Chapter 10 India – Location Of India And Political Divisions Introduction :
Our motherland India, the queen of all nations—is a vast country of the great geographical extent and it is full of diversities in physical as well as cultural features.
There are very few countries in the world that have such variety as in India. No country in the world has such a variety of topography, rivers, lakes, deserts, forests, and climate, all within the national boundary.
The variety of colors, religions, castes, races, and languages make India seem like a continent. So, it is often described as the ‘Sub-continent’. The history of ancient India is glorious. India is the land of the most ancient civilizations. India is also a land of natural as well as cultural heritage.
Its endless natural resources make our country unique. The present Indian Union became independent from the Yoke of British rule on 15th August 1947 and it is the world’s largest democratic country.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 Junior School Geography
Location Of India :
The location of India can be geographically described in three ways :
- According to latitudes and longitudes.
- According to distance from the sea and
- According to neighboring countries.
Location of India according to Latitudes and Longitudes :
Latitudinal Location :
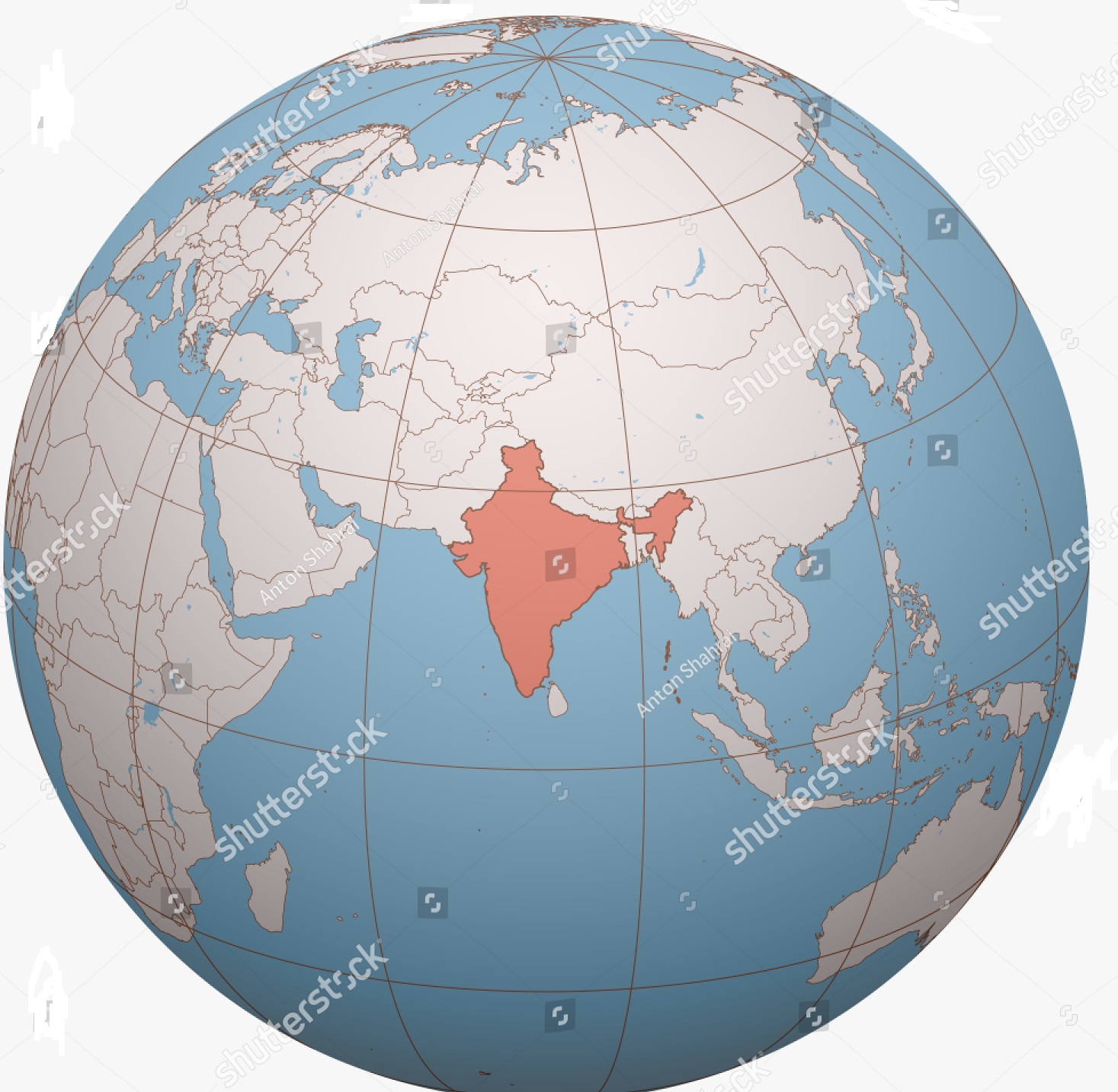
Latitudinally, India is located in Northern Hemisphere to the southern part of the continent of Asia. According to latitude, the mainland of India stretches from 8°04′ North latitude (Kanyakumari or Cape Comorin) in the south to 37°06′ North latitude (Indira col of Siachen glacier in the Northern extreme boundary of Kashmir) in the north.
