Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Sexual Reproduction
Question 1. Clear-cut vegetative, reproductive, and senescent phases cannot be observed in
- Annual plants
- Perennial plants
- Biennial plants
- Ephemeral plants
Answer: 2. Perennial plants
- Perennial plants live for many years, unlike annuals and biennials, which complete their life cycle in one and two years, respectively.
- Therefore, perennials have different flowering periods. So, we cannot distinguish between the juvenile, reproductive and senescent phases in these plants.
“class 12th biology chapter 3 mcq “
Question 2. Which of the following statements is correct about Neelakurinji?
- It blooms once in 12 years
- The flowers are bluish in colour
- It is found in Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra
- All of the above
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Answer: 4. All of the above
- All given statements are correct about Neelakurinji as Strobilanthes kunthiana also called Neelakurinji in local language.
- It is found in the Shola forests on the Western Ghats ranging over Kerala, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. It blooms once in 12 years.
- It attracts tourists in large numbers as it makes the surrounding area appear blue in colour.
Question 3. Which of the following flowers only once in its lifetime?
- Bamboo sp.
- Papaya
- Mango
- Jackfruit
Answer: 1. Bamboo sp.
- Bamboo species are monocarpic, i.e. produces flower only once in its lifetime after 50-100 years.
- Other options are explained as Jackfruit, papaya, and mango are polycarpic, i.e. produce flowers and fruits many times in their lifetime.
“human reproduction mcqs class 12 “
Question 4. Cyclic changes in the activities of ovaries and accessory ducts during .………… is known as oestrus cycle.
- Reproductive (seasonal) period
- Maturation period
- Ageing period
- Juvenile period
Answer: 1. Reproductive (seasonal) period
The oestrus cycle occurs in seasonal breeders. It is the cyclic change in the activity of ovaries and accessory duct during reproductive (seasonal) period.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
NEET Biology polyspermy MCQs with answers
Question 5. The gestation period of elephant is about
- 11 months
- 15 months
- 22 months
- 32 months
Answer: 3. 22 months
Gestation is the duration between fertilisation and parturition. The gestation period of elephant is about 22 months (607-641 days).
Question 6. Which of the following animals show menstrual cycle?
- Gorillas and chimpanzees
- Monkeys and humans
- Orangutans and monkeys
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
“mcq on human reproduction class 12 pdf download “
All given animals show menstrual cycle. Apart from humans, most of the other menstruating animals are primates, the group that includes monkeys and apes as well as humans. Menstrual bleeding is observed in chimpanzees and gibbons.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Sexual reproduction and polyspermy multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 7. Identify from the following groups of animals, which exhibit oestrus cycle.
- Monkey, ape, man and elephant
- Lion, deer, dog and cow
- Lion, dog, monkey and ape
- Cow, monkey, elephant and ape
Answer: 2. Lion, deer, dog and cow
The oestrus cycle is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive changes in most mammalian therian females, e.g. lion, deer, dog and cow, etc.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 8. Which one of the following generates new genetic combinations leading to variation?
- Vegetative reproduction
- Parthenogenesis
- Sexual reproduction
- Nucellar polyembryony
Answer: 3. Sexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction generates new genetic recombination leading to variations. In this process, the male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote.
- Due to the fusion of gametes, the product of sexual reproduction generally generates new genetic
combinations.
Question 9. The events involved in sexual reproduction are given below.
- Pre-fertilisation
- Post-fertilisation
- Fertilisation
- The sequential order of their occurrence is
Choose the correct answer
- 1 → 3 → 2
- 2 → 1 → 3
- 3 → 2 → 1
- 1 → 2 → 3
Answer: 1. 1 → 3 → 2
“human reproduction mcq class 12 “
The sequential events in the sexual reproduction are as follows Pre-fertilisation → Fertilisation → Post-fertilisation.
Thus, option (1) is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. The example of sexual reproduction is
- Fragmentation
- Production of androgenic haploid
- Heterospory
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Production of androgenic haploid
Androgenic haploids are generated by culture of haploid microspores without syngamy. Since haploid gametes are involved, it can be assumed to be a type of sexual reproduction.
