Cancer Biology Mcq -Cancer
Question 1. Oncogenes were discovered by
- SB Prussiner
- FP Rous
- A Fleming
- JM Bishop and HE Varmus
Answer: 4. JM Bishop and HE Varmus
- In the mid-1970s, the American microbiologist’s John Michael Bishop and Harold Varmus tested the theory that healthy body cells contain dormant viral oncogenes that, when triggered, cause cancer.
- They discovered and showed that oncogenes are actually derived from normal genes (proto-oncogenes) present in the body cells of their host.
Question 2. Scientists who study cancer are known as
- Cancerologists
- Oncologists
- Conchologists
- Cancer specialists
Answer: 2. Oncologists
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. The form of tumour remain confined to their original location and not spreading to other parts of the body. Identify it.
- Malignant tumour
- Benign tumour
- Both (1) and (2)
- Leukaemia
Answer: 2. Benign tumour
- A benign tumour is a mass of cells (tumour) that lacks the ability to invade neighbouring tissue or metastasis.
- These characteristics are required for a tumour to be defined as cancerous and therefore, benign tumours are non-cancerous.
- Benign tumours generally have a slower growth rate than malignant tumours.
Cancer Biology Mcq

NEET Biology Cancer MCQs with Answers
Question 4. Malignant tumours
- Are mass of neoplastic cells.
- Are cells that grow very rapidly
- And damage the surrounding normal tissue.
- Are cells that show the property of metastasis.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- All of them
Answer: 4. All of them
- The malignant tumours are the mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumour cells. These cells grow very rapidly, invade and damage the surrounding normal tissues.
- As these cells actively divide and grow, they also starve the normal cells by competing for vital nutrients.
- Cells sloughed from such tumours reach distant sites through blood and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumour there. This property called metastasis is the most feared property of malignant tumours.
“questions about cancer “
Question 5. A benign tumour differs from a malignant one in that
- A benign tumour shows metastasis
- It presses on neighbouring organs to produce acute pain
- It is enveloped within a capsule
- All of the above
Answer: 3. It is enveloped within a capsule
A benign tumour remains confined in the organ affected and does not spread to other body parts. It is enclosed in a connective tissue sheath, (i.e. enveloped within a capsule) whereas a malignant tumour is not enclosed.
Question 6. Cancer is caused by
- Uncontrolled meiosis
- Uncontrolled mitosis
- Rupturing of cells
- Loss of immunity of the cells
Answer: 2. Uncontrolled mitosis
- Cancer is an abnormal and uncontrolled mitotic division of cancer cells that invade and destroy the surrounding tissues.
- Generally, cancer is defined as the uncontrolled proliferation of cells without any differentiation.
Cancer Biology Mcq
Question 7. The spread of cancerous cells to distant sites is termed as
- Metastasis
- Oncogenes
- Proto-oncogenes
- Malignant neoplasm
Answer: 1. Metastasis
Metastasis is the ability of cancer cells to move from one part of the body to the other. This results in the manifestation of malignancy as a secondary growth from the primary growth in a new location.
Question 8. Cancer-causing viruses are called
- Oncogenic viruses
- Retroviruses
- Adenoviruses
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 1. Oncogenic viruses
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumour cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels. Tumour viruses or cancer-causing viruses are called oncogenic viruses.
Important MCQs on Cancer for NEET Biology
Question 9. In humans, the retrovirus is considered as a cause of cancer because
- An oncogene is present in their genome
- Their hereditary material is made up of single-standard rna
- They have a gene for reverse transcriptase
- In their genome, there may be a cellular proto-oncogene
Answer: 4. In their genome, there may be a cellular proto-oncogene
The genome of retrovirus contains cellular proto-oncogenes. Upon mutation, these can become oncogenes and encode oncoproteins. The latter, then can cause cancer in humans.
Cancer Mcq With Answers
Question 10. Which is a cancer-causing virus?
- Myxovirus
- Rubella
- SV-40
- All of these
Answer: 3. SV-40
SV-40 (Simian vacuolating virus) and polyomavirus produce malignant tumours when inoculated into newborn mice or hamsters. These viruses have been widely employed in the study of viral oncogenesis.
