Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Concept Of Electrical Charging And Discharging
As mentioned earlier that an atom usually consists of an equal number of protons (positive charges) and electrons (negative charges) and is, therefore, electrically neutral.
If, however, the charges are not balanced, an electrically neutral object becomes electrically charged (either positively or negatively charged depending upon the number of protons and electrons).
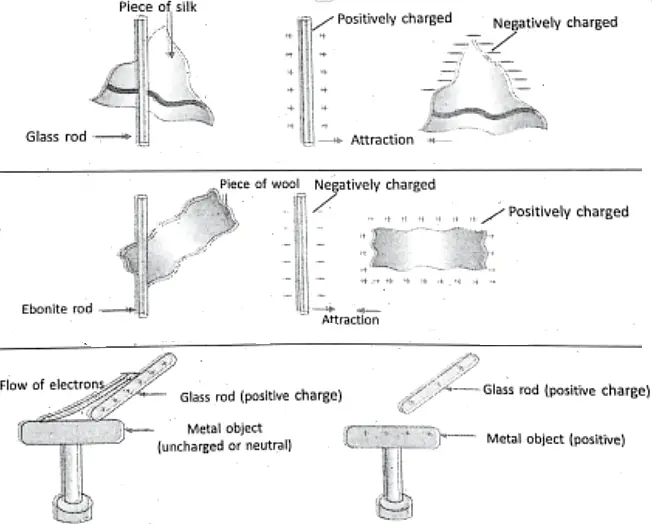
Such a charging can be done by any of the following methods, like
- Charging by friction.
- Charging by conduction.
- Charging by induction.
Read and Learn more WBBSE Notes For Class 8 General Science And Environment
For example, when a plastic comb is rubbed with dry hair or a plastic refill is rubbed with polythene, the objects (comb and hair, refill and poly-then) acquire electric charges. The objects are then called electrically charged objects.- Let us see the following figures to have an idea how charging is done.
How do the charges transfer?
Charges Transfer As follows
Generally, electric charges can be transferred from one charged body to an uncharged body, when they come in contact with one another through a metal conductor so that the electric charges jump from the charged body to the uncharged body till the charges on both of the bodies are equalized. The process is known as charging.
| Class 8 General Science | Class 8 Maths |
| Class 8 History | Class 8 Science LAQs |
| Class 8 Geography | Class 8 Science SAQs |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Geography |
| Class 8 History MCQs | Class 8 History |
“WBBSE Class 8 General Science Chapter 5 notes, Analysis of Natural Phenomena”
On the other hand, the charged bodies lose their charges through air, vacuum or any other gas. The process is known as discharging. An electric spark (which we see at electric switches when they are being turned off) is an example of an electric discharge.

Natural current and natural potential difference :
Throughout the day and night, all over the earth, there is a continuous flow of electric current flowing downwards in the air. The current is very feeble and we never feel it around us. The current is known as natural current.
- When a charged body directly or directly comes in contact with the earth, then the charges are discharged through the earth and the process of such discharging is known as ‘earthing’.
- Our houses, mains and most of the electrical appliances are ‘ earthed’ to protect our lives from electric shocks due to any leakage of electric current.
- Lightning is a huge electric spark in the atmosphere.
What is the source of this current?
Source of this current
There is a potential difference of about .400,000 volts existing between the earth and the atmosphere around 50 km above the earth’s surface. The charged particles (various ions, other minute charged particles) in the airflow due to such a massive potential difference (Which is known as natural potential difference) give rise to the flow of natural current.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Lightning
Lightning occurs because of the transfer of massive electric charges from cloud to cloud, or from one part of the cloud to another part, even from a cloud to the ground.

Let us explain lightning in terms of charges produced by rubbing. It is the fact that the air currents move upward while the water droplets floating in the air move downward. Such vigorous movements separate out electric charges within the clouds, such that, the negative charges accumulate in the lower portion of the clouds while the upper portion carries positive charges.

These charges keep building up and initially, they can not flow through the air, as air is an insulator. But when the magnitude of accumulated charges becomes extremely large, the air is no longer able to resist the flow of the charges. Negative and positive charges meet, i.e., electric discharge occurs.

The electric lightning is accompanied by large amounts of electric current and very very high temperatures. Both discharges occur between two or more clouds, or between the earth and the clouds, and we see streaks as lightning. how the accumulation of charges leads to lightning. show respectively how sheet lightning and for lightning occur in the upper sky.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Lightning Safety
Lightning usually strikes, tall towers, buildings and trees. In this article, we are to discuss about some safety measures to be adopted during a thunderstorm.

Famous scientist Benjamin Franklin proved in 1752 that lightning and the spark which see in our woollen or polyester clothes are essentially the same phenomena.

To find a safe place :
- A house or a building or inside a car (i.e. indoor shelter) is a safe place.
- Open cars or other open vehicles are not safe.
- Not to run across an open field.
- Not to take shelter under a tall tree. If in a forest, then shorter trees are safer.
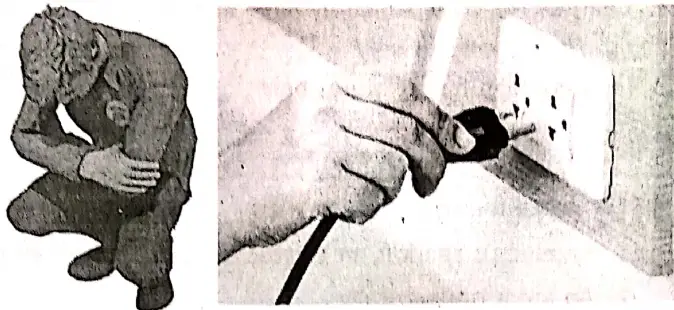
- Not to carry an umbrella during thunderstorms. Stay away from metal poles or other metal objects.
- Not to lie on the ground. Rather, placing hands over the knees and the head between the hands, may lower the risk.
