Class 6 Math Solutions WBBSE Chapter 17 Geometrical Concepts Based On Different Instruments Of Geometry Box Exercise 17
Question 1. I myself drew a quadrilateral and a triangle with the help of scale. I also measured their sides with the scale.
Solution:
ABCD is a quadrilateral
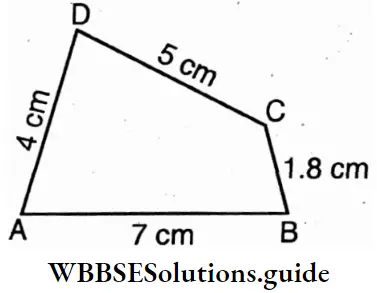
⇒ ABCD is a quadrilateral whose AB = 7 cm, BC = 1.8 cm, CD = 5 cm. and DA = 4 cm.
PQR is a triangle
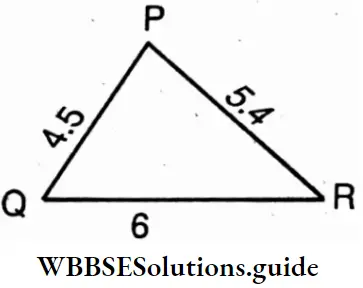
⇒ PQR is a triangle whose PQ = 4.5 cm, QR = 6 cm, and RP = 5.4 cm.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 6 Maths
Question 2. I have drawn two line segments of length 2.8 cm, and 5.3 cm, and named them.
Solution:
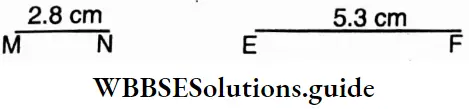
⇒ MN is a line segment whose length = 2.8 cm and EF is another line segment whose length = 5.3 cm.
Class 6 WBBSE Math Solutions Chapter 17 Geometrical Concepts Based On Different Instruments Of Geometry Box Exercise 17.1
Question 1. Let’s draw a line segment of length 4.5 cm with scale and divider.
Solution:
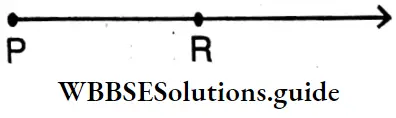
⇒ PR is a line segment whose length is 4.5 cm.
“WBBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 17 geometrical concepts solutions”
Question 2. From a straight line let’s mark out a length – XY equal to 6 cm.
Solution:

Question 3. Using scale and divider, let’s draw two line segments of length 6 cm and 5.7 cm, and name them.
Solution:

Question 4. Using scale and divider let us draw two line segments AB and CD of lengths 3.6 cm and 2.2 cm.
Solution:
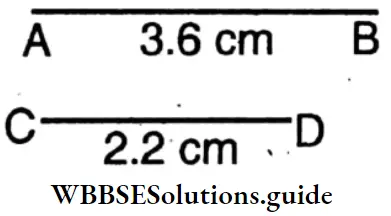
“WBBSE solutions for Class 6 Maths geometry box instruments”
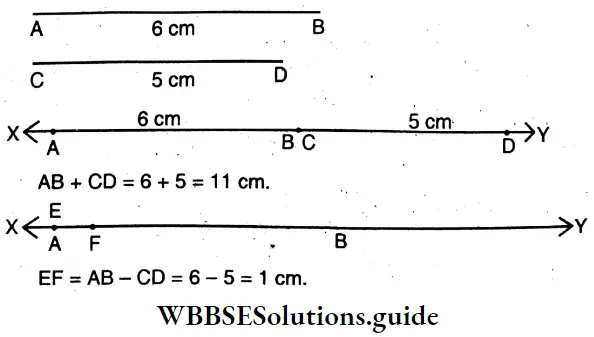
Question 5. On a straight line, let’s draw a line segment XY which is the sum of the line segments AB and CD marked with a divider separately on the line. On another straight line, the segments AB and CD are separately marked in a way with a divider such that the line segment EF is the difference of the line segments AB and CD.
