Chapter 11 Maps Introduction
Map:
Maps have become so much a part of our life that we cannot dispense with them. We often need them to find the location of a place. The most universal use of maps is for locating places and things.
If we do not know the right direction or the actual distance to reach a place where we want to go, a map can help us to capture all information available in that place making it easier to go to that place.
“WBBSE class 6 physical geography chapter 11 notes”
Maps can be and are of considerable use in planning the socio-economic development of a community, a region or a nation.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 Junior School Geography
Map :
The word ‘map’ was originated from the Latin word ‘mappa’ which means a napkin or cloth. In ancient times, maps were drawn on cloth, leather or in cottony paper.
A map is an accurate drawing or representation of the whole or part of the earth’s surface on a flat surface such as paper according to a given scale. A map is a representation of selected features of a part of the Earth’s surface.
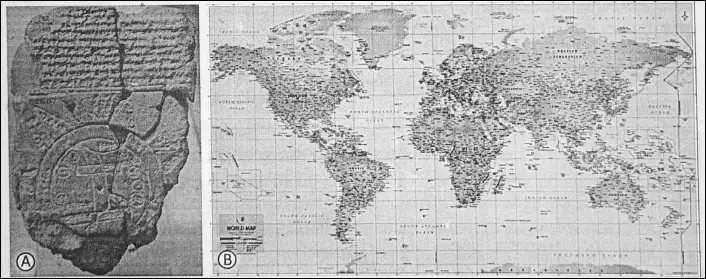
Maps are drawn to show the physical and cultural features of an area. A map gives us information about the places on the Earth’s surface in greater detail. Maps generally show the location of villages, cities, countries and continents.
“maps WBBSE class 6 geography notes”
Natural features like mountains, plateaus, plains, oceans, seas, lakes, rivers etc. are also indicated. Maps also indicate information about certain topics like temperature, rainfall, crops, minerals, industries, roadways, railways, population etc.
The most ancient map of the Earth was discovered in Babylon. This map was drawn on a terracotta plaque in 2500 B.C.
Main characteristics of a Map :
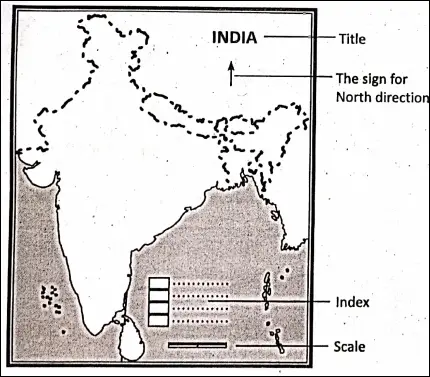
- A map is a representation of an area on a flat sheet of a paper.
- Maps are drawn on a definite scale. Without scale, a map is simply a rough sketch.
- Maps are drawn with the help of lines of latitude and lines of longitude.
- Maps have two dimensions-length and breadth.
- Conventional signs and symbols are used to show the various features of the earth’s surface.
- A map has an index which explains the symbols, colours and letters used in the map.
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
Importance of Map :
Maps are the major tools of geography. Maps serve as a key to geography. Maps are becoming useful in many fields-
- Maps are of vital importance for geographers.
- An easier way to get information about the earth is the map.
- The modern warfare has been guided by maps.
- Maps guide travellers and tourists to reach their destinations.
- Maps are necessary for administrators and politicians to run the state administration.
- Maps are useful for different means, of transportation as they guide the rail, road, sea and air routes.
- Maps are useful for students, teachers, industrialists, economists, historians, engineers and merchants.
- One can now produce a map sitting in a room by getting pictures from satellites through computers.
A map is therefore more widely used as a tool for learning geography.
Disadvantages of Map :
Maps North direction has a few disadvantages also. A flat map cannot show the features of a round surface accurately. The shapes and sizes of the continents and oceans get distorted, especially around the poles. Thus’ every map has some distortions.
The key elements of a map :
A perfect map should have the following elements or essentials :
Types of Map :
There are different types of maps.
Generally, maps are of the following types :
(1) Physical or Relief map :
Maps showing natural features of the earth such as mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, forests etc. are called ‘physical’ or ‘relief’ maps.
