Chapter 3 Location Of A Place On The Earth’s Surface: Where You Are? Introduction :
Location Of A Place On The Earth’s Surface:
A majority of human beings have their homes located in villages or towns on our Earth. Our Earth being a sphere, a poses a problem of where to begin for the location of points.
A globe is a model of the Earth. The parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude make a system of intersecting lines, the former east-west and the latter north-south, found on the globe or in the maps.
“WBBSE class 6 physical geography chapter 3 notes”
Such a system- has many advantages and makes it easier to locate any place on the Earth or on the map.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 Junior School Geography
The Globe :
A globe is the representation of the Earth while a map is a two-dimensional representation of the Earth or Globe according to a scale and it is drawn on a flat surface.
The globe is a true model of the Earth and shows us what the Earth actually looks like. If we take a close look at the globe we can detect the following features and lines which help us to locate the position of a place on the Earth.
Axis Of The Earth :
The imaginary line joining the northern and southern ends of the globe and passing through the centre of it is called Earth’s axis or ‘Axis of the Earth’. The Earth rotates on this axis.
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
The Poles :
The endpoints on the Earth (globe) at the top and the bottom are called the ‘Poles’ of the Earth.

North Pole :
The northern or top end point of the Earth’s axis is called the ‘North Pole’.
South Pole :
The southern or bottom endpoint of the Earth’s axis is known as the ‘South Pole’.

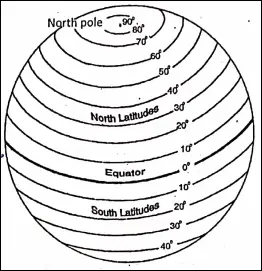
Parallels Of Latitudes :
On either side of the equator east-west extending imaginary circles, lying parallel to each other are called parallels of Latitude or Lines of Latitude.
“location of a place on the earth’s surface WBBSE notes”
Characteristics Of Parallels Of Latitude :
Parallels of latitudes are imaginary full circles on the Earth, all parallel to the equator i.e. they always remain equal and different apart.
- All parallels represent true east-west lines.
- Parallel of latitude intersects meridians at right angles.
- All parallels except the equator are smaller circles.
- The Equator is a ‘Great Circle’ and the only parallel drawn from the Earth’s centre.
- At Every point on the globe, except the North Pole and the South Pole, an infinite number of parallels may be drawn.
- More than one parallel of latitude of the same value does not exist in one hemisphere.
- The value of the parallel of latitude is measured from the equator (0°) northwards to the point of the North Pole (90°N) and southwards to the South Pole (90°S).
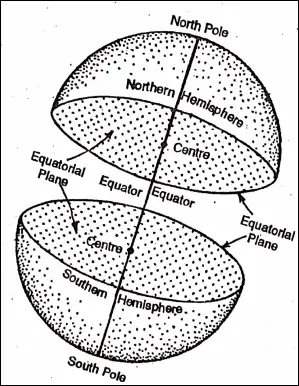
Equatorial Plane :
The plane bounded by the equator of the Earth is known as the ‘Equatorial Plane’.
If the Earth could be sliced into two halves all along the Equator, the Equatorial plane could be seen and the Earth could be divided into two equal halves. The axis of the Earth forms an angle of 90° with this plane.
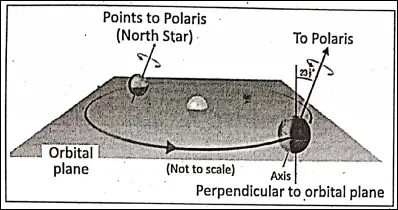
Orbit Of The Earth :
While the Earth is revolving around the Sun on a fixed imaginary elliptical (oval-shaped) path, it is called the ‘Orbit of the Earth’.
“where you are class 6 geography WBBSE”
Orbital PIane :
The Plane containing the orbit of the Earth is known as the ‘Orbital Plane’. The axis of the earth is tilted at an angle of 661/2°to to the orbital plane and 23%° to the vertical.
Importance Of Parallels Of Latitudes :
- Parallels of latitudes help in location of a place for show how far a place is north and south of the Equator.
- These are used to divide the Earth into temperature belts. Thus the latitude of a place gives an idea about climate.
Important Parallels Of Latitudes :
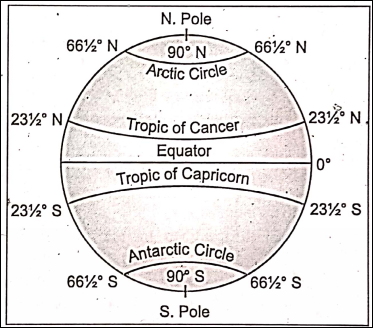
Important parallels of latitude and their distance from the Equator in degrees are given below :
The Equator/Great Circle = 0°
Tropic of Cancer = 231/2°N or’ 23°30’N,
Tropic of Capricorn = 231/2°S or 23°30’S,
Arctic Circle = 661/2°N or 66°30’N,
Antarctic Circle = 66°1/2S or 66°30’S.
The Equator/Great Circle :
- North Pole = 90°N,
- South Pole = 90°S.
The equator is an image on the globe passing through the midpoints between the North Pole and the South Pole. It is a circle whose centre is the centre of the globe. The Equator divides the globe into two hemispheres.
The hemisphere that lies north of the Equator or that contains the Norm Pole is known as the Northern Hemisphere and the Hemisphere south of the Equator or that contains the South Pole is the Southern Hemisphere.
“summary of class 6 physical geography chapter 3 WBBSE”
The word ‘hemisphere’ means half of a sphere or globe. The Equator is also called the ‘Great Circle’ because it is the greatest parallel and other parallels decrease in size gradually.
