Chapter 1 Concept Of History Historical Explanation On The Naming Of The Country Bharatvarsha
There are different interpretations in different scriptures (the Epics and the Puranas) about the origin of the name “Bharatvarsha” Bha (Jnana) + rata (accustomed of) + Varsha (the vast land).
So Bharatvarsha means “the land where the study of Jnana or knowledge is carried on” -Smith. According to the “Markandeya Purana,” the earth is divided into seven diwas named Jambu’, ‘Shalmali’, ‘Saka’, ‘Plakkya’, ‘Puskara’, ‘Kush’ and ‘Cronchya’.
Jambudiwa is the main among these. Bharatvarsha is named as ‘Haimabatabarsh’ in the ‘Bayupurana’. In the Srimadbhagabatapurana it is mentioned as ‘Ajnabhabharshe’.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 7 History
This relates to God Bishnu, who created man. According to the Matshapurana ‘Bharatvarsha’ is named after the king Bharat and Manu.
“WBBSE Class 7 History Chapter 1 notes”
In the Mahabharata the name of the son of Dusmanta and Sakuntala is Bharat and it was believed that Bharatvarsha was named after him. Dr. Romila Thaper also emphasized different religious texts to trace the origin of the name ‘Bharatvarsha’.
Dr. Ramsharan Sharma said in his book ‘Ancient India’ (Page-1) “The name of Bharatvarsha or the land of Bharata was given to the whole country after the name of the ancient tribe called ‘Bharatas'”.
In the later period, Greeks called this land ‘Indus’, Muslims called it ‘Hindusthan’ and the British called it ‘India’. Hindu cosmographers called India as “Jambudiwa” in ancient times.
‘Sindhu’ is a Sanskrit term and the word ‘Hind’ or ‘Hindu’ came from the word ‘Sindhu’. The ancient Persians and Greeks called India as ‘Hind’. The Persians said the word ‘Sindhu’ as ‘Hindu’.
Wbbse Class 7th History Notes
The westerners pronounced the river ‘Sindhu’. They spoke ‘S’ of ‘Sindhu’ as ‘H’ or ‘1’. From then ‘Sindhu’ transformed into ‘Hindu’ and Indians came to be known as Hindu and the land inhabited by them is called ‘Hindustan’.
According to historian A. C. Banerjee “The Word ‘India’ Is derived from the river ‘Sindhu’, which the Iranians called ‘Hindu’ and Greeks ‘Indus'”. This sub-continent is a well-defined land with geographical borders.
“Concept of History Class 7 WBBSE notes”
In ancient times the whole mass of land including present Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nepal, India, Bangladesh, and Bhutan was known as ‘Bharatvarsha’ or ‘Hindustan’. In our Constitution, it is called India, which is Bharata.
What is History?
History is generally considered to be the study of the past. In earlier times, a chronological narration of past events was regarded as the main purpose of history.
Now history is said to be the scientific analysis of human evolution in the context of time and space. “History is an unending dialogue between the present and the past.”
It is the scientific study of our complete past. The word ‘history’ came from the Greek word “Istoria” or the Latin word “Historia”. In the broadest sense, history is the story of people-the study of our complete past.
“WBBSE Class 7 History Chapter 1 summary”
Some scholars put emphasis on events, like wars, revolutions, advancements, and governments, while others are interested in common people’s lives.
The American car manufacturer, Henry Ford once remarked “History is bunk”, but most people would disagree.

Chapter 1 Concept Of History Importance Of Learning History
We come to know about the past from studying history. Man’s evolution through the ages, his walk toward civilization, all can be learned only by studying history.
About three lakh years from today, the discovery of fire by a Peking man is considered to be the first step towards civilization. After this, man has advanced from the stone to the metal age which brought about immense changes in his lifestyle.
Over thousands of years, primitive men learned how to make a fire to keep themselves warm and learned to cook his food, how to make tools, and how to hunt animals. All this can be understood by studying history.
Our world is huge with its different civilizations and lifestyles. This may be observed in every sphere. Man’s food habits, clothing, language, literature, religion, science, etc., are diversified.
This may be learned by studying the history of analyzing man’s progress. We know, changes in the ancient period have brought in the present age. To know how these changes appeared or the evolution of mankind, learning of history is essential.

