Group A Write The Correct Answer From The Given Alternatives:
Question 1. The gorge formed in the arid regions is called as
- Canyon
- V-Shaped valley
- Potholes
- Dhand
Answer: 1. Canyon
Question 2. Bird-foot delta is formed at the mouth of
- River Nile
- Hwang Ho
- Indus river
- Mississippi-Missouri river
Answer: 4. Mississippi-Missouri River
Question 3. The Meteors that come towards the earth get burnt in the layer of
- Ionosphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Exosphere
Answer: 3. Mesosphere
Read and Learn also WBBSE Madhyamik Model Question Paper 2023 Geography And Environment
Question 4. A Tornado, the most destructive cyclone of the world is also called in the USA as
- Cyclone
- Twister
- Typhoon
- Hurricane
Answer: 2. Twister

Question 5. The merging of the cold Labrador current and warm Gulf Stream current creates dense fogs and stormy weather conditions along
- New found land Coast
- Guinea Coast
- Florida Cost
- Peru Coast
Answer: 1. Newfoundland coast
Question 6. On the days of Neap Tides, the sun and the moon are at the following angles to each other in respect of the earth
- 180°
- 360°
- 90°
- 120°
Answer: 3. 90°
Question 7. The following waste material is non-biodegradable by its nature
- Plastic wastes
- Synthetic rubber wastes
- Aluminium sheet
- All are applicable
Answer: 4. All are applicable
WBBSE Madhyamik Geography Model Question Paper 2023 Set 2 PDF Download
Question 8. The Telangana State was formed by separation from
- Madhya Pradesh
- Andhra Pradesh
- Bihar
- Uttar Pradesh
Answer: 2. Andhra Pradesh
Question 9. The plain, which is formed along the foothills of Siwalik Himalaya by the deposition of small rock fragments is called as
- Khadar
- Bhangar
- Bhavan
- Bet
Answer: 3. Bhavan
Question 10. An example of one salt lake in India is
- Pangong lake
- Bhimtal
- Dal lake
- Loktak lake
Answer: 1. Pangong lake
Question 11. The Laterite soil is found in the region of
- Ganga plain
- The western slope of western Ghat
- Sundarban
- Desert region
Answer: 2. Western slope of western ghat
Question 12. Wheat is a
- Rabi crop
- Kharif crop
- Zaidcrop
- Beverage crop
Answer: 1. Rabi crop
Question 13. The proposed fastest National Highway, which will connect Srinagar in the North with Kanyakumari in the South is called as
- The East-West Corridor
- The Golden Quadrilateral
- The North-South Corridor
- The North Central Corridor
Answer: 3. The North-South Corridor
Question 14. The Satellite sent by India is
- IRS
- LANDSAT
- SPOT
- Station
Answer: 1. IRS
Group B If The Statement Is True, Write ‘True’ And If False, Write ‘False’ Against The Following (Answer Any Six Statements):
Question 1. Potholes are formed at the base of the waterfall.
Answer: False
Question 2. The air pressure is measured by the help of Fortin’s Barometer.
Answer: True
Question 3. Changes of seasons is observed in the Equatorial region.
Answer: False
Question 4. The drought conditions develop in the western coast of South America due to the influence of El Nino of the Pacific Ocean.
Answer: False
Question 5. Tropical Evergreen forests are found in the states of Bihar and Chhattisgarh.
Answer: False
Question 6. Petrochemical Industry is called as “Modern Industrial Giant”.
Answer: True
Question 7. ‘Platform’ is the place in space where the Satellites are installed.
Answer: True
West Bengal Madhyamik 2023 Geography and Environment Set 2 Question Paper with Solutions
Fill In The Blanks With Suitable Words (Answer Any Six):
Question 1. According to the name of ______ river, the zigzag course of a river is known as a meander.
Answer: Meanders
Question 2. Horizontal and Parallel cracks or fractures found on the surface of a glacier are called ______.
Answer: Crevasse
Question 3. Temperature increases with the increase of altitude in the atmosphere is called ______.
Answer: Inversion of temperature
Question 4. During high tide, huge tidal waves entering through the mouth of a river from the sea are called as _____.
Answer: Tidal bore
Question 5. The wastes which after decomposition mix with air, water and soil are called as ______.
