Chapter 20 Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangular Region Exercise 20
Important Formulae :
1. Co-ordinates of the mid-point of A(x1,y1) and B(x2,y2) = \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\)
2. In ΔABC, if the coordinates of the vertices are: A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2), and C(x3,y3) then the co-ordinates of its centroid are:
= \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}, \frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3}\right)\)
3. In ΔABC if the coordinates of the vertices are: A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2), and C(x3,y3) then the area of the triangle ABC will be
= \(\frac{1}{2}\left[x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right]\)
4. Three points will be collinear if the area of the triangle formed by them is zero. (v) Area of the quadrilateral formed by the points (x1,y1), (x2,y2),(x3,y3), and (x4,y4)
\(\frac{1}{2}\left[\left(x_1 y_2+x_2 y_3+x_3 y_4+x_4 y_1\right)-\left(y_1 x_2+y_2 x_3+y_3 x_4+y_4 x_1\right)\right] \text { sq.units. }\)Question 1. Find the area of a triangular region with the vertices given below:
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 9 Maths
1. (2,-2), (4, 2), and (-1, 3)
Solution: (2,-2), (4, 2), and (-1,3)
& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{2(2-3)+4(3+2)-1(-2-2)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-2+20+4) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 22 \text { sq. unit } \\
& =11 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
2. (8, 9) (2, 6) and (9, 2)
Solution: (8, 9) (2, 6) and (9, 2)
& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{8(6-2)+2(2-9)+9(9-6)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(32-14+27) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{45}{2} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =22 \frac{1}{2} \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Wbbse Class 9 Maths Chapter 20 Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangular Region Solutions
3. (1, 2), (3, 0) and origin (0,0)
Solution: (1, 2), (3, 0) and origin (0,0)
& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{1(0-0)+3(0-2)+0(2-0)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-6) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =-3 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Question 2. Prove that the points (3,-2), (-5, 4), and (-1, 1) are collinear.
Solution: Here the area of the triangle with vertices (3,-2), (-5, 4), and (-1, 1)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{3(4-1)-5(1+2)-1(-2-4)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(9-15+6) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 0 \text { sq. unit }=0
\end{aligned}\)
∴ The points are collinear.
∴ (3,-2), (-5, 4), and (-1, 1) are collinear points.
Question 3. Let us write by calculating for what value of K, the points (1, -1), (2, -1), and (K, -1) lie on the same straight line.
Solution: (1,-1), (2, -1), and (K, -1)
& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{1(-1+1)+2(-1+1)+K(-1+1)\} \text { sq. unit }=0 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
∴For any real value of K, the points are collinear.
Question 4. Let us prove that the line joining two points (1, 2) and (-2, -4) passes through the origin.
Solution: The coordinate of the origin is (0, 0).
∴ Area of the triangle formed by the points (1, 2), (-2, -4), and (0, 0) as vertices
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{1(-4-0)-2(0-2)+0(2+4)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-4+4+0) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =0
\end{aligned}\)
∴ The three points are collinear.
Wbbse Class 9 Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangle Exercise Solutions
Question 5. Let us prove that the mid-point of the line segment joining two points (2, 1) and (6, 5) lies on the line joining two points (-4, -5) and (9, 8).
Solution: The mid-point of the line joining (2, 1) and (6, 5) is
= \(=\left(\frac{2+6}{2}, \frac{1+5}{2}\right)=(4,3)\)
∴ Now area of the triangle formed by (4, 3), (-4,-5), and (9,8)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\{4(-5-8)+(-4)(8-3)+9(3+5)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-52-20+72) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(72-72) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 0=0
\end{aligned}\)
∴ The three points are collinear.
∴ The mid-point of the line joining (2, 1) & (6, 5) lies on the line joining two points (-4, -5) & (9,8).
Question 6. Let us find the area of the quadrilateral region formed by the line joining four given points each.
1. (1, 1), (3, 4), (5, -2), and (4, -7)
Solution:
Given
The four points are (1, 1), (3, 4), (5, -2), and (4, -7)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\left\{\left(x_1 y_2+x_2 y_3+x_3 y_4+x_4 y_1\right)-\left(y_1 x_2+y_2 x_3+y_3 x_4+y_4 x_1\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}[\{1.4+3(-2)+5(-7)+4.1\}-\{1.3+4.5+(-2) \cdot 4+(-7) .1\}] \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{(4-6-35+4)-(3+20-8-7)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{(8-41)-(23-15)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-33-8) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(-41) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{41}{2} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =20 \frac{1}{2} \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
2. (1, 4), (-2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 3)
Solution:
Given
The four points are = (1, 4), (-2, 1), (2, -3), and (3, 3)
=\(\begin{aligned}
& \left.=\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1 y_2+x_2 y_3+x_3 y_4+x_4 y_i\right)-\left(y_1 x_2+y_2 x_3+y_3 x_4+y_4 x_1\right)\right\} \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{(1+6+6+12)-(-8+2-9+3)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{25-(-12)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(25+12) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{37}{2} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =18.5 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Class 9 Wbbse Maths Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangle Solved Problems
Question 7. The coordinates of three points A, B, and C are (3, 4) (-4, 3), and (8, -6) respectively. Let us find the area of the triangle and the perpendicular length drawn from point A on BC.