According to historian Jones, ‘History is a minefield of experience’. We can make our knowledge complete by using these experiences. We know of the mistakes of the past by studying history, and this makes us alert beforehand. That is why the study of history is so important.
History may be regarded as the ‘fountain of knowledge’. It develops our philosophic consciousness and social awareness. Human success and failure both are parts of history.
“Class 7 History Chapter 1 WBBSE question answers”
The vast period of time from 2.5 million years ago to 500 A. D. saw the appearance of the first human beings and the creation of the first societies and civilizations.
Our earliest ancestors appeared 2.5 million years ago in Africa. So to know about the entire human life, history can be the main source. That is why history is told to be the ‘tower of experience.
To think impartially or to have an inquisitive mind to know about the past, learning of history is essential. No branch of social sciences is complete without the study of history.
All of us are dependent upon history. It may also be told history is the ‘mother of all sciences.’ Thinkers such as Hegel, Miller, and Anatole France believe that history represents knowledge about past events.
According to philosopher Karl Marx, the changes in human society reflect the history of class struggle. To Know about this, only history can help us.
Lastly, it may be said that history makes us aware of the historical past. It builds up love for the country and is important to know about other countries as well.
Karl August Muller has said, ‘Searching for truth is a religion of history’. Thus the main aim of teaching history is to make human civilization meaningful to the students so that they can shape their society in a proper way.
Today our lives are shaped by decisions and actions made decades, centuries, and even thousands of years ago. By knowing the past, we may be able to gain a very balanced view of the present.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Changes Of Sources in Ancient History
Although no books were available in the pre-historic period, our knowledge of history has come from various sources. We know that most of the ancient civilisations were river-valley civilizations.
It was nearly five thousand years ago when the pre-historic age started, there was no written history of man available of that period. However, man’s civilization progressed as he stepped into the age of metal.
“WBBSE Class 7 History Concept of History explanation”
The old stone age, the new stone age or paleolithic, the chalcolithic, and lastly the iron age came one after another. Among the bronze age civilizations 3500-3000 B.C., the important river valley civilizations were the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Chinese, and Harappan civilizations.
By studying history we come to know of the advancements made by Babylonians, Egyptian, Greek, Roman, and Chinese civilizations, as also Indian. To know this history, our sources are mainly of two types, such as archaeological sources and literary sources.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Archaeological Sources
The ancient sources that have been excavated are called archaeological sources such as coins, inscriptions, sculptures, and paintings.
Inscriptions:
Among all archaeological sources, inscription demands a special mention. Inscriptions again may be classified into cave writings, rock, and pillar edicts, etc. These are not spoilt easily.
But if that happens it cannot be brought back to its original. Thus, inscription as a source of ancient history is very important.
‘Brahmi script’ and ‘Kharosthi script’ of King Asoka, ‘The hieroglyphic inscription’ of Egypt, ‘Bahistan inscription’ of Persia, ‘The pictographic script’ of Assyria, and the ‘Cuneiform script’ of Mesopotamia throw much light about that age, particularly on language, literature, and religion.

Due to the absence of paper in ancient times, scripts were also written on leaves, clay tablets, and in the bark of trees. Later, the ancient people used to write on the leaves of a kind of plant called ‘Papyrus’ from which the word ‘paper’ has came.
” chieftains meaning in history”
Dr. R. C. Majumdar said, “Inscriptions have proved the highest source of value for the reconstruction of the political history of ancient India.”
Coins :
Like scripts, and coins to help us to reconstruct ancient history. Coins help us to understand the economy, use of metals, religion, dates, the language of a particular period, etc.

Also, the trade relations among various countries may be understood from coins. The history of the Kushanas has been reconstructed from the copper and gold coins struck by them.
From the coins of Samudragupta, we know that he had a love for music and he knew the playing on the harp.
Art-Architecture and other sources:
Weapons and utensils used by ancient people, house construction, and polished ‘objects of daily use are great archaeological evidence. The relic works on temple walls also help us to know about early history.
The human skull, skeleton, oracle bones, monumental evidence of early civilization, art, and craft, etc. also help us to reconstruct ancient history.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Ancient History And Literary Sources
Literature also constitutes a very important source of ancient history. The Four Vedas (Rig, Sham, Yajur, and Atharva) and ‘Sutra literature’ are the main literary sources of the Vedic Period.