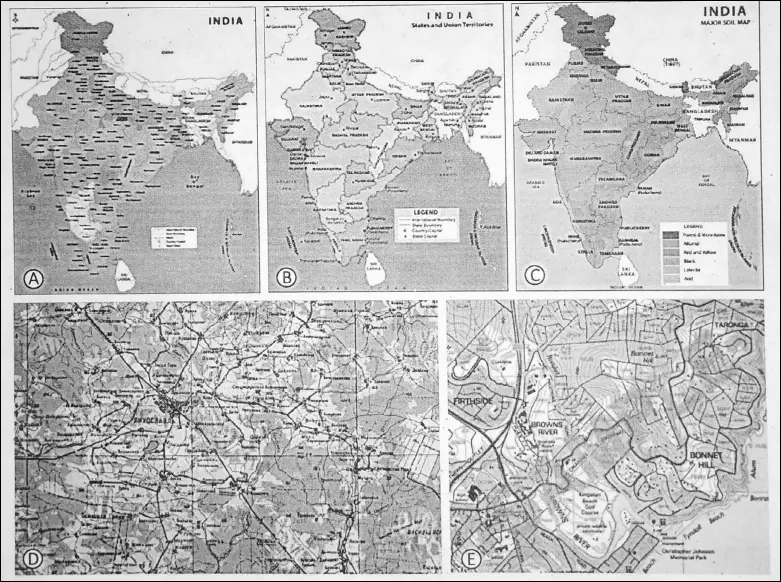
(2) Political maps :
Maps showing countries, states, districts, cities, towns, villages and others with their boundaries are called ‘political maps’.
(3) Thematic maps :
Thematic maps are those maps which show selected or specific themes and inform us about the topics like rainfall, crops, industries, minerals, roadways, railways, population etc.
“summary of class 6 physical geography chapter 11 WBBSE”
In thematic maps use of specific colours, signs, symbols and letters are required. The index in the map explains the meaning of those specified symbols. Thematic maps are more useful than general maps.
Topographical Maps :
A large-scale map of a small area showing physical and cultural features.
Cadastral Maps :
Maps which show the details of roads, fields and property.
Atlas :
A collection of maps bound in a volume is called ‘Atlas’. The term was first used by Gerhard Mercator in 1578 in the title of a collection of maps. He titled it ‘Atlas’ after the Greek God Atlas’. In present times too, a book of maps is known as ‘Atlas’.
Cartography :
The art of making maps is called ‘Cartography’ or the science of map making is known as ‘Cartography’. It studies the methods and principles of map-making. It includes topographical maps, and aerial photographs also.
“important questions from maps class 6 geography”
Globe :
A globe is a sphere and is the true mode of the earth. It is a small-scale spherical model of the earth, usually showing the main surface features, chief towns, and political boundaries. The shapes and locations of different continents and oceans, countries, physical features etc. are shown on a globe more or less accurately.
Like the spherical earth the globe is also a three-dimensional model of it.
- A globe has to be rotated to see all the places on it.
- Imaginary lines called parallels of latitude running from east to west to encircle the globe and there are imaginary lines drawn from north to south poles called meridians of longitude.
- Globes are big and round and cannot be carried easily from place to place.
- Distance cannot be measured on a globe because it is a curved surface.
- Globe is best suited to represent the whole earth.

importance of Globe :
- Globes are the aids of a geographer to represent the earth’s surface.
- A globe is a true model of the earth and is more accurate.
- Globe helps in understanding the correct shape and sizes of continents and oceans.
- With the aid of a globe, it is easily possible to understand the location of the countries.
Limitations of Globe :
Even though the globe is a small model of the earth so it is not possible to get much information about any country or continent.
- It is difficult to carry a globe to all places.
- A globe cannot show the minute details as could be shown on a map.
- At a time the whole earth cannot be studied from a globe.
The difference between a map and a globe :
| Map | Globe |
| 1. A map is a conventional drawing of an area drawn on a flat sheet of paper. | 1. A globe is a sphere and is the true model of the earth. |
| 2. Maps can be shown a large number of details. | 2. Globes do not show a large number of details. |
| 3. Maps can be easily handled. | 3. Large globes are difficult to handle. |
| 4. Map is more useful than a globe. | 4. Globe is more accurate. |
| 5. Distance can be measured on a map. | 5. Distance cannot be measured on a globe because it is a curved surface. |
| 6. At a time, the whole earth can be studied from a map. | 6. The whole earth cannot be studied from a globe. At a time, only one hemisphere can be studied. |
Scale :
Scale is a map-land ratio. A scale is a ratio of the distance between any two points or places on the map and the actual distance between the same two points or places on the ground.
Example :
If a map has a scale of 1 cm: 5 km, it means that one centimetre on the map represents a distance of 5 kilometres on the ground.
