Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Algebra Chapter 1 Revision Of Old Lesson Exercise 1 Solved Problems
Question 1. Choose the correct answer
1. The sum of 9 and (-y) is
1. y – 9
2. 9+ y
3. 9-y
4. None of these
Solution: Sum of 9 and (- y) is 9 + (− y) = 9-y
So the correct answer is 3. 9-y
2. What must be added to (-17) to get 12?
1. -5
2. 5
3. -29
4. 29
Solution: The number which is added to (-17) to get 12 is {12 – (-17)} = 12 + 17 = 29
So the correct answer is 4. 29
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 7 Maths
3. The value of (-2)2 x (-3)2 x (-5) is
1. 180
2. -180
3. 120
4. -120
Solution: (-2)2 × (-3)2× (-5)
= (-2) x (-2) × (-3) x (-3) x (-5)
= 4 × 9 × (-5)
= 36 x (-5)
= – 180
(-2)2 × (-3)2× (-5) = – 180
So the correct answer is 2. -180
Wbbse Class 7 Maths Solutions
Question 2. Write ‘true’ or ‘false‘
1. Profit of -10 rupees mean that loss of 10 rupees.
Solution: The statement is true.
2. If the length and breadth of a rectangle are x and y respectively, its semi-perimeter is 2(x + y).
Solution:
Given
⇒ If the length and breadth of a rectangle are x and y respectively
⇒ Semi-perimeter is (x + y),
⇒ So the statement is false.
3. The difference of the two numbers is x. If the greater number is y, then the least number is (x + y).
Solution:
Given
The difference of the two numbers is x. If the greater number is y,
The least number is (y-x)
So the statement is false.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks
1. The value of (-5)2 x (-7) x (-6) is
Solution: (-5)2 × (-7) × (-6)
= 25 × 42
= 1050
The value of (-5)2 x (-7) x (-6) = 1050
2. If perimeter of a square is x cm, then its area is _____ Sq. cm.
Solution: The perimeter of the square is x cm; the length of each side is \(\frac{x}{4}\) cm
Area is \(\left(\frac{x}{4}\right)^2\) sq. cm
= \(\frac{x^2}{16}\)
3. The absolute value of (-3) is _____
Solution: 3
Wbbse Class 7 Maths Solutions
Question 4. Write in language the following expressions
1. \(\frac{x}{4}-3\)
2. ![]()
3. 3p-2
Solution:
1. \(\frac{x}{4}-3\)
Three less than one fourth of x.
2. ![]()
a is not less than four.
3. 3p-2
2 is less three times of p
Question 5. Form the algebraic expression with signs and symbols
1. 5 is subtracted from 4 times y
2. 4 is not less than x
3. x is not equal to y
4. sum of five times y and 6.
Solution:
1. 4y-5
2. ![]()
3. x ≠ y
4. 5y + 6
Question 6. Subtract using concept of opposite number
1. (-13) – (-16)
2. (+12) – (-15)
3. (-17) – (+18)
4. (+10) – (+15)
Solution:
1. (-13) – (-16)
= (-13) + (opposite number of -16)
= (-13) + (+16)
= +3
2. (+12) – (-15)
= (+12) + (opposite number -15)
= (+12) + (+15)
= + 27
3. (-17) – (+18)
= (-17) + (opposite number of +18)
= (-17) + (-18)
=-35
4. (+10) – (+15)
= (+10) + (opposite number of +15)
= (+10) + (-15)
= -5
Wbbse Class 7 Maths Solutions
Question 7. Simplify 10 -(opposite number of – 25) – (opposite number of +12) – (opposite number of -18) – (-6)
Solution: = 10 – (+25) – (-12) – (+18) – (-6)
= 10 – 25+ 12 – 18+ 6
= (10+ 12 + 6) – (25 +18)
= 28-43
= – 15
Question 8. Add the following on number line
1. (-7), (+2)
2. (+4), (-8)
Solution:
1.
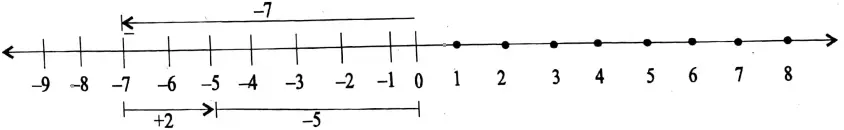
(-7) + (-2) = -5
2.
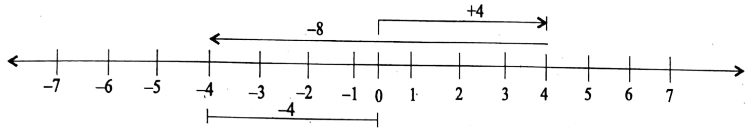
(+4) + (-8) = -4
Wbbse Class 7 Maths Solutions
Question 9. Verify associative property of addition (-5), (3), (+2)
Solution: {(-5)+(-3)}+(+2)
= (-8) + (+2)
= (-6)
(-5)+ {(-3) + (+2)}
= (-5)+(-1)
=-6
So, {(-5)+(-3)} + (+2) = (-5) + {(-3) + (+2)}
Question 10. Find what must be added to the first to get the second
1. (-15), (-10)
2. (+6), (-18)
Solution:
1. The number which added to the (-15) to get (-10) is
(-10) (-15) = (-10) + 15 +5
2. The required number is (-18) (+6)=-18 -6 =-24
Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Algebraic Formula
Algebraic Formula Exercise 12.1
Question 1. To find the square of the algebraic expressions given below using (a + b)² = (a² + 2ab+ b²) let’s find what has to be substituted for a and b in each case, and hence find their squares
Let’s substitute a = x and b = 3.
