NEET Biology Mcqs – Biotechnological Applications In Medicine
Question 1. Maximum utilisation of biotechnological techniques is made in the field of
- Chemical industries
- Medicines
- Agriculture
- Biogas production
Answer: 2. Medicines
Biotechnology has helped maximum in the field of medicine, for example, the preparation of monoclonal antibodies, interferon, insulin and drug.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. Which of the following products is obtained by genetic engineering?
- Lactic acid
- Alcohol
- Insulin
- None of these
Answer: 3. Insulin
Out of the given options, insulin is obtained by genetic engineering. This genetically engineered insulin or humulin is produced by inserting a human insulin gene into a plasmid isolated from the E. coli bacterium and then the production of a number of copies or clones of that recombinant gene into another E. coli bacterium.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 3. Genetically engineered human insulin is prepared by using
- E. Coli
- Rhizopus
- Pseudomonas
- Yeast
Answer: 1. E. Coli
By using genetic engineering or recombinant DNA technology, insulin-producing genes from human beings have been transferred into E. coli bacteria, which produced insulin called ‘humulin’ for clinical use. So, genetically engineered human insulin is prepared by using E.coli
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers

NEET Biology Biotechnological Applications in Medicine MCQs with Answers
Question 4. Insulin obtained from genetically engineered organisms is more useful because
- It provides an unlimited quantity of insulin
- It eliminates the transmission of animal disease through insulin
- Both (1) and (2)
- It is produced through an advanced technique
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Insulin obtained from genetically engineered organisms is more useful because it provides an unlimited quantity of insulin at a time without the risk of transmission of animal diseases through insulin. Thus, option (3) is correct
Question 5. The gene for insulin synthesis is present on
- 10Th chromosome
- 11Th chromosome
- 6Th chromosome
- 8Th chromosome
Answer: 2. 11Th chromosome
The insulin gene is present on the short arm of chromosome 11 in humans.
Question 6. Insulin is formed of
- Only a chain
- Only b chain
- Only c chain
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Insulin contains two short polypeptide chains, i.e. A and B chains which are linked by a disulphide bridge. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 7. Which of the following statements is not correct?
- The proinsulin has an extra peptide called c-peptide
- Functional insulin has a and b chains linked together by hydrogen bonds
- Genetically engineered insulin is produced in e.coli
- In man, insulins synthesised as a proinsulin
Answer: 2. The functional insulin has a and b chains linked together by hydrogen bonds
- The statement in option (2) is incorrect because Insulin is composed of two peptide chains referred to as the A chain and B chain.
- A and B chains are linked together by two disulphide bonds, and an additional disulphide is formed within the A chain. Insulin molecules have a tendency to form dimers in solution due to hydrogen bonding between the C-termini of B chains.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 8. Maturation of insulin involves the removal of
- A-chain (21 amino acids)
- B-chain (30 amino acids)
- C-chain (33 amino acids)
- A and b chains
Answer: 3. C-chain (33 amino acids)
- Insulin contains two short polypeptide chains, A and B chains which are linked by a disulphide bridge. In mammals, insulin is synthesised as a prohormone (that needs to be processed to become a mature and functional hormone).
- It contains an extra stretch called C-peptide of 33 amino acids. It is absent in mature insulin and is removed during the maturation of insulin.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 9. The proinsulin is treated with ………… And …………… To obtain the final insulin product.
- Cyanogen bromide, carboxy ligase
- Cyanogen trypsin, carboxypeptidase
- Ethyl bromide, hydroxy ligase
- Methyl trypsin, carboxy ligase
Answer: 2. Cyanogen trypsin, carboxypeptidase
The proinsulin is treated with cyanogen trypsin and carboxypeptidase to obtain the final insulin product. MetLys human proinsulin could be converted in vitro with the treatment of trypsin and CPB.
Question 10. ….. A……… And ……b……. Are present at the n and c-terminal of b- a chain of insulin.
- A–phenylalanine, b–alanine
- A–glycine, b–asparagine
- A–leucine, b–isoleucine
- A–methionine, b–tryptophan
Answer: 1. A–phenylalanine, b–alanine
Phenylalanine (1) and alanine (2) are present at the N and C-terminal of the B-chain of insulin.
