Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Nutrient Cycling and Ecosystem Services
Question 1. The total amount of nutrients like carbon, phosphorus, calcium, etc., present in soil at any time is referred to as
- Standing Crop
- Standing State
- Nutrient Crops
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Standing State
The total amount of nutrients like carbon, phosphorus, calcium, etc., present in soil at any given time is called standing state. Standing state varies with the kind of ecosystem and season.
Question 2. The movement of nutrient elements through various components (abiotic and biotic) of an ecosystem is called
- Carbon Cycle
- Geochemical Cycle
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- Water cycle
Answer: 3. Biogeochemical Cycle
The term nutrient cycle or biogeochemical cycle is used for the exchange/circulation of biogenetic nutrients between the living and non-living components of the biosphere. Biogenetic nutrients or biogeochemical nutrients are essential elements required by the organisms for their body building and metabolism. These are provided by earth and return to earth again after their death and decay.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Biogeochemical cycles are of
- Two Types
- Three Types
- Four Types
- Five types
Answer: 1. Two Types
“questions for ecology “
The biogeochemical cycles are classified into two types, namely gaseous cycles and sedimentary cycles
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
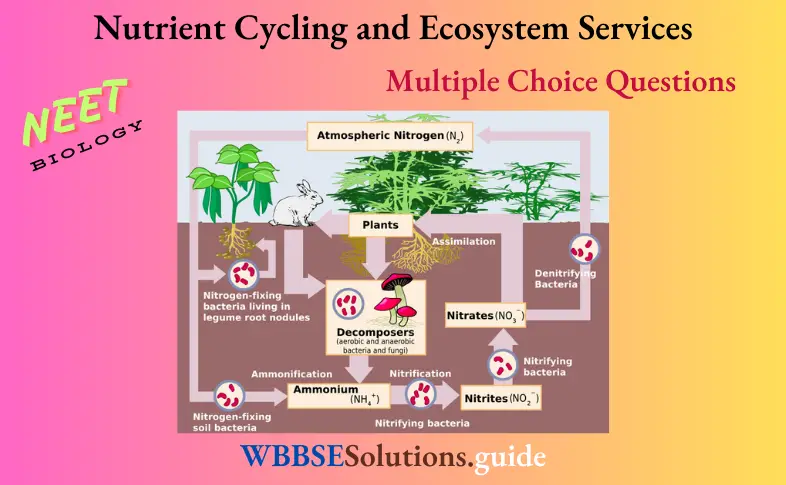
NEET Biology Nutrient Cycling MCQs with answers
Question 4. The biogeochemical cycle may be
- Gaseous
- Sedimentary
- Gaseous and sedimentary
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Gaseous and sedimentary
There are two types of biogeochemical cycles, i.e. gaseous type and sedimentary type. In gaseous type, the atmosphere constitutes the major reservoir of the element that exists there in gaseous phase, e.g. carbon and nitrogen cycles. In sedimentary type, major reservoir is the lithosphere, from which the elements are released by weathering, e.g. phosphorus, sulphur cycles.
Question 5. The reservoir pool for gaseous cycles of matter is
- Atmosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Both 1 And 2
- Lithosphere
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
In gaseous cycles, the materials involved in circulation between biotic and abiotic components of biosphere are gases or vapours and the reservoir pool is atmosphere or hydrosphere, e.g. C, H, O2, N2 and HO2 .
Question 6. Which of the following play a direct role in maintaining the nutrient and energy flow in biogeochemical cycle?
- Decomposers
- Producers
- Consumers
- Herbivores
Answer: 1. Decomposers
Decomposers are heterotrophs capable of reducing the complex organic matters of dead organic remains into simple inorganic forms. Thus, they play a direct role in maintaining the nutrient and energy flow in biogeochemical cycles
Important MCQs on Nutrient Cycling for NEET
Question 7. A cycle in which the elements return to and are withdrawn from the atmosphere. This type of cycle is called
- Gaseous
- Sedimentary
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Gaseous
In a gaseous cycle, the element return to and is withdrawn from the atmosphere as a gas. The four most abundant elements in the living systems (H, C, O, N) have predominantly gaseous cycles.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 8. Biogeochemical cycle of which element has atmospheric phase?
