Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Geometry Chapter 3 Properties Of Triangle Exercise 3 Solved Problems
⇒ Triangle: A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
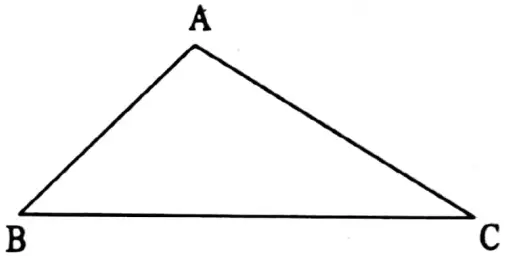
⇒ In triangle ABC, three vertices are A, B and C. There are three sides AB, BC, and CA.
⇒ The side opposite to a vertex of a triangle is its base.
⇒ The sum of the measurement of three angles is 180°.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions for Class 7 Maths
Classification of Triangles:
According to their sides, three triangles are
1. Equilateral triangle
2. Isosceles triangle
3. Scalene triangle
According to their angles, three triangles are
1. Acute angled triangle
2. Right-angled triangle
3. Obtuse angled triangle
Equilateral triangle:
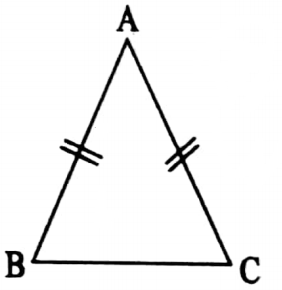
⇒ A triangle whose length of each side are equal is called an equilateral triangle.
⇒ In the equilateral triangle ABC,
⇒ AB = BC = CA and ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
“WBBSE class 7 maths geometry chapter 3 solutions”
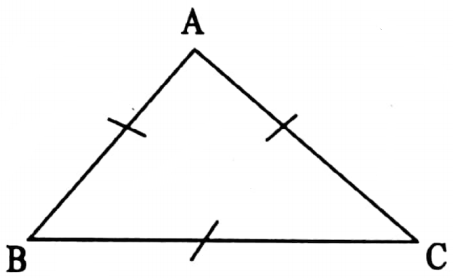
Isosceles triangle: An isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two sides are equal in length.
In isosceles triangle ABC, AB = AC
Wbbse Class 7 Maths Solutions
Scalene triangle:
⇒ A scalene triangle is a triangle whose all sides are unequal in lengths.
⇒ In ΔABC, AB ≠ BC ≠ CA
“properties of triangle WBBSE class 7 maths notes”
⇒ Acute angled triangle: A triangle in which all three angles are acute (i.e. less than 90°) is called an acute angled triangle.
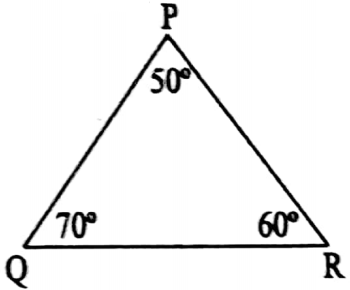
⇒ PQR is an acute-angled triangle in which all angles are acute.
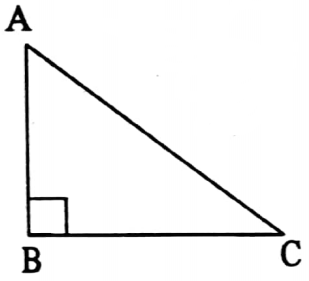
⇒ Right-angled triangle: A triangle whose one angle is a right angle (i.e., 90°) is Q called a right-angled triangle.
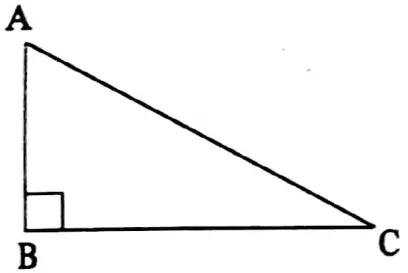
⇒ The side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
⇒ ΔABC is a right-angled triangle whose ∠ABC= 90° and AB2 + BC2 = AC2 [Pythagorus theorem]
Obtuse angled triangle: A triangle in which one angle is obtuse (i.e. more than 90°) is called an obtuse angled triangle.