The Epics, the Upanishads, Buddhist texts like ‘Mahabamsha’ and ‘Dwipabamsha’ I (in Ceylonese language), Jain texts ‘Dwadash Anga’ or ‘Siddhanta’.
Accounts of foreigners such as the ‘Indika’ of Megasthenes “Fo-kio-ki” of Fa-Hien, ‘Si-yu-ki’ by Hien Tsang, ‘Rajatarangini’ of Kalhana, ‘Mricchakatikam’ by Sudraka and our epics the Ramayana and the Mahabharata provide sources about ancient Indian history.

The writings of Herodotus, like ‘Persian’s History’ and “Histories”. ‘Germanika’ written by Thucydides and the ‘Iliad’ and ‘Odessey’ of Homer give an insight into the politics, social structures, and life of ancient Greece.
“Important questions for Class 7 WBBSE History Chapter 1”
Herodotus is called “the father of History”. Roman historians like Plutarch, Justin, and Pliny have written invaluable material on history in the ancient period. Nonetheless, everything about the ancient period is still not known. This requires more research and introspection.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Age In History
The evolutionary process in the history of human civilization from time immemorial till the beginning of the twentieth century is very much eventful and elaborative. This transformation took place slowly.
In course of time, different glorious changes came into being. These changes were revolutionary. Historians considered the prevailing time with its economic, social, political, religious, and other systems to be called as an ‘era’ that means a specific period of History.
On the basis of race and religion a renowned historian Dr. Romila Thaper classified the periods of Indian History as ‘Ancient India is Hindu period, Medieval India is Muslim period and Modern India is British period’.
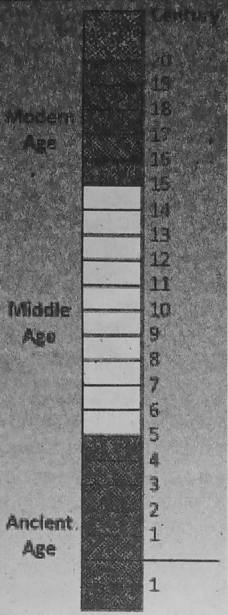
The categorization of the periods of history is generally followed through different ‘terms’ i.e., the Pre-historic Age, the Ancient Age, the Medieval Age, and the Modern Age. Yet there is a debate regarding the categorization or periodization of history.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Periodisation Of History
Although it is not easy to identify the historic eras by any specific event, yet the periodization of history is necessary to understand the time, space, and chronology of history and the advancement of human civilization.
Class Vii History Book Wbbse
No one can define an era from a particular date or year because it is just not possible to identify the progress of civilization from that particular date or year. However, experts are of the opinion that a new era originates from the previous age.
Famous historians E. N. Johnson and J. W. Thomson, in their book “An introduction to the History of Europe” have explained history as a tree that takes roots in one era and grows it into the next era.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Beginning Of The Middle Ages In Europe
A great change came in the history of human civilization at the end of the Fifth Century A.D. The ancient Roman empire was divided into two parts, the Western Roman empire with its capital at Rome, and the Eastern Roman empire with Constantinople as its capital.
In 476 A.D., the Germans under the leadership of General Odovȧcar dethroned the last Roman emperor, the twelve years old Romulus Augustulus. The glory of the western Roman empire came to an end during this time.
Historians marked this event as the end of, Ancient period in Europe and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
The Middle Ages or the Medieval Period:
On 29th May 1453, the Ottoman Turk leader Mohammad II attacked Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. The period of a thousand years, from the fall of Rome in 476 AD to the fall of Constantinople in 1453 A.D. has been defined as the ‘Middle Ages’ in history.
During this time a new social, political, economic, and educational system emerged and transformed into a new era. But we must remember that this ‘Middle Age’ is applicable in Europe only because the characteristics of the ‘Middle Ages’ are more prominent in Europe than elsewhere.

Though in India, the ‘Middle Ages’ started with the downfall of the Gupta Empire, it became more prominent when the Arabs conquered Sindh in 712 AD. With the downfall of the Mughal glory after the death of Aurangzeb (1707 A. D.), the ‘Middle Ages’ came to an end in India.