- During thunderstorms, contact of electrical wires, telephone wires, and metal pipes are quite dangerous. So, avoid these. It is safer to use mobile phones.
- Valuable electrical appliances example Tv, washing machine, refrigerator, computer, etc. should be unplugged immediately
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Lightning Conductors
A lightning conductor is a safety device used to protect tall towers and buildings from the damaging effect of lightning. It comprises of a metallic rod, taller than the building, running from top to bottom along the outer wall of the building. The upper end of the rod is kept out in the air, while the lower end is buried at least 5-6 ft deep in the ground.

It provides a direct, easy path for the transfer of electric charge to enter the ground without passing through the building. Even if lightning strikes the house, no damage occurs, as the high voltage is transferred to the earth through the easy path of the lightning conductor.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Epidemic
All of us more or less have a feeling of disease. We are very much familiar with the term -“Disease”. The disease is a condition of the body or part of it in which functions are disturbed or shown some abnormalities.
“Class 8 WBBSE General Science Chapter 5 notes, Natural Phenomena study material”
When a large number of people (hundreds or thousands) die at the same time or in a short period of time, such as within a few weeks, or months or in every year due to break out of fatal diseases, then this type of disease is called an epidemic.

Sometimes you have noticed that many people die of Diarrhoea, Cholera, Dengue, Black fever or SARC then this disease is declared as an epidemic into that area.
Now the question is why particular diseases turn into an epidemic.
A disease is called an epidemic when it spreads rapidly among a large number of people in a community at the same time period.
Before understanding it we have to find the answers of some questions :
- When the disease has been noticed and where has it occurred?
- Whether this disease occurs for the first time or not?
- How widely the disease has been spread?
- What type of people have been affected?
- What is the cause of the outbreak of this disease?
- What measures could have been taken to avoid its outbreak?
- What steps should be taken to its protection?
If you find the answers of these questions you will understand why a particular disease has become an epidemic.
Types of Epidemic :
Knowledge about various types of epidemics and the condition (such as environment, host, population etc) under which they are occurred can be helpful in managing epidemics.
Common Source Of Epidemic (Epidemic From Common Source)
This type of epidemic is caused by a single source of infection of the diseases causing agents for example poisoning of food, water (Minamata disease), or air (Bhopal MIC gas tragedy). A very common example of this type of the epidemic is causing of food poisoning due to the consumption of contaminated food in the feast.
Sometimes you may notice that a good number of people have been transferred to the hospital after taking contaminated Biryani or other types of food like Lassi etc.
Propagate Epidemic Or Epidemic From Infection
This type of epidemic is generally of infectious origin. In this type of disease-causing agent is directly transmitted from one person to another. This type of epidemic is more likely where a large number of susceptible individuals gather such as at fairs, festivals, playgrounds, meetings etc.
Examples of these types of diseases are Small Pox, Measles, Influenza etc.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Epidemic Of Non-Communicable Diseases (Non-Infectious Epidemics)
Change of lifestyle, less physical activity, and intake of frequent junk-food, causes some diseases like—hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, mental diseases, obesity, lung cancer, etc. These are non-infectious diseases, that break out as epidemics known as non-infectious epidemics.
Besides these major types of epidemics, there are some other types of epidemics on the basis of time periods or seasons.
1. Cyclical epidemics :
Some epidemic diseases break out in cyclic order, such as day, week, month or even years.
“WBBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 5, Analysis of Natural Phenomena study guide”
For example, it has been reported that before the discovery of vaccines of Measles generally occur in intervals of 2-3. years, Influenza in the intervals of 7—10 years.
2. Seasonal epidemics :
Some diseases have a close relationship with the seasons of the year. An epidemic which occurs in particular seasons are known as a seasonal epidemic.
For example, Influenza, Pneumonia, and upper respiratory tract infections are common in the winter season whereas diarrhoea and intestinal infections are more common during the summer and rainy seasons. Measles and chicken pox usually break out on the onset of spring.
Different types of epidemics and their Characteristics :
| Epidemic type | Characteristics | Example |
| 1. Common source epidemic | 1. Single-source infection | 1. Food poisoning (by some toxication) Water Poisoning, Air Poisoning etc. |
| 2. .Propagate epidemic or epidemic from infection. | 2. Infectious origin, transmitted from one person to another directly or indirectly | 2. Influenza, Malaria, Smallpox, Measles etc. |
| 3. Non-infectious epidemic | 3. Change of lifestyle, food habits, pollution etc is the cause of the epidemic. | 3. Lung cancer, Heart disease, Diabetes, Obesity etc. |
| 1. Cyclical epidemic | 1. Occur in cycles of time-Period. | 1. Influenza, Measles |
| 2. Seasonal epidemic | 2. Usually breakout in particular season | 2. Diarrhoea and intestinal infections during the rainy season. |
An endemic disease is a disease which has regular occurrence in a given geographic area example, cholera.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Some Diseases :
Cholera :
Germ :
Cholera is caused by tiny germ (bacteria) Vibrio cholera.
Entry of germ :
This germ (V. cholera) enters the human body through contaminated water and food and through not properly washed contaminated utensils and unwashed hands. Fly also plays a role to contaminate food. An unhygienic environment favours bacteria to growth.
Symptoms :
In cholera severe but painless diarrhoea flowed by sudden vomiting. Loss of water (body fluid) occurs which leads to dehydration of the body. It losses the equilibrium of sodium and potassium and other salts of the body. Other symptoms are muscular cramps, and skin becoming cold and wrinkled.

- 80% of cholera cases today can be prevented by applying a rehydration solution.
- One of the first documented epidemics of cholera occurred in 1817 along the coastal region near the mouth of River Ganges.
- Robert Koch (1883 ) discover the germ of cholera and Tuberculosis.
Prevention :
Dehydration can be prevented by giving the patient ORS or salt-sugar solution. Cholera is a deadly disease if not treated properly patients may die. A hygienic environment should be maintained.
