Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Male Reproductive System
Question 1. Human beings are
- Homosexual
- Monoecious
- Dioecious
- Hermaphrodite
Answer: 3. Dioecious
Dioecious is a characteristic of a species, which mean presence of male and female reproductive. Organs in two individual. So, human beings are dioecious.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. In humans, the primary sexual organs are called
- Gametes
- Gonads
- Mammary glands
- Gemmules
Answer: 2. Gonads
The reproductive system of sexually reproducing animal consists of primary sexual organs called gonads, which produce gametes and hormones.
” human reproduction mcqs class 12″
Question 3. The pouch in which the testes are suspended outside the abdominal cavity is
- Tunica albuginea
- Inguinal canal
- Epididymis
- Scrotum
Answer: 4. Scrotum
Scrotum is a pouch of deeply pigmented skin, divided into two separate sacs. Each sac contains one testis.
Question 4. Scrotum remains connected with abdomen or pelvic cavity by
- Spermatic cord
- Inguinal canals
- Foreskin
- Iobules
Answer: 2. Inguinal canals
The scrotum remains connected with the abdomen or pelvic cavity by inguinal canals.
NEET Biology Male Reproductive System MCQs with answers
Question 5. The passage through which the testes descend from the abdominal cavity in the scrotum is called
- Alimentary canal
- Inguinal canal
- Vertebral canal
- Spinal canal
Answer: 2. Inguinal canal
“what is true for cleavage “
The inguinal canals are two passages in the anterior abdominal wall through which the testis descends from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum.
Important MCQs on Male Reproductive System for NEET
Question 6. If inguinal canals fail to close or reopen, it results in
- Impotency
- Cryptorchidism
- Testes swelling
- Inguinal hernia
Answer: 4. Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of abdominal cavity contents through the inguinal canal in which inguinal canal unable to close or reopen. This may cause pain or discomfort especially during coughing, exercise or bowel movements.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 7. Gubernaculum connects
- Testes with scrotum
- Testes with ovaries
- Ovaries with scrotum
- Testes with epididymis
Answer: 1. Testes with scrotum
“class 12th biology chapter 3 mcq “
- In males, the upper part of the gubernaculum degenerates. The lower part persists as the gubernaculum testis.
- This ligaments connect the testis to the most inferior portion of the scrotum, tether it in place and limit the degree to which the testis can move within the scrotum. So, gubernaculum connects testes with scrotum.
Question 8. Internally scrotum is divided into two compartments by
- Septum scroti
- Trabeculum
- Spermatic cord
- Septum
Answer: 1. Septum scroti
Internally scrotum is divided into two compartments by a muscle septum called septum scroti.
Question 9. Testes are protected in scrotum because they
- Produce heat
- Produce sperm
- Help in micturition
- Control the ambient temperature lower than general body
Answer: 4. Control the ambient temperature lower than general body
In mammals, scrotal sac or scrotum acts as a thermoregulator and maintain the ambient temperature of testes which is 2°C lower than the normal temperature of the body. It protects the sperms against relatively high temperature.
NEET previous year questions on Male Reproductive System
Question 10. In most mammals, the testes are located in scrotal sac for
- More space to visceral organs
- Sex differentiation
- Independent functioning of kidney
- Spermatogenesis
Answer: 4. Spermatogenesis
In mammals, testes are located in scrotal sac to carryout the process of spermatogenesis.
Question 11. What will happen, if the temperature of scrotal sac temporarily goes to about 4°C or more than the body temperature?
- Testes will be pushed into abdomen
- Increased sperm formation
- Scrotal sacs contract and come close to body
- Spermatogenic tissue will be destroyed
Answer: 4. Spermatogenic tissue will be destroyed
Higher temperature (4°C) would damage the sperm inside the testicles due to the damage of spermatogenic tissue.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 12. Consider the following statements.
- During cold, scrotum becomes wrinkled.
- Scrotum prevents heat loss during in low temperature conditions.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
When the temperature is too low, the tunica dartos muscle contracts, thus cause the scrotal skin to wrinkle. Due to this, the scrotum has a smaller surface area and thus, heat loss is prevented.
“hormones secreted by placenta “
Question 13. Which muscle pulls the scrotum towards the body during low temperature?
- Dartos muscles
- Cremaster muscles
- Alary muscle
- Corpora cavernosa
Answer: 2. Cremaster muscles
Cremaster muscles contract and pull the scrotum towards the body during low temperature.
Question 14. The muscles that keep the testes warm are
- Cremaster
- Dartos
- Both 1 and 2
- Mesorchium
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
In cold weather, by contracting simultaneously, cremaster muscles pull the testes toward body and dartos muscle shrink the scrotal sac. Thus, the surface area of scrotum is decreased to retain heat and keep testes warm.
