Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Sex Determination
Question 1. Sex-chromosomes are also called
- Autosomes
- Hybridisation
- Allosomes
- All of these
Answer: 3. Allosomes
Allosomes (also called sexchromosomes) are the chromosomes having a strong causal role in sexdetermination, usually present as a homologous pair in nuclei of one sex (homogametic sex), but occurring either singly (or with partial homologue) in those of other sex (heterogametic sex).
” pedigree analysis questions”
Question 2. The chromosomes except those associated with sex are known as
- Heterosomes
- Autosomes
- Allosomes
- Nucleosomes
Answer: 2. Autosomes
The 22 pairs of chromosomes are called autosomes, other than sex chromosome. So, autosomes are not associated with sex of organisms.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Who discovered sex chromosome Y?
- Robert Brown
- MJD White
- Nettie Stevens
- GJ Mendel
Answer: 3. Nettie Stevens
The Y-chromosome was identified as a sex-determining chromosome by Nettie Stevens at Bryn Mawr College in 1905 during a study of the mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Edmund Beecher Wilson independently discovered the same mechanisms in same year.
NEET Biology sex determination MCQs with answers
Question 4. Balance theory of sex-determination was proposed by
- Calvin Bridges
- Strassburger
- TH Morgan
- Waldeyer
Answer: 1. Calvin Bridges
“questions on principles of inheritance and variation “
The theory of genic balance was given by Calvin Bridges (1926). It states that instead of XY chromosomes, sex is determined by the genetic balance or ratio between X-chromosomes and autosome genomes. The theory is basically applicable to Drosophila melanogaster over which Bridges worked.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
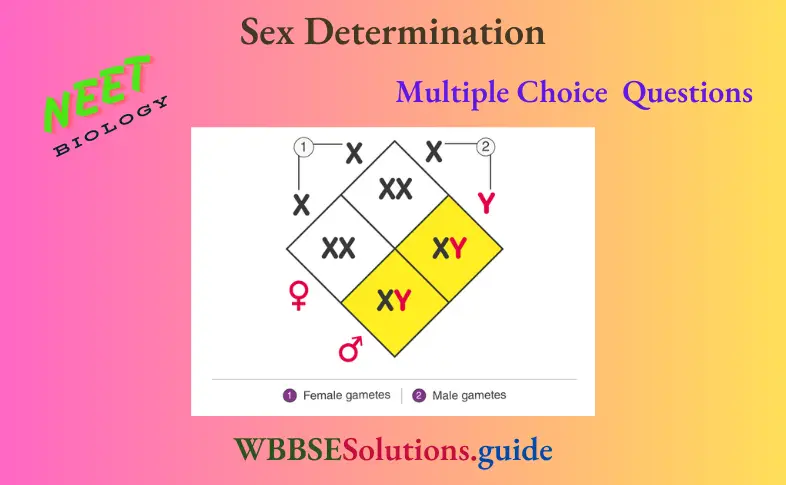
Sex determination multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 5. In which of these, the sex chromosome has been discovered for the first time?
- Melandrium
- Nephrolepsis
- Pinus
- Sphaerocarpus
Answer: 1. Melandrium
In Melandrium, the sex chromosome has been discovered for the first time.
Question 6. Sex-determination in an organism is given by, X/A=1.5, then organism will be
- Male
- Female
- Super female
- Intersex
Answer: 3. Super female
- Genic balance theory gives sexdetermination in Drosophila melanogaster. It states the ratio of number of chromosome to that of complete set of autosome determine the sex of Drosophila.
- According to this theory of sex- determination, if the ratio of X- chromosome to totalnumber of sets of autosome (X/A) is more than 1, the organism will be super female.
- If the ratio of X-chromosome to total number of sets of autosomes (X/A) falls between 1 and 0.5, the genotype will show intersex phenotype.
- The X/A value is 1.0 for normal female and 0.5 for normal male. Thus, in given condition, i.e. X/A=1.5, organism would be super female.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 7. For X-linkage, males are called as
- Heterozygous
- Hemizygous
- Autozygous
- Allozygous
Answer: 2. Hemizygous
inheritance and variation mcq
Hemizygosity is the condition, where only one gene pair is present that determines a particular genetic trait. Males are always hemizygous for X-linked traits, that is why, they can never be heterozygous or homozygous.
