Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Mutation
Question 1. Rarely observed phenotype in population is called
- Wild type
- Mutant type
- Variant type
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Mutant type
The gene whose chemical structure is altered is called mutated gene and the organisms carrying this mutated gene is called mutant. It is rarely observed phenotype in population.
Question 2. One of the parents of a cross has a mutation in its mitochondria. In that cross, that parent is taken as a male. During segregation of F2 progenies that mutation is found in
- One-third of the progenies
- 50% of the progenies
- All the progenies
- None of the progenies
Answer: 4. None of the progenies
questions about genetics
Mitochondria is an organelle present in the cytoplasm. A zygote receives its cytoplasm from the female parent gamete. Hence, in the given question, the F2 progenies do not receive the mitochondrial genome from the male parent and mutation is not passed to progenies.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Assertion (A) Muton gene has fewer nucleotides than a cistron. Reason (R) Benzer coined the term muton to the smallest unit of genetic material capable of mutational change.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Muton has fewer nucleotides than a cistron because muton is the smallest unit in chromosome that can be changed by mutation.
NEET Biology Mutation MCQs with answers
Question 4. Mutagens are
- Chemical agents which cause change in DNA
- Physical agents which cause mutation
- Cancer producing agents
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Mutagen may be physical or chemical agents, which causes change in DNA sequence, e.g. mutation induced by UV-radiation, acridine dye, etc. Thus, option (4) is correct
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Important MCQs on Mutation for NEET
Question 5. Certain mutations are not eliminated from gene pool because they are carried by
- Homozygous individuals
- Recessive homozygous individuals
- Heterozygous individuals
- Dominant heterozygous individuals
Answer: 3. Heterozygous individuals
Harmful mutation does not get eliminated from the gene pool because most of the harmful mutations are recessive and they are carried in heterozygous condition by the individual. If they (mutation) are dominant, then they easily get eliminated by the death of an organism.
Question 6. Haploids are able to express both recessive and dominant alleles/ mutations because there are
- Many alleles for each gene
- Two alleles for each gene
- Only one allele for each gene in the individual
- Only one allele in a gene
Answer: 3. Only one allele for each gene in the individual
In haploid organisms, every gene irrespective of dominant or recessive and every mutation finds expression because there is only one allele for each gene in the haploid individual. Recessive allele is able to express as there is no alternative dominant allele for producing its masking effect on recessive allele.
“which of the following is a hereditary disease “
Question 7. Mutation is
- Recessive
- Useful
- Seldom useful
- Low frequency
Answer: 1. Recessive
Mutations are normally deleterious or recessive and therefore, majority of them are of no practical value.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 8. Which of the following statements about mutation are true?
- Mutations are the source of new alleles for genes.
- Organisms are able to create mutations to meet their specific needs.
- Mutations are random events and can happen in any cell at any time.
- Most mutations tend to be harmful or have no effect on an organism.
Chooe the correct option.
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 1, 3 and 4
All given statements are true about mutation except II. Incorrect statement can be corrected as Mutation occurs itself. It is the spontaneous phenomena and organisms cannot create mutations on their own. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Mutation chapter-wise MCQs for NEET
Question 9. Mark the incorrect statement about mutation?
- Mutation is predestined
- Major source of evaluation
- Usually deleterious and recessive
- It is a reversible process
Answer: 1. Mutation is predestined
Statement in option (1) is incorrect and can be corrected as Mutations are the ultimate source of all genetic variations and these are spontaneous. Rest options are correct about mutation.
Question 10. A recessive mutant is one which is
- Not expressed
- Rarely expressed
- Expressed only in homozygous and hemizygous state
- Expressed only in heterozygous state
Answer: 3. Expressed only in homozygous and hemizygous state
A recessive mutation is one in which both alleles must be mutant in order for the mutant phenotype to be observed, i.e. the individual must be homozygous recessive (rr) or hemizygous (ro) for the mutant allele to show the mutant phenotype.
Question 11. Which of the following is correct for tetrasomic aneuploids?