Question 15. Each compartment of scrotum encloses
- Testis and epididymis
- Testis, epididymis, a spermatic cord
- Testis, spermatic cord and a part of vas deferens
- Testis, epididymis, a spermatic cord and part of vas deferens
Answer: 4. Testis, epididymis, a spermatic cord and part of vas deferens
- Scrotum in male reproductive system is a thin external sac of skin that is divided into two compartments.
- Each compartment contains one of the two testes, the glands that produce sperm and one of the epididymis, where the sperm is stored. It also contains a spermatic cord and part of vas deferens.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 16. The testis during early and middle foetal life is located in the
- Inguinal canal
- Abdominal cavity
- Pelvic cavity
- Scrotal sacs
Answer: 2. Abdominal cavity
During early and middle foetal life, the testes are located in the abdominal cavity. They descend to the scrotal sac during the late foetal development.
Question 17. Testes begin to descend from abdomen during 3rd week of gestation and descend is completed by …… week of gestation.
- 10th
- 15th
- 28th
- 18th
Answer: 3. 28th
- During seventh month or 28th week of development, testes descend permanently into the respective scrotal sacs.
- Thus, testes begin to descend from abdomen during 3rd week of gestation and descend is completed by 28th week of gestation.
“testicular lobules “
Question 18. Failure of descend of testis in scrotal sacs is called
- Vasectomy
- Tubectomy
- Cryptorchidism
- Impotency
Answer: 3. Cryptorchidism
The failure of descend of testes into scrotum is called cryptorchidism. It is caused by deficient secretion of testosterone by foetal testes. It leads to sterility.
Question 19. Testis is ………… in origin.
- Ectodermal
- Mesodermal
- Endodermal
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 2. Mesodermal
Mesoderm is a primary germ layer of the embryo lying between the other two germ layers, namely ectoderm and endoderm. The testis is mesodermal in origin.
Question 20. Assertion Testes are located in the scrotum, outside the coelom. Reason (R) A vaginal coelom partly surrounds the testis in the scrotum.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. Reason can be corrected as Vaginal coelom partly surrounds the testis in scrotum is a wrong statement because vagina is the part of external genitalia (vulva) in the female reproductive system and scrotum is a sac-like structure in which testes are suspended in males.
NEET quiz on Male Reproductive System with solutions
Question 21. Gubernaculum cord is a contractile structure that
- Pulls down the testis during breeding season into the scrotal sac
- Allows daily migration of the testis from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum
- Helps ejaculation of spermatozoa from testis
- Keeps the testis in proper position
Answer: 4. Keeps the testis in proper position
Gubernaculum cord is a structure which keeps the testis in its actual position. It is also called the caudal genital ligament.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 22. A connective tissue cord extending between the testis and abdominal wall is called
- Testis cord
- Gubernaculum
- Mesentric cord
- Spermatic cord
Answer: 4. Spermatic cord
The spermatic cord extends between testes and abdominal wall. This passes through the inguinal canal.
Question 23. Human possess pair of testes
- Two
- One
- Three
- Four
Answer: 2. One
In man, one pair of testis is present.
Question 24. Length and width of testis is
- 4-5 cm and 2-3 cm
- 5-6 cm and 3-4 cm
- 4-5 cm and 4-5 cm
- 7-8 cm and 8-9 cm
Answer: 1. 4-5 cm and 2-3 cm
Each human testis is oval in shape with a length of about 4 to 5 cm and a width of about 2 to 3 cm.
Question 25. An incomplete peritoneal covering of testes is called
- Tunica vaginalis
- Tunica albuginea
- Tunica vascularis
- Tunica reticulosa
Answer: 1. Tunica vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is the pouch of serous membrane that covers the testes. It is derived from the abdominal peritoneum.
Question 26. Innermost covering of testes is
- Tunica reticulosa
- Tunica vaginalis
- Tunica albuginea
- Tunica vasculosa
Answer: 4. Tunica vasculosa
The tunica vasculosa is the innermost vascular layer of the testis. It consists of a plexus of blood vessels held together by delicate areolar tissue.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 27. The capsule enclosing testis of mammal is called as
- Tunica albuginea
- Tunica membrana
- Tunica vaginalis
- Tunica vasculosa
Answer: 1. Tunica albuginea
Each testis is externally covered by a white fibrous capsule called tunica albuginea, which is produced inside the testis as fibrous septa.
Question 28. The compartments in mammalian testes are known as
- Testicular lobules
- Seminiferous tubules
- Sertoli cells
- Interstitial cells
Answer: 1. Testicular lobules
There are about 250 compartments in each human testis called testicular lobules.
Question 29. How many compartments (approximately) are there in each human testis?
- 250
- 300
- 350
- 400
Answer: 1. 250
There are about 250 compartments in each human testis called testicular lobules.