1. x + 3
Solution :
(x + 3)² = (x)² +2.x.3+ (3)²
= x² +6x + 9
(x + 3)² = x² +6x + 9
2. p + 9
Solution:
(p+ 9)²= (p)² +2.p.9+ (9)²
= p²+ 18p + 81
(p+ 9)² = p²+ 18p + 81
3. 6 – x
Solution :
(6-x)² = (6)² -2.6.x + (x)²
= 36-12x +x²
(6-x)² = 36-12x +x²
4. y-2
Solution :
(y-2)² = (y)² -2.y.2 + (2)²
= y² -4y + 4
(y-2)² = y² -4y + 4
5. mn + I²
Solution :
(mn+l²)² = (mn)²+2.mn.l²+(l²)²
= m²n²+ 2mnl²+ l4
(mn+l²)² = m²n²+ 2mnl²+ l4
6. 6x + 3
Solution :
(6x + 3)² = (6x)² + 2.6x.3 + (3)²
= 36x² + 36x + 9
(6x + 3)² = 36x² + 36x + 9
7. 4x + 5y
Solution:
(4x + 5y)² = (4x)²+2.4x.5y + (5y)²
= 16x² + 40xy + 25y²
(4x + 5y)² = 16x² + 40xy + 25y²
8. pqc + 2
Solution :
(pqc + 2)² = (pqc)² + 2.pqc.2 + (2)²
= p²c²q² + 4pqc + 4
(pqc + 2)² = p²c²q² + 4pqc + 4
9. \(\left(\frac{5}{k}+3\right)\)
Solution:
⇒ \(\left(\frac{5}{k}+3\right)^2\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{5}{k}\right)^2+2 \cdot \frac{5}{k} \cdot 3+(3)^2\)
= \(\frac{25}{k^2}+\frac{30}{k}+9\)
\(\left(\frac{5}{k}+3\right)^2\)= \(\frac{25}{k^2}+\frac{30}{k}+9\)
10. \(\left(\frac{3}{r}+\frac{2}{p}\right)\)
Solution:
⇒ \(\left(\frac{3}{r}+\frac{2}{p}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(\frac{3}{r}\right)^2+2 \cdot \frac{3}{r} \cdot \frac{2}{p}+\left(\frac{2}{p}\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{9}{r^2}+\frac{12}{r p}+\frac{4}{p^2}\)
\(\left(\frac{3}{r}+\frac{2}{p}\right)^2\) = \(\frac{9}{r^2}+\frac{12}{r p}+\frac{4}{p^2}\)
11. \(\frac{p}{q}+\frac{m}{n}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(\left(\frac{p}{q}+\frac{m}{n}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(\frac{p}{q}\right)^2+2 \cdot \frac{p}{q} \cdot \frac{m}{n}+\left(\frac{m}{n}\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{p^2}{q^2}+\frac{2 p m}{q n}+\frac{m^2}{n^2}\)
\(\left(\frac{p}{q}+\frac{m}{n}\right)^2\) = \(\frac{p^2}{q^2}+\frac{2 p m}{q n}+\frac{m^2}{n^2}\)
12. m² +n²
Solution :
= (m² +n²)² = (m² )²+ 2.m².n²+(n²)²
= m4+2m²n²+n4
(m² +n²)² = m4+2m²n²+n4
13. 3xy + 4z
Solution:
= (3xy + 4z)2 = (3xy)2 +2.3xy.4z+ (4z)2
= 9x²y² +24 xyz+16z²
(3xy + 4z)2 = 9x²y² +24 xyz+16z²
14. 2x + 3y + z
Solution :
= (2x + 3y + z)2
= (2x)2 + (3y)2+ (z)2 + 2.2x.3y+ 2.2x.z + 2.3y.z
= 4x2 + 9y2 + z2 +12xy + 4xz + 6yz
(2x + 3y + z)2 = 4×2 + 9y2 + z2 +12xy + 4xz + 6yz
15. 102
Solution:
= (102)2 = (100 + 2)2
= (100) 2+ 2.1 00.2+(2)2
= 10000 + 400 + 4 = 10404
(102)2 = (100 + 2)2 = 10404
16. p + q + r + s
Solution :
= (p+ q+.r + s)2
= (p)2 + (q)2 +(r)2 + (s)2+ 2pq+ 2pr + 2ps+ 2qr+ 2qs+ 2rs
(p+ q+.r + s)2 = (p)2 + (q)2 +(r)2 + (s)2+ 2pq+ 2pr + 2ps+ 2qr+ 2qs+ 2rs
Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Algebraic Formula Exercise 12.2
To find the squares of the algebraic expressions given below, using (a- b)2 = (a)2 -2ab + b2 what has to be substituted for a and b in, and hence let’s find the squares.