Answer: Biodegradable wastes
Question 6. ______ is the highest part of the Meghalaya Plateau.
Answer: Shillong
Question 7. According to the 2011 census, the percentage of literacy rate in India is ______.
Answer: 74.04
Madhyamik Geography and Environment Model Paper 2023 Set 2 Free Download
Answer In One Or Two Words (Any Six):
Question 1. What is the name of the Sandy desert in the Sahara?
Answer: Erg
Question 2. In which layer of the atmosphere jet plane flies?
Answer: Stratosphere
Question 3. What is the main food of marine fish?
Answer: Plankton
Question 4. Name one radioactive waste.
Answer: Uranium, Plutonium, Thorium.
Question 5. Which one is the longest river of South India?
Answer: Godavari
Question 6. In which forest of India lion is found?
Answer: Gir Forest in Gujarat
Question 7. Name the common multipurpose river valley project of the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal.
Answer: Damodar Valley Project
Question 8.In which type of map, relief is shown by contour lines?
Answer: Topographical maps
madhyamik physical science question paper 2024
Match The Left Column With The Right Column:
Left column Right column
Tal 1. Coffee Research Centre
Jhum Cultivation 2. Diesel Rail Engine
Chikmagalur 3. Lakes in Western Himalayas
Benaras 4. Soil erosion
Answer:
Tal: 3. Lakes in Western Himalayas
Jhum Cultivation: 4. Soil erosion
Chikmagalur: 1. Coffee Research Centre
Benaras: 2. Diesel Rail Engine
Group C Answer The Following Questions In Brief (Alternatives Should Be Noted):
Question 1. How are the “deflation hollows” formed?
Answer: ‘Deflation hollows’ or deflation basins are formed by sweeping away of loose, light and dry sand particles by wind. They are also known as ‘desert hollows’ or ‘blow-outs’.
Or, What is Iceberg?
Answer:
Iceberg: Huge blocks of ice that break off from glaciers and fall into the sea are called icebergs.
Question 2. What is ‘Chinook’?
Answer:
Chinook: Chinook is a warm, dry, gusty wind blowing down the Rocky mountains by the eastern slopes into the western prairies.
Or, What is the apogean tide?
Answer:
Apogean tide: When the moon is farthest from the earth (4,03,320 km), this position is known as Apogee. Due to the reduced attraction of the moon, the tide is also 20% less high. This is known as Apogean tide.
Question 3. How is the segregation of waste materials done?
Answer:
The separation of wastes at the source of the collection is known as the segregation of wastes. This reduces the cost of transportation, and energy and helps in acquiring organic stock for energy generation. Wastes may be categorised as:
1. Bio-degradable: Kitchen wastes, garden trimmings, paper, etc.
2. Non-biodegradable: Plastics, glass, old medicines, containers, etc.
Or, What do you mean by ‘Recycling the waste’?
Answer:
Waste Recycling: The method by which old items are used once again to produce the same item is called recycling. Ex-paper, glass, plastic, metals, etc. But the materials produced after recycling are lesser in amount than the initial waste material used.
Question 4. Mention two purposes of rainwater harvesting.
Answer:
Two purposes of rainwater harvesting are:
1. It provides an independent water supply during regional water restrictions or droughts.
2. It can mitigate flooding of lowlands.
Question 5. State the importance of terrace cultivation.
Answer:
Importance of terrace cultivation
Terrace cultivation, is a method of growing crops on the sides of hills or mountains by planting on graduated terraces built into the slope.
Or, What is Sustainable development?
Answer:
Sustainable development: Sustainable development refers to the process of meeting human development goals while sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide resources and services upon which the economy and society depend. It is the organising principle for sustaining finite resources necessary to provide for the needs of future generations.
Question 6. What is meant by satellite Imagery?
Answer:
Satellite imagery: The images prepared by information sent by the satellites are called satellite imagery. These are prepared by reading and representing the signals sent by the satellites with the help of high technological know-how.
Or, Define a topographical Map.
Answer:
Topographical map: The map that represents the physical as well as cultural features of a place at a time with the help of certain colours and conventional symbols, is called a topographical map.
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Sample Paper 2023 Set 2 with Answers
Group D Give a brief explanatory answer to the following (Alternatives should be noted):
Question 1. Explain why a delta is formed at the mouth of a river.