“human reproduction class 12 important questions pdf “
Question 30. Testicular lobules contain
- 3-5 seminiferous lobules
- 5-7 seminiferous lobules
- 2-6 seminiferous tubules
- 1-3 seminiferous tubules
Answer: 4. 1-3 seminiferous tubules
Each testicular lobule contains 1-3 seminiferous tubules. These are coiled tubules that constitute most of the testis and enclose spermatogenic tissue.
Question 31. Which of the following is correct about mammalian testes?
- Graafian follicles, Sertoli cells, Leydig’s cells
- Graafian follicles, Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules
- Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig’s cells
- Graafian follicle, Leydig’s cells, Seminiferous tubule
Answer: 3. Sertoli cells, Seminiferous tubules, Leydig’s cells
Option 3. is correct. Other options are incorrect about mammalian testes because Graafian follicles are present in human ovaries.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 32. Consider the following statements.
- The length of single seminiferous tubule is about 50-60 cm.
- Seminiferous tubule constitutes about 90% of testis.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 33. Seminiferous tubules are lined by
- Squamous germinal epithelial cells
- Cuboidal germinal epithelial cells
- Ciliated germinal epithelial cells
- Non-ciliated germinal epithelial cells
Answer: 2. Cuboidal germinal epithelial cells
Seminiferous tubules consist of a multilayered cuboidal germinal epithelium that helps in spermatogenesis.
NEET expected MCQs on Male Reproductive System 2025
Question 34. Inflammation of the seminiferous tubules could interfere with the ability to
- Make semen alkaline
- Secrete testosterone
- Produce spermatozoa
- Eliminate urine from the bladder
Answer: 3. Produce spermatozoa
The main function of seminiferous tubules is to produce spermatozoa. Inflammation of seminiferous tubules could interfere with its function.
Question 35. Inner portion of the seminiferous tubules contains
- Sertoli cells
- Male germ cell
- Both 1 and 2
- Interstitial or Leydig cell
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Inner portion of seminiferous tubules is lined by male germ cells and Sertoli cells. Thus, option is correct.
Question 36. From the germinal epithelium arises
- Sertoli cells
- Interstitial cells
- Spermatogonium
- Sustentacular cells
Answer: 3. Spermatogonium
The cuboidal cells in germinal epithelium of seminiferous tubules undergo mitosis to produce spermatogonium.
Question 37. Sertoli’s cells are found
- Between the seminiferous tubules
- In the germinal epithelium of ovary
- In the upper part of the Fallopian tube
- In the germinal epithelium of the seminiferous tubules
Answer: 4. In the germinal epithelium of the seminiferous tubules
Sertoli cells or nurse cells are found in the germinal epithelium of seminiferous tubules, which nourish the developing sperms.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 38. Sertoli cells are also called
- Sustentacular cells
- Sperm cells
- Interstitial cells
- Leydig cells
Answer: 1. Sustentacular cells
Sertoli cells are also called sustentacular cells because they provide supporting framework in which germ cells are embedded. They are irregular columnar in shape and its basal aspect is attached to basement membrane by hemidesmosomes.
Question 39. Sertoli cells are involved in
- Excretion
- Respiration
- Nutrition of sperms
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Nutrition of sperms
Sertoli cells function as nurse cells as they provide nutrition to sperms. They also help in phagocytising defective sperms and secrete inhibin hormone.
Question 40. The part of blood-testis barrier in males is formed by
- Scrotum
- Epididymis
- Sertoli cells
- Leydig cells
Answer: 3. Sertoli cells
The Blood-Testis barrier (BTB) is an inter-Sertoli functional complex that is found around the basal aspect of seminiferous epithelium. The BTB formed by Sertoli cells isolates developing spermatogonia from blood.
Question 41. All of the following are found in seminiferous tubules except
- Sertoli cells
- Leydig’s cells
- Spermatids
- Spermatogonia
Answer: 2. Leydig’s cells
Leydig’s cells or interstitial cells are present in interstitial space in the outer region of seminiferous tubules.
Question 42. Leydig’s cells are present in
- Kidneys and seminiferous tubules
- Seminiferous tubules of testes
- Connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules of testes
- Cells lining the epidermis of the testes
Answer: 3. Connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules of testes
In between the seminiferous tubules, connective tissue contains the groups of polygonal cells called interstitial or Leydig’s cells.
Question 43. Which of the following is the endocrine tissue of testes?
- Epidermis
- Inguinal canal
- Leydig cells
- Spermatic cord
Answer: 3. Leydig cells
Leydig’s cells are endocrine in function as they secrete male sex hormone, androgens.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 44. Interstitial cells secrete
- Androgens
- Oestrogen
- FSH
- Inhibin
Answer: 1. Androgens
Interstitial cells secrete androgen (testosterone), i.e. male sex hormones.