The necessity of scale :
- Scale is the most important essential of a map. Without scale, we have only a sketch or a diagram and not a geographic map.
- It is necessary to draw a scale to show the relative positions of a different places on the map.
- Every map has a definite ratio to the earth. It is not possible to make a map of the same size because 25000 miles or 40000 km of paper will be required to draw the equator.
- Maps are generally reduced in size. They are said to be “drawn to scale”. Thus scale is a necessity in the drawing of a map.
Importance of Scale :
Scale is the most important item of the study of maps.
- With the help of the scale, we can represent large areas in a reduced shape and size.
- Without a scale, a map is simply a diagram or a sketch. A map is meaningless without scale.
- We can measure the distance between two points on the map without going to the field.
- A map can be reduced or enlarged with the help of a scale.
Types of maps on the basis of scale :
Generally, maps are of two types on the basis of scale. There are ‘small-scale maps’ and ‘large-scale maps’ used to show larger or smaller ground distances.
Small-scale maps :
Maps which show larger regions like the whole world, continent and countries are called ‘small scale maps’. These maps show greater distances in a smaller map. The scale of such a map may be 1 cm = 250 km.
or 1 cm in the map distance = 250 km. on the ground distance. Minute details of any region cannot be shown on such maps.
Large-scale maps :
Maps which show smaller regions like a part of a country, cities or villages are called ‘large scale maps’. These maps show lesser distance in a larger map. The scale of such a map may be 1 cm = 5 km.
“WBBSE class 6 geography chapter 11 key points”
or 1 cm. in the map distance = 5 km on the ground distance. These maps show detailed information of smaller areas.
Distinguish between small-scale maps and large-scale maps :
| Small Scale Maps | Large Scale Maps |
| 1. Small scales are scales of miles to inches or kilometres to centimetres. | 1. Large scales are scales of inches to the miles or cm to the kilometre. The smaller the number of miles, the larger is the scale. |
| 2. For example 1 cm: 10 km. 1 inch: 60 miles |
2. For example 10 cm: 1 km. 6 inches: 1 mile. |
| 3. In this, 1 cm shows a distance of more than 1 Km. | 3. In this, 1 km is shown by a length of more than 1 cm. |
| 4. Atlas maps and wall maps are on small scales. | 4. Cadastral maps are on large scales. |
| 5. These maps do not show details of an area. | 5. These maps show details of an area. |
| 6. These are called small scale due to the smaller size of the map. | 6. These are called large scale due to the larger size of the map. |
| 7. If R. F. is given, the small scales have a larger denomination such as— 1: 50,000,000. | 7. If R.F. is given, the large scales have the smaller denomination such as – 1: 50,000. |
Directions :
Direction is indispensable for the accurate determination of the location of a place. It is, therefore, a very important part of the map. The two ends of the axis of the earth are known as ‘The North Pole’ and ‘South Pole’.
A line joining the north-pole and south-pole is called a true ‘North-South’ line. A line cutting the North-South line at right angles shows the East-West direction. The sun rises in the East and sets in the West.
Thus North-South, East and West are the four major directions. These major directions are called ‘Cardinal points’. Other minor directions can be obtained by bisecting these angles.
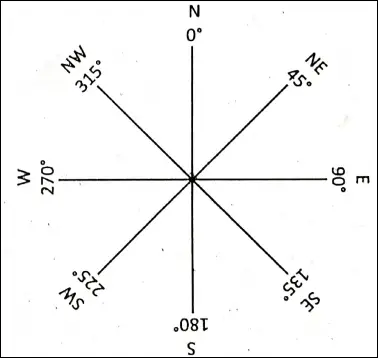
Importance of Directions for maps :
Direction is the fundamental essence of a map. Without direction, a map is meaningless. Direction is shown by an arrow pointing towards ‘North’ at the top of the map. Direction helps in the setting of a map.
Aircraft pilots, navigators, travellers, and tourists, follow their routes with the help of directions. Military movements are also guided by directions of the maps. For surveying an area, the direction is of vital importance. Thus a map must represent the major directions.
Sign and Symbols :
The topographic map contains a variety of information about physical features and cultural features. These are given by using signs and symbols in various letters and colours so that the clarity of the map is maintained. In thematic maps use 6f specific colours, signs, symbols and letters are required.
Conventional Sign and Symbol :
Conventional signs are the symbols used to show different features on the maps. These symbols are recognised all over the world.
These symbols are very useful in understanding the features of the lands shown on the maps. Towns, villages, buildings, railway lines, roads, trees etc. are big features, it is extremely difficult to draw on a map the actual shape and size of these features.