⇒ ABC is an obtuse-angled triangle.
Right-angled isosceles triangle:
⇒ A triangle in which one angle is a right angle and the adjacent sides of a right angle are equal in length is called a right-angled isosceles triangle.
In isosceles right-angled triangle ABC, ∠ABC= 90° and AB = BC.
“exercise 3 solved problems on properties of triangles class 7”
⇒ The altitude or the height of a triangle: The length of the perpendicular from the vertex to the opposite side of a triangle is called the altitude or the height of the triangle.
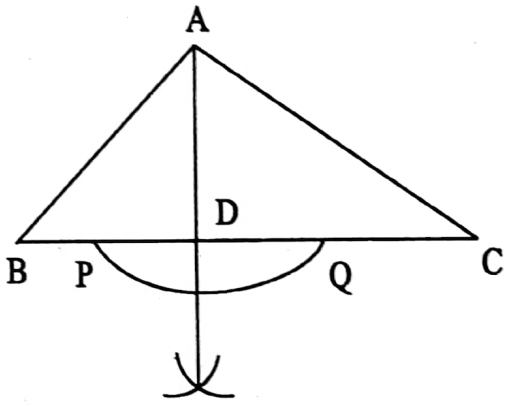
⇒ In the adjacent image, AD is the altitude of the ΔABC.
⇒ The median of the triangle:
⇒ The median of a triangle is the line segment drawn from any vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
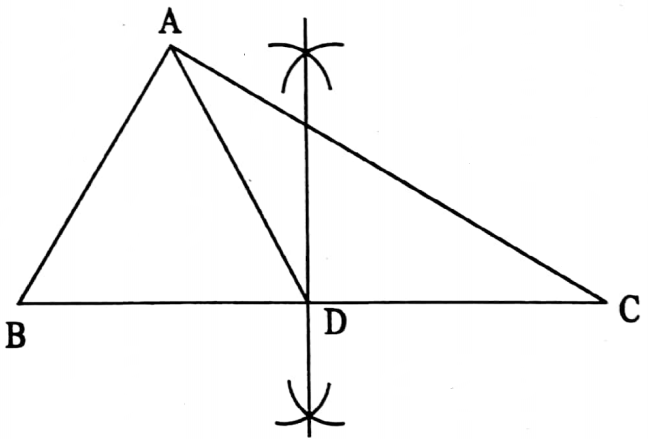
⇒ In ΔABC, AD is a median.
⇒ Area of the triangle = \(/frac{1}{2}\) × base x height.
⇒ The sum of length of any two sides of any triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Question 1. Choose the correct answer
1. The number of medians of a triangle is
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. None of these
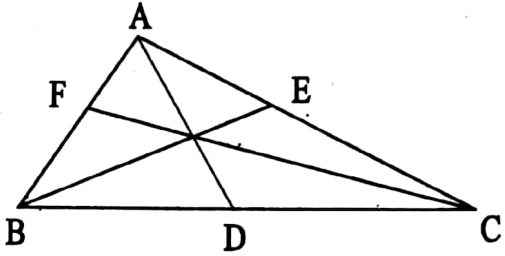
Solution: There are three medians of a triangle ABC
⇒ AD, BE, and CF.
⇒ So the correct answer is 3.3
2. If the measurement of one angle of a triangle is 105° the triangle is
1. Acute angled triangle
2. Right-angled triangle
3. Obtuse angled triangle
4. None of these
Solution: 105° is an obtuse angle. The triangle is an obtuse-angled triangle.
So the correct answer is 3. Obtuse angled triangle
“WBBSE class 7 maths chapter 3 important questions”
3. In which triangle the length of the median and height are same?
1. Equilateral triangle
2. Isosceles triangle
3. Scalene triangle
4. None of these
Solution: In an equilateral triangle height and median are the same.
So the correct answer is 1. Equilateral triangle
Question 2. Write true or false
1. The position of medians of a triangle always inside the triangle.
Solution: The statement is true.
2. The hypotenuse of the right angled triangle is the smallest side.
Solution: The statement is false.
