Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Microbes As Biofertilisers
Question 1. Agriculture involving the use of biofertilizers is called
- Manuring
- Composting
- Inorganic farming
- Organic farming
Answer: 4. Organic farming
Organic farming is a form of agriculture that relies on techniques such as crop rotation, the use of green manure, compost, biofertilizers, and biological pest control.
Question 2. Biofertilizers include
- Nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria only
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria only
- Protistans only
- Bacteria, cyanobacteria, and fungi
Answer: 4. Bacteria, cyanobacteria, and fungi
biofertilizers class 12
- ‘Bio’ means ‘life’. Therefore, by definition, biofertilizers are living organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
- It refers to the use of microbes instead of chemicals to enhance the nutrition of the soil. As a result, it is also less harmful and does not cause pollution. Types of biofertilizers are bacteria, fungi, and cyanobacteria.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
- Green manures are added to the soil
- Fertilizers cause soil and water pollution
- Biofertilizers improve soil fertility
- Berseem is an ideal biofertiliser
Answer: 4. Berseem is an ideal biofertiliser
The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) is green manure. The rest statements are correct.
Question 4. Organic farming is the technique of raising crops through the use of
- Manure
- Resistant varieties
- Biofertilizers
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Organic farming is a form of agriculture that relies on techniques such as crop rotation, the use of green manure, compost, fertilizers, and biological pest control.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers

NEET Biology Microbes as Biofertilizers MCQs with answers
Question 5. Composted manure is formed from
- Farmyard manure and green manure
- Farm refuse and household refuse
- Rotted vegetables and animals refuse
- Organic wastes from which biogas is extracted
Answer: 3. Rotted vegetables and animal refuse
- Manure is composed of animal feces or urine and may contain livestock bedding, additional water, and wasted feed.
- It is a valuable fertilizer that contains a broad range of nutrients such as nitrogen (n), phosphorus (p), and potassium (k) as well as micronutrients such as copper (cu), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn). So, composited manure is formed from rotted vegetable and animal refuse.
Question 6. Humus is Haryana
- Partially decomposed organic matter of soil
- Completely decomposed organic matter of soil
- Partially decomposed inorganic matter
- Completely decomposed organic matter of pond
Answer: 2. Completely decomposed organic matter of soil
Humus is dark, organic material that forms in soil when plant and animal matter decays. When plants drop leaves, twigs, and other material to the ground, it piles up. The thick brown or black substance that remains after most of the organic litter has decomposed is called humus.
7. Which of the following is/are the approach (s) for biological farming?
- Familiarity with various lifeforms inhabiting the field.
- Gain knowledge about the life cycles, patterns of feeding, and habitat of predators and pests.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
“which one of the following is free-living bacterial biofertilizer “
Both statements I and ii are correct. An important part of the biological farming approach is to become familiar with the various lifeforms that inhabit the field, predators as well as pests, and also their life cycles, patterns of feeding, and the habitats that they prefer. This will help to develop appropriate means of biocontrol.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 8. Organisms that can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil are found among
- Mosses
- Green algae
- Soil fungi
- Bacteria
Answer: 4. Bacteria
Rhizobium bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Question 9. An organism used as a biofertilizer while raising a legume crop is
- Nostoc
- Anabaena
- Clostridium
- Rhizobium
Answer: 4. Rhizobium
Rhizobium is used as a biofertilizer for raising any legume crop. It is a symbiotic bacterium that lives in the root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds.
Question 10. For symbiotic nitrogen fixation, the biofertilizer rhizobium enters the leguminous partner through the
- Root nodules
- Stem tissues
- Root hairs before nodule formation
- Root hairs after nodule formation
Answer: 3. Root hairs before nodule formation
- The rhizobium bacteria help leguminous plants by converting atmospheric nitrogen to soluble form for the plant to make proteins and in return the plant provides the bacteria with sugars or food.
- To develop a symbiotic relationship with the legume crop, rhizobium enters into the root hair before the formation of root nodules.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. In a barren land, the soil has been eroded due to overgrazing and wind or the soil also has been leeched. To restore the fertility of the soil, we should add
- Legumes to the soil
- Inorganic nutrients
- Air
- Water
Answer: 1. Legumes to the soil
- Legumes should be added to the soil to restore the fertility. Legumes fix the atmospheric nitrogen, release high-quality organic matter in the soil, and facilitate soil nutrients’ circulation and water retention.