Solution:
let’s draw a line segment
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
Question 6. Using scale and compass and taking two separate points as centres let is draw two circles having radii of lengths 3.2 cm and 2.9 cm
Solution:
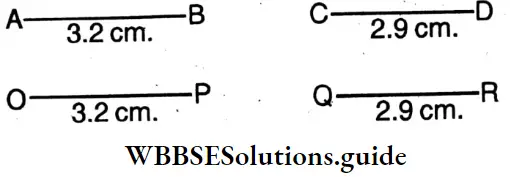
Question 7. Let’s measure and write the values of the angles given below with a protractor. Let’s identify the angles as acute angle or right angle obtuse angle straight angle or reflex angle and arrange them in the increasing order of their values.
Solution:
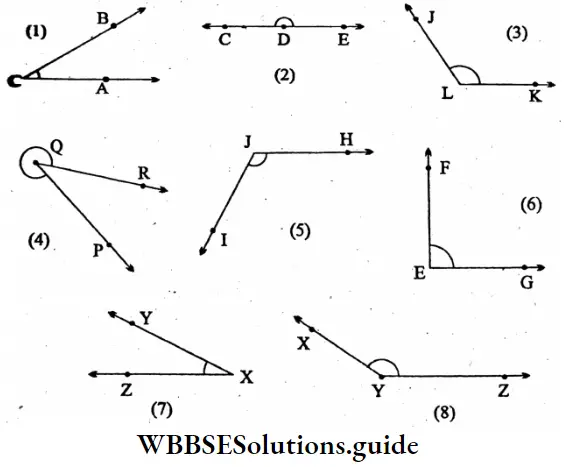
- ∠ACB = 40°; (Acute angle)
- ∠CDE = 180° (Straight angle)
- ∠JLK = 120° (Obtuse angle)
- ∠PQR = 30° (Acute angle)
Reflex Z PQR = 360°-30° = 330°
- ∠IJH = 120° (Obtuse angle)
- ∠FEG = 90° (Right angle)
- ∠YXZ = 30° (Acute angle)
- ∠XYZ = 140° (Obtuse angle)

Question 8. Let’s write the sides and the vertex for each of the following angles.
Solution:
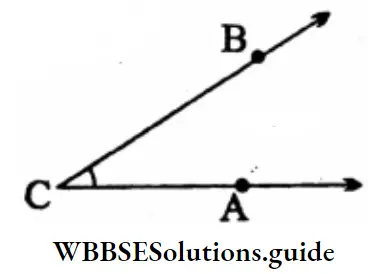
1. Arms: \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}\); \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\)
Sides: \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}} ; \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\)
Vertex: O
“Class 6 Maths WBBSE Chapter 17 geometrical concepts using instruments”
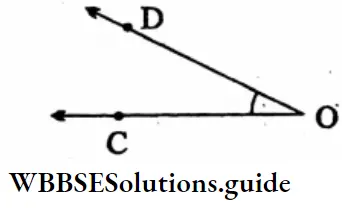
2. Arms: \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OD}}\)
Sides: \(\overrightarrow{O C}, \overrightarrow{O D}\)
Vertex: O

3. Arms: \(\overrightarrow{X Y}, \overrightarrow{Y Z}\)
⇒ Sides: \(\overrightarrow{X Y}, \overrightarrow{Y Z}\)
Vertex: Q
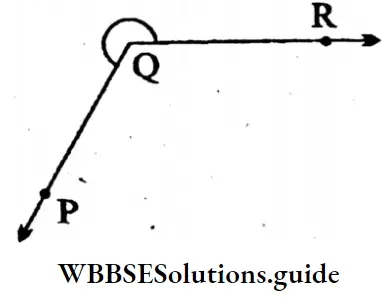
4. Arms: \(\overrightarrow{P Q}, \overrightarrow{Q R}\)
⇒ Sides: \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{QR}}\)
⇒ Vertex: Y
Question 9. Let us draw the following angles with a protractor. Let’s name the angle and write their sides and vertex. Also mention the type of the angles – 38°, 75°, 90°, 145°, 180°, 200°, 270°.
