Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Population Attributes
Question 1. The study of population is called
- Demography
- Bibliography
- Both and (b)
- Cartography
Answer: 1. Demography
Demography is the study of population in all aspects.
Question 2. The term ‘demography’ was first used by
- Darwin
- Guillard
- Millar
- Lamarck
Answer: 2. Guillard
The term demography was coined by Achille Guillard in 1855. But, in fact, John Grant is considered the real founder of demography, who wrote the book ‘Natural and Political Observations Made Upon the Bills of Mortality’, in 1762.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. July 11th is observed
- World population day
- No tobacco day
- World environmental day
- World health day
Answer: 1. World Population Day
World population day – 11th July No tobacco day – 31st May World environment day – 5th June World health day – 7th April
organism and population neet pyq
Question 4. In demography, we study
- Decrease or increase in population
- The ratio of different age groups of males and females
- Distribution of population in different countries
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
In demography, we study the decrease or increase in population, the ratio of different age groups of males and females, distribution of the population in different countries.
Question 5. Population
- Total number of interbreeding individuals of a species found in a particular place
- Total number of interbreeding individuals of a species found in the same geographical area
- Total number of interbreeding individuals of a species found in different geographical areas
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Total number of interbreeding individuals of a species found in a particular place
Population is the total number of interbreeding individuals of a species found in a particular area who share and compete for similar resources.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET

NEET Biology Population Attributes MCQs with answers
Question 6. The significance of the study of population is to know
- The consequences of an uncontrolled population only
- The benefits of planned family
- The population growth, distribution, and density
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The significance of population study is to know the consequence of uncontrolled population, the benefits of family planning, population growth, density, and distribution.
Question 7. The present population of the world is about
- 500 Million
- 100 Billion
- 7 Billion
- 15 Billion
Answer: 3. 7 Billion
The human population of the world is estimated to have crossed 7 billion in the year 2011 (as per the United Nations Organization)
Question 8. The least densely populated state of India is
- Kerala
- Sikkim
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Jammu and Kashmir
Answer: 3. Arunachal Pradesh
The state with the lowest population density is Arunachal Pradesh and the union territory with the lowest density of population is Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The union territory with the highest population density is Delhi.
Question 9. Census
- Official and periodic counting of the population of a species
- Unofficial counting of population
- Official and periodic counting of population of all species in a given area
- Official counting of males only
Answer: 1. Official and periodic counting of the population of a species
A census is an official counting of the population of a species and preparing data about age groups, birth rate, death rate, sex ratio, education, etc
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. According to the latest census, the most densely populated country in the world is
- Pakistan
- India
- Japan
- Bangladesh
Answer: 4. Bangladesh
Among these four Bangladesh is the most densely populated country. Monaco, one of the world’s smallest countries, is also second most densely populated country in the world
Question 11. The increase in population per unit of time is called
- Population growth
- Population dynamics
- Population ratio
- Population density
Answer: 1. Population growth
Population growth can be defined as the increase in population per unit of time.
population attributes
Question 12. What is the most important factor for the success of the animal population?
- Natality
- Unlimited food
- Adaptability
- Inter-species activity
Answer: 3. Adaptability
The process by which a species becomes fit for its survival in the environment is called adaptability. When the environmental factor changes the organism has to adapt to the surroundings by changing its temperature or metabolism over a period of time. Hence, adaptability is the result of natural selection.
Question 13. The technical term that describes population size is
- Population density
- Demography
- Population growth
- Population dynamics
Answer: 1. Population density
- Population size is technically called population density (designated as n).
- The size of a population depends upon several factors like mortality, natality, etc.
- The size in nature could be as low as less than 10 (Siberian cranes at Bharatpur wetlands in any year) or go in millions (Chlamydomonas in a pond).
Question 14. Which of the following is not a dynamic of population?
- Natality
- Mortality
- Sex ratio
- Water potential
Answer: 4. Water potential
The main dynamics of the population are population density, natality, mortality, sex ratio, and age groups. Option (4) is not a dynamics of a population as water potential is the potential energy of water per unit volume relative to pure water.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 15. Disturbed sex ratio is observed in which Indian state?
- Madhya Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Bihar
- Haryana
Answer: 4. Haryana
Among the given states the worst sex ratio is seen in Haryana. As of today, Haryana’s sex ratio is 924 girls for 1000 boys. This is due to sex-selective abortion, infanticide, and neglect of the girl child.
Question 16. Population density means
- The number of individuals per unit area
- The number of individuals in a unit area at a specific time
- The concentration of the human population in a place
- None of the above
Answer: 2. The number of individuals in a unit area at a specific time
Population density is the number of individuals per unit (geographical) area at a specific time.
Question 17. Which of the following states has the highest population density?
- Bihar
- Madhya Pradesh
- Nagaland
- Maharashtra
Answer: 1. Bihar
Bihar is a highly populated state (1106 persons/sq km.) Followed by West Bengal 1028 and Kerala 860.
population attributes
Question 18. Population density can be calculated by
- D = s/n
- D = n/s
- D = s/w
- N = w/sd
Answer: 2. D = n/s
The total number of individuals present in a unit area or volume at a specific time is called its population density.
It can be calculated as
- D = n/s,
- Where, d = density,
- N = total number of individuals in a region and
- S = size of unit area in the region.
Question 19. The formula for the calculation of population density is d = n/a in this formula ‘a represents
- Whole world population
- Unit of time
- Population density
- Area of the land
Answer: 4. Area of the land
The formula for population density is d = n/a, where d is the population density, n is the total population and a is the land area covered by the population.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 20. Find out the population density when n is 1000 and s is 100 m 2.
- 10
- 100
- 1
- 1000
Answer: 1.10
Population density
\(=\frac{\text { Number of individuals }}{\text { Area }}=\frac{1000}{100}=10\)Question 21. If a pond has 20 lotus plants 8 new plants are added through reproduction. Then the birth rate is
- 0.8 offspring per lotus per year
- 0.2 offspring per lotus per year
- 0.4 offspring per lotus per year
- 0.6 offspring per lotus per year
Answer: 3. 0.4 offspring per lotus per year
- Current number of lotus plants = 20
- New plants added = 8
- Birth rate = 8/20 = 0 4. Offspring per
Question 22. The country that shows a negative population growth rate is
- Brazil
- France
- Sweden
- America
Answer: 3. Sweden
Sweden, Germany, Italy, Denmark, and Hungary show negative population growth, i.e. The population is not growing but is actually losing population.
Question 23. The population of any species is
- A static phenomena
- A dynamic phenomena
- Neither (1) nor (2)
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. A dynamic phenomena
population attributes
The population keeps on changing due to various factors like immigration, emigration, natality, and mortality. So, it is a dynamic rather than a stable phenomenon.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 24. The dynamism of the population is
- Increase in population
- Change in population
- Decrease in population
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Population dynamics refers to how populations of a species change over time (i.e. Increase or decrease in population). Important factors in population dynamics include rates of reproduction, death, and migration.
Question 25. The relative proportion of individuals of various age groups in the population is called ………… Of the population.
- Diversity
- Density
- Age structure
- Community
Answer: 3. Age structure
The age structure of a population is the distribution of people of various ages. It is a useful tool for social scientists, public health and health care experts, policy analysts, and policy-makers because it illustrates population trends like rates of births and deaths.
Question 26 The age distribution of a population is determined by the
- Timing of birth and deaths
- The rate at which the population is growing
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
The age distribution of a population is determined by the timing of birth and deaths and the rate at which the population is growing.
population attributes
Question 27. According to the population of the world, India is placed
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Answer: 2. Second
The ten countries with the largest population in the world today are China followed by India, the United States, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Russia, and Mexico, therefore India resulted second.
Question 28. The average population density of developing countries such as India in comparison to developed countries like USA is
- Equal
- Less
- More
- Ever changing
Answer: 3. More
In 2018, the population density of the USA was approximately 36 residents per square kilometer of land area. In 2018, the population density of India was approximately 455 residents per square kilometer (the World Bank data). Therefore, the average density of India is higher in comparison to the USA.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 29. According to which theory will the human population out-run food supply?
- Intrusion theory
- Malthusian theory
- Eltons theory
- Malthusian theory
Answer: 2. Malthusian theory
Thomas R. Malthus put forward a theory of human population growth in 1778. A Malthusian catastrophe was a prediction of a forced return to subsistence-level conditions once population growth had outpaced agricultural production.
Question 30. Which one of the following is a population?
- A spider and some trapped flies in its web
- Earthworm that lives in grassland along with other arthropods
- All the plants in a forest
- All the oak trees in a forest
Answer: 4. All the oak trees in a forest
population attributes
Out of the given option, all the oak trees in a forest are considered as population. Population refers to the number of organisms/individuals of the same species that live in a particular geographic area at the same time with the capability of interbreeding.
Question 31. Who was the first scientist to estimate the human population?
