Gametogenesis or Gametogenesis MCQs
Question 1. The first phase in the sexual reproduction of organism is
- Spermatogenesis
- Ovulation
- Oogenesis
- Gametogenesis
Answer: 4. Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is the first phase in sexual reproduction of organisms.
Question 2. The process of formation of gametes from primordial germ cells of gonad is called
- Gametogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
- Spermatocytogenesis
- Oogenesis
Answer: 1. Gametogenesis
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Gametogenesis is the process of formation of male and female sex cells from primordial germ cells of gonad. It occurs by the division of diploid gametocytes into various gametes.
Question 3. Germ cells in mammalian gonads are produced by
- Only mitosis
- Only meiosis
- Both mitosis and meiosis
- Without cell division
Answer: 3. Both mitosis and meiosis
Gametogenesis involves both mitosis and meiosis, so as to produce the germ cells in mammalian gonads.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 4. Which is not associated with gametogenesis?
- Formation of ova
- Formation of spermatid
- Release of ova
- Change of spermatids to spermatozoa
Answer: 3. Release of ova
Gametogenesis is the process of formation of gametes in sexually reproducing organisms. Release of ova is not associated with it.
NEET Biology Gametogenesis MCQs with Answers
Question 5. In spermatogenesis, a primary spermatocyte produces four similar sperms while in oogenesis, a primary oocyte forms
- Four similar ova
- Three large ova and one polar body
- Two large ova and two polar bodles
- One large ovum and two polar bodies
Answer: 4. One large ovum and two polar bodies
Four haploid sperms are produced in the process of spermatogenesis whereas in oogenesis, primary oocyte forms one large ovum and two polar bodies.
Gametogenesis Class 12

Gametogenesis NEET Biology Important Question
Question 6. How many ova and sperms would be produced from 100 secondary oocytes and 100 secondary spermatocytes during gametogenesis in humans?
- 100 ova, 100 sperms
- 100 ova, 200 sperms
- 50 ova, 100 sperms
- 200 ova, 200 sperms
Answer: 2. 100 ova, 200 sperms
One secondary oocyte produce one ovum and one secondary spermatocyte produces 2 sperms. Thus, 100 secondary oocytes would produce 100 ova and 100 secondary spermatocytes would produce 200 sperms.
Question 7. How many sperms and ova will be produced from 20 primary spermatocytes and 20 primary oocytes?
- 80 sperms and 80 ova
- 80 sperms and 40 ova
- 80 sperms and 20 ova
- 20 sperms and 20 ova
Answer: 3. 80 sperms and 20 ova
One primary spermatocyte gives rise to four sperms and one primary oocyte give rise to one ovum. Thus, 80 sperms would be produced from 20 primary spermatocytes and 20 ova would be formed from 20 primary oocytes.
Question 8. The process of maturation of reproductive cells of testes in male so as to form the male gamete or sperm is known as
- Spermatogenesis
- Gametogenesis
- Ogenesis
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of haploid spermatozoa from diploid germinal cells in seminiferous tubules.
Question 9. Spermatogenesis takes place in
- Epididymis
- Seminiferous tubules
- Vasa deferentia
- Penis
Answer: 2. Seminiferous tubules
Spermatogenesis takes place inside the seminiferous tubules that are present within the testes.
Question 10. Find the odd one out.
- Spermatocyte
- Polar body
- Spermatid
- Spermatogonium
Answer: 2. Polar body
Polar body is formed during oogenesis whereas other three structures are formed during spermatogenesis.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 11. How many days do it take for spermatogenesis to take place?
- 40 to 65 days
- 60 to 75 days
- 70 to 95 days
- 50 to 65 days
Answer: 2. 60 to 75 days
The whole process of spermatogenesis takes about 60- 75 days. In humans, spermatocyte maturation takes 23.5 days, spermiogenesis takes 21.6 days and the total estimated time for spermatogenesis is approximately 74 days
Gametogenesis Class 12
Question 12. Consider the following statements.
- Primary and secondary spermatocytes contain diploid number of chromosomes.
- Spermatids contain haploid set of chromosomes.
Choose the corect option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct. Incorrect statement can be corrected as Primary spermatocytes have diploid set of chromosomes. Secondary spermatocytes and spermatids have haploid set of chromosomes.
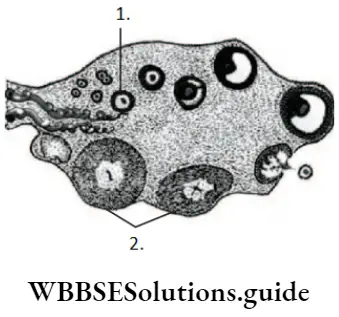
Question 13. Spermatogenesis is promoted by
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
- Oxytocin
Answer: 3. Testosterone
The process of formation of spermatozoa from spermatogenic cells is called spermatogenesis. Testosterone promotes the process of spermatogenesis.
