Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Fertilisation and Implantation
Question 1. The phenomenon of fertilisation was first perceived by
- Hertwig
- Leeuwenhoek
- Wiseman
- Karl Ernst von Baer
Answer: 1. Hertwig
Oscar Hertwig (1875) first described the fusion of sperm and nuclei, i.e. fertilisation in sea urchin.
Question 2. Fertilisation was discovered by
- Strasburger
- Robert Brown
- Darwin
- Lamarck
Answer: 1. Strasburger
Fertilisation was discovered by Edward Strasburger in angiosperms.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. The release of semen by penis into vagina during copulation (coitus) is known as
- Insemination
- Fertilisation
- Zygote
- Gametogenesis
Answer: 1. Insemination
Insemination is another word for sexual intercourse or coitus in which the semen is released through penis into the vagina.
“human reproduction mcqs class 12 “
Question 4. Sperm enters from which part of egg?
- From animal pole in unfertilised egg
- From vegetal pole in unfertilised egg
- Anywhere in unfertilised egg except animal pole
- All of the above
Answer: 1. From animal pole in unfertilised egg
Sperm enters the egg from animal pole in unfertilised egg by dissolving plasma membrane of ovum.
Question 5. In man, coagulated semen liquefies in vagina of female due to the presence of an enzyme. Identify the enzyme.
- Fibrinogenase
- Fibrinolyase
- Fibrinolysin
- Fibrinolysinase
Which is the correct answer?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- Only 1
- Only 2
Answer: 1. 1 and 2
Fibrinogenase and fibrinolyase enzymes help in the liquefication of coagulated semen in the vagina. Thus, option is correct.
“human reproduction mcq class 12 “
Question 6. During the passage of sperms in vaginal tract, many sperms are engulfed by
- Phagocytes
- Macrophages
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Fertilizin
Answer: 1. Phagocytes
Many sperms are engulfed by phagocytes released by female’s immune system during the passage of sperm in vaginal tract of female reproductive system.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 7. Identify the correct match.

Answer: 1. A–2, B–3, C–1
NEET Biology Fertilization and Implantation MCQs with Answers
Question 8. Which one of the following statements is false in respect of viability of mammalian sperm?
- Sperm is viable for only upto 24 hours
- Survival of sperm depends on the pH of the medium and is more active in alkaline medium
- Viability of sperm is determined by its motility
- Sperms must be concentrated in a thick suspension
Answer: 1. Sperm is viable for only upto 24 hours
Statement in option is false. It can be corrected as Sperms remain viable for 48-72 hours after being ejaculated into the female’s reproductive tract. Rest statements are true in respect of viability of mammalian sperm.
Question 9. Consider the following statements.
- Sperm cells die immediately when placed in a petridish right after they are released from the body.
- Semen contains prostaglandins that bring about contraction of uterine smooth muscles in females.
Choose the corect option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct.
Incorrect statement can be corrected as Sperm can survive for some time in petridish, but when they do not get appropriate environment, they will die. At – 196°C, they can be stored for years. This is the temperature which is maintained at sperm bank.
Question 10. Fertilisation in humans is practically feasible only if NEET 2016
- The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to ampullary-isthmic junction of the cervix
- The sperms are transported into cervix within 48 hrs of release of ovum in uterus
- The sperms are transported into vagina just after the release of ovum in Fallopian tube
- The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to ampullary-isthmic junction of the Fallopian tube
Answer: 4. The ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously to ampullary-isthmic junction of the Fallopian tube
The fusion of a haploid male gamete (sperm) and a haploid female gamete (ovum) to form a diploid zygote is called fertilisation. In human beings, it takes place in the ampullary-isthmic junction of the oviduct (Fallopian tube), when ovum and sperms are transported simultaneously at this site.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. Every copulation does not result in fertilisation and pregnancy due to failure of sperm to reach the
- Ampulla
- Cervix
- Endometrium
- Myometrium
Answer: 1. Ampulla
It is necessary for a sperm to reach the ampullary region because, it is the site where ova stay for two days after ovulation. That is why, every intercourse does not result in fertilisation.
Question 12. Grey crescent is the area
- At the point of entry of sperm into ovum
- Just opposite to the site of entry of sperm into ovum
- At the animal pole
- At the vegetal pole
Answer: 2. Just opposite to the site of entry of sperm into ovum
Grey cresent is lightly pigmented crescent-shaped area of marginal cytoplasm on the dorsal side, exactly opposite to the site of entry of sperm into ovum.
“diagrammatic sectional view of male pelvis showing reproductive system “
Question 13. The side opposite to the polar body and nucleus in the ovum is called
- North pole
- Vegetal pole
- South pole
- Animal pole
Answer: 2. Vegetal pole
The side opposite to the polar body and nucleus in the ovum is known as vegetal pole.
Question 14. The point of sperm entry in the secondary oocyte is made possible by the
- Cone of rejection
- Cone of reception
- Fertilisation cone
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
The secondary oocyte forms a projection termed as the cone of reception or fertilisation cone from where the sperm enters into it. Thus, option is correct.
Important MCQs on Fertilization and Implantation for NEET
Question 15. Which enzyme is involved in penetration of sperm into ovum?
