Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Rest And Motion
In our surroundings, we see some objects which do not change their positions with respect to time. They are called stationary objects or they are said to be at rest. Examples are our house, school, bank, post office, hills, trees, etc.
But moving vehicles, flying birds, walking people, falling raindrops, throwing balls, etc. occupy different positions at different instants of time in their immediate surroundings. The objects which change their positions with time are called moving objects or they are all in a state of motion.
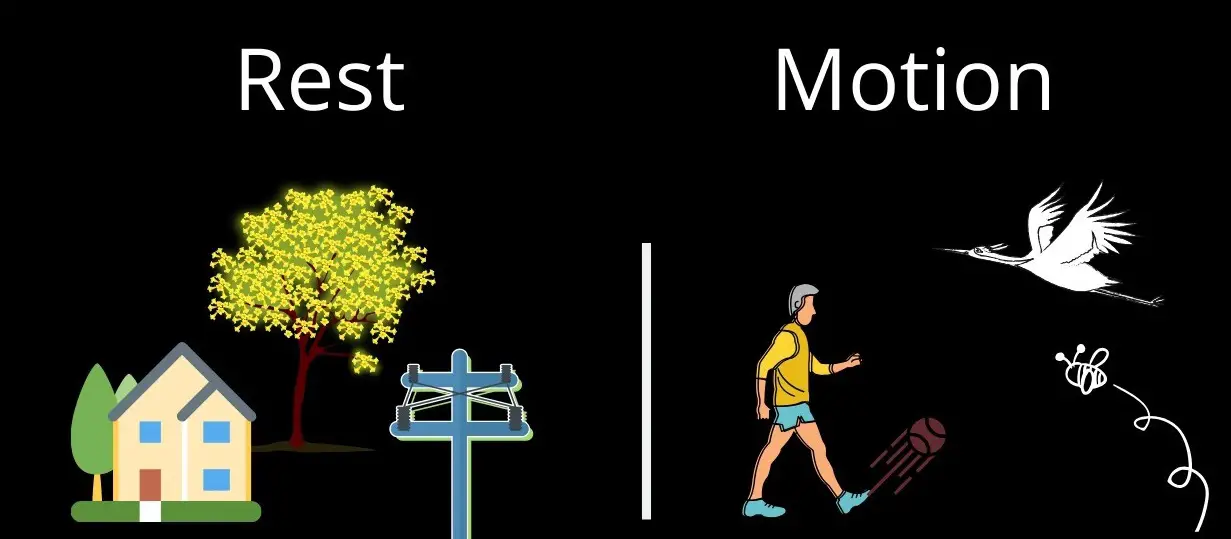

Do you know that the rest and motion of something is always measured relative to a stationary second object in its immediate surroundings. Here, the position of the second object is known as a reference point.
Suppose you are traveling in a train. If you consider the reference point inside the train, you will see other passengers, walls or floors of the train at rest.
But if the reference point is considered to be outside the train like a platform or ground, everything inside the train compartment appears to be moving along with the train.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 General Science and Environment
This is the reason why looking outside the window, the passengers observe that the trees, buildings, etc. are moving backward.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Force
Can you say why does a football moves when kicked? What makes a moving ball on the ground to stop on its own? What makes a spring to elongate or contract? What makes a sponge or ballon to get deformed? How does a body change its speed or its direction of motion?……..
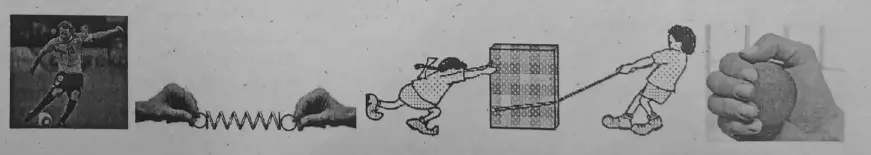
It is our common experience that an external force is a basic cause for all cases. For example-to run a cycle you are to apply a force by your leg on the pedal, you pull your drawer to open, you push your drawer to close, you push a heavy box to displace, you pull a box for displacing it across the ground, in a car the engine supplies a force by which the car moves, etc.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Effect Of Force
A force can be realized only by the effects that it can produce on an object.
