Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution Short Questions With Answers :
Question l. What are the two motions of the Earth?
Answer:
The two motions of the Earth are
(1) Rotation,
(2) Revolution.
Question 2. Who made the first direct experiment to prove the Earth’s rotation?
Answer: In 1851 Jean Bernard Leon Foucault, a French physicist, first made a direct experiment of the rotation of the Earth.
Read and Learn all WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
Question 3. What is the length of the elliptical path of the earth?
Answer: 96 crores km.
Question 4. What is the speed of the earth rotation on the equator?
Answer: 1630 per hour.
Question 5. What is the speed of the earth rotation on Kolkata per hour?
Answer:1536 per hour.
Geography Class 9 West Bengal Board
Question 6. Who did first promulgated the idea of the rotation of the earth?
Answer: Nicolas Copernicus.
Question 7. What do you know about the Earth’s axis?
Answer: The axis is the imaginary line passing through the center of the Earth on which the Earth rotates.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution Solutions
Question 8. In what way does the earth rotate?
Answer: Earth rotates from west to east or in an anticlockwise direction.
Question 9. How much time does the earth take to complete one rotation?
Answer: 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds (24 hours rounded off)
Question 10. What causes day and night on earth?
Answer: Rotation.
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
Question 11. What is the angle of inclination of the earth in its axis?
Answer: 23 (½)°
Question 12. Is the earth’s axis vertical? If not, what is its position?
Answer: The earth’s axis is not vertical. It makes an angle of 23(½)°with the vertical or 66 (½)° with the plane of the Earth’s orbit.
Question 13. What is the speed of rotation at the equator?
Answer: 1630 km/hr.
Question 14. Name the place (latitude) where days and nights are always equal.
Answer: Equator or 0° latitude.
Question 15. Which day is shortest in the Northern Hemisphere?
Answer: 22nd December.
Question 16. Name the dates at which days & nights are equal in northern hemisphere or southern hemisphere.
Answer: 21st March and 23rd September.
Question 17. Which day is longest in southern hemisphere?
Answer: 22nd December.
Geography Class 9 West Bengal Board

Question 18. Which day is shortest in southern hemisphere?
Answer: 21st June.
Question 19. When is it winter solstice in Northern Hemisphere?
Answer: 22nd December
Question 20. What is the speed of revolution of the Earth cause?
Answer: 365 1/4 days (approx).
Question 21. How far away is the Earth from the Sun on Aphelion?
Answer: About 152 r ion kilometers.
Question 22. What is the colourful light seen in the nights in the South Pole called?
Answer: Aurora Australis.
Question 23. What is the distance of the Earth from the sun at perihelion?
Answer: About 147 million kilometers.
Question 24. What is the exact time taken by the earth to move around the sun once?
Answer: The exact time taken by the earth to move round the sun is 365 days 5 hours 48 minutes 46 secs.
Question 25. What is the distance between the earth and the sun? [M.E.-1995]
Answer: The approximate distance between the earth and the sun is 15 crore km.
Question 26. What is the speed of rotation of Earth at Kolkata?
Answer: 1536 km. is the speed of rotation of Earth at Kolkata.
Question 27. How much is the axis of the globe inclined in relation to the plane of the earth’s orbit?
Answer: 66 (½)° the earth’s axis inclined in relation to the plane of the earth’s orbit.
Question 28. What is axis?
Answer: Axis is an imaginary line at which the earth rotates.
Geography Class 9 West Bengal Board Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution True Or False Type
Question 1. The earth revolves around the sun in 365 days 5 hours 48 minutes 46 seconds.
Answer: True
Question 2. After 21st March the sun moves towards the north.
Answer: True
Question 3. In the month of December, days are longer in the Northern Hemisphere.
Answer: False
Question 4. 0° longitude is called Prime Meridian.
Answer: True
Question 5. The speed of the earth at the equator is 1630 km.
Answer: True
Question 6. The earth moves around the sun in 365 ¼ days.
Answer: True
Question 7. There are six seasons in India.
Answer: True
Geography Class 9 West Bengal Board
Question 8. Days and nights are caused because of the rotation of the earth.
Answer: True
Question 9. Seasons are changed because of the revolution of the earth.
Answer: True
Question 10. 21st June is called Winter Solstice.
Answer: False
Question 11. 22nd December is called Summer Solstice.
Answer: False
Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution Class 9 WBBSE Question Answer
Question 12. 4th July is called Aphelion.
Answer: True
WBBSE Class 9 Chapter 2 Geography
Question 13. 3rd January is called Perihelion.
Answer: True
Question 14. Speed of the earth during the revolution is 30 km per sec.
Answer: True
Question 15. 21st March is called Autumn Equinox
Answer: False
Question 16.23rd September called Vernal Equinox
Answer: False
Question 17. On 4th July, the distance between the sun and the earth remains minimum.
Answer: False
Question 18. On December 22nd, the sun comes overhead at the Tropic of Capricorn and the day is called winter solstice.
Answer: True
Question 19. The distance between the earth and the sun is minimum on 3rd January.
Answer: True
Question 20. 1900 A.D. was a leap year.
Answer: True
Question 21. The southern hemisphere has longer days in the month of June.
Answer: False
Question 22. On March 21st at the equator, the sun rises due east and sets due west and the midday altitude of the sun in 90°.
Answer: True
Question 23. 2100 A.D. leap year
Answer: True
Question 24 .21st June is known as summer solstice in northern hemisphere and the winter solstice in sountern hemisphere.
Answer: True
Question 25. The date of Vernal Equinox is 23rd September
Answer: False
Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution Fill In The Blanks
Question l. The distance of the sun from the earth is_______.
Answer:150 million Km.
Question 2. The earth’s axis makes an angle________ of with the ecliptic orbit.
Answer: 66 (½)°
Question 3. ________discovered that the earth revolves around the sun.
Answer: Aryabhatta
Question 4. Winter Solstice occurs on________.
Answer: 22nd December.
Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution 2 Marks Questions And Answers
Question l. Why do we not feel the Rotation of the Earth?
Answer:
We do not feel that the earth on which we live is constantly rotating. The reasons are
(1) There are no heavenly objects nearer to the earth, either stationary or moving opposite of the earth’s rotation by which we can compare the earth’s rotation.
(2) The rate of rotation is uniform and constant for each place on the earth’s surface.
WBBSE Class 9 Chapter 2 Geography
Question 2. What is Twilight and dawn?
Answer:
Twilight :
The time at which the upper edge of the sun appears to sink below the apparent horizon of a place on the earth’s surface is called Twilight.
Dawn: The period of receiving refracted and reflected sunlight before sunrise is called dawn.