- Hyaluronidase
- Zona lysine/Acrosin
- Fertilizin
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
The hyaluronidase enzyme of acrosome hydrolyses the hyaluronic acid of follicular cells. Zona lysine or acrosin digest zona pellucida, so, that the sperm can penetrate the ovum. Thus, option is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 16. Exflagellation of the sperm during fertilisation of egg occurs due to
- Sodium
- Polar body
- Capsule
- Lysosome
Answer: 4. Lysosome
The sperm during fertilisation, loses its flagella (exflagellation) as only the nucleus of the sperm can fuse with the egg nucleus. This process of exflagellation is brought about by lysosome.
Question 17. The sperm obtains energy for movement in female genital tract from
- Hyaluronidase enzyme produced by acrosome
- Proximal centriole in the neck
- Mitochondria in the middle piece
- Axial filament
Answer: 3. Mitochondria in the middle piece
The sperm gets energy for the movement in the female genital tract by ATP produced by the mitochondria found in the middle piece of sperm.
Question 18. Consider the following statements.
- Hyaluronidase is a type of sperm lysin.
- Hyaluronidase distrupts the follicular cells of ovum during penetration into it.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Hyaluronidase is the sperm lysin that acts on ground substances of follicle cells and help the sperm to penetrate the ovum.
Question 19. The chemicals released by gametes which aid in their union in human are
- Pheromones
- Termones
- Gamones
- Desmosomes
Answer: 3. Gamones
Gamones are the chemicals released by human gametes. These chemicals aid in species specific union of gametes.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 20. Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option from the codes given below

Answer: 4. A–4, B–1, C–3, D–2
Process of Fertilization and Zygote Formation MCQs for NEET
Question 21. The initial step in the activation of ovum during the process of fertilisation is
- Formation of the fertilisation cone
- Fertilizin-antifertilizin reaction
- Penetration of sperm in the egg
- Formation of the fertilisation membrane
Answer: 2. Fertilizin-antifertilizin reaction
“hormones secreted by placenta “
During fertilisation, the initial step of ovum activation is fertilizin-antifertilizin compatibility reaction. Fertilizin of egg interacts with antifertilizin of the sperm of same species. This interaction makes the sperm stick to the egg surface. This event is then followed by penetration of sperm into the egg.
Question 22. ‘Fertilizin’ is a
- Carbohydrate
- Glycoprotein
- Phospholipid
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Glycoprotein
Fertilizin is a glycoprotein that is composed of monosaccharides and amino acids.
Question 23. Fertilizins are the substances released from
- Mature egg
- Sperms
- Immature egg
- Polar body
Answer: 1. Mature egg
Fertilizin is found on the membrane of mature egg. It is present as a chemical sheet on the egg and it can only be recognised by antifertilizin.
Question 24. Antifertilizin is present Manipal 2004
- On the tip of sperm
- On the layer of ova
- Both on the tip of sperm and on layer of ova
- All over the sperm
Answer: 1. On the tip of sperm
The tip of sperm contains a proteinaceous substance known as antifertilizin. It is a protein which is composed of acidic amino acids
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 25. Which of the following are secretions produced by the spermatozoa at the time of fertilisation?
- Fertilizin and antifertilizin
- Antifertilizin and sperm lysin
- Fertilizin and sperm lysin
- Only sperm lysin
Answer: 2. Antifertilizin and sperm
Antifertilizin and sperm lysin are the secretions produced by the spermatozoa at the time of fertilisation. Antifertilizins are acid protein to which fertilizin of egg attach at the site of zona pellucida. Sperm lysins such as hyaluronidase, zona lysin or acrosin by acrosome which prepares the sperm to fertilise the ovum.
Question 26. Assertion A sperm sticks to an egg for fertilisation. Reasons (R) Interaction of surface receptors, fertilizin on the egg and antifertilizin on the sperm head makes them adhere together.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Sperm enters into an egg for fertilisation. The attachment of sperm to the egg takes place due to the interaction of surface receptors, fertilizin on the egg and antifertilizin on the sperm head.
Topic-wise Fertilization and Implantation MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 27. The sperm penetrates the ovum
- Mechanically
- Chemically
- Electrostatically
- Thermally
Answer: 2. Chemically
The penetration of the sperm through the corona radiata of ovum is aided by enzymatic substance called hyaluronidase (mucopolysaccharide hyaluronic acid). Thus, it is a chemical reaction.
Question 28. Sperm lysins contain
- Hyaluronidase
- Corona penetrating enzyme
- Acrosin
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
There are many enzymes in the acrosome like hyaluronidase, pectin, corona penetrating enzyme, acrosin, etc. These are collectively called
sperm lysins. Thus, option is correct.
Question 29. Which chemical event of fertilisation involves the presence of hyaluronidase enzyme?
- Acrosomal reaction
- Cortical reaction
- Amphimixis
- Activation of egg
Answer: 1. Acrosomal reaction
Hyaluronidase enzyme assists in acrosomal reaction. This enzyme acts on the ground substances of follicle cells and allow the sperm to penetrate zona pellucida.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 30. When the acrosome membrane of the sperm breaks, it is called
- Activation
- Agglutination
- Capacitation
- Cavitation
Answer: 3. Capacitation
Capacitation is the process in which the acrosome membrane of the sperm breaks and release its enzymes to dissolve the egg membrane.