3. These are three altitudes in a triangle.
Solution: The statement is true.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks
1. The sum of the measurement of three angles of a triangle is _____
Solution:180°
2. The number of vertices is _____
Solution: 3
3. Triangle has _____ diagonal.
Solution: No
Question 4. If the length of two adjacent side of right angle of a right angled triangle are 3 cm and 4 cm. Then find the length of its hypotenuse.
Solution:
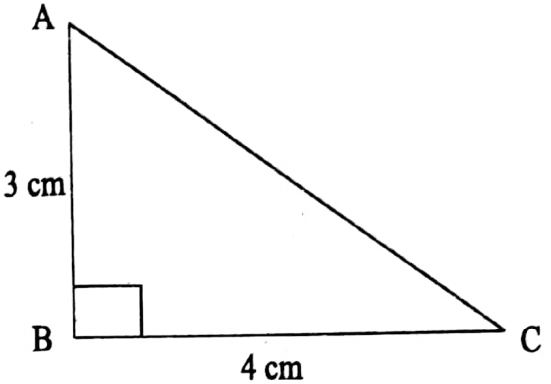
Given
If the length of two adjacent side of right angle of a right angled triangle are 3 cm and 4 cm.
ΔABC its, ∠ABC = 90°
AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm
AC2 =AB2+ BC2 [by applying Pythagorus theorem]
AC2= 32 + 42
AC2= 9+16
AC2= 25
AC = √25 cm = 5 cm
“how to solve triangle problems step-by-step class 7”
Question 5. If length of base and height of a triangle are 10 cm and 8 cm respectively then find the area of the triangle.
Solution
Given
If length of base and height of a triangle are 10 cm and 8 cm respectively
Area of the triangle = \(\)\frac{1}{2}] base x height
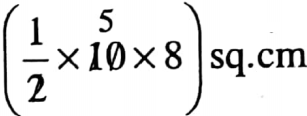
= 40 sq.cm
Area of the triangle = 40 sq.cm
Question 6. Whether the length of three sides of a triangle are 4 cm, 5 cm and 9 cm is possible?
Solution: The length of biggest side of any triangle is less than the sum of lengths of other two sides.
As 4+5=9
So, the given length of three sides of the triangle is not possible.
“sum of angles in a triangle theorem WBBSE class 7”
Question 7. Find the perimeter of the triangle of lengths of sides are 6 cm, 7 cm and 8 cm.
Solution: Perimeter = (6+ 7+ 8) cm = 21 cm.
Properties Of Triangle
Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Properties Of Triangle Exercise 3.1
Question 1. Let us try to draw and find the number of heights (altitudes) for a triangle.
Solution :
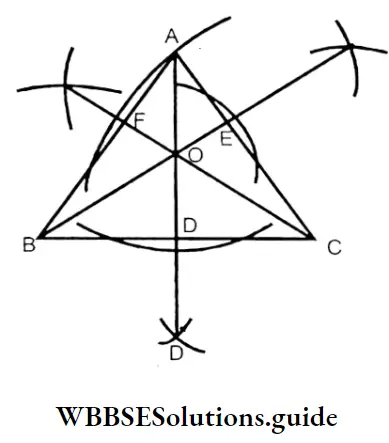
In Δ ABC, AD, BE & CF are three*altitudes, They meet at O on the side of the triangle.
Question 2. Let us try to draw the heights of all the triangles in the same way according to sides and angles, with the help of a compass and scale.
Solution :
1. In case of Isosceles triangle:
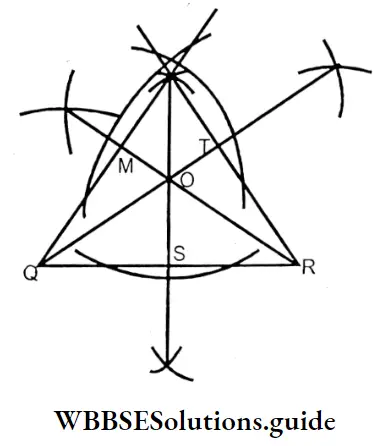
Here PQR is an isosceles triangle PS, QT & RM are three heights of a triangle drawn from vertexes P, Q & R respectively. They meet at point O.