Question 3. What are the effects of revolution of the globe?
Answer:
The effects of revolution of the globe
(1) Change of seasons
(2) Changes in the altitude of the midday sun at different times of the year,
(3) Inequality of the day and night.
Question 4. What is Dusk?
Answer:
Dusk
The short period of receiving reflected and refracted orange light after sunset is called Dusk.
Question 5. Sun rises in the east and sets in the west – why?
Answer:
Sun rises in the east and sets in the west
Since in the earth rotates from west to east, the sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
Question 6. What is sidereal day?
Answer:
Sidereal day
The sidereal day is defined as one 365th of 24 hrs. 3mins 56 secs, shorter than a solar day.
Question 7. What is Coriolis effect?
Answer:
Coriolis effect
Winds do not follow or move in a straight line rather it gets deflected. This deflection of winds caused due to the earth’s rotation is known as Coriolis force or Coriolis effect.
Question 8. What is the speed of the earth’s rotation at Equator and at Poles?
Answer:
1630 km/hr at Equator and 0 km/hr. at poles is the speed of earth’s rotation.
Question 9. Do all the places on the earth spin at the same rate?
Answer:
The solid inner core – a mass of iron comparable to the size of the moon – spins faster than the outer portion of the iron core, which is liquid. A study in 1996 showed that over the previous century, the extra speed caused the inner core to gain a quarter-turn on the planet as a whole. So, the inner core makes a complete revolution in respect of the rest of Earth in about 400 years. Immense pressure keeps it solid.
Question 10. What is the circle of illumination or shadow circle?
Answer:
Circle of illumination or shadow circle
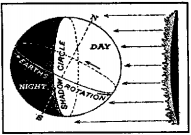
While rotating, the surface of the earth facing the sun experiences day& the opposite side facing away from the sun, night. In between these two areas of day and night, where the boundary of light and boundary of darkness meet in a circle it is called the circle of illumination or shadow circle.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Solved Exercises
Question 11. Why speed of rotation is more at equator than arctic circle?
Answer: Equator forms the largest circle of the earth. North & south of it, the size of the circle of different latitudes become smaller. A point on equator or a point on arctic circle both take 24 hours to complete to a rotation. So the speed of rotation decreases from equator towards the poles.
WBBSE Class 9 Chapter 2 Geography
Question 12. What are the effects of rotation?
Answer:
The effects of rotation are :
(1) Formation of day And night
(2) Sunrise And Sunset
(3) Determination of time
(4) Deflection of planetary winds And ocean currents
(5) Formation of high tides And low tides And
(6) Origin of plants And animals.
Question 13. How fast does the earth spin?
Answer:
The speed at which the earth spins varies upon latitudinal location on the planet. If you’re standing at the North pole, the speed is almost zero but at the equator, where the circumference of the earth is the greatest, the speed is about 1,038 miles per hour (1630km/ hr). The mid-latitudes of the U.S. and Europe speed along is 700 to 900 mph (1125 to 1450 km/hr).
Question 14. What is Equinox?
Answer:
Equinox: Meaning equal nights. At the equinoxes, days and nights are of equal length throughout the world.
Question 15. What is Aurora?
Answer:
Aurora
It is a natural light display, in the dark night sky (Latin word ‘aurora’ means ‘sunrise’), especially in high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic regions). It is caused by collision of Solar wind and charged particles in the high-altitude atmosphere (thermosphere). In Northern latitudes, it is known as Aurora Borealis and in Southern latitudes as Aurora Australis.
Question 16. What do you mean by Ellipse?
Answer:
Ellipse
An ellipse is a curve on a plane surrounding two focal points such that a straight line drawn from one of the focal points to any point on the curve and then back to the other focal point has the same length for every point on the curve. It is a regular oval shape.
Question 17. What do you mean by Epicycles?
Answer:
Epicycles
In the Ptolemaic system of Astronomy, the epicycle (literal meaning circle in Greek) was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the moon, sun, and planets.
WBBSE Class 9 Chapter 2 Geography
Question 18. Write a note on Geocentric model.
Answer:
Geocentric model
In Astronomy, the geocentric model or egocentrism or the Ptolemaic system is a description of the cosmos where earth is at the orbital centre of all celestial bodies.
Question 19. Write a note on Heliocentric model.
Answer:
Heliocentric model
Heliocentrism is the astronomical model in which the earth and the planets revolve around a relatively stationary sun at the centre of the Solar System. (Greek heiios is sun).
Question 20. What is Solstice?
Answer:
Solstice
‘Solstice’ is derived from the Latin Sol (Sun) and sister (to stand still). At solstices, the sun stands still or comes to a stop in the seasonal movements of its path before reversing direction.
Question 21. What is subsolar point?
Answer:
Subsolar point
It is the point on a planet where the sun is perceived to be directly overhead that is where the sun’s rays are hitting the planet exactly perpendicular to its surface.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 22. What is Tangential Speed?
Answer:
Tangential Speed
Linear speed and tangential speed gives the same meaning for circular motion. The direction of motion is always tangent to the path of the object. Tangential speed of the object is linearly proportional to the distance from the center. Increase in distance results in increase in the amount of speed.
Question 23. Why rotation is known as diurnal movement of the Earth?
Answer: The rotation is called ‘diurnal motion’ of the earth as it causes formation of day and night. This diurnal movement is also known as ‘the daily movement of the earth’.
Question 24. What is Geodesy? State the exact dimensions of the earth.
Answer:
Geodesy
Geodesy is the science which studies, determines, and measures the exact shape and dimensions of the earth
1. Equatorial diameter— 12,757 km.
2. Polar diameter —12,714 km.
Question 25. Why does not the sun rise and set at the same time everywhere in the world?
Answer: The inclination of the earth’s axis, together with its revolution around the sun, is the cause of the varying length of day and night and therefore, of sunrise and sunset times.
Question 26. What is the meaning of the word ‘tropic’?
Answer:
Tropic
The word tropic means ‘turning point. The solstices are the turning points in the apparent movement of the sun. After the solstices, the sun turns back to the equator.
Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution 2 Marks Questions And Answers (Short Notes)
Question 1. Land of Midnight Sun or Midnight Sun.
Answer:
Land of Midnight Sun
On 21st June the position of the earth is such that its north pole leans towards the sun. Hence, the vertical rays of the sun fall directly on the tropics of cancer. The region beyond the Arctic Circle towards the pole is popularly known as the “Land of Midnight Sun”. The sun is visible even in Midnight from May 13 to July 29 in Hammerfest in Norway. Hence, Norway is called “the land of midnight Sun’.
Question 2. Leap year.