- Based on these multiple functions, legume crops have a high potential for conservation agriculture, being functional either as growing crops or as crop residue.
Question 12. What is required for nitrogen fixation by rhizobium?
- Potassium
- Phosphorus
- Nitrate
- Sodium
Answer: 2. Phosphorus
Phosphorus plays an important role in symbiotic association for nitrogen fixation in leguminous plants by Rhizobium.
Important MCQs on Microbes as Biofertilizers for NEET
Question 13. Which of the following is a free-living aerobic and non-photosynthetic nitrogen-fixing bacterium?
- Rhizobium
- Nostoc
- Azospirillum
- Azotobacter
Answer: 4. Azotobacter
Azotobacter species are free-living, aerobic, and nonphotosynthetic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. They normally fix molecular nitrogen from the atmosphere without symbiotic relations with plants, although some acetobacter species are associated with plants.
Question 14. The most important of the symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which forms nodules on the roots of legume plants is
- Aspergillus
- Rhizobium
- Penicillium
- Streptococcus
Answer: 2. Rhizobium
Rhizobium is a soil bacterium that fixes nitrogen after being established inside the root nodules of legumes (family Fabaceae). Rhizobia require a plant host, they cannot independently fix nitrogen.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 15. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- Legumes are incapable of fixing nitrogen
- Legumes fix nitrogen only through specialized bacteria living in their nodulated roots
- Legumes fix nitrogen independent of the bacteria that live in their roots
- Legumes fix nitrogen only through bacteria forming nodules on any part of the plant
Answer: 2. Legumes fix nitrogen only through specialized bacteria living in their nodulated roots
- The statement in the option is correct. The rhizobium bacteria help leguminous plants by converting atmospheric nitrogen to soluble form for the plant to make proteins and in return the plant provides the bacteria with sugars or food.
- To develop a symbiotic relationship with the legume crop, rhizobium enters into the root hair before the formation of root nodules.
Question 16. The rhizobium is able to fix atmospheric nitrogen. This ability is due to the
- Presence of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Presence of the enzyme nitrogenase
- Presence of the enzyme nitrate reductase
- Symbiotic association with fungi
Answer: 2. Presence of enzyme nitrogenase
Rhizobium contains the enzyme nitrogenase, a mo-fe protein that helps in the conversion of atmospheric free nitrogen into ammonia.
Question 17. Root and stem nodules fixing atmospheric nitrogen are found in
- Vigna sinensis
- Sesbania aculeata
- Melilotus parviflora
- Sesbania rostrata
Answer: 2. Sesbania rostrata
Sesbania rostrata is a small semi-aquatic leguminous tree. It forms a symbiotic relationship with gram-negative rhizobia which helps in the formation of nitrogen-fixing nodules on both stem and roots.
which one of the following is free living bacterial biofertilizer “
Question 18. Which nitrogen-fixing bacteria is found in the root association of maize?
- Aulosira
- Azotobacter
- Azospirillum
- Exorrhiza
Answer: 3. Azospirillum
Bacterium azospirillum lipoferum forms a loose association with the roots of maize. Azospirillum is free-living bacteria, which absorbs free nitrogen from the soil, and air and converts it into salts of nitrogen like amino acids and enriches the soil.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 19. What happens when we inoculate rhizobium in the wheat field?
- No increase in production (nitrogen content of soil remains same)
- A lot of increase in production (nitrogen content of soil increases)
- The fertility of soil decreases
- Fertility of soil increases
Answer: 1. No increase in production (nitrogen content of soil remains same)
When we inoculate rhizobium in wheat fields, there is no increase in production, and the nitrogen content of soil remains the same because rhizobium is a symbiotic bacterium that lives in the root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds.
Microbes as Biofertilizers chapter-wise MCQs for NEET
Question 20. An example of symbiotic bacteria.