- 2n + 2
- 2n + 2 + 2 + 2
- 2n – 1
- 2n – 1
Answer: 1. 2n + 2
Aneuploidy is also called as heteroploidy which is the condition of having fewer or extra chromosomes than the exact multiple of the genome or whole chromosome set. In tetrasomics, chromosome is present quadruplicate (four times). Among given options 2n+2 represents tetrasomic aneuploids.
Question 12. Monosomic trisomy is represented as
- 2n – 1 – 1
- 2n – 1 + 1
- 2n – 1
- 2n + 1 + 1
- 2n + 1
Answer: 2. 2n – 1 + 1
Monosomy is the absence of one chromosome (2n-1 )and trisomy is presence of an extra chromosome ( 2n+1) The absence of single chromosome and presence of antoher chromosome simultaneously is called monosomic trisomy (2n-1+1 ).
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 13. Find out the correct statement.
- Monosomy and nullisomy are the two types of euploidy
- Polyploidy is more common in animals than in plants
- Polyploids occur due to the failure in complete separation of sets of chromosomes
- 2n-l condition results in trisomy
- Non-homologous chromosomal duplication results in autopolyploidy
Answer: 1. Monosomy and nullisomy are the two types of euploidy
“principles of inheritance “
Statement in option (1) is correct. Other statements are incorrect and can be corrected as 2n+1 condition results in trisomy. Polyploidy is common in plants only. Polyploidy occurs due to duplication of chromosomes and homologous chromosomes duplication results in autopolyploidy.
Question 14. A condition characterised by multiples of haploid set of chromosomes is called
- Polyploidy
- Symploidy
- Aneuploidy
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Polyploidy
Polyploidy is the condition in which the chromosome number is a higher multiple than two of the haploid number (23) of chromosomes.
NEET quiz on Mutation with solutions
Question 15. Polyploidy can result from
- Parthenogenesis
- Monospermy
- Colchicine
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Colchicine
Polyploidy is a condition in which the chromosome number is two or more times than normal haploid number found in gametes. It may occur in nature or can be induced artificially by using colchicine. This type of mutation includes all the cases in which any change in number of chromosomes in set occurs.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 16. Abnormal cell with random number of chromosomes is
- Aneuploid
- Polyploid
- Heterokaryotic
- Haploid
Answer: 1. Aneuploid
Aneuploidy is the condition of cells having more or less than integral multiple of typical haploid chromosome number. Thus, 22 + XXY is an extra sex chromosome due to non-disjunction of a pair of sex chromosome either in an ovum or sperm. So, abnormal cell with random number of chromosomes is aneuploid.
Question 17. An example for an allotetraploid is
- Triticum aestivum
- Gossypium species
- E. coli
- Mango
Answer: 2. Gossypium species
An example of an allotetraploid is Gossypium species of cotton. An allotetraploid is a hybrid that has a chromosome set 4 times that of a haploid organism.
Question 18. Chromosome complement with 2n -1 is called
- Monosomy
- Trisomy
- Nullisomy
- Tetrasomy
Answer: 1. Monosomy
Option (1) is correct. Monosomy occurs due to loss of a single chromosome (2n – 1). Other options are not correct and can be corrected as Nullisomy occurs due to loss of one pair of chromosomes (2n – 2). Hyperploidy may either involve addition of a single chromosome, trisomy (2n + 1) or a pair of chromosomes, tetrasomy (2n + 2).
NEET expected MCQs on Mutation 2025
Question 19. A chromosome may be lost or gained during cell division due to failure of segregation of chromatids. This condition is referred to as
- Aneuploidy
- Hypopolyploidy
- Hyperpolyploidy
- Polyploidy
Answer: 1. Aneuploidy
Chromosomal disorders are caused due to excess, absence or abnormal arrangement of one or more chromosomes. Sometimes the chromatids fail to segregate during cell division, resulting in gain or loss of a chromosome. This is called aneuploidy or heteroploidy.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 20. Occurrence of cells in diploid organisms containing multiples of the 2n genomes is known as
- Aneuploidy
- Haploidy
- Amphidiploidy
- Allopolyploidy
Answer: 1. Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the occurrence of cells in diploid organisms containing multiplies of the 2n genomes. For example, a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes.