NEET Biology Male Reproductive System MCQs with explanations
Question 45. Select the incorrect statement about Leydig cells.
- They are found in groups up to ten cells around seminiferous tubules
- These are known as polygonal cells
- These cells have eosinophilic cytoplasm and large round nucleus
- Lipid content is almost negligible in Leydig cells
Answer: 4. Lipid content is almost negligible in Leydig cells
Statement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as Lipid content is abundant in Leydig cells because they are responsible for testosterone production which is a steroid hormone.
Question 46. Select the option which correctly matches the endocrine gland with its hormone and its function. Endocrine gland > Hormone > Function.
- Ovary > FSH > Stimulates follicular development and the secretion of oestrogens
- Placenta > Oestrogen > Initiates secretion of the milk
- Corpus luteum > Oestrogen > Essential for maintenance of endometrium
- Leydig cells > Androgen > Initiates the production of sperms
Answer: 4. Leydig cells > Androgen > Initiates the production of sperms
Option 4. is correctly matched as Leydig cells > Androgens > Initiates the production of sperms. Other options are incorrectly matched. These can be corrected as
- FSH is secreted by anterior pituitary gland and not by ovary.
- Corpus luteum secretes progesterone to maintain endometrium.
- Placenta secretes oxytocin to initiate milk secretion
Question 47. Assertion (A)Each testis is attached to the abdominal wall by a ligament. Reason (R) Leydig or interstitial cells secrete androgens of which testosterone is the most potent.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Each testis is attached to abdominal wall by a testicular ligament.
- Testes develop retroperitoneally on posterior abdominal wall and descend to scrotum before birth, under the influence of testosterone. This is the most potent androgen and is being secreted by Leydig or interstitial cells of testis.
Question 48. The seminiferous tubules of the testis opens into the vasa efferentia through
- Vasa deferentia
- Rete testis
- Epididymis
- Seminiferous tubules
Answer: 2. Rete testis
The seminiferous tubules are closed at one end, but on the other side they join to a network called rete testis from where fine ciliated ductules called vasa efferentia arises.
Question 49. Numerous fine ducts arising from rete testis are called
- Vas deferens
- Vasa efferentia
- Tubuli recti
- Epididymis
Answer: 2. Vasa efferentia
12-20 Numerous fine ducts called vasa efferentia arise from rete testis to the vas deferens.
Question 50. Vasa efferentia are muscular tubes, each of which connects
- An epididymis to vas deferens
- Vas deferens to seminal vesicle
- Rete testis to vas deferens
- Rete testis to epididymis
Answer: 4. Rete testis to epididymis
Vasa efferentia arise from the rete testis and open into epididymis located along the posterior surface of rete testis. The epididymis leads to vas deferens.
Question 51. If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from
- Testes to epididymis
- Epididymis to vas deferens
- Ovary to uterus
- Vagina to uterus
Answer: 1. Testes to epididymis
If the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system gets blocked, the gametes will not be transported from testes to epididymis because vasa efferentia connects the testis to epididymis.
Question 52. The vasa efferentia exit the testis and open into the …A… located along the …B… surface. Here, A and B refer to
- A–rete testis, B–epididymis
- A–epididymis, B–rete testis
- A–epididymis, B–posterior
- A–epididymis, B–anterior
Answer: 3. A–epididymis, B–posterior
- As the vasa efferentia leave the testis, they enter the larger, upper portion of the epididymis (A), located along the posterior surface.
- The vasa efferentia then join to form a single, coiled ductus epididymis, in the middle region of the epididymis.
Question 53. Consider the following statements.
- Epididymis is small, curved, elongated structure in males.
- Epididymis is found along the anterior side of each testis.
Choose the correct options.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
Statement I is correct, but II is incorrect. The epididymis is a small, curvedshaped elongated structure which is found along the posterior side of each testis.
Question 54. Wolffian duct forms
- Epididymis
- Oviduct
- Ejaculatory duct
- Urethra
Answer: 1. Epididymis
- The Wolffian duct (also known as archinephric duct, Leydig’s duct and mesonephric duct) is a paired organ found in mammals including humans during embryogenesis.
- It connects the primitive kidney, Wolffian body (mesonephros) to the cloaca and serves as the progenitor for certain male reproductive organs.
- In an ale, it develops into a system of connected organs between the testis and the prostate, namely rete testis, efferent ducts, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle and prostate.
Question 55. In man, the epididymis from anterior to posterior is divided into
- Caput, corpus and cauda
- Corpus, vas deferens and caput vas deferens
- Corpus, cauda and caudal region
- Caput, cauda and vas deferens
Answer: 1. Caput, corpus and cauda
The epididymis consists of three parts, i.e. caput, corpus and cauda
Question 56. The head of the epididymis at the head of the testis is called
- Cauda epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Caput epididymis
- Gubernaculum
Answer: 3. Caput epididymis
The caput epididymis is the head region of epididymis and is located on superior side of the testis.