So, the example of sexual reproduction is production of androgenic haploid
Question 11. In papaya plant, flowers are
- Hermaphrodite
- Unisexual
- Monoecious
- Neuter
Answer: 2. Unisexual
Papaya is dioecious or unisexual, i.e. male and female flowers are borne on separate plants. The flowers are yellow and sweet-smelling and open at night to attract moths, the pollinators of the papaya.
Important polyspermy questions for NEET Biology exam
Question 12. Which of the following is a hermaphrodite?
- Ant
- Aphids
- Earthworm
- Cockroach
Answer: 3. Earthworm
Ant, aphids, cockroaches are unisexual, only earthworms have both the sexes in same body, i.e. it is hermaphrodites (bisexual).
Question 13. The condition in which male and female reproductive parts are present on different plant is
- Heterothallic
- Dioecious
- Unisexual
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The terms heterothallic, dioecious, or unisexual are used when the sexes, i.e. male and female are present in different organisms.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 14. In a monoecious plant,
- Male and female sex organs are on different individuals
- Male and female gametes are of two morphologically distinct types
- Male and female sex organs are on the same individual
- All the stamens are fused to form one unit
Answer: 3. Male and female sex organs are on the same individual
In some plants, both male and female sexes are present in same individual. Such plants are called bisexual or monoecious.
“reproduction mcq “
Question 15. Monoecious plant of Chara shows the occurrence of
- Stamen and carpel of the same plant
- Upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant
- Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
- Antheridiophore and archegoniophore on the same plant
Answer: 3. Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
- Chara reproduces by both sexual and vegetative modes. The male sex organs called globules are macroscopic and large.
- The female sex organ is green in and called oogonium. It is always situated singly above the globule or antheridium.
- Thus, monoecious plant of Chara shows the occurrence of upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant.
Question 16. Consider the following statements.
The process of formation of female gamete is called gametogenesis.
Gemetes are haploid cells.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but2 is correct
Statement I is incorrect, but II is correct. Incorrect statement can be corrected as The process of formation of male and female gametes is called gametogenesis. Formation of female gamete is called oogenesis. Gametes are haploid in nature.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 17. In lower organisms, male gametes are also known as
- Antherozoids
- Sperm
- Both (1) and (2)
- Condiophores
Answer: 1. Antherozoids
Male gametes are called antherozoids in case of lower organisms, e.g. fungi and algae and in higher organisms, it is called sperm, e.g. mammals, reptiles, etc.
“reproduction mcq “
Question 18. In a diploid organism, the gamete-producing cells are
- Gamete mother cell
- Meiocytes
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Gamete mother cells are gamete-producing cells. In these, the meiotic cell division takes place hence, they are also called meiocytes.
Thus, option (3) is correct.
Solved MCQs on polyspermy and fertilization for NEET
Question 19. Identify the option which correctly indicates the type of gametes.
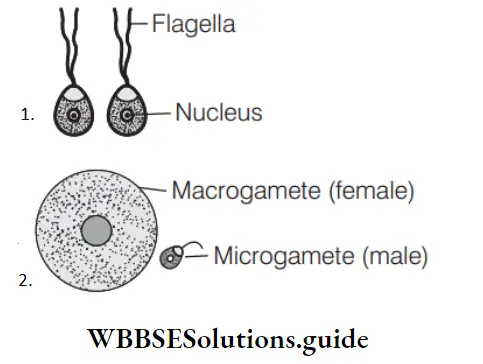
- A–Heterogametes, B–Isogametes
- A–Homogametes, B–Isogametes
- A–Isogametes, B–Heterogametes
- A–Heterogametes, B–Heterogametes
Answer: 3. A–Isogametes, B–Heterogametes
A–indicates homogametes or isogametes because both gametes are identical in shape and size. B–indicates heterogametes because both gametes are different in shape and size.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 20. Pollination refers to
- Interaction between pollinators and flowers
- Transfer of male gametes onto stigma
- Transfer of female gametes onto stigma
- Fusion of male and female gametes
Answer: 2. Transfer of male gametes onto stigma
Transfer of male gametes (pollen) on to the receptacle (stigma) of the female plant is called pollination.
It takes place by various agents, e.g. air, water, animals, insects, etc.