“what are maps and their importance class 6”
Therefore, we use various symbols to show them on the map. All the countries use the same symbols for a particular feature. These are called ‘convectional symbols’ or ‘convectional signs’. All maps of the world use specific colours, signs, symbols and letters to denote universal meaning.
These are called ‘convectional signs and symbols’. Rivers, lakes, seas, oceans and other water bodies are shown in blue colour. Areas coloured green show forests, parks and grasses Yellow colour is used to show cultivated lands. Brown colour for hills and mountains. These are drawn at the bottom of topographical maps. These form the key of map-reading.
Index :
The index is useful for locating places on the maps. It explains the symbols, colours and letters used in the map. In thematic maps use of specific colours, signs and letters are required.
The index in the map explains the meaning of those specified symbols. Atlas contains an index of place names at the end. Names are arranged alphabetically in the index. Map or page number, latitude and longitude references are given for each place.
Sketch :
A sketch is a rough map of an area without scaj£. The main idea of drawing a sketch is to convey the locational information easily with the help of landmarks like the post office, cinema hall etc.
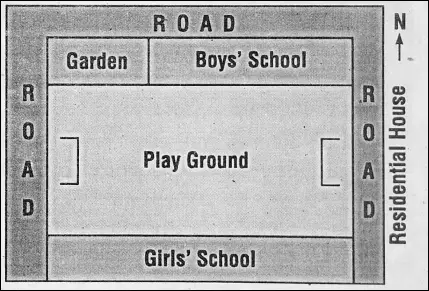
It shows directions only. Since a sketch is not drawn according to a scale, the distance cannot be correctly understood. So, we can get only a general idea about a place or region by a sketch.
“different types of maps and their uses WBBSE”
Plan :
A plan is a detailed map of a small area on a large scale. A plan is drawn accurately to depict a small area like a room, a house, a classroom, a school etc. After proper measuring, the plan is drawn according to the specified scale.
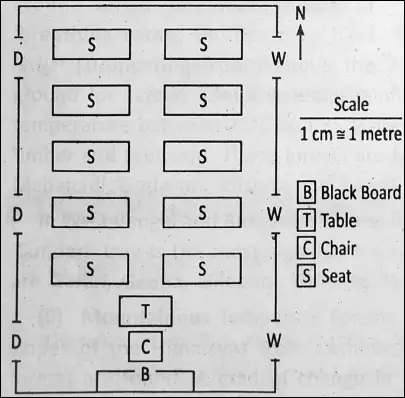
So ‘distance’ and ‘direction’ can both be understood by a plan. Plans are drawn on a large scale, such as one centimetre shows one metre or one inch shows ten feet etc.
The difference between a map and a sketch :
| Map | Sketch |
| 1. A map is a conventional picture of an area drawn on a flat sheet of paper. | 1. A sketch is a rough map of an area without scale. |
| 2. A map is drawn to scale. | 2. A sketch has no scale. |
| 3. A map can show a big area. | 3. A sketch can show a small area. |
The difference between a map and a Plan :
| Map | Plan |
| 1. A map is a conventional drawing of an area drawn on a flat sheet of paper. | 1. A plan is a detailed map of a small area on a large scale. |
| 2. A map shows a large area on a small scale. | 2. A plan shows a small area on a large scale. |
| 3. A map shows only important features. | 3. A plan can show many details. |
The difference between a plan and a sketch :
| Plan | Sketch |
| 1. A plan is a detailed map of a small area on a large scale. | 1. A sketch is a rough map of an area without scale. |
| 2. Plans are drawn on a large scale. | 2. A sketch map is drawn without scale. |
| 3. ‘Distance’ and ‘direction’ both can be understood by a plan. | 3. It shows ‘directions’ only. |
| 4. A plan can show a small area in great detail. | 4. It is useful for locating various parts of a town or of a small area. |
WBBSE Notes for Class 6 Junior School Geography
- Chapter 1 The Universe and Solar System
- Chapter 2 Shape of The Earth: Is The Earth Around?
- Chapter 3 Location of a Place on The Earth’ Surface: Where You Are
- Chapter 4 The Earth’s Motion: The Earth Rotation
- Chapter 5 Water – Land – Air
- Chapter 6 The Ice Capped Continent: Antartica
- Chapter 7 Weather And Climate
- Chapter 8 Air Pollution
- Chapter 9 Noise Pollution
- Chapter 10 India
- Chapter 11 – Maps