ORS = Oral Rehydration Solution
ORT = Oral Rehydration therapy.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Malaria :
Malaria
The world ‘Malaria’ means “bad air”. Malaria fever is one of the oldest most dreadful diseases of mankind. Even now when science and medicine has so advanced about half a million people die every year in the world by malaria.
Germ :
PlasmodiumThis disease vox is caused. falciparum by a tiny and other species of genus Plasmodium. Plasmodium spreads by female Anopheles mosquito (vector) from an infected person to a healthy person. 25th April is observed as World Malaria Day.
Entry of germ :
Plasmodium enters into the mosquitoes body during blood sucking from infected persons and then are transmitted to a healthy person’s body through saliva injected by the mosquito before sucking blood from that person (Some development of Plasmodium also done inside the mosquito’s body therefore Anopheles mosquito is known as a vector).
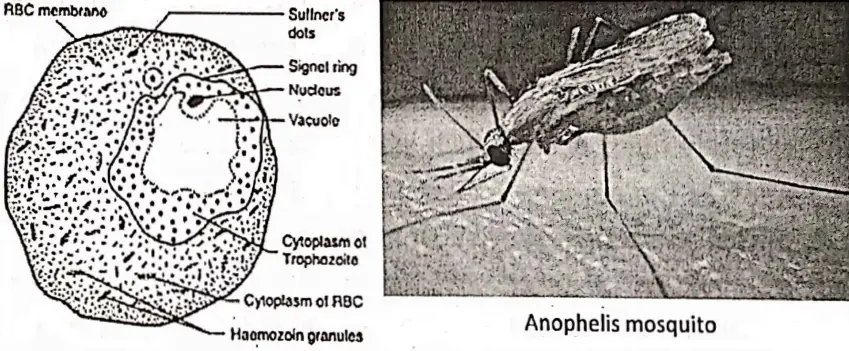
Malaria is the most important of the transmissible parasitic disease over 90 million cases occur each year.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Carriers or vector
Carriers or vector
Though vector and carrier have some differences, you will know it in higher classes. These are those living organisms that spread the germ (Pathogen) from an infected person to a healthy, person. (Some times development of some stages of life cycle of the germ occurs inside them). Vector (example, mosquito), but when direct transmission—carrier (example, house fly).
Symptoms :
The main symptoms of malaria are periodic attacks of shivering followed by high fever (up to 105°F), headache, and muscular pain are also common. When the temperature of the body drops patients sweat heavily. In persons suffering from malaria for a long time the spleen and liver become enlarged. The attack of malaria increases during the summer and rainy seasons with the increase of mosquitoes.
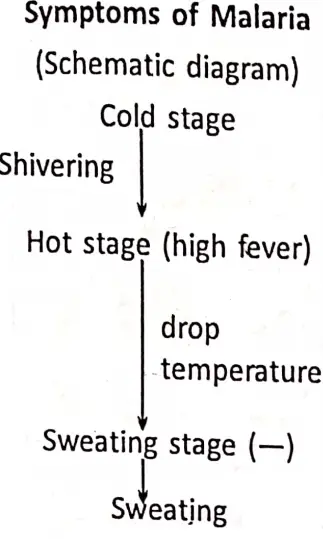
Prevention :
Malaria can be prevented if we able to control its vector, such as, the Anopheles mosquito. Malaria may be fatal if not treated properly
“WBBSE Class 8 Analysis of Natural Phenomena notes, General Science Chapter 5”
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Dengue :
Germ:
Dengue is another fatal mosquito-borne Viral (Flavivirus) disease.
Entry of Germ :
Aedes Egypt mosquito carries the germ (Flavivirus) of dengue from an infected person to a healthy person. Dengue fever is also known as “break-bone fever” for its joint pain-causing features.
Symptoms :
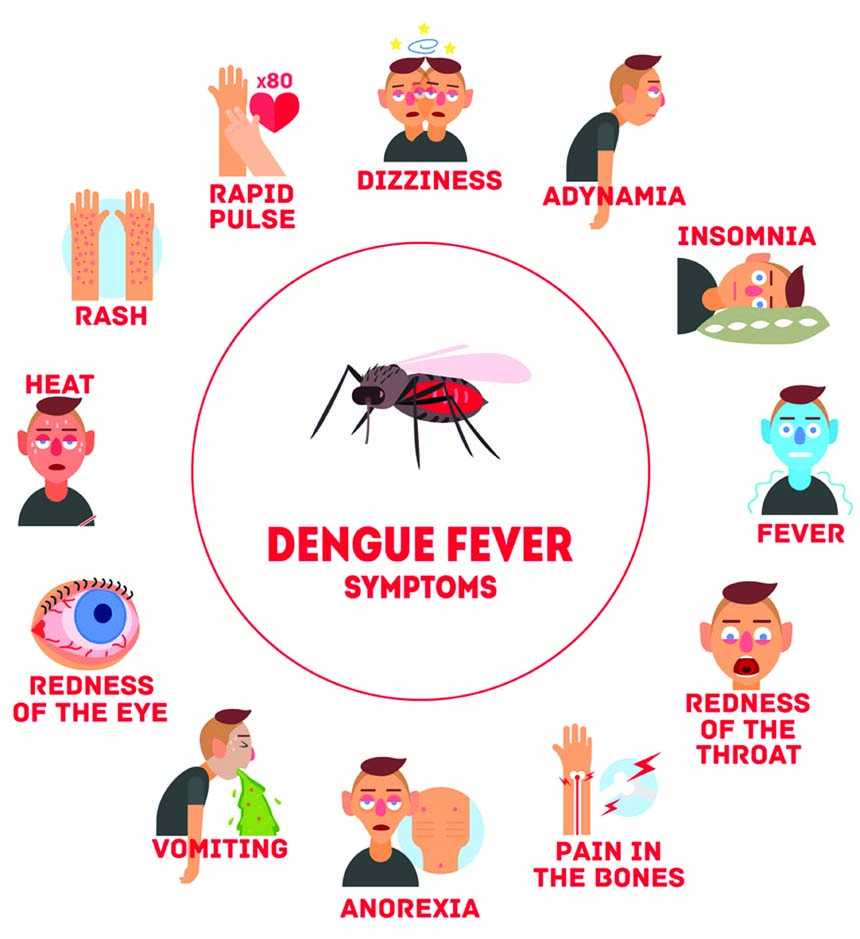
Symptoms of dengue fever are high fever, headache, joint pain, lowering of platelets count and WBC (White Blood corpuscles), and sometimes rashes come out in the body.
