Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Structure and Function of Ecosystem, its Productivity and Decomposition
Question 1. Ecology deals with
- The Earth And Planets
- The Relationship Between Organism And Their Environments
- The Life Under The Sea
- Economical growth of poor people
Answer: 2. The Relationship Between Organism And Their Environments
Ecology deals with the relationship between organism and their environments.
ecosystem pyq neet
Question 2. Ecology is basically concerned with how many levels?
- One
- Three
- Four
- Five
Answer: 3. Four
Ecology is basically concerned with four levels of biological organisation.
They are
- Organisms
- Populations
- Communities
- Biomes
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Identify the basic levels of ecology
- Organisms
- Populations
- Communities
- Biomes
- Human
- Vertebrates
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- 1 2, 3 and 5
Answer: 3. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Organisms, populations, communities and biomes are basic levels of ecology
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers

NEET Biology structure and function of ecosystem MCQs with answers
Question 4. A biome is
- Sum Of Ecosystems In A Geographical Area
- Sum Of All Ecosystems On The Earth
- Biotic Component In A Population
- Biotic component in an ecosystem
Answer: 1. Sum Of Ecosystems In A Geographical Area
A biome is a sum of ecosystems in a geographical area. It can also be defined as ‘biotic community of geographical extent characterised by distinctiveness in the life forms of important climax (final stage) species.
Question 5. Biotic community is the assemblage of populations of
- Same Species Which Live In Particular Area
- Different Species Which Live In Particular Area
- Different Species Which Live In Different Area
- Same species which live in different area
Answer: 2. Different Species Which Live In Particular Area
Biotic community is also called biological community. It is an association of different species of plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc., living in a particular geographical area with interaction among themselves.
Question 6. An ecosystem is
- Different Communities Of Plants, Animals And Microbes Interact Together With Their Physico-Chemical Environments
- Different Communities Of Plants And Microbes Interact With Their Physico-Chemical Environments
- A Localised Assemblage Of Several Plants And Animals
- An assemblage of plants, animals and their surroundings
Answer: 1. Different Communities Of Plants, Animals And Microbes Interact Together With Their Physico-Chemical Environments
An ecosystem may be defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere, comprising living organisms (i.e. plants, animals and microbes) and their non-living environment that interact by means of food chains and chemical cycles. It result in energy flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form a stable, self-supporting system.
Ecosystem productivity and decomposition multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 7. The living organisms of all ecosystems collectively constitute
- Producers
- Decomposers
- Consumers
- Biosphere
Answer: 4. Biosphere
The biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms (biota) and the abiotic (non-living) factors from which they derive energy and nutrients.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 8. Study the following columns and choose the correct option.

Codes:
- 3 2 1 4
- 5 2 3 4
- 2 3 5 1
- 3 2 4 1
Answer: 4. 3 2 4 1
Important ecosystem structure and function questions for NEET Biology
Question 9. The two components of an ecosystem are
- Plants And Animals
- Weeds And Trees, Animals And Man
- Energy Flow And Mineral Cycling
- Biotic and abiotic
Answer: 4. Biotic and abiotic
The components of an ecosystem may be divided into two main types, i.e. biotic component comprising the various kinds of living organisms and abiotic component consisting of environmental factors.
“questions for ecology “
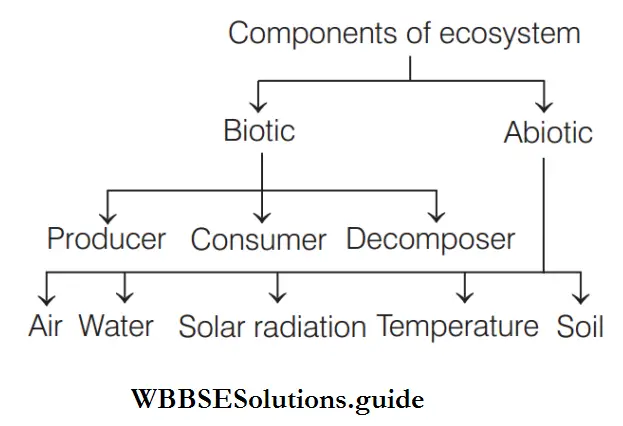
Question 10. Abiotic components refer to
- Non-Living And Physico-Chemical Factors
- Living And Physico-Chemical Factors
- Gases Produced By Industries
- Organisms present in water bodies
Answer: 1. Non-Living And Physico-Chemical Factors
Abiotic components includes the non-living and physico-chemical factors of the environment. These components not only affect the
distribution and structure of organisms, but also their behaviour and inter-relationships. Abiotic factors include inorganic substances, organic compounds, climatic factors and edaphic factors.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. Biotic components are
- Organic Waste
- Nutrient-Deficient Soil
- Living Organisms
- Fossil fuels
Answer: 3. Living Organisms
Biotic component comprises the various kinds of living organisms in an ecosystem.
Question 12. The term ecosystem was coined by
- EP Odum
- AG Tansley
- E Haeckel
- E Warming
Answer: 2. AG Tansley
The term ‘ecosystem’ was introduced by AG Tansley in 1935 to describe the whole complex of living organisms, living together as sociological units in their habitats.
Question 13. The ecosystem consists of Manipal
- Producers
- Decomposers
- Consumers
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
An ecosystem is made up of two types of components, biotic and abiotic. Biotic components of ecosystem further include producer, consumer and decomposer.
Question 14. An ecosystem resists change because it is in a state of
- Homeostasis
- Regular Illumination
- Static Imbalance
- Food accumulation
Answer: 1. Homeostasis
The state of equilibrium in an ecosystem is called homeostasis. Every ecosystem is characterised by possessing an inherent property that it resists to any sort of change in its constitution and physical environment.
ecosystems questions and answers
Question 15. The major functions of an ecosystem include
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Energy flow
- Nutrient flow
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Major functions of an ecosystem includes productivity, decomposition, energy flow and nutrient cycling (flow).
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 16. Among the following, what happens in abiotic components of an ecosystem?