- Darwin
- Malthus
- Garrod
- Vavilor
Answer: 2. Malthus
Malthus was the first man to publicly predict the limits of the human population and how population and well-being are connected. In 1798, Malthus wrote an essay on the principle of population, which explained his predictions and changed the views of many people.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 32. The higher human population in cities is mainly due to
- A lot of opportunities for education
- Availability of clean drinking water
- Better sanitation
- Higher-income resources
Answer: 4. Higher income resources
Birth and death rates are two major factors that determine the population growth of a country. Better medical facilities, food availability, and better economic condition have decreased the death rate as well as the birth rate have increased considerably. Thus, the higher human population in cities is mainly due to higher income resources.
Question 33. The highest and lowest population in India is in ………… And ……………. Respectively.
- Mp, Tripura
- Up, Sikkim
- Maharashtra, Nagaland
- Andhra Pradesh, Assam
Answer: 2. Up, Sikkim
According to the state census 2011, the most populated state in India is Uttar Pradesh with a population of 19.96 crores. The least populated state in the country is Sikkim with a population of 60,7688.
population attributes
Question 34. The socio-religious cause of growth in population is
- Early marriages
- Non-adoption of family planning methods
- Desire to have a male child
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The socio-religious cause of growth in population is an increase in the number of young married couples, high fertility rates for the same ethnic groups, non-adoption of family planning methods, desire to have a male child, inadequate sexual education, and birth control provision.
Question 35. In Delhi, there is a large gap between birth and death rate. This shows that delhi has a population of
- School going children
- More old persons
- Middle-aged persons
- Adult ones
Answer: 1. School going children
Maximum death occurs in infants and old age people and maximum individuals are added by middle-aged persons. School-going children have lower mortality (death rate), hence there should be a large gap between birth rate and death rate in a population that has the maximum population of school-going children.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 36. Categorization of age groups for constituting population pyramids was done by
- Odum
- Karmonby
- Bodenheimer
- Daubenmier
Answer: 1. Odum
A population pyramid or age structure pyramid is a graphical representation of the distribution of various age groups in a population of a country or any particular region. It was developed by the American ecologist Howard Thomas Odum.
Question 37. The number of deaths per 1000 individuals in a population per year is called
- Sex ratio
- Mortality
- Natality
- Age structure
Answer: 2. Mortality
Mortality refers to the death of individuals in the population.
Question 38. The age structure of a population influences population growth. Identify the reason for this statement.
- Different age groups have different reproductive capabilities
- Different age groups have the same reproductive capabilities
- The age of an individual is directly proportional to reproductive capabilities
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Different age groups have different reproductive capabilities
population attributes
Different age groups have different reproductive capabilities due to which population growth is influenced. For example, when the pre-reproductive age group is more than the reproductive and post-reproductive. This type of population is expanding population.
Question 39. Age pyramids are of
- Two types
- Three types
- Four types
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Three types
The age pyramid is the graphic representation of different age groups found in a population with the pre-reproductive group at the base, reproductive ones in the middle, and the post-reproductive group at the top.
Age pyramids are of three types:
- Triangular age pyramid
- Bell-shaped age pyramid
- Urn-shaped age pyramid
Question 40. Which of the following factors regulate human life with reference to population density?
- Availability of food, housing, and health facilities
- Urbanization
- Climatic conditions
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Factors that regulate population density are
- Physical factors water supply, climate, the shape of land, vegetation, soils, and availability of natural resources and energy.
- Human factors are social, political, and economic factors. Thus, option is correct.
Question 41. In India, human population is heavily weighted toward the younger age groups as a result of
- The short lifespan of many individuals and a low birth rate
- The long lifespan of many individuals and a low birth rate
- Short lifespan of many individuals and a high birth rate
- Long lifespan of many individuals and a high birth rate
Answer: 3. Short lifespan of many individuals and high birth rate
In India, there is a short lifespan of individuals and a high birth rate as compared to other countries. That is why the human population is heavily weighted towards the younger age groups.
Question 42. The present century has witnessed a remarkable increase in the population of India. One major factor for this is that
- Older people have begun to live longer
- More children are born in each family
- More children per family have begun to reach the reproductive age
- More people are marrying in the younger age group
Answer: 1. Older people have begun to live longer
population attributes
Due to the advancement in medical facilities, the average lifespan of a human has increased adding to the population of India as older people have begun to live longer with proper medical treatment.
Question 43. In any growing population, the maximum contribution is of
- Post-reproductive members
- Reproductive members
- Pre-reproductive members
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Reproductive members
A country’s age structure tracks the number of people in the pre-reproductive, reproductive, and post-reproductive years. In any growing population, the maximum contribution is of reproductive members.
Question 44. The reproductive value of an individual is greatest just before
- First reproduction
- Death
- Birth
- None of the above
Answer: 1. First reproduction
Fisher defined the reproductive value of individuals of a given age as their expected contribution to future population growth. It is highest just before first reproduction as with subsequent reproduction and increase of age there‘s a decrease in the chances of the individual contributing to future population.
Question 45. In a growing population of a country.
- Pre-reproductive individuals are more than reproductive individuals
- Pre-reproductive individuals are less than reproductive individuals
- Reproductive and pre-reproductive individuals are equal in number
- Reproductive individuals are less than post-reproductive individuals
Answer: 1. Pre-reproductive individuals are more than the reproductive individuals
Whenever the pre-reproductive individuals or the younger population size is larger than the reproductive group, the population will be an increasing population
Important MCQs on Population Attributes for NEET
Question 46. Population pyramids were first made by
- Bodenheimer
- Van Humboldt
- Daubenmire
- Elton
Answer: 1. Bodenheimer
- Bodenheimer (1985) was the first ecologist to propose three major age groups in any population. These are pre-reproductive, reproductive, and post-reproductive.
- A graphical representation of different age groups found in a population with pre-reproductive groups at the base, reproductive ones in the middle, and post-reproductive groups at the top is called age pyramid.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 47 The age pyramid with a broad base indicates
- A high percentage of young individuals
- A high percentage of old individuals
- A low percentage of young individuals
- A stable population
Answer: 1. High percentage of young individuals
- An age pyramid is a pyramid that determines the number of individuals in a particular age group in a particular population. A pyramid with a broad base indicates a high percentage of young individuals. The base of the pyramid is formed by people in the age group of 0-14 years.
- This also indicates the reproductive fertility of the individual of that population. The top of the pyramid is formed by the individuals of older age groups showing increased mortality.
Question 48. The ecological age group of a population includes
- Pre-reproductive
- Reproductive
- Post-reproductive
- Old-age group
- Adolescent age group
- Infertile age group
Choose the correct option for the given statements.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 3, 4 And 5
- 4, 5 And 6
- 1, 5 And 6
Answer: 1.1, 2 and 3
Statements 1, 2, and 3 are correct. A population has three ecological age groups
- Pre-reproductive
- Reproductive
- Post-reproductive this division of population was given by Bodenheimer in 1958.
Question 49. Which of the following age groups fall in the pre-reproductive age category?
- 15-59 Years
- 23-54 Years
- 0-14 Years
- 50-60 Years
Answer: 3. 0-14 Years
population attributes
The portion of individuals in different age groups. Pre-reproductive age (0-14) reproductive age (15-44) post-reproductive age (45+)
Question 50. Age pyramid a, b, and c indicates.
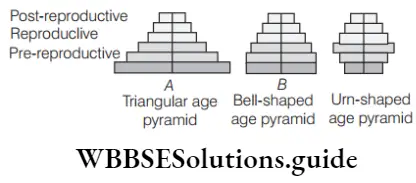
- A–expanding population, b–stable population, c–declining population
- A–expanding population, b–declining population, c–stable
population - A–stable population, b–declining, population c–expanding population
- A–declining population, b–stable, population c–expanding population
Answer: 1. A–expanding population, b–stable population, c–declining population
Question 51. A population having a large number of post-reproductive and a small number of pre-reproductive age groups is called
- Growing population
- Steady population
- Declining population
- Reproductive isolation
Answer: 3. Declining population
A population with a large number of post-reproductive or older individuals and a lesser number of pre-reproductive individuals will show a negative growth rate or decline in growth.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 52. The apex of the age pyramid of a stationary population is
- Very narrow
- Broad
- Almost equal to the base
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Broad
The apex of a diminishing population is broad and an expanding population is narrow, whereas in a stabilized population it is only smaller than pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups.
Question 53. A bell-shaped age pyramid of a population is indicative of
- The number of pre-reproductive and reproductive individuals is almost equal
- Post-reproductive individuals are comparatively fewer
- The population size remains stable
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
In a bell-shaped age pyramid, the number of pre-reproductive and reproductive individuals is almost equal. Post-reproductive individuals are comparatively fewer. Population size is stable.
Question 54. When it is observed that a population is grown then the type of age pyramid obtained is
- Bell-shaped age pyramid
- Urn-shaped age pyramid
- Triangular age pyramid
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Triangular age pyramid
In a triangular age pyramid population size is growing. The number of pre-reproductive individuals is very large whereas the number of reproductive individuals is moderate and post-reproductive are fewer.