Let us see the following examples:
1. Force produces motion in an object or stops motion.
By pushing a car or by pulling a trolley, the car or trolley starts to move. But a moving object can be brought to rest when a force is applied in the opposite direction of its motion.
For example-a, a moving cycle can be stopped by applying brakes.

Sometimes, the applied force is not enough to produce motion in a stationary object. If you push a wall of your classroom, it will not move.
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
2. Force can increase or decrease the speed of a moving object.
If you push a moving cycle from behind, it moves faster. But if you push the moving cycle from the opposite side, the cycle would start to slow down.
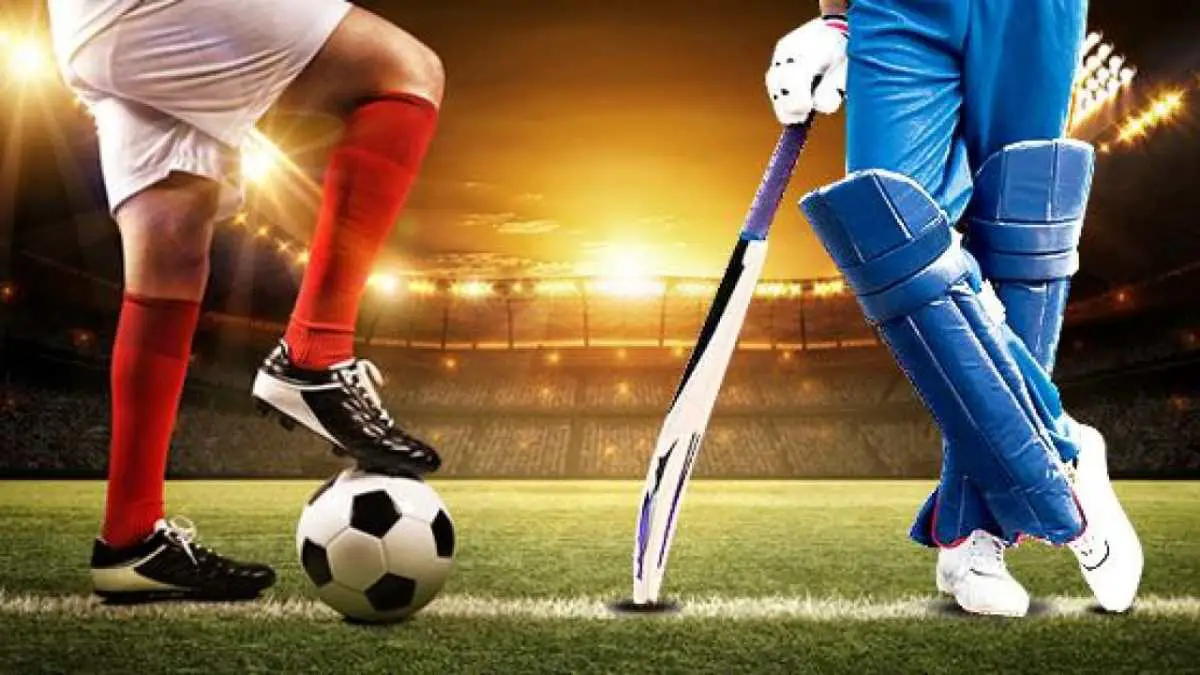

3. Force can change the direction of motion of a moving object.
A player can change the direction of a football by kicking or pushing. A batsman can also change the direction of a cricket ball by hitting with the bat.
4. Force can change the shape and size of an object.
A sponge or ballon or dough (flour mixed with water) or a tube of toothpaste when pressed a little gets deformed. The shape of a toothpaste tube changes on squeezing. The size of the spring gets elongated on pulling and contracted on squeezing.
So, force is the external cause acting on a body that changes or tends to change the state of rest or of motion, the direction of motion or the shape and size of the body.