Question 11. The genes which on activation produce malignant neoplasm are
- Pleiotropic genes
- Multiple genes
- Oncogenes
- Neonatal genes
Answer: 3. Oncogenes
HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus) destroys CD4 T-lymphocytes, i.e. white blood cells that play a large role in helping our body to fight disease. The fewer CD4 T-lymphocytes one have, the weaker is his immune system is becoming.
Cancer Mcq With Answers
Question 12. ‘Blood cancer’ is also known as
- Leucopoenia
- Leucoderma
- Leucocytosis
- Leukaemia
Answer: 4. Leukaemia
Leukaemia is a cancer of blood cells and lymph, (blood cancer).
Question 13. Chemical carcinogens present in smoke have been identified as a major cause of
- Lung cancer
- Liver cancer
- Oral cancer
- Throat cancer
Answer: 1. Lung cancer
Chemical carcinogens present in smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer.
Question 14. Vinyl chloride causes cancer of
- Liver
- Stomach
- Prostate
- Kidney
Answer: 1. Liver
Vinyl chloride exposure is associated with an increased risk of a rare form of liver cancer as well as brain and lung cancers.
Cancer Mcq With Answers
Question 15. A most common form of cancer among women is
- Uterine cervical cancer
- Cancer of breast
- Cancer of lung
- Mouth and throat cancer
Answer: 2. Cancer of breast
- Breast cancer was the most common cancer in women worldwide, contributing 25.4% of the total number of new cases diagnosed in 2018.
- The top three, breast, colorectal and lung cancers contributed 43.9% of all cancers (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer).
Question 16. Which of the following is/are early signs of lung cancer?
- A new cough that is persistent or worsens
- Cough that produces blood
- Lung infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia that would not go away
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
When lung cancer does cause signs in its early stages, they may vary from person to person, but commonly include new cough that is persistent or worsens, or a change in an existing chronic cough, a cough that produces blood, pain in the chest, back or shoulders that worsens during coughing, laughing or deep breathing, shortness of breath that comes on suddenly and occurs during everyday activities, unexplained weight loss, feeling that you are tired or weak, loss of appetite, lung infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia that would not go away, hoarseness or wheezing.
Mcq On Cancer With Answers
Question 17. Cervical cancer can be caused by
- Chlamydia sp.
- Human papilloma virus
- Herpes simplex virus
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Answer: 2. Human papillomavirus
- Cervical cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection with certain types of HPV (Human Papilloma Virus).
- Two HPV types (16 and 18) cause 70% of cervical cancers and pre-cancerous cervical lesions.
- There is also evidence linking HPV with cancers of the anus, vulva, vagina, penis and oropharynx.
Causes and Types of Cancer MCQs for NEET
Question 18. Cancer of bone belongs to
- Sarcoma
- Carcinoma
- Leukaemia
- Malignant lymphoma
Answer: 1. Sarcoma
Sarcoma is a cancer of the connective or supportive tissue, i.e. bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels and soft tissue.
Question 19. Retinoblastoma is an eye cancer caused due to
- Heredity
- Chemicals
- Harmful radiation
- Radiation
Answer: 1. Heredity
- Retinoblastoma occurs when nerve cells in the retina develop genetic mutations. These mutations cause the cells to continue growing and multiplying when healthy cells would die.
- This accumulating mass of cells forms a tumour. Thus, retinoblastoma is an eye cancer caused due to heredity.
Question 20. Cancer of connective tissue is called
- Carcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Sarcoma
- Lipoma
Answer: 3. Sarcoma
Mcq On Cancer With Answers
Question 21. Cells affected in leukaemia are
- Plasma cells
- Erythrocytes
- Thrombocytes
- Leucocytes
Answer: 4. Leucocytes
- Leukaemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells (also called leucocytes or WBCs) fight infections and other diseases.
- In leukaemia, the bone marrow (spongy material inside the bones) makes many white blood cells that are not normal.
- These abnormal WBCs crowd the bone marrow and get into the bloodstream.
Question 22. Cancer of melanocytes of skin is known as
- Lymphoma
- Melanoma
- Leukaemia
- Sarcoma
Answer: 2. Melanoma
The cancerous growth of melanocytes, a type of skin cell is called melanomas.