- Flow of energy
- Cycling of materials
- Consumer
- Flow of energy and cycling of material
Answer: 2. Cycling of materials
Abiotic components of ecosystem include sunlight, temperature, moisture, wind or water currents, soil, etc. Among these components, cycling of essential materials like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc., occurs, so as to release these minerals back to environment.
Question 17. An aquatic ecosystem consists of
- Biotic Factors
- Biotic And Abiotic Factors
- Consumers Only
- Producers only
Answer: 2. Biotic And Abiotic Factors
An aquatic ecosystem consists of both biotic and abiotic factors. It includes phytoplankton, fishes, aquatic plants, water, etc.
Question 18. Which of the following is not a biotic component?
- Phytoplankton
- Herbivores
- Light
- Bacteria
Answer: 3. Light
Light is an abiotic component of an ecosystem. Rest others are biotic components of ecosystem.
Question 19. In an ecosystem, which of the following are important components?
- Energy flow and food chain
- Mineral recycling and energy flow
- Food chain and decomposers
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the given options are important components of an ecosystem.
Question 20. Match the following columns.

Answer: 2. 4 3 1 2
“ecosystem question answer “
Question 21. The animal species controlling the ecosystem functioning is known as
- Edge Species Wb Jee 2015
- Pioneer Species
- Keystone Species
- Umbrella species
Answer: 3. Keystone Species
Keystone species are those species which have significant and disproportionately large influence on the community structure and characteristics. It often has considerably low abundance and biomass as compared to dominant species. Removal of such species causes serious disruption in structure and function of community. Thus, it controls ecosystem functioning.
Question 22. A pond is a
- Biome
- Natural Ecosystem
- Artificial Ecosystem
- Community of plants and animals
Answer: 2. Natural Ecosystem
Natural ecosystems may be terrestrial (such as a desert, forest or
meadow) or aquatic (a pond, river or lake). A natural ecosystem is a biological environment that is found in nature (e.g. a forest) rather than created or altered by man (a farm)
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 23. A natural ecosystem
- Depends On Man
- Depends On Plants
- Depends On Animals
- Is auto-operated
Answer: 4. Is auto-operated
A natural ecosystem is auto-operated because plants and animals, both balance their activities in mutual manner.
Question 24. Artificial ecosystem is
- Man-Made And Stable
- Man-Made And Unstable
- Long Last And Do Not Require Maintenance
- Without minerals
Answer: 2. Man-Made And Unstable
An artificial ecosystem is a manmade system of plants, animals and people living in an area together with their surroundings. It is also unstable due to various activities occurring within the system
Question 25. The man-made ecosystem is
- Highly Efficient And Unstable
- Highly Efficient And Stable
- Inefficient And Unstable
- Inefficient and stable
Answer: 1. Highly Efficient And Unstable
Man-made ecosystems are made for economic benefits, thus are highly efficient. They are unstable because they are mostly monocultures and have very less diversity
Solved MCQs on ecosystem components and productivity for NEET
Question 26. Which of the following can be considered an ecosystem?
- Coral reef
- Lagoon
- Pond
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The ecosystem is a self-sufficient and self-regulating segment of nature comprising of a biotic community and its physical environment, both interacting and exchanging materials, e.g. pond, lagoon, coral reef, etc.
Question 27. Most stable ecosystem is
- Ocean
- Forest
- Desert
- Mountain
Answer: 1. Ocean
The oceans form the most stable ecosystem. They are stable in their chemical composition due to salinity and other features like, dissolved oxygen, light, temperature also remain more or less constant.
Question 28. Largest ecosystem of the world is
- Grassland
- Great Lake
- Ocean
- Forest
Answer: 3. Ocean
Oceans have the largest flora and fauna, hence represent largest ecosystem of the world.
Question 29. Aquatic ecosystem occupies how much area?
- 75%
- 90%
- 10%
- 30%
Answer: 1. 75%
About 75% of earth surface is covered by water, where 97% of water is salt water, 2% of water is from glaciers and only 1% of water is available as freshwater.
“ecological pyramid of grassland ecosystem “
Question 30. Which of the following is an example of man-made ecosystem?
- Herbarium
- Aquarium
- Tissue culture
- Forest
Answer: 2. Aquarium
An anthropogenic, artificial or man-made ecosystem is the one which is created and maintained by human beings, e.g. crop fields, garden, aquarium, etc.
Question 31. A man-made ecosystem is
- Less In Diversity
- More In Diversity
- Man Does Not Make Ecosystem
- More stable than natural ecosystem
Answer: 1. Less In Diversity
Man-made ecosystems are made for economic benefits, thus are highly efficient. They are unstable because they are mostly mono cultures and have very less diversity.
Question 32. Which of the following is an artificial ecosystem?
- Rice-field
- Forest
- Grassland
- Lake
Answer: 1. Rice-field
Artificial ecosystem is a man-made ecosystem, e.g. rice-field, orchard
Question 33. In a comparative study of grassland ecosystem and pond ecosystem, it may be observed that
- The Biotic Components Are Almost Similar
- The Abiotic Components Are Almost Similar
- Primary and secondary consumers are similar
- Both biotic and abiotic components are different
Answer: 2. The Abiotic Components Are Almost Similar
According to Odum (1983), the ecosystem has six components, in which abiotic components are almost similar in every ecosystem.
1. Abiotic components:
- Inorganic substances C, N, S, K, CO2, HO2, temperature, humidity, soil, light, pressure, etc.
- Organic substances Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, etc.
2. Biotic components Producers, macro consumers, micro consumers:
Thus, in grassland and pond ecosystems, the abiotic components are almost similar
Question 34. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true about the ecosystem?
- The term ‘ecosystem’ was coined by Sir AG Tansley
- The size of the ecosystem varies from a small pond to a large forest or sea
- In a forest ecosystem, trees, shrubs, herbs, and grasses occupy various vertical strata
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given statements are true about the ecosystem.
Question 35. …………………. refers to species being distributed in an ecosystem wherein each species occupies a different level of the ecosystem. It occurs as a result of succession.