Question 21. Trisomy and monosomy is represented by
- 2n – 1 and 2n + 1
- 2n + 1 and 2n – 1
- 2n and 2n + 1
- 2n and 2n – 1
Answer: 2. 2n + 1 and 2n – 1
Monosomy occurs due to loss of a single chromosome (2n – 1) whereas trisomy occurs due to addition of a single chromosome (2n + 1).
Question 22. Match the following column.
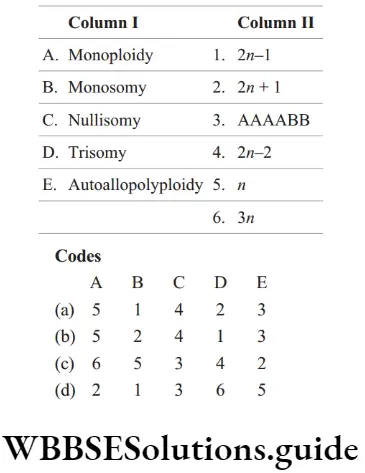
Answer: 1. A–5, B–1, C–4, D–2, E–3
Mutation Extra Questions
Question 1. Sudden and heritable change in a character of an organism is called
Mutation
Heterosis
Inbreeding
Selection
Answer: 1. Mutation
Mutations are the sudden alteration in the chemical structure of a gene or the alteration in its position on the chromosome by breaking and rejoining the chromosome.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 2. Errors during DNA replication, repair or recombination can lead to base-pair substitution. Such changes are
Conditional mutations
Mutagens
Spontaneous mutations
Saltatory changes
Answer: 3. Spontaneous mutations
All types of mutations are produced spontaneously, e.g. base substitutions, frame shifts, insertions and deletions. Errors during DNA replication can lead to spontaneous mutations.
Question 3. Mutations can be induced with
Infrared radiations cbse
IAA
Ethylene
Gamma radiations
Answer: 4. Gamma radiations
Mutation is the process by which genetic variations are created through changes in the base sequence within genes. It is possible to induce mutations artificially through the use of chemicals or radiations like gamma radiations.
“dihybrid cross questions “
Question 4. One of them is efficient in inducing mutations.
X-rays
Hybridisation
Colchicine
Crossing over
Answer: 1. X-rays
Two major causes of mutations are irradiation and chemical mutagens. Irradiation is exposure to radiation like X-rays and chemical mutagens are chemicals that cause changes in DNA sequences.
Thus, X-rays are efficient in inducing mutation.
Question 5. UV radiations cause
Formation of thymine dimers
Deletion of base pairs
Methylation of bases
Addition of base pairs
Answer: 1. Formation of thymine dimers
One of the major sources of DNA damage in all organisms is the UV component of sunlight. The predominant reaction induced by UV light on DNA is the dimerisation of adjacent pyrimidine bases.
Ultraviolet light induces the formation of covalent linkages localised on the C C== double bonds. In dsRNA, uracil dimers may also accumulate as a result of UV radiation.
Two common UV products are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPOs, including thymine dimers) and 6, 4 photoproducts. These premutagenic lesions alter the structure of DNA and consequently inhibit polymerases and arrest replication. So, UV radiation causes the formation of thymine dimers.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 6. The best chemical to induce polyploidy is
Maleic Hydrazide
ABA
Acenaphthene
Ethylene
Answer: 3. Acenaphthene
A number of chemicals are known to cause polyploidy, e.g. chloral hydrate, ethyl mercuric chloride, hexachlorocyclohexane and acenaphthene.
Question 7. The mutations are mainly responsible for
Increasing the population rate
Maintaining genetic continuity
Constancy in organisms
Variation in organisms
Answer: 4. Variation in organisms
Mutations are the sudden alteration of the chemical structure of a gene or the alteration of its position on the chromosome by breaking and rejoining of the chromosome. They rarely occur naturally but may be caused artificially by irradiation or by chemicals (mutagen), e.g. mustard gas.