Answer:
Formation of Delta: The velocity of the river is almost nil where it meets with the sea. Thus, the heaviest amount of depositions occurs here. The main channel is broken into numerous distributaries as more and more depositions take place. The region acquires a triangular shape and looks like the Greek letter Delta, hence the name.
Or, Why does temperature decrease with the increase of altitude in the Troposphere?
Answer:
Atmospheric temperature decreases with an increase in altitude for the following reasons:
1. Insolation first heats up the earth’s surface. This heat is radiated into the atmosphere, gradually heating the layers from bottom to top.
2. The upper layers of the atmosphere are less dense and can rapidly radiate out heat and get cooled.
3. Pressure is less in the upper levels of the air, hence their heat absorbing capacity is also less.
Question 2. What are the methods of controlling gaseous waste material?
Answer:
Method to control gaseous waste: Wet scrubbing is a method of using a liquid to remove solid, liquid or gaseous wastes and pollutants. The scrubbing liquid is sprayed into the disposed of gas in a spray chamber. Contact with the spray liquid removes the particulate pollutants of the gas. Dry scrubbing is also a popular method.
Or, How are the reduction of waste made?
Answer:
Methods of waste management:
1. Reduction: This is a process of waste minimisation at the source itself, and elimination of harmful and persistent wastes. This involves re-designing of products in order to reduce the production of waste at home, work or other places.
2. Reuse: To reuse is to use an item again after it has been used before. Reuse helps to save time, money, energy and resources. E.g. Packing boxes, gift wrappers, toys, etc.
3. Recycling: Recycling is processing used materials into new, useful products. It helps to save raw materials, energy and money and controls pollution and environmental degradation. E.g. Newspapers, iron items, etc.
Question 3. What do you mean by the ‘Modern Communication System’?
Answer:
Modern Communication System
Communication is the exchange of ideas, information, messages and feelings between people, without any physical movement of people concerned and the system that enables this is called the modern communication system. It can be divided into three parts.
1. Collection of information and messages to be communicated (input).
2. Medium through which the messages will be communicated (through-put).
3. Communicating or enabling the messages to reach successfully (output).
Question 4. What are the differences between Topographical Map and Satellite Imagery?
Answer:
The differences between Topographical Map and Satellite Imagery
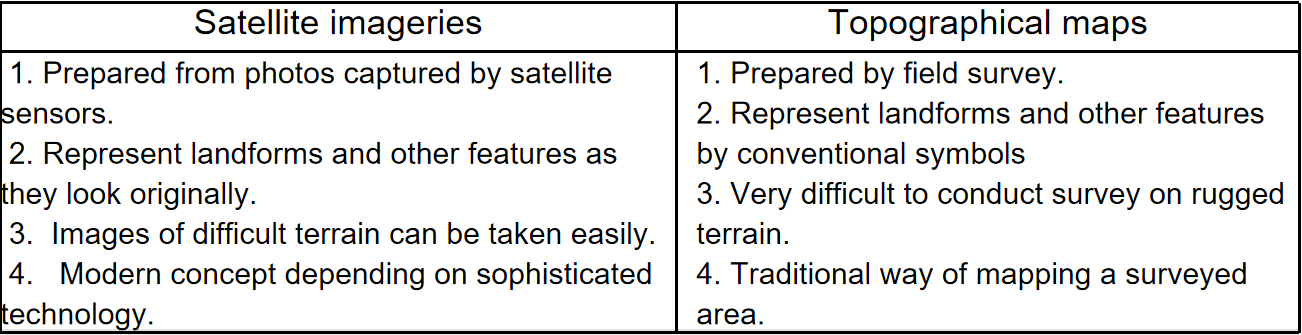
Or, State three uses of Topographical Map.
Answer:
Characteristics of Topographical Map:
1. The topo sheets are prepared to precise scales. Hence location or size of objects can be represented accurately.
2. Relief and landforms can be represented by spot heights accurately.
3. The accurate representation of drainage lines helps to understand the drainage pattern and nature of drainage.
4. Representation of settlements, transport system, etc. helps to understand the economic condition of the region.
Group E Answer Any Two Questions From The Following:
Question 1. Describe with sketches the major landforms produced by fluvioglacial deposition.