- Stratification
- Decomposition
- Fragmentation
- Humification
Answer: 1. Stratification
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification, e.g. in a forest ecosystem, trees occupy top vertical strata or layer, shrubs occupy second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers.
Question 36. Stratification on land is more prominent in
- Tropical Rainforest
- Desert
- Temperate Forest
- Savannah
Answer: 1. Tropical Rainforest
Stratification on land is more prominently seen in tropical rainforest. It occurs vertically and determined by height of organisms. For example, in a forest community, stratification takes place when trees of different species grow to different heights
Question 37. In a forest community, stratification takes place when
- Density And Distribution Of Species Vary Along A Horizontal Gradient
- Physiognomy Or External Appearance Of A Community Remains Constant Due To Dominant Species
- Trees Of Different Species Grow To Different Heights
- Trees of different species grow with same height
Answer: 1. Density And Distribution Of Species Vary Along A Horizontal Gradient
Stratification on land is more prominently seen in tropical rainforest. It occurs vertically and determined by height of organisms. For example, in a forest community, stratification takes place when trees of different species grow to different heights
Question 38. The horizontal distribution of trees is studied in
- Scarification
- Stratification
- Zonation
- Speciation
Answer: 3. Zonation
Zonation refers to the horizontal segregation of organisms in a community. Other options are explained as Stratification refers to vertical layering of a habitat. Scarification involves weakening, opening or altering the coat of a seed to encourage the germination. Speciation is the evolutionary process through which a species evolve into distinct species.
Question 39. Which one of the following is a characteristic feature of cropland ecosystem?
- Absence of soil organisms
- Least genetic diversity
- Absence of weeds
- Ecological succession
Answer: 2. Least genetic diversity
Cropland ecosystem is a manmade ecosystem. It mostly has same type of crop plants, so it has the least genetic diversity
Question 40. The Great Barrier Reef along the East coast of Australia can be categorised as
- Population
- Community
- Ecosystem
- Biome
Answer: 3. Ecosystem
The Great Barrier Reef is a thriving, aquatic ecosystem that covers a length of 2300 kilometres of sea bed off the coast of Queensland, Australia. Though vast and intriguing, the reef is suffering great loss of life as a result of climate change, pollution, overfishing and general disregard
Question 41. One of the following is a true micro ecosystem.
- One liter of water from a pond kept in an air-tight flask
- One liter of tap water in a flask covered over by a cotton plug
- Ten liter of boiled pond water covered over by a lid
- One liter of pond water closed with a cork having gas exchange tube
Answer: 4. One litre of pond water closed with a cork having gas exchange tube
Microecosystems can exist in locations which are precisely defined by critical environmental factors within small or tiny spaces. One litre of pond water closed with cork but having gaseous exchange is a micro ecosystem.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 42. The ecosystem of a pond is referred as
- Lotic
- Xeric
- Lentic
- Benthic
Answer: 3. Lentic
The ecosystem of pond is referred as lentic or standing water type of ecosystem. Other options are explained as Lotic means moving water. Xeric refers to the dry place or desert ecosystem and benthic means the bottom water ecosystem.
Question 43. In a pond ecosystem, benthos means
- Epineuston
- Periphyton
- Zooplankton On The Water Surface
- Primary consumers in the depth of the pond
Answer: 4. Primary consumers in the depth of the pond
In a pond ecosystem, benthos are bottom-dwelling animals that crawl over, buried into or remain attached to the bottoms of the pond. These are primary consumer present in the depth of the pond.
Question 44. Bottom dwellers where no light occurs is found in
- Benthic Zone
- Abyssal Zone
- Pelagic Zone
- Lotic zone
Answer: 2. Pelagic Zone
The benthic zone begins from shore to continental shelf. The deep sea floor where light does not reach is called the abyssal zone. Bottom dwellers are found in this zone.
Question 45. Phytoplanktons are dominant in which of the following zone?
- Limnetic zone
- Profundal zone
- Littoral zone
- Benthic zone
Answer: 1. Limnetic zone
The limnetic zone has a dominant phytoplankton population. These include algae, green flagellates, euglenoids and dinoflagellates.
Role of decomposers in ecosystem NEET MCQs with answers
Question 46. Types of benthic animals in an aquatic environment is determined by
- Type Of Water
- Type Of Sediment Characteristics
- Light availability
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Type Of Sediment Characteristics
Benthic organisms are attached or rest on the bottom sediments. Their diversity and distribution is determined by type of sediment characteristics like rocky or soil surface.
Question 47. Which region of the open sea is devoid of producers?
- Aphotic
- Photic
- Abyssal
- Euphotic
Answer: 3. Abyssal
The abyssal zone is below 2000 m of perpetual darkness. It is devoid of producers.
Question 48. The free-floating organisms in open sea and the shore are collectively called
- Planktons
- Nektons
- Sea Anemone
- Benthic
Answer: 1. Planktons
Planktons are organisms living in the surface layers of the aquatic habitat which float or drift passively along with the water currents either due to the absence of locomotory organs or presence of weak locomotory organs. Planktons are of two types, i.e. phytoplankton (photosynthetic plankton) and zooplankton (phagotrophic plankton). So, the free-floating organisms in open sea and the shore are collectively called planktons.
Question 49. The essential components of the ecosystem, without which ecosystems cannot function, are
- Consumer Organisms Amu 1995
- Secondary Consumer Organisms
- Sunlight, Green Plants
- Decomposer organisms
Answer: 3. Sunlight, Green Plants
Sunlight and green plants are the two essential components of an ecosystem without which the ecosystem cannot function.
Question 50. Autotrophs
- Prepare Their Own Food
- Are The Base Of The Food Chain
- Are Primary Producers
- All of the above
AnswEcosystem Match the following columns 1er: 4. All of the above
Autotrophs are green plants. These are the primary producers of all food chain. Thus, they occupy the base of the ecological pyramid. They can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 51. Which of the following is an ecological energy source?
