Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Infertility
Question 1. Inability to conceive or produce children even after many years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Amniocentesis
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Infertility
Infertility is often defined as the condition of not conceiving even after 12 months of regular sexual intercourse without the use of birth control methods.
Question 2. Primary infertile patient is the person who
- Have never conceived in the past
- Had conceived earlier, but unable to conceive again
- Cannot produce ova
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Have never conceived in the past
Primary infertility denotes those patients who have never conceived in lifetime even after one year of active sexual activity without using birth control methods.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Secondary infertility refers to
- Patients who choose not to conceive
- Sterility
- Impotency
- Previous pregnancy, but failure to conceive subsequently
Answer: 4. Previous pregnancy, but failure to conceive subsequently
Secondary infertility indicates the previous pregnancy, but failure to conceive subsequently, i.e. earlier the couple have conceived but now unable to do so.
Question 4. Consider the following statements
- Infertility is the inability to produce viable offspring due to the defects in the female partner.
- Complete lactation helps in contraception.
- Spreading awareness can help create a reproductively healthy society.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- Only 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 3
Statements 2 and 3 are correct. Statement I is incorrect and can be corrected as Infertility is the inability to produce viable offspring due to defects in female or male partner.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 5. ………… is the type of infertility when exact reason is not known.
- Tubal infertility
- Idiopathic infertility
- Impotency
- Cryptorchidism
Answer: 2. Idiopathic infertility
Unexplained infertility is infertility that is idiopathic in the sense that its causes remain unknown even after infertility check up like semen analysis in man, assessment of ovulation and Fallopian tubes in woman, etc.
Question 6. Which of the following diseases causes male infertility?
- Scrotal hernia
- Phimosis
- Orchitis
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- All the listed factors cause male infertility. Scrotal hernia is the abnormal protrusion of part of an organ or tissue through the structures normally containing it.
- Phimosis is a condition in which tight foreskin cannot be pulled back over the head of the penis. Orchitis is an inflammation of one or both testicles.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 7. Orchitis is caused in males due to
- Elongated prepuce
- Inflammation of testicles
- Swelling of spermatid cord
- Inflammation of vas deferens
Answer: 2. Inflammation of testicles
Orchitis is an inflammatory condition of one or both testicles in males. It is generally caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Most cases of orchitis in children are caused by infection with the mumps virus
Question 8. Tubal infertility in females is caused due to
- Absence of ovaries
- Absence of Fallopian tube
- Ligated Fallopian tubes
- Infections in reproductive tract
Answer: 3. Ligated Fallopian tubes
Tubal infertility occurs when the Fallopian tube(s) prevent sperm from reaching the fertilisation site to fertilise an egg or prevents a fertilised embryo from reaching the uterus for pregnancy. So, tubal infertility in females is caused due to ligated Fallopian tube.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 9. In the production of test tube babies,
- Fertilisation and foetus formation is external
- Fertilisation and foetus formation is internal
- Fertilisation is internal and foetus formation is external
- Fertilisation is external and foetus formation is internal
Answer: 4 . Fertilisation is external and foetus formation is internal
- In the production of test tube babies, an ovum is taken out from a woman’s Fallopian tube and fertilised with preserved sperm in a test tube.
- After that zygote is formed that is implanted in the woman’s uterus for further embryonic development. Thus, fertilisation is external and foetus formation is internal in test tube babies.
Question 10. In vitro fertilisation is a technique that involves transfer of which one of the following into the Fallopian tube?
- Embryo only up to 8 cell stage
- Either zygote or early embryo up to 8 cell stage
- Embryo of 32 cell stage
- A foetus of eight weeks
Answer: 2. Either zygote or early embryo up to 8 cell stage
Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT) is an example of In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF). In this, the zygote or early embryos up to 8 blastomeres are transferred into the Fallopian tube. If the embryo has more than 8 blastomeres then, it is transferred into uterus. This process is called as IUT.
Question 11. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in development of test tube baby?
- Removal of unfertilised ovum → In vitro fusion of sperm and ovum → Development of zygote up to 32 cell stage → Embryo transfer into the uterus of mother
- Fusion of sperm and ovum in vitro → Removal of unfertilised ovum and transfer in to the uterus of mother → Formation and development of zygote up to 32 cell stage
- Embryo transfer into the uterus of mother → Formation and development of zygote up to 32 cell stage → Fusion of sperm and ovum in vitro → Removal of unfertilised ovum
- Formation and development of zygote up to 32 cell stage → Fusion of sperm and ovum in vitro → Removal of unfertilised ovum → Embryo transfer into the uterus
Answer: 1. Removal of unfertilised ovum → In vitro fusion of sperm and ovum → Development of zygote up to 32 cell stage → Embryo transfer into the uterus of mother.