1. x-5
Solution:
(x-5)² = (x)-2.x.5+ (5)2
= x2 -10x + 25
(x-5)² = x2 -10x + 25
2. m – n
Solution :
(m – n)² = (m)² -2.m.n+ (n)2
= m2 -2mn+ n2
(m – n)² = m2 -2mn+ n2
3. 10- x
Solution:
(10-x)2 = (10)² -2.10.x + (x)²
= 100-20x + x²
(10-x)2 = 100-20x + x²
4. x +y
Solution:
(x+y)² = (x)2 +2.x.y +(y)
= x² + 2xy + y²
(x+y)² = x² + 2xy + y²
5. 3x – y
Solution :
(3x-y)² = (3x)² – 2.3x.y +(y)²
= 9x² – 6xy + y²
(3x-y)² = 9x² – 6xy + y²
6. 4m + 2
Solution:
(4m + 2)² = (4m)² +2.4m.2+ (2)2
= 16m² + 16m + 4
(4m + 2)² = 16m² + 16m + 4
7. 5y + x
Solution:
(5y + x)² = (5y)² +2.5y.x +(x)²
= 25y² +10xy + x²
(5y + x)² = 25y² +10xy + x²
8. ce-fg
Solution:
(ce-fg)² = (ce)² -2.ce.fg+ (fg)²
= c² e² -2cefg + f² g²
(ce-fg)² = c² e² -2cefg + f² g²
9. \(p x-\frac{1}{2}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(p x-\frac{1}{2}\)
= (px)² – 2. px \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
= p2x2 – px + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
\(p x-\frac{1}{2}\) = p2x2 – px + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
10. p + q – r
Solution :
(p +q-r)2
= (p+q)²- 2+(p+q). r +(r)2
= p2 + 2pq+ q2+ 2pr- 2qr + r2
= p2 +q2 + r2 – 2pq+ 2pr-2qr
(p +q-r)2 = p2 +q2 + r2 – 2pq+ 2pr-2qr
11. p – q + r
Solution:
(p-q + r)2 = (p-q)²+ 2.(p-q).r + (r)2
= p2 – 2pq + q2 + 2pr- 2qr + r2
= p2 + q2 + r2 -2pq+ 2pr-2qr
(p-q + r)2 = p2 + q2 + r2 -2pq+ 2pr-2qr
12. \(\frac{2 x}{3}-\frac{3 y}{4}\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}-\frac{3 y}{4}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}\right)^2-2 \cdot \frac{2 x}{3} \cdot \frac{3 y}{4}+\left(\frac{3 y}{4}\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{4 x^2}{9}-x y+\frac{9 y^2}{16}\)
\(\left(\frac{2 x}{3}-\frac{3 y}{4}\right)^2\) = \(\frac{4 x^2}{9}-x y+\frac{9 y^2}{16}\)
13. 3m³ – 4n³
Solution :
(3m³-4n³)² = (3m³)² -2.3m³.4n³ +(4n³)²
= 9m6 -24m³n³ +16n6
(3m³-4n³)² = 9m6 -24m³n³ +16n6
14. 2x + y – z
Solution :
(2x + y-z)² = (2x + y)²- 2.(2x + y). z + (z)²
= 4x² +2.2x.y + y² -4xz-2yz + z²
= 4x² +y² +z² +4xy-4xz-2yz
(2x + y-z)² = 4x² +y² +z² +4xy-4xz-2yz
15. 999
Solution :
(1000-1)² = (1000)² -2.1000.1 + (1)²
= 1000000-2000 + 1
= 998001
(1000-1)² = 998001
14. p + q – r – s
Solution :
(p + q-r-s)²
= {(p+q)-(r+ s)}²
= p+ q²-2.(p+ q).(r+ s)+(r+ s)²
= p² + 2pq + q² – 2pr- 2ps- 2qr + 2qs + r² + 2rs + s²
= p² + q² + r² + s² + 2pq- 2pr- 2ps- 2qr + 2qs + 2rs
(p + q-r-s)² = p² + q² + r² + s² + 2pq- 2pr- 2ps- 2qr + 2qs + 2rs
WB Class 7 Math Solution Algebraic Formula Exercise 12.3
Question 1. Which one of the following is equal to the product of (a + b) x (a +b)
- a² + b²
- (a + b)²
- 2(a + b)
- 4ab
Solution: 2. (a + b)²
(a + b) (a + b) = a² + ab + ab + b² = a² + 2ab + b² = (a + b)²
Question 2. Let’s find, which of the following will be the value for k satisfying the identity (x + 7)² = x² + 14x + k.
- 14
- 49
- 7
- None of these
Solution: 2. 49
(x + 7)² = x²+2.x.7+ (7)² = x² +14x + 49
Question 3. Which one of the following algebraic expressions must be added to a² + b² so that the sum is a perfect square? Let’s find.
- 4ab
- – 4ab
- 2ab or – 2ab
- a²+b²+2ab = (a + b)²
Solution: 3. 2ab or – 2ab
a²+b²+2ab = (a + b)²
a² + b² – 2ab = (a – b)²
Question 4. If (a+ b)² = a² +6a + 9, let’s find, which of the following is the positive value for b.
- 9
- 6
- 3
- -3
Solution: 3. 3
(a + b)² = a² + 6a + 9
= a²+2.a.3 + (3)²
Question 5. Let’s find, which one of the following numbers when added to \(x^2+\frac{1}{4} x\) makes it a perfect square
- \(\frac{1}{64}\)
- – \(\frac{1}{64}\)
- \(\frac{1}{8}\)
- None of these
Solution: \(\frac{1}{64}\)
= \(x^2+\frac{1}{4} x\)
= \(x^2+2 \cdot x \frac{1}{8}+\left(\frac{1}{8}\right)^2-\frac{1}{64}\)
= \(\frac{1}{64}\)
Question 6.
1. Let’s find, for which values of k, will the expression c² + kc + \(\frac{1}{9}\) be a perfect square.
Solution:
c² + kc + \(\frac{1}{9}\)
= \((c)^2 \pm 2 \cdot c \cdot \frac{1}{3}+\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^2\)
= \(c^2 \pm \frac{2}{3} c+\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)^2\)
K = ± \(\frac{2}{3}\)
2. Let’s find what must be added or subtracted from \(9 p^2+\frac{1}{9 p^2}\) make it a perfect square.
Solution:
⇒ \(9 p^2+\frac{1}{9 p^2}\)
⇒ \((3 p)^2+\left(\frac{1}{3 p}\right)^2 \pm 2.3 p \cdot \frac{1}{3 p}\)
⇒ \((3 p)^2+\left(\frac{1}{3 p}\right)^2 \pm 2\)
⇒ \(\left(3 p \pm \frac{1}{3 p}\right)^2\)
= (2) or (-2)
3. If (x-y) = 4-4y + y² then let’s find the value of x.
Solution :
(x- y) = 4- 4y + y²
= (x- y)² = (x)² – 2xy + (y)
∴ x²= 4
∴ x = 2
4. If (c-3) = c² + kc + 9 , let’s find the value of k.
Solution :
(c-3) = c²+kc + 9 = (c)²-2.c.3+ (3)² .
∴ K = – 6
Question 7. Let’s simplify by using a formula.
