Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Tools Of Recombinant DNA Technology
Question 1. Restriction enzyme belongs to which of the following classes of enzymes?
- Nucleases
- Transferases
- Polymerases
- Reductases
Answer: 1. Nucleases
Restriction enzymes are nucleases that split only those DNA molecules in which they recognize particular sequences.
biotechnology question bank
Question 2. Following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme restriction endonuclease. Identify the incorrect statement.
- The enzyme cuts dna molecule at an identified position within the dna
- The enzyme binds dna at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands
- The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand
- The enzyme recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the dna
Answer: 2. The enzyme binds dna at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands
- Statements in option (2) are incorrect and can be corrected as Restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognizing a specific sequence.
- Once it finds its specific recognition sequence, it binds to the DNA and cuts each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in its sugar-phosphate backbone. Rest all statements are correct.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. An enzyme catalyzing the removal of nucleotides from the ends of dna is
- Endonuclease
- Exonuclease
- Dna ligase
- Hind 2
Answer: 2. Exonuclease
An enzyme catalyzing the removal of nucleotides from the ends of DNA is exonuclease.
Question 4. During genetic engineering, restricted endonucleases are needed to
- Transform the host cell
- Ligate the foreign dna into the host dna
- Produce nicks in the host dna
- Polymerize the vector molecule
biotechnology question bank
Answer: 3. Produce nicks in the host dna
- Restriction endonucleases are a very important tool used in genetic engineering. These are the enzymes that make cuts (nicks) at specific positions within the double-stranded DNA molecule.
- They recognize the palindromic base sequence in DNA duplex and form nicks in its strands. For example, restriction endonuclease EcoRI recognizes the base sequence GAATTC in the DNA duplex and cuts the strands between G and A.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
NEET Biology tools of recombinant DNA technology MCQs with answers
Question 5. Restriction endonucleases
- Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense mechanism
- Are used for in vitro dna synthesis
- Are used in genetic engineering for the ligation of two dna molecules
- Are present in mammalian cells for the degradation of dna when the cell dies
Answer: 1. Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense mechanism
- Restriction endonucleases are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense mechanism. These are bacterial enzymes that cut double-stranded DNA.
- These enzymes were discovered from E. coli strains that appeared to be restricting the infection by certain bacteriophages.
- Restriction enzymes, therefore, are believed to be a mechanism evolved by bacteria to resist viral attack and to help in the removal of viral sequences.
Question 6. Polylinker dna is one which
- Does not code for any protein
- Has restriction sites for several enzymes
- Is used for dna transfer
- Is seen in single-stranded dna only
Answer: 2. Has restriction sites for several enzymes
A polylinker is a short DNA sequence containing two or more different sites for cleavage by restriction enzymes. Thus, option (2) is correct
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 7. The endonucleases commonly used in genetic engineering are
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Type 3
- Type 4
Answer: 2. Type 2
The endonucleases commonly used in genetic engineering are type-2. This endonuclease cuts the DNA at the site of recognition, unlike the other endonucleases which cut the DNA strand away from recognition sites.
Question 8. The first discovered restriction endonuclease that always cuts dna molecules at a particular point by recognizing a specific sequence of six base pairs is
- Eco ri
- Adenosine deaminase
- Thermostable dna polymerase
- Hind 2
Answer: 4. Hind 2
biotechnology question bank
Hind II was the first discovered endonuclease. It was isolated by Smith Wilcox and Kelley (1968) from Haemophilus influenzae bacterium. It always cuts bacterium DNA at a particular point by recognizing a specific sequence of six base pairs. It is known as the recognition sequence for Hind 2 and reads as
5 – G T C G A C- 3′ ′
3 – C A G C T G -5′ ′
Important multiple choice questions on recombinant DNA tools for NEET
Question 9. The special sequence in the dna recognized by restriction endonuclease is called
- Restriction nucleotide sequence
- Palindromic nucleotide sequence
- Recognition nucleotide sequence
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Palindromic nucleotide sequence
The special sequence in the DNA recognized by restriction endonuclease is called the palindromic nucleotide sequence.
Question 10. Select the dna sequences which would act as a restriction site.

Answer: 4. 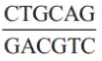
The nucleotide sequence recognized for cleavage by a restriction enzyme is called as the restriction site. Typically, a restriction site is a palindromic sequence of about four to six nucleotides long. Hence, option (4) is the correct answer.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. Given below is a sample of a portion of the DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so special shown to it?
5 ′- Gaattc – 3 ′
3 ′- Cttaag – 5 ′
- Replication completed
- Deletion mutation
- Start codon at the 5′ end
- The palindromic sequence of base pairs
Answer: 4. Palindromic sequence of base pairs
biotechnology question bank
The palindromes in DNA are base pair sequences that are the same when it is read forward (left to right) or backward (right to left) from a central axis of symmetry. The given sequences read the same in 5′ → 3′ direction and 3′ → 5′ direction.
For example
5′- GAATTC´-3′
3′- CTTAAG -5′
Question 12. Which one of the following can give a complimentary and palindromic sequence?
- 5′-Atatcc-3′
- 5′-Ccgaat-3′
- 5′-Gaattc-3′
- 5′-Aggttc-3′
Answer: 3. 5′-Gaattc-3′
The palindromes in DNA are base pair sequences that are the same when it is read forward (left to right) or backward (right to left) from a central axis of symmetry. The given sequences read the same in 5′ → 3′ direction and 3′ → 5′ direction.
For example
5′- GAATTC´-3′
3′- CTTAAG -5′
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 13. Go through the figure and select the option for c and d. Here, a and b are taken as vector/plasmid dna and foreign dna, respectively.
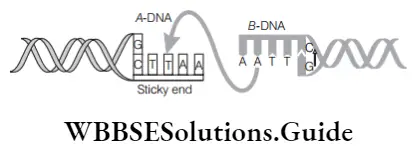
Restriction enzyme recognizing palindrome c → enzyme joining the sticky ends d
- Eco ri → dna ligase
- Dna ligase → eco ri
- Exonuclease → dna ligase
- Dna ligase → exonuclease
Answer: 1. Eco ri → dna ligase
(1) The restriction enzyme that recognizes this palindrome is EcoRI (3). The enzyme that can link these two DNA fragments–DNA ligase (4).
biotechnology question bank
Question 14. Which of the following is known as the joining enzyme or repair enzyme of dna?
- Transcriptase
- Kinase
- Ligase
- Polymerase
Answer: 3. Ligase
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single strands break in duplex DNA, in living organisms.
Solved MCQs on restriction enzymes and DNA ligase for NEET
Question 15. Ligases catalyze the formation of bonds between
- C=c
- P=o
- C-c
- H-h
Answer: 2. P=o
Ligases catalyze the formation of bonds between P==O.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 16. The specific palindromic sequence which is recognized by eco ri is
- 5 3′ ′-Ggaacc – 3′ ′-ccttgg – 5
- 5 3′ ′-Cttaag – 3′ ′-gaattc – 5
- 5 3′ ′-Ggatcc – 3′ ′-Stagg – 5
- 3′ ′-Cttaag – 5
Answer: 4. 3′ ′-Cttaag – 5
Restriction enzyme Eco RI cuts the DNA between base G and A only when the sequence in DNA is GAATTC.