Important MCQs on Medical Biotechnology for NEET
Question 11. During the synthesis of insulin, proinsulin is linked to the lac operon with
- Lactosidase gene
- Permease gene
- Galactosidase gene
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Galactosidase gene
Proinsulin is linked to the lac operon with the galactosidase gene during the synthesis of insulin.
Question 12. The primary structure of insulin was given by
- Frederick sanger
- Banting
- Macleod Eli Lilly
- William Bateson
Answer: 1. Frederick Sanger
In 1954, Frederick Sanger derived the complete structure of bovine insulin.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 13. A step in the rDNA technology that was crucial in the production of human insulin was
- Splitting a and b-peptide chain
- Addition of c-peptide to proinsulin
- Getting insulin assembled into the mature form
- Removal of c-peptide from active insulin
Answer: 3. Getting insulin assembled into the mature form
biotechnology pyq neet
The main challenge for the production of insulin using the rDNA technique was obtaining insulin in a mature form. In 1983, Eli Lilly, an American company, first prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to the A and B chains of human insulin and introduced them into the plasmids of Escherichia coli to produce insulin chains separately.
Question 14. Identify the diagram that shows the maturation of proinsulin to insulin.
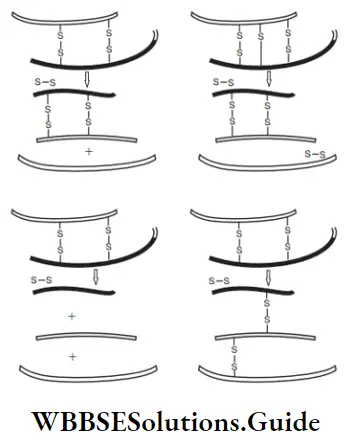
Answer: 1. Diagram (1) correctly represent the maturation of proinsulin into insulin after the removal of the C-peptide.
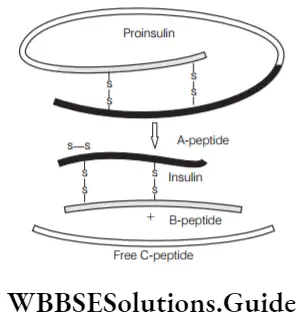
Question 15. Which method is used to prepare cDNA in insulin preparation?
- Transcription
- Reverse transcription
- Replication
- Duplication
Answer: 2. Reverse transcription
Reverse transcriptase is used to create cDNA libraries from mRNA. Thus, reverse transcription is used to prepare cDNA in insulin preparation.
Question 16. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Insulin used to be extracted from the pancreas of slaughtered pigs and cattle.
- Animal insulin is slightly different from the human insulin.
- Animal insulin causes some undesirable side effects such as allergy.
- Bacteria can be made to synthesise insulin from its gene even with the presence of introns.
Choose the correct option.
- Only 1
- 1, 3 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
- Only 4
Answer: 4. Only 4
Statement IV is incorrect. It can be corrected When using bacteria to clone a human gene and express its products as in the case of insulin, the gene cannot contain introns because bacteria do not have the enzymes to process mRNA.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 17. Consider the following statements about insulin.
- Human insulin is made up of 51 amino acids arranged on two polypeptide chains.
- The two polypeptide chains are interconnected by three disulphide bonds.
- In mammals, insulin is synthesised as a prohormone which contains an extra chain called c-peptide.
- C-peptide is not present in mature insulin.
biotechnology pyq neet
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 3 And 4
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 2. 1, 3 And 4
All given statements are correct about insulin, except II because Human insulin is made up of 51 amino acids arranged on two polypeptide chains. A has 21 amino acids and B with 30 amino acids, the two polypeptide chains are interconnected by two disulphide bridges or S-S linkages.