Question 23. TNM stands for
- Tumour, neoplasia, metastasis
- Tumour size, involvement of lymph nodes and metastasis
- Treatment, nodule, metastasis
- Tough, new and malignant
Answer: 2. Tumour size, involvement of lymph node and metastasis
T describes the size of the tumour and any spread of cancer into nearby tissue, N describes spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes and M describes metastasis (spread of cancer to other parts of the body).
Question 24. Lymphoma involving enlargement of lymph glands is known as
- Cushing’s disease
- Melanoma
- Hodgkin’s disease
- Retinoblastoma
Answer: 3. Hodgkin’s disease
Hodgkin’s disease is a type of lymphoma, which is a cancer originating from white blood cells. It is characterised by the orderly spread of disease from one lymph node group to another and by the development of systemic symptoms with advanced disease.
Mcq On Cancer With Answers
Question 25. Cancer of adipose tissue is known as
- Adenoma
- Osteoma
- Lipoma
- Lymphoma
Answer: 3. Lipoma
Lipoma is a cancer of adipose tissue.
Question 26. Cancer of the liver can be caused by
- Alcohol
- Smoking
- Tea
- Coffee
Answer: 1. Alcohol
The chronic use of alcohol causes liver cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver responds to injury or death of some of its cells by producing interlacing strands of fibrous tissue between which are nodules of regenerating cells present.
Question 27. Match the following columns.
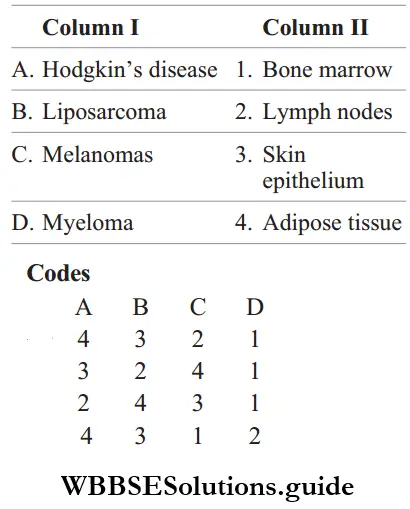
Answer: A–2, B–4, C–3, D–1
Topic-wise Cancer MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 28. Smokers are at increased risk of developing lung cancer as tobacco smoke contains carcinogens such as
- Carbon monoxide
- Aliphatic ring compounds
- Oxides of nitrogen
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Answer: 4. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are made whenever substances are burned. PAHs may cause cancer and may affect the eyes, kidneys and liver.
Question 29. Cancerous cells spread through
- Lymph Haryana
- Blood
- Secondary Growth Of Malignant Tumour
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Lymph, blood and secondary growth of malignant tumour spread cancerous cells.
“cancer questions “
Question 30. Which type of cancer affects lymph nodes and spleen?
- Carcinoma
- Sarcoma
- Leukaemia
- Lymphoma
Answer: 4. Lymphoma
Lymphoma is cancer of lymphoid tissue. Lymphoid organs are those organs where the origin and/ or maturation and proliferation of lymphocytes occurs, for example, bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, and thymus.
Question 31. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
- Carcinomas–Cartilage
- Sarcomas–Connective tissue
- Lymphomas–Lymph node
- Adenomas–Thyroid gland
Answer: 1. Carcinomas–Cartilage
Option (1) is not correctly matched pair and can be corrected as Carcinoma is a malignant growth of epithelial tissue, which lines the body organs, for example, lung cancer, stomach cancer, etc.
Question 32. Consider the following statements.
- The property of metastasis is observed in malignant tumours.
- Carcinogens are agents that cause cancer.
- Benign tumour causes little damage to body cells.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- Only 1
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
- All the given statements are correct.
- A malignant tumour is a cancerous tumour. It shows metastasis and thus invades other body parts.
- The cancer-causing agents are called carcinogens, for example, chemical agents – aniline dyes, physical agents – X-rays, Y-rays, UV-rays and biological agents-oncogenic viruses.
- A benign tumour is a non-cancerous tumour. It is less fatal to the body.
Question 33. Which one of the following is carcinogenic?
- Mustard gas
- Infrared radiations
- Methyl nitro-nitrosoguanidine
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Mustard gas
Mustard gas is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans. It can cause lung, tongue, throat and voice box cancer.