Question 17. Which is not true about restriction endonuclease?
- Restriction endonuclease cuts the dna at specific points
- It used as a tool for gene cloning
- The first word of restriction endonuclease indicates the name of the scientist who isolated it
- Most restriction sites are palindromes
Answer: 3. The first word of restriction endonuclease indicates the name of the scientist who isolated it
(3) Option (3) is not true. While naming restriction endonuclease, the first letter of the enzyme indicates the genus name followed by the first two letters of the species, then the strain of the organism, and finally, a Roman numeric indicating the order of discovery. Rest options are true about restriction endonuclease
biotechnology question bank
Question 18. There is a restriction endonuclease called eco ri. What does the ‘co’ part in it stand for?
- Coelom
- Strain of bacterium
- Coli
- Colon
Answer: 3. Coli
- (3) Option (3) is not true. While naming restriction endonuclease, the first letter of the enzyme indicates the genus name followed by the first two letters of the species, then the strain of the organism, and finally, a Roman numeric indicating the order of discovery.
- Rest options are true about restriction endonuclease. The restriction enzyme derived from Escherichia coli RY13 is called Eco RI. E stands for Escherichia and co stands for coli.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 19. In eco iii, e and r stand for
- Europe and Russia
- England and Russia
- Escherichia and strain ry 13
- Escherichia and strain rough
Answer: 3. Escherichia and strain ry 13
EcoRI comes from Escherichia coli RY13. So, E and R stand for Escherichia and strain RY13, respectively.
Question 20. In hind iii, Roman number iii indicates
- 3 Types of enzymes
- Order of discovery
- Strain of bacteria
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Order of discovery
Roman numbers following the names indicate the order of discovery in which the enzymes were isolated.
Question 21. Hind ii is isolated from
- E. Coli
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Haemophilus aegyptius
- Arthrobacter luteus
Answer: 2. Haemophilus influenzae
The first restriction endonuclease Hind 2 (type 2) was isolated by Smith, Wilcox, and Kelley from Haemophilus influenzae bacterium.
biotechnology question bank
Question 22. When restriction enzymes cut the strand of dna a little away from the center of the palindrome sites between the same two bases of opposite strands, it produces
- Sticky end
- Blunt end
- Flush end
- Non-cohesive end
Answer: 1. Sticky end
When restriction enzymes cut the strands of DNA a little away from the center of the palindrome sites between the same two bases of opposite strands, it produces sticky ends. Sticky ends are also called cohesive ends. They easily form hydrogen bonds with their complementary counterparts.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 23. Eco ri cleaves the dna strands to produce
- Blunt ends
- Sticky ends
- Satellite ends
- Ori replication end
Answer: 2. Sticky ends
Eco RI is a restriction endonuclease, isolated from the bacterium Escherichia coli RY13. It cleaves DNA strands at palindromic sequence which is
5 G AATTC 3′ ↓ ′
3 CTTAA G 5′ ↑ ′
and produces sticky ends.
Question 24. Which of the following restriction enzymes produce sticky ends?
- Sal 1
- Alu 1
- Hae 3
- Hpa 1
Answer: 1. Sal 1
Sal I restriction enzyme produces sticky ends. The other restriction enzymes, Alu I, Hae 3, and Hpa I produce blunt ends.
Question 25. The sticky ends of a fragmented dna molecule are made up of
- Calcium salts
- Endonuclease
- Unpaired bases
- Methyl groups
Answer: 3. Unpaired bases
- The simplest DNA end of a double-stranded molecule is called a blunt end. In a blunt-ended molecule, both strands terminate in a base pair.
- Non-blunt ends are sticky ends that are created by various overhangs. An overhang is a stretch of unpaired nucleotide on either strand, creating either 3′ or 5′ overhangs.
biotechnology question bank
Question 26. Dna fragments with sticky ends are not allowed to undergo self-ligation by
- Unwindase
- Single-strand binding proteins
- Gyrase
- Alkaline phosphatase
Answer: 4. Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase removes 5′ phosphate groups from the vector so that it prevents self-ligation of the vector.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 27. Which of the following restriction enzymes produces blunt ends?
- Sal 1
- Eco rv
- Xho 1
- Hind 3
Answer: 2. Eco rv
Eco RV is a type 2 restriction endonuclease isolated from strains of E. coli. It creates blunt ends. The enzyme recognizes the palindromic 6-base DNA sequence and makes cuts at the vertical lines. The blunt ends are formed as shown below
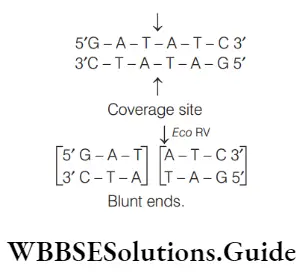
Role of vectors and plasmids in rDNA technology NEET MCQs
Question 28. Restriction endonuclease cleaves the dna molecule by hydrolyzing
- H-bonds
- Phosphodiester bonds
- Oh bonds
- Phosphate bonds
Answer: 2. Phosphodiester bonds
Restriction enzymes are the endonucleases that cleave the DNA at specific sites. These enzymes act on the phosphodiester bond, which attaches two nucleotides in the polynucleotide chain. There are specific restriction sites at which the enzymes make blunt or staggered cuts to produce the fragments of the DNA.
Question 29. The restriction enzyme(s) used in recombinant dna technology that makes staggered cuts in dna leaving sticky ends is/are
- Eco ri
- Hind 3
- Bam hi
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
In staggered cutting or cohesive end style or sticky end style cleavage, the cuts are made in two strands of DNA at two different sites, a few nucleotides away from each other, thus producing two strands with protruding ends. Enzymes Eco RI, Hind 3, Bam HI, Pst I, etc., produce sticky ends.
Question 30. Bam hi, eco ri, sma I am the types of
- Restriction end-oxidases
- Restriction endonucleases
- Restriction exonucleases
- Restriction polymerases
Answer: 2. Restriction endonucleases
The different restriction endonucleases are classified into four different restriction types, 1, 2, 3, and 4. Bam HI, Eco RI, and Sma I are examples of restriction endonucleases, which are used in genetic engineering techniques for cleavage of the desired gene and bacterial plasmid.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 31. Which of the following sequences is cleaved by hind 3?
- 5′ Aagctt 3′ 3′ ttcgaa 5′
- 5′ Gtcgac 3′ 3′ cagctg 5′
- 5′ Gatatc 3′ 3′ ctatag 5′
- 5′ Ggcc 3′ 3′ ccgg 5′
Answer: 1. 5′ Aagctt 3′ 3′ ttcgaa 5′
Hind 3 cleaves the palindromic sequence AAGCTT and produces sticky ends as shown below
5′-A↓ A G C T T-3′
3′-T T C G A ↑ A-5′
These ends can join similar complementary ends of other DNA fragments and form recombinant DNA.
Question 32. Match the following columns.
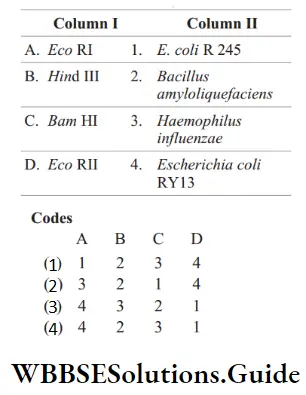
Answer: 3. A–4, B–3, C–2, D–1
Question 33. Select the correct statement from the following.
- Gel electrophoresis is used for the amplification of a dna segment
- The polymerase enzyme joins the gene of interest and the vector dna
- Restriction enzyme digestions are performed by incubating purified dna molecules with the restriction enzymes of optimum conditions
- Pcr is used for the isolation and separation of genes of interest
Answer: 3. Restriction enzyme digestions are performed by incubating purified dna molecules with the restriction enzymes of optimum conditions
(3) Statement in option (3) is correct as restriction enzyme digestions are performed by incubating purified DNA molecules with the restriction enzymes of optimum conditions. Other statements are incorrect and can be corrected as
biotechnology question bank
- Gel electrophoresis is used for separation and isolation of DNA fragments.
- The polymerase enzyme uses DNA templates to catalyze
polymerization of deoxynucleotides. - PCR is Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is used for amplification of a DNA segment.
Question 34. Identify the wrong statement with regard to restriction enzymes.
- They cut the strand of dna at palindromic sites
- They are useful in genetic engineering
- Sticky ends can be joined by using dna ligases
- Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a dna sequence`
Answer: 3. Sticky ends can be joined by using dna ligases
(3) Statement in option (3) is incorrect sticky ends are self-ligating ends that form hydrogen bonding and thus do not require DNA ligase.
Question 35. Which of the following techniques is most widely employed to check the progress of restriction enzyme digestion?
- Agarose gel electrophoresis
- Centrifugation
- Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- Pcr
Answer: 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a technique most widely employed to check the progress of restriction enzyme digestion. Chopped DNA fragments are introduced and passed through an electrophoresis setup containing agarose gel polymer where the fragments get separated on the basis of their size.
Question 36. In a mixture, dna fragments are separated by
- Bioprocess engineering
- Restriction digestion
- Electrophoresis
- Polymerase chain reaction
Answer: 3. Electrophoresis
A molecule of DNA can be cut into fragments by the enzyme restriction endonucleases. These fragments of DNA can be separated by a technique of gel electrophoresis. It is a technique used for the separation of substances with different ionic properties.
Question 37. Gel electrophoresis is used for Kerala
- Separation and isolation of dna fragments
- Construction of recombinant dna by joining with cloning vectors
- Culturing the host cells in a medium at a large scale
- Replication of dna for many times
- (E) cutting of dna into fragments
Answer: 1. Separation and isolation of dna fragments
Gel electrophoresis is used to separate macromolecules, like DNA, RNA, and proteins according to their size and charge. Gel electrophoresis is used for a range of purposes like to get a DNA fingerprint for forensic purposes, for paternity testing, and to check PCR reactions.
38. Agarose is extracted from
- Seaweeds
- Blue-green algae
- Ephedra
- Sargassum
Answer: 1. Sea weeds
Agarose is extracted from seaweed. It is a polysaccharide made up of repeating units of disaccharide, made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 39. The matrix used in electrophoresis is
- Polyethylene glycol
- Agarose
- Ethidium bromide
- Cellulose
Answer: 2. Agarose
In gel electrophoresis, agarose extracted from seaweed is used as a matrix. Gel agarose, made up of 0.7% gel, shows a good resolution of large DNA, and 2% gel shows a good resolution of small fragments.
40. In gel electrophoresis separated dna fragments can be visualized with the help of
- Ethidium bromide in UV radiation
- Acetocarmine in UV radiation
- Ethidium bromide in infrared radiation
- Acetocarmine in bright blue light
Answer: 1. Ethidium bromide in UV radiation
The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualized after staining with ethidium bromide. The separated DNA fragments appear as orange-colored bands while viewed under UV light or radiation.
NEET Biology multiple choice questions on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Question 41. The movement of dna during the process of electrophoresis is
- From positive pole to negative pole
- From negative pole to positive pole
- From cathode to anode
- Both and (c)
Answer: 4. Both and (c)
DNA being negatively charged, migrates from negative pole (cathode) to positive pole (anode) during gel electrophoresis. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 42. What is the criterion for dna fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis?
- The larger the fragment size, the farther it moves
- The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves
- Positively charged fragments move to the farther end
- Negatively charged fragments do not move
Answer: 2. The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves
- During gel electrophoresis, the criterion for the movement of DNA fragments on the gel is that the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
- Gel electrophoresis is the mechanism of separation of macromolecule and fragment on the basis of charge and size. It consists of a positive end and a negative end, molecules are separated after the application of an electric source.
- The molecules or fragments such as the DNA fragments get separated on the basis of their size due to the sieving effect of the agarose gel.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 43. During electrophoresis, the separated bands of dna are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece. This is called
- Elution
- Degradation
- Polymerization
- Denaturation
Answer: 1. Elution
The DNA fragments are seen as orange-colored bands. The separated bands of DNA are cut out and extracted from the gel piece. This step is called elution.
Question 44. Consider the following statements with respect to dna fragmentation.
- Gel electrophoresis and elution are two important processes.
- After staining with ethidium bromide, it has to be exposed to UV light.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- The DNA fragments are seen as orange-colored bands. The separated bands of DNA are cut out and extracted from the gel piece. This step is called elution.
- Agarose is extracted from seaweed. It is a polysaccharide made up of repeating units of disaccharide, made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose.
Question 45. Spooling is
- Amplification of dna
- Cutting of separated dna bands from the agarose gel
- Transfer of separated dna fragments to synthetic membranes
- Collection of isolated dna
Answer: 4. Collection of isolated DNA
Spooling is the method of collection of isolated DNA in the form of fine threads in the suspension. This is done to isolate DNA from the cell during the process of recombinant DNA technology.
biotechnology question bank
46. Which of the following are used in the process of gel electrophoresis?
- Sample dna is cut into fragments
- Restriction endonucleases
- Agarose gel
- Ethidium bromide
- Uv-radiation
- Elution
Mark the correct sequence of their use.
- 1, 2, 3, 6, 5 and 4
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 4, 5, 6, 1, 2 and 3
- 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 and 3
Answer: 2. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. Isolation and cutting of DNA, restriction endonucleases, agarose gel, ethidium bromide, UV radiation, and elution are used in the process of gel electrophoresis. Thus, the correct sequence of the process of gel electrophoresis is shown in option (2).
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 47. Having become an expert on gel electrophoresis, you are asked to examine a gel for a colleague. Where would you find the smallest segment of dna?
- Near the positive electrode, farthest away from the wells
- Near the negative electrode, close to the wells
- Near the negative pole
- Near the middle, they tend to slow down after the first few minutes
Answer: 1. Near the positive electrode, farthest away from the wells
A molecule of DNA can be cut into fragments by the enzyme restriction endonucleases. These fragments of DNA can be separated by a technique of gel electrophoresis. In this process, the smallest segment of DNA travels towards the anode (+ve electrode), farthest away from the wells.
Question 48. Identify the correct match for the given diagram.
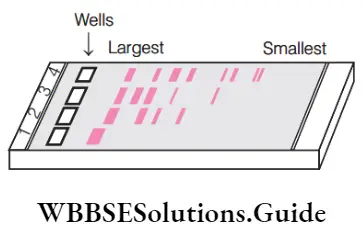
- Electrophoresis–migration of undigested and digested sets of dna fragments
- Bioreactor–raw materials are biologically converted into specific products
- Microinjection–the technique of introducing foreign genes into a host cell
- Gene gun–the technique of obtaining identical copies of a particular dna segment
Answer: 1. Electrophoresis–migration of undigested and digested sets of dna fragments
(1) Option (1) is the correct match for the given diagram as Electrophoresis – Migration of undigested and digested sets of DNA fragments.
Question 49. Study the given figure carefully and read the following statements.
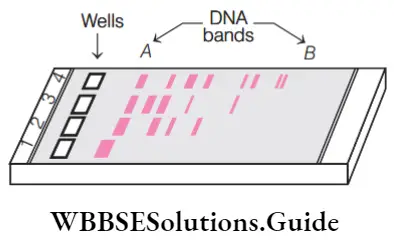
- A typical agarose gel electrophoresis shows differential migration of dna fragments.
- Lane 1 contains undigested dna fragments.
- Lanes 2 to 4 contains digested dna fragment.
- The smallest dna bands are present at position b and the largest dna bands are present at position A.
Choose the option containing
Correct statements.
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 4
- 2 And 3
- 3 And 4
Answer: 1. 1, 2, 3 And 4
All statements are correct.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 50. Given below are four statements pertaining to the separation of dna fragments using gel electrophoresis. Identify the incorrect statements.
- DNA is a negatively charged molecule and so it is loaded on gel towards the anode terminal.
- DNA fragments travel along the surface of the gel whose concentration does not affect the movement of dna.
- The smaller the size of dna fragment, the larger the distance it travels through it.
- Separated DNA fragments can be visualized directly by exposure to UV radiation.
Choose the correct option from the options given below.
- 1, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2 And 4
- Statements 1, 2, and 4 are incorrect and can be corrected as Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size.
- DNA samples are loaded into wells at one end of a gel toward the cathode terminal and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel, DNA fragments are negatively charged, so they move toward the positive (anode) electrode.
- The concentration of gel affects the resolution of DNA because DNA moves through the pores of the gel. So, the concentration of gel must be maintained in separation.
- The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualized after staining with ethidium bromide (EtBr) stain and these appear as orange colored bands under UV light.
Question 51. In the recombinant dna technique, the term vector refers to
- Plasmids that can transfer foreign dna into a living cell
- Cosmids that can cut dna at the specific base sequence
- Plasmids that can join different dna fragments
- Cosmids that can degrade harmful proteins
Answer: 1. Plasmids that can transfer foreign dna into a living cell
- The DNA used as a carrier for transferring a fragment of foreign DNA into a suitable host is called vehicle DNA or cloning vector or gene carrier.
- When the desired gene is introduced into a vector, recombinant DNA is formed. Vectors may be plasmids, a bacteriophage, cosmids, phagemids, Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs), Bacterial Artificial Chromosomes (BACs), etc.
NEET practice questions on biotechnology and genetic engineering tools
Question 52. In genetic engineering, a dna segment (gene) of interest is transferred to the host cell through a vector. Consider the following four agents (I -iv) in this regard and select the correct option about which one or more of these can be used as vector/vectors.
- Bacterium
- Plasmid
- Plasmodium
- Bacteriophage
Choose correct option
- 1, 2 And 4
- Only 1
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 4
Answer: 4. 2 And 4
- 2 and 4 agents are used as vectors. Circular plasmid DNA which is used as a vector, can be cleaved at one site with the help of an enzyme to give a linear DNA molecule.
- A foreign DNA segment can now be inserted, by joining the ends of broken circular DNA to the two ends of foreign DNA, thus regenerating a bigger circular DNA molecule. Bacteriophages provide another source of cloning vectors.
- Since, usually, a phage has a linear DNA molecule, a single break will generate two fragments, which are later joined together with foreign DNA to generate a chimeric phage particle. Rest agents are not used as vectors.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 53. A eukaryotic cloning vector is
- Bacteriophage
- Yeast episomal plasmid
- Cosmid
- Bacterial plasmid
Answer: 2. Yeast episomal plasmid
Yeast Episomal Plasmid (YEP) is a shuttle vector that exists in E. coli as well as in eukaryotic cells.
Question 54. Bac vector is preferred because it contains
- Selectable marker
- F-factor
- Cloning sites
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
BAC vectors are preferred for genetic studies because they accommodate much larger sequences without the risk of rearrangement. They have a selectable marker, F-factor, and cloning site and it is more stable than other cloning vectors. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 55. Which of the following viruses are used as vectors?
- Tmv
- Sv-40
- Adenovirus
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
- The most important viral vectors are retroviruses and adenoviruses. Retroviruses are small RNA-based viruses. They reproduce by integrating their RNA into a host’s DNA. Adenoviruses are medium-sized, non-enveloped viruses.
- TMV is one of the most studied plant viruses and has become the natural choice for vector development. Simian virus (SV-40), an icosahedral papovavirus, was modified to serve as a gene delivery vector. Thus, option (d) is correct.
Question 56. Commonly used bacteriophages as cloning vectors are
- T3 phage
- T4 phage
- M 13 and lambda phage
- Both t3 and t4 phage
Answer: 3. M 13 and lambda phage
Bacteriophages such as M13 and lambda phage transfer their DNA in the host cell and express themselves, thus acting as cloning vectors.
Question 57. Plasmid is
- An autonomously replicating circular extrachromosomal dna
- An autonomously replicating circular extrachromosomal rna
- A circular protein molecules
- An autonomously replicating chromosomal dna
Answer: 1. An autonomously replicating circular extrachromosomal dna
Plasmids are extrachromosomal, self-replicating (autonomously) usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast.
Question 58. Plasmids are extrachromosomal genetic material of
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Algae
- Amoeba
Answer: 1. Bacteria
Plasmids are extrachromosomal, self-replicating (autonomously) usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules found naturally in many bacteria and also in some yeast.
Question 59. Which of the following is not a correct statement about the plasmids? Odisha
- It is the extrachromosomal dna in bacteria
- It is not an integral part, but inert genetic material
- Host chromosomes can be integrated with the plasmid
- Transfer of plasmid can be done from cell to cell without killing the host
Answer: 2. It is not an integral part, but inert genetic material
- All given statements are correct about the plasmids except the statement given in option (2) because In addition to the single large circular chromosome, each bacterial cell contains from 1 to 20 much smaller circular duplex DNA molecules, which are called as plasmids.
- It replicates along with the bacterial chromosome. Their function varies some of them become incorporated into host cell chromosomes and are called episomes. These are sometimes transferred from one bacterial cell to another by the process of conjugation.
Question 60. Assertion plasmids are tools of genetic engineering. Reason (R) virulence plasmids provide pathogenicity to bacteria.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- A is true, but r is false
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 2. Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Plasmids are used in genetic engineering for gene transfer of bacterial cells or to cells of superior organisms, whether other plants animals, or other living organisms to improve their resistance to diseases or to improve their growth.
Question 61. Plasmids are used in genetic engineering because they are
- Easily available
- Able to replicate
- Able to integrate with the host chromosome
- Inert
Answer: 2. Able to replicate
- The most important feature in a plasmid to be used as a vector is the origin of replication (ori). The origin of replication is a specific sequence of DNA bases that is responsible for initiating replication.
- A prokaryotic DNA has a single origin of replication, while eukaryotic DNA may have more than one origin of replication. Thus, plasmids are used in genetic engineering because they are able to replicate.
Question 62. The plasmid that does not show resistance to ampicillin is
- Pbr327
- Pbr322
- Puc 19
- None of these
Answer: 4. None of these
All three plasmids possess resistance to ampicillin. pBR327 and pBR322 contain both ampicillin and tetracyclin resistance. pUC19 contains only ampicillin resistance.
Best MCQs on recombinant DNA tools for NEET preparation
Question 63. The first cloning vector to be developed was pbr322 in the year … a…. It was developed by … b … and … c… from e. Coli plasmid.
- A–1976, b–boliver, c–rodriguez
- A–1975, b–Sibelius, c–rodriguez
- A–1977, b–boliver, c–rodriguez
- A–1978, b–ho smith, c–kw Wilcox
Answer: 3. A–1977, b–boliver, c–rodriguez
- pBR322 vector was the first artificial cloning vector constructed in 1977 (A) by Boliver (2) and Rodriguez (3). It is widely used in gene cloning experiments.
- In pBR322, p denotes that it is a plasmid. BR stands for Boliver and Rodriguez, who constructed this plasmid. 322 is a number given to distinguish this plasmid from others developed in the same laboratory.
Question 64. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a genetic trait carried in the bacterial
- Introns
- Exosomes
- Plasmids
- Chromosome
Answer: 3. Plasmids
Plasmids are extrachromosomal material in bacteria and are used as a carrier DNA because it has an antibiotic resistance gene which makes it easy to isolate the transformed cell with the desired insert in it.
Question 65. Plasmids are suitable vectors for genetic cloning as they
- Have low molecular weight
- Have the ability to combine readily with host cells
- Have several sites for a large number of restriction enzymes
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Plasmids are suitable vectors for gene cloning because they replicate autonomously, have low molecular weight and can integrate within the host cell, and have several sites for a large number of restriction enzymes. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 66. A commonly used plasmid from e. Coli in genetic engineering is
- Yep
- Pbr322
- M 13
- Puc13
Answer: 2. Pbr322
pBR322 of E. coli was the first and most widely used plasmid for the construction of recombinant DNA.
Question 67. The plasmid derived from e. Coli is
- Pbr327
- Pbr322
- Both and (b)
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both and (b)
pBR327 vectors are derived from pBR322 by deletion of nucleotide between 1427 to 2516. Thus, option ( 3) is correct
Question 68. The letters ‘pbr’ of pbr322 stand for
- Plasmid, bacterium
- Plasmid, boliver, Rodriguez
- Pseudomonas, bacillus, rhizobium
- Plasmid, bacteriophage
Answer: 2. Plasmid, boliver, Rodriguez
- pBR322 vector was the first artificial cloning vector constructed in 1977 (1) by Boliver (2) and Rodriguez (3). It is widely used in gene cloning experiments. In pBR322, p denotes that it is a plasmid.
- BR stands for Boliver and Rodriguez, who constructed this plasmid. 322 is a number given to distinguish this plasmid from others developed in the same laboratory.
Question 69. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the pbr322 vector?
- It is the first artificial cloning vector constructed in 1977 by Boliver and Rodriguez
- It is the most widely used, versatile, and easily manipulated vector
- It has two antibiotic resistance genes, tet r, and amp r
- It does not have a restricted site for sale 1
Answer: 4. It does not have a restriction site for sal 1
(4) Option (4) is not a characteristic of the pBR322 vector. It can be corrected as pBR322 has a restriction site for Sal I. Rest options are characteristic of pBR322 vectors.
Question 70. Which one among the following is just a cloning plasmid, not an expression plasmid?
- Pbad18-cam
- Pbc sk
- Puc19
- Pet
Answer: 3. Puc19
- Cloning plasmids are the plasmids that serve to carry the foreign DNA segment into host cells, while expression plasmids carry expression signals also to ensure maximum expression of the foreign gene.
- pBAD18. Cam, pBC SK, and pET are expression plasmids, carrying strong promoter and termination codons to ensure maximum gene expression. pUC19 is a cloning vector only and does not carry the sequences to facilitate gene expression.
Question 71. The given figure is the diagrammatic representation of the e. Coli vector pbr322. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain component(s)?
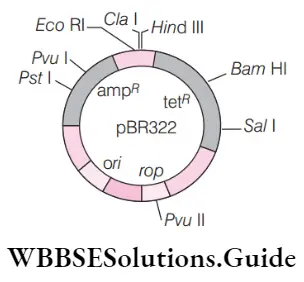
- Ori–original restriction enzymes
- Rop–reduced osmotic pressure
- Hind 3, EcoRI–selectable markers
- Amp r, tet r– antibiotic resistance genes
Answer: 4. Amp r, tet r– antibiotic resistance genes
- (4) Option (4) correctly identify its certain component of pBR322. amp R (ampicillin resistance gene) and tetR (tetracycline resistance gene) are antibiotic resistance genes.
- Rest options are not correct. Ori is the origin of replication rop is a repressor of primer and Hind 3, Eco RI are restriction enzymes
Question 72. Identify a, b, c, and d in the given diagram of. Coli cloning vector pbr322.
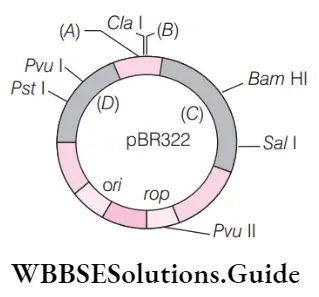
- A–eco ri, b–hind iii, c–tet r, d–amp r
- A–amp r, b–ori, c–bam hi, d–ecori
- A–ori, b–bam hi, c–eco ri, d–amp r
- A–bam hi, b–eco ri, c–amp r, d–ori
Answer: 1. A–eco ri, b–hind iii, c–tet r, d–amp r
Question 73. What are cosmids?
- Plasmids with fragments of e. Coli
- Plasmids with fragments of lambda phage
- Plasmids with fragments of m 13 phage
- Plasmids with fragments of transposon
Answer: 2. Plasmids with fragments of lambda phage
(2) Cosmids are hybrid or recombinant vectors constructed by inserting the cos site of phage lambda heads into plasmid DNA. They infect bacteria and replicate like plasmids. They can clone DNA fragments up to 45 kb of length.
74. Cosmids can clone dna fragments up to
- 45 Kb in size
- 55 Kb in size
- 85 Kb in size
- 75 Kb in size
Answer: 1. 45 Kb in size
(2) Cosmids are hybrid or recombinant vectors constructed by inserting the cos site of phage lambda heads into plasmid DNA. They infect bacteria and replicate like plasmids. They can clone DNA fragments up to 45 kb of length.
Question 75. The plasmid with the largest base pairs are
- λ phage
- Bacteriophage
- P elements
- Yac
Answer: 4. Yac
(4) A cosmid vector can accommodate foreign DNA of about 45 kb. Yeast Artificial Chromosome (YAC) has been developed to accommodate DNA fragments of 200-500 kb length (largest base pairs).
Question 76. The plasmid called recombinant plasmid and used for the introduction of the large genome to host cells is
- Lamda
- Mu (µ)
- Cosmid
- F
Answer: 3. Cosmid
- The plasmid called recombinant plasmid and used for the introduction of the large genome to the host cell is cosmid.
- Cosmids are hybrid or recombinant vectors constructed by inserting the cos site of phage lambda heads into plasmid DNA. They infect bacteria and replicate like plasmids. They can clone DNA fragments up to 45 kb of length.
Question 77. In cloning, which of the following is formed?
- The somatic nucleus is inserted into the cytoplasm of fertilized egg
- Ova are fertilized outside artificially
- Other specialized cells are made for embryogenic development
- Zygote is fused with somatic cells
Answer: 3. Other specialized cells are made for embryogenic development
- Normal mammalian embryonic development results from selective expression of some genes and repression of others. In order for the DNA of a differentiated adult cell to direct embryonic development in cloning, it must be epigenetically reprogrammed.
- The difference in the extent of epigenetic reprogramming in different cloning events leads to dissimilar protein expression and biological properties of cloned stem cells. Thus, other specialized cells are made for embryogenic development in cloning.
Question 78. ……….. Is used as vectors in insects.
- Tmv virus
- Bacteriophage
- Baculovirus
- Yac
Answer: 3. Baculovirus
Baculovirus vectors can be used for a variety of applications. These include producing proteins in insect larvae, insect cells, and mammalian cells. So, baculovirus is used as vectors in insects.
Question 79. Which of the following is a cloning vector?
- Dna of salmonella typhimurium
- Ti-plasmid
- Any dna containing antibiotic-resistance genes
- Ori minus pbr322
Answer: 2. Ti-plasmid
- The Ti-plasmid (tumour-inducing plasmid) is a cloning vector. It is present in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a Gram-negative soil bacterium that infects a wide range of plants and causes tumorous growth, especially at the root /stem junction (crown gall).
- The Ti-plasmid comprises the gene responsible for the tumorous growth, gets incorporated into the genome of infected plant cells.
- This property is of interest for genetic engineering as Ti-plasmid can be used as a DNA vector by replacing the tumor-inducing genes with the gene of interest and a marker gene to enable the selection of transformed cells.
Question 80. Which of the following plasmid is given a name based on the place of its discovery?
- Eco ri
- Puc
- Pbr322
- Hind 3
Answer: 2. Puc
pUC is the plasmid from the University of California.
Question 81. Match the following columns.
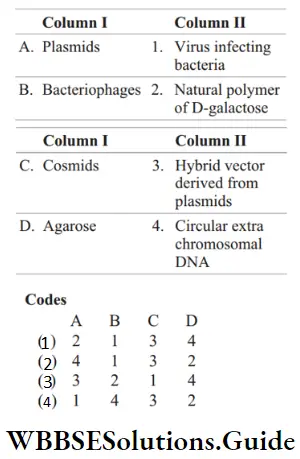
Answer: 2. A–4, B–1, C–3, D–2
Question 82. The recombinant plasmid is introduced into bacterial cells by the process of
- Conjugation
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Transfection
Answer: 2. Transformation
The plasmid can be introduced into a bacterium by the process called transformation. Researchers can insert DNA fragments or genes into a plasmid vector to create a recombinant plasmid.
Question 83. Transformation is defined as the procedure by which a piece of …a… Is introduced into the …b… Host. Here, a and b refer to

Answer: 2. Dna bacteria
A–DNA, B–bacteria.
Question 84. The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked dna in the vector is termed
- Ori site
- Palindromic sequence
- Recognition site
- Selectable marker
Answer: 1. Ori site
- The sequence that controls the copy number of linked DNA in the vector is called on-site. The origin of replication is a sequence from where replication starts and any foreign DNA is linked to this region.
- On-site is also responsible for controlling copy number of linked DNA. Therefore, if any person wants to produce many copies of the target DNA he should close on a vector whose on site supports high copy number.
Question 85. An antibiotic-resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of
- Transformed cells
- Competent cells
- Mutant cells
- None of these
Answer: 1. Transformed cells
An antibiotic-resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of transformed cells.
Question 86. A gene whose expression helps to identify transformed cells is known as
- Selectable marker
- Vector
- Plasmid
- Structural gene
Answer: 1. Selectable marker
Selectable markers play an important role in recombinant DNA technology. These are genes that are present in the vector of cells involved in imparting resistance to a particular toxic substance. It helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and permitting the growth of the transformed cells.
Question 87. The function of a selectable marker is
- Eliminating transformants and permitting non-transformants
- Identify on site
- Elimination of non-transformants and permitting transformants
- To destroy recognition sites
Answer: 3. Elimination of non-transformants and permitting transformants
Selectable markers play an important role in recombinant DNA technology. These are genes that are present in the vector of cells involved in imparting resistance to a particular toxic substance. It helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and permitting the growth of the transformed cells.
Question 88. In recombinant dna technology antibiotics are
- To keep medium bacteria-free
- To detect alien dna
- To impart disease resistance to the host plant
- As selectable markers
Answer: 4. As selectable markers
- In recombinant DNA technology antibiotics are used as selectable markers. Which helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
- Normally, the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, ampicillin, tetracycline, or kanamycin, etc., are considered useful selectable markers for E.coli.
Question 89. Due to the chloramphenicol resistance gene, one is able to select a transformed cell in the presence of chloramphenicol. The chloramphenicol resistance gene in this case is called
- Origin of replication
- Cloning sites
- Selectable marker
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Selectable marker
Due to the chloramphenicol resistance gene, one is able to select a transformed cell in the presence of chloramphenicol. The chloramphenicol resistance gene in this case is called a selectable marker.
Question 90. If a recombinant dna-bearing gene for ampicillin resistance is transferred into e. Coli cells and the host cells are spread on agar plates containing ampicillin,
- Both transformed and untransformed recipient cells will die
- Both transformed and untransformed recipient cells will grow
- Transformed recipient cells will grow and untransformed recipient cells will die
- Transformed recipient cells will die and untransformed recipient cells will grow
Answer: 3. Transformed recipient cells will grow and untransformed recipient cells will die
Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium. DNA bearing ampicillin resistance gene (transformed recipient cells) when introduced into the plate containing ampicillin, will grow. In contrast DNA not bearing the ampicillin resistance gene (untransformed recipient cells) will die.
Question 91. Consider the following statements regarding selectable markers.
- It helps to select the host cells which contain the vector and eliminate the non-transformants.
- Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, or kanamycin, are useful selectable markers for e. Coli.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- (3) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct as the Selectable marker helps to select the host cells which contain the vector and eliminate the non-transformants.
- Genes encoding resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, or kanamycin are useful selectable markers of E. coli. The normal E. coli cells do not carry resistance against any of these antibiotics.
Question 92. How are transformants selected from non-transformants?
- Presence of more than one recognition site in the vector dna
- The presence of alien dna into the vector dna results in insertional inactivation of selectable marker
- The antibiotic resistance gene gets inactivated due to the insertion of alien dna
- Both and (c)
Answer: 4. Both and (c)
- Selectable markers help in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants. The ligation of alien DNA is carried out at a restriction site present in one of the two antibiotic-resistance genes.
- In this case, one antibiotic resistance gene helps in selecting the transformants whereas the other antibiotic resistance gene gets inactivated due to the insertion of alien
DNA and helps in the selection of recombinants.
93. The phenomenon in which the cloned dna fragment disturbs the coding sequence of the gene is called
- Insertional inactivation
- Stimulation-inhibition
- Insertional activation
- Recombination
Answer: 1. Insertional inactivation
Insertional inactivation is a technique used in recombinant DNA technology. In this procedure, a bacteria carrying recombinant plasmid or a fragment of foreign DNA is made to insert into a restriction site inside a gene to resist antibiotics, hence causing the gene to turn non-functional or in an inactivated state.
Question 94. The colonies of recombinant bacteria appear white in contrast to the blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because of
- Insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria
- Insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
- Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in recombinant bacteria
- Non-recombinant bacteria containing beta-galactosidase
Answer: 2. Insertional inactivation of alpha-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
- In blue-white screening or insertional inactivation, recombinant DNA is inserted with a coding sequence ofβ-galactosidase which breaks galactose into lactose.
- This results in the inactivation of enzymes, due to which recombinant colonies do not produce any color and appear white. In contrast, non-recombinant cells appear blue in color due to the presence of a chromogenic substrate.
Question 95. Ti-plasmid transfer works with
- Only monocots
- Only dicots
- All plants
- All of these
Answer: 2. Only dicots
(2) Ti-plasmid can be used for the transfer of a desired gene in dicot plants.
Question 96. The tumor-inducing capacity of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is located in large extrachromosomal plasmids called
- Ri-plasmid
- Lambda phage
- Pbr322
- Ti-plasmid
Answer: 4. Ti-plasmid
(4) Ti-plasmid is found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which produces crown gall (tumor) in a large number of dicot species. A. tumefaciens is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that infects a wide range of plants and causes crown galls.
Question 97. The vector for t-dna is
- Thermus aquaticus
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Escherichia coli
- (E) bacillus thuringiensis
Answer: 3. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
The vector used to introduce new genes into plant cells is most often a plasmid from the soil bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This is the Ti-plasmid (Tumour inducing plasmid). The part of Ti-plasmid transferred into plant cell DNA, is called the T-DNA
Question 98. What is the source of the ti (tumor-inducing) plasmid which is modified and used as a cloning vector to deliver the desirable genes into plant cells?
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Thermophilus aquaticus
- Pyrococcus furiosus
- Aedes aegypti
Answer: 1. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- The delivery of genes by pathogens in their eukaryotic ‘hosts has generated knowledge to transform tools of pathogens into useful vectors for delivering genes of interest to humans or plants.
- The tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been modified into a cloning vector that is no more pathogenic to the plants but is still able to use the mechanisms to deliver genes of our interest into a variety of plants.
Question 99. Which of the following is correctly matched?
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumour
- Thermus aquaticus – bt gene
- Pbr322 – enzyme
- Ligase – molecular scissors
- (E) hind ii – plasmid vector
Answer: 1. Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor
- (1) Option (1) is correctly matched as Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a tumor-inducing organism that carries Ti-plasmid.
- Taq polymerase obtained from Thermus aquaticus, is a type of DNA polymerase that is used in polymerase chain reaction for the polymerisation of nucleotides.
- Ligase is an enzyme that helps in binding DNA by forming a phosphodiester bond. Hind 2 acts as molecular scissors as it is a type of restriction endonuclease that cleaves the DNA strands at a specific recognition site.
Question 100. A dicotyledonous plant forms a crown gall
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens comes in contact with the plant
- Agrobacterium Rhizogenes comes in contact with the plant
- A specific part of dna from the ti-plasmid gets integrated with the plant chromosome
- A specific part of dna from the ri plasmid gets integrated with the plant chromosome
Answer: 3. A specific part of dna from the ti-plasmid gets integrated with the plant chromosome
- (3) Ti (tumor-inducing) plasmid from a soil bacterium, Agrobacterium tumefaciens induces the formation of cancerous growth called crown gall tumor by transferring its DNA into plant cells.
- Thus, a dicotyledonous plant forms a crown gall when a specific part of DNA from the Ti-plasmid gets integrated with the plant chromosome.
Question 101. Assertion agrobacterium tumefaciens is popular in genetic engineering because this bacterium is associated with roots of all cereals and pulse crops. Reason (R) a gene incorporated in the bacterial chromosomal genome gets automatically transferred to the crop with which the bacterium is associated.
- Both a and r are true and r is the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true, but r is not the correct explanation of a
- Both a and r are true
- Both a and r are false
Answer: 4. Both a and r are false
- (4) Both A and R are false and can be corrected as Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a rod-shaped Gram-negative soil bacterium.
- This is used extensively in genetic engineering because of its ability to transfer its DNA into the plants. A. tumefaciens naturally infect the wound sites in dicotyledons and cause crown gall tumors.
- These tumors are incited by the conjugative transfer of DNA segment (T-DNA) from the bacterial tumor-inducing Ti-plasmid.
Question 102. Consider the following statements.
- Dna being a hydrophilic molecule cannot pass through cell membranes.
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens delivers a piece of dna known as ‘z-dna’ in the ti -plasmid which transforms normal plant cells into tumor cells to produce chemicals against pathogens.
- Retrovirus, adenovirus, and papillomavirus are also now used as cloning vectors in animals because of their ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells.
- In genetic engineering, dna from different sources is cut with the same restriction enzymes, so that both dna fragments have the same kind of sticky ends.
Choose the option containing an incorrect statement.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Only 3
- Only 4
Answer: 2. Only 2
(2) Statement II in option (2) is incorrect and can be corrected as Agrobacterium tumefaciens delivers a piece of DNA known as ‘T-DNA’ in the Ti -plasmid which transforms normal plant cells into tumor cells to produce chemicals against pathogens. Rest all statements are correct.
Question 103. The biological enzymes used to synthesize dna segments in retrovirus is
- Reverse transcriptase
- Restriction endonucleases
- Restriction exonucleases
- Restriction DNAase
Answer: 1. Reverse transcriptase
The biological enzyme used to synthesize DNA segments in retrovirus is reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is a polymerase that uses RNA as a template to transcribe a single-stranded DNA molecule as a product.
Question 104. Which one of the following is used as a vector for cloning genes into higher organisms?
- Baculovirus
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Rhizopus nigricans
- Retrovirus
Answer: 4. Retrovirus
(4) Retrovirus has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. Hence, it can be used as a vector for cloning desirable genes into higher organisms and animal cells.
Question 105. Retroviruses in animals including humans are able to change normal cells into
- Germ cell
- Cancerous cells
- Cosmid
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Cancerous cells
(2) Retrovirus has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells. Hence, it can be used as a vector for cloning desirable genes into higher organisms and animal cells.
106. Bacterial cells are made competent by treating it with
- Divalent cation of calcium
- Monovalent cation of calcium
- Divalent cation of potassium
- Monovalent cation of potassium
Answer: 1. Divalent cation of calcium
(1) Making the bacterial cell competent means enhancing the entry of DNA into bacteria through pores on a cell wall. Bacterial cells are made competent by treatment with divalent cations like calcium.