NEET Biology Gametogenesis Practice Questions
Question 14. From the labels given in the diagram below, identify ‘Spermatid and Sertoli cell, Spermatogonium and Spermatozoa’, respectively.

- D and E, A and C
- E and F, A and B
- A and C, B and E
- B and E, F and A
Answer: 4. B and E, F and A
Spermatid –B Sertoli cell–E Spermatogonium–F Spermatozoa–A
Gametogenesis Class 12
Question 15. Given below diagram refers to the TS of testis showing few seminiferous tubules.

A, B, C, and D in the above figure represent.
- A–Sertoli cells, B–Secondary spermatocyte, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
- A–Interstitial cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Sertoli cells, D–Sperms
- A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatozoa, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
- A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
Answer: 4. A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
Question 16. Germinal cell in the testes is known as
- Primordial cells
- Primary spermatocytes
- Spermatogonium
- Spermatozoan
Answer: 1. Primordial cells
The primordial cell is called as germinal cells in the testis. These are cuboidal cells that give rise to sperms.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 17. Which cells are formed earliest in the sequence of sperm production?
- Spermatozoa
- Spermatocyte
- Spermatid
- Spermatogonia
Answer: 4. Spermatogonia
In the sequence of spermatogenesis, spermatogonia is formed earliest. Spermatogonia → Primary spermatocytes → Secondary spermatocytes → Spermatocytes → Spermatozoa.
Question 18. In spermatogenesis, the phase of maturation involves
- The growth of spermatogonia into primary spermatocyte
- The formation of spermatogonia from gonocytes through mitosis
- The formation of spermatids from primary spermatocytes through meiosis
- The formation of oogonia from the spermatocytes through meiosis
Answer: 3. The formation of oogonia from the spermatocytes through meiosis
In the maturation phase of spermatogenesis, spermatids are formed from primary spermatocytes through meiosis.
Question 19. Spermatogonia are formed after which cell division?
- Meiosis-I
- Meiosis-2
- Mitosis
- Amitosis
Answer: 3. Amitosis
Spermatogonia are formed after mitotic (or mitosis) cell division of undifferentiated primordial germ cell.
Mcqs On Gametogenesis
Question 20. Spermatogonia undergo a growth phase to become
- Primary spermatocyte
- Secondary spermatocyte
- Spermatid
- Spermatozoa
Answer: 1. Primary spermatocyte
Formation of primary spermatocyte is called spermatocytogenesis. It occurs during growth phase, involving the growth of spermatogonia.
Question 21. Primary spermatocytes differ from spermatogonium in
- Number of chromosomes
- Size and volume
- DNA content
- Size of chromosome
Answer: 2. Size and volume
During spermatogenesis, one of the spermatogonium enlarges in size and volume and is called primary spermatocytes. Both spermatogonium and primary spermatocyte are diploid (2n). Thus, primary spermatocytes possess more volume and size as compared to spermatogonium.
Question 22. During spermatogenesis, the first meiotic division is observed in
- Sertoli cells
- Spermatids
- Spermatozoans
- Primary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes
Answer: 4. Primary spermatocytes
The first maturation division during spermatogenesis occur in primary spermatocytes. It is reductional or meiotic division. Hence, the primary spermatocyte divides into two haploid daughter cells called secondary spermatocytes.
Question 23. Sperms formed from 4 primary spermatocytes are
- 4
- 1
- 16
- 32
Answer: 3. 16
Spermatogenesis is the formation of sperms or spermatozoa from a germ cell. Four spermatozoa are produced from a primary spermatocyte, therefore, 16 spermatozoa will be formed from four primary spermatocytes.
Question 24. In spermatogenesis, reduction division of chromosome occurs during the conversion of
- Spermatogonia to primary spermatocytes
- Primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes to spermatids
- Spermatids to sperms
Answer: 2. Primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes
In spermatogenesis, reduction division or meiosis I occurs during the conversion of primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes.
Mcqs On Gametogenesis
Question 25. 2 16n = in a primary spermatocyte, which is in metaphase of first meiotic division. What shall be the total number of chromatids in each of the secondary spermatocyte?
- 16
- 24
- 32
- 8
Answer: 1. 16
The total number of chromatids in each of the secondary spermatocytes is 16 because it contains 8 chromosomes, having two chromatids each.
Question 26. Which of the following statements is wrong?
- Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the developing male germ cells
- Leydig cells synthesise and secrete androgens
- Secretions of the acrosome helps the sperm to enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum
- Secondary spermatocytes are diploid
- The fluid filled cavity in the tertiary follicle is called antrum
Answer: 4. Secondary spermatocytes are diploid
Statement in option is wrong because secondary spermatocytes are haploid (n). Rest all statements are correct.