Question 31. The preparation of sperm before the penetration of ovum is called
- Insemination
- Coition
- Spermiation
- Capacitation
Answer: 4. Capacitation
- After insemination, sperms undergo capacitation that provides them the ability to fertilise an ovum. It consists of three processes
neutralisation of inhibitory factors present in semen - weakening of covering membrane of acrosome head by dissolution of cholesterol entry of Ca 2+ into sperms which changes sperm movement from undulations to whiplash motion.
NEET Biology Role of Hormones in Fertilization and Implantation MCQs
Question 32. Consider the following statements.
- Secretions of female genital tract inhibit sperm’s fertilising capability.
- Before penetration, receptor site of acrosomes are exposed.
Choose the corect option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct.
- Incorrect statement can be corrected as The sperms in the female genital tract attain the capability of fertilising the egg by the secretions of female genital tract.
- These secretions of the female genital tract remove the coating on the surface of the sperms, particularly those on acrosome.
- Thus, the receptor sites on the acrosome are exposed and sperm become active to penetrate the egg. This phenomenon of sper activation in mammals is called capacitation.
“testicular lobules “
Question 33. Capacitation takes place in
- 12 hrs
- 10 hrs
- 8 hrs
- 6 hrs
Answer: 4. 6 hrs
Capacitation takes about 5-6 hours. This process enables the sperms to fertilise the egg.
Question 34. Capacitation occurs in
- Rete testis
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Female reproductive tract
Answer: 4. Female reproductive tract
Capacitation involves the series of changes that occur in the sperm, while inside the female reproductive tract.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 35. Consider the following statements.
- Oocyte gets depolarised after the binding of sperm to it.
- Depolarisation prevents monospermy.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect.
Binding of the sperm to the secondary oocyte induces depolarisation of the oocyte plasma membrane. Depolarisation prevents polyspermy, i.e. the entry of more than one sperm into the oocyte. It ensures monospermy.
Question 36. Polyspermy is prevented by
- Formation of fertilisation membrane
- Formation of vitelline membrane
- Agglutination reaction
- Zona pellucide
Answer: 1. Formation of fertilisation membrane
Polyspermy is prevented by the formation of fertilisation membrane. Soon after the entry of sperm into egg, cortical granules present beneath the egg’s plasma membrane release chemical substances to form vitelline membrane which later get converted into fertilisation membrane. It acts as the slow block to polyspermy.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (IVF, ICSI) MCQs for NEET
Question 37. Besides activating the egg another role of a sperm is to carry ……… to egg.
- RNA
- Mitochondria
- DNA
- Ribosomes
Answer: 3. DNA
The head of the sperm cell contains the male’s genetic information in DNA, that is to be
passed on to the next generation. Normally , the head of a sperm cell contains one copy of each chromosome.
Question 38. When more than one sperm establish contact and penetrate into the egg, then it is called
- Monospermy
- Polyspermy
- Both 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
The head of the sperm cell contains the male’s genetic information in DNA, that is to be passed on to the next generation. Normally , the head of a sperm cell contains one copy of each chromosome.
Question 39. What happens during fertilisation in humans after many sperms reach close to the ovum?
- Secretions of acrosome helps only one sperm to enter cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida
- All sperms except those nearest to the ovum lose their tails
- Cells of corona radiata trap all the sperms except one
- Only two sperms nearest to the ovum penetrate zona pellucida
Answer: 1. Secretions of acrosome helps only one sperm to enter cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida
During fertilisation in humans, many sperms reach close to the ovum. As sperm comes in contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum, it induces changes in the membrane that blocks the entry of additional sperm. The secretions of acrosome helps one sperm to enter the cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 40. Acrosome reaction in sperm is triggered by
- Capacitation
- Release of lysin
- Influx of Ca2+
- Release of fertilizin
Answer: 3. Influx of
Acrosome reaction is triggered by Ca2+ ions. It involves the uptake of Ca 2+ ions and efflux of H+ ions to generate high pH and negative surface charge. It thus, help in the release of acrosomal enzyme from acrosome.
Question 41. Binding of sperm to secondary oocyte results in …A… that ensures …B… .The words suitable to fill the blanks are
- A–polyspermy, B–polarisation
- A–polarisation, B–polyspermy
- A–depolarisation, B–monospermy
- A–monospermy, B–depolarisation
Answer: 3. A–depolarisation, B–monospermy.
Question 42. The final event in the process of fertilisation is
- Formation of gametes
- Egg activation
- Amphimixis
- Organisational change in egg cytoplasm
Answer: 3. Amphimixis
Entry of sperm stimulates the secondary oocyte to start the suspended meiosis-II, thus resulting in the formation of one ootid and 2-3 polar body. Ootid changes to ovum whose nuclei fuses with the male pronuclei. This process is called amphimixis (final event of fertilisation).
Question 43. The phenomenon of nuclear fusion of sperm and egg is known as
- Karyogamy
- Parthenogenesis
- Vitellogenesis
- Oogenesis
Answer: 1. Karyogamy
Karyogamy is the process of nuclear fusion of sperm cell and ovum.
Question 44. The resultant product of amphimixis is
- Haploid ovum
- Diploid egg
- Diploid ovum
- Haploid egg
Answer: 2. Diploid egg
Amphimixis involves the fusion of male and female pronuclei that produce a diploid egg called zygote.
