Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Introduction To Genetics
Question 1. The branch of botany dealing with heredity and variation is called
- Geobotany
- Sericulture
- Genetics
- Evolution
Answer: 3. Genetics
Genetics is the branch of botany that deals with the study of heredity and variations.
Question 2. The term heredity refers to
- Transmission of characters
- Mixing of characters
- Blending of inheritance
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Transmission of characters
Heredity (L. Hereditas- Heirship or inheritance) is the transmission of genetic characters from parents to their offspring.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. ‘Father of Genetics’ is
- De Vries
- Mendel
- Bateson
- Robert Hooke
Answer: 2. Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822- 1884) is known as the ‘Father of Genetics’ because he was the first to demonstrate the mechanism of transmission of characters.
Question 4. Term genetics was coined by
- Morgan
- William Bateson
- Johannsen
- Carl Correns
Answer: 2. William Bateson
- Genetics word is derived from the Greek word genesis, which stands for descent. Term genetics was introduced by Bateson in 1906.
- Other options are explained as Morgan gave the function of chromosomes in transmitting heredity. Johannsen coined the term ‘gene’. Carl Correns explained incomplete dominance.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 5. Variation is
- Differences between parents and offsprings
- Differences between individuals of same species
- Differences among the offspring of the same parents
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- All given options describes variation. Variation is the degree of difference in the progeny and between the progeny and the parents.
- The term variation is also used for a single difference in a trait, which can be the difference between individuals of same species or among the offspring of the same parents.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 6. Exact alikeness to parents is absent in humans because of
- Variations produced by crossing over at the time of gamete formation
- Variations produced by chance distribution of chromosome
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
- Genetic variations arise because of recombination or crossing over during gamete formation. Recombination is a very important source of genetic variation among sexually reproducing organisms.
- Variations are also produced by chance distribution or segregation of chromosomes during anaphase-I of meiosis and hence, exact alikeness to parents is absent.
Question 7. Which of the following is the unit of inheritance?
- Phenotype
- Genotype
- Gene
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Gene
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA. Some genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 8. Gene is
- One pair of allele
- Alternative form of a genome
- Present in allelic form on homologous chromosomes
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Gene contain an allelic pair present on homologous chromosomes. These are the alternate form of genome.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 9. Unit of inheritance that expressed a particular trait of organism.
- Factors
- Genes
- Phenotype
- Genotype
Answer: 2. Genes
Genes are the units of inheritance required to express a particular trait of organism. Mendel proposed that something stable was being passed down from parent to F1 to F2- generation and so on, unchanged through the gametes. He called them factors and now these are known as genes.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. Which one of the following best describes a gene?
- A triplet of nucleotide bases
- A specific length of DNA responsible for the inheritance and expression of the character
- A specific length of single-stranded RNA
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 2. A specific length of DNA responsible for the inheritance and expression of the character
Gene is a particular segment of DNA which is responsible for the inheritance and expression of particular character.
Question 11. Genes are composed of
- Histones
- Hydrocarbons
- Polynucleotides
- Lipoproteins
Answer: 3. Polynucleotides
A gene consists of a polynucleotide sequence that encodes a functional polypeptide or RNA sequence.
Question 12. Gene controls
- Heredity, but not protein synthesis
- Protein synthesis, but not heredity
- Both heredity and protein synthesis
- Biochemical action of some enzymes
Answer: 3. Both heredity and protein synthesis
Gene controls protein synthesis through controlling the synthesis of a specific protein and it controls heredity through transmission of hereditary characters from one generation to another. So, it controls both heredity and protein synthesis.
Question 13. Genes are arranged in
- Ribosome
- Chromosome
- Centrosome
- Lysosome
Answer: 2. Chromosome
- Gene is a unit of heredity, composed of DNA and arranged on chromosomes.
- It is a sequence of nucleotides of DNA concerned with a specific function, one or more of these structural genes, coding for protein, may be associated with other genes controlling their expression.