Answer:
Leap year
Normally a year is considered to be of 365 days, while the actual period of the Earth’s one revolution around the sun is 365 days and a little less than 6 hrs. (5hrs. 48 mins and 45.51 secs). It means we have to leave off about 6×4 = 24 hrs. or one day. So, we have a year of 366 days after every four years. Such one year is called a Leap year.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 3. Shadow Circle.
Answer:
Shadow Circle
Due to the earth’s rotation days and nights are caused. At any time one – half of the earth’s surface receives light from the sun and the imaginary line that separates the lit-up half from the darkened half is called the Circle of Illumination or Shadow Circle. Each place of the surface of the earth is swept over twice by the shadow circle one at dawn and again at twilight.
Question 4. Ferrel’s law.
Answer:
Ferrel’s law
Wind does not blow straight from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure for the following reason :
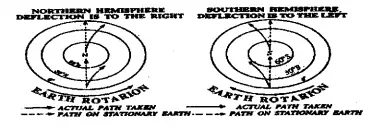
The earth moves around its own axis from West to East but the rate of movement varies. The places on the equator move faster than the places which lie to the North or South of the equator. As a result, air moving on surface is subject to apparent deflection to the right in the Northern hemisphere and to the left in the Southern hemisphere. This is Ferret’s law.
This apparent force called is the Coriolis force. The ocean currents also turn to the right in the Northern hemisphere and to the left in the Southern hemisphere.
Class 9 Geography Movement Of The Earth WBBSE Notes
Question 5.Summer Solstice.
Answer:
Summer Solstice
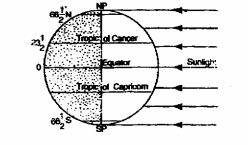
In northern hemisphere, the rays of the sun vertically fall on Tropic of Cancer on June 21 when North pole leans towards the sun and the whole Northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun at the North Pole, continuous daylight is visible for six months. Thus, in the Northern hemisphere, there is summer. Temperature is higher, days are longer and nights are shorter. This position of the earth is known as ‘Summer Solstice’ in Northern hemisphere.

Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 6. Autumnal Equinox.
Answer:
Autumnal Equinox
Equinox means equal night and autumn means when there is autumn season in the Northern hemisphere and spring season in the Southern hemisphere. After June 21 (longest day in Northern hemisphere) the sun appears to be moving southwards and on September 23, while revolving round the sun the earth comes in such a position that the sun appears to be shining vertically on the equator (At this time neither of the poles is inclined towards the sun and both are equidistant from the sun).
Thus, days and nights on this date (23 September) are equal in both the hemispheres. Because this time in Northern hemisphere, there is the autumn season, it is known as ‘autumnal equinox’.
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answer WBBSE
Question 7. Winter Solstice.
Answer:
Solstice
On December 22, the sun is vertically overhead at noon on Tropic of Capricorn. At this position the South Pole and the Southern Hemisphere lean towards the sun’s rays. In the Southern hemisphere the days are longer and the nights are shorter. The reverse is the phenomena in the Northern hemisphere on this date. This is known as winter solstice.

Question 8. Vernal Equinox.
Answer:
Vernal Equinox
The word ‘Equi’ means equal and ‘nox’ means night. While revolving round the sun, the position of the earth becomes such that the sun’s rays fall vertically upon the equator on March 21 and September 23.
Thus, on these two days, days and nights are of equal duration. In the Northern hemisphere, the season of spring begins in the month of March, hence it is known as spring or vernal equinox.
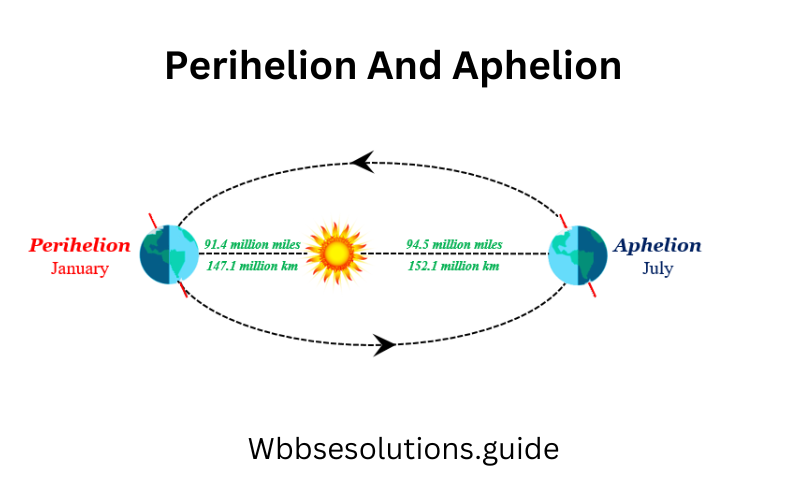
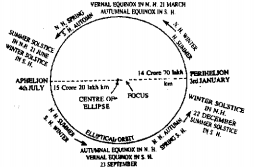
Question 9. Perihelion
Answer:
Perihelion
The earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical path. But the sun is not in the center of this path. The distance between the sun and the earth varies with time. When the distance between the two is the shortest, it is said that the earth is in Perihelion (Greek word Peri means near and helion means sun).
This position takes place on January 3rd when the distance between the two is about 147 million km.
Chapter 2 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Question 10. Local Time.
Answer:
Local Time:
At any place when the sun is at the zenith (i.e. overhead) it is noon at that time and place. Thus, at that place, it is 12 noon, and accordingly the time is calculated. This is local time of that place. The sun’s position changes according to the change in longitude. Thus, the local time of all the places on the same longitude of meridian will be the same.
Question 11. Aphelion.
Answer:
Aphelion
As the earth moves round the sun in an elliptical path, the distance between the sun and the earth vary with time. The average distance between the earth and the sun is 15 crore km. on about July 4, the distance between the sun and the earth is the farthest and it is about 15 crore 20 lakh km, on this date the earth is known to be in Aphelion.
Question 12. Kepler’s law of Planetary Motion: Johannes Kepler (1571-1630).
Answer:
Johannes Kepler
He was a German astronomer who supported the Copernican theory. He discovered that all planets have elliptical orbits. He was deeply religious and believed that the creator made an orderly universe. Armed with a good mathematical mind and great faith in the observational data of the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe, he derived, formulated and verified the three basic laws of planetary motion.
Question 13. Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
Answer:
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
(1) The earth of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus.
(2) The “area rule”: a planet covers equal areas of its orbit in equal periods of time.
(3) The period of revolution of a planet is proportional to its distance from the sun, i.e., it travels most rapidly when it is nearest the sun (from A to B) and most slowly when it is farthest from the sun (from C to D).