2. In case of Equilateral and Acute angled triangles:
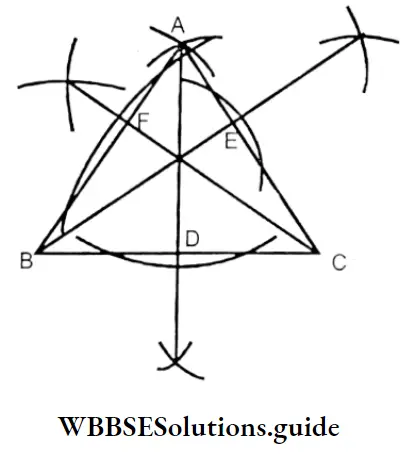
⇒ Here ABC is an equilateral & acute angled triangle. AD, BE & CF are the three heights of the triangle, they meet at 6.
3. In case of the Scalene triangle:
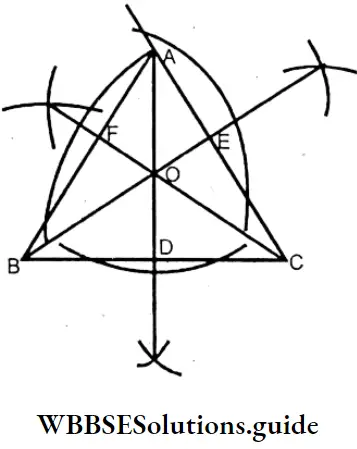
⇒ ABC is a scalene triangle AD, BF & CF are the three heights of the triangle.
4. In the case of the obtuse-angled triangle:
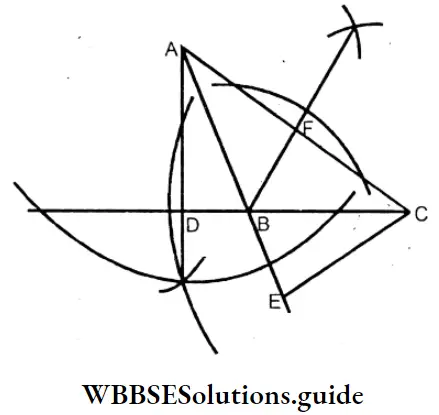
⇒ Here ABC is an obtuse-dangled triangle perpendiculars are drawn from the three vertexes.
5. In case of a right-angled triangle:
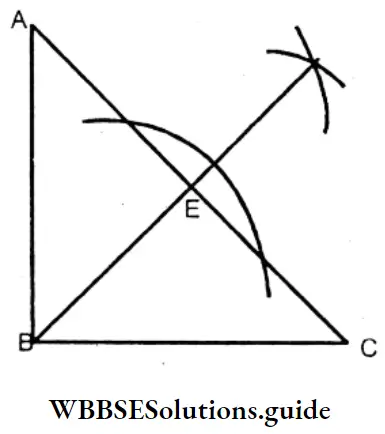
⇒ ABC is a right-angled triangle ∠ ABC = 90°
Question 3. Which of these triangles has its height as one of its sides? Let’s draw and find.
Solution :
⇒ In the case of a right-angled triangle. AB is the height and also one side of the triangle.
Question 4. Which of these triangles have their heights and medians are the same line segment, let’s draw and find.
Solution :
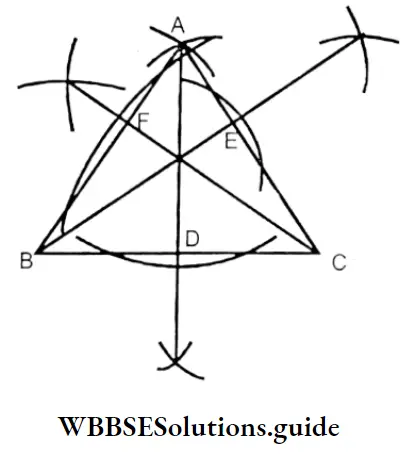
⇒ ABC is an equilateral triangle whose each side is 6 cm.
⇒ Here AD, BE & CF are their height, also AD, BE & CF are the three medians of the triangle, as D, E & F are the midpoints of the side BC, CA & AB, respectively.
∴ Height & medians are the same line segment
Class 7 Math Solution WBBSE Properties Of Triangle Exercise 3.2
Question 1. Given
1. Let’s write how many medians are there in a triangle.
Solution: 3 Medians are there in a triangle.