Question 14. The term factor for gene was coined by
- William Bateson
- Johann Mendel
- Johannsen
- F Griffith
Answer: 2. Johann Mendel
During his experiments, Mendel called factors as ‘something unchanged that pass from parent to offspring through the gametes over successive generation’. So, the term factor for gene was coined by Johann Mendel.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 15. Alleles are
- Alternative forms of a gene
- Alternative forms of a gene that govern similar characters of trait
- Which govern only single character of trait
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Alternative forms of a gene
- Alleles are alternative form of a gene that govern contrasting characters of single trait.
- Alleles are various forms of a gene or Mendelian factor which occur on the same locus on homologous chromosome and control the same trait.
Question 16. Assertion (A) A pair of contrasting characters is termed as allele. Reason (R) Two alleles of a gene express equally in an individual.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. Reason can be corrected as Some genes have just a few alleles, but others have many. A dominant allele is one that is expressed to a greater degree than the other alleles.
Question 17. The term ‘allelomorphic’ implies
- Any two characters
- A pair of contrasting characters
- Sex-linked characters
- A pair of non-contrasting characters
Answer: 2. A pair of contrasting characters
Allelomorphs control different expressions or traits of the same character. The term ‘allelomorphic’ implies a pair of contrasting characters.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 18. A gamete normally contains
- Many alleles of a gene
- All alleles of a gene
- Two alleles of a gene
- One allele of a gene
Answer: 4. One allele of a gene
A gamete is produced by the meiosis in cell division. When gametes are produced, the alleles of the gene separate and go into different sex cells. It means a gamete normally contains one allele of a gene.
Question 19. What is not true about alleles?
- Two or more alternative forms of gene are called alleles or allelomorphs
- Round and wrinkled form of genes are alleles of each other
- Alleles occupy different loci on homologous chromosome
- Alleles do not show incomplete dominance
Answer: 3. Alleles occupy different loci on homologous chromosome
- Option (3) is not true and can be corrected as Genes which codes for a pair of contrasting traits is called alleles.
- They are slightly different forms of the same gene, e.g. TT, tt, Tt. They occupy same locus on homologous chromosome. Rest options are correct about allele.
Question 20. If the genotype of an individual consists of only one type of genes at same locus it is known as
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous
- Monoallelic
- Uniallelic
Answer: 1. Homozygous
- The diploid condition in which the alleles at a given locus are identical is called homozygous. In homozygous condition, organisms have two similar genes or alleles for a particular character in a homologous pair of chromosomes, e.g. TT or tt.
- Organisms containing two different alleles or individual containing both dominant and recessive genes of an allele pair, e.g. Tt is known as heterozygous or hybrid.
Question 21. Pureline breed refers to
- Homozygosity
- Heterozygosity
- Homozygosity with only dominant genes
- Heterozygosity and linkage
Answer: 1. Homozygosity
Pureline breed continue to breed true and are formed in homozygous individuals that are identical. So, it refers to homozygosity.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 22. A homozygous individual produces gametes of ………… types.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Many
Answer: 1. 1
A homozygous have only one type of alleles, so they produce only one kind of gamete.
Question 23. If a genotype consists of different types of alleles, it is called
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous
- Monoallelic
- Uniallelic
Answer: 2. Heterozygous
- In heterozygous individuals or hybrids, a character is represented by two contrasting (different) alleles. Out of the two contrasting alleles, only one is able to express its effect in the individual.
- It is called dominant allele. The other allele which does not show its effect in the heterozygous individual is called as recessive allele, e.g. in case of hybrid tall pea plants (Tt), ‘T’ is dominant allele, whereas ‘t’ is recessive allele.
Question 24. Types of gametes produced by a heterozygous individuals is/are
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Many
Answer: 2. 2
As heterozygous individual have two different types of chromosomes, they produce two types of gametes.