Question 14. Twilight.
Answer:
Twilight
The period between sunset and complete darkness is called twilight.
Cause :
Particles of dust and water vapor in the atmosphere refract and reflect the sunlight after the sun itself sets below the apparent horizon.
Duration :
Twilight of dusk at a place on the earth’s surface begins after sunset and continues till the center of the sun sinks below the horizon 18°. Twilight at the equator is the shortest as the sun sinks there in a vertical path. Twilight is longest at poles.
Question15. Dawn.
Answer:
Dawn
The period of receiving refracted and reflected sunlight before sunrise called dawn.
Chapter 2 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Cause:
Dawn occurs due to particles and water vapour in the atmosphere are refract and reflected by the sunlight before the sun itself rises above the apparent horizon of a place on the earth’s surface.
Duration :
When the sun is within 18° of the horizon it is dawn. At the equator, its duration is 1 hour and 12 minutes. This duration goes on increasing towards the poles. At the poles this duration is 50 days long during 6 months alternating period of day and night.
Question16. Buy Ballot’s law.
Answer:
Buy Ballot’s law
C.H.D Buys Ballot was a Dutch climatologist who in 1857 gave as an interesting general rule for the relationship of wind to pressure, the Boys Ballot’s law states that “If a man stands with bis back to the wind in the Northern hemisphere, then high pressure will be to bis right and low pressure will be to bis left. In the Southern Hemisphere, the high pressure will be to bis left and low pressure to bis right”.
Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution 3 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. Why do the scientist make an expedition to Antarctica in the month of December? [M.E. -1992]
Answer:
Following are the causes for scientists to make expeditions in December to Antarctica –
(1) In the month of December the sun’s rays fall vertically on Tropic of Capri-corn. Hence, summer prevails in the southern hemisphere and therefore temperature is high causing in the melting of snow of the Antarctica.
(2) Due-to inclination of the earth’s axis towards the sun the southern hemisphere experiences day of the six-month duration. There is no night on the Antarctica.
Due to these reasons expeditions are made to the Antarctica in the month of December.
Chapter 2 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Question 2. What are the differences between rotation and revolution?
Answer:
The differences between rotation and revolution
| Revolution | Rotation |
| (1) In revolution, earth moves around the sun in its fixed orbit. | (1) In rotation, earth moves around on its own axis. |
| (2) The revolution speed is uniform all over the Earth. | (2) The rotational speed is not uniform all over the Earth. |
| (3) Time taken to complete one revolution is 365V4 days | (3) Time taken to complete one rotation is 24 hrs. |
| (4) It causes the apparent annual movement of the sun. | (4) It causes apparent daily movement of the sun. |
| (5) It causes variation in length of days and nights. | (5) It causes formation of days and nights. |
| (6) Idea of heat zones is formed due to it. | (6) Idea of time is formed due to it. |
Class 9 WBBSE Geography Chapter 2 Important Questions
Question 3. Differentiate between Perihelion and Aphelion.
Answer:
The differences between Perihelion and Aphelion
| Perihelion | Aphelion |
| (1) During this position the distance between the sun and the earth is minimum. | (1) During this position the distance between the sun and the earth is maximum. |
| (2) The distance between the sun and the earth is about 147 million km. | (2) The distance between the sun and the earth is about 152 million km. |
| (3) This occurs every year on 3rd Jan. | (3) This occurs every year on 4th July. |
| (4) This time the speed of the earth’s revolution is maximum. | (4) This time the speed of earth’s revolution is minimum. |
| (5) In this period the sun looks bigger in size. | (5) This period the sun looks smaller in size. |
| (6.The winter season and summer season is shorter in northern and southern hemisphere. | (6) The summer season and winter season are longer in Northern ane southern hemisphere. |
Question 4. The poles experience 6 months day and 6 months of night. Why?
Answer:
The poles experience 6 months day and 6 months of night.
Due to the inclination of the earth on its axis from 22nd March to 22nd December the sun shines in the northern hemisphere So, the rays fall on the areas of circle and there is 6 months day in the North pole where as 6 months night at South pole.
On the other hand from 24th September to 20th march, the rays of sun fall on the southern hemisphere and the northern hemisphere remains in darkness. So, there is 6 months night at North pole and 6 months day at south pole 21st March and 23rd September is the day of Equinox i.e. equal days and nights.
Chapter 2 Geography Class 9 WBBSE
Question 5. What are the causes for the change of seasons?
Answer:
Seasons are the climatic divisions of the year.
The main causes for the change of seasons are –
(1) Inclination of the Earth’s Axis.
(2) Elliptical shape of the orbit of sun.
(3) Spherical shape of the Earth.
(4) Revolution of the Earth.
(5) Rotation of the Earth.
(6) Elliptical shape of the Earth’s Orbit.
Question 6. What is ‘Solar day’ and ‘Solar Year’?
Answer:
Solar day-
The time taken by the earth to complete one rotation is called solar day. The time taken is approx. 24 hrs or 23 hrs 56 mins and 4.09 secs.
Solar year –
The time taken by the earth to complete one revolution is called solar year. The time taken is approx. 365 ¼ days or 365 days 5 hrs 48 mins and 46 secs.
Question 7. A new day is added after four calendar years, why?
Answer:
A new day is added after four calendar years,
Normally a year is considered to be of 365 days, while the actual period of the Earth’s one revolution round the sun is 365 days and a little less than 6 hrs. (5hrs 48 mins and 45.51 secs). It means we have to leave off about 6×4 = 24 hrs. or one day So, we have a year of 366 days after every four years. Such one year is called a Leap year.
Question 8. What is Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis?
Answer:
Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis
During the 6-month duration of night at the poles, sometimes in the night sky faint but colorful lights like a rainbow is seen. Auroras are glows of light, hundreds of kilometers above the earth’s surface in the atmosphere, are pulled down towards the earth’s magnetic poles. During this pulling collision between the tiny particles occurs resulting in flashes of light. In the south pole it is known as Aurora. Australis and in the north pole it is called Aurora Borealis.
WB class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Questions And Answers
Question 9. What are the effects of inclination of earth’s axis?
Answer:
The effects of inclination of earth’s axis
The earth’s axis is inclined at an angle of 66(½)° to the plane of the orbit and 23(½)° to the vertical plane, it causes these effects
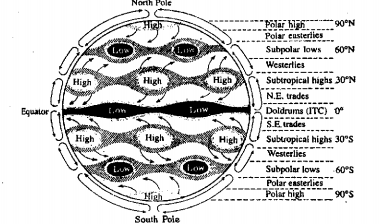
(1)Revolution of the earth on its elliptical orbit.