Answer:
The landforms formed by glacial deposition are:

1. Moraines: Any landform formed by depositions of the valley and continental glaciers is called a moraine. The moraines can be mainly of three types:
(1)Moraines deposited alongside of glacial valley floor are called lateral moraines,
(2)Where two lateral moraines of adjacent glaciers combine, the deposition lying in the middle of the main glacier is called medial moraine,
(3)Moraines deposited at the end of a glacier are called terminal or end moraines.
2. Eskers: Long ridges of material deposited parallel to the direction of the flow of glacial melt water are called eskers. glacial meltwater is called eskers.
3. Erratics: These are depositions of boulders and rock fragments in an area where they are a total mismatch with the surroundings.
4. Drumlins: These are low elongated hills formed by glacial deposits. They are called ‘basket of eggs’ topography.

Question 2. Explain with sketches the origin and direction of planetary winds of the world.
Answer:
Orographic or Relief rain: When clouds on their way dash against hills, plateaus, etc., they rise up. Higher up the clouds condense and then rain falls on the slopes of the mountain and the plateaus. When it goes to the other (opposite) side of the hills, plateaus, etc., it is left with little water vapour.

Therefore, the rainfall is much less on the opposite side. This type of rain is called relief rain as it is caused mainly due to the relief of the land. The opposite side of the hill where the rainfall is much less is called the rain shadow area. The Deccan plateau is an example of a rain-shadow region in India. Orographic or Relief rain.
Question 3. Discuss the major characteristic features of Tropical Monsoon climatic regions.
Answer:
The word monsoon is derived from the Arabic word Muslim meaning season. The monsoon wind is a seasonal wing as it is very much associated with rain, it invariably means the rainy season.
Characteristics of this climatic region are stated below:
1. The monsoon winds change their direction according to seasons (in summer and in winter).
2. The summer monsoons bring rains as they come from the seas winter, monsoons remain rainless as they generally blow from the land.
3. Summers are hot and wet, and winters are pleasantly warm and almost rainless.
4. The summer temperature ranges between 27°C and 32°C.
5. The winter temperature varies between 13°C and 22°C.
6. The range of temperature between day and night, and between summer and winter is considerably wide; it is about 10°C to 15°C.
7. The rains come in the latter half of summer.
8. The amount of rainfall varies from place to place according to landform features. Generally, this region has an average rainfall between 100 cm and 200 cm.
Question 4. Explain the factors responsible for the origin of ocean currents.
Answer:
Causes of Origin of Ocean Currents: The main causes of the origin of ocean currents are:
1. Prevailing winds: The planetary winds or prevailing winds push the surface layers of the ocean water in front of them in a constant flow. If due to seasonal changes, the direction of the wind is changed, the currents also have a similar change in their direction. In Tropical areas, the equatorial currents moving along with trade winds move from east to west. In Temperate regions, westerlies drive the seawater from west to east.
2. Difference in temperature: Temperature is low at the poles and high at the equator. The polar water is cool and becomes heavy and sinks. The equatorial water is warm, light and floats. This creates a convectional current and the polar water moves towards the equator and vice versa.
3. Difference in salinity: The salinity of ocean water varies from place to place. Water of high salinity is denser than water of low salinity. Hence, water of high salinity flows on the surface while the water of high salinity flows at the bottom of the oceans.
4. Rotation of the earth: The rotation of the earth generates a centrifugal force, which causes the generation of currents in the ocean water.
5. Shape of coasts: The shape and direction of the coasts of the landmasses also change the direction of the currents.
6. Centrifugal force: The centrifugal force of the earth is greater at the equator than at the poles. Hence, water currents move from the equatorial region to the poles.
7. Evaporation and rainfall: Evaporation decreases the water level and increases salinity while rainfall increases the water level and decreases salinity. This influences the flow of ocean currents.
8. Melting of ice: The melting of ice raises the sea level and reduces salinity, influencing ocean currents.
West Bengal Board Madhyamik Geography 2023 Set 2 Previous Year Paper
Question 5. Give a brief account of the physiography of Western Himalayas of India.
Answer:
Physiography of Western Himalaya: According to SirS. Burrard, the Himalayas are generally regarded as consisting of the following four main sections which are separated from one another by the gorges of rivers which pass through them:
(1)The Punjab HimalayasThis section between the Indus and the Sutlej is known as the Punjab Himalayas. It is also called Jammu-Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh Himalaya because most of this section is located in these two states. This section is 560 kilometres long. The important ranges of this section are the Ladakh, the Pir Panjal, the Dhaoladhar and the Zanskar. The Zoji La pass is at an altitude of 3,444 metres above the sea-level.