Question 18. The first step in the production of insulin using e.coli is
- Isolation of mRNA transcribing for insulin from pancreas cell
- Isolation of nucleotides transcribing for insulin from pancreas cell
- Isolation of gene-producing insulin from human DNA
- Attachment of gene-producing insulin from human dna to plasmid using ligase
Answer: 3. Isolation of gene-producing insulin from human DNA
Gene Therapy and Its Applications MCQs for NEET
Question 19. Genetically engineered human insulin, humulin was launched by an American drug company on
- 5Th July 1998
- 5Th July 1993
- 5Th July 1973
- 5Th July 1983
Answer: 4. 5Th July 1983
On 5th July 1983, Eli Lilly Company launched the first genetically engineered human insulin by the name of humulin.
Question 20. Assertion humulin is better than conventional insulin. Reason (R) Conventional insulin produces many side effects.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of a
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Humulin is the first genetically engineered pharmaceutical product. It is better than conventional insulin because conventional insulin produces many side effects over a long period.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 21. In 1921, two Canadian scientists, Frederick G. Banting and Charles H. Best successfully purified insulin from a
- Pig’s pancreas
- Camel’s pancreas
- Dog’s pancreas
- Cattle’s pancreas
biotechnology pyq neet
Answer: 3. Dog’s pancreas
- Frederick Banting and Charles Best discovered insulin under the directorship of John Macleod at the University of Toronto.
- With the help of James Collip insulin was purified from a dog’s pancreas, making it available for the successful treatment of diabetes. Banting and Macleod earned Nobel Prize for their work in 1923.
Question 22. Lymphocytes are
- A kind of white blood cells
- A kind of red blood cells
- Blood platelets
- Plasma and white blood cells
Answer: 1. A kind of white blood cells
A lymphocyte is a kind of WBCs in the vertebrate immune system. The three major types of lymphocytes are T-cells, B-cells and Natural Killer (NK) cells.
Question 23. Gene therapy
- Aims to cure genetic disorders
- Is a method to provide the correct version of the defective gene
- Include enzymatic replacement therapy
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows the correction of gene defects diagnosed in a child or embryo. It aims to cure genetic disorders.
- It involves the insertion of normal genes and the defective mutant allele of the genes is replaced and the non-functional gene is compensated. It also employs the use of enzyme replacement therapy. Thus, option (d) is correct.
Question 24. In somatic cell gene therapy, the desirable gene is introduced
- Into sperms
- Into eggs
- Into blood cells
- Into zygote
Answer: 3. Into blood cells
In somatic cell gene therapy, the desirable gene is introduced into any cell other than a gamete, germ cell or stem cell. The changes that are observed are only restricted to the individual and are not carried to the next generation. Thus, the gene is introduced into blood cells in somatic cell gene therapy.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 25. A young girl was treated for a deficiency that occurs due to a genetic disorder. M Blease and wf Andresco made use of gene therapy to correct this disorder. Identify it.
- Cytosine deaminase (cda) –scid
- Adenosine deaminase (ada)–scid
- Tyrosine oxidase –scid
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Adenosine deaminase (ada)–scid
For the first time in 1990, M Blease and WF Andresco attempted gene therapy on a 4-year-old girl with Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency. This is caused due to the deletion of a gene for adenosine deaminase.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 26. Where is ada produced in the human body?
- Bone marrow
- Lymphocytes
- Blood plasma
- Monocytes
Answer: 2. Lymphocytes
The site of production of Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) in the human body is lymphocytes.
Question 27. A person suffering from scid has a defective gene for the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA). As a result of which the person lacks ……………… Thus making him prone to infections.
- B-lymphocytes
- Phagocytes
- T-lymphocytes
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. T-lymphocytes
Patients suffering from SCID have defective genes for the enzyme Adenosine Deaminase (ADA). Functional T-lymphocytes are missing thus, making them prone to infections.
Topic-wise Medical Biotechnology MCQs with Explanation
Question 28. In the treatment of SCID, cDNA is introduced into a patient’s cells using …………………. As a vector.
- E. Coli
- Retrovirus
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- Agrobacterium
Answer: 2. Retrovirus
- A functional ADA cDNA can be introduced into the cells of the patients receiving gene therapy by using a vector constituted by a retrovirus.
- The SCID patient has a defective gene for the enzyme, Adenosine Deaminase (ADA). He/she lacks functional T-lymphocytes and therefore, fails to fight the infecting pathogen.