They may occur in somatic cells or gametes in which case they can be inherited. They lead to variations in organisms and can be accordingly categorised into somatic mutations and gametic mutations.
Question 8. Mutations are caused by
Polyploidy
Hybridisation
Aneuploidy
All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Mutations are caused by polyploidy, hybridisation and aneuploidy. In polyploidy, more than two paired sets of chromosomes are mutated.
In hybridisation, single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules anneal to complementary DNA or RNA.
Aneuploidy is a condition in which the number of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell is not an exact multiple of the monoploid number of a particular species.
NEET Biology Mutation MCQs with explanations
Question 9. Change in single base pair Odisha
May change the phenotype
Quickly change the phenotype
Change the natural process
None of the above
Answer: 1. May change the phenotype
May change the phenotype change in single base pair due to mutation may or may not change the phenotype of an organism.
Question 10. Hereditary variation in plants has been obtained through the use of
X-rays or gamma rays
2, 4-D
DDT
GA
Answer: 1. X-rays or gamma rays
Radiation (X-rays or gamma rays) can increase the natural mutation rate by 1000 to 1 million fold, making the generation of genetic variation very effective.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 11. The action of ultraviolet rays on DNA in Odisha
Induction of thymidine
Deletion of base pairs
Addition of base pairs
Methylation of base pairs
Answer: 1. Induction of thymidine
Commonly, UV radiations cause the formation of thymine dimers and induce mutation. Thus, the action of ultraviolet rays on DNA is the induction of thymidine
“pedigree questions “
Question 12. HJ Muller was awarded Nobel Prize for his
The discovery that chemicals can induce gene mutations
The discovery that ionising radiations can induce gene mutations
Work on gene mapping in drosophila
Efforts to prevent the use of nuclear weapons
Answer: 2. Discovery that ionising radiations can induce gene mutations
HJ Muller studied the effect of radiation on living organisms. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for discovering that ionising radiation can induce gene mutations.
Question 13. Which of the following is not considered a mutagen?
Uv radiation
Nuclear reaction
2-Aminopurine
Low temperature
Answer: 4. Low temperature
Mutation can be artificially induced with the help of mutagenic agents which can be broadly classified as – 1 Physical mutagens, 2 Chemical mutagens. Physical mutagens are mainly radiations like X-rays, gamma rays, beta rays and neutrons.
High temperature also causes mutations. Aminopurine is a chemical artificial base analogue of adenine. It can substitute adenine as well as can pair with cytosine.
Similarly, the nuclear reaction causes a great impact on the DNA and mutations are noticed in several generations due to nuclear reaction or explosion.
So, low temperature does not cause mutation
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 14. The mutation may result in the
Change in genotype
Change in phenotype
Change in metabolism
All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
In most cases, if there is a change in genotype then it ultimately leads to a change in phenotype and metabolism.
Question 15. The mutations can be induced in bacteria by Karnataka
Adding all required substances
Starving the bacteria
Exposure to high-energy radiation
Growing different strains
Answer: 3. Exposure to high-energy radiation
Mutations can be artificially induced in bacteria with the help of high-energy ionising radiation
Question 16. Chromosomal aberration is due to
Physical effects Manipal1995
Change in structure or number of chromosomes
Polyploidy
None of the above
Answer: 2. Change in structure or number of chromosomes
Chromosomal aberration (chromosome mutation) is a change in the gross structure or number of a chromosome.
The main types of chromosomal aberrations that occur due to changes in the structure are deletion, duplication, translocation, inversion and due to change in the number, i.e. euploidy and aneuploidy.
Mutation mock test for NEET preparation
Question 17. Chromosomal mutations occur due to
Deletion
Duplication
Translocation
Inversion
Choose the correct option.