Solution:
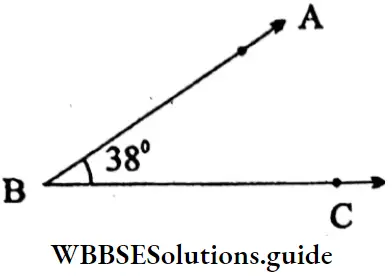
1. ∠ABC =38°(Acute angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}, \overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
Vertex: B
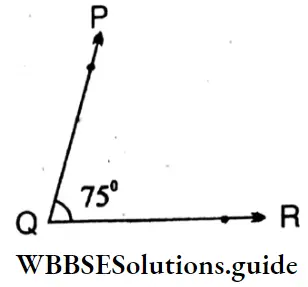
2. ∠PQR = 75°(Acute angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overline{\mathrm{QR}}\)
Vertex: Q
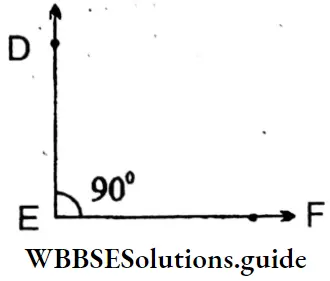
3. ∠DEF = 90°(Rigth angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{DE}}, \overline{\mathrm{EF}}\)
Vertex: E
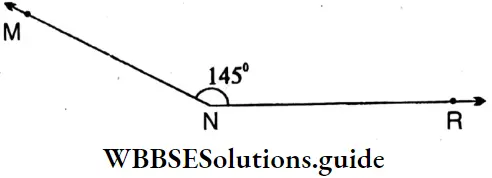
4. ∠MNR = 145°(Obtuse angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}, \overline{\mathrm{NR}}\)
Vertex: N
“Step-by-step solutions for geometrical concepts Class 6 WBBSE”
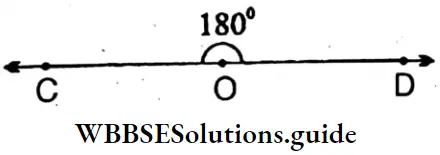
5. ∠COD = 180°(Strigth angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{CO}} ; \overline{\mathrm{OD}}\)
Vertex: O
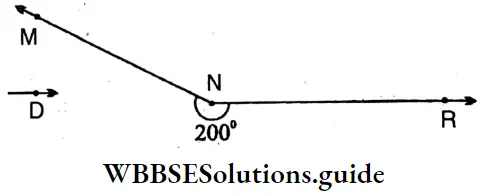
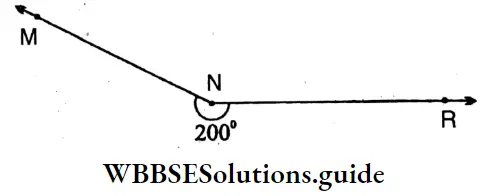
6. ∠IJK = 200°, (Reflex angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{IJ}}, \overline{\mathrm{JK}}\)
Vertex: J
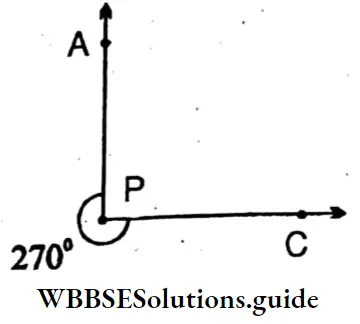
7. ∠APC = 270°(Reflex angle)
Sides: \(\overline{\mathrm{AP}}, \overline{\mathrm{PC}}\)
Vertex: P
Question 10. Let Do It
Solution:
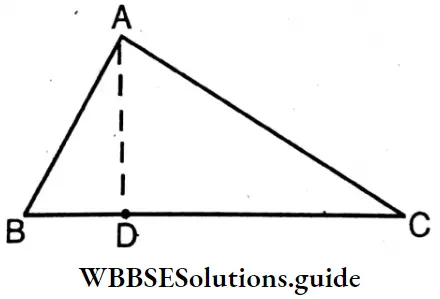
∠BAD = 30°; ∠CAD = 60° and ∠BAC = 90°
∠BAD + ∠CAD = ∠BAC
Again, ∠BAC-∠BAD =∠DAC
∠ADC + ∠ADB = 180° = ∠BDC
∠BDC – ∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
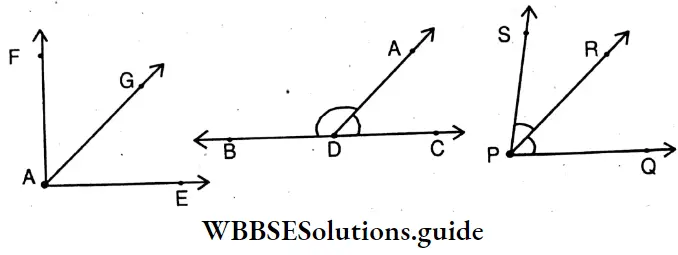
- ∠EAG + ∠GAF = 90°;
- ∠FAE – ∠FAG = 40°
- ∠ADC+ ∠ADB = 180°;
- 180°-∠ADC = 60°
- ∠SPR + ∠RPQ = ∠SPQ