- Carbon
- Sodium
- Phosphorus
- Magnesium
Answer: 1. Carbon
“ecosystems questions and answers “
Carbon has gaseous cycle. Other materials showing gaseous cycles are nitrogen, oxygen and water. All these gaseous cycles has atmospheric phase. The biogenetic materials involved in circulation between the biotic and abiotic components of biosphere are non-gaseous and have lithosphere as the main reservoir pool, e.g. phosphorus, calcium, magnesium.
Question 9. Edaphic nutrient cycle includes
- Gaseous Types
- Partial Sedimentary Types
- Total sedimentary types
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Edaphic nutrient cycles include gaseous types, partial sedimentary types and total sedimentary types cycles. Thus, option is correct.
Question 10. Biogeochemical cycles can be traced in
- Ecosystems
- Biomes
- Water
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 1. Ecosystems
Biogeochemical cycles can be traced in ecosystems.
NEET previous year questions on Nutrient Cycling and Ecosystem Services
Question 11. The reservoir for the sedimentary cycle exists in
- Earth Crust
- Organic Sediments
- Calcareous Sediments
- Limestone
Answer: 1. Earth Crust
In sedimentary cycle, the main reservoirs are soil and rocks (earth crust), e.g. sulphur cycle, phosphorus cycle, etc.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 12. Match Column I with Column II and select the correct option from codes given below.
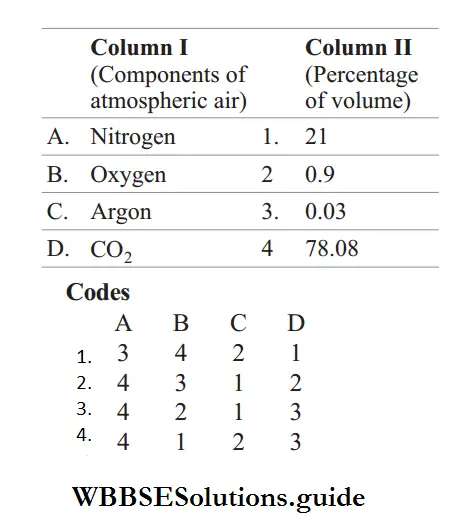
Answer: 1. A–3, B–4, C–2, D–1
Question 13. What is the reason behind deficit arising in nutrient reservoir?
- Due to imbalance in the rate of influx
- Due to imbalance in the rate of efflux
- Due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux
The nutrient reservoir meets the deficit arising due to imbalance in the rate of influx and efflux of nutreint.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 14. The reservoir for the gaseous type of biogeochemical cycle exists in
- Stratosphere
- Atmosphere
- Troposphere
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 2. Atmosphere
In gaseous cycles, the main reservoirs of chemical are the atmosphere and ocean, e.g. carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, oxygen cycle, etc.
Question 15. In which of the following both pairs have correct combination?
- Gaseous nutrient cycle–Nitrogen and sulphur Sedimentary nutrient cycle–Carbon and phosphorus
- Gaseous nutrient cycle–Sulphur and phosphorus Sedimentary nutrient cycle–Carbon and nitrogen
- Gaseous nutrient cycle–Carbon and nitrogen Sedimentary nutrient cycle–Sulphur and phosphorus
- Gaseous nutrient cycle–Carbon and sulphur Sedimentary nutrient cycle–Nitrogen and phosphorus
Answer: 3. Gaseous nutrient cycle–Carbon and nitrogen Sedimentary nutrient cycle–Sulphur and phosphorus
Option represents both pairs as correct combination. In gaseous nutrient cycles, the materials involved in circulation are gases or vapours and the reservoir pool is atmosphere or hydrosphere, e.g. carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and water. In sedimentary nutrient cycles, materials involved in circulation are non-gaseous and the reservoir pool is lithosphere, e.g. phosphorus, calcium, magnesium. Sulphur has both sedimentary and gaseous nutrient cycles.