Question 45. When the site of fertilisation is the ovary, it is called
- Tubal pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Abdominal pregnancy
- Ovarian pregnancy
Answer: 2. Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy refers to the condition in which the implantation occurs outside the uterus, typically in a Fallopian tube or ovary.
Question 46. Consider the following statements.
- Most ecotopic pregnancies occur in Fallopian tube.
- Ecotopic pregnancy causes abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which implantation of embryo takes place at site other than uterus. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the Fallopian tube, which are known as tubal pregnancies and few occur in ovaries. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 47. Which of the following shows the process of fertilisation?
- 2n → n
- n → n
- n + n → 2n
- 2n → 2n
Answer: 3. n + n → 2n
During fertilisation, haploid spermatozoan (n) unites with haploid ovum (n) to form a diploid zygote (2n). Thus, n+n = 2n shows the process of fertilisation.
Question 48. Fertilisation is defined as the process by which Karnataka CET 1994
- A diploid spermatozoan unites with a haploid ovum to form a triploid zygote
- A haploid spermatozoan unites with a haploid ovum to form a diploid zygote
- A diploid spermatozoan unites with a diploid ovum to form a diploid zygote
- A diploid spermatozoan unites with a haploid ovum to form a diploid zygote
Answer: 2. A haploid spermatozoan unites with a haploid ovum to form a diploid zygote
Fertilisation is the fusion of a haploid spermatozoan (male gamete) with human ovum (female gamete), to form a diploid zygote.
Question 49. The given diagram refers to ovum surrounded by few sperms. Identify A, B and C in the diagram.
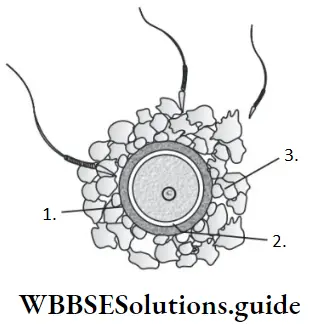
- A–Zona pellucida, B–Perivitelline space, C–Corona reticulata
- A–Zona pellucida, B–Vitelline membrane, C–Theca internal
- A–Zone pellucida, B–Perivitelline space, C–Corona radiata
- A–Oolemma, B–Perivitelline space, C–Corona radiata
Answer: 3. A–Zone pellucida, B–Perivitelline space, C–Corona radiata
Question 50. A layer of cortical granules is found beneath the
- Zona pellucida
- Fertilisation core
- Plasma membrane
- Hyaline layer
Answer: 3. Plasma membrane
The cortical granules are present beneath the egg’s plasma membrane. They release chemical substance between the ooplasm and plasma membrane.
Question 51. For entering the ovum, the sperm penetrates the corona radiata and zona pellucida with the help of
- Mucopolysaccharide in these layers
- Hyaluronic acid
- Enzymes released by ovum
- Zona lysin
Answer: 4. Zona lysin
Zona lysins are proteolytic enzymes that are capable of degenerating the zona pellucida. It enables the passage for sperm cells through the ovum.
Question 52. The granules present beneath the plasma membrane of oocyte cells are called …A… .These granules fuse with the plasma membrane of oocyte and release their content including … B … between the …C… and zona pellucida. This ensures the …D… . Here A, B, C and D refer to
- A–monospermy, B–plasma membrane, C–cortical enzyme, D–cortical granules
- A–cortical granule, B–cortical enzyme, C–plasma membrane, D–monospermy
- A–cortical enzyme, B–cortical granules, C–plasma membrane, D–monospermy
- A–cortical enzyme, B–cortical granules, C–monospermy, D–plasma membrane
Answer: 2. A–cortical granule, B–cortical enzyme, C–plasma membrane, D–monospermy.
Question 53. The fertilisation membrane during fertilisation is synthesised by
- Mitochondria Rajasthan
- Golgi bodies
- Acid mucopolysaccharides of cortical granules
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Acid mucopolysaccharides of cortical granules
During fertilisation process, the fertilisation membrane is synthesised by acid mucopolysaccharides of cortical granules.
Question 54. Why does fertilisation not occur during pregnancy?
- Secretion of high levels of oestrogen and progesterone
- Woman cannot have intercourse during pregnancy
- High level of HCl kills the ovum
- An abnormal ovum is released during pregnancy
Answer: 1. Secretion of high levels of oestrogen and progesterone
During pregnancy, high levels of progesterone and oestrogen are secreted that inhibit the release of follicular stimulating hormones. Therefore, ovulation does not occur and thereby, pregnancy is prevented.
Question 55. Just after fertilisation, the first change is
- Formation of grey crescent
- Activation of egg
- Formation of receptacle cone
- Cortical reaction
Answer: 2. Activation of egg
The entry of sperm stimulates the secondary oocyte to complete meiosis-II. It is called egg activation. Thus, just after fertilisation, the first change is activation of egg.
Question 56. Formation of activation calyx in the egg takes place
- Before fertilisation
- After fertilisation
- At the time of cleavage
- At the time of amphimixis
Answer: 2. After fertilisation
After fertilisation, structural proteins derived from the contents of the cortical granules of egg harden the vitelline membrane and transform it into the fertilisation membrane (envelope) or activation calyx and prevent the entry of other sperms. It is a slow method to prevent polyspermy.