The southernmost point of the Indian Union is ‘Indira Point’ (6°45′ North, previously known as ‘Persons Pygmillion point’) lying to the south of Car Nicobar Island.
Longitudinal Location :
Longitudinally, India lies in the Eastern Hemisphere. It stretches from 68o07′ East longitude (Guhar Moti in the Western extremity of Gujarat) in the west to 97°25′ East longitude (Kibitu in the eastern frontier of Arunachal Pradesh) in the East.
Location Of India According To Distance From The Sea:
India is located to the south of the continent of Asia and to the north of the Indian Ocean.
Ocean, seas, and bay surround India on three sides—
- Indian Ocean in the South, of Bengal an Sea in the West and
- Bay Land st in the South and East.
Lands surrounded by water on three sides is a ‘Peninsula’. Thus the southern portion of India is a peninsula.
Location Of India According To Neighboring Countries :
India is located to the south of China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the east of Pakistan, to the southeast of Afghanistan, to the west of Myanmar and Bangladesh. India is also located to the north of Srilanka and North- East of Maldives.
India at a glance :
- Official Name —Republic of India. India is the largest democratic country of the world.
- Rea —32,87,782 square kilometers.
- Areawise Rank in the world —Seventh (7th)
- The North-South extent of the Indian landmass —is 3214 km.
- The East-West extent of the Indian landmass —2933 km.
- Population —121,01,93,822 (2011)
- Population-wise Rank in the world —Second, next to China
- Literacy Rate —74-04%
- The total number of states —29*
- The total number of Union Territories —07*, including one National Capital Territory (Delhi).
- Largest State —Rajasthan.
- Smallest State —Goa.
- Largest Union Territory —Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Smallest Union Territory —Lakshadweep.
- Newly formed State —Telangana (from Andhra Pradesh)
- Highest populated State —Uttar Pradesh.
- Least populated state —Sikkim.
- Largest city of India —Mumbai.
- Capital of India —New Delhi.
