Chapter 9 Map And Scale Multiple Choice Questions With Answers:
Question 1. 1: 4,00,000,000 — example of which scale?
(1) Statement
(2) R.F
(3) Linear scale
(4) None
Answer: (2) R.F
Question 2. In a map —
(1) Use of scale is not essential
(2) Use of scale is insignificant
(3) Use of scale is a must
(4) Use of scale is not necessary
Answer: (c) Use of scale is a must
Read and Learn all WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
Question 3. For the preparation of map, an arrow sign is used to indicate north line the purpose is —
(1) To determine the height of map
(2) To indicate summit of map
(3) To indicate direction of map or North direction.
(4) None of these
Answer: (3) To indicate direction of map or North direction
Question 4. If there is no scale in map —
(1) It is surely signify a map
(2) It is not a map but a sketch map
(3) It part of whole of the map
(4) It will be nullified
Answer: (2) It is not a map but a sketch map
Question 5. An example of a large-scale map is —
(1) Atlast
(2) Map of a country
(3) Mouza map
(4) Map a landscape
Answer: (3) Mouza map
Question 6. Example of a small-scale map is —
(1) Map of a country or continent
(2) Mouza map
(3) Map of a village
(4) Map of a Landscape
Answer: (1) Map of a country or continent
| Class 9 English Bliss | Class 9 Life Science |
| Class 3 English | Class 9 Geography |
| Class 10 Life Science | Class 9 History |
| Class 9 History | Class 9 Maths |
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 9 Map And Scale Solutions
Question 7. “4 em to 400km”— example of what type of scale?
(1) Linear scale
(2) R.F
(3) Statement scale
(4) None
Answer: (3) Statement scale
Question 8. The conventional representation of Earth’s surface pattern of part of it, drawn on a sheet of paper is called :
(1) A globe
(2) A map
(3) A compass
(4) A painting
Answer: (2) A map
Question 9. The Latin word ‘Mappa’ means :
(1) A paper
(2) A pencil
(3) A sheet of cloth
(4) A book
Answer: (3) A sheet of cloth
Question 10. The signs that show the features on map are called a :
(1) Labels
(2) Conventional signs
(3) Tags
(4) Index
Answer: (2) Conventional signs
Question 11. The ratio of map distance to ground distance is called a:
(1) compass
(2) scale
(3) tape
(4) sketch
Answer: (2) scale
Question 12. The color used to show waterbodies on a map is :
(1) Red
(2) Green
(3) Blue
(4) Yellow
Answer: (3) Blue
Question 13. The rough drawing of any area without a scale is called a:
(1) Sketch
(2) Plan
(3) Language
(4) Symbol
Answer: (1) Sketch
Question 14. The map that shows mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, rivers, seas, etc., is called a:
(1) Political map
(2) Physical map
(3) Cadastral map
(4) Wall map
Answer: (2) Physical map
Question 15. R.F. is the abbreviated form of :
(1) Relative fraction
(2) Representative fraction
(3) Reduced fraction
(4) Recurring fraction
Answer: (4) Representative fraction

Map And Scale Class 9 WBBSE Question Answers
Chapter 9 Map And Scale Short Questions With Answers:
Question 1. Give an example of a Statement Scale.
Answer: 1cm to 50 km.
Question 2. Give an example of Representative fraction.
Answer: 1: 1,00,000.
Question 3. From which word ‘map’ has been derived?
Answer: Mappa.
Question 4. What is the unit of measurement in Large Scale?
Answer: Mile or km.
Question 5. What is the unit of measurement in Small Scale?
Answer: Inch or cm.
Question 6. Give an example of Small Scale.
Answer: 1cm =5 km.
Chapter 9 Map And Scale True Or False Type
Question 1. A thematic map helps us to get an idea about a topic or a theme.
Answer: False
Question 2. The topographical map depicts the weather condition of a place.
Answer: False
Question 3. The direction in a map is shown with the help of a north line\(\left(\begin{array}{l}N \\\uparrow\end{array}\right)\).
Answer: True
Chapter 9 Map And Scale Fill In The Blank
Question 1. The maps prepared to show underlying rock features and structure is called __________ maps.
Answer: Geological.
Question 2. Cadastral maps or ______________ maps are used for demarcating the boundaries of landed properties, fields, gardens, etc.
Answer: Mouza.
Question 3. A’ ____________ scale is drawn as a straight line which is divided into certain lengths, each showing certain on the ground.
Answer: Linear, distance.
Question 4. The box at the corner of a map that shows the conventional signs is called the _______.
Answer: Index.
Chapter 9 Map And Scale 2 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. Define map.