1. (2q- 3z)²- 2 (2q- 3z)(q- 3z)+ (q- 3z)²
Solution:
= (2q- 3z)² – 2 (2q- 3z)(q- 3z)+ (q- 3z)²
= {(2q- 3z)-(q- 3z)}²
= (2q- 3z- q + 3z)²
= q²
2. (3p+ 2q- 4r)² + 2(3p + 2q- 4r)(4r- 2p- q) + (4r- 2p- q)²
Solution :
= (3p+ 2q-4r)² +2(3p+ 2q-4r)(4r-2p-q)+(4r-2p-q)²
= {(3p + 2q- 4r) + (4r- 2p- q))²
= (3p+ 2q- 4r + 4r- 2p- q)²
= (p+ q)²
= p² + 2pq + q²
Question 8. Let’s express the following as a perfect square.
1. 16a ² -40ac+ 25c²
Solution :
16a ² – 40ac + 25c².
= (4a)² – 2. 4a .5c +(5c)²
= (4a -5c)²
16a ² – 40ac + 25c². = (4a -5c)²
2. 4p²- 2p + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Solution:
4p²- 2p + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= (2p)² – 2. 2p. \(\frac{1}{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(2 p-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
4p²- 2p + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\left(2 p-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
3. \(1+\frac{4}{a}+\frac{4}{a^2}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(1+\frac{4}{a}+\frac{4}{a^2}\)
⇒ \((1)^2+2 \cdot 1 \cdot \frac{2}{a}+\left(\frac{2}{a}\right)^2\)
⇒ \(\left(1+\frac{2}{a}\right)^2\)
\(1+\frac{4}{a}+\frac{4}{a^2}\) = \(\left(1+\frac{2}{a}\right)^2\)
4. 9a²+ 24ab + I6b²
Solution:
9a² +24ab+ I6b²
= (3a)² +2.3a.4b + (4b)²
= (3a + 4b)²
9a² +24ab+ I6b² = (3a + 4b)²
Question 9. Let’s express the following as a perfect square and hence find the values.
1. 64a² +16a +1 When 3 = 1
Solution:
= 64a²+ 16a +1
= (8a)² + 2.8a.1 + (1)²
= (8a + 1)²
= (8a + 1+ 1)²
Putting a = 1
= (8+ 1)²
= (9)²
= 81
64a²+ 16a +1 = 81
2. 25a² -30ab + 9b² When a = 3&b = 2
Solution :
= 25a² -30ab + 9b²
= (5a)² – 2. 5a. 3b + (3b)²
= (5a- 3b)²
= (5 × 3-3 × 2)² Putting a = 3, b = 2
= (15-6)² = (9)² =81
25a² -30ab + 9b² =81
3. \(64-\frac{16}{p}+\frac{1}{p^2}\) When p = -1
Solution:
⇒ \(64-\frac{16}{p}+\frac{1}{p^2}\)
= \((8)^2-2 \cdot 8 \cdot \frac{1}{p}+\left(\frac{1}{p}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(8-\frac{1}{p}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(8-\frac{1}{-1}\right)^2\)
Putting p = -1
= (8+1)²
= (9)²= 81
\(64-\frac{16}{p}+\frac{1}{p^2}\) = 81
4. p²q² + 10pqr + 25r² When p = 2, q =-1 and r= 3
Solution:
= p²q² +I0pqr + 25r²
= (pq)² +2.pq.r+ (5r)²
= (pq + 5r)²
= {2.(-1)+ 5.3}²
= (-2+ 15)²
= (13)² =169
p²q² +I0pqr + 25r² =169
Question 10. Let’s apply, (a + b)² +(a-b)² = 2(a²+b²) Or, (a + b)² – (a- b)² = 4ab Or, ab = \(\left(\frac{a+b}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{a-b}{2}\right)^2\) to find the following
1. Let’s find st and (s² + t² ) when s + 1 = 12 and s – 1 = 8
Solution:
st = \(\left(\frac{s+t}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{s-t}{2}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(\frac{12}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{8}{2}\right)^2\)
= (6)²- (4)²
= 36-16= 20
(s² + t²) = (s+t)²+(s-t)²
= (12)² +(8)
= 144 + 64
= 208
s²+t² = \(\frac{208}{2}\)
= 104
2. Let’s find 8xy(x² + y²) when (x + y) = 5 and (x – y) = 5
Solution :
8xy(x² + y²)
= 4xy × 2(x² +y²)
= {(x+ y)² -(x-y)²}× {(x-y)²+ (x-y)²}
= {(5)²- (1)² } × (5)²- (1)² }
= (25-1) (25 + 1)
=(25)²-(1)²
= 625 – 1 = 624
8xy(x² + y²) = 624
3. Let’s find when \(\frac{x^2+y^2}{2 x v}\) = 9 and (x – y) = 5
Solution:
⇒\(\frac{x^2+y^2}{2 x v}\)
= \(\frac{(x+y)^2+(x-y)^2}{2} \times \frac{1 \times 2}{4 x y}\)
= \(\frac{(x+y)^2+(x-y)^2}{(x+y)^2-(x-y)^2}\)
= \(\frac{(9)^2+(5)^2}{(9)^2-(5)^2}\)‘
= \(\frac{81+25}{81-25}\)
= \(\frac{106}{56}\)
= \(\frac{53}{28}\)
4. Let’s express 36 as the difference of two squares[ Hints, 36= 4 × 9 \(\left(\frac{4+9}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{4-9}{2}\right)\)
Solution:
36 = 4 × 9
= \(\left(\frac{4+9}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{4-9}{2}\right)^2\)
5. Let’s express 44 as the difference of two squares.
Solution :
44 = 11 × 4
⇒ \(\left(\frac{11+4}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{11-4}{2}\right)^2\)
= \(\frac{(15)^2}{4}-\frac{(7)^2}{4}\)
= \(\frac{225}{4}-\frac{49}{4}\)
= \(\frac{225-49}{4}\)
6. Let’s express 8x² + 50y² as the sum of two squares.
Solution:
8x² + 50y²
= 2 × (4x² + 25y²) = 4x² + l0xy+ 25y²+ 4x² – 10xy + 25y²
= (2x +5y)² + (2x- 5y)²
8x² + 50y² = (2x +5y)² + (2x- 5y)²
7. Let’s express x as the difference of.two squares.
Solution :
= x = x . 1
⇒ \(\left(\frac{x+1}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{x-1}{2}\right)^2\)
WB Class 7 Math Solution Algebraic Formula Exercise12.4
Question 1. Using the identity (x+ a) (x + b) = x² + (a + b) x + ab, let’s find the product of the following algebraic expressions.