- Erwinia amylovora
- Rhizobium leguminosarum
- Xanthomonas campestris
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Answer: 2. Rhizobium leguminosarum
Rhizobium leguminoserum nitrogen-fixing bacteria living in a symbiotic relationship with legumes. Common crop and forage legumes are peas, beans, clover, and soybean.
Question 21. The symbiotic association of fungi with the roots of higher plants is called
- Eubacteria
- Actinomycetes
- Mycorrhiza
- Lichen
Answer: 3. Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant. They are an important component of soil life and soil chemistry.
Question 22. Mycorrhiza is helpful in
- Synthesis of food
- Getting nutrients from the soil
- Providing resistance against different regulators
- Increase the fertility of the soil
Answer: 2. Getting nutrients from the soil
Mycorrhiza is a mutually beneficial relationship between fungi and the roots of higher plants. It helps in the absorption of water, minerals from organic matter, and protection from soil-borne pathogenic fungi.
Question 23. Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of roots of higher plants with
- Actinomycetes fungi mainly
- Basidiomycetes fungi mainly
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
Answer: 2. Basidiomycetes fungi mainly
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of roots of higher plants with basidiomycetes fungi mainly. The fungi commonly known as mushrooms, toadstools, puffballs, and bracket fungi are the basidiomycetes.
Question 24. The most common fungal partner of mycorrhiza belongs to the genus
- Azotobacter
- Glomus
- Azolla
- Frankia
Answer: 2. Glomus
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (am) fungi and all its species form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizas) with plant roots.
NEET quiz on Microbes as Biofertilizers with solutions
Question 25. A good example of organic fertilizer, which improves phosphorus uptake is
- Vam fungi
- Rhizobium
- Azospirillum
- All of these
Answer: 2. Rhizobium
In endophytic mycorrhiza, fungal hyphae present inside or between the cells of the cortex, act as biofertilizers. In many grasses and some other crops, the fungal hyphae penetrate the cortical cells, which swell to form vesicles or arbuscules. This is called vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza (vam). It has a significant role in phosphate nutrition in plants.
Question 26. Mycorrhiza does not help the host plant in
- Enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
- Increasing its tolerance to drought
- Enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
- Increasing its resistance to insects
Answer: 4. Increasing its resistance to insects
- Mycorrhiza shows the following benefits
- Resistance to root-borne pathogens.
- Tolerance to salinity and drought.
- The overall increase in plant growth and development.
- It has no role in increasing insect resistance in plants.
Question 27. In ectomycorrhizae,
- Hyphae enter the plant cells and produce balloon-like structures
- Fungal mycelia form a mantle on the root surface
- Root nodules are produced
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Hyphae enter the plant cells and produce balloon-like structures
- Hyphae of endomycorrhizal fungi penetrate the cell wall and invaginate the cell membrane. They enter into the plant cells, producing structures that are either balloon-like (vesicles) or dichotomously-branching invaginations (arbuscules).
- The structure of the arbuscules greatly increases the contact surface area between the hypha and the cell cytoplasm to facilitate the transfer of nutrients between them.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 28. An example of endomycorrhiza is
- Nostoc
- Glomus
- Agaricus
- Rhizobium
Answer: 2. Glomus
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi which forms endomycorrhiza, a symbiotic association with plant roots.
Question 29. Ectomycorrhizae absorb and store nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium in
- Host epidermis
- Host cortex
- Root hair
- Fungal mantle
Answer: 4. Fungal mantle
In ectomycorrhizae, fungal hyphae cover the surface of the root and form a fungal mantle around it. The hyphae absorb important plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and water from the soil and stored them in the mantle.
Question 30. Ectomycorrhiza are commonly found on the roots of
- Pinus
- Eucalyptus
- Quercus
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Ectomycorrhizae form in the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from
the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pinus, eucalyptus, Quercus, oak, and rose families, etc. Thus, option.
Question 31. Ectomycorrhizae can be traced in the roots of
- Maize
- Groundnut
- Rice
- Trees like pine and oak
Answer: trees like pine and oak
Ectomycorrhizae form in the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from
the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pinus, eucalyptus, Quercus, oak, and rose families, etc. Thus, the option is correct.