- Air
- Water
- Soil
- Sunlight
Answer: 4. Sunlight
The sunlight is the major source of energy for organisms and ecosystems.
Question 52. Study the diagram carefully and fill in the blanks.
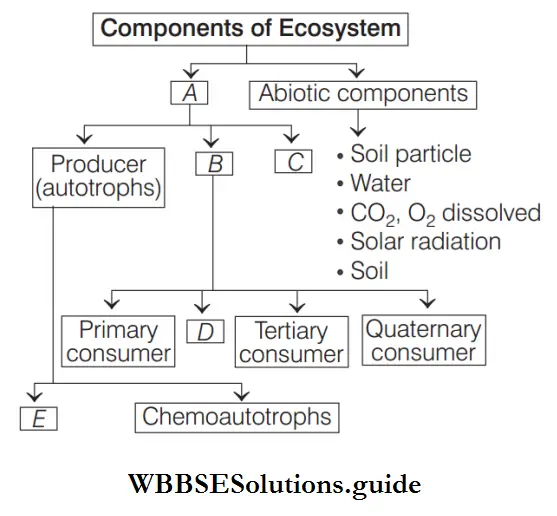
Choose the correct option for A, B, C, D, and E:
- A–Biotic components, B–Consumer, C–Decomposers, D–Secondary consumer, E–Photoautotrophs
- A–Physical components, B–Herbivore, C–Phytoplanktons, D–Plants, E–Parasites
- A–Biotic components, B–Consumer, C–Decomposers, D–Autotrophs, E–Mixotrophs
- A–Physical components, B–Consumer, C–Bacteria and fungi, D–Autotrophs, E–Secondary consumer
Answer: 1. A–Biotic components, B–Consumer, C–Decomposers, D–Secondary consumer, E–Photoautotrophs
Question 53. Consider the following statements.
- Producers are also called as transducers because they are able to change radiant energy into chemical form.
- Consumers are animals, which feed on other organisms or their parts.
- Decomposers are saprotrophs, which feed on dead bodies of organisms.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 1, 2 and 3
All given statements are correct.
Question 54. Which of the following is absolutely essential for the functioning of the ecosystem?
- Only producers
- Producers and herbivores
- Producers and detritivores
- Only detritivores
Answer: 3. Producers and detritivores
Producers can fix light energy and make use of simple inorganic substances to manufacture complex organic food materials. They convert solar radiation into chemical energy. Detritivores feed on and break down dead plants or animals matter and return essential nutrients back to the ecosystem, e.g. fungi, bacteria, etc. Thus, both producers and decomposers (detritivores) are absolutely necessary for the ecosystem.
Question 55. Green plants and green sulphur bacteria, which prepare food themselves with the help of sunlight, are known as
- Chemoautotrophs
- Photoautotrophs
- Heterotrophs
- Oligotrophs
Answer: 2. Photoautotrophs
Photoautotrophs are green plants, some protists such as Euglena and certain bacteria, such as green sulphur bacteria. With the help of their chlorophyll, they entrap light energy from the sun and convert it into the chemical energy in the form of a simple carbohydrate, which is produced by them from simple inorganic compounds, namely carbon dioxide and water. This process is called photosynthesis.
Question 56. In a grassland ecosystem, the largest population is of
- Producers
- Primary Consumers
- Only Grass
- Herbivores
Answer: 1. Producers
A grassland is a place where plenty of grass grows. These are the producers of an ecosystem. Therefore, we can say in any grasslandecosystem, the largest population is of producers.
Question 57. Man is a
- Producer
- Herbivore
- Consumer
- Decomposer
Answer: 3. Consumer
Consumers are animals, which ingest other organisms or their particulate organic matter as they are heterotrophic in nature, e.g. man.
Question 58. In a freshwater environment like pond, rooted autotrophs.
- Nymphaea and Typha
- Ceratophyllum and Utricularia
- Wolffia and Pistia
- Azolla and Lemna
Answer: 1. Nymphaea and Typha
Nymphaea is a rooted hydrophyte with floating leaves and Typha is rooted emergent hydrophyte in freshwater environment like pond. Whereas Azolla, Wolffia, Pistia are free floating plants. Ceratophyllum is a submerged plant.
Question 59. The organisms which physically and chemically break the complex dead organic remains are known as
- Scavengers
- Decomposers
- Both And
- Parasites
Answer: 2. Decomposers
Decomposers (saprotrophs) are the organisms that breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances and in doing so, they carryout the natural process of decomposition.
Question 60. Plant decomposers are CBSE AIPMT
- Monera and Fungi
- Fungi and plants
- Protista and Animalia
- Animalia and Monera
Answer: 1. Monera and Fungi
Microorganisms (bacteria belonging to Monera and Fungi) are decomposers of the ecosystem. They feed upon dead decaying living organisms (both plant and animals) and break them into simpler compounds. These are released free in the atmosphere and are utilised by producers during the synthesis of food materials.
Best multiple choice questions on ecosystem structure and decomposition for NEET preparation
Question 61. Most animals that live in deep oceanic waters are
- Tertiary Consumers
- Detritivores
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary consumers
Answer: 2. Detritivores
Benthos is the community of organisms which live on, in or near the sea bed, also known as the benthic zone.
As no light is available at this zone of sea, the energy source for deep benthic ecosystems is often organic matter from higher up in the water column which drifts down to the depths.
This dead and decaying matter sustains the benthic organisms, and therefore, most organisms in benthic zone, i.e. in deep oceanic waters, are scavengers or detritivores.
Question 62. They are nature’s cleaners.
- Producers
- Consumers
- Symbionts
- Decomposers and scavengers
Answer: 4. Decomposers and scavengers
Scavengers are organisms that consume remains of other dead organisms or their waste products. The scavenger’s role in the ecosystem is to prepare bodies for decomposition.
They open up the bodies so that others can share the food. Scavengers include animals, e.g. crow, vulture, hyena, lion, etc. Decomposers are organisms that transform the bodies of both plants and animals back into the basic constituents they were made from.