“questions about ecosystem with answers “
Question 16. Which of the following is important in water cycle?
- Transpiration through leaves
- Evaporation from ocean
- Percolation of water into the ground
- Absorption of capillary water by plants
Answer: 2. Evaporation from ocean
The water cycle describes how water evaporates from the surface of the earth, rises into the atmosphere, cools and condenses into rain or snow in clouds and falls again to the surface as precipitation. Evaporation occurs when warmth from the sun causes water from oceans, lakes, streams, ice and soils to rise into the air and turn ve water vapour (gas).
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 17. Forest regions receiving water. In this, which cycle is observed?
- Hydrological cycle
- Carbon cycle
- Nitrogen cycle
- Calcium cycle
Answer: 1. Hydrological cycle
The hydrological cycle of the earth is the sum total of all processes in which water moves from the land and ocean surface to the atmosphere and back in form of precipitation. Thus, forest regions receiving water from hydrological cycle.
NEET quiz on Nutrient Cycling with solutions
Question 18. Assertion Sulphur contributes maximum to sedimentary cycle. Reason (R) Most of the sedimentary rocks have fossils.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Sulphur contributes maximally to sedimentary cycle as sulphur is present in majority of rocks, minerals, ocean sediments, etc. Sulphur is also present in fossils that are found in sedimentary cycles.
Question 19. Source of maximum sulphur is
- Ocean
- Land
- Rocks
- Lakes
Answer: 3. Rocks
The majority of the earth’s sulphur is stored underground in rocks and minerals, including as sulphate salts buried deep within ocean sediments that are being found in sedimentary
cycles.
Question 20. The only natural source of sulphur dioxide is …………… which contributes 2 × 109 kg to 5 × 109 kg sulphur per year is
- Acid Rains
- Sea
- Volcano
- Industrial wastes
Answer: 3. Volcano
Sulphur dioxide is produced naturally as a result of forest fires and from volcanoes.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 21. Given below is a simplified model of phosphorus cycling in a terrestrial ecosystem with four blanks (A -D). Identify the blanks.
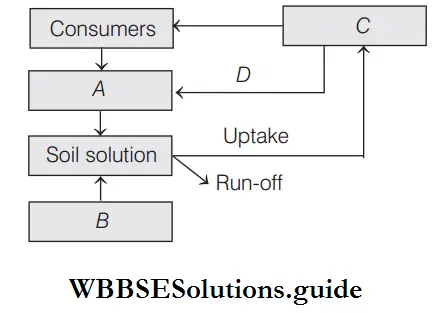
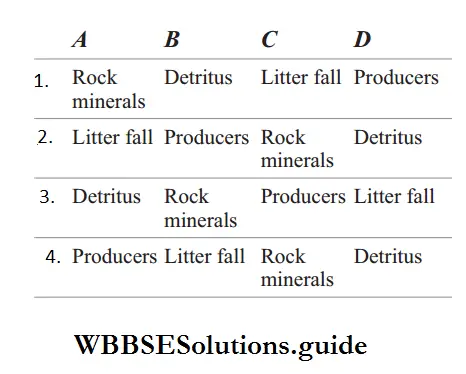
Answer: Option is 3 correct. It can be represented as
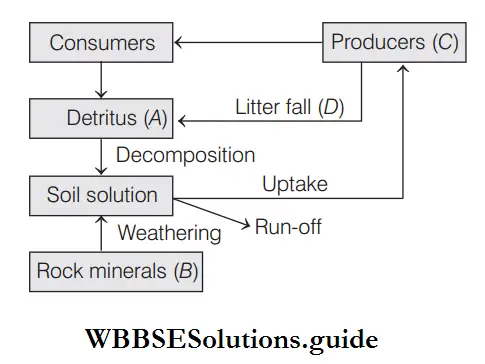
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 22. Phosphorus cycle is a/an
- Gaseous Cycle
- Perfect Cycle
- Imperfect Cycle
- Partly gaseous and partly sedimentary
Answer: 3. Imperfect Cycle
Phosphorus cycle is an imperfect cycle as the biological processes account for considerable losses of the phosphorus from the cycle.