Question 21. Meiosis takes place in
- Meiocyte
- Conidia
- Gemmule
- Megaspore
Answer: 1. Meiocyte
A meiocyte is a type of cell that differentiates into a gamete through the process of meiosis.
Thus, the diploid meiocyte divides into genetically different haploid gametes.
Question 22. Which of the following organisms has the highest number of chromosomes?
- Housefly
- Butterfly
- Ophioglossum
- Onion
Answer: 3. Ophioglossum
Ophioglossum is a species of fern also known as adder’s tongue. It has the largest number of chromosomes, i.e. 1260.
Question 23. The male gametes of rice plant have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome number in the female gamete and zygote will, respectively be.
- 12, 12
- 24, 24
- 24, 12
- 12, 24
Answer: 4. 12, 24
Chromosome number in male gamete of rice plant is n = 12, therefore, chromosome number is female gamete would also be 12. Zygote is diploid hence, the chromosome number is 2n = 24.
Question 24. The chromosome number in meiocyte is 34. The organism could be
- Ophioglossum
- Dog
- Onion
- Apple
Answer: 4. Apple
- The gametes produced by the meiocytes through meiosis are haploid. The apple meiocyte has 34 chromosomes and after meiosis, the gamete would has 17 chromosomes.
- Ophioglossum has 1260 chromosomes, dog has 78 and onion has 32 chromosomes
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 25. The essential and most critical event in sexual reproduction is
- Fertilisation
- Embryogenesis
- Division in male and female gametes
- Pollination
Answer: 1. Fertilisation
The most vital event in sexual reproduction is fertilisation which refers to the fusion of male and female gametes. The terms syngamy and fertilisation are frequently used, interchangeably.
Question 26. The pollen tube usually enters the embryo sac
- Through one of the synergids
- By directly penetrating the egg
- Between one synergid and central cell
- By knocking off the antipodal cells
Answer: 1. Through one of the synergids
The tube cell of pollen grows to penetrate the pollen wall and then, the stigma and style. The pollen tube arrives in the micropyle of the integument of the ovule and enters the embryo sac. The one of the synergids provide path for the pollen tube entry into the embryo sac.
Preventing polyspermy NEET MCQs with answers
Question 27. External fertilisation occurs exclusively in habitats that are
- Warm
- Tropical
- Aquatic
- Crowded
Answer: 3. Aquatic
In most aquatic organisms, such as a majority of algae and fishes as well as amphibians, syngamy occurs in the external medium (water), i.e. outside the body of the organisms. This type of gamete fusion is called external fertilisation.
Question 28. Self-fertilisation occurs in
- Bisexual flower
- Unisexual flower
- Both (1) and (2)
- Monoecious flower
Answer: 1. Bisexual flower
Self-fertilisation is very common phenomenon in plants. It takes place in bisexual flower.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 29. A large number of offspring are produced when
- Fertilisation occurs externally
- Fertilisation occurs internally
- Pollination takes place, via. moth
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Fertilisation occurs externally
Large number of offsprings are produced in case of external fertilisation because there is no direct protection of offspring from the environment and thus, their survival rate is very low.
Question 30. Fertilisation in mammals takes place in
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Fallopian tube
Answer: 4. Fallopian tube
In mammals like humans, sperm passes through the cervix and reaches. Fallopian tube, where it fuses with ovum to form zygote. So, fertilisation takes place in Fallopian tube.
Question 31. Consider the following statements.
Fishes frequently exhibit selffertilisation.
Earthworms and leeches can
undergo both self-fertilisation and cross-fertilisation.
Choose the correct option
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Incorrect statements can be corrected as Fishes are dioecious, therefore, do not undergo self-fertilisation.
- Earthworms, liver fluke, and leeches are hermaphrodites, i.e. capable of both cross-fertilisation and self-fertilisation.
Question 32. Sexually reproducing larva shows
- Isogamy
- Anisogamy
- Paedogamy
- Autogamy
Answer: 3. Paedogamy
Paedogamy simply refers to the reproduction by juveniles. The larvae which can reproduce sexually show this phenomenon, e.g. some flukes and gall midge flies.