Question 34. ___________ causes lung cancer.
- Tobacco smoke
- X-rays
- UV-rays
- Vehicle smoke
Answer: 1. Tobacco smoke
The carcinogens present in tobacco smoke have been identified as a major cause of lung cancer.
NEET Biology Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes MCQs
Question 35. Aromatic amines used in the manufacture of synthetic dyes cause cancer of the
- Skin
- Lung
- Liver
- Urinary bladder
Answer: 4. Urinary bladder
Workers in the rubber, chemical, leather, textile, metal and printing industries are exposed to substances such as aniline dye and aromatic amines that may increase their risk for urinary bladder cancer.
Question 36. Match the following columns.
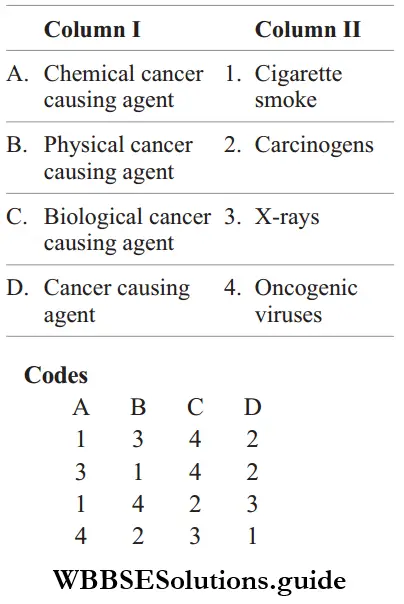
Answer: A–1, B–3, C–4, D–2
Question 37. The human papillomavirus vaccine is used to prevent
- Breast cancer
- Colon cancer
- Uterine cervical cancer
- Ovarian cancer
Answer: 3. Uterine cervical cancer
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines are used to prevent infections by certain types of HPV which are associated with the development of uterine cervical cancer, genital warts and other cancers like vaginal or vulval cancer, anal cancer, cancer of the penis and cancer of the head and neck.
Question 38. Which one of the following is not the property of cancerous cells?
- They do not require extracellular growth factors
- They do not remain confined in the area of formation
- They show contact inhibition
- They divide in an uncontrolled manner
Answer: 3. They show contact inhibition
Normal cells show the property of contact inhibition. Normal somatic cells when grown in culture become growth inhibited when they encounter another cell. Cancerous cells lose the property of contact inhibition.
Mcq On Cancer With Answers
Question 39. Identify the wrong statements.
- The tumour of haematopoietic cells is called leukaemia.
- Cancer arising from the epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred as melanoma.
- Sarcoma is a type of cancer where bone and cartilage are involved.
- Only benign tumours are called as true cancer or neoplasm.
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 2
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 2 and 4
- Statements 2 and 4 are wrong and can be corrected as
- Cancer arising from the epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as carcinomas, while cancerous growth of melanocytes, a type of skin cell is called melanomas.
- Neoplasm is a new abnormal tissue capable of continued growth forming tumours and disrupting the normal cells, while benign tumour are encapsulated localised mass of abnormal tissue, which does not infiltrate to adjacent tissues.
- The rest statements are correct.
Question 40. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- Benign tumour show the property of metastasis
- Heroin accelerates body functions
- Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis
- Patients who have undergone surgery are given cannabinoids to relieve pain
“cancer questions “
Answer: 3. Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis
- Malignant tumour exhibit metastasis. It is the phenomenon in which cancer cells spread to distant sites through body fluids to develop secondary tumour.
- Other statements are incorrect.
- Incorrect statements can be corrected as Benign tumour does not show the property of metastasis.
- Heroin depresses the body functions.
- Patients are given morphine after surgery to relieve pain.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 41. Cancer of the prostate gland is caused due to the exposure to
- Hydrocarbons
- Cadmium oxide
- Methane gas
- Strontium compound
Answer: 2. Cadmium oxide
Cadmium, especially cadmium oxide, is probably a cancer-causing agent in humans. There is evidence that cadmium causes prostate and kidney cancer in humans.
NEET Exam Cancer Detection and Treatment Most Repeated MCQs
Question 42. Which of the following is a carcinogen?