1. (x + 7) (x + 1)
Solution :
(x + 7) (x + 1)
= x² +(7 +1)x + 7
= x² + 8x + 7
2. (x – 8) (x – 2)
Solution :
(x – 8) (x – 2)
= x² +(-8- 2)x + (-8)(-2)
= x²-10x + 16
3. (x + 9) (x – 6)
Solution :
(x + 9) (x – 6)
= x² + (9- 6)x+ (9)(-6)
= x²+ 3x – 54
4.(2x+1)(2x-1)
Solution :
(2x +1 ) (2x – 1 )
= (2x)² + (1- 1)2x + (1)(-1)
= 4x²- 1
5. (xy – 4) (xy + 2)
Solution :
(xy – 4) (xy + 2)
= (xy)²+(-4 + 1)xy + (-4)(+2)
= x²y²- 2xy-8
6. (a² + 5) (a²- 4)
Solution :
(a² +5) (a² -4)
= (a²)² + (5- 4)a²+ + (5)(-4)
= a4+a²-20
Question 2. Using the formula, let’s show that
1. (2x + 3y)² – (2x- 3y)² = 24xy
Solution :
(2x + 3y)²- (2x- 3y)²
= (2x + 3y + 2x- 3y) (2x + 3y- 2x + 3y)
= 4x × 6y
= 24xy RHS.
2. (a+ 2b)² +(a- 2b)²=2 (a² + 4b²)
Solution :
(a + 2b)² +(a- 2b)²
= a² + 4ab + 4b²+ a²- 4ab + 4b²
= 2a² + 8b²
= 2(a² + 4b²) = RHS.
3. (l +m)²= (l-m)²+4lm
Solution :
LHS = (l+ m)² = l²+2 lm + m²
= I² – 2lm + m² + 4lm
= (l- m)² + 4lm = RHS.
4. (2p- q)² = (2p + q)²- 8pq
Solution:
= (2p-q)² = (2p)² -2.2p.q + (q)²
= (2p) -2.2p.q + (q)²- 8pq
= (2p-q)² – 8pq
5. (3m + 4n)² = (3m- 4n)² + 48mn
Solution:
(3m + 4n)²
= (3m)² + 2.3m. 4n + (4n)²
= (3m)² -2.3m.4n +(4n)²+ 48mn
= (3m- 4n)² + 48mn = R.H.S.
6. (6x + 7y)²- 84xy = 36x² + 49.y²
Solution :
(6x+ 7y)² – 84xy
84xy = 36x² + 2.6x.7y + 49 y² – 84xy
= 36x² -2.6x.7y + 9y² -84xy
= 36x² + 49y² = R.H.S.
7. (3a + 4b)² + 24 ab = 9a² +16b²
Solution:
= (3 – 4b)² +24ab
= (3a – 4b)²+ 24ab = 9a²- 2.3a.4b+(4b)² + 24ab
= 9a²- 24ab + 16b² + 24ab
= 9a² + 16 b²
(3a + 4b)² + 24 ab = 9a² +16b²
8. \(\left(2 a+\frac{1}{a}\right)^2=\left(2 a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^2+8\)
Solution:
⇒ \(\left(2 a+\frac{1}{a}\right)^2\)
= \((2 a)^2+2 \cdot 2 a \cdot \frac{1}{a}+\left(\frac{1}{a}\right)^2\)
= \((2 a)^2-2 \cdot 2 a \cdot \frac{1}{a}+\left(\frac{1}{a}\right)^2+8 a \cdot \frac{1}{a}\)
= \(\left(2 a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^2+8\)
= R.H.S
Question 3. Using formula, let’s solve each of the following problems
1. Let’s find the value of x² + y² when x – y = 3, xy = 28
Solution:
x² +y²
– x² + y² =(x- y)² + 2xy
= (3)² +2.2.8
= 9 + 56
= 65
The value of x² +y² = 65
2. Let’s find the value of ab when a² + b² = 52, a – b = 2
Solution:
ab = \(\frac{-\left(a^2+b^2\right)-(a-b)^2}{2}\)
= \(\frac{52-(2)^2}{2}\)
= \(\frac{52-4}{2}\)
= \(\frac{+48}{2}\)
= + 24
The value of ab = + 24
3. Let’s find the value of Im when l² + m² = 13, l + m = 5
Solution:
lm = \(\frac{(l+m)^2-\left(l^2+m^2\right)}{2}\)
= \(\frac{(5)^2-13}{2}\)
= \(\frac{25-13}{2}\)
= \(\frac{12}{2}\)
= 6
The value of Im = 6
4. Let’s find the value of \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\) when \(a+\frac{1}{a}\)= 4
Solution :
⇒ \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\)
\(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}=\left(a+\frac{1}{a}\right)^2-2 \cdot a \cdot \frac{1}{a}\) – 2
= (4)² – 2
= 16-2 = 14
The value of \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\) = 14
5. Let’s find the value of \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\) when = \(a-\frac{1}{a}\)= 4
Solution :
⇒ \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\)
= \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}=\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^2+2 \cdot a \cdot \frac{1}{a}\)
= (4)²+4
= 16 +2 = 18
The value of \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}\) = 18
6. If \(5 x+\frac{1}{x}\) = 6 lets show 25x²+ \(\frac{1}{x^2}\) = 26
Solution:
⇒ \(5 x+\frac{1}{x}\)= 6
= \(\left(5 x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^2\)
= (6)²= 36
L.H.S = \(25 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+2.5 x \cdot \frac{1}{x}\) = 36
L.H.S = \(25 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\) = 36 – 10
= 26 R.H.S
7. If \(2 x+\frac{1}{x}=5\) 1 let’s find the value of \(4 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\)
Solution:
= \(4 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\)
= \(4 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=\left(2 x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^2-2 \cdot 2 x \cdot \frac{1}{x}\)
= (5)²- 4
= 25-4
= 21
The value of \(4 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\) = 21
8. \(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}\)= 3 , let find the value of \(\frac{x^2}{y^2}+\frac{y^2}{x^2}\) ,