Answer:
Map
The word ‘map’ has been derived from the Latin word ‘Mappa’ which means a napkin or cloth. This indicates that the earlier maps used to be drawn on cloth or on tree leaves. A map is defined as a representation of the earth’s surface or a part of it, showing natural or man-made features, drawn to scale on a flat surface.
Question 2. What do you mean by Cartography?
Answer:
Cartography
The earth is spherical in shape, making it difficult to represent it on a flat surface. The representation of three-dimensional features like mountains, valleys, rivers, and other geographical phenomena involves special techniques so that they are drawn on a uniform basis. This are and science of mapping is called cartography. The word ‘Cartography’ has been derived from two French words ‘carte’ and ‘graphic’ meaning ‘map’ and ‘drawing’ respectively.
Question 3. What do you mean by scale?
Answer:
Scale
The scale of a map denotes the proportion that the distance between any two points on a map bears to the distance between any two points on a map bears to the distance between the same two points on the surface of the earth. The scale is also defined as the ratio between the distance of any two points on the map and the actual distance of the same points on the ground. It can be expressed as :
\(\text { Scale }=\frac{\text { Map distance between two points }}{\text { Ground distance between the same points }}\)
Question 4. Define Physical maps. State its classification.
Answer:
Physical maps
The maps which describe physical features like relief, rivers, climate, natural vegetation, etc.
Classification Of Physical maps :
(1) Astronomical maps.
(2) Relief maps.
(3) Geological maps.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography Chapter 9 Solved Exercises
Question 5. Define Graphical Scale.
Answer:
Graphical Scale
When we draw a scale by using one or more straight lines it is called a graphical scale.
Question 6. Why graphical method of representing scale is preferred?
Answer:
The graphical method is preferred to represent scale of a map due to the following reasons :
(1) It combines both R.F. and verbal statements.
(2) This is valid if the map is reduced, enlarged or only a small portion of it is used.
Chapter 9 Map And Scale 3 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. What are the major elements of map?
Answer:
Elements of a Map: There are five basic elements of a map
(1) Title: It denotes what the map portrays, e.e., the distribution of natural vegetation.
(2) Scale: It denotes the relationship between map distances and actual ground distances.
(3) Key: It explains the meaning of the symbols that are used in the map.
(4) Direction: It refers to the cardinal directions, i.e., North, South, East, and West. Conventionally, a map is aligned with the North towards the top.
(5) Grid System: It is a network of lines that help in pinpointing the location of a place on a map. Usually, a grid is formed by lines of latitudes and longitudes.
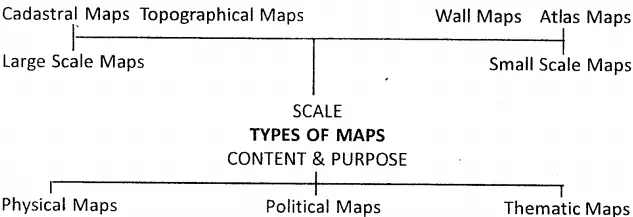
Question 2. Classify maps on the basis of their purpose and content.
Answer:
Maps can also be classified on the basis of their purpose and content as:
(1) Physical Maps :
These maps provide details about the natural features of an area or a country.
(2) Political Maps :
These maps portray different countries of the world along with their states, national and international boundaries, political units and administrative divisions, etc.
(3) Thematic Maps :
These maps show a particular feature or theme of the area. All types of cultural maps, most of the atlas maps, industrial maps, agricultural maps, military maps, linguistic maps fall in this category.
Class 9 Geography Map And Scale WBBSE Notes
Question 3. Explain the importance of scale.
Answer:
Importance of scale
(1) The use of scale in the map is very important. It indicates the distance of two points on the map according to the corresponding distance on the ground.
(2) The écale is used to determine the distance of the two points of the ground
on the map.
(3) Scale provides a very useful method of representing large areas within a convenient space. By means of scale, the entire earth’s surface can be mapped within a small space of paper.
(4) By enlarging and reducing the scale, special maps can be devised in accordance to the object and purpose, such as, topographical maps, cadastral maps (map which are used for demarcating the boundaries of landed properties) mouza maps, field map for planning or for a strategy of war.
Question 4. What are the uses of scale for the preparation of Map?
Answer:
Uses of Scale for the preparation of Map :
(1) To measure distances between two points on the map.
(2) To measure out a certain length from the scale.
(3) To show the actual shape of a country or a continent.
(4) To enlarge or reduce a map according to scale.
Question 5. State the advantages & disadvantages of using a Linear Scale.
Answer:
Advantages of using a Linear Scale:
(1) Distances can easily be measured with the help of a linear scale.
(2) If the map is photographically enlarged or reduced, the linear scale is also enlarged or reduced in the same ratio and remains true to the map.
