climatic conditions and other ecological factor favour species richness in Western ghats.
Question 17. Which one is odd for species diversity?
- α-diversity
- γ-diversity
- β-diversity
- δ-diversity
Answer: 4. δ-diversity
δ-diversity is odd for species diversity. Ecosystem diversity is of three types, i.e. α β, and γ. Alpha (α) diversity is within the community, beta (β) diversity is between the community and gamma (γ) diversity is the diversity present in ranges of communities as represented by the diversity of habitats /ecosystems over a total landscape or geographical area.
NEET Biology Biodiversity Hotspots and Conservation Strategies MCQs
Question 18. The table below gives the population (in thousands) of ten species (A-J) in four areas (I-IV), consisting of the number of habitats given within the brackets against each. Study the table and answer the question which follows.
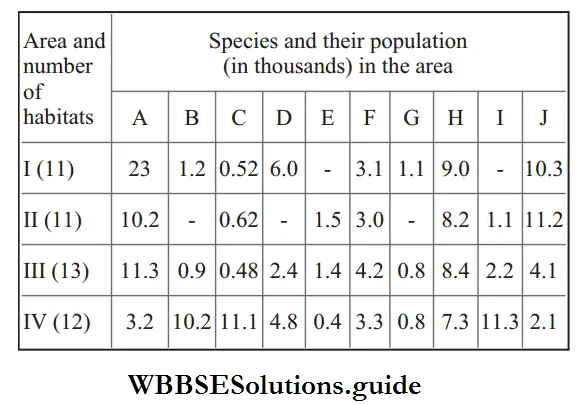
Which area out of I to IV shows the maximum species diversity?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
Answer: 3. 4
In the given table, area ‘4’ has the maximum species diversity, as there are 10 species (A-J) residing in 12 habitats, while in area 3, the 10 species reside in 13 habitats, so they exhibit less diversity than area 4.
Question 19. Which of the following regions of the globe exhibits higher species diversity?
- Madagascar
- Himalayas
- Amazon forests
- Western Ghats of India
Answer: 3. Amazon forests
The Amazonian rainforest in South America has the greatest biodiversity on earth. Rainforests have high biodiversity because they are abundant in nutrients, energy and have a favourable climate for the biodiversity to prosper
“biodiversity quiz “
Question 20. The number of species per unit area is called
- Species Richness
- Species Evenness
- Species Equitability
- Genetic richness
Answer: 1. Species Richness
Species diversity is the variety in number and richness of the species of a region. The number of species per unit area is called species richness. It is simply a count of species and it does not take into account the abundance of the species.
3 Levels Of Biodiversity
Question 21. Biodiversity is determined by
- Evolution
- Species Richness
- Species evenness
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Biodiversity is defined and measured as an attribute that has two components, i.e. richness and evenness. Richness is a number of groups of genetically or functionally related individuals. Evenness is the proportions of species or functional groups present on a site. The more equal species are in proportion to each other the greater the evenness of the site. A site with low evenness indicates that a few species dominate the site.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 22. Ecological diversity includes
- Species Diversity
- Genetic Diversity
- Ecosystem diversity
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Ecosystem diversity
Ecological diversity is made up of a community of plants and animals, which consist of different species in an ecosystem. It is known as ecosystem diversity.
NEET Exam Biodiversity and Its Conservation Most Repeated MCQs
Question 23. The term ‘alpha diversity’ refers to
- Species Diversity Web Jee
- Genetic Diversity
- Community And Ecosystem Diversity
- Diversity among the plants
Answer: 3. Community And Ecosystem Diversity
The term ‘alpha diversity refers to the diversity within a particular area or ecosystem, usually expressed by the number of species (i.e. species richness) in that ecosystem.
Question 24. The diversity of the habitats over the total geographical area is called
- Alpha Diversity
- Beta Diversity
- Gamma Diversity
- Delta diversity
Answer: 3. Gamma Diversity
Gamma diversity is the diversity of habitat over a total landscape (regional species pool or geographical area).