Question 32. Mycorrhiza promotes plant growth by
- Absorbing inorganic ions from the soil
- Helping the plant in utilizing atmospheric nitrogen
- Protecting the plant from infection
- Serving as a plant growth regulator
Answer: 1. Absorbing inorganic ions from soil
- Mycorrhiza promotes plant growth by absorbing inorganic ions from the soil.
- The fungal hyphae absorb phosphorus from the soil and pass it to the plant.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 33. The benefits of mycorrhiza are
- Resistance to root-borne pathogen
- Tolerance to salinity and pathogen
- The overall increase in plant growth and development
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- Only 2
Answer: 1. 1, 2 And 3
- Resistance to root-borne pathogens.
- Tolerance to salinity and drought.
- The overall increase in plant growth and development.
- All the given benefits of mycorrhiza are correct.
Question 34. Mycorrhiza helps in the absorption of
- Nitrogen and phosphorus
- Potassium and calcium
- Water
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
which one of the following is free living bacterial biofertilizer “
- All given nutrients help in absorption. In ectomycorrhizae, fungal hyphae cover the surface of the root and form a fungal mantle around it.
- The hyphae absorb important plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and water from the soil and store them in the mantle.
Question 35. Which one of the following microbes forms a symbiotic association with plants and helps them in their nutrition?
- Azotobacter
- Aspergillus
- Glomus
- Trichoderma
Answer: 3. Glomus
- Glomus is endomycorrhiza that helps in the absorption of nutrition especially phosphorus from soil.
- Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi which forms endomycorrhiza, a symbiotic association with plant roots.
NEET expected MCQs on Microbes as Biofertilizers 2025
Question 36. The angiosperms having mycorrhiza are
- Orchids
- Sarcodes
- Monotropa
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Mycorrhiza is found to be associated with all three given plants, i.e. Orchids, sarcodes, and Monotropa.
Question 37. Some blue-green algae can be used as biofertilizers as they are Karnataka
- Photosynthetic
- Surrounded by mucilage
- Growing everywhere
- Capable of fixing nitrogen
Answer: 4. Capable of fixing nitrogen
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 38. The cyanobacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen in
- Cystolith
- Heterocyst
- Sheath
- Leaves
Answer: heterocyst
A heterocyst is a differentiated cyanobacterial cell that carries out nitrogen fixation. The heterocysts function as the sites for nitrogen fixation under aerobic conditions. They are formed in response to a lack of fixed nitrogen (nh4 or no3).
Question 39. Heterocysts produce nitrogenase enzymes in the presence of
- Oxygen
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide
Answer: 1. Oxygen
- Heterocysts are the special, pale yellow-colored cells in the filament of algae.
- Each heterocyst is distinctly different from other blue-green cells in the filament and possesses one or two polar nodules.
- Nitrogen fixation is done by the heterocysts. These produce the nitrogenase enzyme in the presence of oxygen.
Question 40. Nitrogen fixation in cyanobacteria requires two enzymes named
- Amylase-lipase
- DNA polymerase-ligase
- Nitrogenase-hydrogenase
- Nuclease-diastase
Answer: 3. Nitrogenase-hydrogenase
Nitrogen fixation in cyanobacteria requires two enzymes named as
- Nitrogenase catalyzes the reduction of n2. Ammonia is the end product of the reaction.
- Hydrogenase certain strains of Rhizobium sp. Have been found to produce nodules that lose little or noh2 during periods when nitrogenase is operative.
These strains are more efficient in n2 fixation because they possess a mechanism whereby h2 evolved by nitrogenase is recycled. The first step in the recycling process is the uptake of h2 catalysed by the enzyme hydrogenase in bacteroids.
Question 41. Which of the following elements acts as an enzyme activator in nitrogen fixation?
- Mg
- Fe
- Mo
- N
Answer: 3. Mo
During nitrogen fixation, the enzyme nitrogenase is activated in an anaerobic atmosphere by an enzyme activator molybdenum (mo).
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 42. Bga is chiefly used as fertilizer in
- Wheat
- Paddy
- Mustard
- Gram
Answer: 2. Paddy
Bga (blue-green algae) is used as a biofertilizer in paddy crops which increases fertility by nitrogen fixation. Mostly anabaena, nostoc, aulosira are used as fertilizer.