Middle Ages in India :
The old schools of historians were of the opinion that the Middle Ages in India started at the end of the Hindu period (i.e., the Sen era) and the beginning of the Muslim period (i.e., from the rise of the Delhi Sultanate).
But modern historians believe that the Middle Ages in India started in the fifth century A.D. when the Huns from Central Asia invaded the Gupta Empire in India.
From then certain changes took place in the socioeconomic system of India. Towards the end of the Gupta Age, the system of slavery was on the decline and it marked the rise of the feudal system.
The land belonged to the feudal lords who deprived the farmers like the feudal lords of Western Europe. After the downfall of the Gupta Empire, foreign tribes like the Huns and Gujjars entered India and became a part of Indian Society.
“Concept of History Class 7 WBBSE textbook solutions”
As a result of this, the social structure of ancient India changed drastically. In ancient India, society was formed depending on the “Chaturbarna System” (the four castes) but now a new social system came into being.
In this new society, the descendants of the Huns and Gujjars and the untouchables became a part of the society. However, we must remember that the feudal system in India was not so prominent as it was in Europe.
The Buddhist monasteries and Hindu temples played an important role in keeping the process of education with high esteem.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Middle Ages In Different Parts of The World
It should be kept in mind that the Middle Ages was not ushered or did come to an end at the same time in different parts of the world.
For example:
The Middle Ages began in the third century B.C. with the downfall of the Chow dynasty in China, in the seventh century A.D. in Arabia, and in the eighth century A.D. in Korea.
In Japan, the Middle Ages spanned from the twelfth century to the middle of the nineteenth century A.D. and in the South-East Asian countries feudal system existed from the ninth century to the thirteenth century A.D.
Class Vii History Book Wbbse
An era means a vast period, so it cannot be defined from a particular time. Historians consider the period of one thousand years, from the fifth century A.D. to the middle of the fifteenth century A.D., to be the Middle Ages of the history of human civilization.
To understand the span of the Middle Ages in the history of human civilization, we should see the chart given above.
The Feudal System in India-
In the later part of the Gupta period, there was a remarkable change in the socioeconomic condition of the country.
According to historian Ram Sharan Sharma, the Feudal system was based on the ‘Agrahar’ system i.e., the gift of tax-free land to the Brahmanas. In ancient times royal officers of the high ranks named ‘Samanta’/ ‘Mahasamanta’ became powerful.
During this time slave system was not totally abolished but the farmers used to cultivate land independently and enjoyed a share of the crop. The feudal lords enjoyed the revenue.
In this way, the socio-economic condition named the feudal system (Samanta Pratha) existed in the Gupta period (330 AD-550 AD).
The characteristics of the Middle Ages-
A new era came into view in the cycle of world civilization with the fall of the Roman Empire.
The main characteristics of the Middle Ages are as follows:
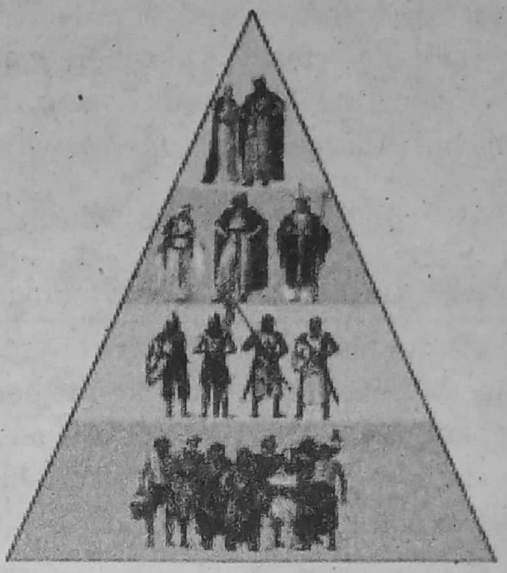
- The rise of Feudalism was the main characteristic of this Age.
- Another characteristic of this Age is the formation of the deprived farmer class. But in Europe, it was through the Serf system, and in India, it was through the misappropriation of the fruits of farmer’s labour by the landlords and the feudal.
- Religious institutions preserved the educational system. In this respect, the Church in Europe and in India Buddhist monasteries, and Hindu temples had an important role.
- King was merely a name but the Feudal lords were more powerful in this Age in Europe.