NEET expected MCQs on Nutrient Cycling 2025
Question 23. Phosphorus of ocean becomes available to land plants due to
- Sea Birds
- Deep Sea Activities
- Ocean spray
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Sea Birds
Phosphorus moves from the ocean to the land by birds feeding on fish or ocean plants and excreting ‘guano’ onto land. Without the role of birds, phosphate would remain in oceans.
Question 24. The phosphorus rich fertiliser obtained from sea birds along the coast of Chile and Peru, is
- Guano
- Bone Meal
- Dung
- Urea
Answer: 1. Guano
The excess of phosphate in the bodies of animals is excreted out through faeces. Sea bird guano (excreta) along the coast of Chile and Peru contains a large amount of phosphate.
Question 25. Natural reservoir of phosphorus is
- Animal Bones
- Rock
- Fossils
- Sea water
Answer: 2. Rock
The natural reservoir of phosphate is rock which contains phosphorus in the form of phosphates. When rocks weather away, minute amounts of this phosphate dissolves in soil solution and is absorbed by the roots of the plants. Herbivores and other animals obtain this element from plants.
Question 26. The phosphorus cycle differs from those of carbon and nitrogen as well as those of sulphur, oxygen and hydrogen as it lacks
- Water
- Dust Particles
- Gaseous phase
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Gaseous phase
Phosphorus cycle has no atmosphere phase as it lack geseous phase. The ultimate source of phosphate in the ecosystem is crystalline rocks.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 27. Which one of the following element is the critical limiting factor in the function of ecosphere because of its irretrievable loss into the ocean?
- Phosphorus
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Iron
Answer: 1. Phosphorus
A large amount of phosphorus is lost in the sea by sedimentation. This is an irretrievable loss and due to this, phosphorus acts as critical limiting factor in ecosphere functioning.
Question 28. Phosphorus is needed for the production of
- Bones And Teeth
- Cellular Membranes
- DNA and RNA
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Phosphorus is needed for the production of DNA and RNA, cellular membranes, bones and teeth.
Thus, option is current
Question 29. Phosphorus is the major constituent of
- Biological membranes.
- Nucleic acids.
- Cellular energy transfer system.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
Phosphorus is the major constituent of biological membrane, nucleic acids and cellular energy transfer systems.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
“ecosystem question answer “
Question 30. Phosphorus cycling occurs in the form of
- HPO3-
- P2 (gas)
- PO43−
- AI2(PO4)3
Answer: 3. PO43−
Phosphorus cycling occurs in the form of Organic phosphorus circulates in nature from plants to animals. Phosphate is released by decomposers (phosphatising bacteria) back to soil.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 31. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as salts, this process is called
- Mineralisation
- Humification
- Leaching
- Fragmentation
Answer: 3. Leaching
Leaching is the process of extracting substances from a solid by dissolving them in a liquid, naturally.
Question 32. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the phosphorus cycle?
- Phosphates are the major form of phosphorus reservoir
- Phosphorus solubilising bacteria facilitate the release of phosphorus from organic remains
- There is an appreciable respiratory release of phosphorus into the atmosphere
- It is a sedimentary cycle
Answer: 3. There is the appreciable respiratory release of phosphorus into the atmosphere
- The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as
- There is no respiratory release of phosphorus into the atmosphere because phosphorus is an inorganic nutrient that does not take part in respiration.
- The phosphorus cycle is a type of sedimentary cycle, i.e. its main reservoirs are soil and rocks. It is mainly found as phosphates in rocks.
- During this cycle, phosphorus solubilising bacteria like Pseudomonas, Acetobacter, etc., help to release phosphorus from organic remains. A large amount of phosphate is lost in sea by sedimentation.