Question 55. Zero growth in population is observed when
- Less number of births happen
- Less number of reproductive females are present
- The number of reproductive individuals is equal to pre-reproductive individuals
- A smaller number of males than females are present
Answer: 3. Number of reproductive individuals is equal to pre-reproductive individuals
Zero growth of population is indicated when various age groups are evenly balanced. This is observed in a bell-shaped age pyramid. The number of pre-reproductive and reproductive individuals is almost equal. Post-reproductive individuals are comparatively fewer thus population size is stable.
Question 56. Which of the following statements correctly correlates with the diagrams?
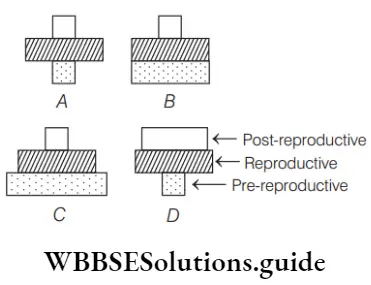
- A and B are steady population
- A and D are declining population
- C and D are growing population
- B and D are declining population
Answer: 2. A and D are declining population
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 57. A country with a high rate of population growth took measures to reduce it. The figure below shows age-sex pyramids of populations a and b twenty years apart. Select the correct interpretation of the interpretations
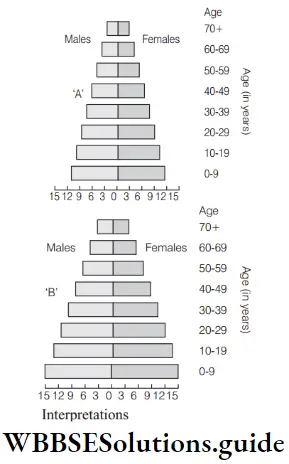
population attributes
- B is the earlier pyramid and shows a stabilized growth rate
- B is more recent showing that the population is very young
- A is the earlier pyramid and no change has occurred in the growth rate
- A is more recent and shows a slight reduction in the growth rate
Answer: 4. A is more recent and shows a slight reduction in the growth rate
Question 58. Consider the following statements.
- The proportion of the reproductive age group is higher than the individuals in the pre-reproductive age group.
- The number of post-reproductive individuals is moderate.
- Declining or diminishing population.
Choose the pyramid that is descriptive of the above population characteristics.
- Bell-shaped age pyramid
- Triangular age pyramid
- Sphere-shaped age pyramid
- Urn-shaped age pyramid
Answer: 4. Urn-shaped age pyramid
The pre-reproductive and reproductive stages are less than the post-reproductive stages of this population. In this population, more older people are present. This type of age structure indicates the population is declining. This type of pyramid is known as an urn-shaped age pyramid
Question 59. The average ratio of men and women in the human population is
- 3:4
- 1:1
- 3:5
- 1:2
Answer: 2. 1:1
Sex ratios are defined as the number of females per thousand males sex ratio in India as percenus 2011 is 940 females per 1000 males
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 60. Natality refers to
- Number of individuals leaving the habitat
- Birth rate
- Death rate
- Number of individuals entering a habitat
Answer: 2. Birth rate
Natality is the number of young individuals produced in a unit of time in a population in a given area and is added to the density. It is equivalent to the birth rate. It is measured either as an absolute (crude) natality rate or a specific natality rate.
Question 61. The total national income is divided by the total population of the country, then it is known as
- Per capita income
- Population income
- Per capita production
- Per capita gross income
Answer: 1. Per capita income
(1) Per capita income (PCI) or average income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) In a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area’s total income by its total population.
NEET quiz on Population Attributes with solutions
Question 62. Which of the following is not an attribute of a population?
- Natality
- Mortality
- Species interaction
- Sex ratio
Answer: 3. Species interaction
Species interaction is not an attribute of a population. Rest options natality (birth rate), mortality (death rate), and sex ratio are population attributes.
Question 63. The sex ratio is defined as the
- The ratio of females to males in a population
- The ratio of males to females in a population
- Both (1) and (2)
- The ratio of infant to old people in a population
Answer: 1. Ratio of females to males in a population
The number of females and males per 1000 individuals in a given time is called as sex ratio.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 64. Natality refers to
- Death rate
- Number of individuals entering a habitat
- Number of individuals leaving the habitat
- Birth rate
Answer: 4. Birth rate
Natality refers to the birth rate.
- The death rate is mortality.
- Number of individuals entering a habitat is immigration.
- A number of individuals leaving the habitat are emigration.
Question 65. The permanent decrease in population number occurs due to
- Mortality
- Natality and migration
- Territoriality
- Emigration
Answer: 1. Mortality
Mortality is the state of death it reduces the component and population and thus causes a permanent decrease in population number.
Question 66. To keep a population balanced reproduction is the phenomenon, an opposite in order to reduce it is
- Biotic control
- Mortality
- Fecundity
- Normality
Answer: 2. Mortality
Mortality is the average number of natural deaths per unit population per unit time.
Question 67. The number of individuals in the population who left the habitat and went elsewhere during the time period under consideration is known as
- Natality
- Mortality
- Emigration
- Immigration
Answer: 3. Emigration
Emigration refers to the number of individuals in a population who left the habitat and went elsewhere during the time period under consideration. Emigration decreases the size of a population. It is caused mainly due to calamities.
Question 68. Emigration pertains to
- One-way inward movement
- One-way outward movement
- Periodic departure and return
- Two-way movement of the entire population
Answer: 2. One-way outward movement
Emigration pertains to one-way outward movement.
Question 69. Periodic departure and return of an individual to an area is known as
- Immigration
- Migration
- Emigration
- Immigrant
Answer: 2. Migration
Migration is the temporary departure and return of organisms to an area due to unfavorable conditions of the environment, for example. Bird migration from Siberia and other extremely cold northern regions. Whereas, immigration and emigration are permanent phenomena.
Question 70. When new individuals come into a population from outside, it is described as
- Immigration
- Emigration
- Growth rate
- Natality
Answer: 1. Immigration
When a number of individuals of the same species come into a population from outside, it is described as immigration.
Question 71. The large gap between natality and mortality will result in
- Less old people in relation to children
- More old people
- Low dependency ratio
- Prosperous country
Answer: 2. More old people
The population will show an increase in the number of older people if there exists a large gap between natality and mortality.
Question 72. The disturbing aspect of the sex ratio in the population of India is due to
- Increased number of females
- Decreased number of females
- Decreased number of males
- Increased number of females and males
Answer: 2. Decreased number of females
India is one of the few countries where the number of males is more than the number of females. There has been a steady decrease in the female population since 1901. Thus, an option is correct.
Question 73. If the birth rate is 100, the death rate is 10, and the number of individuals in the population group is 1000, then what will be the percentage of the natural growth rate?
- 0.09%
- 9.0%
- 0.9%
- 90%
Answer: 2. 9.0%
Birth rate = 100
Death rate = 10
Number of individuals in the population = 1000
Natural growth rate = 100 − 10 = 90
So, the percentage of the growth rate
[Latex]=\frac{90}{100} \times 100=9 \%[/latex]
Question 74. According to the law of population growth, if an initial population of yeast cells 10 in number was allowed to grow for 6 hours, the expected number of individuals in the final population will be about
- 600
- 100
- 50
- 200
Answer: 4. 200
The projection of population
Growth in yeast is given by
[Latex]\mathrm{n}=n_o e^{r t}[/latex]
Where e = national logarithmic base = 2.72;
No = initial population;
R = intrinsic rate of increase;
T = time.
N = ×10×272(0.5×6)
Hence, n = 200.86, i.e. After 6 hours, the population is expected to have about 200 individuals.
Question 75. Information on the birth rate, death rate, sex ratio, and age distribution of a population can be obtained from
- Natality table
- Mortality table
- Age distribution table
- Life table
Answer: 4. Life table
The life table represents the survivorship of people from a certain population.
Question 76. The rapid decline in population due to a high mortality rate is called
- Population density
- Population crash
- Population explosion
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Population crash
The term population crash is most often used when referring to a drastic decline in the human population, which impacts the economy and the quality of life of individuals in the population.
Question 77. The rate of natural increase in human population refers to
- Birth rate
- Mortality
- Natality minus death rate
- Birth rate plus death rate
Answer: 3. Natality minus death rate
The rate of natural increase is defined as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate. It is expressed as a rate per 1000 population.
Question 78. The impact of immigration on population density is
- Negative
- Positive
- Both (1) and (2)
- Neutralized by natality
Answer: 2. Positive
- Population density is the number of individuals present per unit area or volume at a given time. It is calculated by the formula d n s= /, where d = density, n = total number of individuals, and s = number of units of space.
- Since immigration increases the number of individuals in an area, population density increases. Thus, immigration has a positive impact on population density.