Question 57. The narrow middle part of epididymis is called
- Caput epididymis
- Cauda epididymis
- Corpus epididymis
- All of the above
Answer: 3.Corpus epididymis
The corpus epididymis is narrow middle and highly convoluted part which connects the caput epididymis to cauda epididymis.
Male Reproductive System mock test for NEET preparation
Question 58. Sperms are stored temporarily in
- Vasa deferentia
- Vasa efferentia
- Epididymis
- Rete testis
Answer: 3. Epididymis
In epididymis, the sperms are stored for few hours to a few days until it comes out along with ejaculations.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 59. In the male reproductive system, sperm are concentrated in the
- Rete testis
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicle
Answer: 2. Epididymis
In males, sperms are concentrated in the epididymis. Sperm concentration refers to the number of sperm per unit volume of semen.
Question 60. The sperm becomes mature and completely motile while in the
- Rete testis
- Cauda epididymis
- Vasa deferentia
- Seminal vesicle
Answer: 2. Cauda epididymis
Spermatozoa formed in the testis enter the caput epididymis, progress to the corpus and finally reach the cauda region, where they are stored, become matured and gain motility.
Question 61. The movement of spermatozoa from the epididymal duct and seminal fluid into the ejaculatory duct to urethra is under the control of
- Parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve
- Parasympathetic nerve only
- Sometimes sympathetic and sometimes parasympathetic nerves
- Sympathetic nerve only
Answer: 4. Sympathetic nerve only
The movement of spermatozoa, from the epididymal duct and seminal fluid into the ejaculatory duct to the urethra is under the control of sympathetic nervous system.
Question 62. Cauda epididymis leads to
- Vas efferent
- Vas deferens
- Ejaculatory duct
- Urethra
Answer: 2. Vas deferens
Vas deferens is large duct that arises from cauda epididymis and reaches up to seminal vesicles.
Question 63. ‘XX’ is a thick structure of male reproductive system which arises from cauda epididymis. ‘XX’ are 2 in number and its lining has many stereocilia. Identify ‘XX’.
- Vasa efferentia
- Vasa deferentia
- Penis
- Scrotum
Answer: 2. Vasa deferentia
Vasa deferentia emerge from the cauda epididymis on each side leave the scrotal sac and enter the abdominal cavity through inguinal canal. They are lined by many stereocilia to transport the sperms.
Question 64. Vas deferens is also known as
- Spermatic ducts
- Seminiferous tubule
- Seminal ducts
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 3. Seminal ducts
The vas deferens is also called seminal duct. It is a part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates
Question 65. Vas deferens passes through
- Haversian canal
- Inguinal canal
- Neural canal
- Central canal
Answer: 2. Inguinal canal
The vas deferens pass through the inguinal canal into pelvis where it is joined by the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct. The latter passes through the prostate into the urethra.
Question 66. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines one of the following.
- Vas deferens
- Buccal cavity
- Bowman’s capsule
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Vas deferens
The mucosa of the vas deferens forms low longitudinal folds which are lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
NEET Male Reproductive System practice test online
Question 67. If the vas deferens of a man is surgically disconnected
- Sperms in the semen will be without nuclei
- Semen will be without sperms
- Spermatogenesis will not occur
- Sperms in the semen will be non-motile
Answer: 2. Semen will be without sperms
Function of vasa deferentia is the conduction of sperms from epididymis to penis. If it is surgically disconnected, the semen would not contain sperms.
Question 68. Vasa deferentia and seminal vesicle together form the
- Caput epididymis
- Corpus epididymis
- Ejaculatory duct
- Rete testis
Answer: 3. Ejaculatory duct
The vas deferens loops over urinary bladder, where it joins a duct from seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 69. Ejaculatory duct contains
- Sperms
- Secretion of seminal vesicles
- Both 1 and 2
- Testosterone
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Ejaculatory ducts carry sperms and secretion of seminal vesicles because it is formed by the union of vas deferens and the duct of seminal vesicle. Thus, option is correct.
Question 70. Both ejaculatory ducts open into
- Urinary bladder
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle
- Urethra
Answer: 4. Urethra
Both ejaculatory ducts pass through prostate gland and open into urethra at the seminal colliculus.
Question 71. The shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary system in the human male is
- Urethra
- Ureter
- Vas deferens
- Vasa efferentia
Answer: 1. Urethra
Urethra is the urinary duct which originates from the neck of urinary bladder and opens to the exterior at the tip of penis in males. It is a common pathway for passage of urine and semen.