(2)Variation in lengths of days and nights.
(3)Thermal variation.
(4)Change of seasons.
(5)Change of apparent position of the sun.
Question 10. Why are leap years necessary?
Answer:
The exact length of a year is 365 days 5 hrs 48 mins and 46 secs. Since the difference between the actual length of the year and 365 days is nearly 6 hrs which is ¼th day, adding an extra day to February every 4 years.
(1)Keeps the calendar accurate.
(2)Enables the seasons to recur at the same date each year.
Question 11. Equator is almost devoid of seasons – why?
Answer:
Equator is almost devoid of seasons
Equator is located at the middle of the Earth. It receives vertical sun light almost every day throughout the year. So, the range of temperature is almost 2°- 3°C. Daily temperature variation between days and nights are also negligible. High temperature with regular rainfall at afternoon known as – “4 O’clock rain’ is the most striking feature of equatorial region. As the day receives light it is heated and that heat is released at night. So, this results in equal temperature and de void of seasons.
WB class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Questions And Answers
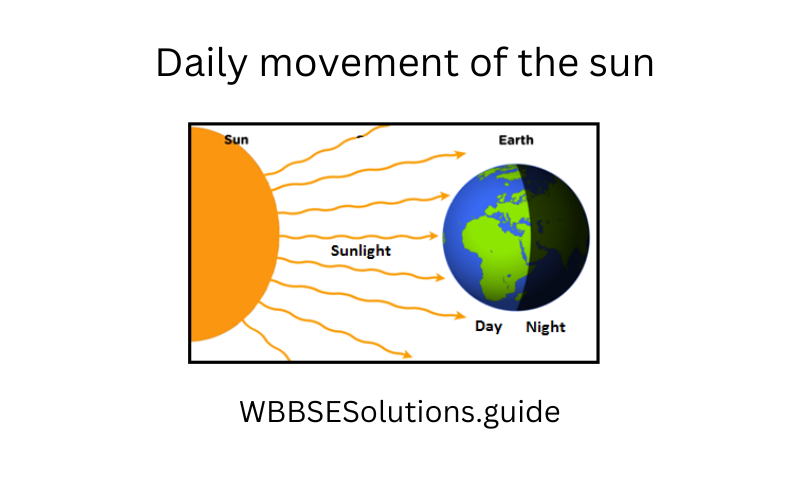
Question 12. What do you understand by apparent daily movement of the sun?
Answer:
Movement of the sun
We see that the sun rises in the East and sets in the West. This is the sun’s apparent daily movement caused by the rotation of the earth from West to East.
Question 13. What are meant by Perihelion and Aphelion?
Answer:
Perihelion and Aphelion
The orbit (path of revolution) of the earth is not circular but elliptical and the sun is not in the center of this ellipse. Thus, when the sun is farthest from the earth (15 crore 20 lakh km.) it is known as Aphelion (ap = away and helios = sun). This position comes on July 4. When the sun is nearest to the earth (14 crore 70 lakh km) it is known as Perihelion (peri = close and helios = sun). This occurs on January 3.
Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution Class 9 WBBSE Short And Long Answers
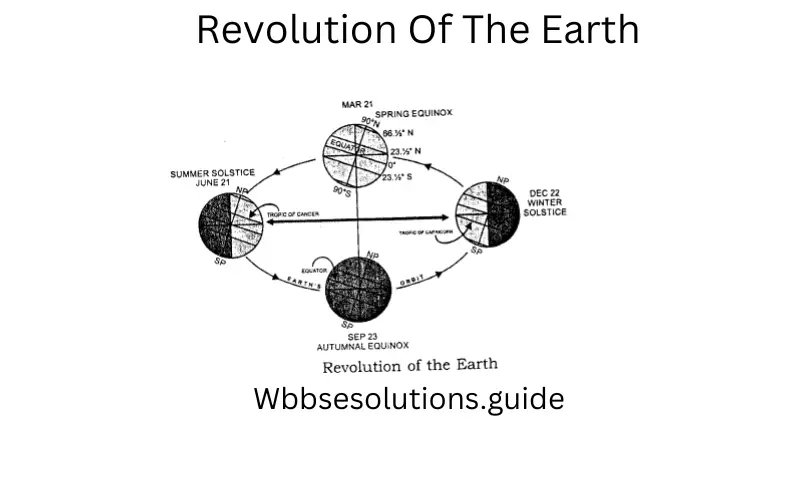
Question 14. What do you understand by the rotation and revolution of the earth?
Answer:
Rotation: The earth rotates on its own axis from West to East. In this way the part of the earth facing the sun experiences day and the opposite part night. This is called the ‘rotation’ of the earth
WB class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Questions And Answers

Revolution: Rotating on its axis, the earth revolves around the sun in an elliptical path, in 365 ¼ of days. This is called the revolution of the earth.
Question 15. State the differences between summer solstice and winter solstice. (S.Question)
Answer:
The differences between summer solstice and winter solstice.
| Summer Solstice | Winter Solstice |
| (1) The position of 21st June is called summer solstice. | (1) The Position of 22nd December is called Winter solstice. |
| (2) The sun’s rays fall vertically on the Tropic of Cancer at this position. | (2) The sun’s rays fall vertically on the tropic of Capricorn at this position. |
| (3) The Northern hemisphere leans towards the sun. | (3) The Southern hemisphere leans towards the sun. |
| (4) These is summer season in Northern Hemisphere and winter season in Southern Hemisphere. | (4) These is the winter season in Northern Hemisphere and summer season in Southern. |
Question 16. Why the Australians celebrate the X-mas in the summer?
Answer: Australia is situated in the Southen hemisphere. When we have our winter months, then the people of Southern hemisphere have the summer months. But Xmas is fixed all over the world. So, the people of Australia or Southern hemisphere celebrate X-mas in summer as 25th December is fixed as X-mas day all over the world.
WB class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Questions And Answers
Question 17. How day and night are caused?
Answer: The Days and Nights are caused by the rotation of the earth. The earth rotates from West to East. As the earth is a sphere, only half of it facing the sun receives sunrays. The other half remains dark. As a result, days occur in the lightened-half of the earth and night in the darkened half of it.
Question 18. What are the causes of the change of seasons?
Answer:
The change of seasons is caused due to the changes of the earth’s position in course of its revolution around the sun and due to the inclination of its axis.
Thus, seasons are caused by
(1)the revolution of the earth round the Sun.
(2) the inclination of the earth’s axis at an angle of 66° to the plane of orbit.
(3) the parallelism of the earth’s axis throughout its all positions at the plane of its orbit. Seasons would not have occurred if the axis of the earth had remained perpendicular to the plane.