1, 2 and 3
2, 3 and 4
1, 3 and 4
1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3, and 4
All the given ways are correct. The chromosomal mutation is the sudden inheritable change in the hereditary material of an organism. It is caused due to several ways like deletion, duplication, translocation, inversion, etc. Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 18. The gene mutation is UP
Mutation in the genes of DNA
Mutation in the phosphodiester linkage
Mutation in the chromosomes
Change in the sequence of nitrogenous bases
Answer: 4. Change in the sequence of nitrogenous bases
A gene mutation is a change in the sequence of the nitrogenous bases due to a change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene
Question 19. A gene mutation which does not result in phenotypic expression is termed as
Non-sense mutation
Silent mutation
Mis-sense mutation
Frameshift mutation
Answer: 2. Silent mutation
Mutations which involve the substitution of a base by another base in such a manner that the new codon also codes for the same amino acid and thus, does not produce any faulty protein or no phenotypic changes are called silent mutations
Question 20. A non-sense mutation results into
Stoppage of transcription pm 2001
Change in protein structure
Stoppage of protein synthesis
Termination of the polypeptide chain
Answer: 2. Change in protein structure
A non-sense mutation is one which stops polypeptide synthesis due to the formation of a termination of the non-sense codon, viz. ATT(UAA), ATC (UAG), ACT(UGA)
Question 21. The creation of mutations is called
Mutagenesis
Evolution
Saltatory changes
Radiations
Answer: 1. Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed, resulting in a mutation.
It may occur spontaneously in nature or as a result of exposure to mutagens. It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. So, the creation of mutations is called mutagenesis.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 22. Chemical mutagens are more dangerous than radiation. Justify from the following statements.
Exposure to them is more frequent
There is protection from radiation but no chemicals
Both 1 and 2
Chemically caused mutations are far more deleterious
Answer: 4. Chemically caused mutations are far more deleterious
A chemical mutagen is a substance that can alter a base that has already been incorporated into DNA and thereby, change its hydrogen bonding specificity.
Chemical mutagens are prevalent in the environment and a potential threat to the health of future generations.
Question 23. After a mutation at a genetic locus, the character of an organism changes due to the change in
Protein structure
DNA replication
Protein synthesis pattern
RNA transcription pattern
Answer: 1. Mutagenesis is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed, resulting in a mutation.
It may occur spontaneously in nature or as a result of exposure to mutagens.
It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. So, the creation of mutations is called mutagenesis.
Question 24. Assertion 5-Bromouracil can cause mutations. Reason (R) It is called a base analogue.
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
A is true, but R is false
Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
NEET practice test on Mutation
Question 25. Change in one base in mRNA leading to termination of the polypeptide is known as which type of mutation?
Non-sense
Mis-sense
Gibberish
Frameshift
Answer: 1. Non-sense
A non-sense mutation is one which stops polypeptide synthesis due to the formation of a termination of the non-sense codon, viz. ATT(UAA), ATC(UAG), ACT(UGA).
Other options are explained as A missense mutation is one which involves a change in a codon that produces a different amino acid at the specific site in a polypeptide, often resulting in its non-functioning.
Frame-shift or gibberish mutations are those mutations in which the reading of the frame of the base sequence shifts laterally either in the forward direction due to the insertion of one or more nucleotides or in the backward direction due to the deletion of one or more nucleotides.
Question 26. X-ray causes mutation by
Transition
Transversion
Deletion
Base substitution
Answer: 3. Deletion
High-energy radiations, such as X-rays, gamma rays, cosmic rays and UV light have been found to be mutagenic in almost all organisms. They produce mutations by causing breaks in the DNA molecule, i.e.
deletion.
Question 27. Name the type of mutation in which the cause of the mutation is not known.
Spontaneous mutation
Suppressor mutation
Non-sense mutation
Mis-sense mutation
Answer: 1. Spontaneous mutation
Spontaneous mutations are those in which the cause of the mutation is not known. These types of mutations arise due to a tautomeric shift in nitrogenous bases of DNA.