Solution:
Given
The coordinates of three points A, B, and C are (3, 4) (-4, 3), and (8, -6) respectively.
Area of the triangle ABC
\(=\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\} \text { sq. unit }\) \(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\{3(3+6)-4(-6-4)+8(4-3)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(27+40+8) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{75}{2} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =37.5 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Length of BC = \(\sqrt{(-4-8)^2+(3+6)^2} \text { unit }\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\sqrt{(-12)^2+(9)^2} \text { unit } \\
& =\sqrt{144+81} \text { unit } \\
& =\sqrt{225} \text { unit } \\
& =15 \text { unit }
\end{aligned}\)
∵ Area of ΔABC \(\frac{1}{2}\) x base x height
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x BC x height
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x 15x height
= \(\frac{75}{2}\)
Height of the triangle = \(\frac{75 \times 2}{2 \times 15}\) = 5 unit
Wbbse Class 9 Maths Chapter 20 Area Of Triangular Region Notes
Question 8. In triangle ABC, the coordinates of A are (2, 5) and the centroid of a triangle is (-2,1), let us find the coordinates of the mid-point of BC.
Solution:
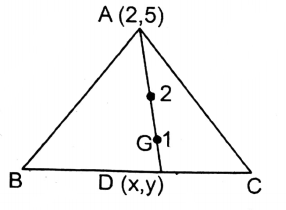
Given
In triangle ABC, the coordinates of A are (2, 5) and the centroid of a triangle is (-2,1),
In ABC the coordinates of vertex A are (2, 5).
Co-ordinates of the centroid of AABC = G (-2, 1) & the co-ordinate of A = (2,5).
∵ We know the centroid intersects the median at G in the ratio 2: 1.
\(therefore \frac{2 \times x+1 \times 2}{2+1}=-2\)or, \(\frac{2 x+2}{3}=-2\)
or, 2x+2 = -6
or, 2x = -6-2
or, 2x = -8
or, \(x=\frac{-8}{2}=-4\)
and \(\frac{2 \times y+1 \times 5}{2+1}=1\)
or, 2y+5=3
or, 2y=3-5
or, 2y=-2
or, \(y=\frac{-2}{2}=-1\)
∴ The coordinate of the mid-point of BC= (-4, -1).
West Bengal Board Class 9 Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangle Chapter Solutions
Question 9. The coordinates of vertices of a triangle are (4, -3), (-5, 2), and (x, y); let us find the values of x and y if the centroid of a triangle is at the origin.
Solution:
Given
The coordinates of vertices of a triangle are (4, -3), (-5, 2), and (x, y);
We know the coordinates of the centroid
\(\begin{aligned}& =\left(\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}, \frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3}\right) \\
& =\left(\frac{4-5+x}{3}, \frac{-3+2+y}{3}\right) \\
& =\left(\frac{-1+x}{3}, \frac{-1+y}{3}\right)
\end{aligned}\)
∵ The centroid of the triangle is the origin.
∴ The coordinate of the centroid is (0,0).
∴ \(\frac{-1+x}{3}=0\)
or, -1+x=0
or, x = 1
and \(\frac{-1+y}{3}=0\)
or, – 1+ y = 0
or, y = 1
∴ x=1,y=1
Wbbse Class 9 Area Of Triangular Region Important Questions
Question 10. The vertices at AABC are A(-1,5), B(3,1) and C(5,7). D, E, and F are the midpoints of BC, CA, and AB respectively. Let us find the area of the triangular region ΔDEF and prove that ΔABC=4ΔDEF.
Solution:
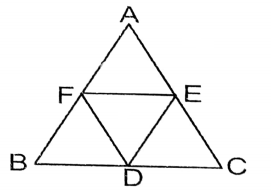
Given
The vertices at AABC are A(-1,5), B(3,1) and C(5,7). D, E, and F are the midpoints of BC, CA, and AB respectively.
As D, E & F are the mid-points of BC, CA & AB respectively.