Question 8. In XX and XY chromosomal sexdetermination, females are
- Homogametic
- Heterogametic
- Undetermined
- All of these
Answer: 1. Homogametic
- XX and XY type sex-determination seen in many insect and mammals including humans. Males have X and Y-chromosomes along with autosomes and females have pair of X- chromosome along with autosomes.
- Thus, since females produce same type of gametes it is known as homogametic sexdetermination.
Question 9. Genes of sex-linked characters are located on the ………………. .
- Chromosome 18
- Chromosome 13
- Chromosome 14
- Sex chromosome
Answer: 4. Sex chromosome
The characters are said to be sexlinked if their genes are located on the sex chromosome. According to modern genetics, the X-chromosome linked character, is called sex-linked character, while Y-linked characters are called male limited characters.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 10. Males are haploid whereas females are diploid in
- Drosophila
- Amoeba
- Honeybee
- Neurospora
Answer: 3. Honeybee
- Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilised eggs and are haploid and females develop from fertilised eggs and are diploid.
- Haplodiploidy determines the sex in all members of the insect orders– Hymenoptera (bees, ants, honeybee and wasps) and Thysanoptera (thrips).
“pedigree questions “
Question 11. In Melandrium, the sexdetermination type is
- XX-XY type
- XX-XO type
- ZZ-ZW type
- XY-XO type
- XO-ZZ type
Answer: 1. XX-XY type
In Melandrium, staminate or male plants are XY and pistillate or female plants are XX. So, Melandrium shows XX-XY type of sex-determination
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 12. In Melandrium plants, presence of 2 pairs of autosome and an allosomal composition of XXY would make them
- Males
- Females
- Sterile
- Intersexes
Answer: 1. Males
- Melandrium album, a dioecious plant species, has two heteromorphic sex chromosomes. XY constitution is typical for male and the XX for female plants.
- This plant represents an experimental model system of sex-determination in which the Y-chromosome plays a strongly dominant male role. In Melandrium plants, presence of 2 pairs of autosome and an allosomal composition of XXY would make them males.
Question 13. Holandric genes are ones situated on
- X-chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- Both 1 and 2
- Autosomes
Answer: 2. Y-chromosome
Holandric genes are present on the differential region of the Y-chromosome. The differential regions carry completely sex-linked genes and they do not undergo crossing over.
Important sex determination questions for NEET exam
Question 14. Homologous chromosomes which are present in male and female both are known as
- Heterosomes
- Replosomes
- Androsomes
- Autosomes
Answer: 4. Autosomes
Autosomes are homologous chromosomes, i.e. chromosomes which contain the same genes (regions of DNA) in the same order along their chromosomal arms.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 15. Which one is found in the males only?
- X-chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- 2X-chromosomes
- X+X-chromosomes
Answer: 2. Y-chromosome
The sex chromosome of male is denoted by ‘Y’. Since, males are heterogametic, the chromosome component is written as 44 + XY. They do not contian two X-chromosomes together.
“mcq on principles of inheritance and variation “
Question 16. Sex-linked characters have one distinct feature.
- Always follow criss-cross inheritance
- Never follows criss-cross inheritance
- May be present on Y-chromosome
- Only present on X-chromosome
Answer: 1. Always follow criss-cross inheritance
Criss-cross inheritance is applicable to most sex-linked disorders in humans, e.g. red-green colour blindness, haemophilia. So, sex-linked characters always follow criss-cross inheritance.
Question 17. Recessive characters are expressed
- On any autosome
- When they are present on X-chromosomes of male
- On both the chromosomes of male
- When they are present on one X-chromosome of female
Answer: 2. When they are present on X-chromosomes of male
Recessive characters are expressed when they are present in homozygous condition or when other chromosome of the chromosome pair does not possess that character, e.g. in male, the sex chromosomes are XY, as Y does not possess any recessive gene, only X is enough to express that recessive characters.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 18. In case of birds, the females are
- Homogametic
- Heterogametic
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Heterogametic
In birds, females are heterogametic, i.e. ZW, whereas males are homogametic, i.e. ZZ.
Solved MCQs on sex determination for NEET Biology
Question 19. Which of the following symbols are used for representing chromosome of birds?