Question 72. Select the correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system.
- Testis → Epididymis → Vasa efferentia → Rete testis → Inguinal canal → Urethra
- Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Urethral meatus
- Seminiferous tubules → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Inguinal canal → Urethra
- Testis → Epididymis → Vasa efferentia → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Inguinal canal → Urethra → Urethral meatus
Answer: 2. Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Urethral meatus
The correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system is Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Urethral meatus.
Question 73. Identify A to F in the diagram given below.
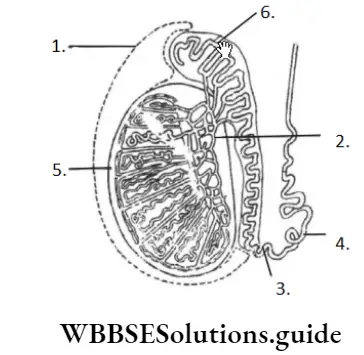
- A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Caput epididymis, D–Vas deferens, E–Septa of testis, F–Cauda epididymis
- A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Cauda epididymis, D–Mediastinum testis, E–Vas deferens, F–Caput epididymis
- A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Cauda epididymis, D–Vas deferens, E–Tunica albuginea, F–Caput epididymis
- A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Caput epididymis, D–Mediastinum testis, E–Vas deferens, F–Cauda epididymis
Answer: 3. A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Cauda epididymis, D–Vas deferens, E–Tunica albuginea, F–Caput epididymis
In given diagram, A–Tunica vaginalis, B–Rete testis, C–Cauda epididymis, D–Vas deferens, E–Tunica albuginea, F–Caput epididymis.
Question 74. External genitalia of male is called
- Testis
- Penis
- Scrotum
- Hemipenis
Answer: 2. Penis
External genitalia of male is called penis. It serves as the passage for both urine and sperm.
Question 75. Penis is located
- In front of scrotum
- Inside the abdomen
- Both 1 and 2
- Behind the scrotum
Answer: 1. In front of scrotum
The penis is located above or in front of the scrotum. It is made up of spongy tissue and blood vessels. The shaft of the penis surrounds the urethra and is connected to the pubic bone.
Question 76. ……………… is the external opening of penis.
- Ureter
- Urinary bladder
- Urethral meatus
- Prepuce
Answer: 3. Urethral meatus
The urethra originates from the urinary bladder and extends through the penis to its external opening called urethral meatus.
Question 77. Prepuce is
- Covering of glans penis
- Copulatory organs of birds
- Female organ equal to penis
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Covering of glans penis
The prepuce is the primary covering for the glans and inner mucosal lining of the penis. These internal organs are shielded by the foreskin to prevent abrasion, drying and contamination by dirt.
Question 78. Select the correct statement with respect to prepuce.
- It is a junctional mucocutaneous tissue
- It is composed of squamous pentalaminar epithelium
- It is also called as frenulum or foreskin
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the given statements are correct regarding prepuce.
Question 79. The anterior tissue of penis is called
- Corpora cavernosa
- Corpus spongiosum
- Dartos muscle
- Cremaster muscle
Answer: 2. Corpus spongiosum
Corpus spongiosum is a column of spongy tissue that runs through the shaft and glans of the penis and thus, it forms the anterior tissue of penis.
It surrounds the urethra. It contains blood vessels that fill with blood aid in penis erection.
Question 80. The glans penis is enlarged due to
- Corpus cavernosum
- Corpus spongiosum
- Corpus callosum
- Corpus albicans
Answer: 2. Corpus spongiosum
The penis becomes enlarged, hardened and erect as a result of increased blood pressure in corpus spongiosum that is also considered erectile tissue.
Question 81. The glans surface of penis which has sebaceous glands produces a waxy secretion called
- Smegma
- Sebum
- Wax oil
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 1. Smegma
Smegma is a waxy secretion of the oil (sebaceous) glands around the genitals. In men, smegma often found under the foreskin of the penis.
Question 82. Consider the following statements.
- The human penis consists of four erectile tissues.
- Corpus spongiosum forms the dorsal column in penis.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 4. Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect and can be corrected as The penis consists of three columns of erectile tissue that are wrapped in connective tissue and covered with skin.
- The two dorsal columns are the corpora cavernosa. The single, midline ventral column surrounds the urethra and is called as corpus spongiosum.
Question 83. In the body of penis, postero-lateral tissues are called
- Corpus spongiosum
- Dartos muscles
- Cremaster muscles
- Corpora cavernosa
Answer: 4. Corpora cavernosa
Corpora cavernosa is the postero-lateral tissue of penis. It is the sponge-like tissue which contains most of the blood in penis during erection.
Question 84. Given below are various structures of male reproductive system and their characteristics.