Question 12. The first test tube baby was born in
- USA
- France
- England
- India
Answer: 3. England
In, 1978, Louise Joy Brown was the world’s first baby conceived, via. In Vitro fertilisation (IVF). He was born in Manchester, England.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 13. A woman whose womb is used as a substitute for the biological mother to nurse the embryo is called
- Interrogate mother
- Surrogate mother
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Surrogate mother
During IVF, developing embryo is transplanted in the uterus of another female. A woman who nurse the embryo is called surrogate mother.
Question 14. Reduced sperm count in males is referred to as
- Oligospermia
- Azoospermia
- Absolute impotency
- Cryptorchidism
Answer: 1. Oligospermia
Oligospermia is the technical term for reduced sperm count in males.
Question 15. Condition in which motility remains very less is
- Azoospermia
- Polyspermia
- Oligospermia
- Asthenospermia
Answer: 4. Asthenospermia
Asthenospermia refers to the less motility of sperms.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 16. When very less or nil sperms are present in semen, such a condition is referred to as
- Oligospermia
- Polyspermia
- Azoospermia
- None Of These
Answer: 3. Azoospermia
- Azoospermia is the medical condition in which semen contains very little or no sperm. It is associated with infertility, but many forms are amenable to medical treatment.
- In humans, azoospermia affects about 1% of the male population and may be seen in up to 20% of male infertility situations.
Question 17. Infertile couples can now have children with the help of
- Art
- Family planning
- Rch programme
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Art
Infertile couples can now have children with the help of ART, which is Assisted Reproductive Technology. It include in vitro fertilisation, ZIFT, IUT, GIFT, etc.
Question 18. Which of the following is a technique of direct introduction of gametes into the oviduct?
- GIFT
- ET
- IVF
- POST
Answer: 1. GIFT
The technique of direct introduction of gametes into oviduct is called Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT).
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 19. Assisted reproductive technology does not include
- Zygote extra Fallopian transfer
- In vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer
- Artificial insemination
- Gamete intra Fallopian transfer
Answer: 1. Zygote extra Fallopian transfer
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) includes Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
- In vitro Fertilisation (IVF) and Embryo Transfer (ET) Artificial insemination (AI) Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT), ART does not include zygote extra Fallopian transfer.
Question 20. Which of the following techniques are used in IVF?
- ZIFT
- IUT
- ICSI
- AI
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
All the listed techniques are used in 4 F. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 21. Match the following columns.
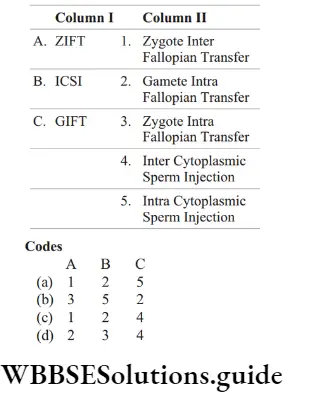
Answer: 2. A–3, B–5, C–2
Question 22. Consider the following statements.
- Both ZIFT and IUT are embryo transfer techniques.
- In both ZIFT and IUT, the number of cells in zygote is same.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect because ZIFT (Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer) is the technique in which zygote or early embryo with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred into the Fallopian tube of female.
- Whereas in IUT, embryo with more than 8 blastomeres is transferred into the uterus. Thus, difference between ZIFT and IUT lies in number of the cells of the zygote.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 23. Artificial insemination means
- Artificial introduction of sperms of a healthy donor into the vagina
- Introduction of sperms of a healthy donor directly into the ovary
- Transfer of sperms of a healthy donor to a test tube containing ova
- Transfer of sperms of husband to a test tube containing ova
Answer: 1. Artificial introduction of sperms of a healthy donor into the vagina
- In artificial insemination technique, the semen of a healthy donor male is collected and is introduced artificially through a flexible polyethylene catheter into the vagina or uterus.
- Best results are obtained when the motile sperm count is more than 10 million. The fertilising capacity of spermatozoa (sperms) is for 24- 48 hours. The procedure may be repeated 2-3 times over a period of 2-3 days.
Question 24. Read the statements below and match them to their respective technologies that are given.
- Collected gametes are made to form the zygote in the laboratory.
- Zygote or early embryo with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred into the oviduct.
- Zygote with more than 8 blastomeres, is transferred into the uterus.
- Fusion of the gametes in the female reproductive tract.
- Transfer of the ovum from a donor to the oviduct of the recipient.
- Sperm is injected into the ovum, in vitro.
Choose the correct answer
- GIFT
- ZIFT
- AI
- ICSI
- IUT
- IVF
- IVI
- In vivo fertilisation
Codes
- 1-F, 2-B, 3-E, 4-H, 5-A, 6-D
- 1-G, 2-B, 3-F, 4-H, 5-A,6-D
- 1-G, 2-B, 3-F, 4-H, 5-C, 6-F
- 1-F, 2-B, 3-A, 4-H, 5-A, 6-G
Answer: 1. 1-F, 2-B, 3-E, 4-H, 5-A, 6-D
Question 25. In case of a couple, where the male is having a very low sperm count, which technique will be suitable for fertilisation?