NEET Biology Microbes as Biofertilizers MCQs with explanations
Question 43. In rice fields, which of the following operates?
- Anabaena
- Ferrobacterium
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
Answer: 1. Anabaena
Certain species of Anabaena have been used on rice paddy fields, proving to be an effective natural fertilizer.
Question 44. Anabaena azollae is an endophytic cyanobacteria found in
- Cycas roots
- Anthoceros thallus
- Azolla
- Pinus stem
Answer: 3. Azolla
Anabaena azollae is an endophytic cyanobacteria found in Azolla. Tiny aquatic water fern (Azolla) and a microscopic filamentous blue-green alga or cyanobacterium (Anabaena azollae) grow together at the surface of quiet streams and ponds throughout tropical and temperate regions of the world.
Question 45. Blue-green algae are mainly used as biofertilizers in the field of which crop?
- Gram
- Millet
- Rice
- Maize
Answer: 3. Rice
- Blue-green algae is used as biofertilizers, in the field of rice or paddy.
- Bga (blue-green algae) is used as a biofertilizer in paddy crops which increases fertility by nitrogen fixation. Mostly anabaena, nostoc, aulosira are used as biofertilizers.
46. Which of the following cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen?
- Volvox
- Oscillatoria
- Nostoc
- Anabaena
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 4
- 2, 3 And 4
- 3 And 4
Answer: 3. 2, 3 And 4
All given cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen except volvox. Cyanobacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase the organic matter of the soil through photosynthetic activity, Nostoc, anabaena, oscillators, etc. Thus, the option is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
47. A free-living nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium that can also form a symbiotic association with the water fern Azolla is
- Tolypothrix
- Chlorella
- Nostoc
- Anabaena
Answer: 4. Anabaena
Anabaena is a genus of filamentous cyanobacteria that exist as plankton. It is known for nitrogen-fixing abilities and forms symbiotic relationships with certain plants, such as the water fern Azolla.
Question 48. Who reported the presence of associative nitrogen-fixing bacteria with the roots of maize plants?
- Hellriegel and beijerinck
- Gc fogg
- J doberiner
- Nj borlaug
Answer: 1. Hellriegel and beijerinck
- Biological nitrogen fixation in maize plants was discovered by the German agronomist Hermann Hellriegel and Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck.
- Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) occurs when atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by an enzyme called nitrogenase.
Microbes as Biofertilizers mock test for NEET preparation
Question 49. Free-living bacteria that can fix n 2 from the soil is
- Clostridium
- Azotobacter
- Beijerinckia
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Free-living nitrogen fixers include the cyanobacteria, anabaena, nostoc, and genera such as Azotobacter, beijerinckia, and Clostridium.
Question 50. Which of the following is a non-symbiotic, anaerobic, and non-photosynthetic n 2-fixing bacterium?
- Nostoc
- Clostridium
- Chlorobium
- Azotomonas
Answer: 2. Clostridium
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which are present in the soil convert free nitrogen into soluble compounds, which are absorbed from the soil by plants. Free-living non-photosynthetic anaerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria is Clostridium.
Question 51. Azolla pinata has been found as an important fertilizer for paddy crops. This quality is due to the presence of
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Fungi
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria, anabaena azollae is present in the leaves of azolla pinnata. Due to this, Azolla is used as a biofertilizer in paddy crops.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 52. Which is the best fertilizer?
- Synthetic fertilizer
- Bacillus thuringiensis and lichens
- Azolla and cyanobacteria
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Azolla and cyanobacteria
An effective cyanobacterial biofertilizer is azolla-anabaena symbiosis, which is a very efficient biological nitrogen fixer. Azolla is mostly used in agriculture, particularly in rice fields. Farmers have observed over 50% higher yields by using Azolla as a biofertilizer.
Question 53. Which of the following is common to azo spirillum, anabaena, nostoc, and oscillatory?
- They are n2-fixer microbes
- They are prokaryotic organisms
- Both (1) and (2)
- They are eukaryotic organisms
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
- Azospirillum is a gram-negative free-living bacteria, which absorbs free nitrogen from soil and air and converts it into salts of nitrogen-like amino acids and enriches soil nutrients.