Decomposers are mostly bacteria and fungi. Hence, decomposers and scavengers are nature’s cleaners.
Question 63. Osmotrophs are
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Top Carnivores
- Decomposers
Answer: 4. Decomposers
Osmotrophs are also called decomposers.
Question 64. If the decomposers from an ecosystem go on strike from functioning as decomposers, the functioning of ecosystem will be adversely affected because
- Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Will Be Blocked
- Cycling Of Mineral And Material Will Be Stopped
- Both 1 And 2
- Adversely Affected For A Short Period And Then Function Normally
Answer: 2. Cycling Of Mineral And Material Will Be Stopped
Decomposers decompose the waste organic matter and release energy back in the environment. They recycle various minerals between the environment and living organisms. Hence, if the decomposers from an ecosystem go on strike from functioning, the ecosystem functioning will be adversely affected because cycling of mineral and material will be stopped.
Question 65. The amount of organic matter (biomass) accumulated at any trophic level in unit time is called
- Structure Of An Ecosystem
- Function Of An Ecosystem
- Spatial Pattern Of An Ecosystem
- Productivity of an ecosystem
Answer: 4. Productivity of an ecosystem
In ecology, productivity refers to the rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystem. It is usually expressed in units of mass per unit surface (or volume) per unit time.
Question 66. Fill up the blanks.
- …A… and …B… of an ecosystem comprise of living and non-living components.
- The term ‘ecosystem’ was coined by …C… .
- The interaction of structural and functional attributes of a community and their environment is called …D….
- The rate of biomass production is called …E….
Choose the correct option:
- A–Physical, B–chemical, C–Charles Elton, D–biotic environment, E–food chain
- A–Biotic, B–abiotic, C–Tansley, D–ecosystem, E–productivity
- A–Autotrophic, B–heterotrophic, C–Mobius, D–abiotic environment, E–food web
- A–Producer, B–decomposer, C–Hult, D–ecosystem, E–ecological pyramid
Answer: 2. A–Biotic, B–abiotic, C–Tansley, D–ecosystem, E–productivity
Question 67. Primary productivity is
- The Rate Of Formation Of New Organic Matter By Consumers
- The Rate Of Conversion Of Light Into Chemical Energy In An Ecosystem
- The rate of energy production per unit area over a time period during photosynthesis
- None of the above
Answer: 2. The Rate Of Conversion Of Light Into Chemical Energy In An Ecosystem
Primary Productivity (PP) is defined as the rate at which radiant
energy or light is converted by the photosynthetic and chemosynthetic autotrophs to organic substances or chemical energy.
Question 68. Productivity is the rate of production of biomass expressed in terms of
- (kcal m) −3 yr−1
- g −2 yr −1
- g −1 yr−2
- (kcal m−2) yr−1
Choose the correct option:
- Only 2
- Only 3
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 4
The rate of biomass production per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called productivity. It is expressed in g −2 yr−1 or (kcal m−2) yr-1 .
Question 69. The sunlight directly affects primary productivity as
- Gross Primary Productivity Is Utilised By Plants In Respiration
- The Plants Perform Respiration With The Help Of Sunlight
- The plants perform photosynthesis with the help of sunlight
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 3. The plants perform photosynthesis with the help of sunlight
The sunlight directly regulates the primary productivity because the plants perform photosynthesis with the help of sunlight. The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period in plants during photosynthesis is called primary production.
Question 70. Primary productivity is affected by
- Temperature
- Sunlight
- Moisture
- Availability of nutrients
Choose the option containing correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Factors affecting primary productivity are as follows
1. Plant species inhabiting a particular area or habitat.
2. Environmental factors including
- Sunlight directly regulates the primary productivity because the plants perform photosynthesis with the help of sunlight. As trophic region receives maximum sunlight, so it exhibits higher productivity.
- Temperature regulates the activity of enzyme. So, optimum temperature is required for proper functioning of enzymes.
- Moisture, rain or humidity is required for higher primary productivity.
- Deserts have the lowest primary productivity as the soil is deficient in moisture. Greater availability of nutrients ensures the greater primary productivity.
Question 71. Primary productivity depends upon
- Availability Of Nutrients
- Photosynthetic capacity of plants
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period in plants during photosynthesis is called primary production. Primary productivity depends upon photosynthetic capacity of plants and nutrient availability.
Question 72. Assertion Primary productivity is contributed by green plants. Reason (R) Primary productivity is shown by chemosynthesisers.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Green plants trap the light from the sun and converts the photo-chemical energy into food and are considered as major contributor to primary productivity. Chemosynthesisers also contribute to primary productivity by converting carbon dioxide into organic food molecules.
Question 73. Primary productivity is
- 10% less than secondary productivity.
- The rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
- Expressed in terms of weight or energy.
- The amount of biomass produced per unit area in a time period by plants during photosynthesis.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
Answer: 3. 3 and 4
Statements 3 and 4 are correct, but 1 and 2 are incorrect. The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants or autotrophs during photosynthesis is called primary production. It is expressed in the terms of weight (g −2) or energy (kcal m−2). It is more than secondary productivity.
Question 74. Primary productivity can be measured by
- Harvest Method
- Chlorophyll Content
- Oxygen given out
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Primary productivity can be measured from the amount of oxygen consumed by a volume of water in afixed period of time. This oxygen production indicates net primary productivity only. Primary production can also be measured by determining the amount of functional chlorophyll present in leaves. Chlorophyll is extracted with acetone and determined spectrophotometrically or fluorometrically. Harvest method measures the productivity of a water body, such as of fish pond by harvest at the end of the season.
Question 75. Which most often limits the primary productivity of the ecosystem?
- Solar radiation/light
- Oxygen
- Consumers
- Nitrogen
Answer: 1. Solar radiation/light
Light limits the primary productivity of an ecosystem. The primary production is regulated by factors such as light, temperature, herbivory and the supply of water and nutrients.
Question 76. Which atom is limiting the primary productivity mostly?