- Lymphocytes are extracted from the patient’s bone marrow and a normal functional copy of human gene coding for ADA is introduced into these lymphocytes with the help of retrovirus.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 29. Which one of the following vectors is used to replace the defective gene in gene therapy?
- Ti plasmid
- Adenovirus
- Cosmid
- Ri plasmid
Answer: 2. Adenovirus
Adenovirus vectors can be replication defective, certain essential viral genes are deleted and replaced by a cassette that expresses a foreign therapeutic gene. Such vectors are used for gene therapy as vaccines and for cancer therapy.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 30. Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency can be cured by …………… And ……………….
- Gene therapy, radiation therapy
- Bone marrow transplantation, enzyme replacement therapy
- Organ transplantation, hormone replacement therapy
- Radiation therapy, enzyme replacement therapy
Answer: 2. Bone marrow transplantation, enzyme replacement therapy
In some cases, adenosine deaminase deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation and enzyme replacement therapy, but it is not fully curative.
Question 31. What might be an advantage of beginning gene therapy prior to birth?
- This would give the body plenty of time
- The body would not reject it as it has not yet recognised ‘self’
- The cells being extremely young are more receptive to gene therapy
- None of the above
Answer: 2. The body would not reject it as it has not yet recognised the ‘self’
Gene therapy can be initiated prior to birth too. An advantage of this technique is that the body would not reject it as it has to yet recognise itself.
Question 32. The genetic defect adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency may be cured permanently by
- Introducing bone marrow cells producing ada into cells at early embryonic stages
- Enzyme replacement therapy
- Periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes having functional ada cdna
- Administering adenosine deaminase activators
Answer: 1. Introducing bone marrow cells producing ada into cells at early embryonic stages
By introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into cells at early embryonic stages, Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency may be cured permanently.
Question 33. Arrange the following steps occurring during gene therapy in chronological order.
- Lymphocytes are obtained from the patients.
- Lymphocytes are transferred to the culture dishes.
- Lymphocytes are transfected with the normal ADA genes.
- The transfected cell is returned to the patient’s body.
The chronological order should be
- 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
- 2 → 1 → 3 → 4
- 1 → 3 → 2 → 4
- 3 → 2 → 4 → 1
Answer: 1. 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 34. The assertion the ada gene provides instruction for producing the enzyme, adenosine deaminase. Reason (R) This enzyme is found throughout the body but is most active in lymphocytes.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. The ADA gene provides instructions for producing the enzyme, adenosine deaminase.
- This enzyme is produced in all cells, but the highest levels of adenosine deaminase occur in immune system cells called lymphocytes. In the absence of adenosine deaminase enzyme, purine metabolism is disturbed and T-lymphocytes fail to function.
Question 35. What is true for monoclonal antibodies?
- These antibodies obtained from one parent and for one antigen
- These antibodies were obtained from the parent and for two antigens
- These antibodies obtained from one parent and for many antigens
- These antibodies are obtained from many parents and for many antigens
biotechnology pyq neet
Answer: 1. These antibodies are obtained from one parent and for one antigen
(1) Option (1) is true for monoclonal antibodies as Monoclonal antibodies are identical molecules specific for one type of antigen. These are obtained from one parent by injecting the target antigen into a rat or mouse.
Question 36. The assertion the term hybridoma is applied to fused cells. Reason (R) they are formed by the fusion of lymphocyte cells and myeloma cells.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of a
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of a
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Hybridoma technology is a technology of the formation of hybrid cell lines, i.e. hybridomas by the fusion of a B-lymphocyte cell and a myeloma cell. The hybrid cell produced is selected on the basis of its ability to grow in tissue culture.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 37. Hybridomas are the result of the fusion of
- Normal antibody-producing cell with a myeloma
- Abnormal antibody-producing cell with myeloma
- Male reproductive cell with a myeloma
- Female reproductive cells with myeloma
Answer: 1. Normal antibody-producing cell with myeloma
Hybridomas are hybrid cells resulting from the fusion of a normal antibody-producing B-lymphocyte and a multiple myeloma cell from the lymphoid tumour. This hybrid cell is capable of producing a continuous supply of antibodies.