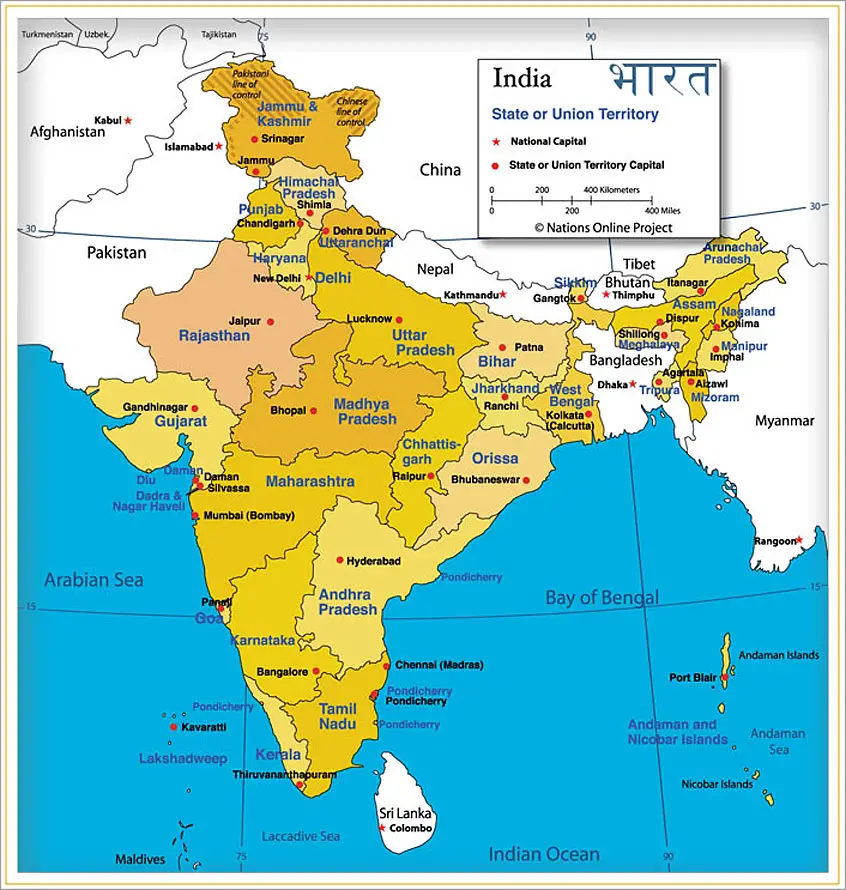
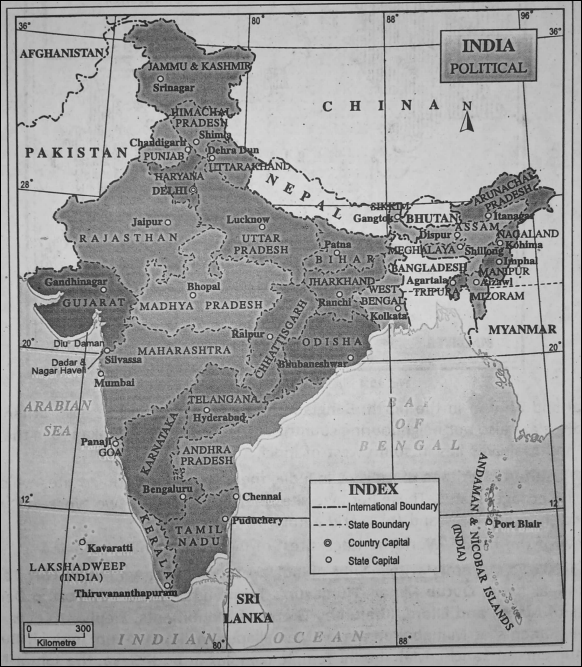
The States Of India And Their Capitals :
Before independence (15th August 1947) there were 562 princely states and 9 British provinces in India. After independence, India became a Republic on 26th January 1950.
The different states or provinces of India were demarcated or reorganized according to the recommendation of ‘The State Reorganisation Commission7 which was set up in 1953.
The process of reorganization of states has continued since 1st November 1956 based on some criteria. These were
- Language
- Culture
- Physical and Geographical similarities
- Administrative Efficiency and
- Economic Stability.
In India, at present, there are 29* states and 7* Union Territories (including one ‘National Capital Territory7, Delhi’).
A table is given below to show the Indian States, Union Territories and their capitals.
| State | Capital |
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | Hyderabad |
| 2. Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 3. Assam | Dispur |
| 4. Bihar | Patna |
| 5. Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| 6. Goa | Panaji |
| 7. Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| 8. Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 9. Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 10. Jammu and Kashmir* | Srinagar |
| 11. Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| 12. Karnataka | Bengaluru |
| 13. Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 14. Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| 15. Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| 16. Manipur | Impal |
| 17. Meghalaya | Shillong |
| 18. Mizoram | Aizawl |
| 19. Nagaland | Kohima |
| 20. Odisha | Bhubaneshwar |
| 21. Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 22. Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| 23. Sikkim | Gangtok |
| 24. Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 25. Telangana | Hyderabad |
| 26. Tripura | Agartala |
| 27. Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| 28. Uttarakhand | Dehra Dun |
| 29. West Bengal | Kolkata |
| Union Territories | Capital |
| 1. Andaman and Nicober | Port Blair |
| 2. Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli | Silvasa |
| 4. Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 5. Delhi | New Delhi |
| 6. Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| 7. Puducherry | Puducherry |
Recently (5th August 2019) according to the declaration of the Parliament of India, the State of Jammu and Kashmir is divided into two Union Territories—
- Jammu and Kashmir and
- Ladakh.