- C
- P
- O
- N
Answer: 1. C
Limiting factor is that factor which directly affect a process if its quantity is changed. Since, carbon is one of the main component of photosynthetic process, the primary productivity is mostly affected by amount of carbon.
NEET Biology energy flow and productivity in ecosystem MCQs
Question 77. Higher primary productivity requires higher …A… . …B… has the lowest primary productivity as the soil is deficient in moisture.
Choose the correct option for A and B.
- A–rainfall, B–Desert
- A–heat, B–Forest
- A–snowfall, B–Desert
- A–humidity, B–Rainforest
Answer: 1. A–rainfall, B–Desert
Question 78. Maximum primary productivity of pond is achieved by Manipal
- Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton
- Floating Plants
- Red algae
Answer: 1. Phytoplankton
Highest primary productivity of pond is achieved by phytoplankton.
Question 79. Which of the following ecosystem has very little primary productivity?
- Forest
- River
- Sea
- Grassland
Answer: 3. Sea
Primary productivity is lowest in deserts, the tundra, ocean or sea, lakes and stream biomes.
Question 80. One of the following ecosystems has the highest primary productivity.
- Pond ecosystem
- Lake ecosystem
- Grassland ecosystem
- Forest ecosystem
Answer: 4. Forest ecosystem
The highest net primary productivity in terrestrial environments occurs in swamps or marshes and tropical rainforest ecosystem.
Question 81. Which of the following is the most productive ecosystem?
- Rice
- Wheat
- Maize
- Sugarcane
Answer: 4. Sugarcane
In an ecosystem, the productivity is the rate of generation of biomass in the given ecosystem in a given time. Sugarcane is the most productive agroecosystem.
Question 82. Which of the following aquatic ecosystems has the maximum primary productivity?
- Ocean
- Estuary
- River
- Pond
Answer: 2. Estuary
Estuary has the maximum primary productivity due to rapid circulation of nutrients, quick removal of wasteproducts and year round succession of organisms.
Question 83. Estuaries are considered as nutrient trap due to the mixing of
- River And Sea Water
- Pond And Lake
- Lake And River
- Ocean and pond
Answer: 1. River And Sea Water
An estuary is the place where a river meets the sea. The mixing up of sea and freshwater produces turbulence. In a tidal estuary, there is low vertical turbulence, but high horizontal turbulence.
Question 84. Secondary productivity is
- The rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers
- Greater than primary productivity
- 5% less than primary productivity
- Equal to the gross primary productivity
Answer: 1. The rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers
The rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers is called secondary productivity.
Question 85. Total energy fixed by an ecosystem is known as its
- Primary Production
- Gross Production
- Net Production
- Secondary production
Answer: 2. Gross Production
Total energy fixed by an ecosystem is called gross production.
Question 86. The rate at which organic compounds are formed in a green plant or in a population of green plants per unit time and area is known as the
- Net Primary Productivity
- Gross Primary Productivity
- Biomass Productivity
- Cellular productivity
Answer: 2. Gross Primary Productivity
The rate at which organic compounds are formed in green plants or in a population of green plants per unit time and area is known as the gross primary productivity. It is usually measured as an increase in stored energy or an increase in biomass.
Question 87. Energy obtained during gross primary productivity is utilized by …A… in …B….
- A–plants, B–photosynthesis
- A–plants, B–respiration
- A–animal, B–respiration
- A–animal, B–digestion
Answer: 2. A–plants, B–respiration
Gross primary productivity is utilised by plants in respiration (2).
Question 88. The total energy stored by photosynthetic plants is
- NPP
- Secondary productivity
- GPP
- Community productivity
Answer: 3. GPP
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) is the total energy stored in the food materials synthesized by the green plants or total rate of photosynthesis including the organic matter used up in the respiration during total photosynthesis or total assimilation.
Question 89. The rate at which light energy is converted to the chemical energy of organic molecules in the ecosystem’s CBSE AIPMT
- Net Primary Productivity
- Gross Primary Productivity
- Net Secondary Productivity
- Gross secondary productivity
Answer: 2. Gross Primary Productivity
The rate at which light energy is converted to the chemical energy of organic molecules in the ecosystem is called gross primary productivity.
Question 90. Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m 2/yr) in a grassland ecosystem?
- Secondary production
- Tertiary production
- Gross Production (GP)
- Net Production (NP)
Answer: 3. Gross Production (GP)
Productivity at the producer’s level is known as primary productivity. Gross primary productivity is primary productivity including the amount which is utilised in respiration and other metabolic activities. Since, gross production includes total production it is more than other forms of productivity.
Question 91. The biomass available for consumption by herbivores and the decomposers is called
- Net Primary Productivity
- Secondary Productivity
- Standing Crop
- Gross primary productivity
Answer: 1. Net Primary Productivity
The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and decomposers is called net primary productivity. It is equal to the rate of organic matter created by photosynthesis minus the rate of respiration and other losses.
Question 92. ……………… obtain the net primary productivity.
- Autotrophs
- Decomposers
- Heterotrophs
- All of these
Answer: 3. Heterotrophs
The amount of organic matter produced by the autotrophs that is not used by them and is available for consumption by heterotrophs represents the net primary production.
Question 93. Net primary productivity
- Part Of Total Energy Stored By Producers
- Energy Produced By Producers
- Energy Stored By Primary Consumers
- Energy received by primary consumers
Answer: 4. Energy received by primary consumers
Net primary productivity represents food potentially available to primary consumers and decomposers. i.e. Net primary productivity = Gross productivity – Respiration and other losses.
Question 94. The net primary productivity of an ecosystem is
- Total Weight Of Green Plants – Respiratory Losses
- Total Weight Of Green Plants + Respiratory Losses
- Respiratory Losses Alone
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
Net primary productivity represents food potentially available to primary consumers and decomposers. i.e. Net primary productivity = Gross productivity – Respiration and other losses.
Question 95. Which one of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity?
- Tropical deciduous forest
- Temperate evergreen forest
- Temperate deciduous forest
- Tropical rainforest
Answer: 4. Tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are found in the equatorial regions where rainfall exceeds 140 cm. The warm humid climate supports broad leaved evergreen plants. Thus, they possess highest annual net primary productivity.