Question 57. Meiotic division of the secondary oocyte is completed
- Time of copulation
- After zygote formation
- At the time of fusion of a sperm with an ovum
- Prior to ovulation
Answer: 3. At the time of fusion of a sperm with an ovum
Meiotic division of secondary oocyte is completed after the entry of sperm in secondary oocyte, which lead to the formation of a large ovum and a tiny 2nd polar body.
Question 58. Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs
- After entry of sperm, but before fertilisation
- After fertilisation
- Before entry of sperm into ovum
- Simultaneously with first cleavage
Answer: 1. After entry of sperm, but before fertilisation
Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs after the entry of sperm, but before fertilisation. The entry of sperm into the ovum induces completion of the meiotic division of the secondary oocyte. Entry of sperm causes breakdown of Metaphase Promoting Factor (MPF) and turns on the Anaphase Promoting Complex (APC).
Question 59. In human zygote, the male sex is determined by which of the following criteria?
- Mother gets good nutrition
- Father is stronger than mother
- Strength of male chromosome
- Required composition of chromosomes
Answer: 4. Required composition of chromosomes
In a human zygote, male sex is determined by the required composition of chromosomes, i.e. ‘X’ and ‘Y’. Male sex is denoted by XY and female sex is denoted by XX chromosomes.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 60. The number of autosomes in human female ovum is
- 11 pairs
- 12 pairs
- 22
- 23
Answer: 3. 22
A normal human female ovum has 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome. Thus, it contains haploid set or 23 chromosomes.
Question 61. In man, sperms contain autosomes and
- Only Y-chromosome
- Only X-chromosome
- Either X or Y-chromosomes
- Both X and Y-chromosomes
Answer: 3. Either X or Y-chromosomes
The sperms contain haploid set of chromosomes, i.e. 22 autosomes and either X or Y chromosomes, so that the total number of chromosomes is 23.
Question 62. Freshly released human egg has
- One Y-chromosome
- One X-chromosome
- Two X-chromosomes
- One X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome
Answer: 2. One X-chromosome
Human female has two X chromosomes. When eggs are formed through meiosis, each egg carries 22 autosomes and one X chromosome, i.e. the haploid set of chromosomes, 23.
Question 63. Identify the sex of baby A, B, C and D.
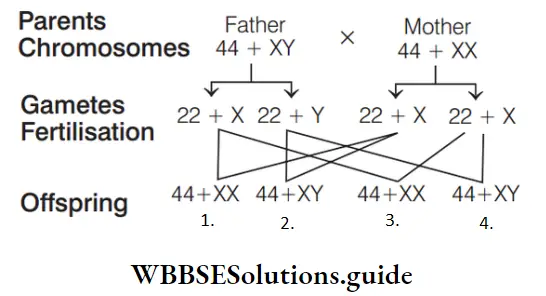
- A–Girl, B–Boy, C–Girl, D–Boy
- A–Boy, B–Girl, C–Boy, D–Girl
- A–Boy, B–Boy, C–Girl, D–Girl
- A–Girl, B–Girl, C–Boy, D–Boy
Answer: 1. A–Girl, B–Boy, C–Girl, D–Boy
Number of autosomes in both male and female is same, i.e. 44 or 22 pairs. Sex chromosomes in female is XX and in male is XY. Thus, in the given diagram, 44 + XX–Girl (A and C), 44 + XY–Boy (B and D)
Question 64. Assertion In humans, the gamete contributed by the male determines whether the child produced will be male or female. Reason (R) Sex in humans is a polygenic trait, depending upon a cumulative effect of some genes on X-chromosome.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. In humans, the gametes contributed by male determines the sex of a child. Reason can be corrected as Sex in humans is a polygenic trait, depending upon a cumulative effect of some genes present on Y-chromosome and not on X-chromosome.
Question 65. The cell division that takes place in a zygote is known as
- Meiosis
- Mitosis
- Cleavage
- Differentiation
Answer: 3. Cleavage
Cleavage is the division that takes place in a zygote.
Question 66. Type of cleavage in fertilised egg depends on
- Amount of yolk
- Number of cells
- Number of mitochondria in the sperm
- Number of testes
Answer: 1. Amount of yolk
The rate and nature of cleavage is much affected by the factors like light, temperature, medium, amount of yolk, cytoplasmic organisation, mitosis, etc.
Question 67. Consider the following statements.
- During cleavage, all divisions are meiotic.
- Cleavage occurs two hours after fertilisation.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 4. Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect and can be corrected as Mitotic division takes place at the time of cleavage. It produces unequal cells. It occurs about 30 hours after fertilisation.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 68. In human, cleavage is
- Slow and synchronous
- Fast and synchronous
- Slow and asynchronous
- Fast and asynchronous
Answer: 1. Slow and asynchronous
Cleavage in human is slow and synchronous. Cleavage in mammalian ovum takes place during its passage through the Fallopian tube to the uterus.
Question 69. Cleavage is a unique form of mitotic cell division in which
- There is no growth of cells
- No spindle develops to guide the cells
- The nucleus does not participate
- The plasma membranes of daughter cells do not separate
Answer: 1. There is no growth of cells
Cleavage division does not bring any appreciable increase in the mass of protoplasm in the developing embryo. Cells do not grow in size during cleavage.