Constitution-recognized languages :
There are total 22 numbers of constitutionally recognized languages in India. These languages are
- Hindi
- Bengali
- Telegu
- Oriya
- Tamil
- Urdu
- Gujarati
- Malayalam
- Kannada
- Marathi
- Punjabi
- Assamese
- Kashmiri
- Sindhi
- Manipuri
- Nepali
- Boro
- Maithili
- Dogri
- Santhali
- Sanskrit
- Konkani.
Hindi is the official National Language of India. The common language of communication is English.
Neighbouring countries of India :
A person who dwells near another is called a ‘neighbour7. The adjoining countries or the countries lying near or beside a particular country are called ‘neighbouring countries.
Indian Union or the Republic of India is bordered by certain countries of the continent of Asia as well as the world. These countries lie in and around India and are called our neighbouring countries.
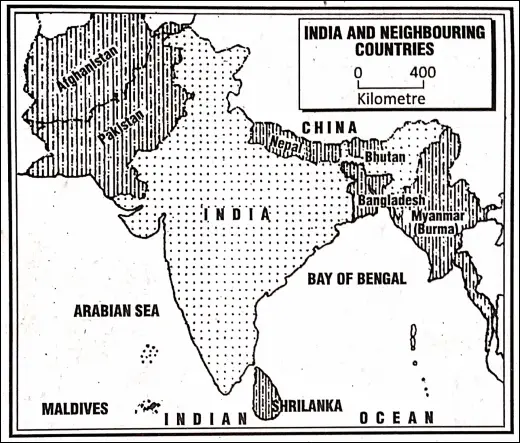
India’s neighboring countries that share common borders with it are Pakistan in the north-west, China, Nepal and Bhutan in the north, and Bangladesh and Myanmar in the east.
Srilanka and Maldives are also our neighboring countries lying as islands. Srilanka lies in the south¬east and Maldives lies in the southwest of India.
Cultural Heritage Of India :
In India, there are many heritage sites that have ‘World heritage’ status. These heritage sites may be divided as two types—
- World-cultural heritage sites and
- World-natural heritage sites.
A Few Of The Major ‘World Heritage Sites Of India Are Mentioned Below :
1. World Cultural Heritage Sites of India :
Taj Mahal at Agra, Agra-Fort, Fatehpur Sikri (near Agra), Qutub Minar, ‘Humayun’s Tomb’ (grave) and Red Fort in Delhi, the caves of Ajanta and Ellora, Khajuraho Group of Monuments, Elephant Caves, Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram or Mamallapuram, Konark-Sun Temple, Buddhist Monuments of Sanchi, Mahabodhi Temple complex at Bodh Gaya, the Jantar-Mantar of Jaipur and Hill forts of Rajasthan, Mountain Railways of India—Darjeeling.
2. World Natural Heritage Sites Of India :
India’s famous ‘World natural heritage’ sites are—The Sundarbans, The^anda Devi Peak and Sanctuary, Manas Wildlife Sanctuary, Kaziranga National Park (Reserve Forest),-Valley of flowers, Western Ghats, etc.
WBBSE Notes for Class 6 Junior School Geography
- Chapter 1 The Universe and Solar System
- Chapter 2 Shape of The Earth: Is The Earth Around?
- Chapter 3 Location of a Place on The Earth’ Surface: Where You Are
- Chapter 4 The Earth’s Motion: The Earth Rotation
- Chapter 5 Water – Land – Air
- Chapter 6 The Ice Capped Continent: Antartica
- Chapter 7 Weather And Climate
- Chapter 8 Air Pollution
- Chapter 9 Noise Pollution
- Chapter 10 India