In fact, force is the basic cause of motion.
Units of force :
The commonly used unit of force is kilogram-force (symbol kg).
The SI unit of force is Newton (symbol, N).
In the CGS system, the unit of force is dyne (symbol dyn).

Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Force Without Touch
In our daily life, we come across several cases of forces.
All forces are categorized into two groups:
- Contact forces and
- Non-contact forces or forces acting at a distance.
1. A force that is applied on an object by another object due to actual contact between the objects is termed as a contact force.
For example-kicking, a football, hitting a cricket ball with a bat, hammering a nail, writing with a pen, etc. are contact forces.
2. Non-contact forces come into play without any physical contact between the objects. This type of force act from a distance.
Examples are:
- Gravitational force.
- Electrical (or electrostatic) force.
- Magnetic force.
1. Gravitational force:
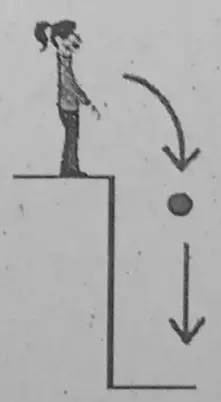
If you drop a stone from a certain height, it falls down. You know that the earth exerts pull (force) on the stone without touching it. In fact, the earth attracts everything towards its center.
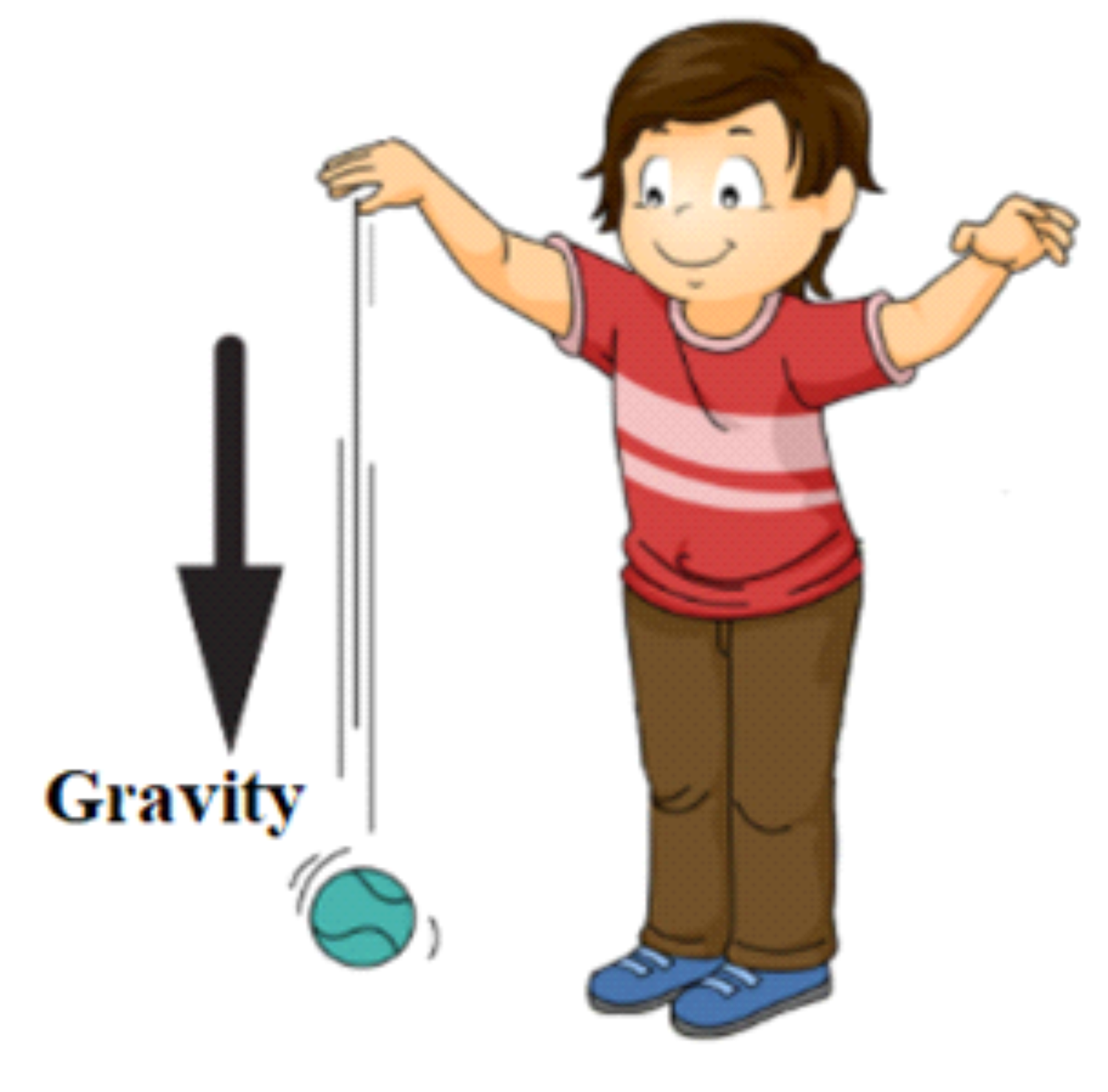
This force is called gravitational force. We call this force as the weight of the object. So, the SI unit of weight is the newton.
Do you know that the weight of an object can be measured with a spring balance?
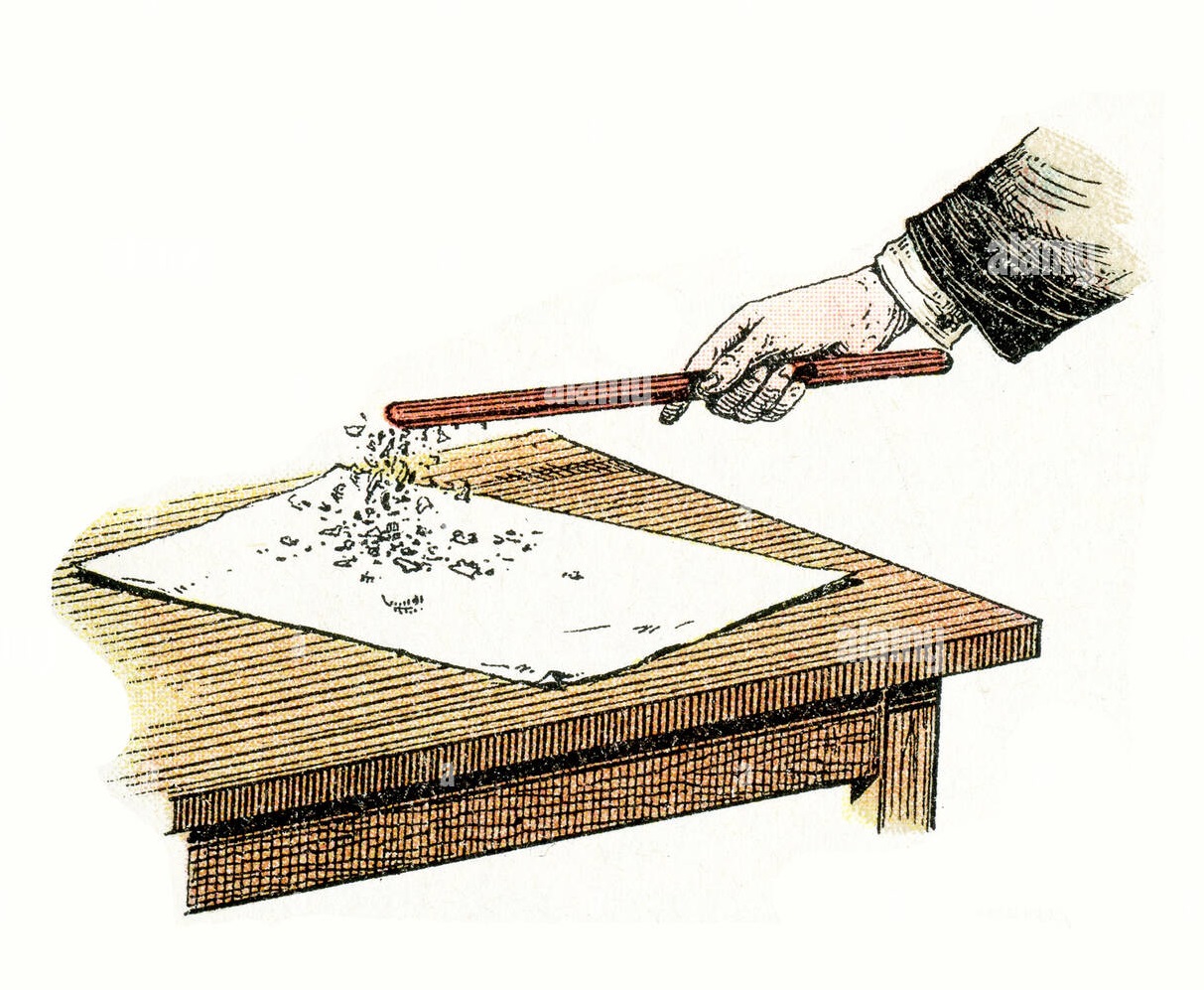
2. Electrostatic force:
Suppose you rub a plastic comb on your dry hair. Bring the comb near small pieces of paper. You will see that the papers are pulled towards the comb. Here also there is no actual contact between the comb and the papers.
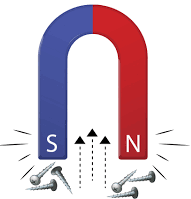
3. Magnetic force:
When you bring a bar magnet near some iron nails, then the nails are pulled toward the magnet. Here, the magnet itself applies a force on the nails.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Energy And Its Different Forms
After playing football for one half you get tired and take some rest. You are asked to say the reason of such tiredness. You will say that energy is spent from your body while doing work.
Do you feel the same tiredness if you do not work hard for a long time ?-Certainly not. When energy is spent from your body you lose the ability of doing work. So, it is rightly said that energy is the ability to do work.
We get energy from the food that we eat daily. A body which is able to do some work is said to possess some energy. This means that work and energy are closely related to each other.
Types of energy:
In nature, energy can be found in different forms.
The different forms are:
- Mechanical energy
- Heat energy
- Light energy
- Electrical energy
- Chemical energy
- Magnetic energy
- Sound energy
- Nuclear energy.
Do you know that this energy can neither be created nor destroyed? Only one form of energy can be transformed into other forms.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Mechanical Energy
It is the energy possessed by an object due to its state of rest or of motion.
This energy is of two types:
- Kinetic energy and
- Potential energy.
You must have an idea that an object in motion gains some ability to do work, and it is called its kinetic energy. On the other hand, an object by virtue of its position, configuration, and shape gains some ability to do work, and it is called its potential energy.

Let us explain the idea with some examples:
- You see that before taking a long jump (or high jump), an athlete brings his body in a state of motion by running for some distance. If he jumps standing at a point, he could not jump long. Actually, when the athlete runs, he gains an ability to jump by which he can jump a long distance due to his kinetic energy.
- A cricket ball at rest possesses no kinetic energy. But, a moving ball possesses kinetic energy due to its motion and blows the stationary stumps away.
- A bullet fired from a gun possesses kinetic energy due to its tremendous motion.
- Moving wind gains the ability to do work due to its motion. A boat with a sail moves forward due to the kinetic energy of the wind. Moving wind can run a windmill due to its kinetic energy.
- A hammer while coming down from a height acquires an ability to do work. Due to this ability, the hammer possesses kinetic energy and drives a nail into the wood on striking.
- See A book kept on a table at rest possesses potential energy due to its position. Here, ‘position’ refers to the height of the table top from the floor.