Question 27. In humans, at the end of the first meiotic division, the male germ cells differentiate into the
- Spermatids
- Spermatogonia
- Primary spermatocytes
- Secondary spermatocytes
Answer: 4. Secondary spermatocytes
- During embryonic development, the primordial germ cells migrate to the testes, where they become spermatogonia.
- At puberty, the spermatogonia proliferate rapidly by mitosis. Some undergo growth phase to become primary spermatocytes that further undergo meiotic division-I to become secondary spermatocytes.
Question 28. How many sperms are formed from a secondary spermatocyte?
- 4
- 8
- 2
- 1
Answer: 3. 2
Each secondary spermatocyte gives rise to two spermatids that undergo transformation to form two sperms. Overall, both secondary spermatocytes give rise to four sperms.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 29. Each secondary spermatocyte after second meiotic division produces
- Four haploid spermatids
- Only one haploid spermatid
- Two haploid spermatids
- Two diploid spermatids
- Four diploid spermatids
Answer: 3. Two haploid spermatids
After second meiotic division, each secondary spermatocyte produces two haploid spermatids.
Mcqs On Gametogenesis
Question 30. Consider the following statement
- The immediate predecessors of spermatids are secondary spermatocytes.
- Spermatids are formed after the meiotic division.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement I is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement I is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements I and 2 are correct
- Both statements I and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements I and 2 are correct.
The spermatid is the haploid male gamete that is formed by the division of secondary spermatocyte. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocytes.
Question 31. Spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa by
- Spermiation
- Spermatogenesis
- Meiosis
- Spermatosis
- Spermiogenesis
Answer: 5. Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis is the final stage of spermatogenesis, which results in the maturation of spermatids into mature, motile spermatozoa.
Question 32. At which stage of spermatogenesis, sperms acquire their structural maturity and contain a haploid nucleus and other organelles?
- Spermiogenesis
- Maturation phase
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
Answer: 1. Spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis is the process of transforming spermatids into mature sperm having haploid nucleus and other organelles.
Mcqs On Gametogenesis
Question 33. Spermioteleosis is another name of
- Maturation of ovum
- Spermiogenesis
- Spermatogenesis
- Degeneration of sperms
Answer: 2. Spermiogenesis
Spermioteleosis is also known as spermiogenesis.
Question 34. What do you mean by the term spermioteleosis ?
- Conversion of spermatids to sperm
- Conversion of spermatogonium to spermatid
- Conversion of spermatid to spermatogonium
- Conversion of primary spermatocyte to secondary spermatocyte
Answer: 1. Conversion of spermatids to sperm
Question 35. The term, ‘spermatozoan’ was coined by
- Von Baer
- Leeuwenhoek
- Spemann
- Swammerdam
Answer: 1. Von Baer
The term spermatozoan was coined by von Baer.
Question 36. In the formation of spermatozoa, the spermatids attach to
- Leydig cells
- corona radiata cells
- Sertoli cells
- First polar body
Answer: 3. Sertoli cells
The spermatids attach to the Sertoli cell during spermatogenesis because Sertoli cell produce testicular fluid, including a protein that binds to and concentrates testosterone. It is essential for the development of the spermatozoa.
Question 37. Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) is secreted by
- Interstitial cells
- Leydig cells
- Sertoli cell
- None of these
Answer: 2. Leydig cells
FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells to secrete androgen-binding protein into the lumen of seminiferous tubules.
Gametogenesis NEET Previous Year Questions with Solutions
Question 38. The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is
- In spermiogenesis, spermatids are formed, while in spermiation, spermatozoa are formed
- In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation, spermatozoa are released from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules
- In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the Cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
- In spermiogenesis spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation, spermatids are formed
Answer: 3. In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the Cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
Spermiogenesis involves transformation of spermatids so as to form spermatozoa whereas spermiation is the release of the spermotozoa from Sertoli cells into the lumen of seminiferous tubule.
Question 39. What is the correct sequence of sperm formation?
- Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatozoa, spermatid
- Spermatogonia, spermatozoa, spermatocyte, spermatid
- Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoa
- Spermatid, spermatocyte, spermatogonia, spermatozoa
Answer: 3. Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoa
- In testis, the immature male germ cells or spermatogonia (2n) multiply by mitotic division and increase in number to form primary spermatocytes (2n).
- The latter divide meiotically to form secondary spermatocytes (n). The secondary spermatocytes undergo second meiotic division to produce spermatids (n) which gets transformed into spermatozoa (sperms) by the process called spermiogenesis.
Thus, option 3 represents correct sequence of sperm formation.