Disadvantages of using a Linear Scale:
(1) Like the statement of scale, this scale can only be used by those who are familiar with the unit of measurement used in the scale.
(2) It requires time and proficiency in drawing a graphic scale.
Chapter 9 Map And Scale 5 Marks Questions And Answers
Question 1. State the uses and importance of maps.
Answer:
Maps are used in many ways :
(1) As a general reference :
When we want to know where a place is we need a map. They give us idea of the direction and distance of a place.
(2) As an effective tool for navigation, control, and route planning :
We rely greatly on maps, whether we move on land, at sea or in the air. We plan our routes and maintain our course with the help of maps. There are hiking and biking maps, maps for moving through caves, highway maps, aeronautical charts, etc. We use these maps to plan our routes and then to navigate when we are in motion.
(3) Maps provide a lot of information to the planners. Planning of roads, residential complexes, factories, parks, location of schools and public facilities, sewer and water networks, etc., can be done on the basis of information provided by a map.
(4) Maps are used as legal documents showing ownership of land and boundaries.
(5) Maps are useful to sailors, pilots, drivers, miners, surveyors, engineers, environmentalists, and many other people.
(6) The strategies of an army even depend on the information provided by a map.
(7) Maps can show continents, countries, states, districts, cities, and even a local area with all the details.
(8) Maps are useful for students and the common people alike. They are easy to handle and can be carried everywhere.
Class 9 WBBSE Geography Chapter 9 Important Questions
Question 2. Write a note on the Linear graphic method of representing scale.
Answer:
A linear graphic Scale:
This is another method of expressing a scale on a map. A linear scale represents the same relationship by means of straight line which is divided into certain lengths each of which represents a certain distance on the ground.
A linear scale is generally divided into two divisions; viz.,
(1) Primary divsions and
(2) Secondary divisions.
In such a scale there are as many number of primary divisions and secondary divisions as required [or as stated]
Merits :
(1) A linear scale helps to determine easily the idea of a distance between the two places on a map by visual observation or by a simple scale of measurement.
(2) Hence, the distance on the map is easily measurable.
(3) Enlargement or reduction does not change the measurement of the scale of the map as the scale also be reduced or enlarged thereby. This merit is not available in case of R.F. scale.
Demerits :
(1) Drawing of a linear scale requires much time; it may also involve drawing defects.
(2) The respective unit of scale may not be acceptable all over.
(3) Change in the unit of measurement (cm/inch) of the scale may involve loss of accuracy.
Question 3. Write the advantages and disadvantages of the statement of scale method of representing scale.
Answer:
Advantages :
(1) This is a very simple method which is understood even by a common man. For example, if we tell an ordinary man that the scale of a map is 1cm:1km, he would immediately understand that one centimeter on the map corresponds to the kilometer on the ground.
(2) It requires little time to express this scale.
(3) It gives correct idea about distances.
Disadvantages :
(1) It can be understood only by those who are familiar with the unit of measurement used. For example, if we say that the scale of a map is 41cm: 1km, he would be understood by only that person who is familiar with the metric system of measurements.
(2) When a map is reduced or enlarged from the original, the scale does not remain the same. This created problems in measurement.
Question 4. Write the advantages and disadvantages of the representative fraction method of representing scale.
Answer:
Advantages :
Since it is only a fraction and is independent of any particular unit of measurement, it can be used in all countries. Even if a person is not familiar with various units such as inch (British), verst (Russian), and centimeter (French), he can easily use this scale.
Suppose the R.F. of a map is 1,00,000. To a Britisher, it would mean that 1 inch on the map represents 1,00,000 inches on the ground. Similarly, to a Frenchmen, it would mean that 1 cm on the map represents 1,00,000 cm on the ground and to a Russian, 1 verst on the map represents 1,00,000 verbs on the ground.
Thus, this scale can be converted into any unit of measurement and has universal application. It is, therefore, also termed as International Scale or Natural Scale. It has become a very popular method of expressing the scale.
Disadvantages :
(1) It is only a fraction in which no system of units is used. Hence, distances cannot be directly measured from it.
(2) Whenever a map is photographically enlarged or reduced, the R.F. will no longer be true.
(3) This is not easily understood by a common man.
Map And Scale Class 9 WBBSE Short And Long Answers
Question 5. Classify maps on the basis of their scales.
Answer:
Classification Of maps on the basis of their scales.
On the basis of scales, maps can be classified as large-scale maps and small-scale maps.
Large-Scale Maps :
(1) Topographical Maps: They are prepared after a careful and accurate survey of the area.
They show natural features (such as hills and rivers) and man-made features (such as buildings, and canals). These maps are very useful for planning, defense, tourism, etc.