Question 33. In the prothallus of a vascular cryptogam, the antherozoids and eggs mature at different times. As a result,
- There is high degree of sterility
- One can conclude that the plant is apomictic
- Self-fertilisation is prevented
- There is no change in success rate of fertilisation
Answer: 3. Self-fertilisation is prevented
In the prothallus of a vascular cryptogam, the antherozoids and eggs mature at different times. As a result, self-fertilization is prevented and cross-fertilisation occurs.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 34. Syngamy can occur outside the body in
- Fungi
- Mosses
- Algae
- Ferns
Answer: 3. Algae
Syngamy occurs outside the body in algae. This type of gametic fusion is called external fertilisation. Fungi, mosses, and ferns show internal fertilisation.
Best multiple choice questions on polyspermy and fertilization for NEET preparation
Question 35. Eggs of which one of these can develop parthenogenetically by chemicals?
- Man
- Frog
- Sea urchin
- All of these
Answer: 3. Sea urchin
Artificial parthenogenesis can be induced in eggs of both frogs and sea urchins but chemical induction occurs in sea urchins.
Question 36. Natural parthenogenesis occurs in
- Frog to form female
- Honeybee to produce drones
- Cockroach
- Vegetarian eggs
Answer: 2. Honeybee to produce drones
Natural parthenogenesis occurs in honeybees to produce drones. In honey bees, only females are developed from fertilised eggs, while males or drones develop from unfertilised egg.
Question 37. Drones in a colony of honeybees originate by
- Thelytoky
- Arrhenotoky
- Cyclic parthenogenesis
- Diploid parthenogenesis
Answer: 2. Arrhenotoky
Based on the sex of offspring, there are four types of parthenogenesis, e.g. arrhenotoky, thelytoky, amphitoky, and deuterotoky. In arrhenotoky parthenogenesis, only males or drones are produced. It occurs in honeybees, wasps, ticks, mites, etc
Question 38. Parthenogenetic eggs develop into any sex by
- Arrhenotoky parthenogenesis
- Thelytoky parthenogenesis
- Amphitoky parthenogenesis
- Artificial parthenogenesis
Answer: 3. Amphitoky parthenogenesis
In amphiboly parthenogenesis, parthenogenetic eggs may develop into individual of any sex (i.e. male or female). It occurs in Aphis (aphid).
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 39. In thelytoky type of parthenogenesis,
- Only males are produced parthenogenetically
- Only females are produced parthenogenetically
- Both males and females are produced parthenogenetically
- Parthenogenetic eggs may develop into any sex
Answer: 2. Only females are produced parthenogenetically
The production of female offspring by parthenogenesis is referred to as thelytoky, e.g. aphids.
Question 40. An aphid has two modes of reproduction, sexual when food is sufficient and ……………. when there is scarcity of food.
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Parthenogenesis
- Gemmules
Answer: 3. Parthenogenesis
- Aphids can reproduce sexually or asexually. They reproduce by sexual methods when the food is available.
- The asexual method involves parthenogenesis, which occurs when there is a scarcity of food. With a few exceptions, all aphids are females in spring and summer, that expand exponentially.
Question 41. In some plants, the female gamete develops into embryo without fertilisation. This phenomenon is known as
- Autogamy
- Parthenocarpy
- Syngamy
- Parthenogenesis
Answer: 4. Parthenogenesis
The phenomenon in which female gamete develops into embryo without getting fused with male gamete (fertilisation) is called parthenogenesis.
NEET Biology mechanisms of polyspermy prevention MCQs
Question 42. Consider the following statements.
In all sexually reproducing organisms, life begins from zygote.
Zygote is considered a single cell with two nuclei.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct. Zygote is considered as a single cell with two nuclei.
It is formed after the union of male and female gametes, which are haploid. Two haploid cells fuse to form diploid cell that contain two pronuclei.
Question 43. In frog, the zygote is formed in
- Ovary
- Oviducts
- Water
- Coelom
Answer: 3. Water
- A female frog lays eggs in the water, which are fertilised by sperm derived from a male frog.
- The resulting zygote is then formed in water. It goes through embryonic development to become a free-living tadpole.