Gametogenesis Mcq With Answers
Question 40. The release of ………………… leads to initiation of spermatogenesis.
- GnRH
- lactin
- Testosterone
- oestrogen
Answer: 1. GnRH
The release of Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) from hypothalamus at puberty initiate spermatogenesis.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 41. GnRH stimulates two hormones ……… and ……… from anterior lobe of pituitary.
- FSH and GH
- FSH and LH
- LH and testosterone
- Testosterone and LH
Answer: 2. FSH and LH
GnRH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins, Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) from the anterior lobe of pituitary gland in males to commence gametogenesis.
Question 42. Synthesis of testosterone by Leydig cells is stimulated by
- LTH
- TSH
- FSH
- ICSH
Answer: 4. ICSH
ICSH is the Luteinizing hormone. In male, it stimulates the synthesis of testosterone by Leydig cell.
Question 43. Spermatogenesis is induced by
- FSH
- ICSH
- STH
- ATH
Answer: 1. FSH
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) is secreted by anterior pituitary and it stimulates spermatogenesis in males. It stimulates Sertoli cells for the conversion of spermatids to sperms (spermiogenesis).
Question 44. The hormone which acts on Sertoli cells and stimulates the process of spermiogenesis is
- GnRH
- Androgen
- FSH
- LH
Answer: 3. FSH
FSH stimulates Sertoli cells of the testes to secrete an Androgen-Binding Protein (ABP) that concentrates testosterone in the seminiferous tubules. It helps to stimulate the process of spermiogenesis.
Gametogenesis Mcq With Answers
Question 45. Consider the following statements.
- The receptors for FSH and testosterone are not found on germ cells, but on Sertoli cells.
- In males, LH is known as ICSH.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement I is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement I is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements I and 2 are correct
- Both statements I and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 46. A boy sustains injury to his anterior pituitary even before attaining puberty. FSH is no longer released, but LH secretion is normal. What changes will be observed once he grows into an adult?
- He will develop secondary sex characters
- He will be sterile
- He will have improper functioning of testicular interstitial cells
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 2. He will be sterile
Secondary sexual characters and functioning of testicular interstitial cells depends upon the LH and spermatogenesis depends upon FSH. Thus, after the injury to anterior pituitary the boy will be sterile due to complete absence of spermatogenesis.
Question 47. If spermatogenesis proceeds too rapidly, inhibin is released and reduces the secretion of
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Testosterone
- Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone (ICSH)
Answer: 2. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- FSH stimulates Sertoli cells of testes to secrete an Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) that concentrates testosterone in the seminiferous tubules.
- It also secretes a peptide hormone, inhibin which suppresses FSH synthesis and release by negative feedback effect.
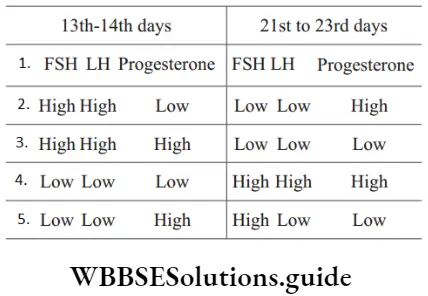
Question 48.

Identify A and B in the above figure.
- FSH and GH
- LH and androgen
- GH and LH
- GH and lactin
Answer: 2. LH and androgen
A–LH, B–androgens
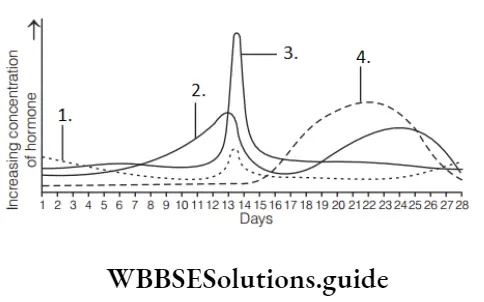
Question 49. Identify A, B, C and D hormones in the diagram below.
Gametogenesis Mcq With Answers
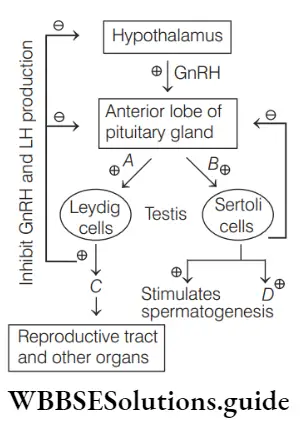
- A–Inhibin, B–FSH, C–Testosterone, D–LH
- A–Testosterone, B–Inhibin, C–LH, D–FSH
- A–FSH, B–LH, C–Inhibin,D–Testosterone
- A–LH, B–FSH, C–Testosterone, D–Inhibin
Answer: 4. A–LH, B–FSH, C–Testosterone D–Inhibin
Question 50. Assertion In testis, spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules and testosterone is secreted by Sertoli cells. Reason (R) Testosterone promotes growth and maturation of primary sex organs but has no role in accessory sex characters.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 4. Both A and R are false
Both A and R are false and can be corrected as
In testis, spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules and testosterone is secreted by interstitial cells. Testosterone promotes growth and maturation of secondary sex organs. It also promotes the development of secondary sex characters.