- Intrauterine transfer
- Gamete intracytoplasmic Fallopian transfer
- Artificial insemination
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Answer: 4. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Infertility due to low sperm count in male partner is overcome by using artificial insemintaion method. In case, the sperm count is very low, a single healthy sperm is injected into an ovum. It is called intra cytoplasmic sperm injection.
Question 26. Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into
- Uterus
- Fallopian tube
- Fimbriae
- Cervix
Answer: 1. Uterus
Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres, formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into uterus for implantation.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 27. First case of IVF-ET technique success was reported by
- Bayliss and Starling Taylor
- Robert Steptoe and Gilbert Brown
- Louis Joy Brown and Benting Best
- Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwar
Answer: 4. Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwar
- First test tube baby (IVF-ET technique) was Louis Joy Brown. He was born to Lesley and Gilbert Brown on July 1978 in England under the assistance of Dr. Patrick Steptoe and Dr. Robert Edward.
- Dr. Robert Edward got Nobel Prize in 2010 for developing a technique for the production of test tube baby.
Question 28. The technique called Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females
- Who cannot produce an ovum
- Who cannot retain the foetus inside uterus
- Whose cervical canal is too narrow to allow passage for the sperms
- Who cannot provide suitable environment for fertilisation
Answer: 1. Who cannot produce an ovum
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females who cannot produce an ovum.
- In this process, the eggs of the donor woman are removed and in a form of mixture with sperm transferred into Fallopian tube of another woman who cannot produce ovum, but can provide suitable environment for fertilisation. Thus in GIFT, site of fertilisation is Fallopian tube, not laboratory.
Question 29. GIFT technique is useful for women,
- Whose fimbriae fail to capture ovum
- Who have sperm antibodies in their cervical secretion
- Who have at least one potent Fallopian tube
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
GIFT is useful for women with atleast one potent Fallopian tube. It can help those where fimbriae does not function efficiently or presence of spermicidal antibodies in cervical secretions.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 30. Which of the following is wrongly matched?
- IUT – Semen collected from husband or donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus
- GIFT – Transfer of embryos with more than 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube
- ICSI – Sperm directly injected into the ovum
- ZIFT – Transfer of embryos with up to 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube
- IVF – Fertilisation outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body
Answer: 2. GIFT – Transfer of embryos with more than 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube
Option (2) is wrongly matched pair and can be corrected as GIFT or Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer is a method of transfer of an ovum collected from a donor female into the Fallopian tube. Rest options are correctly matched pairs.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 31. The stage of cells at which it is transferred into the uterus after induced fertilisation of ova in the laboratory is
- Embryo at 4 blastomeres stage
- Embryo at 2 blastomeres stage
- Morula
- Zygote
Answer: 3. Morula
After induced fertilisation, embryo at morula stage is transferred into the uterus.
Question 32. The technique that involves transfer of embryo into oviduct is called
- ZIFT
- IUT
- GIFT
- AI
Answer: 1. ZIFT
Question 33. In which of the following techniques, the embryos are transferred to assist those females who cannot conceive?
- GIFT and ZIFT
- ICSI and ZIFT
- GIFT and ICSI
- ZIFT and IUT
Answer: 4. ZIFT and IUT
- Option (4) is the correct answer because the techniques by which the embryos are transterred to assist those females who cannot conceive are ZIFT and IUT. Both are Embryo Transfer (ET) methods.
- Options (1), (2) and (3) are incorrect. In GIFT, gamete is transferred into the Fallopian tube of female who cannot produce ova. In ICSI, sperm is directly injected into the ovum.
Question 34. The test tube baby programme employs which one of the following techniques?
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
- Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
- Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Answer: 4. Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
- In test tube baby programme, ova from the female and sperms from the male are collected and are induced to form zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory.
- The zygote with up to 8 blastomeres could then be transferred into the Fallopian tube (ZIFT or Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer) and embryos with more than 8 blastomers, into the uterus (IUT or Intra Uterine Insemination) to complete its further development. Thus, the test tube baby programme employs ZIFT technique.
Question 35. In which technique, the donor semen is artificially introduced to the uterus?
- Intravaginal insemination
- Intrauterine insemination
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
- Gamete intra-Fallopian transfer
Answer: 2. Intrauterine insemination
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) is a method of Artificial Insemination (AI) in which sperms collected either from the husband or a healthy donor are artificially introduced into the uterus of female.
- In this technique, about 0.3 mL of washed and concentrated semen (placing unwashed semen directly into uterus can cause severe cramps) having at least 1 million sperms are artificially introduced through a polyethylene catheter into the uterus of the female.
Question 36. Artificial reproductive techniques are not always applicable because
- It is an expensive technique, hence only few people can afford it
- It is not possible in women with damaged uterine wall
- It has raised ethical, legal, and moral concerns
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
ART is expensive and raise ethical moral and legal issues. Although it help to overcome most infertilities, in case of damaged uterine tissue, it cannot be employed. Thus, option (4) is correct.