Prevention :
Plenty of water to be taken and the patient should be under proper treatment and rest. Prevention from a mosquito bite.
“Class 8 WBBSE General Science Chapter 5, Natural Phenomena easy explanation”
Dengue spread to more than 100 countries in Asia, the Pacific, the Americas, Africa and the Caribbean islands. According to WHO (World Health Organization), nearly 50—100 million people are infected by Dengue in every year
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Plague :
Germ :
Plague Is a bacterial disease transmitted by rat fleas (Xenopsylla coreopsis). The bacteria responsible for the plague is Yersinia pestis.
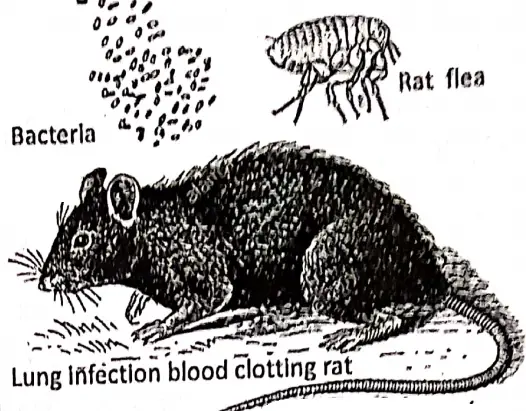
Entry of Germ :
Rat fleas leave the rats (plague infected) that die of Plague and bite human beings and infect the person. This disease can be transmitted by various other means also such as sneezing, and direct body contact. Plague germ be spread through the air.
Symptom :
The main symptoms of plague are high fever, extreme weakness, enlargement of lymph glands, vomiting tendency, headache, lung infection, blood clotting, and blood comes with cough. The plague epidemic in Europe in 1347 was so severe that the population of the continent was reduced to one-third.
Prevention :
This dreadful disease can be avoided in a great extent by an awareness of cleaning the environment and can be controlled by prompt and proper treatment. In 1899 a devastating plague broke out in Calcutta (now Kolkata). Sister Nivedita with her team took a great role to fight against this disease. Waldemar Haffkine (1897) invented a vaccine of the Plague in Bombay (Now Mumbai).
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Smallpox :
Germ :
Smallpox is a highly infectious viral disease also known as “Red plague”. Variola virus is the causative agent of smallpox.
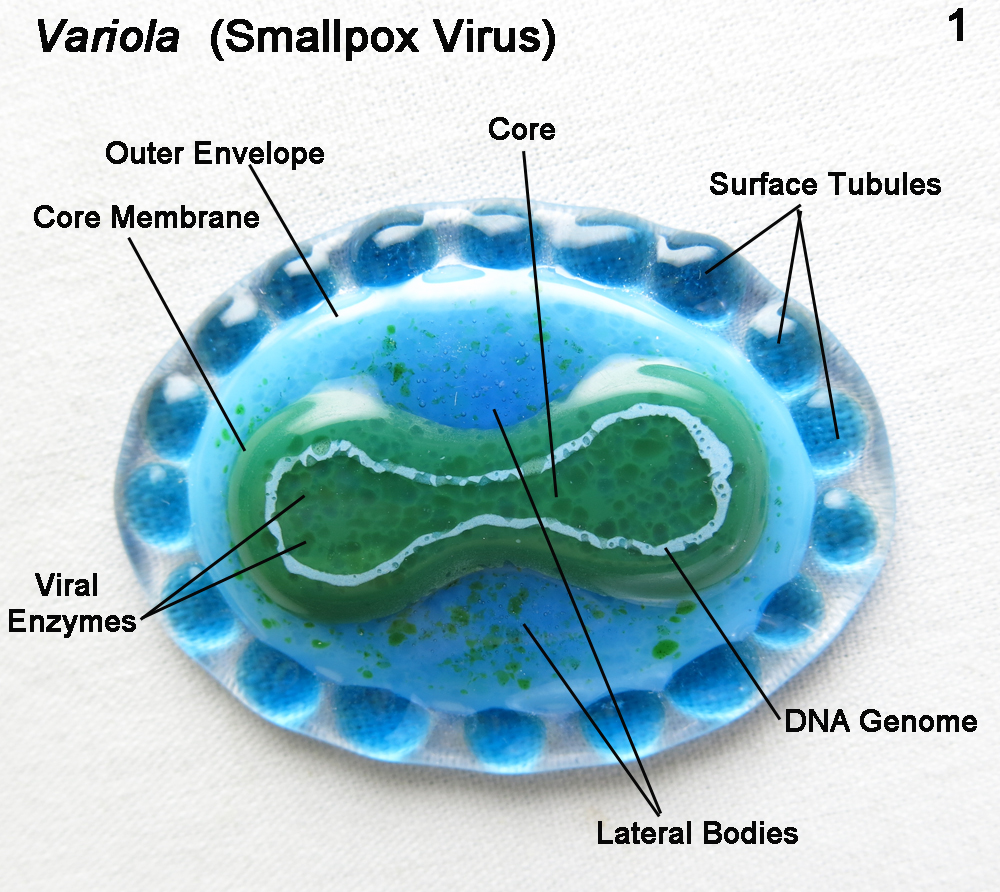
Entry of germ :
Before the invention of the vaccine of smallpox, it was so a deadly disease that ruined many civilizations. It spread through air. Most infections are caused by body contact.