Question 51. Identify A, B and C in the diagram below.

- A–Acrosome, B–Tail, C–Mitochondria
- A–Plasma membrane, B–Acrosome, C–Mitochondria
- A–Mitochondria, B–Acrosome, C–Plasma membrane
- A–Mitochondria, B–Plasma membrane, C–Tail
Answer: 2. A–Plasma membrane, B–Acrosome, C–Mitochondria
Gametogenesis Mcq With Answers
Question 52. Sperm is also called
- Male gamete
- Paternal gamete
- Male gamete sex cells
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Sperms are also referred as male spermatozoa, or paternal gamete or simply male gamete.
Question 53. The cell organelle that is absent in human sperm is
- ER
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Centriole
Answer: 1. ER
In human sperms, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is absent.
Question 54. Which of the following contains the actual genetic part of a sperm ?
- Whole of it
- Tail
- Middle piece
- Head
Answer: 4. Head
Head is the main part of the sperm containing nucleus, DNA, etc. The head containing the haploid nuclei possess the genetic material.
Question 55. Sperm lysins are found in
- Neck region of sperm
- Tail region of sperm
- Head region of sperm
- Middle and tail regions of sperm
Answer: 3. Head region of sperm
Sperm lysins are found in the head region of sperm within the acrosome.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 56. Head of a mature sperm comprises of
- Elongated haploid nucleus covered by acrosomal material/cap
- Two centrioles and axial filament
- Acrosome without nucleus
- Mitochondrial sheath and cytoplasm
Answer: 1. Elongated haploid nucleus covered by acrosomal material/cap
The mature sperm consists of a head, middle piece and tail. The head is covered by the acrosome cap and contains a nucleus of dense genetic material comprising 23 chromosomes.
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Question 57. Acrosome of human sperm is rich in
- Hyaluronidase and acrosin
- Hyaluronic acid and acrosin
- Hippuric acid and uric acid
- Creatinine
Answer: 1. Hyaluronidase and acrosin
The acrosome of human sperm is rich in sperm lysins called hyaluronidase and acrosin.
Question 58. Acrosome of sperm is formed from
- Nucleus of spermatid
- Mitochondria of spermatid
- Golgi complex of spermatid
- Centrosome of spermatid
Answer: 3. Golgi complex of spermatid
The acrosome is a cap-like specialised structure that is derived from the Golgi complex during the maturation of the sperm.
Objective Questions on Gametogenesis for NEET
Question 59. Which one of the following statements about human sperm is correct?
- Acrosome has a conical pointed structure used for piercing and penetrating the egg, resulting in fertilisation
- The sperm lysins in the acrosome dissolve the egg envelope facilitating fertilisation
- Acrosome serves as a sensory structure leading the sperm towards the ovum
- Acrosome serves no particular function
Answer: 2. The sperm lysins in the acrosome dissolve the egg envelope facilitating fertilisation
Option is correct. Acrosome a small pointed structure at the tip of nucleus. It breaks down just Option is correct. Acrosome a small pointed structure at the tip of nucleus. It breaks down just
Question 60. Which of the following is true regarding sperm?
- Fertilizin–for penetrating egg membrane
- Hyalurodinase–for penetrating egg membrane
- Acrosin–dissolves corona radiata
- Capacitation–takes place in penis
Answer: 2. Hyalurodinase–for penetrating egg membrane
- Option is true regarding sperm as Hyaluronidase is a hydrolytic enzyme present in the acrosome of sperm. It lyses the glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular matrix, holding the cell of the corona radiata together.
- Thus, it helps the sperm to penetrate the egg membrane. Other options represent incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as Fertilizin is the receptor on ovum that is involved in species-specific fertilisation. Acrosin helps in penetrating zona pellucida and capacitation occurs in female reproductive tract.
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Question 61. Acrosome is a type of
- Lysosome
- Flagellum
- Ribosome
- Basal body
Answer: 1. Lysosome
Acrosome is a lysosome-like organelle that is derived from the Golgi apparatus. The acrosome contains digestive enzymes (including hyaluronidase and acrosin) needed to penetrate the ovum.
Question 62. Select the incorrect statement.