- The rest other statements are correct regarding the phosphorus cycle.
Question 33. What is true about the phosphorus cycle?
- Rocks are the natural reservoirs of phosphorus.
- Weathering of sedimentary rocks makes phosphate available to the soil.
- Nitrosomonas plays a key role in fixing phosphorus to the soil.
- Herbivores and carnivores obtain phosphorus from plant directly or indirectly.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 4
All given statements are true except 3. The incorrect statement can be corrected as: Nitrosomonas helps in fixing atmospheric nitrogen to soil.
The major reservoir for phosphorus is phosphate rocks and fossil bone deposits, laid down in the past geological ages. There is no atmospheric phase in the phosphorus cycle. Phosphorus becomes available in the soil for plants use by natural erosion of rocks and by human efforts.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 34. In the phosphorus cycle, weathering makes phosphate available first to Punjab PMET
- Producers
- Decomposers
- Consumers
- None of these
Answer: 1. Producers
In the phosphorus cycle, weathering makes phosphate available to the soil from where plants or producers get them first. Inorganic phosphates are absorbed by the plants from soil and water bodies which eventually pass into animals through food chain.
Entry of phosphorus in the green plants (producers) occur, via. labile inorganic pool. From plants, it travels to various trophic levels in the form of organic phosphates.
NEET Biology Nutrient Cycling and Ecosystem Services MCQs with explanations
Question 35. An overabundance of phosphorus in coastal areas and at the mouth of rivers causing overgrowth of algae which results in the depletion of oxygen and killing of aquatic life is called
- Mineralisation
- Eutrophication
- Leaching
- Humification
Answer: 2. Eutrophication
Eutrophication (meaning ‘well-nourished’) or hypertrophication occurs when a water body becomes overly enriched with minerals and nutrients which induce excessive growth of algae.
This process may result in oxygen depletion of the water body. Eutrophication is often induced by the discharge of nitrate or phosphate-containing detergents, fertilisers or sewage into an aquatic system.
Question 36. The concentration of nitrogen remains constant by
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Thundering And Light
- Enzymes
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
The concentration of nitrogen remains constant by nitrogen cycle, thundering and light.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 37. The organisms which participate most actively in nitrogen cycle in nature are
- Saprophytic Angiosperms
- Parasitic Fungi
- Bacteria
- Legumes
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Bacteria mostly participate actively in nitrogen cycle.
Question 38. The major chunk of nitrogen in nature is fixed by
- Lightning
- Symbiotic Bacteria
- Denitrifying Bacteria
- Chemical industries
Answer: 2. Symbiotic Bacteria
An important and major nitrogen fixing bacteria, Rhizobium leguminosarum, lives in the root nodule of the plants of Leguminosae family can fix direct atmospheric nitrogen. It is a mutualistic, symbiotic bacteria.
Other important symbiotic bacteria are Frankia, associated with certain dicotyledonous species (actinorhizal plants) and certain Azospirillum species, associated with cereal grasses.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 39. The conversion of ammonia into nitrites and nitrates is called
- Ammonification
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Nitrification
The conversion of ammonia into nitrites and nitrates is called nitrification. It involves the oxidation of ammonia to nitrates through nitrites in the presence of nitrifying bacteria. Nitrite bacteria (Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus) convert ammonia to nitrites whereas nitrate bacteria (Nitrobacter and Nitrocystis) convert nitrite to soluble nitrates.
Question 40. One of the useful activities of most of the bacteria is
- Nitrogen-Fixation
- Nitrification
- Operation of biogeochemical cycles
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
One of the useful activities of most of the bacteria is nitrogen fixation, nitrification and operation of biogeochemical cycles.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 41. Denitrification is
- Reduction Of NO2
- To Ammonia By Bacteria In The Soil
- Conversion Of Ammonia To Amino Acids
- Conversion Of Ammonia And Nitrates To Gaseous Nitrogen
- Oxidation Of Ammonia To Nitrate
Answer: 3. Conversion Of Ammonia And Nitrates To Gaseous Nitrogen
The part of nitrogen cycle where ammonium is converted into nitrate is called nitrification. Denitrification is the process in which reduction of nitrate occur into nitrogen gas.