- ∠SPQ – ∠SPR = ∠RPQ
Class 6 Math WBBSE Solutions Chapter 17 Geometrical Concepts Based On Different Instruments Of Geometry Box Exercise 17.2
Question 1. Using the outer and inner scales of the protractor, let’s draw the following angles
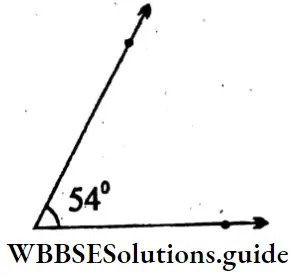
1. 54°
Solution: Angle POQ = 54°
“WBBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 17 important questions and answers”
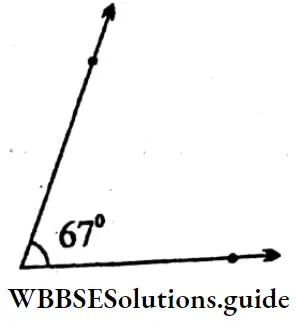
2. 67°
Solution: ∠CDE = 67°
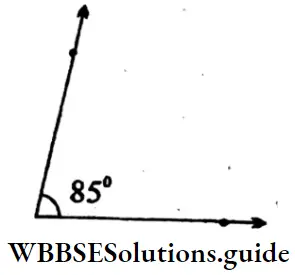
3. 85°
Solution: ∠ABC = 85
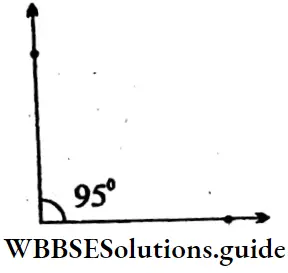
4. 95°
Solution: ∠MNK = 95°
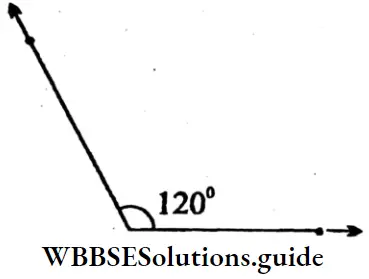
5. 120°
Solution: ∠RPK = 120°
Question 2. Let’s draw 187°, 235°, 310° and 325° angles using protractor:
Solution: 187°
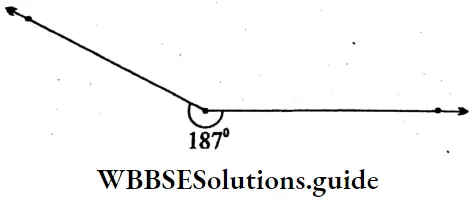
Reflex ∠ABC = 187°
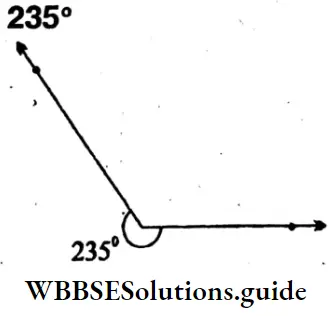
Reflex ∠PQR = 235°
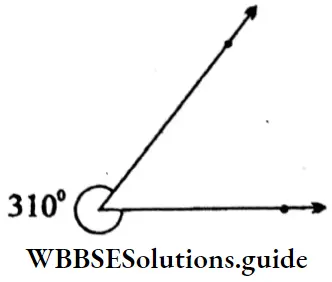
Reflex ∠MKL = 310
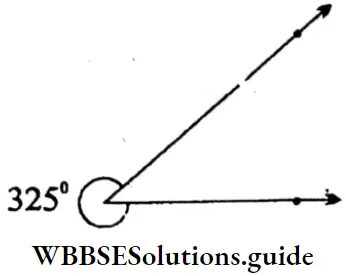
Reflex ∠CDE = 325°
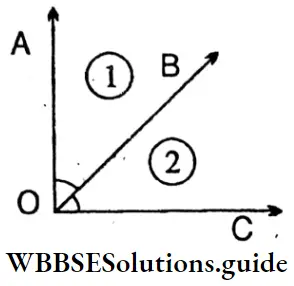
Question 3. Let’s observe the figure and comprehend and write:
- Let’s measure angle number 1, name the angle, type of angle. [Measure with protractor]
- Let angle number 2 be measured with a protractor, name the angle, and write the type of angle.
- The measures of angles 1 and 2 are added and the angle formed.
Solution:
1. ∠1 =40° (Acute angle)
∠BOC= 40°
2. ∠2 = 50° (Acute angle)
∠AOB = 50°
3. ∠1 + ∠2 = 40° + 50° = 90° (Right angle)
∠AOC = 90°
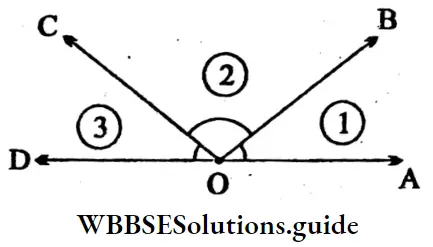
Question 4. In the figure, let’s take angle number 1 = ∠AOB; angle number 2 = ∠BOC; angle number 3 = ∠COD
