Chapter 1 Concerns About Our Environment Broad Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is good fuel?
Answer:
Good fuel: Good fuel should have many desirable characteristics. Some of these are as follows:
- It should produce a high amount of energy for each limit of mass or volume.
- It should be easily available and should be easy to transport.
- It should be economical.
Question 2. What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Answer:
The advantages of nuclear energy
The advantages of nuclear energy are as follows: A small amount of radioactive material can generate a huge amount of energy. It does not produce air pollution. A nuclear power plant is more efficient than other power plants.
Question 3. Hydrogen has been used as a rocket fuel would you consider it a cleaner fuel than LPG? Why and why not?
Answer:
Hydrogen is a much cleaner energy source than CNG. CNG is derived from biomass and hence burning the CNG causes air pollution, although on a much smaller scale than coal and petroleum. The use of hydrogen as an energy source does not pollute gases.

Question 4. Can any source of energy be pollution free? Why and why not?
Answer:
Many sources of energy can be pollution free when the burning of biomass is not involved in the production of energy, then there is no chance of pollution. For example, wind energy, solar energy, hydel energy, etc are pollution free.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 1 long answer questions, Concerns About Our Environment”
Question 5. What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Answer:
Limitations of energy that can be obtained from the oceans:
These forms of energy can be used only in coastal areas, which would leave a vast portion of human habitation. The technologies for using these energies are still at the experimental stage and hence are very costly and less efficient.
Question 6. Why are looking for an alternate source of energy?
Answer:
Because of the growing population, the energy demand is rising. Fossil fuels are going to be exhausted in the near future and burning them is causing air pollution. Hence, we need to find an alternate source of energy which renewable and environmentally friendly.
Question 7. How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Answer:
- Before the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, wind and water energy were used for serving many purposes but the ways of their use were not efficient. For example, windmills were used to power smaller mills like flour mills or sawmills.
- The flow of water was used for transporting wooden logs. Now a day, both wind energy and water energy are being widely used to produce electricity, which means better and more efficient use of these forms of energy.
Question 8. What kind of mirror, concave or convex, or plain would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Answer:
Explanation: A concave mirror is best suited for use in a solar cooker. The reason for this is the ability of a concave mirror to converge the solar energy at a point. This enables the concave mirror to produce a larger amount of heat compared to other types of mirrors.
Question 9. Short Note-Ozone Layer.
Answer:
-Ozone Layer:
- The ozone layer is contained within the stratosphere. In this layer, ozone concentrations are about 2 to 8 parts per million which is much higher than in the lower atmosphere but very small compared to the main components of the atmosphere.
- It is mainly located in the lower portion of the stratosphere from about 15:35 km though the thickness varies seasonally and geographically. About 90% of the ozone in the Earth’s atmosphere is contained in the atmosphere.
Question 10. What is ultraviolet light? How can the ozone Layer deplete?
Answer:
Ultraviolet light:
Although the concentration of ozone in the ozone layer is very small. It absorbs biologically harmful ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun: Extremely short or vacuum UV is screened out by nitrogen. UV radiation is capable of penetrating nitrogen.
- The Ozone layer can be depleted by free radical catalysts including nitric oxide, hydroxyl, atomic chlorine, and atomic bromine. While there are natural sources for all of these species.
- The concentrations of chlorine and bromine increased markedly in recent decades due to the release of large quantities of man-made organohalogen compounds, especially chloroform carbons, and bromoform carbons.
Question 11. Short Note-Exosphere.
Answer:
Exosphere: The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from the exobase, Which is Located at the top of the Thermosphere at an altitude of about 700 km. above sea level, to about 10,000 km.
The exosphere merges with the emptiness of outer space, where there is no atmosphere. This layer is mainly composed of extreme hydrogen, helium, and several heavier molecules including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide closer to the exobase.
Question 12. Draw a diagram of a solar cell.
Answer:
Diagram of a solar cell
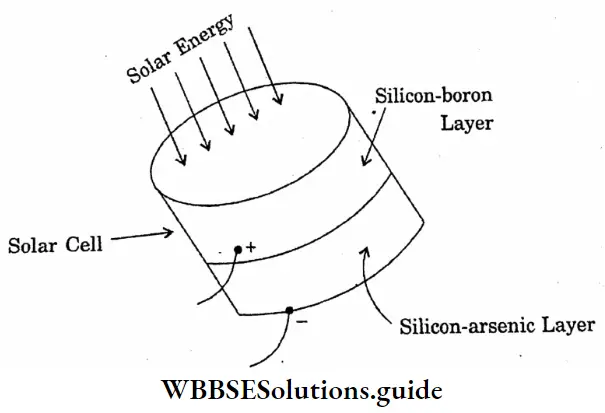
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 1 long answer questions, Concerns About Our Environment study material”
Question 13. Short Note. Thermosphere.