- see the normal state of the spring coil in a watch. When the coil is wound up, then potential energy is stored in it due to the change in its configuration.
- In the dotted line shows the normal position of a bow. When the bow is bent, then due to the change of shape of its different parts, potential energy is stored in it.



Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Transformation Of Energy
There are many examples of the transformation of energy.
- A ball lifted from the ground to a certain height has only potential energy due to its position. When the ball falls down, its potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases by the same amount. So it is an example of the transformation of potential energy into kinetic energy.
- A hammer raised at a certain height possesses potential energy. To drive a nail, when it is brought down then the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
- When a stretched bow is released as shown in the potential energy of the bow imparts kinetic energy to the arrow by which the arrow can move forward with high speed. So, this is an example of the conversion of potential energy into kinetic energy.
- As shown in a ball is placed on a spring and the ball kept at rest ball remains initially at rest. If the spring is compressed and released immediately, it is seen that the compressed, spring has acquired the ability to push the ball.


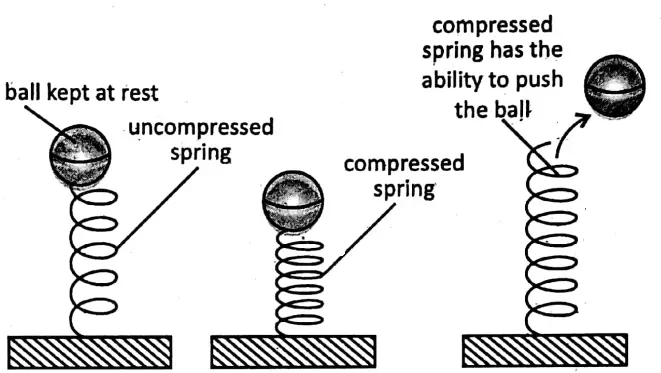
Here, the spring on compression gains potential energy which on being released is converted into the kinetic energy of the ball.
More examples:
- When you rub your palms, you feel hot. If you rub for a long time, you feel hotter. In this occasion, mechanical energy is converted into heat energy.
- When you play tabla or hit the drum with sticks, the sound is produced. So mechanical energy is converted into sound energy.
- Bring a magnet near a nail. You see the nail to move toward the magnet. In this case, magnetic energy (of the magnet) is converted into mechanical energy (or kinetic energy of the nail).
- 1. Switch on a bulb. 2. Switch on a fan. 3. Switch on an electric iron.
- In the first case, the bulb gives light. So electrical energy is transformed into light
energy. - In the second case, the fan starts moving, Here, electrical energy is transformed into mechanical energy.
- In the third case, the iron becomes hot. So in this occasion, electrical energy is transformed into heat energy.
- In an electric bell, when the switch is pressed current flows and electrical energy is converted into sound energy.
- In the explosion of crackers, its chemical energy is converted into light, sound, and heat energies.
- When you pour water into some quicklime taken in a pot, you watch that heat is produced. Here, the chemical energy of quicklime is transformed into heat energy.
- When coal burns, the chemical energy changes into heat energy.
- In a microphone, sound energy is transformed into electrical energy.
- In an electric cell, chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy.

Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Sources Of Energy
It is a common fact that from food we get energy for our daily activities. Broadly speaking, these food come from both plants and animals.
Plant sources: Rice, Dal, Vegetables, Fruits, etc.
Animal sources: Fish, Meat, eggs, Milk, etc.
We know that sun is the main source of energy on earth.
Green plants absorb solar energy and prepare food by the process of photosynthesis. So, plants convert solar energy into chemical energy in food. Animals get food from plants. As a whole, both plants and animals directly or indirectly depend on solar energy.
Coal, mineral, petroleum, etc. are produced by the conversion of plants and animals of an earlier age which remained buried for thousands of years under the earth. So, the chemical energy stored in coal or mineral is actually solar energy.
Water from ponds, rivers, and lakes is evaporated by means of solar heat and forms the clouds which provide rainfall on earth.