- Let’s measure angle number 1 with a protractor and note its value.
- Let’s measure angle number 2 with a protractor and note its value.
- Let’s measure angle number 3 with a protractor and note its value.
- By adding angle number 1 and angle number 2, we get an angle, name that angle from the figure. ‘
- By adding angle number 2 and angle number 3, the angle that is formed is named from the figure.
- The angle formed by adding angle number 1, number 2, and number 3 is named from the figure and let’s express it as the sum of three angles.
Solution:
- ∠1 = ∠AOB = 60°
- ∠2 = ∠BOC = 90°
- ∠3 =∠COD = 30°
- ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠AOB + ∠BOC = 60° + 90° = 150°
- ∠2+ ∠3 = ∠BOC + ∠COD.= 90° + 30° = 120°
- ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠AOB+ ∠BOC+ ∠COD= 60° + 90° + 30° = 180°
Question 5. Let’s answer from the figure:
- Let’s name one acute angle: ∠AOB
- Let’s name one obtuse angle:∠BOD
- Let’s name one right angle: ∠COD
- Let’s name one straight angle: ∠AOD
- Let’s name a reflex angle: ∠AOE
- ∠AOB + ∠BOC =∠AOC
- ∠BOC + ∠COD = ∠BOD
- ∠AOC – ∠BOC = ∠AOB
- ∠BOD – ∠BOC = ∠COD
Class 6 Maths Solutions WBBSE Chapter 17 Geometrical Concepts Based On Different Instruments Of Geometry Box Exercise 17.3
Question 1. Lengths of the sides of triangles are given. Let’s identify the types, of triangles according to angles:
- 18 cm 18 cm 10 cm;
- 5.2 cm, 5.2 cm, 5.2 cm;
- 8 cm, 2 cm, 9 cm
Solution:
1. 18 cm, 18 cm, 10 cm: Here the lengths of two sides of a triangle are equal, then it is an isosodes, triangle.