- ZZ-ZW
- XX-XY
- XO-XX
- ZZ-WW
Answer: 1. ZZ-ZW
- In birds, some reptiles and fishes, the females have heteromorphic (ZW) sex chromosomes and are hence they are heterogametic (A + Z, A + W).
- W-chromosome determines the female sex. The males have homomorphic sex chromosomes (ZZ) and hence, they are homogametic (A+Z).
Question 20. Genic balance theory of sexdetermination, stated by CB Bridges, is related to
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Rumex
- Snapdragon
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Drosophila melanogaster
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 21. Criss-cross inheritance means
- X-chromosome from male will pass to a male of next generation
- X-chromosome from a male will pass to a female of next generation
- X-chromosome from female will pass to female of next generation
- X -chromosome from male will pass to either male or female of the next generation
Answer: 2. X-chromosome from a male will pass to a female of next generation
- Criss-cross inheritance is a type of sex-linked inheritance, where a parent passes the traits to the grand child of the same sex through offspring of the opposite sex, that is, father passes the traits to grandson through his daughter (diagynic), while the mother transfers traits to her grand-daughter through her son (diandric).
- It was first studied by Morgan (1910) in case of eye colour in Drosophila. Thus, option (b) is correct.
Question 22. Which one of the following conditions correctly describes the manner of determining the sex in the given example?
- XO type of sex chromosomes determine male sex in grasshopper
- XO condition in humans as found in Turner’s syndrome, determines female sex
- Homozygous sex chromosomes (XX) produce male in Drosophila
- Homozygous sex chromosomes (ZZ) determine female sex in birds
Answer: 1. XO type of sex chromosomes determine male sex in grasshopper
- XO type of sex chromosomes determines the male sex in grasshopper. In grasshopper, the males lack a Y-sex chromosome and have only one X-chromosome.
- They produce sperm cells that contain either an X-chromosome or no sex chromosome, which is designated as O.
“which of the following is a hereditary disease “
Question 23. In gynandromorphs,
- Some cells of body contain XX and some cells with genotype XY
- All cells have XX genotype
- All cells have XY genotype
- All cells with genotype XXY
Answer: 1. Some cells of body contain XX and some cells with genotype XY
- Gynandromorphs arise when proper segregation of XX and XY-chromosome doe not take place in development phase of a organism.
- Therefore, some cells gets XX-chromosome, while other get XY-chromosomes. As a result, some part of the organisms appears as female and some part appeared as male. Thus, option (1) is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 24. Calvin Bridges demonstrated sex determining factor is the ratio of number of
- X-chromosome and autosomes
- autosome and X-chromosome
- Y-chromosome and X-chromosome
- Y-chromosome and autosome
Answer: 1. X-chromosome and autosomes
Calvin Bridges (1926) stated that sex in Drosophila is determined by the genic balance or ratio between X-chromosomes and autosomes.
Question 25. …………… variations are inheritable.
- Germinal
- Physical
- Mental
- Accidental
Answer: 1. Germinal
Germinal variations arise due to changes in germ cells. They may be caused due to radiations, modification of chromosome structure. These variations are inheritable.
Question 26. Example of environmental determination of sex is/are
- Alligators
- Turtles
- Bonellia
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
- All given options represents example of environmental sex-determination. In Bonellia, a marine worm, the swimming larva has no sex. If it settles on the bottom of the water body alone, it develops into a large (2.5 cm) female.
- If it lands on or near an existing female, a chemical from female causes the larva to develop into a tiny (1.3 mm) male.
- In turtles and alligators, a temperature below 28°C produces more males and temperature above 33°C produces more females.
- Temperature between 28°C-33°C produces males and females in equal proportion. Thus, option (4) is correct.
“which of the following is a hereditary disease “
Question 27. Haploid-diploid mechanism of sexdetermination (haplodiploidy) takes place
- Bees
- Wasps
- Ants
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Haploid-diploid mechanism of sex-determination (haplodiploidy) occurs in hymenopterous insect such as bees, wasps and ants. These insects have unique phenomena in which an unfertilised egg (N) develops into male and female develops from fertilised egg (2N).
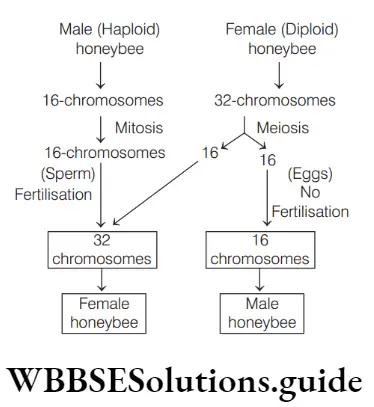
Thus, option 4. is correct.