- The presence of Feudal Castles or Feudal Forts, nominal king, feudal lord, Mailed horsemen or Knight and Chivalry or heroic vows (popularly called the “blossoming flower of feudalism”), etc., were the most important characteristics of the Middle Ages.
Differences of socioeconomic Conditions in India and Europe
In the Middle Ages slave system was abolished in Europe. The Germans settled in the different provinces of Rome. The hard-working German laborers grew bumper crops in farming. Some became landlords.
Ultimately German landlords employed free farmers in the field of agriculture. But German landlords were the owner of the land only and the farmers were their subjects. The farmers were not the personal property of the landlords.
Class 7 History Chapter 7 Wbbse
The farmers used to live independently within the jurisdiction of the landlord and they enjoyed a share of the cultivated crop. With the free mixing of the Romans and Germans, a new socioeconomic system emerged in West Europe.
In India, socio-economic changes took place with the fall of the Gupta Empire. By the end of the Gupta Age, the slave system came to an end. The farmers used to cultivate the agricultural land and enjoyed a share of the cultivated crop.
But the owners of the land were the feudal lords. They used to enjoy the revenue without giving any physical labor and were the absolute ruler or master.
So, the socioeconomic condition in Europe and India was not the same. It was quite different.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Influence Of Roman Culture In German Tribes
- German tribes had the quality to adopt different cultures and make it their own.
- They had no traditional state law which the Romans had.
- They had a separate type of law and judiciary.
- Their religious beliefs were primitive and simple. Roman historian Tacitus mentioned it in his book ‘Germania’.
- The Germans worshipped their forefathers and nature. For example from the name of the god moon, ‘Monday’, the god of the sky was Tyre. The god of thunder was Thor from which ‘Thursday’ had come. The god of war was Tue from which ‘Tuesday’ had come. The goddess of energy and love was Friga from which ‘Friday’ had come. The god of poetry and the supernatural elements was Oden from which ‘Wednesday’ had come and from the name of the god Satan ‘Saturday’ and from the Sun god the name ‘Sunday’ had come.
- After the Germans started their interaction with the Romans they adopted the Roman laws, administrative system, and architecture.
- They learned moral values and decency from the Romans. Gradually they became more civilized. Thus the ancient European civilization was saved from destruction.
- On the other hand, the Romans were also influenced by certain characteristics of the Germans, such as their bravery, skill, respect for women, and faith in democracy. This confluence of German and Roman cultures formed the foundation of modern European culture.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Beginning Of The Middle Ages-Not The Beginning Of A Dark Age
Dark Age is an old concept :
Some historians call the period from the fourth to the seventh century A.D. as the ‘Dark Ages’. While others consider the period from 500 A.D. to 1000 A.D. to be the dark ages. It was a period of political and social chaos and instability.
Anarchy also prevails during this time. This was the opinion of some of the historians. But it is debatable and not a full-fledged truth. According to a group of historians, the light of civilization was put off during this time.
Is there any base of this concept that the Middle Ages is a Dark Age?
It is already told that some of historians call the period from the fourth to the seventh century as the “dark age”. During this time the authority of the Roman administrator over the Roman administrative system collapsed.
Different sects and tribes of Germans attacked the Romans. The instability and the rise and fall of kingdoms created chaos and anarchy. This chaotic condition almost wiped out the Germans heritage of the Roman empire.
There was no peace in the country, so the concept of the dark age came to the mind of historians. Some of them named it as ‘Dark Age’.
Middle Age was not a Dark Age: Why?
However, the first three centuries of the Middle Ages cannot be called the ‘Dark Age’ because-
- It is known that during this time although the practice of science and knowledge had diminished, it had not ended totally. It was being continued within a limited scope by the initiative of temples and monasteries.
- Many aspects of education and moral values were discussed here.
- ‘Latin’ was the main language that was practiced by priests and monks in temples and monasteries.
- Many ancient manuscripts were preserved here. The monks made copies of these manuscripts and translated them into different languages. Many new manuscripts were composed during this time.
- In fact, the Germans did not devastate the Roman empire. The empire had its inner weakness.
- The slave system overburdened the empire. The old civilization faced a transformation. The Germans accelerated this process of transformation. This was a transition period and not a dark age.
- Christian priests helped a lot in rousing respect for the monasteries in the mind of people. It is true that civilization was not lost and everything did not plunge into darkness.