- HS2
- Asbestos
- Pb
- Suspended particles
Answer: 2. Asbestos
Asbestos present in the atmosphere due to industrial emissions cause lung cancers (asbestosis). Thus it is a carcinogen.
Question 43. Which of the following statements is not true for cancer cells in relation to mutations?
- Mutations in proto-oncogenes accelerate the cell cycle
- Mutations destroy telomerase inhibitor
- Mutations inactivate the cell control
- Mutations inhibit the production of telomerase
Answer: 4. Mutations inhibit production of telomerase
- The statement in option (4) is not true for cancer cell in relation to mutation.
- It can be corrected as Cancer is caused by increased telomerase activity, making the cancerous cells immortal and not by inhibition of telomerase production.
- Rest statements are correct.
Question 44. Epstein Barr virus may cause
- Lymphomas
- Carcinoma
- Polio
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Lymphomas
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV), originally discovered through its association with Burkitt lymphoma, is now etiologically linked to a remarkably wide range of lymphoproliferative lesions and malignant lymphomas of B, T and NK-cell origin. It causes lymphomas.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 45. Cancer cells show unlimited growth because of Haryana
- Differences in surface proteins, cytokines
- Difference in cholesterol
- Abnormal cytoplasm
- Abnormal nucleus
Answer: 1. Differences in surface proteins, cytokines
Cancer cells show unlimited growth because of differences in surface proteins, and cytokines.
Question 46. The symptoms of cancer include
- Change in bowel or bladder habit
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- Thickening of mass in the breast or other body parts
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The symptoms of cancer include change in bowel or bladder habits, unusual bleeding or discharge, and thickening of mass in the breast or other body parts.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 47. Which is not a warning sign of cancer?
- Appearance of moles and warts
- Change in bowel and excretory movements
- Loss of appetite and weight
- Lump in breast
Answer: 1. Appearance of moles and warts
The appearance of mole is not necessarily cancerous. Enlargement of the mole also does not necessarily mean a mole is malignant. Some regular moles may increase in size and darken in pregnancy. Common warts never turn cancerous.
Question 48. Assertion (A) Cancer cells are virtually immortal until the body in which they reside, die. Reason (R) Cancer is caused by damage to gene regulation of the cell division cycle.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Cancer is caused by damage to genes regulating the cell division cycle. It is an uncontrolled proliferation of the cells. All types of cancer have five basic characteristics. They are
- Uncontrolled cell growth.
- Loss of cell differentiation (specialisation).
- Invasion of normal tissues.
- Metastasis or spread to multiple sites.
- Loss of contact inhibition.
- All these characteristics make the cancer immortal until the body in which they reside die.
Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy MCQs for NEET
Question 49. Physical carcinogens are
- UV-rays
- X-rays
- γ -rays
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
“cancer questions “
- The term ‘physical carcinogens’ includes a wide range of agents. Ionising radiations like X-rays and gamma rays and non-ionising radiations like UV-rays causes DNA damage, leading to neoplastic transformation.
- It also includes radiation from radioactive materials in industry and in the general environment. Therefore, physical carcinogens include UV-rays, X-rays and γ-rays.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 50. Which one of the following techniques is safest for the detection of cancers?
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Radiography (X-ray)
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- Histopathological studies
Answer: 1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- The histopathological study is an invasive technique. Radiography and
- CT scans involve X-rays which are harmful. In MRI, strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiation are used to detect any physiological changes in the sample tissue.
- Thus, among given options, MRI is the safest technique for detection of cancer.
Question 51. Which of the following techniques can be used to detect cancer of the internal organs?
- Radiography
- Computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Techniques like radiography (use of X-rays), CT (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs.
- Computed tomography uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internals of an object. It provides a different form of imaging known as cross-sectional imaging.
- MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in living tissue.
Question 52. Match the following columns.