Symptoms :
Infection occurs in the veins and venules of the skin, in the mouth, in the throat may be in other organs. Affected body parts get covered with liquid-filled blisters. Pockmarks after drying leave permanent marks on the skin. In many cases, vision of the patient have been affected. Initially, fever, body aches, headache, and rash appear 48-72 hours after initial symptoms.

Edward Jenner introduced vaccination against smallpox for the first time. He used the cowpox virus to create resistance power in the human body against smallpox. The earliest evidence of smallpox is found in the ‘Egyptian mummies’, people who died some 3000 years ago.
Prevention :
Now this disease has almost been eradicated from the globe after the discovery of the vaccine.

Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural PhenomenaKala Azar (Leishmaniasis)
Germ :
Kala-azar is commonly known as ‘Dumdum fever’ or ‘Black fever’. Kala-azar is caused by tiny unicellular protozoa – Leishmania Donovan. Sand-fly is the carrier of Leishmania. Germs spread by the bite of sand fly from the infected person to a healthy person.
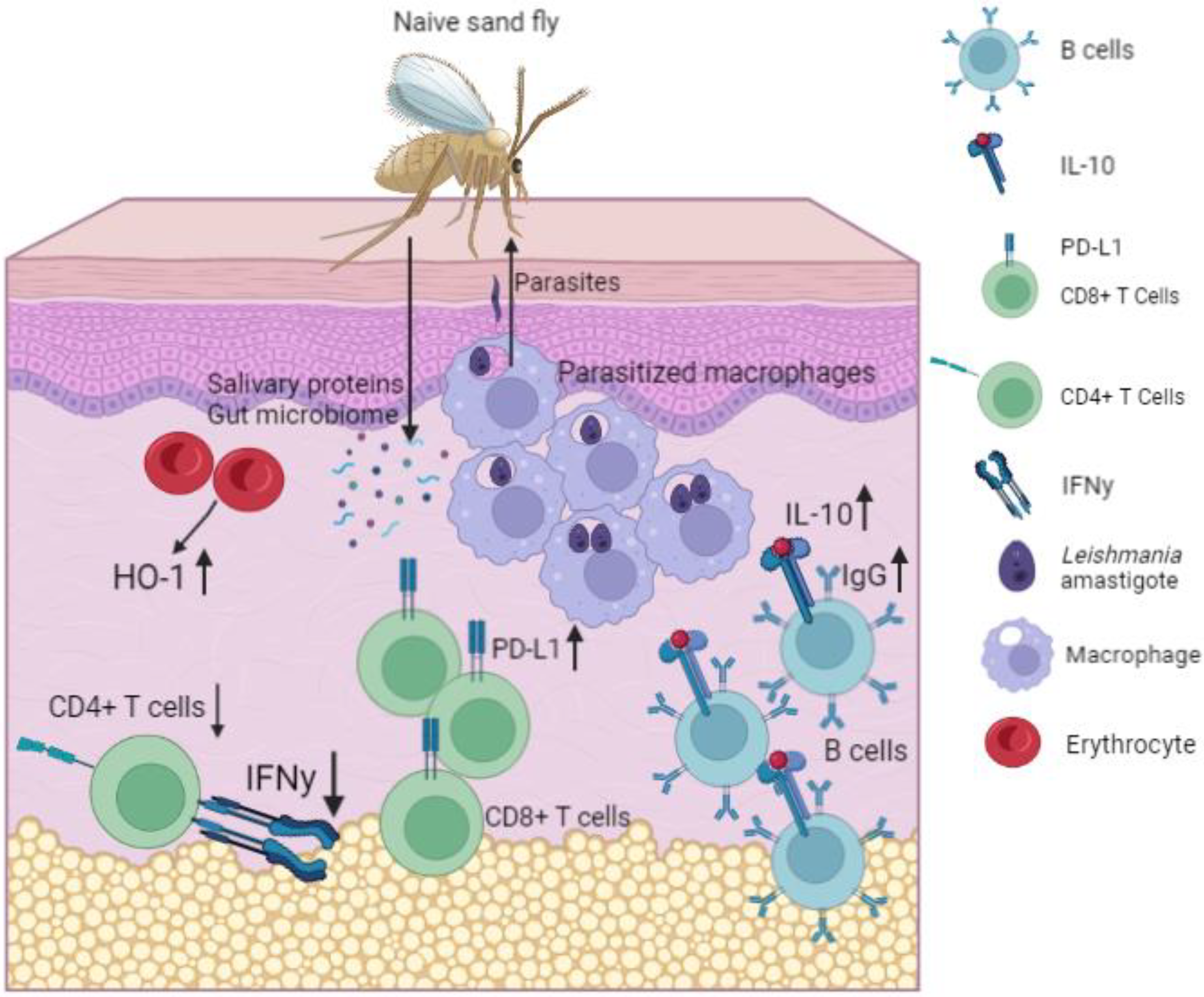
Symptoms :
Symptoms of the disease are continuous fever, loss of appetite and weight, fatigue, anaemia, and enlargement of the spleen and liver. In 1901 British physician Lishman first noticed the germ. Charles Donovan confirm it. So the name of this germ is Leishmania Donovan.
Indian (Bengali) Scientist Upendra Nath Brahmachari invented the medicine of Kala-azar. He was nominated for the Nobel prize though he did not get it.
Prevention :
Now, this disease is curable and can be controlled by proper treatment. A clean environment also helps to control the disease. Kala-azar acquired its name because of patchy muscular darkening of the skin caused by deposits of melanin (a pigment), these develop later on in the disease. Patches are most marked over the forehead and temples and on the mid-abdomen.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Diarrhoea (To Flow) :
Many of you have an experience of diarrhoea. Diarrhoea is the passing of loose stool at frequent intervals.
Germs :
Various agents may responsible for diarrhoea like protozoans, bacteria, viruses, food poisoning etc.
