Biotechnology And Its Applications
Biotechnology has a wide range applications such as biopharmaceuticals, therapeutics, diagnostics, genetically modified crops for agriculture, processed food, bioremediation, waste treatment, and energy production.
Biology Class 12 Notes For Neet
Biotechnology has 3 critical research areas:
- Providing the best catalyst in the form of an improved organism usually a microbe or pure enzyme.
- Creating optimal conditions through engineering for a catalyst to act.
- Downstream processing technologies to purify the protein/organic compound
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Class 12 Notes
Applications In Agriculture
Applications In Agriculture
Options for increasing food production:
- Agro-chemical based agriculture.
- Organic agriculture.
- Genetically engineered crop-based agriculture.
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) or transgenic organisms are the plants, bacteria, fungi and animals whose genes are altered by manipulation.
Biology Class 12 Notes For Neet
Advantages of genetic modification in plants:
- It makes crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, salt, heat, etc.).
- Pest-resistant crops reduce the use of chemical pesticides.
- It helps to reduce post-harvest losses.
- It increases the efficiency of mineral usage by plants (it prevents early exhaustion of fertility of soil).
- It enhances the nutritional value of food. example, Vitamin A-enriched rice.
- To create tailor-made plants to supply alternative resources (starches, fuels, pharmaceuticals, etc.) to industries.
“short notes on biotechnology “
Pest Resistant Plants:
- They act as bio-pesticides.
- It reduces the need for insecticides.
- For example, Bt cotton, Bt corn, rice, tomato, potato, soybean, etc.
Bt Cotton:
Some strains of Bacillus thuringiensis have proteins that kill insects like coleopterans (beetles) lepidopterans (tobacco budworm, armyworm), and dipterans (flies, mosquitoes).
- B. thuringiensis forms a toxic insecticidal protein (Bt toxin) crystal during a particular phase of their growth. It does not kill the Bacillus as it exists as inactive protoxins.
- When an insect ingests the toxin, it becomes active due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilizes the crystals.
- The toxin binds to the surface of mid-gut epithelial cells and creates pores. It causes cell swelling lysis and death of the insect.
- Bt toxin genes were isolated from B. thuringiensis and incorporated into crop plants such as cotton.
- Most Bt toxins are insect-group-specific. The toxin is
- Coded by a gene named cry. for example, proteins encoded by the genes cryIAc and cryIIAb control the cotton bollworms of cryIAb control corn borer.
Biology Class 12 Notes For Neet
Nematode resistance in tobacco plants:
- A nematode Meloidogyne incognitia infects the roots of tobacco plants causing a reduction in yield.
- It can be prevented by RNA interference (RNAi) strategy.
- RNAi is a method of cellular defense in all eukaryotic organisms. It prevents the translation of a specific mRNA (silencing) due to a complementary dsRNA molecule.
- The source of this complementary RNA is from infection by RNA viruses or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
- Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode-specific genes (DNA) are introduced into the host plant. It produces both sense and anti-sense RNA in host cells.
- These RNAs are complementary. So they form double-stranded (ds) RNA.
- It initiates RNAi and silences the specific mRNA of the nematode. Thus the parasite cannot survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA.

NEET Biology Class 12 Biotechnology and Its Applications Notes
Applications In Medicine
Medicine:
- The recombinant DNA technology helps for the mass production of safe and more effective therapeutic drugs.
- The products from non-human sources induce unwanted immunological responses. However recombinant therapeutics do not have such problems.
- At present, about 30 recombinant therapeutics have been approved. Of these, 12 are being marketed in India.
“importance of biotechnology “
1. Genetically Engineered Insulin:
- Insulin is used to manage adult-onset diabetes.
- Insulin from the pancreas of animals (cattle and pigs) causes allergies or other types of reactions to the foreign protein.
- Now, it is possible to produce human insulin using bacteria.
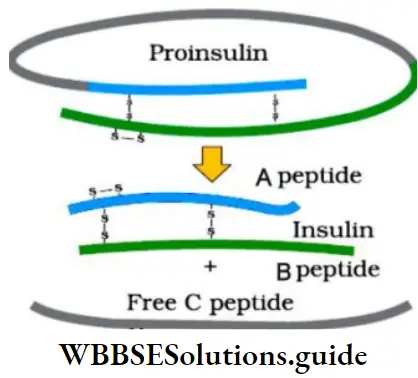
- Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains (chain A and chain B) that are linked by disulfide bridges.
- In mammals, insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone (pro-insulin). It needs processing to become a mature and functional hormone.
- The pro-hormone contains an extra stretch called the C peptide. This is removed during maturation into insulin.
- In 1983, Eli Lilly (an American company) prepared two
- DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and introduced in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains.
- Chains A and B were combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin
Biotechnology and Its Applications NEET Notes
2. Gene Therapy:
- It is a method to correct a gene defect in a child/embryo.