Solution:
⇒ \(\frac{x^2}{y^2}+\frac{y^2}{x^2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{x^2}{y^2}+\frac{y^2}{x^2}\)= \(\left(\frac{x}{y}+\frac{y}{x}\right)^2-2 \cdot \frac{x}{y} \cdot \frac{y}{x}\)
= (3)²- 2
= 9-2= 7
The value of \(\frac{x^2}{y^2}+\frac{y^2}{x^2}\) = 7
9. If x² +y² = 4xy , let’s prove that .x4+ y4 = 14x²y²
Solution :
x² + y² = 4xy
⇒ Or, (x²+y²)= (4xy)²
⇒ Or, x4 + y4 + 2x²y²= 16x²y²
⇒ Or, x4 +y4 =16x²y²=14x²y²
⇒ x4+ y4 = 14x²y²
10. If \(2 a+\frac{1}{3 a}\)= 6, then let’s find the value of \(4 a^2+\frac{1}{9 a^2}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(4 a^2+\frac{1}{9 a^2}\)
= (2a)²+ \(\left(\frac{1}{3 a}\right)^2+2 \cdot 2 a \cdot \frac{1}{3 a}-\frac{4}{3}\)
= \(\left(2 a+\frac{1}{3 a}\right)^2-\frac{4}{3}\)
= (6)² – \(\frac{4}{3}\)
= 36 – \(\frac{4}{3}\)
= \(\frac{108-4}{3}\)
= \(\frac{104}{3^{-}}\)
= 34 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
The value of \(4 a^2+\frac{1}{9 a^2}\) = 34 \(\frac{2}{3}\)
11. If \(\) = 5, Then let’s find the value of \(25 a^2+\frac{1}{49 a^2}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(25 a^2+\frac{1}{49 a^2}\)
= \(\left(5 a+\frac{1}{7 a}\right)^2-2 \cdot 5 a \cdot \frac{1}{7 a}\)
= \((5)^2-\frac{10}{7}\)
= \(25-\frac{10}{7}\)
= \(\frac{175-10}{7}\)
= \(\frac{165}{7}\)
= \(23 \frac{4}{7}\)
The value of \(25 a^2+\frac{1}{49 a^2}\) = \(23 \frac{4}{7}\)
12. If \(2 x-\frac{1}{x}=4\) , lets show that \(x^2-\frac{1}{4 x^2}\)
Solution:
⇒ \(2 x-\frac{1}{x}=4\)
⇒ Or, \(x-\frac{1}{2 x}=2\)
⇒ Or, \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2 x}\right)^2\) = (2)
⇒ Or, \(x^2+\frac{1}{4 x^2}-2 \cdot x \cdot \frac{1}{2 x}=4\)
⇒ Or, \(x^2+\frac{1}{4 x^2}\)
= 4+1
= 5
\(x^2-\frac{1}{4 x^2}\)13. lf m + \(\frac{1}{m}\) = -p, let’s show that \(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) p²- 2
Solution :
m + \(\frac{1}{m}\) = -p
⇒ or,\(\left(m+\frac{1}{m}\right)^2\) =(- p)²
⇒ Or, \(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}+2 \cdot m \cdot \frac{1}{m}\) = p²
⇒ Or,\(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) = p² – 2
\(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) p²- 2
14. lf a² + b² = 5ab, let’s show that \(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{b^2}{a^2}\) – 23.
Solution :
= a² + b² = 5ab
⇒ Or, \(\frac{a^2}{a b}+\frac{b}{a b}=\frac{5 a b}{a b}\)
⇒ Or, \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\) = 5
⇒ Or, \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\right)^2\) = (5)²
= 25
⇒ Or, \(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{b^2}{a^2}+2 \cdot \frac{a}{b} \cdot \frac{b}{a}\) = 25
⇒ Or, \(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{b^2}{a^2}\) = 25 -2
= 23
\(\frac{a^2}{b^2}+\frac{b^2}{a^2}\) – 23.
15. If 6x² +1 = 4x> let’s show \(36 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\) = 28
Solution:
= 6x² +1 = 4x
⇒ Or, \(\frac{6 x^2}{x}-\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ Or, 6x \(\frac{1}{x}\) = 4
Squaring both sides
⇒ \(\left(6 x-\frac{1}{x}\right)^2=(4)^2\)
⇒ Or, \(36 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\)
= 16 +12
= 28
\(36 x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\) = 28
16. If \(m+\frac{1}{m}\)= p-2, then let’s show \(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) = p² – 4p + 6
Solution :
⇒ \(m+\frac{1}{m}\) = p-2
⇒ Or, \(\left(m+\frac{1}{m}\right)^2\) + = (p-2)²
⇒ Or, \(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) + 2m.\(\frac{1}{m}\) = p² -4p + 4
⇒ Or, \(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) = p²-4p+ 4-2.
= P² – 4p + 2
\(m^2+\frac{1}{m^2}\) = p² – 4p + 6
18. If m= \(m-\frac{1}{m-2}\) = 6, then lats find the value of \((m-2)^2+\frac{1}{(m-2)^2}\)
Solution:
= m- \(\frac{1}{m-2}\) = 6
Or, m-2-\(\frac{1}{m-2}\)
= 6 – 2 = 4
Squaring both sides
⇒ \((m-2)^2-2 \cdot(m-2) \times\left(\frac{1}{m-2}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{m-2}\right)^2\) = (4)2
⇒ Or, \((m-2)^2-2+\frac{1}{(m-2)^2}\) = 16
⇒ Or, \((m-2)^2+\frac{1}{(m-2)^2}\) = 16+2
⇒ Or, \((m-2)^2+\frac{1}{(m-2)^2}\) = 18
The value of \((m-2)^2+\frac{1}{(m-2)^2}\) = 18
WB Class 7 Math Solution Algebraic Formula Exercise 12.5
Question 1. In the identity No. (4) if x = a and a = b, then let’s find if it becomes identity No. (1).