Question 19. Why is 23rd September called Autumnal Equinox?
Answer: On 23rd September, the earth comes up at such a position that the sun appears vertically overhead on the equator and neither the North pole nor the South pole is inclined towards the sun. The North and South pole remain equidistant from the sun. Therefore, the days and nights are equal all over the earth. So, the position of the earth on 23rd September is known as Autumnal Equinox.
Question 20. Describe in brief the effects of revolution of the earth.
Answer:
The effects of the revolution of the earth are
(1) Inequality of day and night:
Variation in the length of days and nights occurs (due to the inclination of earth’s axis on its orbit at an angle of 66 (½)° at different times of the year in accordance with the position of the earth vis-a-vis the sun.
(2)Change of seasons:
The seasons (winter, spring, summer and autumn) change from one to another due to the revolution of the earth. They change due to special positions of the earth in relation to the sun and the transition from one to the other follows the movement of the earth round the sun.
Class Ix Geography Book WBBSE
(3) Heat zones and latitudes on the earth:
The latitudes and heat zones are also found as a result of the revolution. At different times of the year, the rays of the sun strike the earth at different points and these points have led the geographers to arrive at the positions of the Equator, Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circles. Determination of these lines automatically leads one to divide the earth into different heat zones on the basis of temperature.
Question 21. There is no season at the equator— Why?
Answer:
There is no season at the equator
The equator is Stretching our the middle part of the earth. The sun shines here vertically round the year. So the region gets vertical rays of the sun round the year and the range of temperature between the summer and the winter is very low only 2° — 3°C. The range of temperature between days and night is also very low. High temperature with regular rainfall in the afternoon is the feature of the equatorial region. That is why it is said that there is no season at the equator.
Question 22. Why we don’t feel the rotation of the Earth? Give reasons.
Answer: We do not feel that the earth on which we live is constantly rotating. The reasons are—
(1) There are not heavenly objects nearer to the earth, either stationary or moving opposite of the earth’s rotation by which we can compare the earth’s rotation,
(2) The rate of rotation is uniform and constant for each place on the earth’s surface,
(3) The atmosphere also rotates with the earth uniformly.
Question 23. Why is 21st March important in geography?
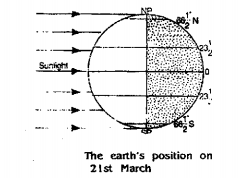
Answer: As the Earth further continues to revolve, the Sun appears to move northwards and on 21st March it again appears just vertically overhead on the equator at noon. The north and the south poles remain equidistant from the Sun. The Sun’s rays fall vertically on the equator. All places on the Earth have equal days and nights. It is spring (after the winter) in northern hemisphere and Autumn (after the summer) in southern hemisphere. This position of the Earth on 21st March is known as Vernal Equinox.
Class ix Geography Book WBBSE Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation And Revolution 5 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. Explain the causes of change of seasons.
Answer:
Causes:
The change of seasons is caused due to –
(1) Revolution of the Earth around the sun
(2) Elliptical Orbit of the sun
(3) Inclination of the Earth’s axis at an angle of 66(½)° to the plane of its orbit.
(1)Summer Solstice:
In Northern hemisphere, the rays of the sun vertically fall on Tropic of Cancer on June 21 when the North pole leans towards the sun and the whole Northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun at the North Pole, continuous daylight is visible for six months.
Thus, in Northern hemisphere there is summer. Temperature is higher, days are longer and nights are shorter. This position of the earth is known as ‘Summer Solstice’ in Northern hemisphere.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 2 Summary
(2)Winter Solstice:
On December 22, the sun is vertically overhead at noon on Tropic of Capricorn. At this position, the South Pole and the Southern Hemisphere lean towards the sun’s rays. In the Southern hemisphere, the days are longer and the nights are shorter. The reverse is the phenomena in the Northern hemisphere on this date. This is known as winter solstice.
(3)Equinox:
The word Equinox means Equal night. On 21st March And 23rd September, the length of days and night are equal. There are two Equinox –
(1) Vernal Equinox:
– While revolving round the sun, the position of the earth becomes such that the sun’s rays fall vertically upon the equator on March 21 and September 23. Thus, on these two days, days and nights are of equal duration. in the Northern hemisphere, the season of spring begins in the month of March (i.e, after winter ends) hence it is known as spring or vernal equinox.
Class Ix Geography Book WBBSE
(2) Autumnal Equinox:
Equinox means equal night and autumn means when there is autumn season in the Northern hemisphere and spring season in the Southern hemisphere. After June 21 (longest day in Northern hemisphere) the sun appears to be moving southwards and on September 23, while revolving round the sun the earth comes in such a position that the sun appears to be shining vertically on the equator (At this time neither of the poles is inclined towards the sun and both are equidistant from the sun).
Thus, days and nights on this date (23 September) are equal in both the hemispheres. Because this time in Northern hemisphere, there is the autumn season (i.e, after Summer ends), it is known as ‘autumnal equinox’.
Question 2. What is Earth’s rotation? State three proofs in support of Earth’s Rotation.
Answer:
Rotation:
The spinning of the earth on its own inclined axis in its fixed orbit is called Rotation.
Proofs: The three proofs in support of Earth’s Rotation are :-
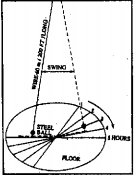
(1) Foucault’s pendulum Experiment:
Jean Bernard Leon Foucault, the famous French scientist gave an excellent proof of the earth’s rotation. Foucault suspended a cannonball (28kg) from the dome of the pantheon in Paris, using a slender wire about 61m. long.
A pin was attached to the bottom of the weight so that it could touch a heap of sand lying below. He then made it swing to and for just above a circle of sand spread over the ground on which it could draw lines while swinging in the north-south direction.
As the time passed the pendulum was seen oscillating in a line different from what it was tracing at the outset. This showed that the earth was slowly turning below it. The lines showed that the earth was turning from west to east as it rotates round the axis.
(2) East – wast movement of the sun:
Since the earth rotates from west to east, we seen the sun rising in the east and setting in the west. Not only the sun, but all the heavenly bodies in the sky seem to move from east to west every day.
Class Ix Geography Book WBBSE
(3) Drop of stone from a high tower:
When the air has no movement if a stone is dropped from a very high tower it falls slight to the east than the vertically. It proves that earth has a movement i.e. rotation.

Question 3. Explain the process of deflection of planetary winds due to earth’s rotation.