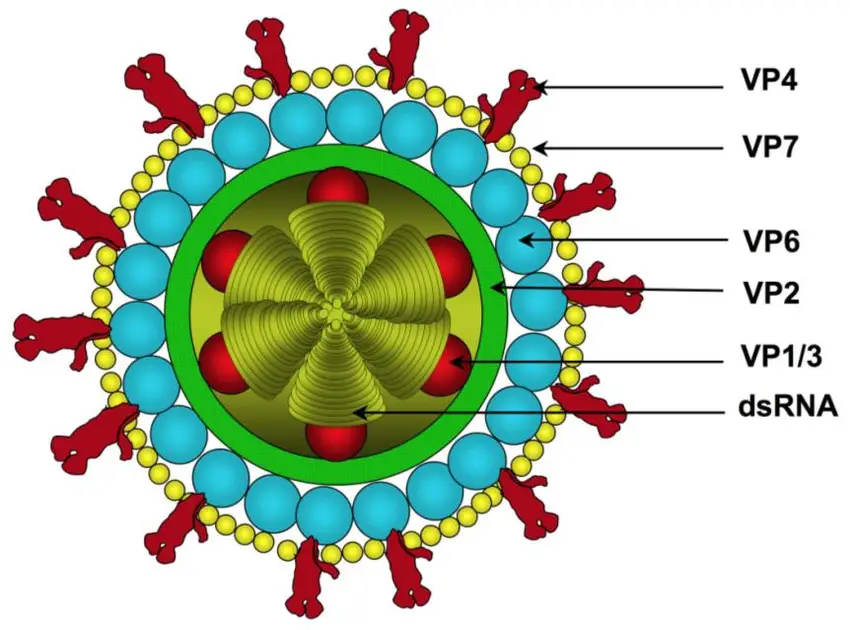
Entry of Germ :
From recent studies, it has been found that the most common diarrhoea-causing virus is the Rotavirus. This virus is normally spread by the faecal-oral route. Contaminated mainly through water and contaminated food.
Symptoms :
During diarrhoea body loses water, it leads to dehydration of the body. The skin, tongue, and inner parts of the mouth became dry, patient may also have fever, stomach pain, vomiting tendency, and weakness. Sometimes blood appears in stool. Salt and acid-alkali equilibrium of the body is disturbed.
Preventions :
Frequent intake of ORS, as well as [ORS = Oral rehydration solution], salt-sugar solution, helps to maintain water-salt balance. Diarrhoea can be controlled by drinking pure water and contamination-free food.
Personal hygiene and community hygiene to be maintained to check this disease. A good percentage (%) of cases may be checked by washing of hands before taking food.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena SARS :
SARS (SARS = Severe acute respiratory syndrome)
Germs :
SARS is a deadly and highly infectious viral disease. SARS was the first broke out in Asia in 2003. Then it spread to Europe and America.
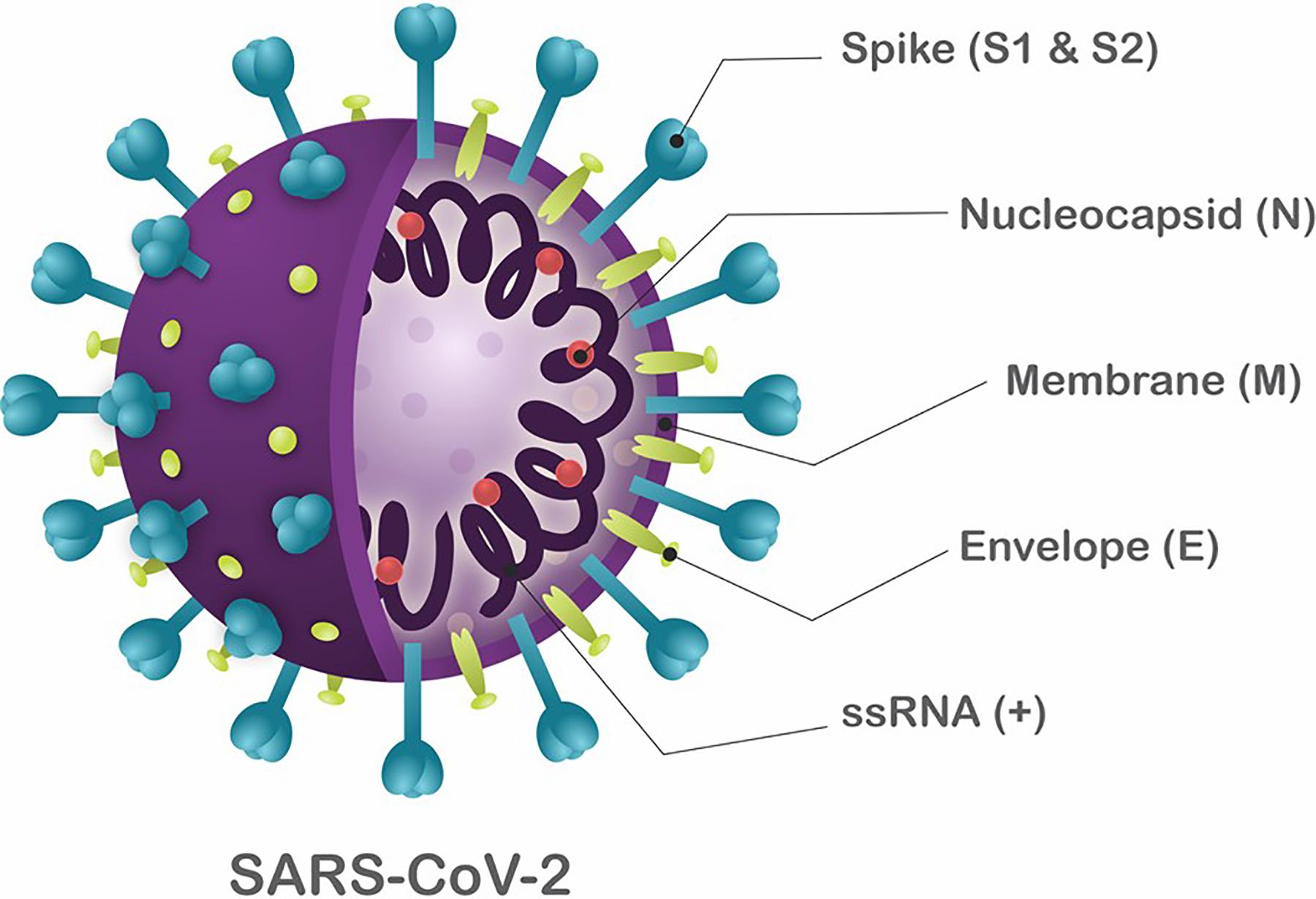
Entry of Germ :
It enters into a healthy person’s body from infected persons through air, sneezing, coughing etc.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of SARS is high fever, severe headache, including muscle aches, sometimes diarrhoea, in late stage shortness of breath, and dry cough with a high fever.