2. Let’s find how many do the three medians of a triangle meet.
Solution: Three medians of a triangle meet at a point.
3. Let’s write how many heights are there in a triangle.
Solution: There are 3 heights of a triangle.
4. Let’s find how many points the three heights (altitudes) of a triangle meet.
Solution: Three heights (altitudes) of a triangle meet at a point.
5. Let’s identify the triangles whose medians and heights (altitudes) are the same.
Solution: Equilateral & Isosceles triangle.
“types of triangles and their properties class 7 maths”
Question 2. Let us draw all the types of triangles classified according to sides and angles and then draw 3 medians for each of these triangles using a scale and compass. From the figure drawn, let us try to find if the medians always remain inside the triangle.
Solution:
1. In the case of equilateral triangle:
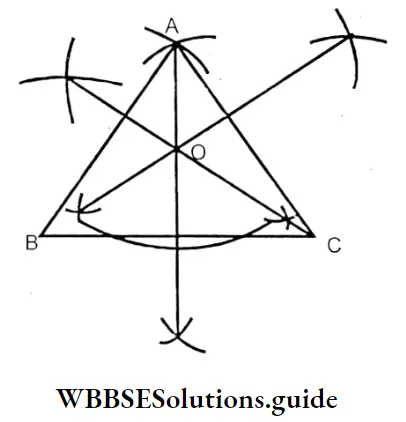
In this case, medians meet at ‘O’ inside the triangle.
2. In the case of Isosceles + Acute angled triangle:
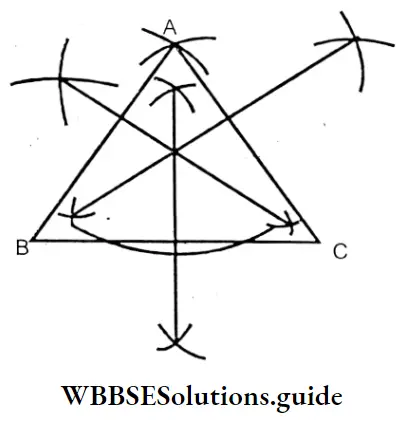
In this case, medians meet at ‘O’ inside the triangle.
3. In the case of scalene triangle:
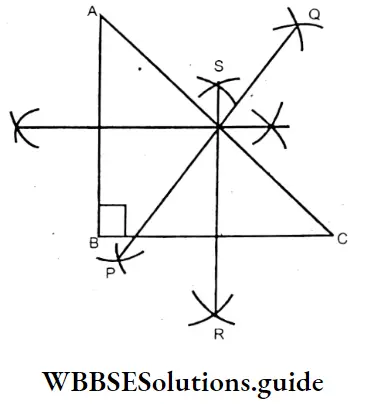
⇒ In these medians meet at ‘O’ in the side of the triangle.
4. In the case of right-angled triangle:
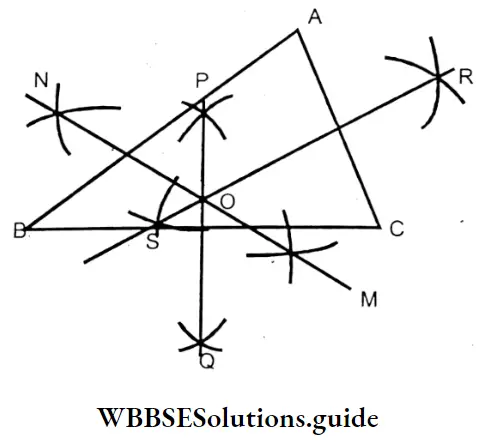
⇒ In these medians meet at ‘O’ which is the mid-point of the hypotenuse
5. In the case of the obtuse-angled triangle:
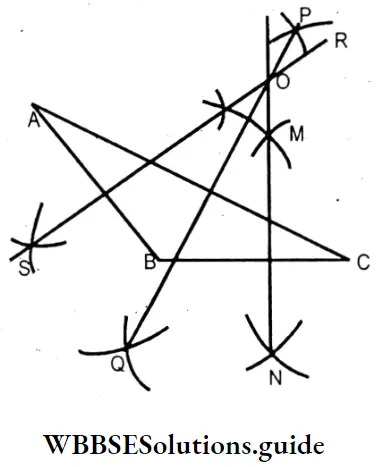
⇒ In these medians meet at ‘O’ which is outside the triangle.