Answer:
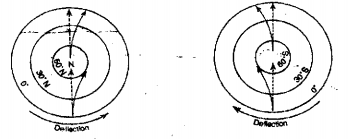
Explanation for deflection of planetary winds: The rotation of the spherical-shaped earth from west to the east once in 24 hours results in the deflection of its planetary winds, i.e. latitudinal winds.
All points on the earth’s surface make one resolution in 24 hours. A point on the equator moves eastward at a greater velocity than a point on any higher latitude, say arctic circle or Antarctic circle, because the equator is longer than any of these circles.
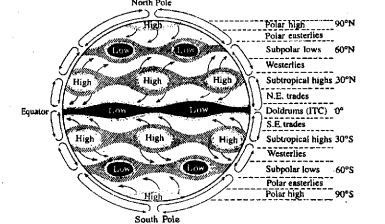
A mass of air on parallel of the latitude say 66 (½)° N. (i.e., arctic circle) will have an east-ward speed equal to that of the parallel. If this mass of air moves towards the equator it will cross over parallels whose eastward speeds increase with decreasing latitudes.
If we want to show the path of the mass of air with the dots, it appears as a curve which bends to the right (from the starting point in the northern hemisphere) of the path from it would have taken, should the earth not rotate.
If a similar air mass had moved from a high latitude to a low latitude in the southern hemisphere its path of movement would appear as curve to the left of the path it would have taken, should the earth not rotate.
Because of rotation, the path of any moving objects over the earth tends to veer from a straight line. This tendency of deflection is known as the Coriolis Effect or the Coriolis Force named after the nineteenth-century French mathematician and engineer Gaspard Gustave de Coriolis who first described it in 1835. The concept was developed by W. Ferrell in 1855. The Coriolis Effect or Force is also stated as Ferrell’s Law.
Ferrell’s Law states that winds and ocean currents moving poleward or equatorward over the earth’s surface is deflected, owing to the earth’s rotation, to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
Class 9 Geography Movement Of The Earth WBBSE MCQs With Answers
Question 4. Explain the effects of earth’s rotation.
Answer:
The major effects of earth’s rotation are –
(1)Formation of Days And Nights:
The earth rotates around its own axis from west to east in 24hrs. So when a particular side comes in front of sun it experiences daytime
 .
.
(2) Apparent daily movement of the sun:
The apparent movement of the sun and the stars round the earth from east to west. Every day is also the result of the rotation of the earth.
(3) Sense of time:
The earth takes a full day i.e. 24 hrs. to complete one rotation. We divide the hours into 60 mins. And a minute into 60 secs. Thus we get the idea of calculating time.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
(4) Difference of time:
Due to the rotation of the earth, different places on it have different local time.
(5) Deflection of planetary winds:
Due to the rotation of the earth the planetary winds do not move in a straight line but get deflected to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. This is known as ‘Ferrell’s Law’.
(6) Distribution of temperature:
As a result of rotation of the earth the distribution of temperature on the earth’s surface is not the same.
(7) Others: Other important effects are
(1) Formation of Tides
(2) Determination of Direction
(3) Shape of the Earth
(4) Determination of longitude
(5) Variation of Daily Temperature etc.
Question 5. Give at least three proofs supporting the annual motion of the Earth.
Answer:
It can be proved by the following examples that earth has annual motion i.e. Revolution –
(1) Observation of stars:
While observing some specific stars in the night sky, it is seen that they rise every day a little to the west of their previous position and after some days they disappear. Instead of these stars, later different stars are seen in the night sky and gradually they also disappear until after an year these stars again rise in their previous position. This proves that while revolving around the sun the earth comes back to its previous position in the orbit after one year.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
(2) The Apparent change in sun’s position:
There is an apparent annual movement of the sun in the sky because of the Earth’s Revolution. On 21st March and 23rd September the sun rises right in the east and sets in the west. But during the rest of the year it rises and sets a little to the north or to the south. If the earth rotates at the same sunset would be right in the west.
(3) Observation of Other Planets:
With a powerful telescope it can be seen that other planets of the solar system Mercury, Mass, Venus, Jupiter etc. revolve around the sun. Earth being another planet in solar system, it is natural for it too, to revolve around the sun.
Question6. What are the effect of revolution?
Answer:
Some effects of revolution are
(1) Variation in length of days and nights:
Except the equatorial region, the rest of the earth experiences varying length of days and nights at different times of the year i.e. sometimes the days are longer than nights or the days are shorter than nights. This is caused due to the revolution of the earth and the spherical shape of the earth.
(2) Change of seasons:
There are four main seasons in a year namely – spring, summer, autumn and winter. These seasons are changed periodically due to the earth’s revolution.
(3) Idea of leap year:
Earth takes 365 days and a little less than 6 hrs. to complete its one revolution. This 6 hrs. is left in every year and hence we have 6×4 = 24 hrs or 1 day at every 4th year. This 1 day is added in every 4th year. This year is known as Leap year.
(4) Apparent Annual Movement of the sun:
To us on the earth, it appears as if it is the sun that moves between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Tropic of Cancer for six months northward. It is called Uttarayan. Similarly for six months journey of the sun (from June to December) towards south is known as
Dakshinayan.
(5) Idea of latitudes And heat zones:
As a result of the earth’s revolution, the sun’s rays strike on the earth’s surface at different parts on different times of the year. This give us Idea of Equator, Tropic of Cancer, Tropic Capricorn etc. as well as heat zones of the earth.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
Question 7. What are the causes leading to variation in length of days and nights?
Answer:
Except the Equator days and nights are not equal on all the places of the earth. Surch variation in the length of days and nights is caused by
(1) Spherical shape of the earth,
(2) Rotation and revolution of the earth,
(3) Elliptical shape of the earth’s orbit,
(4) Tilling of the earth’s axis at 66 (½)°to the orbital plane and
(5) parallelism of the earth’s axis. As the earth is tilled on its axis, it means that in one part of the year earth is tilled towards the sun and in another part away from the sun. As a result different places on earth receive different amounts of sunshine at different times of the year. Above reasons are responsible for varying lengths of days and nights which has been discussed below.
(1) 21st June :
On June 21 the northern hemisphere is tipped towards the sun. From March 22 to September 22, days are longer and nights are Shorter in the norther hemisphere having the longest day and shortest night on June 21 every year. The reverse condition in the southern hemisphere having the longest night and shortest day on June 21 every year. This is because the rays of the sun fall vertically at the Tropic of Cancer [23(½)°N ]
(2) 23rd September and 21st March :
On September 23 and March 21 the earth is so located on these two dates that the subsolar points lie on the equator. The shadow circle passes through both the poles and coinsides with meridian. Thus these phenomena cause day and night equal all over the earth on these two dates 23rd September and 21st March.