Prevention :
Personal hygiene, and avoid inhaling contaminated air. If not treated properly patient may die. The use of a mask covering the nose and mouth is effective. It is an airborne viral disease.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Tuberculosis (TB) :
Germs :
Tuberculosis is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Though in tuberculosis mainly the lung is affected but it may occur in other parts of the body, such as bone, lymph glands, intestine etc.
Entry of germs:
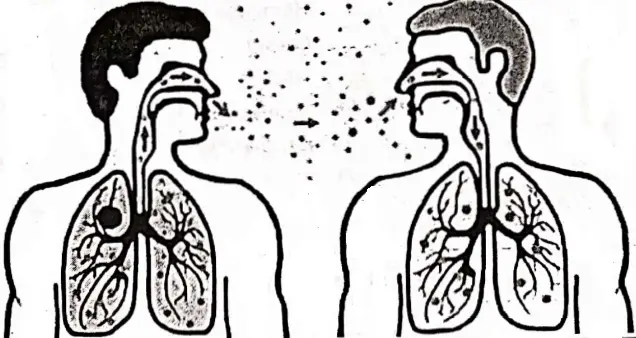
Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease and is transmitted by air from one person to another person infected by droplets released through coughing, sneezing, and spitting by the patient.
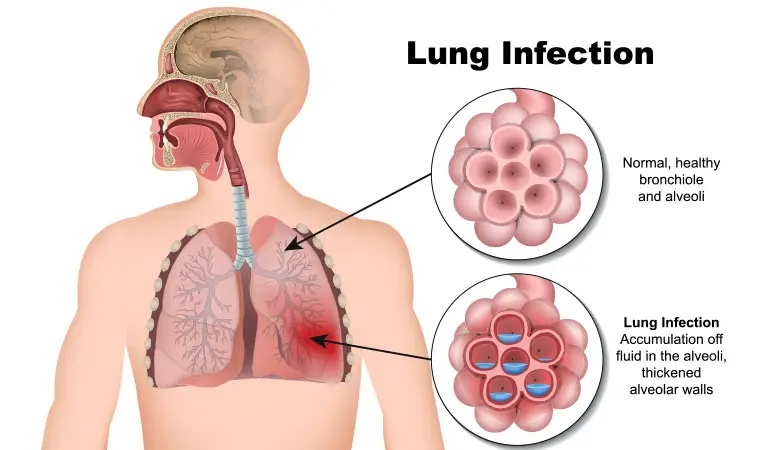
Symptoms Of Tuberculosis :
Symptoms of Tuberculosis include continuous mild fever, sweating at night, loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss, and late-stage blood in cough, and chest pain. TB can be prevented with proper care and treatment.
“Class 8 General Science Analysis of Natural Phenomena notes, WBBSE syllabus”
Preventions For Tuberculosis :
This disease now can be cure completely by using a continuous specific drug.
DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment short course) is a popular treatment and children should be immunized with BCG (Bacille Calmitte Guerin) vaccine. According to WHO India has the highest number of TB cases reported in 2016.
“WBBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 5 notes, Analysis of Natural Phenomena PDF”
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Hepatitis :
Germs :
Hepatitis is mainly a viral disease of the liver. Hepatitis are of five types— Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E. It is an inflammatory condition of liver. Hepatitis may also be caused by drugs, alcohol or certain medical condition.
Entry of germs :
Among these types hepatitis A and E infections are caused by contaminated water and food (faecal oral route) and the other three types i.e. Hepatitis B, C, and D by body fluid and blood.
Symptom :
Due to liver infection liver cells are damaged, releasing yellow pigment— ‘bilirubin’. WHO has declared 28th July as World Hepatitis Day.
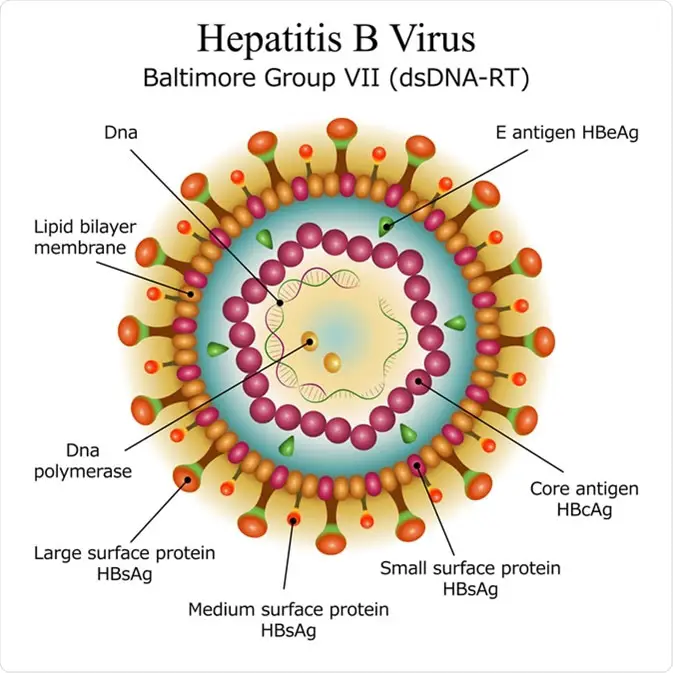
General symptoms of hepatitis is yellowing of the skin and eyes, temperature, fatigue, general weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting tendency, and stomach pain. This condition is referred to as ‘Jaundice’.