Question 3. Let us measure the height of each of the triangles given below with a scale and pencil.
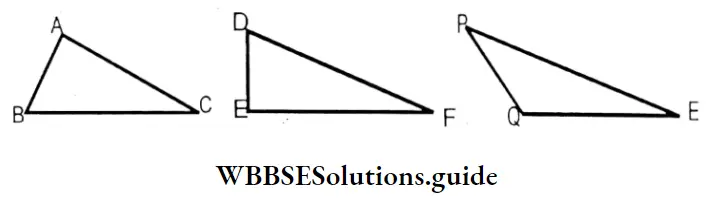
Solution:
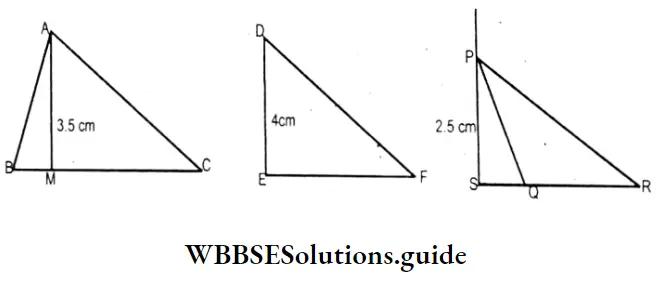
⇒ In the 1st figure, right of Δ ABC = 3.5cm, In the 2nd fig. height of
⇒ A DEF = 4cm & in the 3rd figure height of Δ PQR = 2.5 cm.
“Pythagoras theorem and right-angled triangles WBBSE”
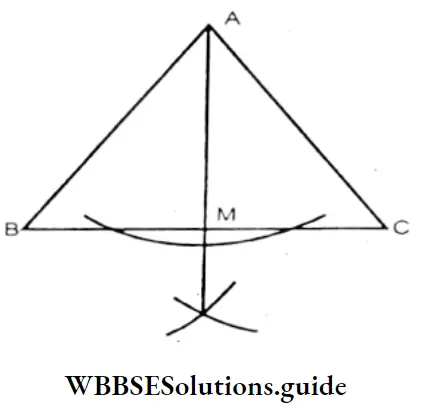
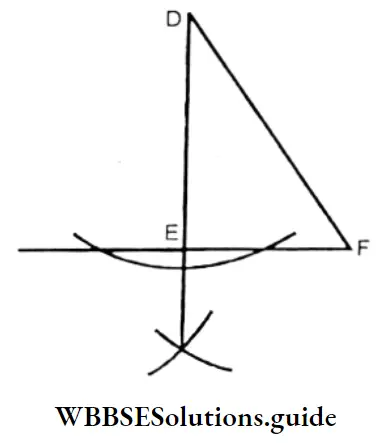
Question 4. Let us draw the triangles classified according to the angles. Let us draw the height (altitudes) using a scale and compass and find if all the heights remain inside the triangle.
Solution :
1. In the 1st figure ABC is an acute-angled triangle Height AM = 4cm
2. In the 2nd figure, DEF is a right-angled triangle Height DE = 3cm.
3. In the 3rd figure PQR is an obtised angled triangle. Height PS = 5.2cm.
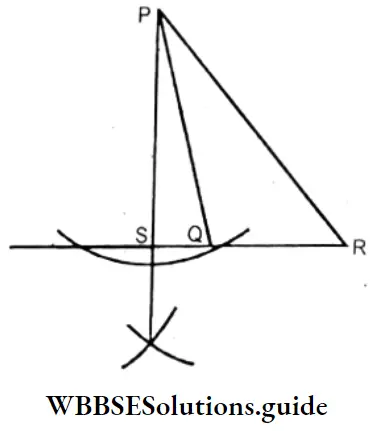
4. ln> The first two figure height is inside the triangle. But in 3rd figure oblused angled triangle height is outside the triangle)