Question 96. Which ecosystem has the highest gross primary productivity?
- Deserts
- Coral reefs
- Mangroves
- Grasslands
Answer: 2. Coral reefs
Gross primary productivity is maximum in the coral reefs because of large number of aquatic phototrophs and abundant nutrients.
Question 97. In relation to gross primary productivity and net primary productivity of an ecosystem, which one of the following statements is correct?
- Gross primary productivity is always more than net primary productivity
- Gross primary productivity and net primary productivity are one and same
- There is no relationship between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity
- Gross primary productivity is always less than net primary productivity
Answer: 1. Gross primary productivity is always more than net primary productivity
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Net primary productivity is GPP–respiration losses. Hence, gross primary productivity is always more than Net Primary Productivity (NPP).
Question 98. Which ecosystem has the maximum biomass?
- Forest ecosystem
- Grassland ecosystem
- Pond ecosystem
- Lake ecosystem
Answer: 1. Forest ecosystem
A forest ecosystem shows highest amount of biomass. The number of organisms occupying each trophic level in a forest ecosystem is much high than other ecosystems. The order of biomass productions is
- Tropical rainforest
- Coral reef
- Estuaries
- Sugarcane fields
Question 99. The rate of biomass production and the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis are called, respectively.
- Total Productivity, Primary Production
- Gross Primary Productivity, Gross Secondary Productivity
- Net Primary Productivity, Secondary Productivity
- Net Productivity, Gross Secondary Productivity
- Productivity, gross primary productivity
Answer: 5. Productivity, gross primary productivity
The productivity of an ecosystem refers to the rate of biomass production, i.e. the amount of organic matter accumulated by any trophic level per unit area in unit time. Gross primary productivity is the total organic matter synthesised by the producers in the process of photosynthesis per unit time and area.
Question 100. The biomass available for consumption to heterotrophs and the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers are defined as
- Gross Primary Productivity And Net Primary Productivity, Respectively
- Net Primary Productivity And Gross Primary Productivity, Respectively
- Gross Primary Productivity And Secondary Productivity, Respectively
- Net Primary Productivity And Secondary Productivity, Respectively
- Secondary productivity and net primary productivity, respectively
Answer: 4. Net Primary Productivity And Secondary Productivity, Respectively
Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs (herbivores and decomposers). Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question 101. Consider the following statements.
- Primary production is expressed in term of weight (g −2) or energy (kcal/m2/yr).
- Sugarcane have more efficiency to trap sunlight, so they accumulate more primary productivity.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 102. Select the formula for ecological efficiency.
- \(\frac{Gross primary productivity}{Incident total solar radiation}\) × 100
- \(\frac{Food energy assimilated}{Food energy ingested}\) × 100
- \(\frac{Net primary productivity}{Gross primary productivity}\) × 100
- \(\frac{Energy in biomass at a trophic level}{Energy in biomass production at previous topic level}\) × 100
Answer: 4. latex]\frac{Energy in biomass at a trophic level}{Energy in biomass production at previous tophic level} × 100
Ecological efficiency or trophic level efficiency rfers to the percentage of energy converted into biomass by a higher trophic level over the energy of food resources available at the lower trophic level. The formula is as follows Ecological efficiency
= \(\frac{Energy in biomass at a trophic level}{Energy in biomass production at previous tophic level}\) × 100
Question 103. Which of the following statements about productivity is true?
- Primary productivity of all ecosystems is a constant
- The annual net primary productivity of the whole of the biosphere is 7 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter
- Net primary productivity is the amount of biomass available for consumption by carnivores
- Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by decomposers
- Primary productivity depends on the plant species inhabiting a particular area
Answer: 5. Primary productivity depends on the plant species inhabiting a particular area
- Primary productivity is the rate of biomass production per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis and it is expressed as.
- It depends on the photosynthetic efficiency of the plant species inhabiting a particular area. Other statements are not true and can be corrected as
- Primary productivity of all ecosystems varies depending upon the number of producers in an ecosystem.
- The annual net primary productivity of whole biosphere is 17 billion tons of organic matter.
- Net primary productivity is the amount of biomass available for consumption by all consumers.
- Secondary productivity is rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
Question 104. The process of breaking down complex organic matter into simpler compounds such as CO2, water and nutrients is known as
- Humification
- Disintegration
- Decomposition
- Leaching
Answer: 3. Decomposition
Decomposition is the process of breaking down a substance into its constituent parts. Decomposition of dead organic matter (plants, animals and waste products of animals) occurs in nature and it is also called decay or putrefaction. In a terrestrial ecosystem, the upper layer of soil is the main site of decomposition.
Question 105. The important steps in the process of decomposition are AMU
- Fragmentation And Mineralisation
- Leaching And Catabolism
- Humification and mineralisation
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Decomposition is physical and chemical breakdown of complex organic remains with the help of organisms called decomposers. The decomposition processes include fragmentation of detritus, catabolism, leaching, humification and mineralisation.
Question 106. The word detritus refers to
- Dead Plant Parts
- Remains Of Animals
- Animal Excretions
- All of the abvoe
Answer: 4. All of the above
Detritus is non-living particulate organic material. It typically includes the bodies or fragments of dead organisms like plants and animals as well as faecal material.
Question 107. Detritivores are
- Animals Feeding On Plant Matter
- Animals Feeding On Dead And Decaying Organic Matter
- A Plants Feeding On An Animal
- Animals feeding on dead and decaying animals
Answer: 2. Animals Feeding On Dead And Decaying Organic Matter
Detritivores feed on and breakdown the dead plants and animal matter and thus, return essential nutrients to the ecosystem. They include microorganisms such as bacteria and protists as well as larger organisms such as fungi, insects, worms and crustaceans.
Question 108. Decomposition of organic matter is brought about by
- Protozoans
- Plants
- Microorganisms
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Microorganisms
Decomposition is physical and chemical breakdown of complex organic remains with the help of organisms called decomposers. Microorganisms including bacteria, soil mites, fungi, etc., are chief decomposers of ecosystem.