Genetic basis of sex determination NEET MCQs with answers
Question 28. Females in haplodiploidy sex determination are
- n
- 2n
- 4n
- 3n
Answer: 2. 2n
Females in haplodiploidy sex-determination are (2n).
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 29. In haplodiploidy, determination of male sex is
- Haploid
- Diploid
- Haplodiploid
- Diplohaploid
Answer: 1. Haploid
In haplodiploidy sexdetermination, male sex is haploid (N).
Question 30. How many conditions exhibit in dissimilar sex chromosomes?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 3. 4
Four conditions exhibit in dissimilar sex chromosomes. These are
-
- XX and XY
- XX and XO
- ZW and ZZ
- ZO and ZZ
Question 31. Drosophila with 2A+XO are
- Fertile female
- Infertile female
- Sterile male
- Intersexes
Answer: 3. Sterile male
- If there is one X-chromosome in a diploid cell (1X:2A), the fly is male. If there are two X-chromosomes in a diploid cell (2X:2A), the fly is female (Bridges 1921, 1925).
- Thus, XO Drosophila are sterile males. In flies, the Y-chromosome is not involved in determining sex.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 32. A fruitfly is heterozygous for sex-linked genes. When mated with a normal female fruitfly, the male specific chromosome will enter egg cells in the proportion of
- 1: 1
- 1: 2
- 3: 1
- 7: 1
Answer: 1. 1: 1
In sex-determination, the male specific chromosome will have half as much chance as the other to enter the egg cell. Hence, the proportion will be 1: 1.
Question 33. XO type of sex-determination is seen in
- Man
- Grasshopper
- Drosophila
- Birds
- Horse
Answer: 2. Grasshopper
Insect, grasshopper, cockroaches and bugs have XX and XO type of sex determination in which XO happens to be male and XX happens to be female.
Question 34. In XO type of sex-determination,
- Females produce two different types of gametes
- Males produce two different types of gametes
- Females produce gametes with Y- chromosomes
- Males produce single type of gametes
- Males produce gametes with Y- chromosome
Answer: 2. Males produce two different types of gametes
- In XX-XO type of sexdetermination, the females have two sex chromosomes and are designated as XX, while the males have only one sex chromosome X, therefore, they are designated as XO.
- The females are homogametic because they produce only one type of egg (A + X). The males are heterogametic with half the male gametes carrying X-chromosome (A+X), while other half being devoid of it (A + O). The sex ratio produced in progeny is 1: 1.
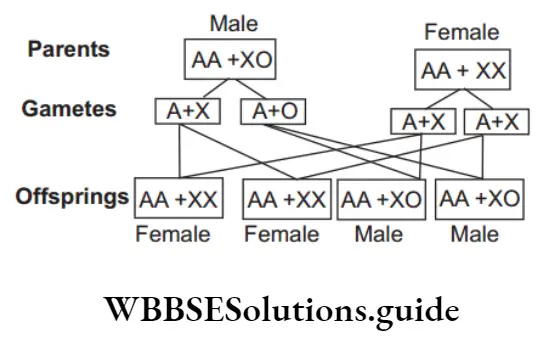
Thus, males produce two different types of gametes.
Best multiple choice questions on sex determination for NEET preparation
Question 35. The condition in which females lack one sex chromosome whereas males are homogametic, the sex chromosomal representation is
- ZO-ZZ
- XY-XX
- XX-XO
- ZW-ZZ
Answer: 1. ZO-ZZ
ZO and ZZ type of sexdetermination mechanism occurs in certain butterflies and moths. The female is heterogametic and produces two types of eggs, half with Z and half without Z-chromosome. The males are homogametic and forms only one kind of sperms, each with Z-chromosome.