Question 79. The animal population becomes too large for its feeding source or its habitat, and its members starve/die but humans escape this disaster by
- Immigration only
- Emigration only
- Transportation of food
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 2. Emigration only
Humans are the most evolved organisms on earth. They are able to escape disaster by both emigration and transportation of food, unlike other animals on earth.
Question 80. Certain characteristic demographic features of developing countries are
- High fertility, low or rapidly falling mortality rate, rapid population growth, and a very young age distribution
- High fertility, high density, rapidly rising mortality rate, and a very young age distribution
- High infant mortality, low fertility, uneven population growth, and a very young age distribution
- High mortality, high density, uneven population growth, and a very old age distribution
Answer: 1. High fertility, low or rapidly falling mortality rate, rapid population growth and a very young age distribution
- Demography is the study of population in all aspects. Fertility refers to the number of children per couple. The mortality rate is the average number of natural deaths per unit population per unit time. Age distribution refers to the proportionate occurrence of individuals of the three age groups.
- Developing countries usually have a high rate of population growth, because of increasing fertility and declining mortality.
Question 81. Population explosion means
- Sudden loss of population
- Reduction in biotic potential
- Sudden increases in the old age population
- Tremendous increase in overall population
Answer: 4. Tremendous increase in overall population
The rapid increase of population in a short duration is called population explosion. It happens with unlimited resources and the least resistance.
Question 82. Which one of the following causes population explosion?
- Decrease in infant mortality rate and increase in death rate
- Decrease in death rate, maternal mortality rate, and infant mortality rate
- Decrease in infant mortality rate and decrease in the number of people of reproductive age
- Decrease in death rate and increase in maternal mortality rate
Answer: 2. Decrease in death rate, maternal mortality rate, and infant mortality rate
Question 83. Bio-index number means
- Natality – mortality
- Mortality/natality
- Natality × mortality
- Natality/mortality
Answer: 4. Natality/mortality
The percentage ratio of natality over mortality is known as vital or bio index, i.e. Natality/mortality × 100. It determines the growth of a population.
Question 84. The change in population size at a given time interval t, is given by the expression, n nt = + + − −0 b I d e, i, b and d, respectively stand for
- I–rate of immigration, b–mortality rate, d–natality rate
- I–the rate of emigration, b–the natality rate, d–the mortality rate
- I–mortality rate, b–natality rate, d–rate of immigration
- I–mortality rate, b–rate of immigration, d–natality rate
- (E) i–rate of immigration, b–natality rate, d–mortality rate
Answer: 5. I–the rate of immigration, b–natality rate, d–the mortality rate
Stands for the rate of immigration, b stands for the natality rate, and d stands for the mortality rate.
Question 85. Which of the following are the most convincing reasons for increasing population growth in a country?
- The low population of old people
- High birth rate
- The high population of young children
- Low mortality rate
Answer: 3. High population of young children
- A population with a large number of pre-reproductive individuals (below the age of 18 years) or young children will show a rapid increase while the one with large numbers of postreproductive individuals (age group of 19 – 45 years) will show a decline.
- The young children will attain the reproductive age group in the next 10-15 years and contribute to the increase in population
Question 86. Consider the following statements?
- In a population, birth rate and death rate refer to per capita births and deaths, respectively.
- Isolated individuals of a species are rarely observed in nature.
- The size of a population always remains stable at any given point in time.
- Ecological effects of any factors on population growth are generally reflected in its size/population density.
Choose the option containing
Correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2 And 4
All statements are correct except 3. The incorrect statement can be corrected as the size of the population keeps on changing due to various factors or phenomena like birth rate, death rate, emigration, or immigration. So, it is a dynamic phenomenon rather than a stable one.
Question 87. Natality is balanced by mortality. There will be
- Decrease in population growth
- Zero population growth
- Increase in population growth
- Overpopulation
Answer: 2. Zero population growth
- The standard formula for calculating growth rate is gr = n/t
- Here, gr is the growth rate expressed as a number of individuals. N is the total change in population size for the entire time period also expressed as a number of individuals. Therefore if. Birth = death then n (b–d) = 0 hence, gr = 0/t = 0 so, the correct option is zero population growth.
Question 88. A biologist studied the population of rats in a barn. He found that the average natality was 250, average mortality was 240, immigration was 20, and emigration 30. The net increase in population is
- 15
- 05
- Zero
- 10
Answer: 3. Zero
Net increase in population (natality + immigration) − (mortality + emigration) (250 + 20) − (240 + 30) = 270 − 270 = 0 thus, option is correct.
Question 89. The declining phase of a population occurs when
- Mortality > natality
- Natality > mortality
- Mortality = natality
- Natality = mortality = 0
Answer: 1. Mortality > natality
The declining population has a higher death rate than the birth rate. So, the population of young members is lower than that of old members, for example. Japan.
Question 90. If there are non-limiting or unlimited conditions are provided then what will happen to the population?
- Natality increases
- Mortality decreases
- Mortality increases
- Natality decreases
Choose the correct combination.
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 1 And 4
- 4 And 3
Answer: 1. 1 And 2
Statements I and ii are correct as if there is unlimited condition provided to a population then the population will grow fast by increasing their birth rate and decreasing their death rate.
Question 91. Choose the incorrect statement.
- Drastic and sudden changes in the surrounding environment do not affect the population density
- Mortality and emigration decrease the population density
- Natality and immigration increase the population density
- Food availability and predation pressure affect population density
Answer: 3. Natality and immigration increases the population density
The statement in option (3) is incorrect and can be corrected as adverse conditions affect the population by influencing the natality and mortality of the population. It also affects immigration and emigration. Rest all statements are correct.
Question 92. Population grows due to
- Natality + emigration
- Natality + immigration
- Mortality + immigration
- Mortality + emigration
Answer: 2. Natality + immigration
The addition of new individuals by reproduction, i.e. Natality, and entry of individuals from outside, i.e. Immigration contributes to population growth.
Question 93. Which of the following is correct?
- Population change = (birth + immigration)–(death + emigration)
- Population change = (birth + immigration) +(death + emigration)
- Population change = (birth + emigration) + (death–immigration)
- Population change = (birth – immigration)–(death + emigration)
Answer: 1. Population change = (birth + immigration)–(death + emigration)
Population change = (birth + immigration) − (death + emigration)
Question 94. The ratio of natality and mortality of a population expressed in percentages is
- Vital index
- Growth rate
- Survival rate
- Biotic potential
Answer: 1. Vital index
The percentage ratio of natality over mortality is known as vital index natality/ mortality × 100. It determines the growth of a population.
Question 95. What is true about the isolated small tribal populations?
- There is a decline in population as boys marry girls only from their own tribe
- Hereditary diseases like color blindness do not spread in the isolated population
- Wrestlers who develop strong body muscles in their lifetime pass this character on to their progeny
- There is no change in population size as they have a large gene pool
Answer: 1. There is a decline in population as boys marry girls only from their own tribe
In isolated small tribal populations if boys marry girls only from their own tribe then there will be a decline in population because at some stage marriage will stop due to isolation (neither immigration nor emigration will occur) on the other hand marriages within the same tribe will lead to homozygosity of disease and ultimately death, thus leading to a decline in population.
Question 96. Two opposite forces operate in the growth and development of every population. One of them relates to the ability to reproduce at a given rate. The force opposing to it is called
- Mortality
- Fecundity
- Biotic control
- Environmental resistance
Answer: 4. Environmental resistance
- The environmental factor that can check the growth of population size constitutes environmental resistance. These include predators, food, water, nesting sites, etc. All living things tend to reproduce until the point at which their environment becomes a limiting factor.
- No population human or otherwise, can grow indefinitely eventually some biotic or abiotic variable will begin to limit population growth.
Question 97. The stationary phase of a population occurs when
- Natality > mortality
- Natality = mortality
- Mortality > natality
- Natality = 0
Answer: 2. Natality = mortality
The stationary phase results from a situation in which the growth rate and death rate are equal, i.e. Natality equals mortality
Question 98. Population dispersion can be defined as
- Movement from one place to another and as well as immigration
- Spatial distribution of individuals
- Migration from a natal site
- Random mixing of two populations
Answer: 2. Spatial distribution of individuals
Dispersion patterns or distribution patterns refer to how the individuals in a population are distributed in space at a given time.
Question 99. Assertion natural populations are capable of rapid number increase but remain constant in size. Reason (R) Human interference has led to the constancy of the size of natural populations.
- Both a and r are true and r is the, but correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but r is false
Question 100. Match the following columns. Column 1 column 2

Answer: 3. A-3, b-2, c-1
Question 101. Study the figure and identify a to d.