(2)The Kumaon Himalayas This section runs for a distance of 320 kilometres between the Satluj and the Kali rivers. This is higher than the Punjab Himalayas. Great rivers like Ganga and Yamuna have their sources in the Kumaon Himalayas.
(3)The Upper HimalayasThis is situated between the Kali and the Tista rivers and is 800 kilometres long. This is the highest part of the Himalayas where lofty peaks like the Mt. Everest, the Kanchenjungha, the Dhaulagiri, the Annapurna, the Makalu, etc. are located. The flat Kathmandu valley is also situated in the Nepal Himalayas.
(4)The Assam HimalayasIt extends for a distance of 720 kilometres between the Tista and the Dihang (Tsangpo-Brahmaputra).
Question 6. Describe the favourable physical conditions required for cultivation of cotton in India.
Answer:
The favourable conditions for growing cotton are:
Geographical:
1. Temperature: 23° – 32°C with an average around 27°C.
2. Sunshine: Plenty of sunshine during the growing period and cooler conditions during harvest.
3. Rainfall: 50-80 cm of rainfall well-distributed during the growing period. But rainfall is injurious after the budding period.
4. Frost: At least 200 frost-free days are required.
5. Soil: Black cotton soil or regular soil is the best for cotton.
6. Land: Flat or undulating land with good drainage and no water logging is good for cotton.
Economic:
1. Labour: Much labour is required for planting, thinning of seedlings, hoeing, an inspection of pests, picking of balls, etc.
2. Transport: Good transport system helps in carrying raw cotton to factories and finished products to markets.
3. Fertilisers and pesticides: Cotton is highly soil-exhaustive. Hence fertilisers are necessary to maintain soil fertility. Pesticides are used to control pest attacks.
4. HYV: High yielding variety of seeds like MCU-4, MCU-5, Hybrid-4, Sujata, Varalaxmi, etc. help to raise the yield of cotton per hectare.
Madhyamik Geography and Environment Question Paper 2023 Set 2 in Bengali
Question 7. Explain the major factors responsible for the development of Iron and Steel industry in Eastern and Central India.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the development of the Iron and Steel Industry: Most of the iron and steel plants of India, such as Jamshedpur, Burnpur, Durgapur, Rourkela, Bhilai and Bokaro are located in Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Chattisgarh. The causes for the concentration of iron and steel plants in eastern India are:
1. Iron ore: About 80% of India’s iron ore is available in this region. The major mines are
(1) Noamundi, Guwa, Budaburu, Pansiraburu of Singhbhum district, Jharkhand,
(2) Gurumahishani, Badampahar, Sulaipat and Bonai of Mayurbhanj district and Bagiyaburu of Keonijhar district, Odisha.
2. Coal: About 97% of India’s coal is mined in this region. The steel plants of Kulti, Burnpur, and Durgapur get their coal from the mines in Raniganj and Asansol. The steel plants of Jamshedpur, Bokaro and Rourkela get their coal from Jharia, Bokaro, Ramgarh and Giridih in Jharkhand.
3. Other raw materials: Limestone, dolomite, manganese, etc. are collected from Kalahandi, Gangapur and Kara put of Odisha. Other raw materials like chromium, tungsten, nickel, etc. are easily collected from the Chotanagpur plateau.
Question 8. Discuss the causes of Urbanisation in India.
Answer:
Causes of Urbanisation in India: The different causes of urbanization in India are
1. Limited size of agricultural land: The limited size of agricultural land in India cannot provide employment to the whole rural population. Hence, unemployment, poverty and other problems push the rural population to the urban centres.
2. Change in thought: The mentality of rural people is also changing. They wish to settle in urban areas for educational facilities, trade, commerce, industrial jobs, etc.
3. Free lifestyle: Urban life is much more liberal and free from superstitions. Rural people thus tend to settle in urban areas.
4. Employment: The scope of employment is much higher and varied in urban areas. Hence, the rural population is attracted towards urban areas.
5. Entertainment: Urban areas have much more scope for entertainment and relaxation. This attracts much rural population.