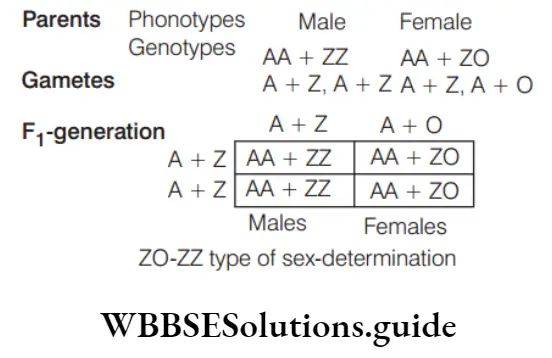
ZO-ZZ type of sex-determination
Question 36. ZW method of sex-determination is applicable to
- Birds
- Fish
- Butterfly
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
ZW and ZZ-type of sex determination mechanism operates in certain insects (butterflies and moths) and in vertebrates (fishes, reptiles and birds).
Question 37. Heterogamety is the term where an individual produces two types of gametes. The most appropriate answer is
- Male Drosophila fly
- Female Drosophila fly
- Female bird
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 3
- Heterogamety is the term used where an individual produces two types of gametes. Depending upon the sex-determination mechanism in the species, either males or females can be heterogametic sex, producing two different types of gametes.
- In Drosophila, female has XX genotype and male has XY genotype. In birds, female has ZW genotype and males have ZZ genotype. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 38. Match the following columns.
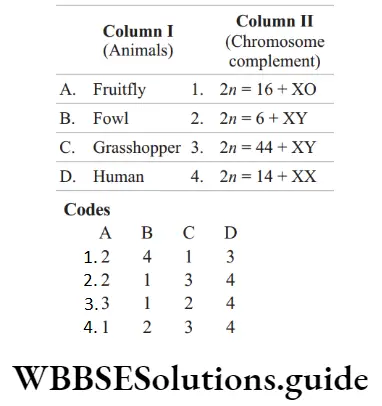
Answer: 1. A–2, B–4, C–1, D–3
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 39. The traits which are not expressed due to a particular gene, but are expressed by products of sex hormones are
- Sex influenced traits
- Autosomal traits
- Allosomic traits
- Sex-linked traits
Answer: 1. Sex influenced traits
- The traits are not expressed due to particular genes, but are expressed by products of sex hormones are sex influenced traits, e.g. low pitched voice, bearding moustaches.
- In males, pattern baldness is related to both autosomal genes as well as excessive secretion of testosterone.
Question 40. An unfertilised human egg contains
- Two X-chromosomes
- One X-and one Y-chromosome
- One Y-chromosome only
- One X-chromosome only
Answer: 4. One X-chromosome only
An unfertilised human egg contains only one X-chromosome. A human sperm contains either an X or a Y-chromosome, thereby determining the sex of the offspring after fertilisation (XX = female, XY = male).
NEET Biology X and Y chromosome sex determination MCQs
Question 41. If the expression of a trait is limited to one sex, it is sex ……………. trait.
- Linked
- Influenced
- Expressed
- Limited
Answer: 4. Limited
Sex limited genes are those which express characters in only one sex and are located on allosomes or autosomes. For example, beard in man due to testosterone and breast development in female.
Question 42. In human sex-determination, the key factor is
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
- Both 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 1. Y-chromosome
The Y-chromosome carries a gene that encodes a testis determining factor. Unlike the situation in Drosophila, the mammalian Y-chromosome is a crucial factor for determining sex in humans.
Question 43. Human females have
- 46 autosomes
- 44 autosomes
- 2 pairs of allosomes
- 23 pairs of autosomes
Answer: 2. 44 autosomes
- In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. 22 of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females.
- The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differs between males and females. Thus, human female has 22 pairs or 44 autosomes and one pair or 2 allosomes
Question 44. As per Denver Convention, the autosomes of man have been classified in …….. groups.
- 7
- 4
- 3
- 16
Answer: 1. 7
- The Denver system of classification divide human chromosomes including sex chromosomes into 7 groups from A to G in order of decreasing length.
- Group A includes chromosomes pairs 1, 2, 3 group, B has pairs of 4 and 5 chromosomes, group C has pairs of 6 to 12 chromosomes, group D has pairs of 13 to 15 chromosomes, group E has pairs of 16 to 18 chromosomes, group F has pairs of 19 and 20 chromosomes and group G has pairs of 21 and 22 chromosomes.
Question 45. In man, sperms contain autosomes and
- Both X and Y-chromosomes
- Either X or Y-chromosomes
- Only Y-chromosome
- Only X-chromosome
Answer: 4. Either X or Y-chromosomes
XX and XY type of sexdetermination is seen in many insect and mammals including humans. Males have X and Y-chromosome along with autosome and females have pair of X- chromosome along with autosome. In man, sperm contains autosomes and either X or Ychromosomes.