Accumulated rainwater in the mountain comes down with high speed by which the water turbine is rotated and in this way, hydroelectric power can be generated.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Concept Of Energy Flow
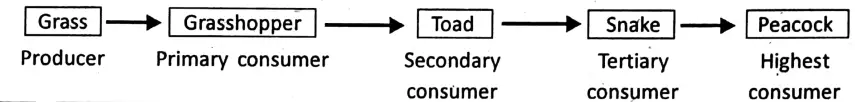
Green plants are able to prepare food. So, they are called producers. It is a fact that green plants maintain the ecosystem.
The organisms which feed on plants and plant products e.g. animals are called consumers.
The animals which live directly upon green plants are called primary consumers.
Example: Goat, Rabbit, Deer, Cow, etc. Primary consumers are herbivores.
Man is omnivores-because man eats both plants and animals and their products. The animals which eat primary consumers or herbivores are called secondary consumers.
Example: Frog (eats insects), Tiger (eats deer), etc.
The animals which eat secondary consumers are called tertiary consumers.
Example: Snake.
Food chain:
In nature, there is a predator-prey relationship of plants and animals in a chain-like structure. It is called a food chain.
Food web:
A food web consists of many food chains. It shows how different consumers are connected through different food chains. So, the food web can be considered as the natural interconnection of different food chains.
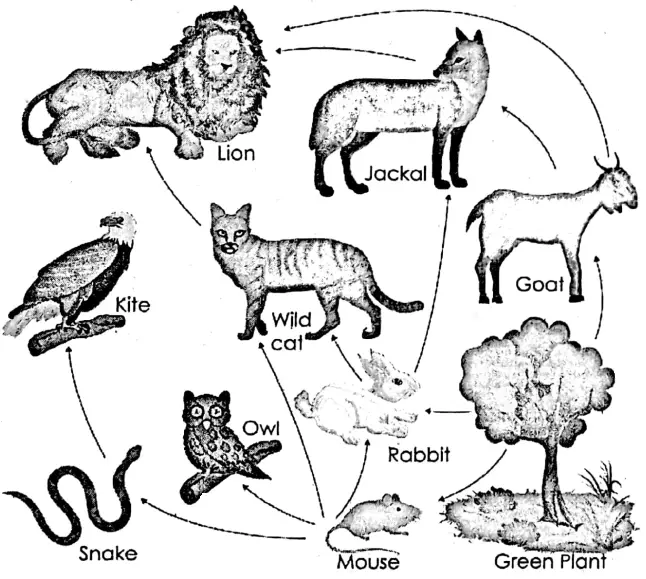
Examples of a food web
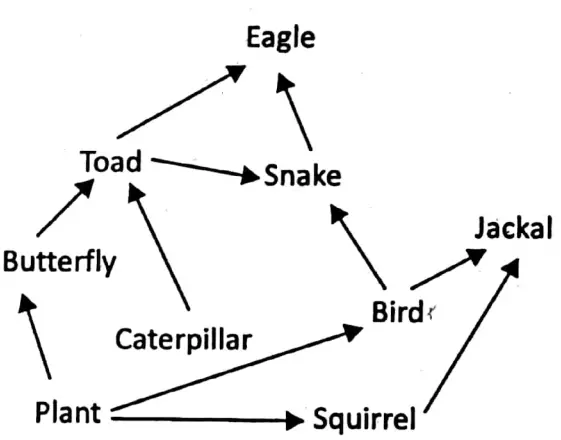
Food pyramid:
A food pyramid is a triangular diagram representing an arrangement of plants and animals of a food chain step by step from bottom to top. Each step in a food pyramid is known as the trophic level.