Question 109. Dried leaves, bark, flowers, etc., and remains of animals including faecal matter, present on/in the soil constitute
- Below Ground Detritus
- Above Ground Detritus
- Litter fall
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 3
Dried plant parts such as leaves bark, flower, etc., and dead remains of animals including faecal matter drop over the soil, constitute the above ground detritus and litter fall.
Question 110. The similarity between earthworm, soil mites and dung beetle.
- They all are detritivores
- They all are primary consumer
- They all are secondary consumer
- They all are tertiary consumer
Answer: 1. They all are detritivores
Detritivores are animals which feed on dead bodies of other organisms, e.g. earthworms, termites, carrion beetles. They are helpful in quick disposal of the dead bodies. So, the earthworm, soilmites and dung beetle, all are detritivores.
Question 111. Detritivores like earthworm, breakdown detritus into smaller particles. This process is called
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Humification
- Mineralisation
Answer: 1. Fragmentation
Detritivores like earthworm breakdown detritus into smaller particles. This process is called fragmentation
Question 112. Rate of decomposition is maximum in which layer of soil?
- Upper layer of soil
- Middle layer of soil
- Lower layer of soil
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Upper layer of soil
Upper layer of soil comprises of detritus, thus decomposition rate is highest here.
Question 113. Product(s) of decomposition is/are
- Humus
- Inorganic Nutrients
- Organic nutrients
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
The end result of decomposition is the production of dark brown, humus and inorganic nutrient like carbon dioxide, water, etc.
Question 114. The enzymatic process by which detritus is converted into simpler inorganic substances is referred to as
- Catabolism
- Leaching
- Mineralisation
- Anabolism
Answer: 1. Catabolism
During the process of catabolism, the extracellular enzymes released by bacteria and fungi carryout enzymatic conversion of the decomposing detritus to simpler compounds and inorganic substances.
Question 115. The degradation of humus by microbes releases inorganic nutrients and this process is called
- Leaching
- Fragmentation
- Mineralisation
- Humification
Answer: 3. Mineralisation
Mineralisation is the final step of decomposition process. It is the process of the degradation of the humus to release inorganic nutrients.
Question 116. Humus is
- Dark Coloured Amorphous Organic Matter Rich In Lignin
- Dark coloured organic matter rich in cellulose
- Both 1 and 2
- Dark coloured organic matter containing only animal remains
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Humus is dark coloured amorphous substance rich in lignin and cellulose.
Question 117. Bacteria, fungi release extracellular enzyme on detritus to carryout
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Catabolism
- Humification
Answer: 3. Catabolism
Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called catabolism
Question 118. Formation of humus by the process of decomposition is called
- Fragmentation
- Humification
- Mineralisation
- Leaching
Answer: 2. Humification
Humus is a complex organic substance resulting from the breakdown of plant material in a process called humification. This process occurs naturally in soil.
Question 119. A process in which essential water soluble inorganic nutrients are lost from the soil and get precipitated as unavailable salts is called as
- Fragmentation
- Leaching
- Photooxidation
- Mineralisation
Answer: 3. Photooxidation
By the process of leaching, water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
Question 120. What will happen if all the bacteria and fungi are destroyed?
- There will be fixation of carbon dioxide
- Amount of nitrogen in soil increases
- Dead bodies and excretions will pile up
- Soil will become rich in all nutrients
Answer: 1. There will be fixation of carbon dioxide
As decomposers are primary weapons to decompose dead organic matter, hence extinction of decomposers will severely destroy nature as the remains of plants and animals will accumulate and will not get decomposed. As a result, the soil will not get nutrients and will become infertile. So, if all the bacteria and fungi are destroyed then dead bodies and excretory products will pile up
Question 121. Higher amounts of …………………… increases rate of decomposition.
- Nitrogen And Sugar
- Phosphorus And Sugar
- Calcium And Sugar
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 1. Nitrogen And Sugar
The decomposition rate is higher when detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars.
Question 122. Which of the following factors affect decomposition?
- Chemical quality of detritus
- Temperature
- Soil moisture and pH
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Decomposition is affected by chemical quality of detritus, temperature, soil moisture and pH.
Question 123. The rate of decomposition is faster in the ecosystem due to following factors.
- Detritus Rich In Sugars
- Warm And Moist Environment
- Presence Of Aerobic Soil Microbes
- Detritus richer in lignin and chitin
Answer: 4. Detritus richer in lignin and chitin
The rate of decomposition is faster in the ecosystem if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars. The warm and moist environments also favor decomposition. But if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin, the decomposition rate gets slower.
Question 124. Excessive moisture inhibits the process of decomposition due to
- Anaerobiasis
- Aerobiosis
- Photooxidation
- Photosynthesis
Answer: 1. Anaerobiosis
Warm and moist environment favor decomposition. Low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition.
Question 125. Which one of the following processes during decomposition is correctly described?
- Humification–Leads to the accumulation of a dark colored
substance humus which undergoes microbial action at a fast rate - Catabolism–Last step decomposition under fully anaerobic condition
- Leaching–Water soluble inorganic nutrients rise to the top layers of soil
- Fragmentation–Carried out by organisms such as earthworms
Answer: 4. Fragmentation–Carried out by organisms such as earthworms
- Option correctly described the process of decomposition. Other options are incorrect and can be corrected as
- Catabolism is degradation by fungal and bacterial enzymes.
- Leaching is seeping of nutrients into the soil during decomposition.
- Humification is the formation of humus.
Question 126. The presence of the large amount of N2 in the atmosphere is due to the presence of
- Producer
- Fertilizers
- Decomposer
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Decomposer
Decomposers help to breakdown the complex organic remains into both non-mineral and mineral forms by physical and chemical processes. Decomposition helps in recycling of biogeochemicals, by which the atmosphere receives inorganic nutrients like N2, CO2, P, etc. Thus, large amount of N2 in the atmosphere is due to the presence of decomposers.