- Vasa efferentia – Arise from rete testis
- Epididymis – Leads to vas deferens
- Suspensory ligament – Found at the tip of penis
- Number of suspensory – Four ligaments
Choose the option containing incorrectly matched pairs.
- 1 and 2
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 3
Answer: 2. 3 and 4
Pairs 3 and 4 are incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as Two suspensory ligaments that are composed of primarily elastic fibres, support the penis at its base. Other options are correctly matched pairs.
Question 85. Which of the following is/are the accessory gland/s of the male reproductive system?
- Seminal vesicles
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The accessory genital glands in male, along with their duct systems are collectively called secondary sex organs. These are seminal vesicles, prostate and Cowper’s glands. Thus, option 4. is correct.
Question 86. Seminal vesicles are present at the base of
- Penis
- Bladder
- Testis
- Prostate gland
Answer: 2. Bladder
Seminal vesicles are present at the base of urinary bladder and join the ejaculatory duct.
Question 87. Seminal vesicle is present between
- Prostate gland and urethra
- Urinary bladder and rectum
- Above the testis
- Near epididymis
Answer: 2. Urinary bladder and rectum
The seminal vesicles are located between the urinary bladder and the rectum as it is present below the seminal vesicle and above the rectum.
Question 88. Select the incorrect statement.
- Seminal gland is derived from the mesonephric duct
- Prostaglandins in seminal gland secretions suppress female immune response to foreign semen
- Secretion of seminal gland is acidic in nature
- Inner layer of seminal gland is comprised of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Answer: 3. Secretion of the seminal gland is acidic in nature
Statement in option is incorrect. Secretions of seminal gland are alkaline in nature. It neutralises acidity of male urethra and vagina to facilitate the survival of spermatozoa.
Question 89. 60% of semen is produced by the
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle
- Cowper’s gland
- Testes
Answer: 2. Seminal vesicle
Seminal vesicle produces 60% of the semen and provides alkaline medium in the sperm for the neutralisation of vaginal acidic medium.
Question 90. The nutritive medium in the ejaculated sperm is obtained from
Seminal fluid
Vaginal fluid
Uterine fluid
Prostatic fluid
Answer: 1. Seminal fluid
Seminal fluid contains sugar, citric acid, proteins, inorganic phosphorus, prostaglandins and various enzymes. The sugar is a source of energy (nutritive medium) for the sperms.
Question 91. Which male accessory reproductive structure secretes fluid containing ascorbic acid, flavins and prostaglandins?
- Epididymis
- Seminal vesicles
- Vas deferens
- Prostate gland
Answer: 2. Seminal vesicles
Seminal vesicle secretes seminal fluid containing ascorbic acid, flavins and prostaglandins. It form a 1.5 to 2.5 mL volume of ejaculate.
Question 92. Seminal plasma in human males is rich in
- Fructose and calcium
- Glucose and calcium
- DNA and testosterone
- Ribose and potassium
Answer: 1. Fructose and calcium
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes. It provides a medium for transport of sperms, nourishes and activates sperms.
Question 93. Select the correct statement regarding the function of seminal fluid is
- Maintain motility of sperms
- Maintain the viability of Sperms
- Provide energy and nourishment
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The seminal fluid helps to maintain motility, viability and provides energy for the nourishment of sperm.
Thus, option is 4. correct.
Question 94. Prostate gland is a
- Digestive gland
- Sperm producing gland
- Semen secreting accessory gland of male
- Hormone producing gland of the ovary
Answer: 3. Semen secreting accessory gland of male
- The prostate gland is a single large accessory gland that surrounds the urethra. It produces a milky, slightly acidic secretion (about 6.5pH) which forms 25% of the volume of semen.
- This secretion contains citric acid, enzymes and prostaglandins. Secretion of the prostate gland nourishes and activates the spermatozoa to swim.
Question 95. Prostate gland is present
- Below the kidney
- Below the ureter
- Between the urinary bladder and penis
- Between the penis and scrotum
Answer: 3. Between the urinary bladder and penis
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis, just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the centre of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
Question 96. Select the incorrect statement regarding prostate gland.
- It secrete proteolytic enzymes
- It comprises 90% of semen volume
- The secretions of prostate gland are slightly acidic in nature
- None of the above
Answer: 2. It comprises 90% of semen volume
Statement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as The prostate gland secretes prostate fluid, one of the components of semen and constitutes 30% of it.
Question 97. The function of prostate gland is
- Storage of semen
- Provide motility to sperms
- Formation of semen
- Release of hormones
Answer: 2. Provide motility to sperms
Prostatic secretion contains substances important for sperm motility. These are notably albumin and proteolytic enzymes, fibrinolysin and fibrinogenase.