Question 44. Embryogenesis is the process of development of
- Embryo
- Endosperm
- Internal organs
- Sperm
Answer: 1. Embryo
Embryogenesis refers to the development of embryo from the zygote. During embryogenesis, zygote undergoes cell division (mitosis) and cell differentiation.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 45. Assertion (1) Zygote is the link between two generations. Reason (R) Zygote is the product of two gametes and producer of next generation.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Zygote is the product of two gametes. It is the vital link that ensures continuity of species between organisms of one generation and the next. Every sexually reproducing begin life as a single cell, zygote.
Question 46. Identify the sequence of events in the diagram.
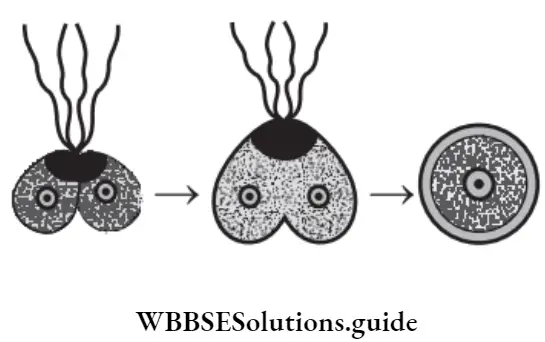
- Fission of gametes → New individual → Zygote
- Fusion of gametes → Zygote → New individual (cell 2n)
- Fission of gametes → Zygote → New individual (cell 2n)
- Stages in the gametogenesis
Answer: 2. Fusion of gametes → Zygote → New individual (cell 2n)
- The first figure indicates the fusion of male and female gametes. Second figure indicates the zygote because there are two nuclei visible in a completely fused condition.
- Third figure indicates a complete cell after completion of fusion.
Thus, option (2) is correct
Question 47. Which among the following is not a post-fertilisation event?
- Fruit formation
- Gametogenesis
- Seed formation
- Embryogenesis
Answer: 2. Gametogenesis
- Post-fertilisation events occur after the process of fertilisation such as embryogenesis, seed formation, and fruit formation.
- Gametogenesis is the process of formation of gametes which later undergo fertilisation. It is a pre-fertilisation (not post-fertilisation) event.
Question 48. Select the correct sequence of events.
- Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote → Cell division → Cell differentiation →
Organogenesis - Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote → Cell division → Organogenesis → Cell differentiation
- Gametogenesis → Syngamy → Gamete transfer → Zygote → Cell division → Cell differentiation →
Organogenesis - Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote → Cell differentiation → Cell division →
Organogenesis
Answer: 1. Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote → Cell division → Cell differentiation → Organogenesis
The correct sequence of events in sexual reproduction is Gametogenesis → Gamete transfer → Syngamy → Zygote → Cell division → Cell differentiation → Organogenesis.
Question 49. Identify the incorrect statements regarding post-fertilization development.
- The ovary wall develops into a pericarp.
- The outer integument of ovule develops into tegmen.
- The fusion nucleus (triple nucleus) develops into endosperm.
- The ovule develops into fruits.
- The ovary develops into seed.
Choose the correct option.
- 2, 4 and 5
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 5
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 2, 4 and 5
- Statements 2, 4, and 5 are incorrect regarding post-fertilization development and can be corrected as
- The outer integument of ovule develops into a seed coat. The ovule develops into a seed. The ovary develops into fruit. Rest statements are correct regarding post-fertilization development.
Question 50. Birds are
- Oviparous with internal fertilisation
- Oviparous with external fertilisation
- Ovoviviparous
- Viviparous
Answer: 1. Oviparous with internal fertilisation
- Oviparous animals lay eggs with little or no other embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method in most fishes, amphibians, reptiles, all birds, etc.
- In some oviparous animals, fertilisation is external, e.g. arthropods and fishes and while in some oviparous animals, fertilisation is internal, e.g. birds.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 51. In oviparous individuals, partial development of zygote takes place
- Outside the body
- Inside the body
- In a freshwater medium
- In a marine water medium
Answer: 1. Outside the body
Oviparous individuals lay eggs outside the body hence, further partial development of zygote takes place outside the body. But, the process of fertilisation takes place inside their body.
Question 52. In oviparous individuals, the fertilised egg is covered by
- Calcareous shell
- Hardshell
- Both (1) and (2)
- Phosphorus shell
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Oviparous individuals lay eggs that are white in color with a hard shell around them and this white hard shell is made up of calcium (i.e. calcareous shell).
Thus, option (3) is correct.