- Nostoc, anabaena, and oscillatory fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase the organic matter of the soil through their photosynthetic activity. So, they all are prokaryotic, nitrogen fixing organisms. Thus, the option is correct.
Question 54. Azospirillum, a nitrogen-fixing bacteria, has been found in the root association of maize, and anabaena is found in the roots of
- Rice
- Cycas
- Sorghum
- All of these
Answer: 2. Cycas
which one of the following is free living bacterial biofertilizer “
Azospirillum lipoferum, is a n2-fixing bacterium that is found in association with the roots of certain tropical grasses like cycas. It has been found to supply the plants with nitrogen.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 55. Which of the following statement is correct?
- Cyanobacteria such as anabaena and Nostoc are important mobilizers of phosphates and potassium for plant nutrition in the soil
- At present it is not possible to grow maize without chemical fertilizers
- Runoff from agricultural areas rich in chemicals fertilizers may lead to the eutrophication of nearby water bodies
- Both azotobacter and rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen in root nodules of plants
Answer: 3. Runoff from agricultural areas rich in chemicals fertilizers may lead to eutrophication of nearby water bodies
- Excess fertilizer in the environment, especially nitrogen and phosphorus can pollute local groundwater as well as lakes and streams resulting in eutrophication. Other statements are incorrect and can be corrected as
- Cyanobacteria anabaena and nostoc have heterocysts that help in nitrogen fixation. Hence, these are important mobilizers of nitrogen.
- Maize can be grown without chemical fertilizers, by using organic farming.
- Azotobacter is a free-living bacteria that fix nitrogen but do not occur in root nodules like rhizobium.
Question 56. Vam is
- Vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae
- Variable adenine mutation
- Variable associative mutualism
- Vitamins and minerals
Answer: 1. Vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae
NEET practice test on Microbes as Biofertilizers
Question 57. Vam helps in
- Nitrate nutrition
- Phosphate nutrition
- Preventing infection
- Denitrification
Answer: 2. Phosphate nutrition
Vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae (vam) has a significant role in phosphate nutrition in plants.
Question 58. Vam is seen in
- Pea
- Oak
- Peach
- Grasses
Answer: 4. Grasses
Vam is vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae which are endomycorrhizal found in association with grasses and members of the family– Orchidaceae. Eucalyptus, oak, and pinus have only ectomycorrhizae.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 59. Using green manure increases crop yield by
- 5-10%
- 15-25%
- 30-50%
- 80-90%
Answer: 3. 30-50%
Quick-growing crops cultivated in soil plowed with green manure increase crop yield by 30-50%.
Question 60. The following are commonly used as green manure in India
- Lentil
- Sunnhemp
- Cowpea
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Sunn hemp is a tropical plant of the legume family. It is used as a source of green manure, fodder, and lignified fiber. Cowpea is also a legume used as grain or vegetables. Lentil prevents soil erosion.
61. Manure supply following nutrients to plants
- Nitrogen (n)
- Phosphorus (p)
- Potassium (k)
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Indian soils are usually very poor in organic matter and nitrogen content where constant leaching and removal of crops deprive the soil of mineral contents. Manure can help to supply vital nutrients like n, p, k to plants.
Question 62. Assertion (A) Leguminous plants are best preferred for crop rotation. Reason (R) They have root nodules, which have nitrogen-fixing bacteria clostridium.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but r is false
- A is true, but r is false because, in the rotation of crops, leguminous crops like pulses, beans, peas, and groundnut are used. The leguminous plants are grown alternately with non-leguminous plants to restore the fertility of the soil.
- These plants have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen to form nitrogen compounds through the help of certain bacteria (rhizobium) present in their root.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 63. Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using the biofertilizer
- Azolla pinnata
- Cyanobacteria
- Legume – rhizobium symbiosis
- Mycorrhiza
Answer: 1. Azolla pinnata
Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using the biofertilizer Azolla pinnata
Question 64. A straight fertilizer is one, which is
- Absorbed by roots directly
- Absorbed by the plants from aerial spray
- Having only one primary nutrient
- Not easily leached
Answer: 3. Having only one primary nutrient
A fertilizer, which contains only one primary nutrient is known as straight fertilizer or simple fertilizer.