Question 70. Meroblastic cleavage refers to which type of division of eggs?
- Incomplete
- Total
- Horizontal
- Spiral
Answer: 1. Incomplete
In meroblastic cleavage, segmentation line does not pass through the egg and remain confined to a part of the egg. Thus, it is an incomplete cleavage.
Question 71. What is true for cleavage?
- Size of embryo increases
- Size of cells decreases
- Size of cells increases
- Size of embryo decreases
Answer: 2. Size of cells decreases
Option is true. Immediately after fertilisation, the fertilised ovum undergoes a series of cell division in close succession. These divisions are cleavage divisions. The cell size decreases during cleavage. Rest options are not true for cleavage.
Question 72. If the first cleavage furrow divides the zygote completely into, the cleavage type is
- Radial
- Equatorial
- Meroblastic
- Holoblastic
Answer: 4. Holoblastic
The complete division of an isolecithal or microlecithal egg into blastomeres is called holoblastic cleavage. In such cleavage, furrow divides the cell completely in two halves.
Blastocyst Formation and Implantation Process MCQs for NEET
Question 73. Holoblastic cleavage may occur in eggs which are
- Oligolecithal only
- Mesolecithal only
- Microlecithal only
- Both oligolecithal and mesolecithal
Answer: 3. Microlecithal only
Holoblastic cleavage occurs in microlecithal eggs. The blastomeres formed by holoblastic cleavage may be equal or unequal in size.
Question 74. Assertion Holoblastic cleavage with almost equal-sized blastomeres is a characteristic of placental animals. Reason (R) Eggs of most mammals, including human are of centrolecithal type.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Holoblastic cleavage is found in the eggs, which are microlecithal (little yolk). In such eggs, the cleavage is complete and thus, it is called holoblastic cleavage. Reason can be corrected as Human eggs are microlecithal not centrolecithal.
Question 75. What is true about cleavage in the fertilised egg in humans?
- It starts while the egg is in Fallopian tube
- It starts when the egg reaches uterus
- It is meroblastic
- It is identical to the normal mitosis
Answer: 1. It starts while the egg is in Fallopian tube
- Option is true about cleavage in the fertilised egg in human. Cleavage in the mammalian zygote occurs during its passage through the Fallopian tube to the uterus. Rest options are not true and can be corrected as Cleavage in humans is holoblastic.
- Cleavage is not identical to mitosis because in former, size of daughter cells decreases but in latter daughter cells are identical to parent cells.
Question 76. The organelles of the sperms that play an important role in the first cleavage of the zygote after syngamy is
- Mitochondria
- Golgi bodies
- Centriole
- Head
Answer: 3. Centriole
In the neck of human sperm, one pair of centriole is present. They also enter with nucleus in the ovum. Rest of sperm is left behind. The first division in zygote takes place due to centrioles. They form spindle fibre for first cell division.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 77. Which organelle of the sperm plays an important role in first cleavage of zygote?
- Distal centriole
- Proximal centriole
- Axial filament
- Mitochondria
Answer: 2. Proximal centriole
Proximal centriole plays an important role in first cleavage of the zygote. The distal centriole degenerates whereas mitochondria and axial filament do not enter the ovum.
Question 78. Select the correct statement?
- Cleavage follows gastrulation
- Yolk content of egg has no role in cleavage
- Cleavage is repeated mitotic division of zygote
- Gastrulation and blastulation are followed by each other
Answer: 3. Cleavage is repeated mitotic division of zygote
- Statement in option is correct. Cleavage is repeated mitotic cell divisions that increase the number of cells, but does not change the size of the original mass of zygote.
- Other statements are incorrect and can be corrected as Cleavage follows fertilisation and the type of cleavage depends upon the amount of yolk present in cell. In the events of fertilisation, blastulation is followed by gastrulation.
Question 79. During second cleavage,
- Division is vertical at right angles to the first division
- Division is horizontal at right angles to the first division
- Two blastomeres divide resulting into four-celled stage
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
The second cleavage occurs within forty hours after fertilisation .It occurs vertically at right angles to the plane of the first, resulting in four blastomeres. Thus, option is correct.
Question 80. The cells formed by cleavage are called
- Blastocysts
- Blastomeres
- Morula
- Trophoblast
Answer: 2. Blastomeres
The cells formed by cleavage are called blastomeres.
Question 81. Cleavage converts zygote into a mass of cells called
- Blastomere
- Blastula
- Gastrula
- Morula
Answer: 4. Morula
Cleavage converts zygote into a mass of cells called morula. Morula is a solid ball of cells resulting from the division of zygote.
Question 82. Cleavage continues up to
- Blastula
- Morula
- Gastrula
- Implantation
Answer: 2. Morula
Cleavage continues up to morula stage in humans. After this, other events of embryonic development begin to occur, e.g. blastulation, formation of germ layer, organogenesis, etc.
Question 83. Embryo at 8-16 cell stage is called
- Blastula
- Morula
- Trophoblast
- All of these
Answer: 2. Morula
Embryo at 8 to 16 stages is called morula stage of embryo.
Question 84. Which one of the following statements about morula in humans is correct?