Question 42. The limiting factor in nitrification of soil is
- pH
- Temperature
- Light
- Air
Answer: 1. pH
Soil pH is the limiting factor in soil nitrification. 8.5 is the optimal pH for nitrification. A pH lower than 7.5 slows down the nitrobacteria activity.
“ecological pyramid of grassland ecosystem “
Question 43. Role of nitrifying bacteria in nitrogen cycle is to
- Convert Ammonia Into Nitrates
- Fix Atmospheric Nitrogen
- Convert Ammonia Into Nitrogen
- Convert amino acids into ammonia
Answer: 1. Convert Ammonia Into Nitrates
Nitrifying bacteria such as Nitrobacter converts nitrites to nitrates, while Nitrosomonas converts ammonia to nitrites.
Thus, option 1 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 44. Which two distinct microbial processes are responsible for the release of fixed nitrogen as dinitrogen gas (N2) to the atmosphere?
- Aerobic nitrate oxidation and nitrite reduction
- Decomposition of organic nitrogen and conversion of dinitrogen to ammonium compounds
- Enteric fermentation in cattle and nitrogen-fixation by Rhizobium in root nodules of legumes
- Anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification
Answer: 4. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification
Denitrification is a chemical process in which nitrates in the soil are reduced to molecular nitrogen (N2) which is then released into the atmosphere. It is done by denitrifying bacteria like Pseudomonas denitrificans. Anaerobic oxidation of ammonium (NH4) also releases nitrogen in atmosphere.
Question 45. ……… is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
- CO2
- O2
- SO2
- NO2
Answer: 2. O2
The main product of photosynthesis is glucose, which is the molecule that produces energy to run the processes of the cell. Oxygen is mainly a byproduct of the process of photosynthesis.
Question 46. Assertion Maximum contribution of oxygen is from phytoplankton. Reason (R) 90% of the photosynthesis with oxygen evolution is contributed by them.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Phytoplanktons are the major producers of ocean ecosystem. They release about 90% of the oxygen in the atmosphere, via. photosynthesis.
Question 47. Match the following columns.
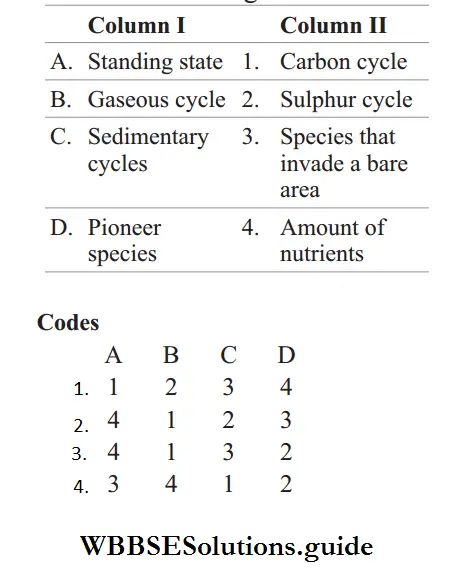
Answer: 2. A–4, B–1, C–2, D–3
Mock test on Nutrient Cycling for NEET preparation
Question 48. Identify the incorrect statement from the following.
- Atmospheric inputs of phosphorus through rainfall are much smaller than carbon inputs
- The reservoir pool for the phosphorous cycle is the earth’s crust whereas the atmosphere is the reservoir pool for the carbon cycle
- Gaseous exchanges of phosphorus between organisms and the environment are negligible
- During the carbon cycle and phosphorus cycle, there is very little respiratory release of carbon and phosphorus, respectively
Answer: 4. During the carbon cycle and phosphorus cycle, there is very little respiratory release of carbon and phosphorus, respectively
The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as the Carbon cycle is an example of a gaseous biogeochemical cycle in which the major reservoir is the atmosphere. The phosphorus cycle is a sedimentary cycle, in which the major reservoir are the sediments of the earth. Both carbon and phosphorus are part of living organisms, but only carbon is released by respiration in an environment in form of CO2 gas.