3 Levels Of Biodiversity
Question 25. Differences in the composition of species between a coral reef and the adjoining intertidal zone are termed as
- α-diversity
- β-diversity
- γ-diversity
- δ-diversity
Answer: 2. β-diversity
Differences in the composition of species between a coral reef and the adjoining intertidal zone are termed as beta (β)-diversity. It represents the differences in species composition among sites.
Question 26. The rate of replacement of species within given geographical areas is called
- α-diversity
- β-diversity
- γ-diversity
- δ-diversity
Answer: 2. β-diversity
Beta diversity refers to the rate of replacement of species along a gradient of habitat or communities within a given geographical region.
Question 27. Consider the following statements.
- The diversity observed in the entire geographical area is called gamma diversity.
- Biodiversity decreases from high altitude to low altitude.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
Statement I is correct, but II is incorrect. Incorrect statements can be corrected as Biodiversity varies with a change in altitude. The diversity increases as move from high to low altitudes (i.e. from poles to equator). Tropics harbour more species than temperate or polar areas.
Question 28. The State of Gujarat has river, desert, forest and lake ecosystem, thus exhibiting a diversity of life. Which measure do you use to denote the total diversity in such a case?
- α (alpha)
- β (beta)
- γ (gamma)
- δ (delta)
Answer: 3. γ (gamma)
Gamma (γ) diversity represents the total richness of the species in all the habitats found within a region, geographical area or landscape. The State of Gujarat represents γ-diversity because it has diverse forms of life in a total landscape.
Question 29. Match the following columns.
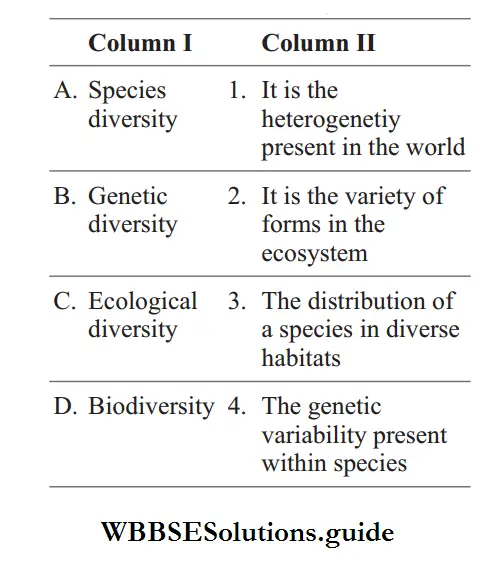
Codes:
- 1 3 2 4
- 2 1 4 3
- 4 2 3 1
- 3 4 2 1
Answer: 4. 3 4 2 1
Causes and Threats to Biodiversity MCQs for NEET with Answers
Question 30. Which one of the following expanded form of the following acronyms is correct?
- UNEP – United Nations Environmental Policy
- IUCN – International Union for Conservation of Nature
- EPA – Environmental Pollution Agency
- IPCC – International Panel for Climate Change
Answer: 2. IUCN – International Union for Conservation of Nature
Option 2 is a correct expanded form of the acronym. The headquarter of IUCN or the International Union for Conservation of Nature is at Morges, Switzerland. It studies the threat to biodiversity in all the parts of the world by gathering information about the geographical distribution, population size and population changes of various taxa. It prepares a red list or Red Data Book. Rest options are incorrect expanded form of acronyms and can be corrected expanded form as UNEP – United Nations Environment Programme EPA – Environmental Protection Agency IPCC – Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Question 31. According to the IUCN, the total number of plant and animal species described so far is over
- 2.5 million
- 2 million
- 1.5 million
- 1 million
Answer: 3. 1.5 million
According to the IUCN (2004), the total number of plant and animal species described, so far is slightly more than 1.5 million, but there is no clear idea of how many species are yet to be discovered and described.