- It has almost equal quantity of cytoplasm as an uncleaved zygote, but with much more DNA
- It has far less cytoplasm as well as less DNA than in an uncleaved zygote
- It has more or less equal quantity of cytoplasm and DNA as in uncleaved zygote.
- It has more cytoplasm and more DNA than an uncleaved zygote
Answer: 1. It has almost equal quantity of cytoplasm as an uncleaved zygote, but with much more DNA
Statement in option is correct. During cleavage, growth of blastomeres does not occur. Repeated divisions increase the DNA content but increase in the amount of cytoplasm does not occur. Thus, morula has almost equalquantity of cytoplasm as an uncleaved zygote, but with much more DNA. Rest statements are not correct about morula in humans.
Question 85. Consider the following statements.
- In morula stage, the cell divides without increase in size.
- Zona pellucida disappears before the cleavage starts.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statemen t 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect.
Incorrect statement can be corrected as The zygote is covered by zona pellucida, which remains intact till the end of the cleavage.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 86. The mulberry-shaped stage of embryo is called
- Morula
- Gastrula
- Blastula
- Blastomere
Answer: 1. Morula
The fourth cleavage division in embryo results in the formation of 16 celled mulberry-shaped solid mass of cells termed morula
Question 87. Rearrangement of blastomere and formation of central fluid-filled cavity in the morula is called
- Blastulation
- Morulation
- Gastrulation
- None of these
Answer: 1. Blastulation
Blastulation is the formation of a blastula from a morula. The morula is an embryo filled evenly with cells (blastomeres), but the blastula contains a fluid-filled cavity called blastocoels.
Question 88. Blastulation starts in the
- Ovaries
- Fallopian tubes
- Uterus
- Vagina
Answer: 3. Uterus
Blastulation starts inside the uterus after the completion of cleavage.
Question 89. Select human developmental stages and its place of occurrence in normal pregnant woman.
- Late morula –Middle part of Fallopian tube
- Blastula–End part of Fallopian tube
- Blastocyst–Uterine wall
- 8-celled morula–Starting point of Fallopian tube
Answer: 3. Blastocyst–Uterine wall
In a pregnant woman, blastocyst attaches to the uterine wall. Other options represent incorrect place of occurrence of given stages. These can be corrected as Late morula – End part of Fallopian tube Blastula – Uterus 8-celled morula – Middle-end point of Fallopian tube
Question 90. Identify A and B in the figure.
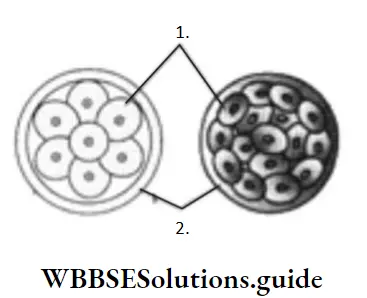
- A–Blastocyst, B–Blastomere
- A–Blastula, B–Plasma membrane
- A–Blastomere, B–Zona pellucida
- A–Zona pellucida, B–Blastomere
Answer: 3. A–Blastomere, B–Zona pellucida
Question 91. Zona pellucida disintegrates at
- Morula stage
- Blastula stage
- After fertilisation
- Gastrula stage
Answer: 2. Blastula stage
Zona pellucida is glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of the ovum. It disintegrates at the blastula stage.
Question 92. Assertion Zona pellucida does not disappear when blastocyst reaches the uterus. Reason (R) Role of zona pellucida is to check the implantation of the blastocyst at the vaginal site.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 4. Both A and R are false
Both A and R are false and can be corrected as Zona pellucida disappears when blastocyst reaches to the uterus and check the implantation of blastocyst at the uterine wall.
Question 93. Assertion Twins may arise from a single egg or from two eggs. Reason (R) One egg gives rise to identical twins by the separation of blastomeres and two eggs produces non-identical twins.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Twins are of two types Identical twins (maternal twins) One egg gives rise to identical twins by complete separation of blastomere. Non-identical twins (paternal twins) Two eggs fertilised by two sperms form non-identical twins
Question 94. Identical twins are also known as
- Monozygotic twins
- Dizygotic twins
- Fraternal twins
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 1. Monozygotic twins
Identical twins or monozygotic twins are two individuals that develop from a single fertilised egg cell (zygote) by its division into two genetically identical parts. Each part eventually gives rise to a separate individual and these twins are therefore, identical in every respect.
Question 95. The structure which differentiate gastrula from blastula
- 3 germ layers
- Micromeres
- Blastocoel
- None of the above
Answer: 1. 3 germ layers
In triploblastic organisms, the gastrula is trilaminar (three – layered) structure. Thus, the structure of three germ layers differentiates the gastrula from blastula.
Question 96. The process of gastrulation begins soon after blastulation and ends with the
- Formation of three germinal layers
- Formation of organs
- Formation of gut
- Development of heart
Answer: 1. Formation of three germinal layers
During gastrulation, the blastula transforms and the cells begin to manifest their different fates. By the end of gastrulation, three different germ layers are formed namely, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Question 97. During gastrulation, the blastocoel is replaced
- Archenterone
- Pseudocoelom
- Coelom
- None of these
Answer: 1. Archenterone
- Gastrulation is the rearrangement of cells that are already present in blastula. On the dorsal side of the blastula, some blastomeres invaginate on the grey crescent and form a slit or groove. This groove forms an archenterone cavity.
