Diversity in Living Organism Long Answer Questions
Directions: Give answer in four to five sentences.
Question 1. What are the characteristic features of the Phylum Fungi? Give examples also.
Answer:
Characteristic features of the Phylum Fungi:
- Fungi includes heterotrophic eukaryotes. These fungi are heterotrophic as they do not have chlorophyll and cannot prepare their own food by photosynthesis, live as saprophytes, parasites and symboints.
- The cell has well defined nucleus and organelles. Cell wall is made of chitin, a complex nitrogen containing sugar that imparts toughness to cell wall.
- Mostly multicellular, only yeast is unicellular.
- Plant body consists of thread like hyphae (network is called mycelium).
- Reproduction occurs by spore formation.
NEET Biology Class 9 Chapter 3 Long Answer Type Questions with Solutions
Examples: Rhizopus (pin mould), Aspergillus, Penicillium and Mushroom (Agaricus, an edible fungus).
Read And Learn More: NEET Class 9 Biology Long Question And Answers
Question 2. Mention the general characteristics, and classification of Phanerogams (Spermatophyta).
Answer:
Phanerogams (Spermatophyta) are divided into Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Gymnosperms:
- The seeds are naked.
- Are perennial, evergreen and woody.
- Have well-developed vascular issues (xylem and phloem) for transport of materials within the plant body. Xylem lacks vessels and phloem lacks companion cells.
- Reproductive organs are present in the cones.
- External water is not required for fertilization.
Examples: Cycas, Pinus, Cedrus (Doedar).

Detailed Answers for Diversity in Living Organisms NEET Exam Preparation
Angiosperms:
Angiosperms are flowering vascular plants:
- Have seeds enclosed within the fruit.
- Have diverse body forms.
- Vascular tissues are well developed; xylem contains
- vessels and phloem contains companion cells.
- Reproductive organs are flowers.
- External water is not required for fertilisation.
Angiosperms include two classes viz. dicotyledoneae and monocotyledonae.- Dicotyledoneae includes plants having two cotyledons in the seed; reticulate venation; tap root system and secondary growth. Examples: Grain, Mango.
- The Monotyledoneae group comprises plants, having one cotyledon in the seed; parallel venation; firous root system; secondary growth is lacking. Examples: Wheat, Maize.
NEET Biology Class 9 Diversity in Living Organisms Long Questions
Question 3. What are the characteristic features of Platyhelminthes?
Answer:
- The body is flat, leaf-like or tapelike, bilaterally symmetrical (left and right side of the body are similar).
- They are triploblastic (have three germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) with organ system level of organisation.
- Respiratory and circulatory systems are under developed.
- Excretion occurs through flme cells.
- The nervous system is primitive but with brain.
- Mostly parasites, some are free living like Planaria.
Question 4. What are the characteristic features of Reptilia?
Answer:
- Reptilia are r land vertebrates of warmer regions.
- Horny scales are present on skin.
- Exchange of gases take place through lungs only; gills are absent.
- These are tetrapods with pentadactyle limbs.
- Body is divided into head, neck and trunk; tail may or may not be present.
- Heart is three-chambered.
- They are cold blooded.
- They lay eggs, which have a thick shell.
NEET Biology Diversity in Living Organisms Important Long Answer Questions
Question 5. How are organisms named and classified?
Answer:
Taxonomy is the science by which organisms are classified and placed into hierarchical categories that reflect their evolutionary relationships. The eight major categories, in order of decreasing inclusiveness, are
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Division or Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species.
The scientifi name of an organism is composed of its genus name and species name. A hierarchical concept was first used by Aristotle, but in the mid-1700s Linnaeus laid the foundation for modern taxonomy. In the 1860s, evolutionary theory proposed by Charles Darwin provided an explanation for the observed similarities and differences among organisms, and modern taxonomists attempt to classify organisms according to their evolutionary relationship.
Question 6. Whales belong to class Mammalia. Mammals are basically terrestrial. Mention the important changes that have occurred in whales which-enable them to lead an aquatic life.
Answer:
Important changes in whales to lead aquatic life are as follows:
- Fusiform tapering body.
- Horizontally expanded tail for propulsion.
- Formation of a thick layer of fat beneath the skin, the blubber.
- Presence of whale-bone or baleen.
- Absence of external ear, nostril moved to the apex of the head.
Best Long Questions for Class 9 Biology Diversity in Living Organisms
Question 7. What are the characteristic features of Mammals?
Answer:
Characteristics features of Mammals:
- Body is covered with hair.
- Skin is provided with sweat and sebaceous glands.
- Heart is four-chambered.
- Fertilization is internal.
- Females have mammary glands to produce milk to nourish their young ones.
- External ear-pinna present.
- Eyes have eyelids.
- Warm-blooded.
- Respiration through lungs.
- Body cavity is divided into thorax and abdomen by the muscular diaphragm.
Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9 NEET Descriptive Questions
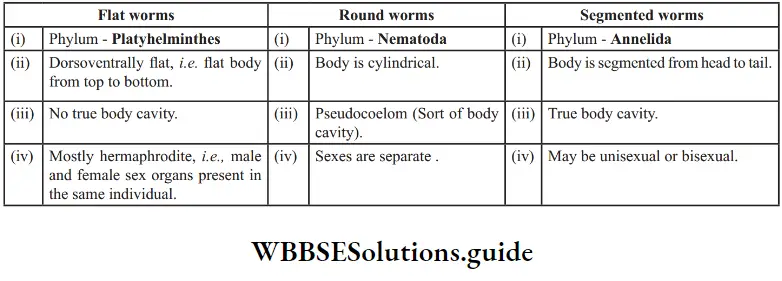
Question 8. Give the characteristics of flatworms, roundworms and segmented worms. Give their phylum
Answer: