Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Transcription
Question 1. The process of copying genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA is termed as
- Transamination
- Replication
- Transcription
- Deamination
Answer: 4. Transcription
- The process in living cells in which the genetic information of DNA is transferred to a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA) is the first step in protein synthesis.
- This is known as transcription. It takes place in the cell nucleus or nuclear region and is regulated by transcription factors.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. Transcription unit
- Starts with the Tata box
- Starts with palindrome regions and ends with the rho factor
- Starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region
- Starts with the chat region
Answer: 3. Starts with the promoter region and ends in the terminator region
molecular basis of inheritance
The transcription unit comprises sites of initiation and termination by RNA polymerase, i.e. It extends from the promoter to the terminator sequences
Question 3. During transcription, holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle-like structure at that point. What is that sequence called?
- Aaat box
- Tata box
- Ggtt box
- Chat box
Answer: 2. Tata box
Tata box is present in the promoter region of the eukaryotic transcription unit. It is located 20 bp upstream of the start point.
During transcription, RNA polymerase holoenzyme binds to the tata box due to which DNA assumes a saddle-like structure at that point.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
NEET Biology transcription MCQs with answers
Question 4. RNA polymerases are also called
- DNA-independent DNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Answer: 2. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase form RNA by working on the DNAtemplate strand which is why, it is called DNA- dependent RNA polymerase
Question 5. RNA polymerase contains multiple polypeptide units. For initiating RNA synthesis, it requires j&k cet 2007,
- Σ -subunit
- Α -subunit
- Ρ-factor
- Spliceosome
Answer: 1. Σ -subunit
In bacterial systems like e. Coli, a single RNA polymerase (map) is responsible for the synthesis of all kinds of RNAs (mRNA, tRNAs, and rrna).
The sigma ( σ ) factor helps in the recognition of start signals on DNA molecules and directs RNA polymerase in selecting the initiation sites
Question 6. Given below are various components of the transcription unit and their characteristics.
- Pribnow box – atata sequence
- Hogness box – found in eukaryotes
- Chat box – located 75-80 bases upstream of the transcription initiation site.
“molecular biology mcq “
Choose the option containing incorrectly matched pairs.
- 1 Only
- 2 And 3 only
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1 And 2 only
Answer: 1. 1 Only
I am an incorrectly matched pair and can be corrected as The Pribnow box is a sequence of six nucleotides data at the promoter site in the prokaryotic transcription unit.
The rest others are correctly matched pairs.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 7. RNA polymerase catalyzes only ………… Process of transcription.
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- Amino acylation
Answer: 2. Elongation
RNA polymerase only catalyzes the elongation process of transcription. The initiation of transcription is done by the sigma ( σ) unit. Termination of the transcription is achieved by the rho (ρ) protein.
These two structures are not the part of RNA polymerase.
Transcription multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 8. During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called
- Enhancer
- Promoter
- Regulator
- Receptor
Answer: 2. Promoter
The promoter is the sequence that provides the point of attachment to RNA polymerase required for the transcription of structural genes.
It is a Pribnow box in prokaryotes and a hotness box in eukaryotes.
Question 9. In bacteria, which enzyme catalyzes the transcription of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA?
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Answer: 1. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
In bacteria, there is no specific RNA polymerase or dependent RNA polymerase to catalyze the different types of RNAs (rRNA, tRNA, mRNA).
“rna polymerase diagram “
Only one DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the formation of all types of RNAs (rRNA, tRNA, mRNA). In eukaryotes, there are three types of RNA polymerase for catalyzing different types of RNAs
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. Regions of transcriptional units are
- Exon
- Intron
- Promoter
- Structural gene
- Terminator
- Cistron
Choose the correct option
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2, 3 And 4
- 3, 4 And 5
- 4, 5 And 6
Answer: 3. 3, 4 And 5
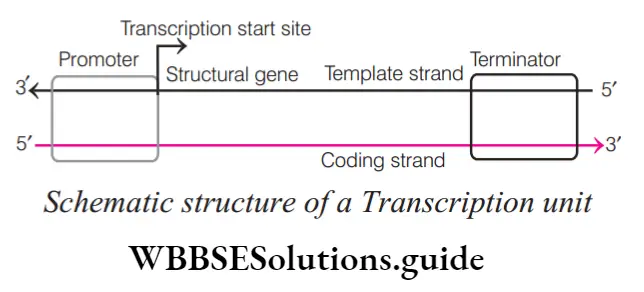
The transcriptional unit contains three main regions The promoter is the binding site for RNA polymerase for initiation.
It is located toward the 5′ end (upstream). The reference is made with respect to the polarity of the coding strand. Structural genes code for enzymes or proteins.
The terminator is the region of DNA where transcription stops. It is located at 3 ′-end (downstream)
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. The structural genes which are transcribed in prokaryotes are called
- Monocistronic
- Polycistronic
- Bicistronic
- Tricistronic
Answer: 2. Polycistronic
The structural gene is called polycistronic when the transcriptional unit codes for many polypeptides. It is mostly found in prokaryotes
Question 12. Monocistronic transcriptional unit codes for
- Single polypeptide
- Double polypeptides
- No polypeptide
- Triple polypeptides
Answer: 1. Single polypeptide
When the transcription unit codes for a single polypeptide, it is called monocistronic. It is mostly found in eukaryotes
“which one of the following is not applicable to rna “
Question 13. Consider the following statements.
- A monocistronic mRNA can produce several types of polypeptide chains.
- The terminator codon is present on the mRNA.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
The incorrect statement can be corrected as monocistronic mRNA produces only one type of polypeptide. They are found only in eukaryotes. Terminator codons (uaa, uag, uga) are found on the mRNA.
Important transcription questions for NEET Biology
Question 14. Consider the following statements.
- In prokaryotes, different RNA polymerase transcribes mRNA,
tRNA and rRNA. - RNA polymerase-i transcribes 28s, 18s, 5.8s rRNA.
- RNA polymerase-iii transcribes 5s rRNA and tRNA.
- RNA polymerase-ii transcribes hnRNA.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2 And 3
- 3 And 4
- 1, 4 And 3
Answer: 1. 2, 3 And 4
All given statements are correct except The incorrect statement can be corrected as a single RNA polymerase is responsible for transcribing all types of RNA in the prokaryotic system
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
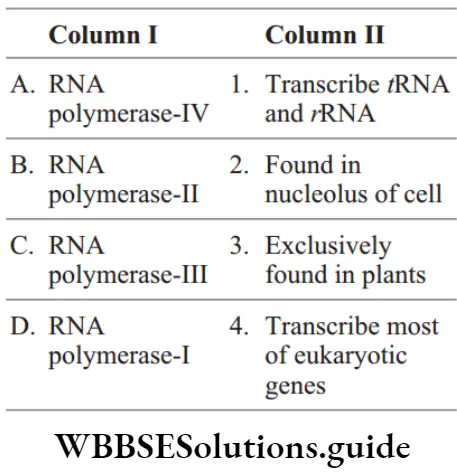
Question 15. Match the following columns.
Codes
- 2 3 4 1
- 3 4 1 2
- 1 2 3 4
- 4 1 2 3
Answer: 2. 3 4 1 2
Question 16. Formation of polysome does not require
- RRNA
- MRNA
- TRNA
- SnRNA
Answer: 4. SnRNA
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is a number of small RNA molecules found in the nucleus. These RNA molecules are important in RNA splicing, maintenance of the telomeres, etc.
Polysomes are aggregates of ribosomes bound together on a mRNA, molecule. They are formed during active protein synthesis and consist of ribosomes (containing rRNA), mRNA, and tRNA but not snRNA.
“class 12th biology molecular basis of inheritance “
Thus, the formation of polysome does not require snRNA
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 17. In the transcription unit, the promoter is located towards ….a… End.
This end is also called ….b….. Choose the correct option for a and b.
- A–5′, b–upstream
- A–5′, b–downstream
- A–3′, b–upstream
- A–3′, b–downstream
Answer: 1. A–5′, b–upstream
Usually, the promoter is present at the beginning of the RNA strand, this beginning point is called 5′ end or upstream with respect to the coding strand.
Question 18. Holoenzyme consists of a core enzyme that is composed of
- Α 2-subunit
- Β1-subunit
- Β2-subunit
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The core enzyme consists of α β β2 1 2, subunits. When the core enzyme gets associated with (σ) factor, a holoenzyme is formed. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Solved MCQs on transcription for NEET exam
Question 19. The strand of DNA which synthesize mRNA is
- Sense strand
- Antisense strand
- Non-sense strand
- Half sense strand and half non-sense strand
Answer: 2. Antisense strand
Both the strands of DNA do not take part in transcription. The DNA strand which functions as a template for RNA synthesis is known as the template strand, minus (−) strand, or antisense strand.
Question 20. In the given diagram, find out a-e.
- Promoter site
- Structural gene
- Terminator site
- Template strand
- Coding strand
Codes
- 5 1 4 2 3
- 5 1 4 3 2
- 5 4 1 2 3
- 1 4 5 2 3
Answer: 3. 5 4 1 2 3
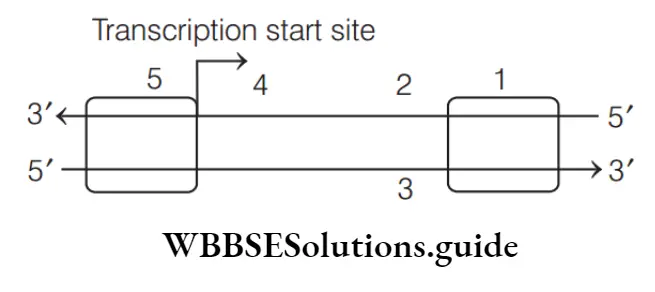
Promoter site-5 (binding of RNA polymerase), structural gene – 4(formation of functional protein), terminator site-1 (stopping of transcription), template strand-2 (part of DNAthrough which RNA is transcribed), coding strand-3 (a complementary strand of DNA to RNA).
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 21. Feminism is also called as
- Reverse transcription
- Transcription
- Translation
- Replication
Answer: 1. Reverse transcription
According to Crick (1958), information flows from DNA to mRNA and then to protein, which is called central dogma.
But later two american workers, h Temin and D Baltimore reported the formation of DNA on the RNA template, or DNA is also formed from RNA by using reverse transcriptase.
“which of the following is an initiation codon “
This process is called reverse transcription or feminism after the name of the scientist. This process is found in the transcription start site promoter structural gene template strand terminator schematic structure of a transcription rous sarcoma virus or RNA tumor virus.
For this work, Temin and Baltimore were awarded nobel prize in 1975
Question 22. The process of reverse transcription was discovered by
- Temin and Baltimore
- Watson and crick
- Alfred Hershey
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Temin and Baltimore
According to Crick (1958), information flows from DNA to mRNA and then to protein, which is called central dogma. But later two american workers, h Temin and D Baltimore reported the formation of DNA on the RNA template or DNA is also formed from RNA by using reverse transcriptase.
This process is called reverse transcription or feminism after the name of the scientist.
This process is found in the transcription start site promoter structural gene template strand terminator schematic structure of a transcription rous sarcoma virus or RNA tumor virus.
For this work, Temin and Baltimore were awarded nobel prize in 1975
Question 23. Reverse transcriptase is odisha
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Answer: 2. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
The formation of DNA from RNA is called reverse transcription. The genetic material of HIV is ssRNA. HIV has to synthesize DNA from ssRNA by using reverse transcriptase or RNA-dependent DNA polymerases.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 24. In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase-ii transcribes kerala
- HnRNA
- 18S rRNA
- 28S rRNA
- TRNA
- SnRNAs
Answer: 1. HnRNA
RNA polymerase-ii transcribes hnRNA which after undergoing processing, form mRNA.
Question 25. Transcription in the case of eukaryotes takes place in
- Nucleus
- Nucleolus
- Cytoplasm
- Ribosome
Answer: 1. Nucleus
Transcription in prokaryotes occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, transcription takes place in the nucleus and the RNA is transferred out to the cytoplasm for translation.
Question 26. The template strand is also known as
- Non-coding strand
- Antisense strand
- Master strand
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The template strand is also called the master/non-coding/antisense strand. It has sequences complementary to that of mRNA. Coding strand is the strand of DNA, which does not get transcribed and has the polarity 5′-3′. Its sequences are the same as that of RNA.
Role of RNA polymerase in transcription NEET MCQs
Question 27. Consider the following statements.
- The primary transcript contains only coding sequences.
- Introns are non-coding sequences in eukaryotes.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
The incorrect statements can be corrected as the primary transcript contains both coding and non-coding sequences. It is therefore, processed after the completion of transcription.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 28. In eukaryotic genes, coding sequences are called kerala
- Introns
- Exons
- Regulatory sequence
- Repetitive DNA
- Histones
Answer: 2. Exons
In eukaryotes, genes are split genes that contain both exons (expressing or coding sequence) and introns (intervening/non-coding sequences).
Introns do not code for any protein and are removed during RNA processing (splicing).
Question 29. Removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called
- Tailing
- Transformation
- Capping
- Splicing
Answer: 4. Splicing
Splicing is the removal of introns and joining the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit. MRNA is not made directly in a eukaryotic cell.
It is transcribed as heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) in the nucleus. HnRNA contains introns and exons. The introns are removed by RNA splicing, leaving behind the exons
Question 30. Heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) is converted to mRNA by
- Splicing
- Capping
- Tailing
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The primary transcript obtained after transcription is called heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA. Post-transcriptional processing is required to convert primary transcript into functional RNA.
Following the removal of introns or splicing, additional nucleotides are added to the ends of RNA for specific functions, e.g. Cca segment in tRNA cap nucleotides at 5′ end of mRNA (capping) or poly-a segments (200-300 residues) at 3′ end of mRNA (tailing).
Cap is formed by the modification of gtp into 7-methyl guanosine. Thus, option (2) is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 31. Self-splicing introns are called
- Coenzyme
- Apoenzymes
- Ribozyme
- Holoenzyme
Answer: 3. Ribozyme
Ribozyme is the enzyme used for removing introns. It is an RNA molecule that can act as an enzyme, catalyzing changes in its own molecular structure. So, self-splicing introns are called a ribozyme
Question 32. Spliceosomes are not found in cells of
- Plants
- Fungi
- Animals
- Bacteria
Answer: 4. Bacteria
Spliceosomes are used in the removal of introns during post-transcriptional processing of hnRNA in eukaryotes. Split genes are absent in prokaryotes like bacteria therefore, they lack spliceosomes.
They are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms.
Best multiple choice questions on transcription for NEET preparation
Question 33. 5 ′-3 ′ End of DNA strand is called
- Non-template strand
- Sense strand
- Coding strand
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
5′-3′ Strand of DNA is called a non-template strand or sense strand or coding strand. The non-template strand does not take part in transcription or code for anything.
The genetic code present in this strand is similar to the genetic code on mRNA except that uracil is replaced by thymine. Thus, the option is correct.
Question 34. The addition of methyl guanosine triphosphate at 5 ′ ends of hnRNA in a transcription unit is called
- Splicing
- Capping
- Tailing
- Transcribing
- Tautomerism
Answer: 2. Capping
The primary transcript obtained after transcription is called heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA. Post-transcriptional processing is required to convert primary transcript into functional RNA.
Following the removal of introns or splicing, additional nucleotides are added to the ends of RNA for specific functions, e.g. Cca segment in tRNA cap nucleotides at 5′ end of mRNA (capping) or poly-a segments (200-300 residues) at 3′ end of mRNA (tailing).
Cap is formed by the modification of gtp into 7-methyl guanosine.
Question 35. The addition of adenylate residues at 3 ′ ends in a transcription unit is called
- Tailing
- Splicing
- Capping
- Coding
Answer: 1. Tailing
In tailing, adenylate residues are added at 3′ end in a template-independent manner
Question 36. About ……….. Adenylate residues are added at the 3 ′ end of mRNA.
- 300-400
- 200-300
- 400-500
- 100-200
Answer: 2. 200-300
In tailing, about 200-300 adenylate residues are added at 3′ end of hnRNA
Question 37. The terminator in a transcriptional unit is present in the ….a… End.
It is also called ….b…… It defines the ….c… Of the process of transcription.
Choose the correct option for a, b and c.
- A–3′, b–downstream, c–end
- A–3′, b–upstream, c–end
- A–3′, b–upstream, c–beginning
- A–5′, b–upstream, c–beginning
Answer: 1. A–3′, b–downstream, c–end
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 38. Which of the following sequences will be produced as a result of transcription of the DNA sequence cgattacag?
- Gcuaauguc
- Cguaaucug
- Gctaatgtc
- Gcuaatctg
Answer: 1. Gcuaauguc
(C g a t t a c a g)
↓ transcription
(g c u u g u c) thus, option (1) is correct.
Question 39. MRNA is synthesised on DNAtemplate in which direction.
- 5′ → 3′
- 3′ → 5′
- Both (1) and 2)
- All of the above
Answer: 1. 5′ → 3′
The RNA polymerase read the template DNA strand in 3′ → direction and the mRNA is formed in 5′→ 3′ direction.
Question 40. If double-stranded RNA is produced during transcription, it
- Would prevent RNA from being translated into protein
- Would not prevent RNA from being translated into protein
- This will lead to the continuous synthesis of RNA
- Will give rise to double-stranded RNA with lower stability
Answer: 1. Would prevent RNA from being translated into protein
Double-stranded RNA has more stability than single-stranded DNA.
If double-stranded RNA is formed during transcription, then it would be difficult to separate the strands of RNA, due to which the translation will be halted.
NEET Biology differences between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes MCQs
Question 41. What can be observed if both strands are copied simultaneously during transcription?
- The segment of DNA would be coding for two different proteins
- Two RNA will be produced simultaneously, complementary to
each other - Formation of double-helical RNA
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
If both strands are copied during transcription, then two complementary helical RNAs are produced simultaneously that might code for different proteins.
They would have the tendency to form double-stranded helical RNA resulting in non-translation of coded information into proteins.
The whole exercise of transcription would then appear futile. Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 42. Consider the following statements.
- RRNA provides the template for the synthesis of proteins.
- TRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
- RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and initiates transcription.
- A segment of DNAcoding for polypeptide is called intron.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 And 3
- 1 And 2
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 4
Answer: 4. 2 And 3
Statements 2 and 3 are correct as tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and initiates transcription.
Statements 1 and 4 are incorrect and can be corrected as mRNA provides a template for protein synthesis and a DNA segment that codes for proteins is called cistron or exon.
Question 43. Identify the correct statement.
- Transcription can only occur after
- Transcription and translation occur simultaneously in some organisms
- Translation occurs before transcription
- Transcription and translation are alternative terms for the same process
Answer: 2. Transcription and translation occur simultaneously in some organisms
The statement in the option is correct as transcription and translation occur simultaneously in some bacteria and eukaryotes.
Rest statements are incorrect. Transcription occurs before translation in most eukaryotes.
Transcription involves mRNA formation whereas translation involves protein synthesis.
Question 44. Consider the following statements.
- The primary transcript produced in eukaryotes is translated without undergoing any modification or processing.
- The hnRNA in humans has exons and introns.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct.
Incorrect statements can be corrected as the primary transcript in eukaryotes undergoes post-transcriptional processing to form functional mRNA.
This includes capping at 5′ end, tailing at 3′ end, and splicing.
The primary mRNA transcript is longer and localized into the nucleus, where it is also called heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA) or pre-mRNA. It has both exons and introns.