Question 65. Which one of the following is not used in organic farming?
- Snail
- Glomus
- Earthworm
- Oscillatoria
Answer: 1. Snail
Organic farming is a method of a farming system that primarily aimed to keep the soil alive and in good health by use of organic wastes and other biological material along with beneficial microbes (biofertilizers) to release nutrients to crops for increased sustainable production in an ecofriendly, pollution free environment. Glomus (fungi), earthworms,s, and oscillators are used in organic farming. Snails are not used in it.
Question 66. Which of the following is used as fertilizer?
- Cyanobacteria
- Yeast
- Symbiotic bacteria
- Free-living bacteria
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 3 And 4
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 4
Answer: 2. 1, 3 And 4
- All given organisms are used biofertilizers except yeast. Cyanobacteria or blue-green algae is the most suitable source of biofertilizer, particularly in rice fields,
- Example: nostoc, anabaena. Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacterium that lives in the root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds.
- Azospirillum and acetobacter are free-living bacteria that absorb free nitrogen from soil, and air and convert it into salts of nitrogen like amino acids and enrich soil nutrients.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 67. Match the items in column I with those in column ii and choose the correct answer.
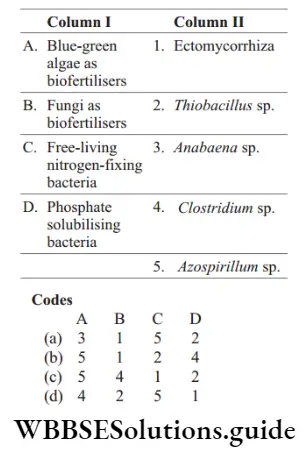
Answer: 1. A–3, b–1, c–5, d–2
Question 68. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
- Rhizobium – a parasite in the roots of leguminous plants
- Mycorrhizae – mineral uptake from the soil
- Yeast – production of biogas
- Myxomycetes – the disease ringworm
Answer: 2. Mycorrhizae – mineral uptake from the soil
Matched pair. Other options are incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as rhizobium is a genus of bacteria associated with the formation of root nodules on plants. Myxomycetes, also called metazoa is a phylum of fungus-like organisms within the kingdom–Protista, commonly known
Question 69. Which one of the following is not a nitrogen-fixing organism?
- Anabaena
- Pseudomonas
- Azotobacter
- Nostoc
Answer: 2. Pseudomonas
Pseudomonas perform denitrification or the reduction of nitrates into nitrogen gas. It is not a nitrogen–fixing organism. Anabaena, nostoc, and azotobacter help in nitrogen fixation.
Question 70. Which one of the following is a non-symbiotic biofertilizer?
- Azotobacter
- Anabaena
- Rhizobium
- Vam
Answer: 1. Azotobacter
Azotobacter is a free-living nitrogen-fixing bacterium, so it is a non-symbiotic biofertilizer. Rhizobium is symbiotic and found in the root nodules of leguminous plants. Anabaena occurs in association with Azolla. Vam is vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae.
Question 71. Which of the following belongs to free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- Rhizobium
- Azospirillum
- Azotobacter
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 3. 2 And 3
All given species belong to nitrogen-fixing bacteria except rhizobium. Azospirillum and acetobacter are free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Free-living n2-fixing bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and make it available for the higher plant. Thus, the option is correct.
72. A natural source of nitrogenous fertilizer is
- Tobacco leaves
- Urea
- Guano
- Bonemeal
Answer: 3. Guano
Guano is a natural nitrogenous fertilizer obtained from bird droppings.
Question 73. Match the following columns and choose the correct option from the codes given below.
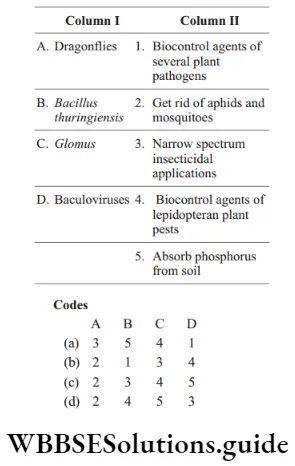
Answer: 4. A–2, b–4, c–5, d–3