Question 28. Normally DNA molecule has A-T, G-C pairing. However, these bases can exist in alternative valency status, owing to re-arrangements called
Point mutation
Frameshift mutation
Analogue substitution
Tautomerisational mutation
Answer: 4. Tautomerisational mutation
Transitions may be tautomeric shifts (ionisation) of bases, which leads to mistaken A-C base pairing and more frequently mistaken G – T base pairing.
So, these bases can exist in alternative valency status, owing to rearrangement called tautomerization mutation.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 29. Gibberish mutations are
Reverse
Frameshift
Transitions
Transversions
Answer: 2. Frameshift
Acridines (e.g. acriflavine, proflavine, flavine, acridine orange) enter the DNA chains in between two base pairs and cause deletion or addition of a few nucleotides.
The frame of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is thus, disturbed and read differently. It is also known as frame-shift or gibberish mutation
Question 30. Name the term given to the type of mutation which depends on the conditions of the environment.
Forward mutation
Reverse mutation
Conditional lethal mutation
Gain of function mutation
Answer: 3. Conditional lethal mutation
In conditional lethal mutation, lethality depends on the conditions of the environment, e.g. auxotrophs, temperature-sensitive mutants and suppressor mutation.
Question 31. Gene mutation occurs at the time of
DNA repair BHU 1996
RNA transcription
DNA replication
Cell division
Answer: 3. DNA replication
During replication, double strands of DNA are separated. Each strand is then copied to become another double strand.
About 1 out of every 100,000,000 times, a mistake occurs during copying, which can lead to a mutation. Mutations can also be caused by environmental foes. So, gene mutation occurs at the time of DNA replication.
Question 32. A genomic mutation involves
Change in genes am 2008
Change in chromosomal structure
Change in the number of chromosomes
All of the above
Answer: 3. Change in the number of chromosomes
The genomic mutation is the change in chromosome number due to errors in meiosis or mitosis
Question 33. The loss of a chromosomal segment is due to Kerala
Polyploidy
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Answer: 2. Deletion
The mutation involving the removal of one or more base pairs in the DNA sequence is called a deletion.
Question 34. Which of the following is the main category of mutation?
Somatic mutation
Genetic mutation
Heterosis
Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Mutations may occur in somatic cells or gametes. In the latter case, they can be inherited. They lead to variations in organisms. So, they can be accordingly categorised into somatic mutations and genetic mutations. Thus, option 4 is correct
Question 35. Which of the following is not heritable?
Point mutation
Gene mutation
Somatic mutation
Chromosomal mutation
Answer: 3. Somatic mutation
Somatic mutations are those mutations which occur in a cell other than germ cells and are not passed to the next generations, i.e. these are not heritable.
Question 36. Point mutation may occur due to
Alteration in DNA sequence
Change in a single base pair of DNA
Deletion of a segment of DNA
Gain of a segment in DNA
Answer: 2. Change in a single base pair of DNA
Point mutation or gene mutation involves only the replacement of one nucleotide with another or a change in a single base pair of DNA.
One type of point mutation is a missense mutation. These are base changes that alter the codon for an amino acid resulting in its substitution with a different amino acid
Question 37. Which base is considered a hotspot for spontaneous point mutations?
5-bromouracil
50 methylcytosine
Guanine
Adenine
Answer: 3. Guanine
Mutations are rare events in nature and are described as spontaneous mutations. Some of these mutations originate from mistakes in the normal duplication of DNA.
Transitions may be produced by tautomeric shift or ionisation of bases which leads to mistaken, A-C base pairing and more frequently mistaken G-T base pairing.
Guanine pairs with the rare enol form of thymine and is thus, considered a hotspot for spontaneous point mutations.
Question 38. A mutation in which thymine is replaced by cytosine is called
Transition
Transversion
Mis-sense
None of these
Answer: 1. Transition
Transitions are substitution gene mutations in which a purine (say adenine) is replaced by another purine (say guanine), or a pyrimidine (say thymine) is replaced by another pyrimidine (say cytosine). Change of codon ATC to GTC or ATT or ACC is an example of a transition
Question 39. When purine is substituted by pyrimidine, the resulting mutation is
Transition mutation
Transversion mutation
Point mutation
Suppressive mutation
Answer: 2. Transversion mutation
A transversion is a substitution gene mutation in which a purine (A or G) is replaced by a pyrimidine (T or C) or vice-versa.