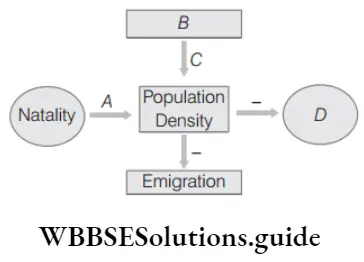
- A–immigration, b–decrease, c–mortality, d–decrease
- A–decrease, b–immigration, c–decrease, d–increase
- A–increase, b–immigration, c–increase, d–mortality
- A–increase, b–decrease, c–decrease, d–mortality
Answer: 3. A–increase, b–immigration, c–increase, d–mortality
Question 102. The mathematical expression of population growth is called
- Population curve
- Growth curve
- Density curve
- Biotic curve
Answer: 2. Growth curve
The mathematical expression of population growth is called a growth curve.
Question 103. Geometric representation of age structure is a characteristic of
- Biotic community
- Population
- Landscape
- Ecosystem
Answer: 2. Population
Geometric representation of age structure is a characteristic of the population. In most populations, individuals are of different ages. The proportion of individuals in each age group is called the age structure of that population.
Question 104. Population a–has an intrinsic rate of natural increase of 0.2. Population b–has an intrinsic rate of natural increase of 0.3. Population c–has an intrinsic rate of natural increase of 0.4. Population d–has an intrinsic rate of natural increase of 0.5. Which population will increase fastest?
- D
- C
- B
- A
Answer: 1. D
The population having the highest (0.5) intrinsic rate will increase fastest among all of the given populations. Thus, population d will increase fast.
Question 105. Who stated that a population is a self-regulating system?
- Wynne Edward
- Tr Malthus
- Lamarck
- Darwin
Answer: 2. Tr Malthus
Thomas R. Malthus was an economist of England who in 1838 wrote an article on ‘principles of population’. According to him, increasing population creates an imbalance in population and environment. When the imbalance reaches a certain value, some factors like hunger, epidemics, floods, earthquakes, war, etc., Will bring the population to a desired level. It means the population is a self-regulating system.
Question 106. Who said that the population would exceed food resources?
- Oparin theory
- Malthus theory
- Darwin theory
- Theory of Lamarck
Answer: 2. Malthus theory
Malthus in his book ‘Essay of Human Population’ said that the human population increases in geometrical ratio whereas food and space increase in an arithmetic ratio.
Question 107. Who stated that the human population grows geometry
- Malthus
- Darwin
- Cannon
- Lamarck
Answer: 1. Malthus
Firstly, Malthus calculated that the number of organisms can increase geometrically (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, …) and food supply increases arithmetically (1, 2, 3, 4, …).
Question 108. The equation represents which of the following?
- Natality
- Growth rate
- Mortality
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Natality
Natality is the rate of production of new individuals per unit of time. It can be represented by
Question 109. The correct statement is
- In a population, the number of births is different from the birth rate
- A sigmoid growth curve is a depiction of exponential growth
- In a logistic growth curve, the asymptote is beyond the carrying capacity
- ‘R’ is equal to the difference between the number of births and the number of deaths in a population
Answer: 1. In a population, the number of births is different from the birth rate
- (1) Option (1) is correct. Birth, i.e. Production of new offspring is an attribute of an individual whereas birth rate, i.e. Production of new individuals per unit population per unit time is an attribute of population.
- Other options are incorrect and can be corrected as a sigmoid growth curve is a depiction of logistic growth, a more realistic growth model where individuals compete for limited resources and the fittest individual survives and reproduces.
- In an exponential growth curve (j-shape curve) the asymptote is beyond carrying capacity as resources are unlimited. ‘R’ is the intrinsic rate of natural increase.
Question 110. The aggregates of a process that determine the size and composition of any population is called
- Population dispersal
- Population dynamics
- Population explosion
- Population density
Answer: 2. Population dynamics
Population dynamics is the study of how and why populations change in size and structure over time. Important factors in population dynamics include rates of reproduction, death, and migration.
Question 111. Density-dependent population regulation results when
- Only birth rate changes in response to density
- Only death rate changes in response to density
- Both (1) and (2)
- Population density fluctuates very little
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Density-dependent population regulation results when there are changes in the birth rate and death rate in a population.
NEET expected MCQs on Population Attributes 2025
Question 112. If the rate of addition of new members, increases with respect to the individual lost from the population, then the graph obtained has
- Declined growth
- Zero population growth
- Exponential growth
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Exponential growth
If the rate of addition of members in a population increases with respect to the loss of members of the population, then the population is under exponential growth. Exponential growth is a form of population growth in which the rate of growth is related to the number of individuals present.
Question 113. In a population, unrestricted reproductive capacity is called as
- Biotic potential
- Fertility
- Carrying capacity
- Birth rate
Answer: 1. Biotic potential
Biotic potential is the maximum (unrestricted) reproductive capacity of an organism under optimum environmental conditions. Carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals that can be sustained by the environment. Birth rate refers to number of births per unit population.
Question 114. A rapid increase in the population or positive growth is observed if
- Less number of young ones are present
- A large number of young ones are present
- A large number of old ones are present
- A large number of childbirth are present
Answer: 2. Large number of young ones are present
A population having a large number of young individuals will show a rapid increase in population. It is called positive growth.
Question 115. Presently human population is following which of these trends?
- Sigmoid
- J-shaped
- Stagnant
- None of these
Answer: 1. Sigmoid
- Sigmoid curves are observed in all those populations that show a vigorous acceleration and never level off for long enough to establish carrying capacity, i.e. The number of individuals is never static but rises and falls about an average.
- J -curve is seen in populations that have precise survival limits and unfavorable changes such as accumulation of toxic wastes or scarcity of food will kill individuals quickly. Thus, presently human population is following sigmoid trends.
Question 116. Exponential growth in the human population occurs in
- Lag phase
- Log phase
- Plateau stage
- First stage
Answer: 2. Log phase
Exponential growth in the human population occurs in the log phase.
Question 117. Carrying capacity is the capacity of
- The habitat to sustain a certain number of individuals at par with the resources
- Population reproduce and compete with each other for resources
- Individuals to adjust to the changes in the environment
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 1. The habitat to sustain a certain number of individuals at par with the resources
Carrying capacity can be defined as a species’ average population size in a particular habitat. The species population size is limited by environmental factors like adequate food, shelter, water, and mates. Thus, option (1) is correct.
Question 118. Below diagram indicates.
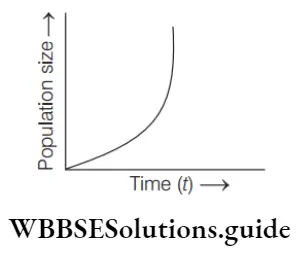
- Exponential growth curve
- Logistic growth pattern
- J-shaped curve
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (3)
As we can see clearly in the given diagram the growth of the population is unlimited and increasing. That is the distinguishing feature of the exponential growth model or curve. As it has a j-shaped appearance so, it is also called a j-shaped curve.
119. Population termed r-strategists
- Have j-shaped growth curves
- Have type-iii survivorship curve
- Are usually pioneer species
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- During about period of time, some populations produce many offspring that require little care. Therefore, these populations usually have a survivorship curve similar to type 3.
- These tend to have j-shaped growth curves until some environmental change causes them to decline usually within a short time.
- From an evolutionary point of view, such species have undergone selection to maximize their rate of natural increase and for this reason, they are termed as r-strategist. So, the correct answer is a have j-shaped growth curves.
Question 120. Exponential growth in plants can be expressed as
- Lt = LO + rt
- Le = Lt rt
- Wt = WO en
- Wt = Wo en
- Wt = Wo + en
Answer: 3. W w et = 0 rt
The exponential growth can be expressed as
Where, wt = final size of population (weight, height, number, etc.).
0 = Initial size of population at the beginning of the period
r = growth rate
t = time of growth
e = base of natural logarithms
Question 121. The integral form of the exponential growth equation as
N = Noen
Identify a, b, c, and d from the given equation.
- Population density after time t.
- Population density at time zero.
- Intrinsic rate of natural increase.
- The base of natural logarithms (2.71828).
Choose the incorrect statements.
- A–r, b-e, c–n0, d–ne
- A–nt, b–n0, c–r, d–e
- A–n0, b–ne, c–r, d–e
- A–n0, b–ne, c–e, d–r
Answer: 2. A–nt, b–n0, c–r, d–e is the integral form of the exponential growth equation. It is also called the Verhulst-pearl logistic growth curve.
Question 122. Identify true statements pertaining to exponential growth.
- No population can follow the exponential growth for long
- Exponential growth slows down as the population nears its log phase
- Bacterial colonies have been observed to maintain exponential growth always
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 1. No population can follow the exponential growth for long
No population can grow exponentially because
- Limited resources
- Carrying capacity
- Interspecies competition
- Natural resistance
Question 123. No resource is …a… For populations of any species thus resulting in …b… For limited resources and limiting exponential growth. Only the survival of the …c… Is observed. Choose the correct option for a, b, and c.