Question 46. There are five daughters and no son in a family. It may be due to
- Father produced only X containing sperms
- Father produced no sperms at all
- Y type sperms are weaker and not effective
- By chance each time X sperm fertilised the egg
Answer: 4. By chance each time X sperm fertilised the egg
There are five daughters and no son in a family because by chance, each time X sperm fertilised the egg.
Question 47. Sex-limited and sex-linked genes are located on
- Autosomes
- X-chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 2. X-chromosome
The traits which are carried on sex chromosomes are called sex linked traits. The genes for the traits are only located on X-chromosomes (sex-linked and sex-limited) of both male and female organisms. X-chromosome is large and contains more genes, whereas Y-chromosomes are small.
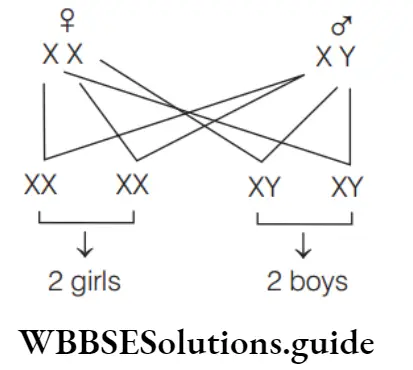
Question 48. A couple has 6 children, 5 of which are girls and 1 is boy. The percentage of having a girl child on next time is
- 10%
- 20%
- 50%
- 100%
Answer: 3. 50%
Probability of child being boy or girl is 50% during each pregnancy.
Thus, option 3. is correct.
Question 49. Find out A, B and C in the diagram given below.
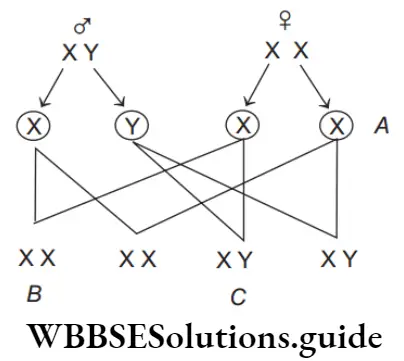
- A–Male gamete, B–Female, C–Gametes
- A–Male, B–Female, C–Sperm
- A–Female, B–Male, C–Gametes
- A–Gametes, B–Female, C–Male
Answer: 4. A–Gametes, B–Female, C–Male
A–Gametes, B–Female, C–Male
Question 50. A mother in a family of five daughters is expecting her sixth baby. The chance of this being a son is
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%
Answer: 3. 50%
Humans has 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosome which are XX in females and XY in males. So, every time, the chance of son or daughter is 50% depending upon which sex chromosome from male fertilises the ovum.
Question 51. Gamete mother cells of the chromosome 44 + XY suffers from non-disjunction at first meiotic division. Identify the set of gametes in which this condition would occur
- 22 + XX, 22 + YY and 22, 22
- 22 + XY, 22 + XY and 22, 22
- 22 + X, 22 + Y and 22+Y, 22
- 22 + X, 22 +X and 22+Y, 22+Y
Answer: 2. 22 + XY, 22 + XY and 22, 22
- Non-disjunction is the condition in which the separation of chromosome does not take place during cell division. In 44+XY gametes there is non-separation of XY gene.
- It leads to the formation of sperm having genotypes, 22 + XY and 22. In such condition, XY would be inherited together due to non-disjunction of XY chromosome.
Question 52. Mr. Kapoor has Bb autosomal gene pair and d allele sex-linked. What shall be proportion of Bd in sperms?
- zero
- 1/2
- 1/4
- 1/8
Answer: 3. 1/4
Genotype of Mr. Kapoor will be Bb, hence one fourth of the sperms will have Bd.
Question 53. Probability of four sons to a couple is
- 1/4
- 1/8
- 1/16
- 1/32
Answer: 3. 1/16
In each pregnancy, there is 1/2 probability of having either sex, i.e. male or female. Hence, probability of four sons to a
(\(\frac{1}{2}\))4 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)×\(\frac{1}{2}\)×\(\frac{1}{2}\)×\(\frac{1}{2}\)
=\(\frac{1}{16}\)