Solution :
In the identity No. (4) ie.
x = a and a = b
⇒ (x + a) (x + b) = x² + (a + b)x + ab
⇒ When x = a & a = b
⇒ (a + b) (a + b) = a² + 2ab + b²
⇒ or, (a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b² . It is identified as No. (1)
Question 2. In the identity No. (4), let’s substitute x = a and a = – b, and verify if it becomes identity No. (3).
Solution:
x = a and a = – b,
In the identity No. (4) ie.
(x + a) (x + b) = x² + (a + b)x+ ab
(a-b) (a + b) = a² +(a-a)0 + (-b)(b)
= a²- b² It is identify No. (3)
Question 3. In identity (4), let’s substitute x = a and a = – b, and try to identify which identity it changes to.
Solution :
In identity No (4) ie.
x = a and a = – b
(x + a) (x + b) = x²+ (a + b)x + ab
(a- b)(a +b) = a² + -ab + ab- b²
= a² – b²
Question 4. Using the formula (a² – b²) = (a + b) (a – b) let’s find the values
1. (37)² – (13)²
Solution :
(37)² – (13)²
= (37+13) (37-13)
= 50 × 24 = 1200
(37)² – (13)² = 1200
(2.06)² – (0.94)²
Solution :
(2.06)² – (0.94)²
= (2.06 + 0.94) (2.06 – 0.94)
= (3.00) (1.12) = 3. 36
(2.06)² – (0.94)² = 3. 36
3. (78) × (82)
Solution :
(78) × (82)
= (80 – 2) (80 + 2)
= (80)² – (2)²
= 6400 – 4 = 6396
(78) × (82) = 6396
4. 1.15 × 0.85
Solution :
1.15 × 0.85
= (1.00 + .15) (1.00 – .15)
= (1)2-(.15)² = 1 – .0225
= 0.9775
1.15 × 0.85 = 0.9775
5.(65)²- (35)²
Solution :
(65)²- (35)²
= (65 + 35) (65 – 35)
= 100 × 30 = 3000
(65)²- (35)² = 3000
Question 2.
1. If k – p² = (9 + p) (9 – p) let’s find the value of k.
Solution :
k – p²= (9 + p) (9 – p)
= (9 + p)(9-p) =81 -p²
k = 81.
The value of k = 81.
2. If (25 – 4x²) = (5 + ax) (5 – ax) let’s find the positive value of a.
Solution:
25 -4x² = (5 + ax) (5 – ax)
= 25 – a²x²
∴ a² = 4
∴ a = \(\sqrt{4}\) =2
3. Let us fill in the box, so that the identity (4 – x) x = (16 – x²) is satisfied.
Solution :
(4 – x) x = (1 6 – x²)
= (4)² – (x)²
= (4 – x) (4 + x)
= 4 + x
Question 3. Let’s express the following in the product form using a formula.
1. 25I² – 16m²
Solution:
25l²-16m²
= (5l)²-(43)²
= (5I + 4m) (5I – 4m)
25l²-16m² = (5I + 4m) (5I – 4m)
2. 49x4 – 36y4
Solution :
49x4 – 36y4
= (7x²)² – (6y²)²
= (7x² + 6y²) (7x² – 6y²)
49x4 – 36y4 = (7x² + 6y²) (7x² – 6y²)
3. (2a + b)² – (a + b)²
Solution :
(2a + b)² – (a + b)²
‘= (2a + b + a + b) (2a + b – a – b)
= (3a + 2b) (a) = a(3a + 2b)
(2a + b)² – (a + b)² = a(3a + 2b)
4. (x + y)² – (a + b)²
Solution :
(x + y)² – (a + b)²
= (x + y + a + b) (x + y – a – b)
(x + y)² – (a + b)² = (x + y + a + b) (x + y – a – b)
5. (x + y – z)² – (x – y + z)²
Solution :
(x + y – z)² – (x – y + z)²
= (x + y – z + x – y + z) (x + y – z – x + y – z)
= 2x (2y – 2z) = 4x (y – z)
(x + y – z)² – (x – y + z)² = 2x (2y – 2z) = 4x (y – z)
6. (m + p + q)² – (m – p – q)²
Solution :
(m + p> + q)² – (m – p – q)²
= (m + p + q + m – p – q) (m + p + q – m + p + q)
= 2m (2p + 2q) = 4m (p + q)
(m + p> + q)² – (m – p – q)² = 2m (2p + 2q) = 4m (p + q)
Question 4. Using the formula, let’s find the continued product of the following
1. (c + d) (c-d) (c² + d²)
Soluion :
(c + d) (c – d) (c² + d²)
= {(c)² -(d)²} (c² + d²)
= (c² – d²) (c² + d²)
= (c²)² – (d²)² = c4 – d4
(c + d) (c – d) (c² + d²) = c4 – d4
2. (1 + 3x²) (1 + 3x²) (1 + 9x4)
Solution :
(1 + 3x²) (1 + 3x²) (1 + 9x4)
= {(1 )² – (3x²)²} (1 +9x4)
= (1 – 9x4) (1 + 9x4)
= (1² ) (9x4)²
= 1 – 81 x8
(1 + 3x²) (1 + 3x²) (1 + 9x4) = 1 – 81 x8
3. (a² + b²) (a² – b²) (a4 + b4) (a8 + b8)
Solution :
(a² + b²) (a² – b²) (a4 + b4) (a8 + b8)
= {(a²)² – (b²)²} (a4 + b4) (a8 + b8)
= (a4 – b4) (a4 + b4) (a8 + b8)
= {(a4)2 – (b4)2} (a8 + b8)
= (a8 – b8) (a8 + b8)
= (a8)2 – (b8)2
= a16 – b16
(a² + b²) (a² – b²) (a4 + b4) (a8 + b8) = a16 – b16
Question 5. Let’s express the following in the product form.