- Limited, b–competition, c–fittest
- A–unlimited, b–sharing, c–most intelligent
- A–unlimited, b–competition, c–fittest
- A–limited, b–sharing, c–weakest
Answer: 3. A–unlimited, b–competition, c–fittest
Question 124. Population exploiting a resource rapidly and showing the unbound increase in numbers are
- K – selected
- R – selected
- Growth selected
- Unselected
Answer: 2. R – selected
Population exploiting a resource rapidly and showing an unbound increase in numbers are r-selected species. These are the species that produce many cheap offspring and live in unstable environments.
Question 125. Which of the following is correct for r-selected species?
- A large number of progeny with small size
- A large number of progeny with large size
- A small number of progeny with small size
- A small number of progeny with large size
Answer: 1. Large number of progeny with small size
R-selected species are the ones that are found in the sparsely crowded ecological niche to exploit it and aim at the production of a large number of small-sized progeny with lower survival rates due to the short gestation period and early attainment of maturity.
Question 126. When food and space for a population are unlimited.
- Each species has the ability to realize fully its inherited potential to grow.
- Then it is equal to dn
- It is described by the j-shaped curve.
- It is described by an S-shaped curve.
- There is more competition among themselves.
Choose the incorrect statements.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2, 3 And 4
- 4 And 5
- 1, 4 And 5
Answer: 3. 4 And 5
When food and space are unlimited then the population.
- Increases by using its maximum biotic potential.
- Shows exponential growth where dn dt rn
- Shows an exponential growth curve also called a J-shaped curve.
- Show greater intrinsic rate. Rest statements iv and v are incorrect as an s-shaped curve and competition is shown by population when food is limited.
Question 127. Which of the following is correct?
- Birth rate: number of young ones per 100 individuals in a year
- Carrying capacity: maximum number of children which a female
can carry in her lifetime - Replacement level: the number of young ones that a female should produce to replace her in the population
- Exponential growth: the phase of rapid or geometrical growth
Answer: 4. Exponential growth: the phase of rapid or geometrical growth
NEET Biology Population Attributes MCQs with explanations
Question 128. If resources are unlimited the population density can scale greatly. Then this is said to be a …a…. If left unchecked then …b… Animals such as elephants, as proved by Darwin, can grow into large numbers and this characteristic is known as …c….
- A–logistic growth, b–fast-growing, c–carrying capacity
- A–logistic growth, b–slow growing, c–biotic potential
- A–exponential growth, b–slow growing, c–biotic potential
- A–exponential growth, b–fast-growing, c–biotic potential
Answer: 3. A–exponential growth, b–slow growing, c–biotic potential
Question 129. Logistic growth is observed when
- No resistance to increasing population occurs
- Unlimited food is present
- Fixed carrying capacity is present
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Fixed carrying capacity is present
Logistic growth model, no population can continue to grow exponentially, as the resource availability becomes limiting at a certain point in time. Logistic growth models have fixed carrying capacity. It is described by the equation
Rate of change in population density
N = population density at t
R = intrinsic rate of natural increase
K = carrying capacity
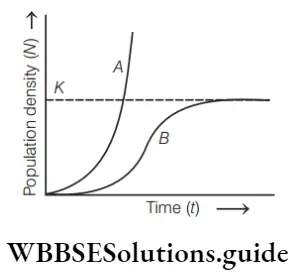
Question 130. Exponential growth is observed
- Only when there is sexual reproduction
- Only when there is asexual reproduction
- Only when there is a fixed carrying capacity
- Only when there is no inhibition from crowding
Answer: 4. Only when there is no inhibition from crowding
When the resource availability is unlimited in the habitat, the population grows in an exponential or geometric fashion. As resources are unlimited then there is no inhibition from crowding.
Question 131. The ability to produce maximum offspring is
- Carrying capacity
- Biotic potential
- Environmental resistance
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Biotic potential
- Biotic potential refers to the rate at which a population of a given species will increase when there are no limits of any sort on its rate of growth. It is defined by the formula
- Where n is the number of individuals in the population is the rate of change of its numbers over time and r is the intrinsic rate of natural increase for the population.
Question 132. Choose the correct sequence of stages of the growth curve for bacteria.
- Lag, log, stationary, decline phase
- Lag, log, stationary phase
- Stationary, lag, log, decline phase
- Decline, lag, log phase
Answer: 1. Lag, log, stationary, decline phase
The growth curve for bacteria is sigmoid. The first phase is the phase of slow growth − the lag phase. The second phase is the period of accelerated growth − the log phase. The third phase is the phase when the growth rate becomes stable − the stationary phase. Finally growth rate declines.
Question 133. …a… Is the initial phase in a logistic growth curve where the resources are …b… . This phase is followed by acceleration, deceleration and then becomes an asymptote
- A–lag phase, b–unlimited
- A–log phase, b–unlimited
- A–lag phase, b–limited
- A–stationary phase, b–limited
Answer: 1. A–lag phase, b–unlimited
Question 134. The logistic population growth model describes a population’s growth when an upper limit to growth is assumed. This upper limit of growth is known as the population …a…and as ‘n’ gets larger, dn dt …b….
- A–carrying capacity, b–decrease
- A–carrying capacity, b–increases
- A–reproductive fitness, b–increases
- A–reproductive fitness, b–decreases
Answer: 1. A–carrying capacity, b–decreases.
Mock test on Population Attributes for NEET preparation
Question 135. Exponential growth occurs in
- Yeast
- Asexual reproduction
- Bacteria
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Exponential growth occurs when the increase in population becomes rapid and soon attains its full potential rate due to constant requirements with respect to the availability of food and other requirements. Exponential growth occurs in bacteria, yeast as well and amoeba asexual reproduction.
Question 136. After an exponential increase, population growth declines and stagnates. The growth curve is
- S-shaped
- J-shaped
- Straight line
- Circular
Answer: 1. S-shaped
In a S-shaped growth curve, first, there is a slow increase in population. Following this, there is a rapid increase in growth. After this, the growth becomes stagnant and the population becomes stable.
Question 137. Which of the following shows Verhulst-pearl logistic growth?
- \(\frac{d N}{d t}=r N\left(\frac{K-N}{K}\right)\)
- Nt = Noert
- \(\frac{d N}{d t}=r N\)
- \(N\left(\frac{K-N}{K}\right)\)
Answer: 1. \(\frac{d N}{d t}=r N\left(\frac{K-N}{K}\right)\)
- A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows initially a lag phase, followed by phases of increase and decrease, and finally, the population density reaches the carrying capacity.
- A plot of n in relation to time (t) results in a sigmoid curve. This type of population growth is called Verhulst-pearl logistic growth as explained by the following equation \frac{d N}{d t}=r N\left(\frac{K-N}{K}\right)
- where n = population density at a time t, r = intrinsic rate of natural increase, and k = carrying capacity.
Question 138. Which option is correct for curves A and B?
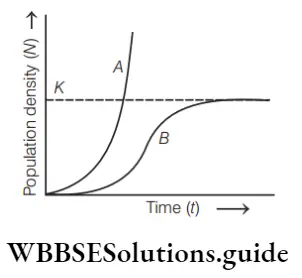
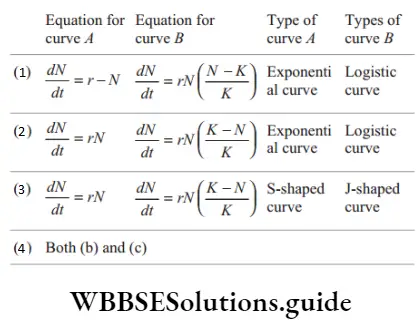
Answer: 2. 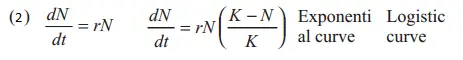
An exponential growth curve is also called a J-shaped curve or geometric growth curve. A logistic curve is also called a sigmoid growth curve or s-shaped curve. Thus, option (2) is correct for curves a and b.
Question 139. A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows four phases of growth in the following sequence.
- Acceleration → deceleration → lag phase → asymptote
- Asymptote → deceleration → deceleration → lag phase
- Lag phase → acceleration → deceleration → asymptote
- Acceleration → lag phase → deceleration → asymptote
Answer: 3. Lag phase → acceleration → deceleration → asymptote
When the population grows in a habitat with limited resources it first increases slowly, i.e. Lag phase, then the population grows rapidly in the acceleration phase. After the acceleration phase, the rate of growth slows down and reaches the asymptote phase when the population density reaches carrying capacity.
Question 140. The asymptome stage of the population is the stage of
population in which the population is
- Changing
- Decreasing
- Increasing
- At equilibrium
Answer: 4. At equilibrium
The asymptome stage of the population is the stage of population in which the population birth rate is equal to the death rate in other words population is stabilised or at equilibrium.
Question 141. When in a population birth rate and death rate exactly balance each other, it is called
- Plateau phase
- Acceleration phase
- Exponential phase
- Initial growth
Answer: 1. Plateau phase
The plateau phase is also called a steady state when the population is in equilibrium, i.e. Birth rate balances the death rate.