2. 5.2 cm, 5.2 cm, 5.2 cm: Here the lengths of three sides of a triangle are equal, then it is an equilateral triangle.
3. 8 cm, 8 cm, 9 cm: Here the lengths of the three sides of a triangle are not equal, then it is a scalene triangle.
“Solved exercises for geometry box instruments WBBSE Class 6”
Question 2. The measures of the three angles of the triangles are given below. Let’s identify the types according to angles:
- 90°, 45°, 45°
- 90°, 30°, 60°
- 75°, 70°, 35°
- 60°, 60°, 60″
- 120°, 30°, 60°
Solution:
1. 90°, 45°, 45°: Here one angle of a triangle is 90° and the other two angles are equal. So it is a right-angled isosceles triangle.
2. 90°, 30°, 60°: Here one angle is 90°; so, it is a right-angled triangle.
3. 75°, 70°, 35°: Here three angles of a triangle are not equal so it is a scalono trianglo.
4. 60°, 60°, 60°: Here three angles of a triangle are equal; so, it is an equilateral triangle.
5. 120°, 30°, 60°: Here one angle is 120°, greater than 90°- it is an obtuse angle. So tho triangle is an obtuse, angled triangle.
Question 3. A, B, and C are non-collinear points. Let’s join A, B; B, C, and C, A, and try to find answers of the following.
- Let’s identify the geometric figure formed by joining the line segments.
- Let’s write the angle opposite to side BC.
- Let’s write the angle opposite to side AC.
- Let’s write the side opposite to ∠BAC.
- Let’s write the side opposite to ∠ACB.
Solution:
- It is a triangle.
- ∠BAC
- ∠ABC
- Side BC
- Side AB
Question 4. Let’s find if the statements given below are correct or not
Solution:
- Hypotenuse is the smallest side of a right-angled triangle.(x)
- One angle of a right-angled triangle is 90°. (√)
- There are at least two acute angles in a triangle. (√)
- Each equilateral triangle is called an isosceles triangle. (√)
- The sum of three angles of a triangle is 360°. (X)
- The right-angled triangle can never be an equilateral triangle.(√)
- The right-angled triangle can not be an isosceles triangle. (X)
Question 5. Let’s try to draw 120°, 135°, 150° angles using set squares.