1. 16c4 – 81 d4
Solution :
16c4 – 81
16c4 – 81 = (4c²)° – (9d²)²
16c4 – 81 = (4c² – 9d²) (4c² + 9d²)
16c4 – 81 = {(2c)² – (3d)²} (4c² + 9d²)
16c4 – 81 = (2c + 3d) (2c – 3d) (4c ²+ 9d²)
16c4 – 81 = (2c + 3d) (2c – 3d) (4c ²+ 9d²)
2. p4q4 – r4s4
Solution :
p4q4 – r4s4
p4q4 – r4s4 = (p²q²)² (r²s²)²
p4q4 – r4s4 = (p²q² + r²s²) (p²q² – r²s²)
p4q4 – r4s4 = (P²q² + r²s²) {(pq)²- (rs)²}
p4q4 – r4s4 = (p²q²+r²s²) (pq + rs) (pq – rs)
p4q4 – r4s4 = (p²q²+r²s²) (pq + rs) (pq – rs)
3. 81 – x4
Solution :
81 – x4
= (9)² – (x²)²
= (9 – x²) (9 + x²)
= {(3)² – (x)²} (9 + x²)
= (3 + x) (3 – x) (9 + x²)
81 – x4 = (3 + x) (3 – x) (9 + x²)
4. 625 -a4b4
Solution :
625 -a4b4
= (25)²- (a²b²)²
= (25 – a²b²)(25 + a²b²)
= {(5)²-(ab)²} (25 + a²b²)
= (5 + ab) (5 – ab) (25 + ab)
625 -a4b4 = (5 + ab) (5 – ab) (25 + ab)
Question 6. Let’s prove (p + q)4– (p – q)4 = 8pq (p² + q²)
Solution :
(p + q)4– (p – q)4 = 8pq (p² + q²)
LHS = {(P + q)² + (p – q)²} {(p + q)² – (P – q)²}
= (P² + 2pq + q² + p² – 2pq + q²) (p² + 2pq – q²)
= (2p² + 2q²) × 4pq
= 2 (p²q²) × 4pq
= 8pq (p² + q²) = RHS
Question 7. Using formula let’s multiply: (a + b + c) (b + c – a) (c + a – b) (a + b – c)
Solution :
(a + b + c) (b + c – a) (c + a – b) (a + b – c)
= (a + b + c) (a + b – c) (b + c – a) (c + a – b)
= {(a + b)² – c²} {c – (a – b)} {c + (a – b)}
= {(a + b)² – c²} {c² – (a -b)²}
= c² (a + b)² – c4 – (a – b)² (a + b)² + c² (a – b)²
= c² {(a + b)² + (a – b)²} – c4 – (a2 – b²)² .
=.c² (2a² + 2b²) – c4 – (a4 – 2a²b² + b4)
= 2a²c²+ 2b²c² + 2a²b² – a4 -b4 – c4
(a + b + c) (b + c – a) (c + a – b) (a + b – c) = 2a²c²+ 2b²c² + 2a²b² – a4 -b4 – c4
Question 8. If x = \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\) and Y = \(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{b}{a}\) then ,let’s show that x4 + y4 – 2x²y² =16
Solution:
Given
x = \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\) and Y = \(\frac{a}{b}-\frac{b}{a}\)
LHS= x4+y4-2x²y²= (x²)²+(y²)²-2x²y²
= (x² – y²)² = {(x + y) (x – y)}²
= \(\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}+\frac{a}{b}-\frac{b}{a}\right)^2\left(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}-\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\right)^2\)
= \(\left(2 \frac{a}{b}\right)^2 \times\left(2 \frac{b}{a}\right)^2\)
= \(4 \frac{a^2}{b^2} \times 4 \frac{b^2}{a^2}\)
= 16 = RHS
Question 9. Using formula let’s multiply : (a² + a + 1) (a² – a + 1) (a4 – a² + 1)²
Solution :
(a² + a + 1) (a² – a + 1) (a4 – a² + 1)
= (a² +1 + a) (a² + 1- a) (a4 – a² + 1)
= { (a² + 1- a² }(a4 +1- a²)
= (a4+2a² +1-a²)(a4 +1-a²)
= (a4 +1 + a²)(a 4 +1-a²)
= (a4 )+ 2a4 +1- a4
= a8 +2a4 +1-a4
= a8+ a4+1
(a² + a + 1) (a² – a + 1) (a4 – a² + 1) = a8+ a4+1
Question 10. If x = \(\left(a+\frac{1}{a}\right)\) and y= \(\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)\) , then lets find the value of x4 + y4-2x²y².
Given
x = \(\left(a+\frac{1}{a}\right)\) and y= \(\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)\)
x4 + y4 -2x²y² .
= \(\left(x^2-y^2\right)^2\)
= \((x+y)^2(x-y)^2\)
= \(\left(a+\frac{1}{a}+a-\frac{1}{b}\right)^2\left(a+\frac{1}{a}-a+\frac{1}{a}\right)^2\)
= \((2 a)^2 \times\left(\frac{2}{a}\right)^2\)
= \(4 a^2 \times \frac{4}{a^2}\)
= 16
The value of x4 + y4-2x²y² = 16
Question 11. Let’s express (4x² + 4x + 1- a² + 8a-16) as the difference of two squares, using the formula, (in the form a² – b² )
= (4x² + 4x +1)- (a² – 8a +1 6)
= (2x +1)²-(a-4)²
(4x² + 4x + 1- a² + 8a-16) = (2x +1)²-(a-4)²
Question 12. Let’s express \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}-3\) as the difference of two squares (in the form a² – b²)
Solution:
⇒ \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}-3\)
= \(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}-2-1\)
= a²- 2a \(\frac{1}{a}\)+ \(\frac{1}{a^2}\) – (1)²
= (a- \(\frac{1}{a}\))² – (1)²
\(a^2+\frac{1}{a^2}-3\) = (a- \(\frac{1}{a}\))² – (1)²