Question 142. Most of the invertebrates and plant populations have
- Less biotic potential
- More biotic potential
- The high mortality rate in the younger stages
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Most of the invertebrates and plant populations have more biotic potential and a high mortality rate in the younger stages.
Question 143. Which of the following is an r-strategist?
- Human
- Insect
- Rhinoceros
- Whale
Answer: 2. Insect
Organisms that show r-strategy are relatively small organisms with short lifespans and often live in unstable environments. Their survival depends on their ability to produce a large number of offspring rather than on their ability to compete.
NEET practice test on Population Attributes
Question 144. The rapid decline in the population, due to the high mortality rate, is called
- Population explosion
- Population crash
- Population density
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Population crash
Population crashes may occur due to any sudden environmental change or occurrence of natural calamities such as earthquakes, famine, epidemics, drought, etc. In these situations, a rapid death toll may occur which might cause a rapid decline in the population.
Question 145. The best way to reduce the population of undesirable species is
- Reduce the carrying capacity of the environment for that species
- Elimination of females
- Elimination of the young generation
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Reduce the carrying capacity of the environment for that species
The best way to reduce the population of undesirable species is by reducing the carrying capacity of the environment for that species.
Question 146. If the mean and the median pertaining to a certain character of a population are of the same value, the following is most likely to occur
- A bi-modal distribution
- A t-shaped curve
- A skewed curve
- A normal distribution
Answer: 4. A normal distribution
If the mean and the median pertaining to a certain character of a population are of the same value a normal distribution is most likely to occur.
Question 147. The period or the duration required to double the population is called
- Doubling time
- Growth period
- Exponential (log) period
- All of these
Answer: 1. Doubling time
Doubling time is the amount of time it takes for a given quantity to double in size or value at a constant growth rate.
Question 148. Find out, when carrying capacity is 400, population size is 300 and r is 0.01.
- 0.01
- 0.8
- 0.75
- 0.45
Answer: 3. 0.75
In the given question k is the carrying capacity, i.e. 400, Population size (N) is 300, and ‘r’ is the intrinsic rate of natural increase is 0.01.
Question 149. A population increases in size on adjusting to the changes in its environment. This is observed in the
- Log phase
- Lag phase
- Decline phase
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Lag phase
The lag phase represents a population adjusting new environment. It is the initial phase in which a population adapts themself according to the environment and starts to increase its number even with the availability of unlimited resources.
Question 150. The equation = rn (the law of population growth) given by French mathematician pf Verhulst suggests the rate of increase of population per unit of time depends upon
- Innate capacity for increase
- Population size
- Unutilized opportunity for population growth
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Verhulst published in 1838 the
- Where n represents the number of individuals at time t, r is the intrinsic growth rate and k is the carrying capacity. So, the rate of increase of population per unit of time depends upon population size, innate capacity for increase, and unutilized opportunity for population growth.
Question 151. The population of an insect species shows an explosive increase in numbers during the rainy season followed by its disappearance at the end of the season. What does this show?
- S-shaped or sigmoid growth of this insect
- The food plants mature and die at the end of the rainy season
- Its population growth curve is of j-type
- The population of its predators increases enormously
Answer: 3. Its population growth curve is of j-type
Question 152. Match column 1 with column 2 and choose the correct option.
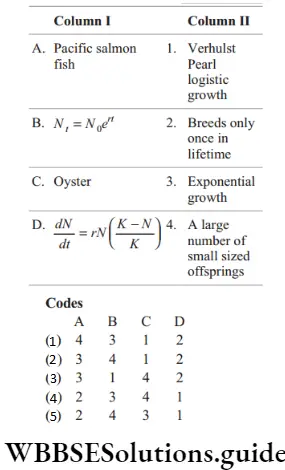
Answer: 4. A–2, b–3, c–4, d–1
Question 153. In the sigmoid growth curve given by the side, the alphabets indicate the sequence of events. Choose the correct option where the alphabet specifies the event.
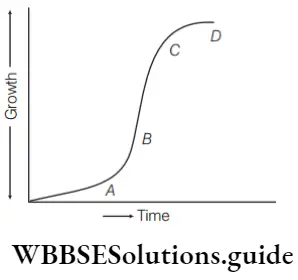
- A – phases of slow growth, b – phases of exponential growth, c – phases of diminishing growth, d – stationary phase
- A – phase of rapid growth, b – phase of diminishing growth, c – stationary phase, d – phase of slow growth
- A – diminishing growth, b – exponential growth, c – slow growth, d – stationary growth
- A – stationary phase, b – phase of slow growth, c – phase of rapid growth, d – phase of diminishing growth
Answer: 1. A – phases of slow growth, b – phases of exponential growth, c – phases of diminishing growth, d – stationary phase
Question 154. Given population growth curve represents the logistic growth curve. In this curve find out what A, B, and C indicate.
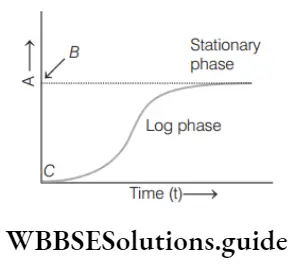
- A–log phase, b–population size, c–stationary phase
- A–population density, b–lag phase, c–carrying capacity
- A–population density, b–carrying capacity, c–lag phase
- A–carrying capacity, b–log phase, c–population density
Answer: 3. A–population density, b–carrying capacity, c–lag phase
Question 155. Which model is considered a more realistic one?
- Logistic model
- Exponential model
- Spherical model
- J-shaped model
Answer: 1. Logistic model
No population have the unlimited resources to survive and reproduce. Every population in nature has given a certain amount of limited natural resources that is limited. Keeping this point of view logistic growth is more realistic than the exponential growth curve.
Question 156. Identify the statement pertaining to the logistic model of population growth.
- The growth rate increases as the size of the population approaches the
carrying capacity. - All individuals have the same effect on population growth.
- There are unlimited natural resources.
As population increases the competition goes on increasing. Select the correct combination.
- 1 And 2
- Only 4
- 4 And 3
- 1 And 3
Answer: 2. Only 4
Statement iv is correct as the logistic model shows that as the population increases the competition goes on increasing. No population can continue to grow exponentially, as resource availability becomes limiting at a certain point in time. Logistic growth models have fixed carrying capacity.
Question 157. The carrying capacity of an environment is represented by
- S
- K
- J
- C
Answer: 2. K
A given habitat has limited resources to support a certain number of individuals of a population beyond which no further growth is possible. This limit is called nature’s carrying capacity (k) for that species.
Question 158. Match the terms in column 1 with column 2 and select the correct option.
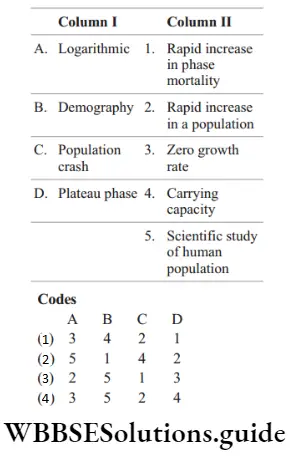
Answer: 3. A–2, b–5, c–1, d–3
Question 159. As a country becomes industrialized, its population growth
- Gradually increases
- Gradually decreases
- Rapidly comes down
- Becomes stable
Answer: 1. Gradually increases
Industrialization resulted in an increase in population.
Question 160. The maximum growth rate occurs in
- Stationary phase
- Senescent phase
- Lag phase
- Exponential phase
Answer: 4. Exponential phase
Maximum growth rate occurs in exponential acceleration or log phase. The point at which the exponential growth begins to slow down is known as inflection point
Question 161. Exponential growth in a given population of a microorganism is limited by
- Competition for food
- Accumulation of waste matter
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
- The exponential phase is characterized by the vigorous growth of the bacteria where it is in the constant state of division. As the bacterial population continues to grow, all the nutrients in the growth medium are used up by the microorganism for their multiplication.
- This results in the accumulation of waste materials. The reproduction rate will slow down, the cells undergoing division will be equal to the number of cell death, and finally, bacteria stops its division completely. Thus, the correct answer is option (3).
Question 162. Identify the condition in which the logistic and exponential growth of the population have zero growth rate.
- B = d
- R = 0
- K = n
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
In the stationary phase of logistic growth K = N then the population growth becomes zero. In the exponential phase when b = d or r (increase rate) =0 then the population increase becomes zero (stable).
Question 163. When environmental conditions are non-limiting what will happen?
- Maximum mortality and minimum natality
- Mortality minimum
- Natality minimum
- Mortality maximum
Answer: 2. Mortality minimum
Maximum reproductive capacity or biotic potential (R) can be realized only when environmental resources are non-limiting and conditions favor minimum mortality (specific mortality). However, the environment has a limiting effect on the rise of population. The sum of abiotic (e.g. Temperature, water, space, etc.) And biotic (e.g. Food, competition, disease, predation, etc.) Factors check the rise in population size and prevent the species from realizing its biotic potential. It helps in limiting population size below the carrying capacity.