∴ Co-ordinates of D = \(\left(\frac{3+5}{2}, \frac{1+7}{2}\right)=(4,4)\)
Co-ordinates of E = \(=\left(\frac{5-1}{2}, \frac{7+5}{2}\right)=(2,6)\)
Co-ordinates of F = \(\left(\frac{-1+3}{2}, \frac{5+1}{2}\right)=(1,3)\)
Area of ΔABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\left\{x_1\left(y_2-y_3\right)+x_2\left(y_3-y_1\right)+x_3\left(y_1-y_2\right)\right\}\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\{(-1)(1-7)+3(7-5)+5(5-1)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\{(-1) \times(-6)+3 \times 2+5 \times 4\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& ==\frac{1}{2}(6+6+20) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 32 \text { sq. unit } \\
& =16 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔDEF = \(\frac{1}{2}\{4(6-3)+2(3-4)+1(4-6)\} \text { sq. unit }\)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\frac{1}{2}\{4 \times 3+2(-1)+1(-2)\} \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2}(12-2-2) \text { sq. unit } \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \times 8 \text { sq. unit } \\
& =4 \text { sq. unit }
\end{aligned}\)
Area of ΔABC = 16 sq. unit
Area of 4ΔDEF = 4 x 4 sq. unit
= 16 sq. unit
∴ ΔABC = 4ΔDEF
Wbbse Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangle Chapter 20
Question 11. Multiple choice question
1. The area of the triangular region formed by the three points (0, 4), (0, 0) and (-6, 0) is
1. 24 sq. unit
2. 12 sq. unit
3. 6 sq. unit
4. 8 sq. unit
Solution: (0.4), (0,0), and (-6, 0)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) {(0(0-0)+0(0-4)+(-6)(-4-0)} sq. unit
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (0+0+24) sq. unit
= 12 sq. unit
∴ 2. 12 sq. unit
2. The coordinates of the centroid of a triangle formed by the three points (7,-5), (-2, 5), and (4, 6) are
1. (3,-2)
2. (2, 3)
3. (3, 2)
4. (2,-3)
Solution: (7,-5), (-2, 5), and (4, 6)
\(\begin{aligned}& =\left(\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}, \frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3}\right) \\
& =\left(\frac{7-2+4}{3}, \frac{-5+5+6}{3}\right)
\end{aligned}\)
= (3,2)
∴ 3. (3,2)
3. If ABC is a right-angled triangle whose ZABC 90°, co-ordinates of A and C are (0,4) and (3,0) respectively, then the area of triangle ABC is
1. 12 sq. unit
2. 6 sq. unit
3. 24 sq. unit
4. 8 sq. unit
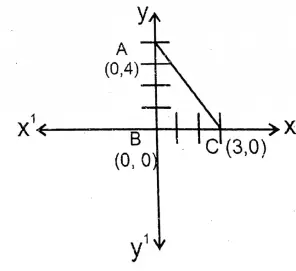
Solution: In ABC ∠ABC = 90°
Co-ordinates of A = (0, 4)
Co-ordinates of B = (3,0)
Co-ordinates of C = (0, 0)
∴ \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) = 4 unit
and \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\) = 3 unit
∴ Area of ΔABC = \(\frac{1}{2} \times \overline{\mathrm{BC}} \times \overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) Χ 3 Χ 4 sq.unit = 6 sq.unit
Wbbse 9th Class Maths Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangle Step By Step Solutions
4. If (0, 0), (4,-3), and (x, y) are collinear then
1. x = 8, y = -6
2. x = 8, y = 6
3. x = 4, y = -6
4. x = -8, y = -6
Solution: The area of the triangle formed by (0, 0), (4, -3), and (x, y) is zero.
∴ 0(-3- y) + 4 (y-0) + x (0 + 3) = 0
or, 3x + 4y = 0 ….(1)
Now, of the options given, putting in equation (i) only x = 8 and y = 6 satisfies the equation.
Because 3 x 8+4(-6)=24-24=0
∴ 1. x = 8, y = -6
5. If in triangle ABC, the co-ordinates of vertex A are (7, -4) and the centroid of the triangle (1,2), the the co-ordinates of mid-point of BC are
1. (-2,-5)
2. (-2,5)
3. (2,-5)
4. (5,-2)
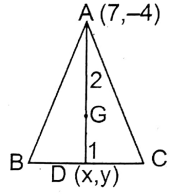
Solution: D is the midpoint BC, let the coordinate of D be (x, y).
∴ G (1, 2) cuts median AD in the ratio 2:1
∴ \(\frac{2 \times x+1 \times 7}{2+1}=1\)
or, 2x+7=3
or, 2x = -4
or, 2x = -2
and \(\frac{2 \times y+1(-4)}{2+1}=2\)
or, 2y-4=6
or, 2y = 6+4
or, 2y= 10.
or, y = 5
∴ Co-ordinates of the midpoint of BC = (-2,5)
∴ 2. (-2, 5)
Question 12. Short answer type questions:
1. The coordinates of midpoints of the sides of a triangle ABC are (0,1), (1,1), and (1,0); let us find the coordinates of its centroid.