Prevention :
Hepatitis is dangerous if not treated properly. Adequate rest and proper treatment is very much needed for hepatitis patient. About 250 million people globally are thought to be affected by hepatitis C and while300 million people are thought to be carriers of hepatitis B.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Influenza Or Flu :
Germs:
It is a highly contagious viral disease (Myxoviruses) mainly infected the respiratory tract (nose, throat arid lung). Besides common influenza different other types of flu are found, among them swine flu and bird flu deserve special attention. Influenza occurs more commonly in the colder months and colder region.
“WBBSE Class 8 General Science Chapter 5, Natural Phenomena important questions”
Entry of Germ :
Influenza is spread easily from person to person contact and by droplet infection via coughing, sneezing or talking. H1N1Swine flu is an influenza virus that was found in April 2009. It causes illness in people worldwide (Pandemic). Many people die of this disease.
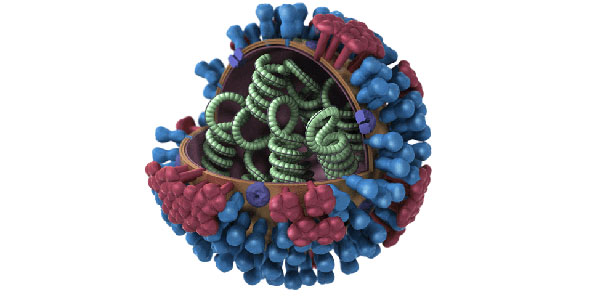
symptoms Of Influenza Or Flu :
The common symptoms of influenza on set of chills, discharge from nose, sneezing, fever, headache, muscular pains, joint pain, coughing, general weakness.
Prevention Of Influenza Or Flu :
Personal hygiene, adequate rest, and plenty of water intake relieve patients, it usually stays 3-7 days.
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena AIDS (AIDS – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) :
Germs :
AIDS is a fatal viral disease. It causes by the retrovirus known as Human Immuno¬deficiency virus (HIV).
Symptoms Of AIDS :
AIDS virus attacks human WBC (White Blood cells) particularly lymphocytes (T4 helper cells) and destroys the self-defence mechanism or human body immunity.
AIDS patients are prone to many other diseases such as tuberculosis, influenza, diarrhoea, fever, skin disease and many other secondary problems as the body’s immunity power weakens or is destroyed. AIDS spreads by sexual contact, blood transfusion, and the use of contaminated syringes.
Entry of Germ :
AIDS is transmitted through blood, (during blood transfusion), or through cuts, if come into contact with an infected person blood or body fluid (mucous, vaginal fluid, siemens etc) or through infected needles. AIDS virus also can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy.
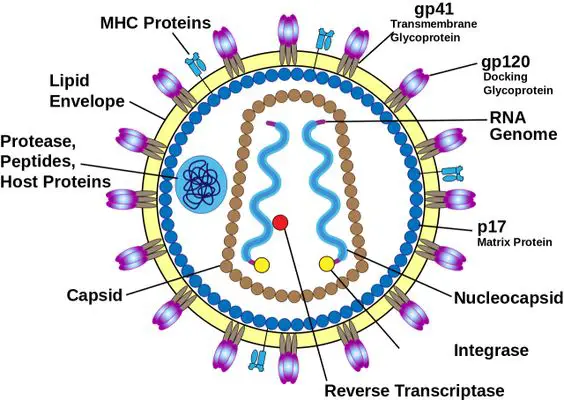
Prevention Of AIDS :
As there is not yet any direct medicine to cure AIDS, prevention is the best method to combat this fatal disease. Social awareness to be developed from every corner.
What Is the basic difference between an epidemic and a Pandemic
Basic difference between an epidemic and a Pandemic
An epidemic occurs when an Infectious disease spreads quickly and affects many people at once In at a short or moderately large area. While pandemic is a global outbreak of disease that kills millions of people in larger areas.
For example—the epidemic of SARS killed 800 people in 2003, while the Spanish flu pandemic killed as many as 50 million people in 1918. Asian influenza pandemic that killed 2 million people In 1957. Cholera In early 19th century.
| Some Days to be remember | |
| 4th February | World Cancer day |
| 24th March | WorldTuberculosis day |
| 7th April | World Health Day |
| 25th April | World Malaria Day |
| 28th July | World Hepatitis Day |
| !st December | World AIDS Day |
Contaminated disease Complete the table (One example given)
| Name of the Disease | Responsible germ/Causative agent | Types of germ | Mode of Transmission | Prevention |
| 1. Cholera | Vibrio cholera | Bacteria | Contaminated by water, food | Personal hygiene, pure water and not taking any contaminated food. |
| 2. Malaria | ||||
| 3. Dengue | ||||
| 4. Plague | ||||
| 5. Influenza | ||||
| 6; Tuberculosis | ||||
| 7. Kala-azar | ||||
| 8. Hepatitis | ||||
| 9. SARS | ||||
| 10. AIDS | ||||
| 11. Diarrhoea |
Chapter 5 Analysis Of Natural Phenomena Table 2
The epidemic of non-infectious diseases
| Food habits and lifestyle | Symptom/ diseases |
| 1. Excess food intaking,. Junk food intaking, less physical work •. | 1. Obecity 2. Diabetes 3. Heart Disease |
| 2. Excess fat Intake, alcohol consumption | 1. Fatty liver 2. Heart disease |
| 3. Irregular food habits, Junk food, intake | Heart disease, gastric ulcer. |