Question 40. Which of the following type of mutation involves the reverse order of genes in a chromosome?
Deletion Haryana
Duplication
Inversion
Reciprocal translocation
Answer: 3. Inversion
An inverse mutation is a type of intra-chromosomal modification in which the segment of chromosome separates and rejoins in the reverse position
Question 41. Frame-shift mutation and base pair substitution change the
Nucleotide structure
Nucleotide sequence
Nucleoside sequence
Sugar-phosphate sequence
Answer: 2. Nucleotide sequence
The nucleotide sequence is also called the base-pair sequence. In frame-shift mutation or base pair substitution, the nucleotide sequence gets changed.
Question 42. The mechanism that causes a gene to move from one linkage group to another is called
Inversion
Duplication
Translocation
Crossing over
Answer: 3. Translocation
Translocation is a phenomenon of transfer of a gene segment between non-homologous chromosomes, i.e. different linkage groups.
Question 43. A normal gene sequence in a chromosomal sequence is ABCDEFGH. If it is changed to ACGH, this is a case of
Frame-shift mutations
Deletions
Inversions
Duplication
Answer: 2. Deletions
In genetics, deletion is also called gene deletion or deficiency.
It is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome.
Question 44. If the ABCDEFGH gene sequence changes to ABCABCDEFGH, then ………………. has occurred.
Deletion
Point mutation
Inversion
Duplication
Answer: 4. Duplication
A duplication consists of a piece of DNA that is abnormally copied one or more times. This type of mutation may alter the function of the resulting protein. In the given sequence, ABC duplication has occurred.
Question 45. Identify the type of mutation in the given diagram.
Inversion
Insertion
Deletion
Substitution
Answer: 2. Insertion
In the given diagram, there is an insertion of T in the given segment of the gene, so the diagram depicts the insertion type of mutation.
Question 46. The chromosome shown in the diagram below is broken at the points which are indicated by the arrows and the genes between these points became inverter. The resulting order of the genes will be
PQUTSRVW
WVUTSRQP
PQTURSVW
VWUTSRPQ
Answer: 1. PQUTSRVW
The given example represents inversion mutation in which the order of genes in a chromosome gets inverted. Thus, the resultant gene order would be PQUTSRVW
Question 47. Ochre mutations are mutations of ………… codon.
UAG
UAA
AUG
UGA
Answer: 2. UAA
Stop codons were historically given many different names, as they each corresponded to a distinct class of mutants that all behaved in a similar manner.
Amber mutations (UAG) were the first set of non-sense mutations to be discovered, isolated by Richard Epstein and Charles Steinberg and named after their friend Harris Bernstein (whose last name means ‘amber’ in German).
Ochre mutation (UAA) was the second stop codon mutation to be discovered.
Given a colour name to match the name of amber mutants, ochre mutant viruses had a similar property in that they recovered
infectious ability within certain suppressor strains of bacteria
Question 48. When a segment of chromosome breaks and later rejoins after 180° rotation, it is known as
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Interstitial translocation
Reciprocal translocation
Answer: 3. Inversion
In the inversion mutation, the chromosome breaks and later rejoins in an inverted (180° rotation) position.
Question 49. A transition type of gene mutation is caused when
GC is replaced by TA
AT is replaced by CG
CG is replaced by GC
AT is replaced by GC
Answer: 4. AT is replaced by GC
Transitions are substitution gene mutations in which a purine (say adenine) is replaced by another purine (say guanine) or a pyrimidine (say thymine) is replaced by another pyrimidine (say cytosine).
Change of codon ATC to GTC or ATT or ACC is an example of transition.
Question 50. Given below is a representation of a kind of chromosomal mutation. What is the kind of mutation represented?