- Here, genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a hereditary disease. It compensates for the nonfunctional gene.
- The first clinical gene therapy (1990) was given to a 4-year-old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
- This disorder is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase (an enzyme crucial for the immune system to function).
- This can be cured by bone marrow transplantation or by enzyme replacement therapy (injection of ADA). But these are not completely curative.
- In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the patient’s blood are grown in a culture.
- Then, a functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is introduced into lymphocytes.
- Then, they are returned to the patient. This should be periodically repeated as these cells are not immortal.
- If the ADA gene (from marrow cells) is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, it could be a permanent cure.
Biology Class 12 Notes For Neet
3. Molecular Diagnosis:
- Early diagnosis of diseases is not possible using conventional methods (serum and urine analysis).
- It is possible by techniques such as Recombinant DNA technology,
“application of biotechnology “
PCR & ELISA. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
- The presence of a pathogen is normally suspected only based on symptoms.
- By this time, the concentration of pathogens is already very high in the body.
- However, very low concentrations of bacteria or viruses can be detected by amplification of their nucleic acid by PCR.
Uses of PCR:
- To detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients.
- To detect gene mutations in suspected cancer patients.
- To identify many other genetic disorders.
- A single-stranded DNA or RNA, tagged with a radioactive molecule (probe) is hybridized to its complementary DNA in a clone of cells followed by detection using autoradiography.
- The clone having a mutated gene will not appear on the photographic film, because the probe will not have complementarity with the mutated gene.
NEET Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications Important Notes
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay):
- It is based on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction.
- Infection by pathogens can be detected by the presence of antigens (proteins, glycoproteins, etc.) or by detecting the antibodies synthesized against the pathogen.
Biology Class 12 Notes For Neet
Transgenic Animals
These are the animals whose genome has been altered by the introduction of an extra (foreign) gene by manipulation.
- Examples are transgenic rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep, cows, and fish.
- Over 95% of the transgenic animals are mice.
Benefits of transgenic animals:
To study the regulation of genes and their action on normal Physiology & development:
- For example, Study of complex factors such as insulin-like growth factor. Genes (from other species) that alter the formation of this factor are introduced and the biological effects are studied.
- This gives information about the biological role of the factor in the body.
“biotechnology notes “
To Study the contribution of genes in the development of a disease and thereby new treatments:
For example, transgenic models for many human diseases such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis & Alzheimer’s.
Class 12 Biology Notes For Neet
Biological products:
- Some medicines contain expensive biological products. Transgenic animals are used to produce useful biological products by introducing genes that code for a particular product.
- For example, human protein (α-1-antitrypsin) is used to treat emphysema, products for the treatment of phenylketonuria (PKU) and cystic fibrosis, etc.
- In 1997, Rosie (the first transgenic cow) produced human protein-enriched milk (2.4 gm per liter).
- It contains the human α-lactalbumin and is a nutritionally more balanced product for human babies than natural cow milk.
Best Short Notes for Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and Its Applications
Vaccine safety testing:
- Transgenic mice are used to test the safety of the polio vaccine.
- If it is reliable, they can replace the use of monkeys to test the safety of vaccines.
Chemical safety testing (toxicity testing):
- Some transgenic animals carry genes that make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
- They are exposed to the toxic substances and the effects studied. It gives immediate results.
- The problem of unpredictable results: Genetic modification may cause unpredictable results.
“biotechnology applications “
Ethical Issues
The problem of unpredictable results: Genetic modification may cause unpredictable results.
- Indian Government has set up organizations like GEAC (Genetic
- Engineering Approval Committee) to make decisions about the validity of GM research and the safety of GM organisms for public services.
Problems of patent:
- Certain companies have patents for products and technologies that make use of genetic materials, plants, etc.
- That has been identified, developed, and used by farmers and indigenous people of a country. Examples, are Basmati rice, and herbal medicines (turmeric, neem, etc).
Class 12 Biology Notes For Neet
Basmati rice:
- Basmati rice has a unique aroma & flavor. India has 27 varieties of Basmati.
- In 1997, an American company got patent rights on Basmati rice through the US Patent and
- Trademark Office. This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati. This was derived from
- Indian farmer’s varieties. Indian Basmati was crossed with semi-dwarf varieties and claimed as a novelty.
- Other people selling Basmati rice could be restricted by patent.
Biotechnology and Its Applications Class 12 NEET Key Concepts and Summary
Biopiracy:
It is the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organizations without proper authorization from the countries and people concerned.
- Most of the industrialized nations are poor in biodiversity and traditional knowledge.
- The developing and underdeveloped world has rich biodiversity and traditional knowledge related to bio-resources.
- It has to develop laws to prevent unauthorized exploitation of bio-resources and traditional knowledge.
- Indian Parliament has cleared the second amendment of the
- Indian Patents Bill that has considered patent terms emergency provisions and research and development initiatives.