Another name of the Equator is the ‘Line of Equinox’ because throughout the year the equatorial region has equal lengths of day and night.
Properties Of The Euator/Great Circle :
- The Equator or Great circle divides a giobe into two hemispheres.
- It is the largest circle on a sphere.
- A plane passing through the centre of a sphere only can produce a great circle.
- The value of the great circle is 0°.
- An arc of a great circle is the shortest surface distance between any two points on a sphere.
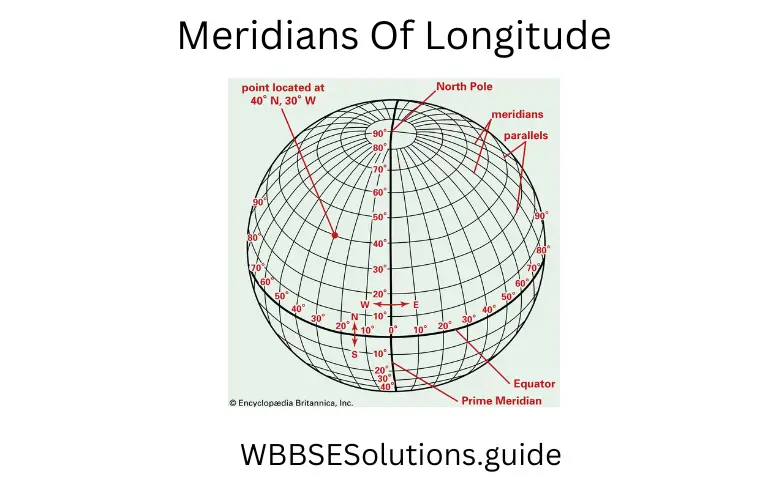
Meridians Of Longitude :
Lines of Longitude or Meridian of Longitudes are imaginary lines joining places located at the same angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Characteristics of Meridians of Longitude :
- Meridians of longitudes are half circles.
- These are measured from the Prime Meridian.
- These lines extend in a north-south direction on the Earth.
- All lines of longitudes are of equal in length but not parallel to each other.
- The distance between two lines of longitude is maximum at the equator and decreases gradually away from the equator.
- The longitude of a meridian has a definite value.
- Value of the meridians of longitude increases from the Prime Meridian to the east and west up to 180°.
- 180°E and 180°W meridian of longitude is one line.
- The lines of longitudes are converge at the two poles.
- All places on the same meridian have sunrise, noon and sunset at the same time.
Important Meridians :
Prime Meridian :
North-South extended semicircular the particular imaginary line drawn along the Royal Observatory of Greenwich near London is called the ‘Prime Meridian’ whose value is 0°. This is also known as the ‘Greenwich Meridian’.
“important questions from location of a place on earth class 6”
Eastern Hemisphere, Western Hemisphere :
The Prime Meridian divides the Earth into two equal halves or the eastern and western hemispheres. The eastern half (from the Prime Meridian to ISO E) is known as Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Half 0°. (from the Prime Meridian#* to ISO’W) is the Western Hemisphere.
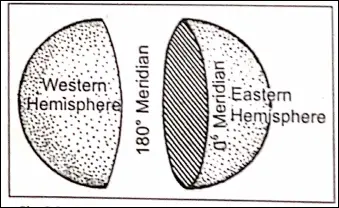
180° Meridian of longitude :
The 180° meridian of longitude is just on the opposite meridian of longitude of 0° (Prime Meridian). The International Date Line (IDL) is drawn almost along this meridian from which each new date starts and each date ends at last.
“WBBSE class 6 geography chapter 3 key points”
Difference between Parallels of Latitudes and Meridians of Longitude :
| Parallels of Latitudes | Meridians of Longitude |
| 1. The Imaginary horizontal circular lines drawn by joining places have the same longitude arc called Parallels of Latitudes. | 1. The Imaginary vertical semicircular lines drawn by Joining places having the same longitude are called Meridians of longitude. |
| 2. These lines encircle the Earth in east-west lines | 2. These lines extend In a north-south direction on the Earth. |
| 3. These are measured from the Equator. | 3. These are measured from the Prime Meridian. |
| 4. These are nearly equidistant from each other. | 4. These are not at equidistance everywhere. |
| 5. Every parallel of latitude are full circle except the two poles. | 5. Meridians of longitudes arc half circles. |
| 6. The length of the parallels of longitudes gradually lessens from the equator to the Poles. | 6. All meridians of longitudes have the same length. |
| 7. In the same parallel at different places sunrise, noon and sunset occur at different times. | 7. All places on a particular meridian sunrise, noon and sunset occur at the same time. |
| 8. The highest value of the parallels of latitude is 90° | 8. The highest value of meridians of longitude is 180°. |
| 9. The lowest value is 0°. | 9. The lowest value Is 0°. |
| 10. Parallels of latitude help in dividing the Earth’s surface into heat belts or temperature zones. | 10. Meridians of longitude help In determining the time zones. |
WBBSE Notes for Class 6 Junior School Geography
- Chapter 1 The Universe and Solar System
- Chapter 2 Shape of The Earth: Is The Earth Around?
- Chapter 3 Location of a Place on The Earth’ Surface: Where You Are
- Chapter 4 The Earth’s Motion: The Earth Rotation
- Chapter 5 Water – Land – Air
- Chapter 6 The Ice Capped Continent: Antartica
- Chapter 7 Weather And Climate
- Chapter 8 Air Pollution
- Chapter 9 Noise Pollution
- Chapter 10 India
- Chapter 11 – Maps