(2) Cadastral Maps :
The term ‘Cadastral’ has been derived from the French word “Cadestre’ which means register or territorial property. Cadastral maps provide complete details of an area such as the boundaries of properties and individual buildings.
These maps are, therefore, used to register the ownership of landed property by demarcating the boundaries of fields, buildings, etc. They are specially prepared by the government for the administration and realization of taxes, management of estates, and identification of the property in legal documents. Examples of Cadastral maps are — Revenue maps, Settlement maps,
village maps and City plan maps.
Small Scale Maps :
(1) Wall Maps :
These maps are meant to represent large areas that could be viewed at a glance. They may show features like relief, temperature, population, industries, and vegetation. They are used for display purposes in classrooms and museums.
(2) Atlas Maps :
These maps are drawn on a smaller scale and are used to represent a whole country on a single sheet. Since these maps are drawn on a smaller scale, they give a condensed and generalized picture of different areas of the world.
The features generally shown by Atlas maps include relief, drainage, vegetation, soils, crops, minerals, industries, population, cities, etc. Despite lack of details, these maps are best suited for educational purposes.
WBBSE Class 9 Geography And Environment Chapter 9 Summary
Question 6. State the methods of representing scale.
Answer:
There are three main methods of representing the scale on the map.
(1) A Statement: In this method, scale is stated in words or we make a statement about it.
Example:1cm.to1km
1 inch to 5 miles.
The value on the left-hand side usually represents the map distance. This method is not suitable, as we require to know the units of measurement in different countries. Moreover, when the map is reduced or enlarged from the original, the scale does not remain the same. This creates problems in measurement.
(2) Linear or Graphic Scale :
In this method, the scale is represented by a straight line divided into equal parts (primary and secondary) to show what these markings represent on the actual ground.
The Primary Divisions are the major divisions on the scale that graduated from left to right. The Secondary Divisions are smaller units graduated from right to left on one primary division. Te total length of this linear scale represents a distance of 25 kilometers.
Each p.imary division denotes a distance of 5 kilometers. Each secondary division denotes a distance of one kilometer on the actual ground.
(3) Representative Fraction :
In this method, the scale is represented as the ratio of the length of a line on the map and the corresponding actual distance on earth’s surface. The numerator is always expressed as unity i.e., one unit map- distance is equivalent to a number of units of ground distance. This fraction is called Representative Fraction.
\(\text {Representative Fraction (R.F. })=\frac{\text { Distance on the map }}{\text { Distance on the ground in the same unit }}\)
The most important point in a Representative Fraction is that the unit of measurement of distances in the numerator and the denominator is the same. For example, if the R.F. of a map is 1/1,00,000 or 1: 1,00,000, it means that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground.
If the unit of measurement is centimeters, we will say that 1 centimeter on the map represents 1,00,000 centimeters on the ground. If, however, the unit of measurement is an inch, then we will say that 1 inch on the map represents 100,000 inches on the ground.
The main advantage of R.F. is that it is only a fraction and is independent of any particular unit of measurement. It can be converted into any unit of measurement and has universal application. It is, therefore, also known as International Scale or Natural Scale.
Class 9 Geography Map And Scale WBBSE MCQs With Answers
Question 7. What are the conventional signs & symbols used in maps and scales?
Answer:
Conventional signs & symbols used in maps and scales are
Topographical maps use symbols to represent certain relief features and human activities. These are called conventional signs and symbols. They are used on a map because they. give plenty of information in a small space and maps can be drawn easily.
They are simple to read. Many of the signs and symbols are standardized and used throughout the world. The key or legend of a map has the list of signs and symbols as well as their meanings.
Hindi Terms Used in Survey Maps
1. Nadi — rivers;
2. nala — small stream;
3. phar — hill;
4. Parbat — hill or mountain;
5. Piao — a place where drinking water is available generally along roads or at railway stations. This is found mostly in north and northwest India where it be- comes very hot and water is scarce.
6. Police chowki— police outpost;
7. Talab — tank or reservoir or pond;
8. khera — kiln for baking bricks;
9. Tahsil or taluk — part of a district under a tahsildar who collects revenue from the area;
10. Dak bungalow — a government-owned bungalow for travelers to stay for a night or two,
WBBSE Solutions for Class 9 Geography and Environment
- Chapter 1 Earth As A Planet
- Chapter 2 Movement Of The Earth Rotation & Revolution
- Chapter 3 Determination Of The Location Of A Place On Earth Surface
- Chapter 4 Geomorphic Processes And Land Forms Of The Earth
- Chapter 5 Weathering
- Chapter 6 Hazards And Disasters
- Chapter 7 Resources Of India
- Chapter 8 West Bengal