Question 107. The polyethylene glycol method is used for
- Biodiesel production
- Seedless fruit production
- Energy production from sewage
- Gene transfer without a vector
Answer: 4. Gene transfer without a vector
- (4) Direct gene transfer is the transfer of naked DNA into plant cells, but the presence of a rigid plant cell wall acts as a barrier. Therefore, protoplasts are the favored target for direct gene transfer without a vector.
- Polyethylene glycol-mediated DNA uptake is a direct gene transfer method that utilizes the interaction between polyethylene glycol, naked DNA, salts, and the protoplast membrane to bring about the transport of the DNA into the cytoplasm.
Question 108. In order to induce the bacterial uptake of plasmids, the bacteria are made ‘competent’ by first treating
- Sodium chloride
- Potassium chloride
- Magnesium chloride
- Calcium chloride
Answer: 4. Calcium chloride
- (4) In order to induce the bacterial uptake of plasmids, the bacteria are made competent by first treating them with calcium chloride. Calcium salts increase the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
- Recombinant DNA can then be forced into such cells by incubating cells with the recombinant DNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 42°C (heat shock) and then putting them back on ice.
Question 109. Consider the following statements.
- Dna being a hydrophilic molecule cannot pass through cell membranes.
- The bacteria should be made competent to accept the dna molecule.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- (3) Both statements I and II are correct as Hydrophobic molecules can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane and not hydrophilic molecules. DNA being hydrophilic with the sugar-phosphate backbone, cannot pass through the cell membrane.
- Bacterial cells can be made competent to take up the recombinant DNA from a medium with the help of electroporation.
Question 110. The significance of the heat shock method in bacterial transformation facilitates
- Binding of dna to the cell wall with the help of proteins
- Uptake of dna through membrane transport proteins
- Uptake of dna through transient pores in the bacterial cell wall
- Expression of antibiotic resistance gene
Answer: 3. Uptake of dna through transient pores in the bacterial cell wall
- (3) DNA is a hydrophilic molecule that cannot pass through cell membranes. Therefore, the bacteria should be made competent to accept the DNA molecule.
- In this case, the cell is treated with a specific concentration of a divalent cation such as calcium to increase pore size in bacterial cell walls.
- The cells are incubated with recombinant DNA on ice, followed by placing them briefly at 42°C and then putting it back on ice. This is called heat shock treatment. The bacterium now takes up the recombinant DNA.
Question 111. One physical method of gene transfer is
- Shotgun technique
- Use of enzymes
- Peg application
- Use of salts
Answer: 1. Shotgun technique
(1) Physical method of gene transfer is shotgun cloning. It involves cutting the DNA of the entire genome into pieces with a restriction enzyme, inserting these pieces or fragments into bacteria or yeast with plasmids or viruses, and allowing the organism to reproduce, making copies or clones of the DNA fragments.
Question 112. Biolistics (gene gun) is suitable for
- Disarming pathogen vectors
- Transformation of plant cells
- Construction recombinant dna by joining with vectors
- Dna fingerprinting
Answer: 2. Transformation of plant cells
(2) The biolistic method is a method of transformation of plant cells. It is used to transfer foreign DNA into a plant cell. For this purpose, cells are bombarded with high-velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
Question 113. For transformation, microparticles coated with dna to be bombarded with gene guns are made up of
- Silver or platinum
- Platinum or zinc
- Silicon or platinum
- Gold or tungsten
Answer: 4. Gold or tungsten
(4) For gene transfer into the host cell without using a vector, microparticles made up of tungsten and gold coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity.
Question 114. Consider the following statements about the gene gun method.
- This method is also known as the biolistic technique.
- Important crop plants like maize, rice, and wheat have now been transformed by this method.
Choose the option containing
Correct statements.
- 1 And 2
- Only 1
- Only 2
- None of the above
Answer: 1. 1 And 2
(1) Both statements are correct as In the biolistic or gene gun method, cells are high-velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA in plants. Important crop plants like maize, rice, and wheat have now been transformed by this method.
Question 115. Consider the following statements.
- In recombinant dna technology after several treatments, the purified dna is precipitated by adding chilled ethanol.
- The bacterial/plant, animal cell is broken down by enzymes to release dna, along with RNA, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
(3) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 116. In the microinjection method, the RDNA is incorporated into the host cell by using
- Micropipettes
- Microneedles
- High voltage electric impulse
- Both and (2)
Answer: 4. Both and (2)
- (4) In the microinjection method, foreign DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell or plant cell by using microneedles or micropipettes.
- This method of gene transfer is used to introduce DNA into large cells such as oocytes, eggs, and the cells of early embryos. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 117. Consider the following statements.
- The microinjection method is used in oocytes, eggs, and embryos.
- Electroporation is the formation of temporary pores in the plasma membrane of the host cell by using lysozyme or calcium chloride.
- In chemical mediated gene transfer method, certain chemicals such as ca help foreign dna to enter the host cell.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- Only 1
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1 And 3
Answer: 1. 1, 2 And 3
- (1) Statement 1 is correct and statements 3 and 4 are incorrect. These can be corrected as
- Electroporation involves the application of a high-voltage pulse to protoplasts/cells/tissues to make transient (temporary) pores in the plasma membrane which facilitates the uptake of foreign DNA.
- Chemical-mediated gene transfer chemicals like Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and dextran sulfate induce DNA uptake into plant protoplasts. Calcium phosphate is also used to transfer DNA into cultured cells.
Question 118. Select the incorrect statement.
- The presence of chromogenic substrate gives blue color colonies if the plasmid in the bacteria does not have an insert
- Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells
- In microinjection, cells are bombarded with high-velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated with dna
- Since dna is a hydrophilic molecule it cannot pass through cell membranes
- (E) dna is a negatively charged molecule
Answer: 3. In microinjection, cells are bombarded with high-velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated with dna
- (3) Statement in option (3) is incorrect and can be corrected as In the microinjection method of DNA transfer, foreign DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of animal cells or plant cells by using microneedles or micropipettes.
- It is used in oocytes, eggs, and embryos. In the gene gun method, tungsten or gold particles coated with foreign DNA are bombarded into the target cell at a very high velocity. Rest options are true statements.
Question 119. Plant cells can be transformed by
- Electroporation
- Electrophoresis
- Electrocution
- Electrolysis
Answer: 1. Electroporation
- (1) Plant cells can be transformed by electroporation. It is a well-established method for the production of transgenic plants.
- Short high-voltage pulses can permeabilize the protoplast plasma membrane, facilitating the uptake of plasmid DNA that can become expressed transiently and eventually incorporated into the genome.
Question 120. Electroporation procedure involves
- Fast passes of food through sieve pores in phloem elements with the help of electric stimulation
- Opening of stomatal pores during the night by artificial light
- Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
- Purification of saline water with the help of a membrane system
Answer: 3. Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
(3) Electroporation method is used for the introduction of recombinant DNA into the host. In this procedure, temporary (transient) pores are formed in the plasma membrane of the host cell by high voltage current. These pores permit the entry of foreign DNA.