Answer:
Thermosphere:
The thermosphere is the second highest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It extends from the Mesopause at an altitude of about 80 km. upto the thermopause at an altitude range of 500-1000km.
- The height of the thermopause varies considerably due to changes, in solar activity. This layer is completely cloudless and free of water vapor.
- However non-hydrometeorological phenomena such as aurora Borealis and aurora australis are occasionally seen in the thermosphere. The Internation Space Station orbits in this layer, between 320 and 380 km.
Question 14. Short Note-Mesosphere.
Answer:
Mesosphere:
The mesosphere is the third highest layer of Earth’s atmosphere, occupying the region above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere. It extends from the stratopause at an altitude of about 50 km. to the mesopause at 80-85 km above Sea level.
- Temperatures drop with increasing altitude to the mesopause that marks the top of this middle layer of the atmosphere. It is the coldest place on earth and has an average temperature around-85°C.
- The mesosphere is the layer where most meteors burn up upon the atmospheric entrance. It is too high above Earth to be accessible to aircraft and balloons and too low to permit orbital spacecraft. The mesosphere is mainly accessed by sounding rocks.
Question 15. Short Note-Stratosphere.
Answer:
Stratosphere :
The Stratosphere is the second lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It lies above the troposphere and is separated from it by the tropopause. This layer extends from the top of the troposphere at 12km about the earth’s surface to the stratopause at an altitude of about 50 to 55 km.
- The atmospheric pressure at the top of the stratopause is 1/1000 the pressure at sea level. It contains the ozone layer, which is the part of Earth’s atmosphere that contains relatively high concentrations of gas.
- The stratospheric temperature profile creates very stable atmospheric conditions, So The layer lacks the weather-producing air turbulence that is prevalent in the troposphere.
Question 16. Short Note-Green House Effect.
Answer:
Green House Effect: The earth’s atmosphere is transparent to the visible light and infrared radiations of short wavelengths coming from the sun.
- The high-energy radiations (gamma rays. X-rays, Ultraviolet rays) are absorbed by the ozone layer while the low-energy radiations (infrared radiation) of long wavelengths and radiowaves are reflected back into space by the ionosphere.
- The solar radiations which pass through the atmosphere of the earth are absorbed by the clouds, earth, surface, and seawater due to which the earth’s surface gets heated up.
- Now earth’s surface radiates infrared radiations of long wavelengths, but these radiations are reflected back by the clouds and absorbed by the gases present in the atmosphere of the earth and thus the clouds and gases prevent them from escaping into space. Thus keeping the earth’s atmosphere warm.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 1, Concerns About Our Environment long answer solutions”
“WBBSE Class 10 Concerns About Our Environment long answer questions, Physical Science Chapter 1”
Question 17. Briefly describe the thermal power plant.
Answer:
Thermal power plant :
A power plant in which the heat required to make steam to drive turbines is obtained by burning fuels is called a thermal power plant.
- Coal is burned in a furnace F to produce heat. This heat boils the water in a boiler B to form steam.
- The steam formed from the boiling water builds up. a pressure. The hot steam at high pressure is introduced into turbine chamber C having a steam (Picture) turbine T, The steam passes over the blades of the turbine as a high-pressure jet making the turbine rotate.
- The shaft S on cooling, stem condenses to form water. This water is again sent to the boiler to form fresh steam. The process is repeated again and again.
- Since it is easier to transmit electricity over long distances than to carry coal over the same distance, therefore, many thermal power plants are established near coal fields.
- We produce a major part of our electricity by burning fossil fuels. Due to this, large amounts of fossil fuels are being burnt every day at thermal power plants to generate electricity.
- Because our supplies of coal, oil, and gas are running out at a rapid rate and because of the pollution caused by burning fossil fuels, other ways of generating electricity must be found.
- Please note that electricity is not fuel. It is a form of energy. At thermal power plants. It is the chemical energy of fossil fuels that is transformed into electrical energy.
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 1, Concerns About Our Environment detailed answers”
Question 18. What is the cause of global warming? What are the effects of global warming? Write the advantages of generating hydroelectricity.
Answer:
The cause of global warming :
- The concentration of chlorofluorocarbons has increased by 5% per year.
- The concentration of methane has doubled due to agricultural sources (vice cultivation, animal husbandry, natural gas exploration, burning of biogas)
- The concentration of carbon dioxide has increased up to 25% due to industrial growth, combustion of fossil fuel, and clearing of forests.
The effect of global warming :
- It will increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events (floods, droughts, heat waves, hurricanes) because of changes in the pattern of winds and ocean currents.
- It will result in low agricultural yield.
The advantages of Generating Hydroelectricity?
- The generation of electricity from flowing water does not produce any environmental pollution.
- The construction of dams on rivers helps in controlling floods, and in irrigation.
- Flowing water is a renewable source of electric energy that will never get exhausted.