Chapter 1 Concept Of History Some Remarkable Scholars Of This Age
During this era of so-called darkness, different books on Mathematics, Geometry, Astronomy, Grammar, etc., were translated into Latin. Casiodorus, the monk took initiative. Boethius was another learned personality of the Middle Ages.
He translated the theories of the Greek Philosopher Aristotle, into Latin. Bithius wrote the famous book, “Consolation of Philosophy”. In the sixth century, a learned man Gregory wrote the ‘History of the Franks’.
Saint Benedict was a Christian monk who influenced the Germans to lead a peaceful and organized life through the concept of religion, education, and service to others.
Thus the Christian ideas helped the people to know what is right and what is wrong. Christianity preached the idea of love for mankind and Christian humanism. As a consequence of it, the renaissance came into being.

Chapter 1 Concept Of History The Impact Of The Middle Ages
- In the Middle Ages, the Christian missionaries preached to Saint Benedict that those who were charitable, benevolent, and involved in the welfare work of others, would attain salvation and would get the bliss of the lord after death.
- Those who were selfish, fraud, and ill-behaved, would suffer agony in hell.
- Through the impact of Christianity, the people became aware of the difference between right and wrong, morality and immorality. So it can be said that all good values did not vanish in the Middle Ages.
- Within a few centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, a new civilization gradually started to develop. A new social, economic, and political condition came into existence. In the field of knowledge and industry, there came a novel (new) inspiration.
- These changes led to the birth of a new culture-‘Renaissance’ in Europe in the 15th century. So, the period from the 4th century to the 7th century cannot be regarded as the ‘dark age’, in the history of Europe.
- In the history of human civilization the ‘Middle Ages’ is of equal importance as the Ancient or Modern Ages. We must remember that human civilization flourished in different ways in different ages, which has culminated into the present form of the Modern Age.
The Muslim Age or the Mediaeval Age which term is more reasonable in the context of the post-ancient Indian Age?
According to ancient scholars, Muslim Age came after the Hindu Age. But the modern historian thinks that due to the weakness of the central power and the decline of the Gupta empire and because of the Hun invasion many feudal leaders arose.
Historian A. L. Basham described this society in the 6th century as a “Feudal pattern of society”. As a result, feudalism became a specialty in Mediaeval Age, which abolished the slavery system in Ancient Age.
But the historians like Thompson and Johnson say that the division of ages in history is only for the sake of discussions but in reality, such division is not at all possible. Because the root of one age is embedded into another age.
Indian history was divided into three parts namely Hindu, Muslim, and British civilization by the first British historian and philosopher James Mill (1773-1836 A.D.) in 1817 A.D. It was written in his book “History of British India”.
Sir H. S. Elliot has supported this communal thought. The main object of the British historian was to divide Hindus and Muslims from each other. In that sense, it can be said that the ‘Ancient Age’ is the ‘Hindu Age’.
‘Mediaeval Age’ is ‘Muslim Age’ and ‘Modern Age’ is “British Age” or Christian Age. But this theory is unscientific, and it suffers from narrowness because there were also other communities other than Hindus in Ancient Age.
Similarly, there were people of many non-Muslim communities though the Muslims had political supremacy in the Medieval Age. There were many Hindu kings under the Muslim rulers though the central power was with the Muslims.
“Easy notes for Class 7 WBBSE History Chapter 1”
This age was the age of coordination between Hindus and Muslims. Because due to the expansion of the Bhakti and Sufi communities in the field of religion, the Hindus and the Muslims came nearer to each other.
Besides this, some Muslim rulers appointed Hindu employees. If the period between 1206 A.D. and 1707 A.D. is called the Muslim Age in the history of India, then the basic existence of many Hindus residing at the time is disregarded altogether.
But it is not possible. During the regime of the Sunni Muslim Aurangzeb, there were many Hindu kings belonging to Sikh, Rajput, and Maratha, who also ruled with their own identity in that period.
Hence history will be distorted if the Mediaeval Age is called the Muslim Age. There was a combined upsurge of cultural consciousness by following the Hindu-Muslim unity though Muslim domination was there in the field of religion, economics, society, politics, language, literature, and art.
Considering these factors, we can identify the post ancient age as the Mediaeval Age instead of calling it Muslim Age.