- Nucleus of sperm contain nucleolus and chromatin
- Perforatorium is the narrow space between nucleus and acrosome within sperm’s head
- The centrioles of sperm are present at right angles to each other
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Nucleus of sperm contain nucleolus and chromatin
Statement in option is incorrect because the nucleus of sperm do not contain nucleoplasm and nucleolus. It is very small and contains only chromatin. Rest all statements are correct.
Question 63. Sperm releases lysozyme as it
- Aids in fertilisation
- Dissolves oocyte membrane
- Increases sperms motility
- Delays fertilisation
Answer: 1. Aids in fertilisation
The sperm releases lysozyme, which helps to dissolved egg membrane and thus, aids in fertilisation.
Question 64. A cross section at the midpoint of the middle piece of a human sperm will show
- Centriole, mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules
- Centriole and mitochondria
- Mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules
- 9 2+ arrangement of microtubules only
Answer: 3. Mitochondria and 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules
- The cross section of the sperm middle piece shows the axial bundle of microtubules or axoneme surrounded by a microtubular sheath in which the mitochondria of the spermatid have been arranged in a helical manner.
- The microtubular structure enables the sperm to swim through the reproductive tract of the female. The microtubules are present in 9 + 2 arrangement.
Question 65. Neck of sperm contains
- Mitochondria
- Centriole
- lysosomes
- Nucleus
Answer: 2. Centriole
Neck of sperm contains two centrioles namely, proximal centriole and distal centriole.
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Question 66. Nebenkern represents
- Mitochondrial spiral of sperm
- Acrosome of sperm
- Centriole of sperm
- Tail of sperm
Answer: 1. Mitochondrial spiral of sperm
Neberkern represents the mitochondrial spiral in the middle piece of sperm.
Question 67. The ……………… gives rise to the axial filament of the sperm.
- Distal centriole
- Acrosome
- Proximal centriole
- Fibrillar sheath
Answer: 1. Distal centriole
The distal centriole gives rise to the axial filaments of the sperm. It is located away from the head of sperm, attached to the base of axoneme.
Question 68. The 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules is found in ………….. of sperm.
- Head only
- Head and neck
- Tail
- Middle piece
Answer: 3. Tail
Among given options, the tail part of the sperm possesses 9+2 arrangement of microtubules as it is a flagellar structure.
Question 69. Except the end piece, the entire sperm is covered by
- Cytoplasmic membrane
- Tunica vaginalis
- Peritoneum
- Tunica albuginea
Answer: 1. Cytoplasmic membrane
Almost all parts of the sperm is covered by cytoplasmic membrane except the end piece.
Question 70. Which is the longest part of sperm?
- Head
- Neck
- Middle part
- Tail
Answer: 4. Tail
The tail portion is the longest part of sperm. It is a slender, hair-like bundle of filaments that connects to the head and middle piece.
Question 71. The tail of sperm consists of …………regions.
- Two
- Three
- Four
- Single
Answer: 1. Two
The tail of sperm consists of two parts Main part – cytoplasm surrounded by two fibres. End piece – axonema is present.
Question 72. Optimum temperature for sperm production is
- 25-30°C
- 40-50°C
- 35 -40°C
- 30-35°C
Answer: 4. 30-35°C
Optimum temperature for sperm production in humans is 30-35°C. It is about 2°C lower than the normal body temperature.
Question 73. Consider the following statements.
- Clupein protein is not found in human sperm.
- Clupein protein is highly basic arginine rich protein.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement I is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement I is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements I and 2 are correct
- Both statements I and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement I is incorrect, but 2 is correct.
Incorrect statement can be corrected as Clupein is a type of protein found in the human sperm.
Question 74. The fluid containing secretion of seminal vesicles, prostate gland and sperms from the testis is known as
- Serum
- Semen
- lymph
- Coelomic fluid
Answer: 2. Semen
Seminal plasma is the combined secretion of three glands named, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, Cowper’s gland. Together with sperm, they collectively form semen.
Question 75. Human male ejaculates …A… to …B…million sperm. At least …C… should have normal shape and size and …D… should show vigorous motility.
Here A, B, C, and D refer to
- A–100, B–200, C–30%, D–40%
- A–200, B–300, C–60%, D–40%
- A–300, B–400, C–60%, D–40%
- A–400, B–500, C–60%, D–40%
Answer: 2. A–200, B–300, C–60%, D–40%
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Question 76. Seminal plasma in humans is rich in
- Fructose and calcium, but has no enzymes
- Glucose and certain enzymes, but has no calcium
- Fructose and certain enzymes, but poor in calcium
- Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
Answer: 4. Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes
- Seminal plasma in humans is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes. Fructose is the source of energy for the sperm.
- Enzymes nourish and activate the spermatozoa to swim. Calcium apparently have role in sperm motility.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 77. The volume of the semen released per ejaculation is ………… in man.