Question 53. Viviparity is found in
- Frog
- House lizard
- Scoliodon
- Pigeon
Answer: 3. Scoliodon
- Some animals give birth to young ones. This characteristic is called viviparity. Some animals lay eggs and this habit is called oviparity.
- In viviparous animals, the fertilisation is internal and the zygote develops inside the body of female animals, e.g. Scoliodon.
Question 54. The chances of survival of young ones are more in the case of ………………… individuals.
- Oviparous
- Viviparous
- Ovoviviparous
- None of these
Answer: 2. Viviparous
- In viviparous animals, the zygote develops into a young one inside the body of the female organism. After attaining a certain stage of growth, the young ones are delivered out of the
body. - Because of proper embryonic care and protection, the chances of survival of young ones is greater in viviparous organisms
Question 55. Animals who give birth to young ones are
- Oviparous
- Viviparous
- Ovoviviparous
- None of these
Answer: 2. Viviparous
Animals that give birth to offspring (young ones) are called viviparous. In viviparous animals, both fertilisation, as well as the development of the embryo takes place inside the female parent.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 56. Physiological polyspermy is a characteristic of
- Birds
- Insects
- Reptiles
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
- Physiological polyspermy or penetration of the oocyte by more than a single sperm occurs in numerous species including insects, reptiles, and birds.
- Mammalian polyspermic fertilisation is considered abnormal, which leads to developmental failure of the zygote and spontaneous abortion in humans. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 57. Match Column 1 with Column 2 and select the correct option using the codes given below.
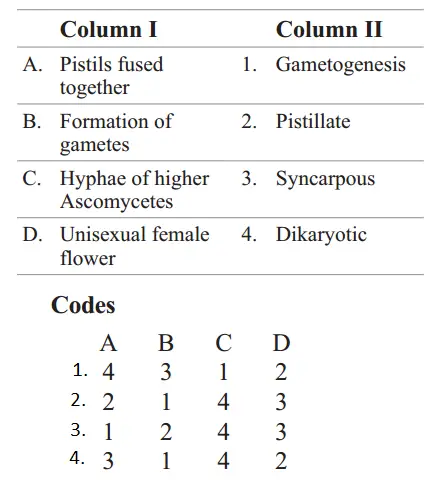
Answer: A–3, B–1, C–4, D–2
Reproduction In Organisms Miscellaneous MCQs
Question 1. Match the terms in Column 1 with suitable terms in Column 2 and select the correct option from the codes given below.
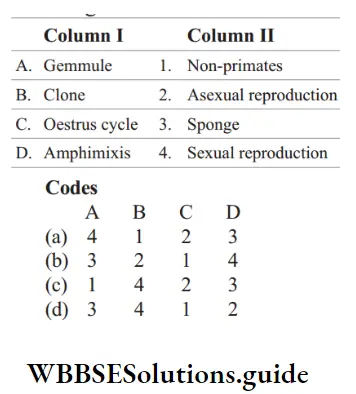
Answer: A–3, B–2, C–1, D–4
Question 2. Which of the following statements supports the view that ‘elaborate sexual reproductive processes appeared much later in organic evolution’?
- Lower groups of organisms have complex body design.
- Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups.
- Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms.
- High incidences of sexual reproduction are visible in angiosperms and vertebrates.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 2 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 4
- Statements 2 and 4 support the view that elaborate sexual reproductive processes appeared much later in organic evolution.
- Whereas statements 1 and 3 do not support this view. Incorrect statements can be corrected as
- The organisms which evolve earlier reproduced by asexual mode o reproduction because of their simpler body plans.
- In complex organism, which evolve later have complex body plan and they reproduce by means
of sexual reproduction which is complex than the asexual method.So, sexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms.
Question 3. Which one of the following statement is not correct?
- Genetic traits are maintain through vegetative multiplication
- The zygote develops into the embryo
- Sponges and coelenterates are unisexual animals
- A middle piece of sugarcane serves as vegetative propagule
Answer: 4. A middle piece of sugarcane serves as vegetative propagule
Statement in option (4) is not correct and can be corrected as New buds arise from node, not from internode, hence a middle piece of sugarcane cannot serve as a vegetative propagule.
Rest statements are correct.