Question 32. The species diversity of plants on earth is
- 2.4%
- 22%
- 8.1%
- 85%
- 70%
Answer: 2. 22%
When we discuss earth’s biodiversity, more than 70% of all the species recorded are animals, while plants (including algae, fungi, bryophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms) comprise not more than 22% of the total.
Question 33. An estimate of the number of species said to be present on earth is DUMET
- 0.5-1.55 million
- 11.1-15.2 million
- 6.7-9.7 million
- 2.5-3.0 million
Answer: 3. 6.7-9.7 million
There are about 8.7 million (±1.3 million) organisms on earth, the most precise calculation ever offered with 6.5 million species on land and 2.2 million in oceans. So, an estimate of the number of species said to be present on Earth is 6.7-9.7 million.
Question 34. Insects comprise ………………… of the total number of animals.
- Less Than 70%
- Equal To 70%
- More than 70%
- None of the above
Answer: 3. More than 70%
Among animals, insects are the most species-rich taxonomic group,
making up more than 70% of the total. That means, out of every 10 animals on this planet, at least 7 are insects.
NEET Biology Mcqs
Question 35. Given below are pie diagrams I, II and III related to the proportionate number of species of major taxa of invertebrates, vertebrates and plants, respectively. Critically study and fill in the blanks A, B, C and D.
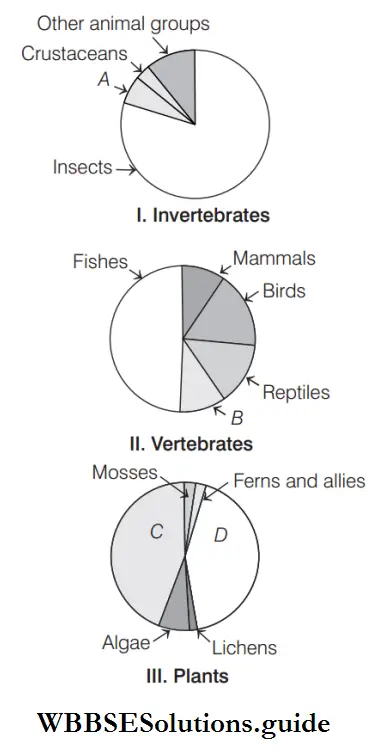
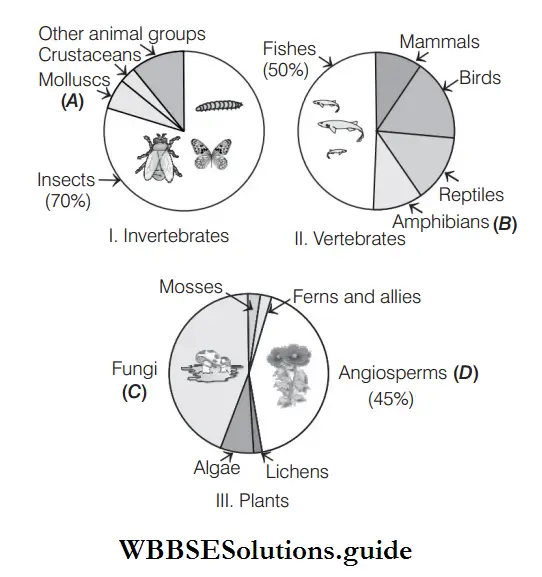
- A–Molluscs, B–Amphibians, C–Angiosperms, D–Gymnosperms
- A–Molluscs, B–Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
- A–Turtles, B–Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
- A–Hexapoda, B–Amphibians, C–Fungi, D–Angiosperms
Answer:
In-situ and Ex-situ Conservation MCQs for NEET
Question 36. Which of the following is the largest taxon among plants in terms of the number of species?
- Algae
- Mosses
- Ferns
- Fungi
Answer: 4. Fungi
According to the estimate made by Robert May, the largest taxon
among plants in terms of the number of species are fungi, followed by algae, mosses and ferns.