- 2-5 mL
- 5-8 mL
- 1-2 mL
- 6-10 mL
Answer: 1. 2-5 mL
The average volume of semen released during ejaculation is 2 to 5 mL. Volumes consistently less than 1.5 mL (hypospermia) or more than 5.5 mL (hyperspermia) are probably abnormal. Lower volumes may occur after very frequent ejaculation and higher volumes might be ejaculated after prolonged abstinence.
Question 78. Ejaculation is a …A…response. Erection is a …B…response. Identify, A and B refer to
- A–parasympathetic, B–sympathetic
- A–parasympathetic, B–parasympathetic
- A–sympathetic, B–parasympathetic
- A–sympathetic, B–sympathetic
Answer: 3. A–Sympathetic, B–Parasympathetic.
Question 79. ……% of sperms is present in the semen.
- 30
- 50
- 60
- 10
Answer: 4. 10
The semen contains 10% of sperms of its total volume.
Question 80. Azoospermia means
- More than one ovum produced
- Unable to bear an offspring
- Cessation of menstruation
- Absence of sperm in semen
Answer: 4. Absence of sperm in semen
Azoospermia is the medical condition in which semen does not contain sperm.
Question 81. A person is said to be suffering from infertility when the sperm cells display
- A count more than 120 million/mL semen
- Increased acrosomal activity
- Normal morphology
- Count of less than 200 million/mL semen
Answer: 4. Count of less than 200 million/mL semen
The count of less than 200 million /mL semen signifies infertility.
Question 82. Manchette is
- Condensed nucleus in male cell
- Condensed nucleolus in male cell
- Condensed nucleoplasm in sperm
- Condensed centromere in sperm
Answer: 3. Condensed nucleoplasm in sperm
The manchette is a transient skirt-like structure surrounding the elongating spermatid head and is only present during spermatid elongation. Manchette is condensed nucleoplasm in sperm.
Question 83. Consider the following statements.
- The process of ova formation is called oogenesis.
- Oogenesis begins at the onset of puberty in ovaries.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect and can be corrected as Oogenesis is the process by which ova is formed inside the mammalian ovary. It is initiated in the embryonic stage.
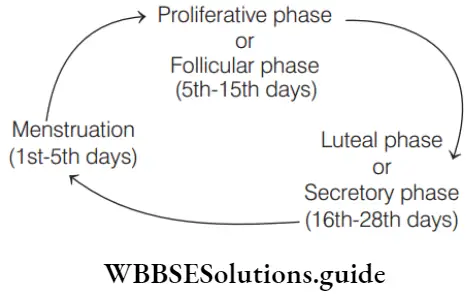
Question 84. Oogenesis comprises
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
- Maturation phase
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Oogenesis is the process of formation, development and maturation of haploid ova from diploid germinal cells of ovary. Oogenesis comprises of three phases
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
- Maturation phase
Question 85. During oogenesis, how many ova are formed at the end of two maturation divisions from a single primary oocyte?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: 1. One
During oogenesis, only one ovum is formed from a single primary oocyte and rest polar bodies are formed.
Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis MCQs for NEET
Question 86. In humans, what is the ratio of number of gametes produced from one male primary sex cell to the number of gametes produced from one female primary sex cell?
- 1: 4
- 1: 1
- 4: 1
- 1: 3
Answer: 3. 4: 1
- From a diploid primary spermatocyte, four haploid spermatozoa are produced through meiosis.
- While, from a diploid primary oocyte, only one haploid ovum is formed, rest are polar bodies. Hence, the ratio between male gametes and female gametes produced from respective primary sex cells is 4: 1.
Question 87. One oogonium forms
- 1 ovum + 3 polar bodies
- 1 ovum + 1 polar body
- 1 ovum without centrioles + 3 polar bodies
- single ovum and no polar body
Answer: 3. 1 ovum without centrioles + 3 polar bodies
One oogonium forms one ovum without centriole and three polar bodies.
Question 88. In human females, at the time of birth, there are two million ova. How many of them normally reach maturity in the course of normal reproductive life?
- 500
- 1,000
- 2,000
- 5,000
Answer: 1. 500
At birth, there are approximately 2 million eggs and by the time of puberty, only about 300,000 remain in ovary. Of these, only 400 to 500 reach maturity and ovulate during a women’s reproductive life time.
Question 89. Female gamete mother cells are also known as
- Oogonia
- Ovum
- Ootid
- Oocyte
Answer: 1. Oogonia
Female gamete mother cells are called oogonia.
Question 90. A human female has the maximum number of primary oocytes in her ovaries
- At birth
- Just prior to puberty
- Early in her fertile years
- Midway through her fertile years
Answer: 1. At birth
No more oogonia are formed and added in ovary after birth. A larger number of these follicles degenerate during the phase from birth to puberty. Therefore, maximum number of primary oocytes are found at the time of birth.