Question 164. A population fluctuates when it attains carrying capacity
- Due to unlimited natural resources
- Due to exponential growth
- Due to limiting factors
- Due to Darwin’s fitness
Answer: 3. Due to limiting factors
Due to limiting factors, increased competition, and environmental resistance, the population fluctuates when it reaches carrying capacity.
Question 165. Asymptote in a logistic growth curve is obtained when
- The value of ‘r’ approaches zero
- K = n
- K > n
- K < n
Answer: 2. K = n
A population growing in a habitat with limited resources shows a logistic growth curve.
For logistic growth,
If k = n then
The population reaches an asymptote.
Question 166. When does the growth rate of a population following the logistic model equal zero? The logistic model is given as dn/dt or rn (1-n/k).
- When n/k is exactly one
- When n nears the carrying capacity of the habitat
- When n/k equals zero
- When the death rate is greater than the birth rate
Answer: 1. When n/k is exactly one
When N/k is exactly one, the growth rate of a population following the logistic growth model is equal to zero. The logistic model is given as
Where n = population density at the time ‘t’.
R = intrinsic rate of natural increase
K = carrying capacity
When n/k = 1 , then 1 − n/k = 0
Therefore, dn/dt = 0
Question 167. In the sigmoid growth curve, the upper asymptote represents the period of
- Establishment
- Positive acceleration
- Negative acceleration
- Equilibrium
Answer: 4. Equilibrium
The upper limit of the sigmoid curve is known as the upper asymptote. This represents the period of equilibrium. A sigmoid curve is also known as an s-shaped growth curve. The point of stabilization or zero growth value (symbolized by k) or carrying capacity of the environment for that organism.
Question 168. The semi-log of per minute growing bacteria is plotted against time. What will be the shape of the graph?
- Sigmoid
- Hyperbolic
- Ascending straight line
- Descending straight line
Answer: 3. Ascending straight line
Semi-log of per minute growing bacterium when plotted against time would yield an ascending straight line.
Question 169. Consider the following statements.
- Populations evolve in their habitats, to maximize their reproductive fitness, also called Darwinian fitness.
- The population growth rate r is inversely related to generation time.
- The short lifespan housefly producing a large number of eggs could be considered as a k-selected species.
- Under a particular set of selection pressures, organisms evolve toward the most efficient reproductive strategies.
- Studies regarding traits from the history of organisms show that these traits have evolved in relation to the constraints imposed by biotic and abiotic factors in their habitat.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1, 3 And 4
- 3, 4 And 5
- 1, 2, 4 And 5
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 4 And 5
All statements are correct except statement iii and it can be corrected as the housefly which has a short lifespan, produces a large number of eggs, hence can be considered as ‘r’ selected species. Depending on the number of offspring an organism gives birth to, there are two types of species
- R-selected species of organisms of this type give birth to more young ones during their life cycle. Parents care for their offspring less and their size is also small.
- K-selected species of organisms of this kind give less birth during their life cycle. They care more about their children. Their size and lifespan are more than r-selected species, e.g. Man, mammal, bird, etc.
Question 170. Which mechanism prevents the integrity of species?
- Geographical isolation
- Reproductive isolation
- Recombination
- Mutation
Answer: 2. Reproductive isolation
Reproductive isolation prevents the integrity of species. Sexual attraction between males and females of a given species may be weak or absent. In most animal species, members of the two sexes must first search for each other and come together.
Question 171. The various factors like environment, weather, climate, food, and various other factors limit the population of an area near its
- Carrying capacity
- Biotic potential
- Negative effective point
- Managing capacity
Answer: 1. Carrying capacity
Carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals that can be sustained by the environment.
Question 172. An association of individuals of different species living in the same habitat and having functional interactions is
- Ecosystem
- Population
- Ecological niche
- Biotic community
Answer: 4. Biotic community
A biological or biotic community is an assemblage of populations of different species of plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi that live in a particular area and interact with one another through competition, predation, mutualism, etc.
Question 173. Life history traits of organisms have evolved in relation to the constraints imposed by which components of habitat. Ecological studies pertaining to adaptations of organism’s reproductive traits are due to
- Water
- Abiotic components
- Biotic components
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Life history traits of organisms have evolved in relation to the constraints imposed by biotic and abiotic components of the habitat in which they live
Question 174. Community is
- Groups of independent populations of the same species interact with each other.
- Groups of independent populations of the same species interact with each other in a specific area.
- Group of independent interacting populations of different species in a specific area.
- Group of independent and interacting populations of different species in different areas
Select the correct option.
- 1, 2 And 4
- 1, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 3
- Only 3
Answer: 4. Only 3
Statement iii is correct as a community in an assemblage of populations of different species of plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc., Which live in a particular area and interact with one another. Each biotic community has a specific composition and structure.
Question 175. Species differ from each other due to
- Mutations
- Adaptations
- Variations
- Isolation
Answer: 4. Isolation
The field of biology describes ‘isolation’ as a process by which two species that could otherwise produce hybrid offspring are prevented from doing so.
Question 176.
- Species-level
- Population-level
- Individual level
- Community level
At which level does selection come into existence?
- 1 And 2
- Only 2
- 3 And 4
- Only 4
Answer: 2. Only 2
- Level selection operates on the population level. Population is a grouping of similar individuals in a particular geographical area or space. The different populations of the same organism present in particular geographical areas are called local populations/demes.
- Selection operates only at the population level. A local population adapted genetically to its particular environment is called ecotype.
Question 177. Some animals do not like others to enter their habitat. This habitat is
- Territory
- Parasitism
- Predation
- Symbiosis
Answer: 1. Territory
Some animals do not like others to enter their habitat. This habitat is territory Animals that defend territories in this way are referred to as territorial
Question 178. Organisms compete for resources to survive and sustain and be able to reproduce efficiently, so as to increase their population. They have evolved ways of doing so and this can be referred to as
- Mendel’s fitness
- Darwinian fitness
- Lamarck’s fitness
- Individual fitness
Answer: 2. Darwinian fitness
When food and space for the population are unlimited. Each species has the ability and potential to grow, as Darwin observed while developing his theory of natural selection. He called this the reproductive or Darwinian fitness.
Question 179. Aspects such as sedentary habit, territoriality, etc., Not aiding diversification are classified as
- Reproductive isolation
- Mutational effects
- Biological barriers
- Genetic incompatibility
Answer: 3. Biological barriers
- Biological barriers are factors that prevent species migration, interbreeding, or free movement. What determines the barrier depends on the species and its method of movement.
- For some species, biological barriers are sedentary habits, physical like bodies of water, mountains, or deserts. Mutation effects is the formation of altered protein from mutated genes. When the species are not able to cross-breed it is called genetic incompatibility. Thus, option (3) is correct.
Question 180. Which factor maintains the distinctive traits of species?
- Specific niche
- Reproductive isolation
- Cooperative interaction
- Continuous inter-communication
Answer: 2. Reproductive isolation
- A species is a group of individuals, which resemble with each other in morphological, physiological, biochemical, and behavioral characters.
- These individuals are capable of breeding, feeding in between themselves under natural conditions, but are incapable of breeding with members of other species. This is referred to as reproductive isolation.
Question 181. Keystone species is one which
- Is present in a maximum number
- Governs the property of the ecosystem
- Is present in the minimum number
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Governs the property of the ecosystem
Keystone species help maintain the structure and functioning of an ecosystem. This is because compared to other species in a given habitat, their numbers are greater. Keystone species also determine the numbers and types of other species in an ecosystem. It governs the property of the ecosystem.
Question 182. What is a keystone species?
- A rare species that has minimal impact on the biomass and on other species in the community
- A dominant species that constitutes a large proportion of the biomass and which affects many other species
- A species that makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community yet has a huge impact on the community’s organization and survival
- A common species that has plenty of biomass yet has a fairly low impact on the community’s organization
Answer: 3. A species that makes up only a small proportion of the total biomass of a community yet has a huge impact on the community’s organization and survival
A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance. They play a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological community, affecting many other organisms in an ecosystem and helping to determine the types and number of various other species in the community. Thus, option (3) is correct
Question 183. The removal of ‘keystone’ species will affect
- The producers
- The consumers
- The ecosystem
- The decomposers
Answer: 3. The ecosystem
Without the keystone species, the ecosystem would be dramatically different or cease to exist altogether. Keystone species have low functional redundancy This means that if the species were to disappear from the ecosystem, no other species would be able to fill its ecological niche.
Question 184. Keystone species deserve protection because these
- Are capable of surviving in harsh environmental conditions
- Indicate the presence of certain minerals in the soil
- Have become rare due to overexploitation
- Play an important role in supporting other species
Answer: 4. Play an important role in supporting other species
- Keystone species deserve protection because they play an important role in supporting other species. A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance.
- They play a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological community, affecting many other organisms in an ecosystem and helping to determine the types and number of various other species in the community. Thus, option (3) is correct.