The rest statements are correct.
“the rate of biomass production is called “
Question 49. In green plants, the fixation of CO2 occurs by
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Pollination
- Mineralisation
Answer: 1. Photosynthesis
Carbon fixation or carbon assimilation is the conversion process of inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide) to organic compounds by living organisms. The most prominent example is photosynthesis, although chemosynthesis is another form of carbon fixation that can take place in the absence of sunlight.
Question 50. The quantity of CO2 in the atmosphere is about
- 0.003%
- 0.03%
- 0.3%
- 3.0%
Answer: 2. 0.03%
The percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere remains constant at around 0.03% by volume.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 51. Which of the following is the source of carbon to plants?
- Atmospheric CO2
- CO2 of carbonate rocks
- Fossils
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Atmospheric CO2
The source of carbon dioxide in plants is the atmosphere.
Question 52. The carbon and nitrogen atoms circulating in the biogeochemical cycles are the same atoms that were in
- Insects Of the Cenozoic Era
- Dinosaurs, Insects And Trees Of the Mesozoic Era
- Mammals of the Cenozoic era only
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Dinosaurs, Insects And Trees Of Mesozoic Era
Since, the formation of earth, the cycling of material is occurring in the atmosphere. Therefore, carbon and nitrogen atoms circulating in the biogeochemical cycles are the same atoms that were in dinosaurs, insects and trees of the Mesozoic area.
Question 53. ……… of the dry weight of an organism constitutes carbon.
- 49%
- 59%
- 69%
- 39%
Answer: 1. 49%
Carbon constitutes 49% of the dry weight of an organism.
Question 54. Which of the following acts as a medium for the carbon cycle to occur?
- Atmosphere
- Oceans
- Living and dead organisms
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The carbon cycle occurs through the atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms. It is estimated that 4×1013 kg of carbon is fixed in the biosphere through photosynthesis annually.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 55. About 70% of total global carbon is found in
- Grasslands
- Agro-Ecosystems
- Oceans
- Forests
Answer: 3. Oceans
About 70% of total global carbon is found in oceans. This oceanic reservoir regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Atmosphere contains only about one per cent of total global carbon.
Question 56. The amount of carbon fixed annually through photosynthesis in the biosphere is
- 4 × 1013 kg
- 5 × 1013 kg
- 4 × 1016 kg
- 5 × 1016 kg
Answer: 1. 4 × 1013 kg
Question 57. Carbon is available to crop plants in the form of
- Amino Acids
- Carbon Dioxide
- Elemental Carbon
- Carbonates
Answer: 2. Carbon Dioxide
For photosynthesis, green plants take carbon dioxide from the air.
Question 58. Animals obtain all their carbon through
- Plants
- Soil
- Air
- Water
Answer: 1. Plants
Plants fix atmospheric carbon through photosynthesis. Animals eat plants. Thus, animal obtains all their carbon through plants.
Question 59. The reservoir pool of carbon is
- Air And Water
- Fossil Fuels
- Rocks
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
- Carbon is present in the abiotic environment in the following forms
- CO2 in the air or atmosphere
- Dissolved CO2 or carbonic acid and bicarbonates in water or hydrosphere
- Carbonates and graphite in the rocks and fossils.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 60. Which of the following contributes to the carbon cycle?
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Fossil fuel combustion
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Carbon enters the biotic system through photosynthesis. In photosynthesis, green plants utilise CO2 and incorporate the CO2 in glucose. In respiration, burning of biomass and fossil fuels, a lot of CO2 is released. Burning of fossil fuels adds 6×1012 kg of carbon into the atmosphere.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 61. Identify the activities that result in the release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
- Burning of wood
- Volcanic activity
- Combustion of organic matter
- Fossil fuels
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
- 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Burning of wood, forest fire, volcanic activity, and combustion of organic matter and fossil fuels area are some essential sources for releasing CO2 in the atmosphere.