Question 98. A constituent of the fluid of prostate gland
- Citrate
- lactic acid
- Fructose
- Mitochondria
Answer: 1. Citrate
The fluid secreted by the prostate gland makes up about one-third of the total volume of semen and contains various enzymes, zinc and citrate.
Question 99. The fluid rich in calcium citrate, fibrinolysin and acid phosphatase is secreted by
- Cowper’s glands
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicles
- Epididymis
Answer: 2. Prostate gland
The fluid secreted by the prostate gland contains various enzymes such as fibrinolysin, acid phosphatase and inorganic compounds like zinc and calcium citrate.
Question 100. Seminal fluid coagulates on ejaculation due to
- Acid phosphate
- Sugar fructose
- Calcium and fibrinogen content from prostatic secretion
- Secretion of epididymis
Answer: 3. Calcium and fibrinogen content from prostatic secretion
The secretion of prostate gland contains calcium and fibrinogen which combine with the secretion of seminal vesicles and thus, the semen gets coagulated after ejaculation.
Question 101. Human semen is liquid at ejaculation but soon coagulates and again undergoes secondary liquefaction by ……… enzyme released by the prostate.
- Erepsin
- Cathepsin
- lysin
- Plasmin
Answer: 4. Plasmin
Human semen contains plasmin which aids in liquefaction of coagulated semen in female genital tract.
Question 102. Label A, B, C and D in the following diagram.
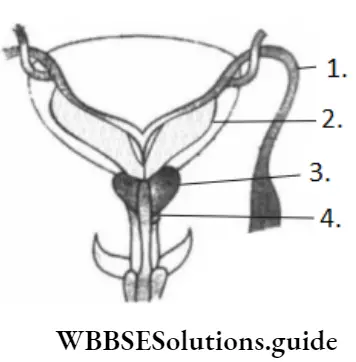
- A–Ureter, B–Seminal vesicle, C–Prostate, D–Bulbourethral gland
- A–Ureter, B–Prostate, C–Seminal vesicle, D–Bulbourethral gland
- A–Vas deferens, B–Seminal vesicle, C–Prostate, D–Bulbourethral gland
- A–Vas deferens, B–Vesicle, C–Bulbourethral gland, D–Prostate
Answer: 3. A–Vas deferens, B–Seminal vesicle, C–Prostate, D–Bulbourethral gland
Question 103. Bulbourethral gland is also known as
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- Perineal gland
- Salivary gland
Answer: 2. Cowper’s gland
Bulbourethral gland is also called as Cowper’s gland. It is pea-shaped gland and is located beneath the prostate gland.
Question 104. Function of bulbourethral gland is
- lubrication of penis
- To increase motility of sperm
- To enhance the sperm count
- All of the above
Answer: 1. lubrication of penis
Bulbourethral gland secretes mucus, which lubricate penis during intercourse. This reduces the friction during the copulation.
Question 105. Consider the following statements.
- Bulbourethral glands are present on either side of urethra in males.
- Bulbourethral glands secrete alkaline fluid.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 106. Starting from the maximum, arrange the following male reproductive accessory organs in the correct order, based on the amount of secretion.
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle
- Bulbourethral gland
Choose the correct answer
- 1 > 2 >3
- 3 > 2 > 1
- 2 > 3 > 1
- 2 > 1 > 3
Answer: 4. 2 > 1 > 3
Composition of seminal plasma is Seminal gland-60%, prostate gland-30% and bulbourethral gland-1%. Thus, the correct order is 2 > 1 > 3.
Question 107. Which of the following is not seen in male reproductive system?
- Mesosalpinx
- Bulbourethral glands
- Epididymis
- Seminal vesicles
Answer: 1. Mesosalpinx
Mesosalpinx is a double fold of peritoneum which supports the Fallopian tube in females. Thus, it is not seen in male reproductive system. Rest three structures are found in male reproductive system.
Question 108. Temperature of the scrotum which is necessary for the functioning of testis is always below body temperature. This difference is
- 2 ºC
- 3 ºC
- 4 ºC
- 6 ºC
Answer: 1. 2 ºC
Question 109. ‘Testes are extraabdominal in position’. Which of the following is the most appropriate reason?
- Narrow pelvis in male
- Special protection for testis
- Prostate gland and seminal vesicles occupy maximum space
- Requires lower temperature than normal body temperature
Answer: 2. Special protection for testis
Question 110. Wrinkling of scrotum is brought about by
- Dartos muscles
- Cremaster muscles
- Alary muscles
- Cardiac muscles
Answer: 1. Dartos musules
Wrinkling of scrotum is brought about by involuntary dartos muscle.
Question 111. In humans, the unpaired male reproductive structure is
- Seminal vesicle
- Prostate
- Bulbourethral gland
- Testes
- Vas deferens
Answer: 2. Prostate gland is an unpaired male accessory sex gland.