- The outer of archenterone is the blastopore and its upper margin is the dorsal lip of blastopore. So, the blastocoel is replaced by archenterone during gastrulation.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 98. The 32 cell stage of the human embryo is
- Smaller than the fertilised egg
- Same size as the fertilised egg
- Two times the size of the fertilised egg
- Four times the size of the fertilised egg
Answer: 2. Same size as the fertilised egg
In human embryo , the 32-celled stage is of same size as the fertilised egg.
Question 99. Which is the correct sequence in the development of man?
- Fertilisation → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
- Zygote → Morula → Blastula → Differentiation
- Fertilisation → Cleavage → Gastrula → Morula → Blastula
- Cleavage → Zygote → Blastula → Morula → Gastrula
Answer: 1. Fertilisation → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
The correct sequence in the development of man is Fertilisation → Zygote → Cleavage → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula Thus, option is correct.
Question 100. Which is a nutritive membrane?
- Trophoblast
- Embryonal knob
- Mesoderm
- Ectoderm
Answer: 1. Trophoblast
Trophoblasts cells form the outer layer of a blastocyst. They provide nutrients to the embryo. Thus, trophoblast is known as nutritive membrane.
Question 101. The cells of the trophoblast in contact with inner mass of cells are called
- Cells of embryo
- Cells of Rauber
- Cells of organogenesis
- Cells of blastula
Answer: 2. Cells of Rauber
Cells of Rauber are the cells of trophoblast in contact with inner mass of cells over the embryonic disc.
Question 102. The formative movements that take place during gastrulation are
- Invagination and involution
- Epiboly and emboly
- Invagination and ingression
- Ingression and delamination
- Only involution
Answer: 2. Epiboly and emboly
Epiboly is a cell movement that occurs in the early embryo at the same time as gastrulation. It is one of many movements in the early embryo. Emboly means the insertion of cells. It is a type of morphogenetic movement that occurs during gastrulation.
Question 103. Ingression is defined as
- The rolling movement of meso and endodermal cells
- Overgrowth of meso on the endodermal
- Detachment of meso and endodermal cells in groups
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
Ingression involves the separation of mesoderm from ectoderm and segregation of these two primary germ layers.
Question 104. Study the figure given below. Identify the option that correctly describes the A, B and the function ofA and B, repectively.
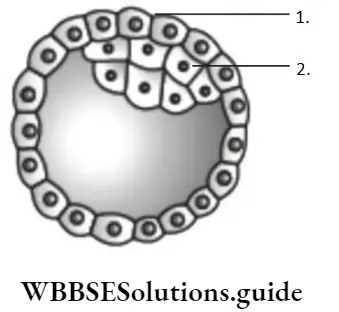
- A–Trophoblast gets attach to the endometrium, B–Inner cell mass differentiated as embryo
- A–Inner cell mass gets attach to the endometrium, B–Trophoblast differentiated as embryo
- A–Trophoblast mass differentiated as embryo, B–Inner cell gets attach to the endometrium
- A–Ectoderm differentiated as embryo, B–Endoderm gets attach to the endometrium
Answer: 1. A–Trophoblast gets attach to the endometrium, B–Inner cell mass differentiated as embryo
Option correctly describe A and B and their respective functions. In the given diagram, A is trophoblast which attaches to endometrium and B is inner cell mass which differentiates as embryo. Rest options are incorrect.
Question 105. Inner mass of cell gives rise to
- Foetal part
- Embryo
- Notochord
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Embryo
The trophoblast encircles the blastocoel and inner mass cell. The inner mass cell is the precursor of the embryo. It means that inner mass gives rise to embryo.
Question 106. In the process of implantation, the blastocyst begins to attach to
- Inner walls of the mesosalpinx
- Endometrium of ovary
- Endometrium of the uterus
- Myometrium of the uterus
Answer: 3. Endometrium of the uterus
Implantation is a process in which a developing embryo, moving as a blastocyst through a uterus, makes contact with the endometrium of the uterus and remains attached to it until birth.
Question 107. After what time duration does the fertilised ovum transplant in the uterus?
- 6 days
- 9 days
- 14 days
- 7 days
Answer: 4. 7 days
Fertilised ovum is transplanted in the uterus 7 days after the fertilisation.
Question 108. During implantation, level of which hormone is highest?
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- LH
- FSH
Answer: 2. Progesterone
Progesterone stimulates the proliferation of endometrium of uterus and prepares it for implantation. Thus, its level is the highest during implantation.
Question 109. Which of the following is a correct sequence in human embryodevelopment?
- Cleavage → Gastrulation →Blastulation
- Blastulation → Cleavage → Gastrulation
- Cleavage → Blastulation → Gastrulation
- Gastrulation → Blastulation → Cleavage
Answer: 3. Cleavage → Blastulation → Gastrulation
The correct sequence in human embryo development is Cleavage → Blastulation → Gastrulation. Thus, option is correct.
Question 110. Termination of gastrulation is marked by
- Obliteration of archenteron
- Closure of neural tube
- Obliteration of blastocoel
- Closure of blastocoel
Answer: 3. Obliteration of blastocoel
Gastrulation starts with the morphogenetic movements of cells of gastrula and terminates with the complete obliteration of cavity of blastula, i.e. blastocoel.