Solution:
Given
The coordinates of midpoints of the sides of a triangle ABC are (0,1), (1,1), and (1,0);
Let the co-ordinates of A= (x1,y1)
Co-ordinates of B = (x2,y2)
Co-ordinates of C = (x3,y3)
∴ The mid-point of AB = \(\left(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\right)\)
∴ \(\frac{x_1+x_2}{2}=0\) or, x1+ x2 = 0
and \(\frac{y_1+y_2}{2}\) or, y1 + y2 =0
The mid-point of BC = \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}_2+\mathrm{x}_3}{2}, \frac{\mathrm{y}_2+\mathrm{y}_3}{2}\right)\)
∴ \(\frac{x_2+x_3}{2}=1\) or, x2+x3=2
and \(\frac{y_2+y_3}{2}=1\) or, y2+y1 = 2
Again, the mid-point of CA = \(\left(\frac{x_3+\dot{x}_1}{2}, \frac{y_3+y_1}{2}\right)\)
∴ \(\frac{x_3+x_1}{2}=1\) or, x3 +x1 = 2
and \(\frac{y_3+y_1}{2}=0\) or, y3+ y1 =0
Adding (1), (3), and (5),
x1 + x2 + x2 + x3 + x3 + x1 = 0 + 2 + 2
or, 2x1 + 2x2 +2x3 = 4
or, 2(x1 + x2+x3)= 4
or, x1 + x2+x3 \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2
Again, adding (2), (4), and (6),
\(2 y_1+2 y_2+2 y_3=4\)
or, \(2\left(x_1+x_2+x_3\right)=4\)
or, \(y_1+y_2+y_3=\frac{4}{2}\)
or, \(y_1+y_2+y_3=2\)
Co-ordinates of the centroid of ΔABC =
\(=\left(\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}, \frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3}\right)=\left(\frac{2}{3}, \frac{2}{3}\right)\)∵ \(\left[x_1+x_2+x_3=2 \text { and } y_1+y_2+y_3=2\right]\)
Wbbse Class 9 Maths Area Of Triangle Using Coordinate Geometry Formula And Examples
3. The coordinates of the centroid of a triangle are (6,9) and the two vertices are (15,0) and (0, 10); let us find the coordinates of the third vertex.
Solution:
Given
The coordinates of the centroid of a triangle are (6,9) and the two vertices are (15,0) and (0, 10);
Let the coordinates of the 3rd vertex of the triangle be (x, y).
Co-ordinates of the centroid
\(\begin{aligned}& =\left(\frac{15+0+x}{3}, \frac{0+10+y}{3}\right) \\
& =\left(\frac{15+x}{3}, \frac{10+y}{3}\right)
\end{aligned}\)
By the problem,
\(\frac{15+x}{3}=6 \text { and } \frac{10+y}{3}=9\)
or, 15+ x = 18
or, x = 18-15
or, x = 3
or, 10+ y = 27
or, y = 27-10
or, y = 17
∴ The co-ordinate of the third vertex of the triangle is (3, 17)
3. If the three points (a, 0), (0, b), and (1, 1) are collinear then let us show that \(\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}\) = 1
Solution:
Given
If the three points (a, 0), (0, b), and (1, 1) are collinear
Area of the triangle formed by (a, 0), (0, b), and (1, 1) = 0
∴ \(\frac{1}{2}{a(b-1)+0(1-0)+1(0-b)}\)= 0
or, ab-a-b=0
or, – a – b = – ab
or, a + b = – ab
or, \frac{1}{b}+\frac{1}{a}=1\) \(\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}=1\)
Class 9 Wbbse Coordinate Geometry Area Of Triangular Region Chapter 20 Solved Exercises
4. Let us calculate the area of the triangular region formed by the three points (1, 4), (1, 2), and (-4, 1).
Solution: The area of the triangle formed by three points (1, 4), (-1, 2), and (-4, 1)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) {1(2 − 1) + (− 1)(1 − 4) + (−4) (4 – 2)} sq. unit ((2-1)+(-1)(1-4)+(-4)(4-2)}
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (1+3-8) sq. unit
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (-4) sq. unit
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) Χ 4 sq. unit = 2 sq. unit
5. Let us write the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle formed by the three points (x-y. y-z), (-x, -y), and (y, z).
Solution: Co-ordinates of the centroid of the triangle formed by (x-y, y-z), (-x, -y), and (y, z)3
& =\left(\frac{x-y-x+y}{3}, \frac{y-z-y+z}{3}\right) \\
& =\left(\frac{0}{3}, \frac{0}{3}\right) \\
& =(0,0) .
\end{aligned}\)