Question 38. Consider the following statements.
- Hybridoma cells are shifted to a medium deficient in nutrients which cannot be synthesised by myeloma cells.
- This medium allows the selection of hybridoma cells.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 39. Elisa is based on
- Antigen-antibody interaction
- Antigen-protein interaction
- Lectin-antibody interaction
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Antigen-antibody interaction
biotechnology pyq neet
ELISA is based on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction. It can detect very small amounts of proteins (antibody or antigen) with the help of enzymes (for example peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase).
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 40. How many antibodies are used in Elisa?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 1. 2
Performing ELISA involves one antibody with specificity to a particular antigen. After the antigen is immobilised, the second detection antibody is added which is also called a secondary antibody. It is linked to an enzyme through bioconjugation. So, two antibodies are used in ELISA.
Question 41. Elisa is used to detecting viruses where the key reagent is
- Rnase
- Alkaline phosphatase
- Catalase
- Dna probe
Answer: 2. Alkaline phosphatase
ELISA test is a technique which can detect any amount of an antibody or antigen with the help of an enzyme. The commonly used enzymes are alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase.
Question 42. Identify the molecular diagnostic technique used to detect the presence of a pathogen in an early stage of infection.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- Radiography
- Enzyme replacement technique
- Angiography
Answer: 1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- The presence of a pathogen (bacteria, viruses, etc.) is usually suspected only when the pathogen has produced a diseased symptom.
- By that time, the number of pathogens is already very high in the body but the very low count of bacteria or viruses (when the symptoms of the disease are not yet visible) can be detected by multiplication of their nucleic acid by PCR.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 43. Which of the following is a recent application of genetic engineering in diagnostic techniques?
- Pcr
- Abc blood groups
- Elisa test
- Gravidax test
Answer: 1. Pcr
The historical development of techniques for altering genetic information on the molecular level can be included in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) based gene manipulation. Genetic engineering with PCR forms powerful methods for assembling designer genes.
Question 44. A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called
- Plasmid
- Recombinant dna
- Probe
- Selectable marker
Answer: 3. Probe
Molecular probes are usually single-stranded pieces of DNA (sometimes RNAs), labelled with radioisotopes such as 32 P. They are available for many genetic disorders such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, etc.
Question 45. A novel use of PCR is to
- Detect hiv in suspected aids patients
- Detect mutations in suspected cancer patients
- Diagnose many genetic disorders
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
PCR can detect very low amounts of DNA. It is now usually used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients. It is also used to detect mutations in the genes in suspected cancer patients. It is a good technique to identify many other genetic disorders. Thus, option (4) is correct.
NEET Biology Monoclonal Antibodies and Vaccines MCQs
Question 46. A doctor while performing surgery on an HIV (+) patient accidentally cut himself with a scalpel. A test that he will have to undergo in order to verify or rule out the suspicion of infection from the HIV virus is
- Pcr
- Routine urine examination
- Tlc
- Dec
Answer: 1. Pcr
PCR is now, used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 47. In which method, is a probe allowed to hybridise to its complementary dna in the clone of cells?
- Gene therapy
- Recombinant dna technology
- Polymerase chain reaction
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Recombinant dna technology
- In recombinant DNA technology, a probe is allowed to hybridise with its complementary DNA in the clone of cells. The cells are then detected by autoradiography.
- The cells with mutated genes will not be observed on the photographic film because the probe was not complementary to the mutated genes.
Question 48. Protein-protein hybridisation results in
- Southern blotting
- Northern blotting
- Western blotting
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Western blotting
The Western blot is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It is used to detect the particular protein in a protein mixture. So, protein-protein hybridisation results in Western blotting.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 49. The technique used to detect the dna in a clone is called
- Gel electrophoresis
- Autoradiography
- Gene therapy
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Autoradiography
A single-stranded DNA or RNA joined with a radioactive molecule (probe) is allowed to hybridise with its complementary DNA in a clone of the cells in recombinant DNA technology. It is followed by the detection of DNA using autoradiography.