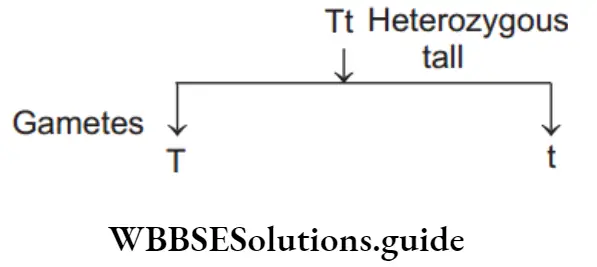
Question 25. The allele which expresses itself in both homozygous and heterozygous condition is called
- Dominant allele
- Recessive allele
- Incomplete dominant allele
- Inherited allele
Answer: 1. Dominant allele
- In heterozygous individuals or hybrids, a character is represented by two contrasting factors called alleles or allelomorphs.
- Out of the two contrasting alleles, only one is able to express its effect in the individual. It is called dominant factor or dominant allele.
- The other allele which does not show its effect in the heterozygous individual is called recessive factor or recessive allele.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 26. The factors which expresses only in homozygous condition is
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Hidden
- Cryptic
Answer: 2. Recessive
The allele which does not show its effect in heterozygous individual is called recessive factor or recessive allele. It expresses itself in the absence of dominant factor or allele or in homozygous condition.
Question 27. Genotype is
- Genetic constitution of an organism
- Genetic constitution of somatic cells
- Genetic constitution of plastids
- Genetic constitution of germ cells
Answer: 1. Genetic constitution of an organism
Genotype designates the genetic make up or genetic constitution of an organism.
Question 28. Group of genes present in an ecosystem is called
- Genotype
- Gene pool
- Genome
- Phenotype
Answer: 2. Gene pool
Aggregate of all the genes and their alleles present in population is called gene pool.
Question 29. Gene flow is the
- Transfer of genes between genetically distinct, but inbreeding population
- Transfer of genes from outside to chromosomes
- Transfer of genes from females to males of an organism
- Transfer of genes from sperms to eggs
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Transfer of genes between genetically distinct, but inbreeding population
- In population genetics, gene flow (also known as gene migration or allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation from one population to another.
- If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations are considered to have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore, effectively be a single population. Thus, option (1) is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 30. The total set of DNA present in a cell is called as
- Genome
- Codon
- Anticodon
- Gene
Answer: 1. Genome
In classical genetics, a genome is a haploid set of chromosome (gamete). In modern molecular biological term, the genome is the heredity information encoded in DNA. Genome is the total set of DNA present in a cell.
Question 31. Gametes are pure because
- They are formed from one parent
- They have one gene
- They have only one allele
- They have one character
Answer: 3. They have only one allele
Gametes are pure because they have only one allele. A gamete may be defined as a haploid cell taking part in sexual fusion. Nuclei from both the gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote.
Question 32. Genes are responsible for the growth and differentiation in an organism through regulation
- Of translocation
- Of transduction and translation
- Of transformation
- Of translation and transcription
Answer: 4. Of translation and transcription
- Different genes in an organism are meant for the synthesis of different proteins. A variety of mechanisms are now known, which regulate gene expression at different levels including transcription, i.e. processing of mRNA and translation.
- Eukaryotic structural gene has two types of interspersed regions, i.e. exons and introns.
Question 33. Identify the correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest.
- Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
- Chromosome, genome, nucleotide, gene
- Chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide
- Genome, chromosome, nucleotide, gene
Answer: 1. Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
- The correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest is genome, chromosome, gene, and nucleotide. In genome, all the genes are contained in a single set of chromosomes.
- The instructions in our genome are present in the form of DNA. A gene is a segment of DNA or
chromosome situated at a specific locus (gene locus). - A nucleotide is the basic unit of DNA, made up of a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid, and a nitrogenous base.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 34. Phenotype of an organism is the result of
- Genotype and environment interactions
- Mutations and linkages
- Cytoplasmic effects and nutrition
- Environmental changes and sexual dimorphism
Answer: 1. Genotype and environment interactions
- The external manifestation, morphological, physiological expression of an individual with regard to one or more characters is called phenotype. For recessive genes, phenotype and genotype are similar.
- For dominant genes, the phenotype is same for both homozygous states. Phenotype is influenced by environment as well as age. Many phenotypes are determined by multiple genes.
- Thus, the identity of phenotype is determined by genotype and environment.