(3) 22nd December :
On December 22 the subpolar points arrives at the tropic of Capricorn [23(½)°S]. The south pole is inclined towards the sun and the north pole is away from it. The rays of the sun fall vertically on the 23(½)°s latitude. From September 23 to December 21 days are longer and nights are shorter in the Southern hemisphere having the longest day and shortest night on December 22 every year. The reverse conditions prevail in the northern hemisphere. These phenomena cause the longest night and shortest day on December 22.
Question8. Write a note on Uttarayan And Dakshinayan.
Answer:
Uttarayan And Dakshinayan
The sun does not move; the Earth moves. But to us on the Earth, it appears as if it is the sun that moves between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. This means that all latitudes between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn have the sun vertically overhead at least once between June and December and once again between December and June. Therefore, places between the tropics have the sun overhead twice a year. Places beyond the two tropics have the sun directly overhead only once a year.
(1) Northward apparent migration (Uttarayan):
For six months of a year, the sun appears to be moving north. This northward migration begins after December 22 and is completed on June 21, when the sun is directly overhead 23(½)°N latitude (Tropic of Cancer). The last day of northward migration of the sun is 21 June and this day is known as day of Uttarayan and last time limit of northward movement of the sun is 23 (½)°N latitude.
Class 9 Geography Solution WBBSE
(2) Southward apparent migration (Dakshinayan) :
For six months of the year, the sun appears to be moving south. This southward migration begins after June 21 and is completed on December 22, when sun is directly overhead at 23 (½)°of latitude (Tropic of Capricorn), The last day of southward migration of the sun is 22nd December, and this day is known as the day of Dakshinayan and last limite of the southward movement of the sun is Tropic of Capricorn or 23 (½)°s • This Northward and Southward migration of the sun is known as Rabimarg.
Question 9. State the Salient features of Earth’s Rotation.
Answer:
Salient features of the Earth’s Rotation are :
(1) Direction of Rotation :
If we look down upon the Earth (Globe) from outside, the Earth is found to rotate from West to East or in an anticlockwise direction. Since the Earth rotates in a West-east direction, we see the sun rising every day in the east and setting in the west.
(2)Axis:
(1) Rotation is the turning around of the Earth on its axis, from west to east.
(2) The axis is the imaginary line passing through the centre of the Earth on which the Earth rotates.
(3) The Earth spins west to east around its axis once in 24 hours.
(4) The North Pole and the South Pole lie at the ends of the axis.
(5) The earth’s axis is not vertical. It makes an angle of 66 (½)° Earth’s orbit.
(6) The Earth’s axis always remains pointed in the same direction (towards the Pole star) as the Earth journeys around the sun.
(7) The tilt of the Earth’s axis is also known as the inclination of the Earth’s axis.
(3) The Speed of Rotation :
Being spherical in shape the surface speed of rotation of the earth is variable. It is highest at the equator, gradually diminishing towards north and south and become zero at the poles. The surface speed at the equator (0°) is 1630 km/hr.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Notes
Question10. Give a brief account of different experiments and the Earth’s motion in ancient times.
Answer:
Different experiments and the Earth’s motion in ancient times
(1)Ancient Times :
Though lacking in the technological advances of today as well as the scientific knowledge which scientists enjoy today, ancient astronomers and mathematicians did not let this deter them from making sense of the beauty of the night sky. Armed with the limited mathematics of the day, namely geometry and trigonometry, as well as the desire to describe the movements of the celestial objects, early astronomers and mathematicians laid the foundations to explain planetary motion.
Eudoxas [409-356 BC] :
Eudoxas is credited with being the first person to create a model of our solar system. His geocentric model placed our earth at the center of the known universe. Other known objects the sun, the moon, five planets, and the stars rotated around the earth on a series of 27 concentric sphere moving at different speeds and inclinations.
Aristarchus [310-230 BC]:
The contributions of Aristarchus are significant. Aristarchus is considered to be the first person in recorded history to suggest the idea of a heliocentric solar system in which the earth was not the center.
Claudius Ptolemy [85-165 AD]:
Ptolemy is most associated with the geocentric model of our solar system. Ptolemy used the idea of epicycles (the orbital paths of the celestial objects) and deferants (the orbital paths of the epicycles) to account for the retrograde motion of the planets.
(2) Middle Ages :
Models of planetary and celestial motion remained relatively unchanged throughout the Middle Ages. Most of the astronomers and mathematicians who made contributions did so in the form of simply altering the Ptolemaic model, rather than transforming it completely.
(3) Renaissance :
Birth of Modern Astronomy: The renaissance period is just one of many steps in the natural progression of humankind. It is in this period where many topics, such as art, politics, religion, etc., received a newfound interest. The change from the geocentric view to the heliocentric view of the solar system did not happen overnight. The most important people involved in this transition were Nicolaus Copernicus, Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei, and Sir Isaac Newton.
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) :
He was a polish astronomer. With him began the age of modern astronomy. Copernicus became acquainted with the idea of the Greek philosopher Aristarchus that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the sun. He became convinced of the correctness of the theory. He constructed the Solar System with the sun at its center and Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn orbiting it. Copernicus proposed that the Earth rotates, which better explained the daily motions of the heavens.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Notes
Tycho Brahe (1546-1601) :
He held the view that the son and moon revolved around the earth while everything else revolved round the sun.
Galileo Galilei (4564-1642) :
His work relating to Jupiter and its satellites helped greatly to form his opinions on planetary motion. While observing Jupiter with newly invented telescope. He noticed four small stars near the giant planet. After months of observations, he determined the “small stars” must be orbiting Jupiter. He thus disapproved the idea everything in the universe revolved around the earth.
(4) Giordano Bruno:
One of Copernicus’s followers, Giordano Bruno was burned at the stake for refusing to denounce the Copernican theory.
(5) Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) :
He was a German astronomer who supported the Copernican theory. He discovered that all planets have elliptical orbits. He was deeply religious and believed that the creator made an orderly uni¬verse. Armed with a good mathematical mind and great faith in the observational data of the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe, he derived, formulated, and verified the three basic laws of planetary motion.
Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion :
(1) The path of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus.
(2) The “area rule”: a planet covers equal areas of its orbit in equal periods of time.
(3) The period of revolution of a planet is proportional to its distance from the sun, i.e., it travels most rapidly when it is nearest the sun and most slowly when it is farthest from the sun.
WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
- Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet
- Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface
- Chapter 4 Geomorphic Processes And Land Forms Of The Earth
- Chapter 5 Weathering
- Chapter 6 Hazards And Disasters
- Chapter 7 Resources Of India
- Chapter 8 West Bengal
- Chapter 9 Map & Scale
