Chapter 9 India Today Government Democracy And Autonomous Rule Introduction
The basic principle of history is the dynamism with the changes of time; everything is changing today. It is very interesting to note that the fundamental structures in many cases remain unchanged.
For example, the Persian word “Sarkar” used by Pathan’s ruler Sher Shah first means province and its ruler. He divided his whole empire into 47 ‘Sarkars’. So in the medieval period the ‘Sarkar’ was used to understand both rule and ruler.
“Class 7 History Chapter 9 WBBSE India Today detailed notes”
For the welfare of the subjects Sher Shah used the term “Sarkar”, which is now called “Government” in the English language, and the word “Govern” means act of administering.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 7 History
Chapter 9 India Today Government Democracy And Autonomous Rule Democracy
Every country has a government of its own people. The country India, where we live in also has a government. The government of India is now formed not by force, but by election.
“WBBSE Class 7 History Chapter 9 India Today Government Democracy and Autonomous Rule notes PDF download”
India is a “Democratic” country because common people by casting their votes form the government. The Latin word “Democracy” has come from “Demos” (people) and “Cratos” (rule).
So the government of the people, by the people, and for the people is called democracy or in Bengali “Ganatantra” (Gana means public and “tantra” means system) denotes a kind of public system.

Our democracy is mainly based on democracy or a system of administration where the elected members of government are to be responsible to the countrymen.
Democracy is the opposite term of monarchy and “Monarchy” is a system of government run by a king, queen, sultan or emperor. England and Japan have monarchies but at the same time, they have democratic governments as well.
“India Today Government Democracy and Autonomous Rule summary for Class 7 WBBSE”
India does not have a monarchy. In our democracy, the President is the constitutional head and the Prime Minister is the real head of India.
Chapter 9 India Today Government Democracy And Autonomous Rule Constitution
Constitution is a law book of every independent sovereign country. So India’s rules of administration are called “Constitution”. All most all the countries in the world have their own written constitution.
The largest written constitution of the world is the Indian constitution. There are few countries in the world who do not have written constitutions and therefore those countries follow their conventions of hundreds of years.
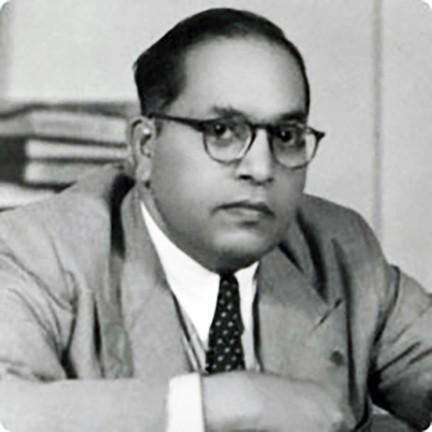

Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar (1891-1956) was the chairman of the “Drafting Committee of the Constitution” (1949) under whose guidance the Indian constitution was written. Before writing the constitution a “Constituent Assembly” was formed.

Its first president was Dr. Rajendra Prasad. The constitution was completed on 26th November 1949 and it came into force on 26th January 1950. This day was celebrated as the first “Republic Day” of India.
“WBBSE Class 7 History Chapter 9 important questions and answers”
The Constitution of India has recognized single citizenship for the citizens. They can cast their vote to elect a government. The state government is formed for five years with the elected members by the people of the concerned state of India.
The central government is formed for five years with the elected members by the people of the whole of India.
Federal Government:
According to the constitution, India is a “Federal Government” because the central and state governments have a co-relation. This system of administration recognizes three power lists like ‘Central list’, ‘State list’, and ‘Concurrent list’.
In many cases, the central and states help each other. For this reason, India is called “a federal country”, but political scientist K. C. Wheare said, “India is not federal, but a quasi-federal state”.

As in many matters central dominates over the state, it is not a fully federal state.
Functions of Government:
The functions of the Government of India are as
- To build India as a welfare state.
- To collect taxes and revenue.
- To preserve the sovereignty of the country.
- To maintain peace and development.
- To help the helpless, poor, old, and orphans.
- To punish the criminals and offenders on behalf of the countrymen.
- The government also has to obey various provisions of the constitution and its guidelines in each and every step of functions,
- “Legislative” functions of a government to enact the laws for the administration of India.
- “Executive” functions mean to administer the country as per constitutional laws.
- “Judicial” activities are to take actions against violation of laws of the land and to oversee – whether the country is being properly ruled as per prescribed laws or the rights of people are properly preserved.
Thus the policy of power separation adopted first by French philosopher Montesquieu has been initiated in Indian administration.
“Government and democracy in India Class 7 WBBSE notes”
The rules for the local Self-Government of West Bengal is an important part of the constitution. In the local Self-Government, people can directly participate in the administration and enjoy autonomous powers.
In West Bengal “Local Self-Government” are of two types. Such as
- “Corporation” (for a big city) and “Municipality” (for urban and semi-urban areas) and
- “Panchayat System” for rural areas. It is not the features of modern administration, in the ancient and medieval Indian administrative system this type of local Self-Government was seen.
Corporation and Municipality:
The main activities of the Corporation and Municipality are as
- The welfare of local people.
- Local public health.
- Improvement of local roads and drainage system.
- Supply of drinking water.
- Construction of roads.
- Establishment of new schools, hospitals, and health centers.
- Spread of education.
- Maintain of local public health, hygiene, cleanliness, and other awareness for the public.
- Control of pollution and others.
‘Mayor’ the head of the Corporation and ‘Chairman’, the head of Municipal rule conducts the duties and responsibilities of their respective administrative areas.
Panchayat System
The village panchayat system is the lowest rank of the Indian administration. The elected members of villagers form the Panchayat Pradhan. Like Municipality, the Panchayat Pradhan of every village carries the overall developmental activities out of the village.
“Government and democracy in India Class 7 WBBSE notes”
Like the Panchayat system, the “Block” is a kind of local Self-Government unit. A Block is generally formed with many villages. Each and every block has a “Panchayat Samity”. A district is formed with many blocks, for which a “Zilla Parishad” is constituted.
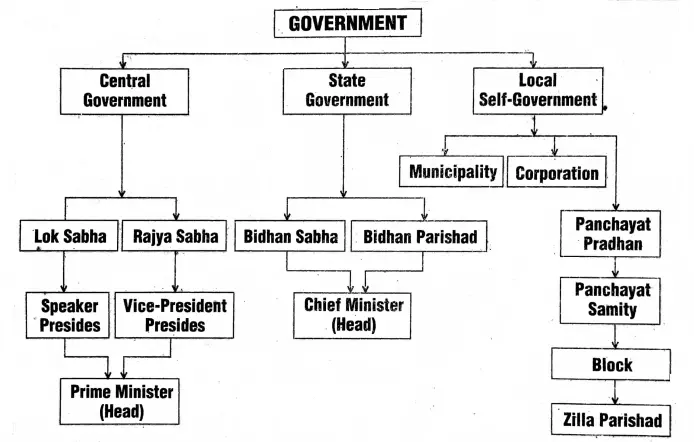
In the local Self-Government system, the “Panchayat Samity” and Zilla Parishad are the most entrusted units of administration. All these local Self-Government bodies are generally formed with elected members for every five years.
Thus the grass-root level of the Indian administration has been recognized for strengthening democracy.