“which one is an endangered species in the following “
Question 37. India ranks …………… in the world in respect of the richness of flowering plants (17,500 sp.) and mammals (350 sp.).
- 2nd
- 1st
- 10th
- 3rd
Answer: 3. 10th
India ranks tenth (10th) in the world both in respect of richness of flowering plants (17,500 sp.) and mammals (350 sp.) and fourth in Asia in plant diversity. India is also a centre of crop diversity, a homeland of as many as 167 species of crops and 320 species of wild crop relatives.
Question 38. India is one of the twelve mega diversity countries with ……………… of genetic resources of the world.
- 12.1%
- 18.1%
- 38.1%
- 8.1%
Answer: 4. 8.1%
India has only 2.4% of the world’s land area, its share of the global species diversity is about 8.1%. It makes India one of the 12 mega-diversity countries of the world. Nearly 45,000 sp. of plants and twice as many of animals have been recorded from India.
Question 39. Given below is the representation of the extent of global diversity of vertebrates. What groups do the portions represent?
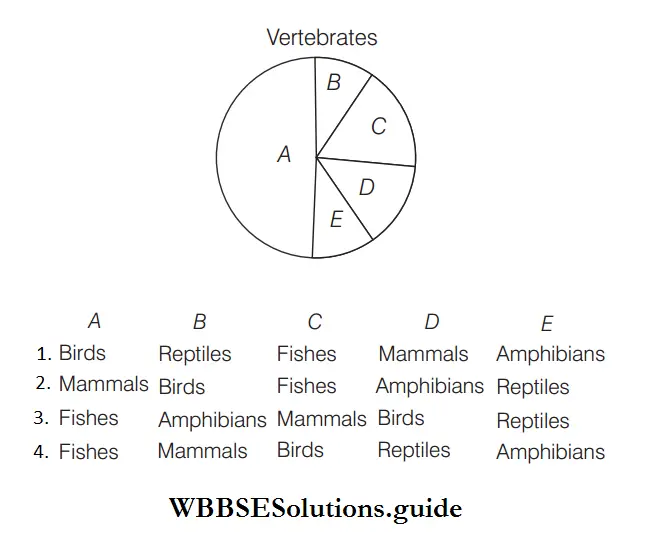
Answer: 4. Fishes, Mammals, Birds, Reptiles, Amphibians
- A–Fishes have the highest diversity among the vertebrates. B–Mammals, constitute the second highest group.
- C–Birds comprises rank third.
- D–Reptiles comprises rank fourth.
- E–Amphibians comprise the last position in the extent of global diversity.
Question 40. Wildlife is
- All biota excluding man, domestic animals and cultivated crops
- All vertebrates of reserve forests
- All animals of reserve forests
- All animals and plants in the reserve forest
Answer: 1. All biota excluding man, domestic animals and cultivated crops
Wildlife comprises all the living organisms (plants, animals and microorganisms) in their natural habitats which are neither cultivated no domesticated.
NEET Biology Mcqs
Question 41. What is the correct ascending order in respect of complexity of the following?
- Ecosphere
- Species
- Population
- Community
- Ecosystem
Choose the correct Option:
- 1,2,3,4,5
- 3,2,4,5,1
- 1,3,2,4,5
- 2,3,4,5,1
Answer: 4. 2,3,4,5,1
As we move from lower to higher organisation the complexity increases. So, species is followed by population by community and group of communities make an ecosystem and group of ecosystems make ecosphere.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 42. Which of the following represents the maximum number of species among global biodiversity?
- Lichens
- Fungi
- Mosses and ferns
- Algae
Answer: 2. Fungi
The number of species of fungi is 72,000 which is the maximum in respect to other options. The number of fungus species in the world is more than the combined total of species of fishes, amphibians, reptiles and mammals.