Thus, option 1 is correct.
Question 62. The role of bacteria in the carbon cycle is
- Breakdown Of Organic Matter
- Photosynthesis
- Assimilation
- Chemosynthesis
Answer: 1. Breakdown Of Organic Matter
Bacteria are essential to the proper functioning of the carbon cycle on earth. Along with fungi, they are the main decomposers that break down organic molecules and release carbon back into the carbon cycle, via. the air and soil.
NEET practice test on Nutrient Cycling and Ecosystem Services
Question 63. Of more immediate concern regarding carbon cycle is
- Increased Output Rate Of Carbon Locked In Deposits Of Coal, Petroleum And Natural Gas
- Greenhouse Gases
- Increase in the total mass of carbon in earth’s atmosphere by 12-14%
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The immediate concern regarding carbon cycle is greenhouse gases, increase in the total mass of carbon in earth’s atmosphere by 12-14% and depleting fossil fuels due to increased output rate of carbon locked in deposits of coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Thus, option 4 is corect.
Question 64. An action of humans that is rapidly increasing and is resulting in an overload of the carbon cycle.
- Use of green energy
- Biotechnology
- Deforestation
- Afforestation
Answer: 3. Deforestation
Human activities like deforestation and burning of fossil fuel has caused an increase in the amount of CO2 in atmosphere.
Question 65. Assertion Oceans acts as a global sink for CO2. Reason (R) Human activities are increasing CO2 concentration in the air.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Carbon dioxide is almost certainly being absorbed by the oceans, which act as a global ‘sink’ for CO2. It is not clear how much more CO2 ocean can hold. Human activities like deforestation, massive burning of fossil fuel for energy and transport has caused an increase in the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Question 66. Consider the following statements about the carbon cycle.
- The atmospheric input of carbon from rainfall is greater.
- Carbon gas is exchanged between organisms and the atmosphere during respiration.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 67. Human activities affecting carbon cycle is
- Burning of fossil fuels
- Burning and ploughing of tropical rainforest
- Growing paddy
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Human activities that are affecting carbon cycle are burning of fossil fuels, growing excessive paddy and burning and ploughing of rainforests.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 68. Ecological services include
- CO2 fixation, release of O2, pollination
- O2 fixation, release of CO2, fertilisation
- Nitrogen-Fixation, Release Of Nh3, Syngamy
- Phosphorus Fixation, Release Of Phosphate, Transformation
Answer: 1. CO2 fixation, release of O2, pollination
All the natural processes, arising from healthy ecosystems that are beneficial to the living components of the ecosystem are called as ecological services, e.g. CO2 fixation, release of O2, pollination.
Question 69. According to Robert Costanza, 50% of the total cost for ecosystem services goes to Karnataka CET
- Nutrient Cycling
- Recreation
- Soil Formation
- Climate regulation
Answer:
Out of the total cost of various ecosystem services, the soil formation accounts for about 50%. Contributions of other services like recreation and nutrient cycling are less than 10% each. The cost of climate regulation and habitat for wildlife are about 6% each.
Question 70. Fill up the blanks.
- The products of ecosystem processes are called …A….
- …B… are the major source of ecosystem services.
- …C… and his colleagues tried to put price tags on nature’s life support services which, came up to US …D… a year.
Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
- A–Ecosystem services, B–Plants, C–Robert Brown, D–31 trillion
- A–Ecology services, B–Plants, C–Robert Costanza, D–32 trillion
- A–Ecosystem services, B–Forests, C–Robert Costanza, D–33 trillion
- A–Ecology services, B–Pond C–Robert Brown, D–34 trillion
Answer: 3. A–Ecosystem services, B–Forests, C–Robert Costanza, D–33 trillion