Question 50. Which one of the following is the correct explanation for autoradiography?
- It is used for the detection of mutated genes
- Clone which has mutated genes do not appear on the photographic film
- The probe has only complementary genes with unmuted protein of dna
- All of the above
Answer: 3. The probe has only complementary genes with unmuted protein of DNA
All given explanations are correct for autoradiography. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Ethical Issues in Medical Biotechnology MCQs for NEET
Question 51. Choose the correct option for the use of the PCR technique in diagnosis.
- It is used to detect HIV in suspected aids patients.
- It is used to detect mutations in the genes in suspected cancer patients.
- It is used to detect swine flu in human beings.
- It is used to detect different common diseases in pigs, sheep and cows.
- It is a good technique to identify many other genetic disorders.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 And 2
- 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 5
- 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 3. 1, 2 And 5
- Statements 1, 2 and 5 are correct for the use of PCR technique in diagnosis. PCR can detect very low amounts of DNA. It is now usually used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients. It is also used to detect mutations in the genes in suspected cancer patients.
- It is a good technology to detect many other genetic disorders. Statements 3 and 4 are not correct. PCR is not used to detect common diseases in animals and swine flu in humans.
Question 52. Which of the following techniques are related to gene therapy?
- Bone marrow transplantation.
- Enzyme replacement therapy.
- Pcr
- Hybridoma technique.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 1. 1 And 2
Bone marrow transplantation and enzyme replacement therapy are related to gene therapy. PCR is used to obtain copies of normal genes outside the body and then used for gene therapy. The Hybridoma technique is a method of producing identical antibodies in large amounts. Thus, option (1) is correct.
Question 53. Modified antibiotics are manufactured by the technique of
- Ultrafiltration
- Ultracentrifuge
- Vernalisation
- Genetic engineering
Answer: 4. Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering has produced many modern antibiotics through biotechnology, for example. hybrid antibiotic, i.e. molecules that have bits from two different antibiotics. This is done by putting selected enzymes from two different antibiotic-producing cells into one bacterium.
Role of rDNA Technology in Medicine MCQs for NEET
Question 54. Consider the following statements about therapeutic drugs.
- Recombinant dna technology is used for the production of safe and effective therapeutic drugs.
- It avoids unwanted immunological responses, observed with products isolated from non-human sources.
- About thirty recombinant therapeutics have been approved for human use around the world.
Which of the following statements given above are correct?
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 And 3
All given statements are correct about therapeutic drugs. Thus, option (4) is correct.
biotechnology pyq neet
Question 55. Match the following columns.
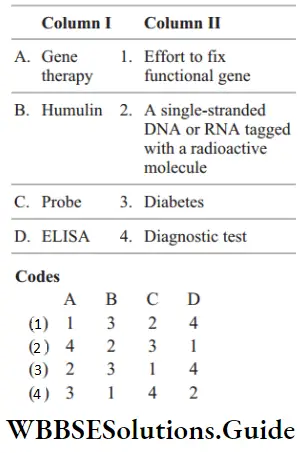
Answer: 1. A–1, B–3, C–2, D–4
Question 56. Which of the following techniques are utilised for early diagnosis of aids, cancer, etc?
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Recombinant dna technology
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 And 3
All given statements are utilised for early diagnosis of AIDS, cancer, etc. Early detection of a disease is not possible by conventional diagnosis methods. Some techniques used for early diagnosis are
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Recombinant DNA technology
- Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA)
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 57. The maximum application of animal cell culture technology today is in the production of
- Edible proteins
- Insulin
- Interferons
- Vaccines
Answer: 4. Vaccines
The maximum application of animal cell culture technology today is in the production of vaccines.
Question 58. Pure vaccines are
- Mhc antigens
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Bacteria treated fungi
- Certain proteins
Answer: 2. Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal Antibody (MAb) is a homogeneous antibody derived from a single clone of cells. MAb recognises only one chemical structure and is useful in a variety of industrial and medical capacities since it is easily produced in large quantities and has remarkable specificity. Thus, pure vaccines are monoclonal antibodies.