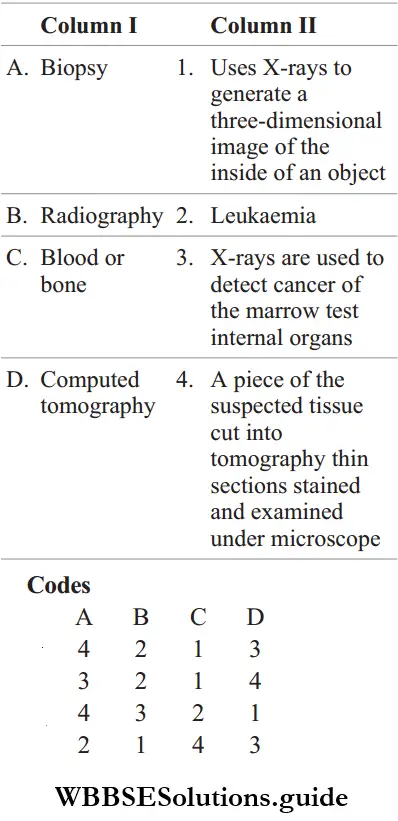
Answer: A–4, B–3, C–2, D–1
Role of Carcinogens and Mutations in Cancer MCQs for NEET
Question 53. Histological examination of affected tissues to detect the cancer is known as
- Autopsy
- Biopsy
- Postmortem
- Pap test
Answer: 2. Biopsy
- When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy.
- Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous and inflammatory conditions.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 54. A pap test is done for
- Detecting cervix cancer
- Detecting uterus cancer
- Detecting breast cancer
- Detecting oral cancer
Answer: 1. Detecting cervix cancer
A Pap smear is used to screen for cervical cancer. The Pap smear is usually done in conjunction with a pelvic exam.
Question 55. The common weed Catharanthus roseus or Vinca rosea is a source of
- High fever
- Two carcinogens, i.e. Vincristine and vinblastine
- Two anticancer drugs, i.e. Vincristine and vinblastine
- Skin rashes
Answer: 3. Two anticancer drugs, i.e. Vincristine and vinblastine
The common weed, Sada bahar (Catharanthus roseus or Vinca rosea) is a source of two anticancer drugs, i.e. vincristine and vinblastine, which are used in the treatment of leukaemia.
Question 56. Which of the following is not a part of radiation therapy?
- X-rays
- Cobalt – 60
- Radium
- Triethylene
Answer: 4. Triethylene
“cancer questions “
- Cobalt-60 ( 60Co) has been used for radiotherapy cancer treatment, food irradiation and industrial applications. In radiation therapy. nowadays, gamma rays have replaced X-rays.
- Radiation therapy began with radium and with relatively low-voltage diagnostic machines.
- So, trimethylene is not a part of radiation therapy.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 57. Electron beam therapy is a kind of radiation therapy to treat
- Enlarged prostate gland
- Gallbladder stones by breaking them
- Certain types of cancer
- Kidney stones
Answer: 3. Certain types of cancer
- Electron beam therapy or radiation therapy involves the use of radioactive waves to treat certain types of cancer.
- Electron beams are of low energy. They are often used in skin conditions and cancers. Then procedure to deliver external beam radiation is somewhat similar to giving an X-ray.
- This beam therapy involves iodine, cobalt, protons and electrons.
- This therapy is used in cancer of cervix, cancer of larynx, germ cell cancer, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, etc.
Question 58. Cancer treatment is a difficult process. Which of the following is a reason for it?
- Cancer cells can undergo uncontrolled divisions
- Cancer cells adapt and evolve in response to treatment
- Cancer cells become unresponsive to growth signals
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Cancer treatment is a difficult process due to the metastatic (uncontrolled division) nature of cancer cells.
- It is contributed by the unresponsive behaviour of cancer cells toward growth signals. Thus, they grow and invade new tissue sites rapidly.
- They also exhibit heterogeneity due to which they evolve and adapt rapidly.
Question 59. Current treatment for cancer does not include which of the following?
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
- Physiotherapy
Answer: 4. Physiotherapy
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality. So, physiotherapy is not used to treat cancer.
Question 60. Which of the following is not used for the treatment of cancer?
- 131I
- 60Co
- Taxol
- Streptokinase
Answer: 4. Streptokinase
Streptokinase (SK) is a thrombolytic medication and enzyme. It is not used for the treatment of cancer.
Question 61. Alpha-interferons
- Activate the immune system
- Help in destroying the tumour
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
- Tumour cells have been shown to avoid detection and destruction by the immune system.
- Therefore, the patients are given substances called biological response modifiers such as α-interferon, which activates their immune system and helps in destroying the tumours.