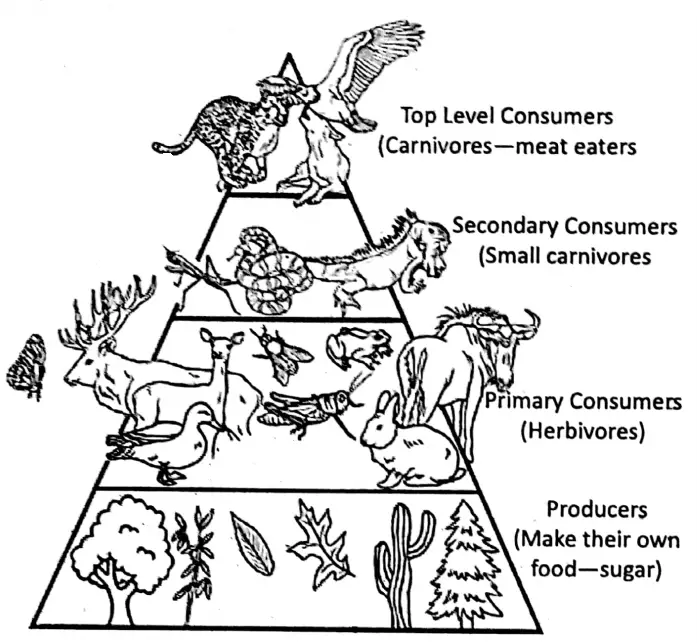
In general, the producers occupy the first step and gradually the next upper steps are occupied by the primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers respectively.
In regard of energy transfer from one step to another, Lindermann’s law of ten percent is very important.
According to this law:
About 10% of energy assimilated at each trophic level is needed for the building of body mass and the rest 90% of energy is consumed for metabolic activities.

Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Energy Crisis
Most of our energy requirements are met by the burning of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These are known as non-renewable sources of energy. These are being done so widely that in the coming days, we will face a crisis of energy.
Scientists have named such scarcity of energy sources as ‘energy crisis’. Do you know that 150 years ago the world population was approximately 100 crores; And, now it has become near about 600 crores? To fulfill the demands of such a huge population, we are using underground fossil fuels.
But their stock is limited. To overcome this situation, we are to be alert in using natural energies, side-by-side, to think about the use of non-conventional (or alternate) sources of energy such as solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, co-thermal energy, biomass energy, etc. These are renewable sources of energy.
Chapter 6 Primary Concept Of Force And Energy Frictional Force In Our Daily Life
We see that a ball moving on the grass gradually slows down and stops on its own after moving through a distance.
Why?
Certainly, there is an external force that opposes the motion of the moving ball occurring between two surfaces (One of the ball and another of grass) which are in contact with each other. This force is called the force of friction or simply frictional force. It is a contact force.
Does the ball travel more distance on the floor than over the grass?
Actually, the ball faces more obstruction while moving over the grass. That is, the frictional force depends on the smoothness or roughness of the two surfaces which are in contact with one another.
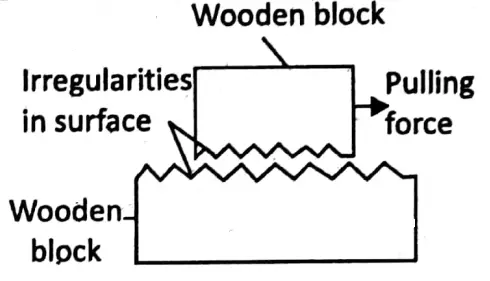
Any surface, however rough or smooth, has a lot of irregularities like hills and valleys when viewed through a microscope. When two such surfaces slide (or tend to slide) over one another, the irregularities are interlocked with each other.
This is the reason why frictional force acts in a direction opposite to the direction of motion.
WBBSE Notes For Class 6 General Science and Environment
-
- Chapter 1 Interdependence of Organisms and the Environment
- Chapter 2 Phenomena Around Us
- Chapter 3 Element, Compound and Mixture
- Chapter 4 Rocks and Minerals
- Chapter 5 Measurement
- Chapter 6 Primary Concept of Force and Energy
- Chapter 7 Statics and Dynamics of Fluid
- Chapter 8 The Human BodyChapter 9 Common Machines
- Chapter 10 Biodiversity and its Classification
- Chapter 11 Habits and Habitats of Some Important Animals
- Chapter 12 Waste Products