Solution:
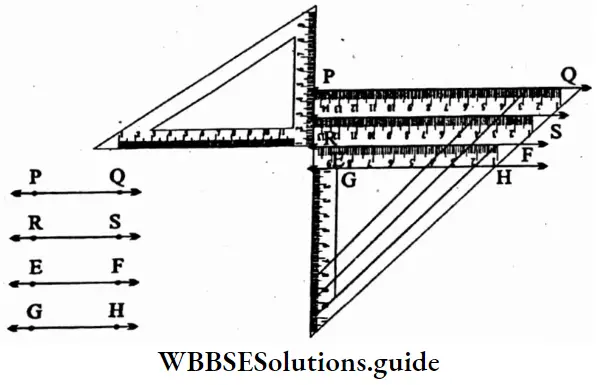
⇒ ∠ABC = 90° + 45° = 135°
To draw 120°
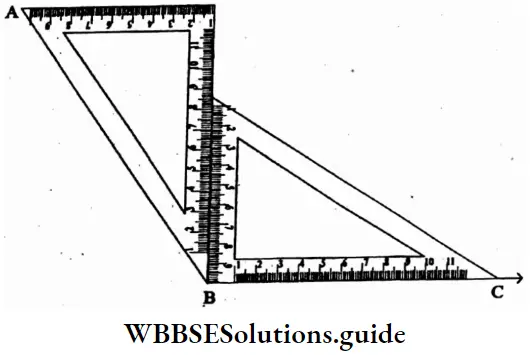
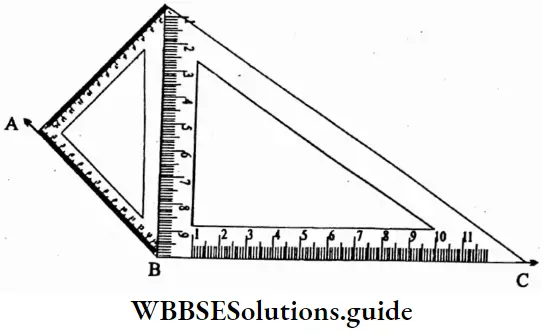
⇒ ∠ABC = 90°+ 60° = 150°
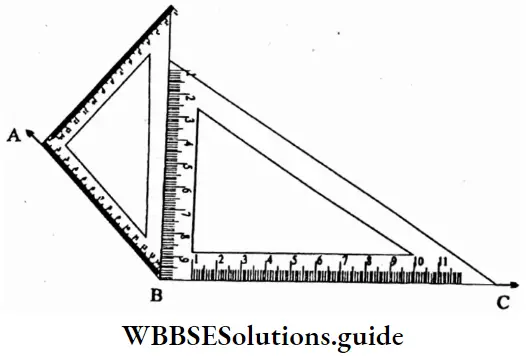
⇒ To draw 150°
⇒ ∠ABC = 90°+ 60° = 150°
6. Let’s write the observations in a tabular form.
Solution:
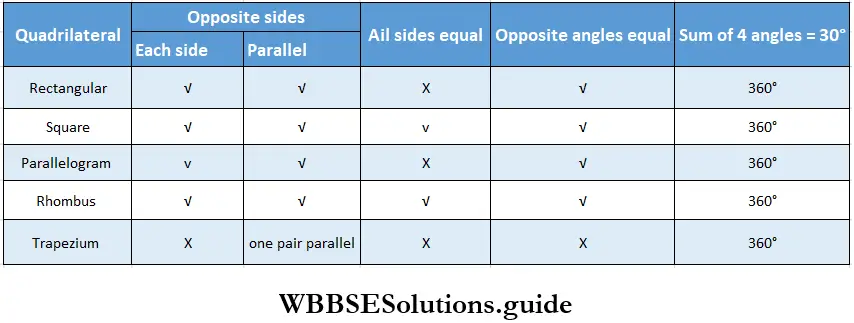
Question 7. Let’s write a logical statement for the set of words given below.
1. Square, Rectangle, Parallelogram — are all quadrilateral.
Solution: Square, rectangle, parallelogram — all have 4 sides, so they are quadrilateral.
2. A rectangle is a special type of parallelogram.
Solution: A rectangle is a special type of parallelogram as opposite sides of the rectangle are equal and parallel.
“Best guide for Class 6 Maths WBBSE geometrical concepts”
3. Parallelogram is a special trapezium.
Solution: Parallelogram is a special type of trapezium as its two sides are parallel.
4. Rhombus is a special type of parallelogram.
Solution: Rhombus is a special type of parallelogram as its opposite sides are equal and parallel.
Question 8. Let’s mark (√) and (X) the incorrect and correct statements respectively given below:
- A rectangular figure has all the sides equal. (X)
- Each angle of a square is a right angle. (√)
- Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel. (√)
- For any trapezium, all its sides are equal. (X)
- None of the angles of a rhombus are right angles. (√)