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Reciprocal translocation
Answer: 3. Inversion
The kind of mutation represented is inversion. During inversion, a segment of the chromosome gets inverted in the process of reattachment.
Thus, a chromosome having the genes ABCDEFGH in linear order may get the segment BCD inverted. The new arrangement will be A D C B E F G H.
It is a chromosome aberration entailing two breaks in a chromosome followed by a reversal of the segment and consequently of the gene sequence in the segment.
Pericentric inversion includes the centromere in the inverted segment, whereas paracentric inversions do not include the centromere.
Question 51. Which of the following alterations of the codons ATTGCC is most serious?
ATCGCC
ATTGCA
ATTCCCGCC
ATTTGCC
Answer: 4. GC
In options 1 and 2, the given sequence is changed from ATTGCC to ATCGCC and ATTGCA respectively, by replacement of one base with another or substitution.
It changes only a single codon and thereby, replaces single amino acid with another, but the entire reading frame is not affected.
In option 3, the given sequence is changed from ATTGCC to TGCC by the addition of three bases and thus, one amino acid but there is no effect on the rest of the reading frame.
In option 4, the given sequence is changed from ATTGCC to AGC by the addition of T in 4th place.
The gene mutations that alter the base sequence of the whole genetic frame from the point of the mutation are called frame-shift mutations.
Here, the reading frame of the base sequence is shifted forward due to the insertion of one nucleotide base which in turn, changes the succeeding codon sequence from ATT- GCC to ATTTGC- C and causes the most serious alternation among the given options. Hence, option 4 is the correct answer
Question 52. The insertion or deletion of a base pair into the genetic code will cause a frame-shift mutation unless the number of base pairs inserted or deleted is
1
2
3
10
Answer: 3. 3
Frame-shift mutation occurs when one or two nucleotides are either added or deleted from DNA. The result of such mutation is the non-functioning of protein because the sequence of codons is altered.
However, when three or multiple of three base pairs are altered, frame-shift mutations do not occur
Question 53. In a mutational event, when adenine is replaced by guanine, it is a case of
Frameshift mutation
Transcription
Transition
Transversion
Answer: 3. Transition
Transitions are substitution gene mutations in which a purine (say adenine) is replaced by another purine (say guanine) or a pyrimidine (say thymine) is replaced by another pyrimidine (say cytosine).
Change of codon ATC to GTC or ATT or ACC is an example of transition.
Question 54. Translocation is a type of chromosomal aberration where
Parts of the chromosome are exchanged between homologous chromosomes
A part of one chromosome is exchanged between non-homologous counterpart
A part of one chromosome is shifted to its homologous counterpart
A part of one chromosome is shifted to another part of the same chromosome
Answer: 2. A part of one chromosome is exchanged between non-homologous counterpart
In translocations, when a portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome.
There are two main types of translocations. In a reciprocal translocation, segments from two different chromosomes have been exchanged.
In a Robertsonian translocation, an entire chromosome has attached to another at the centromere; these only occur with
chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21 and 22.
So, translocation is a type of chromosomal aberration where a part of one chromosome is exchanged between non-homologous counterparts.
Question 55. The type of chromosomal aberration indicated in the diagram is
Interstitial translocation
Reciprocal translocation
Pericentric inversion
Paracentric inversion
Interstitial deletion
Answer: 3. Pericentric inversion
The given diagram represents pericentric inversion as the centromere is included in it.
Question 56. Which one of the following is a wrong statement regarding mutations?
Deletion and insertion of base pairs cause frame-shift mutations
Cancer cells commonly show chromosomal aberrations
Uv and gamma rays are mutagens
Change in a single base pair of DNA does not cause mutation.
Answer: 4. Change in a single base pair of DNA does not cause mutation.
The statement in option 4 is wrong and can be corrected as a Change in single base pair of DNA is also a type of mutation called a point mutation.
It is a type of mutation that causes the replacement of a single base nucleotide with another nucleotide of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. For example, a point mutation is the cause of sickle cell disease. Rest all statements are correct regarding mutations.