Question 91. Primordial follicles within the female ovary start to develop
- At puberty
- Around age 5
- At birth
- During prenatal development
Answer: 4. During prenatal development
Primordial follicles start developing at the foetal or prenatal stage and after birth, this development stops.
Question 92. In which phase of oogenesis, the oogonium develops into primary oocyte under the influence of FSH?
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
- Maturation phase
- Cleavage
Answer: 2. Growth phase
In growth phase of oogenesis, the oogonia develop into primary oocyte under the influence of follicle– stimulating hormone.
Question 93. Tremendous increase in volume of cytoplasm and organelles in primary oocyte takes place during
- Previtellogenesis
- Vitellogenesis
- Ovulation
- Cleavage
Answer: 1. Previtellogenesis
Previtallogenesis is characterised by an intensive synthesis of rRNA and by change in the cytoplasm morphology. There is an increase in the quantity of endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and Golgi complex.
Question 94. At the time of birth, the oocyte is present in …… stage of cell cycle.
- Prophase- 1
- Prophase-2
- Meiosis-2
- Mitosis
Answer: 1. Prophase- 1
Oogenesis starts in the foetal stage. Till the time of birth, they remain in prophase-I stage. Oogenesis resumes at the time of puberty when GnRH is produced by hypothalamus.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 95. The cortex of human ovary contains thousands of immature ova within small spheres that are composed of a single layer of cells. These are
- Mature follicles
- Primary follicles
- Secondary follicles
- Corpus luteum
Answer: 2. Primary follicles
A primary follicle is an immature ovarian follicle. It is surrounded by single layer of cuboidal granulosa cells.
Question 96. Meiosis during ovum formation occurs in
- Primordial germ cell
- Primary oocyte
- Oogonium
- Secondary oocyte
Answer: 2. Primary oocyte
Meiosis during ovum formation occurs in primary oocyte. It result in the formation of secondary oocyte and first polar body.
Mcq On Gametogenesis
Question 97. In humans, the oocyte is maintained in a state of meiotic arrest by the secretions of
- Granulosa cells
- Zona pellucida
- Cumulus oophorus
- Theca
Answer: 1. Granulosa cells
The follicular cells are surrounded by granulosa cells, which secrete oestrogens and Meiosis Inhibiting Factor (MIF) that leads to meiotic arrest.
Question 98. At which stage of the cell cycle does the development of secondary oocyte get arrested before pregnancy?
- Anaphase-1
- Prophase-2
- Metaphase-2
- Telophase-1
Answer: 3. Metaphase-2
Before pregnancy, the secondary ooctye gets arrested at the metaphase-2 stage of cell cycle.
Question 99. Primary oocyte surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells is called
- Secondary follicle
- Ootid
- Primary follicle
- Tertiary follicle
Answer: 3. Primary follicle
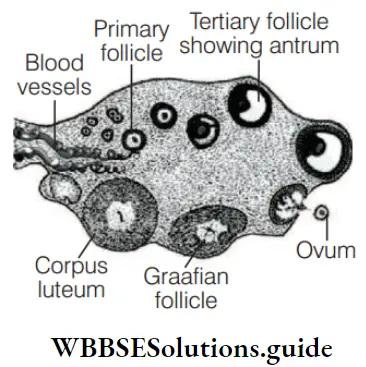
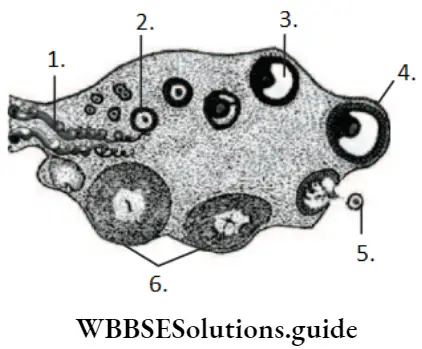
Primary oocyte surrounded by a layer of granulosa cell is called primary follicle, which are 2n in number.
Question 100. Vitellogenesis occurs during the formation of
- Ootid in the Fallopian tube
- Secondary oocyte in the Fallopian tube
- Primary oocyte in the Graafian follicle
- Oogonial cell in the Graafian follicle
Answer: 3. Primary oocyte in the Graafian follicle
In ovary, vitellogenesis occurs during the formation of primary oocyte in the Graafian follicle.
Question 101. Oocyte is liberated from ovary under the influence of LH after completing
- Mitosis and before liberating polar bodies
- Meiosis-1 and before liberating polar bodies
- Both mitosis and meiosis
- Meiosis-1 and after releasing polar body
Answer: 4. Meiosis-1 and after releasing polar body
Oocyte is released from the ovary in the secondary oocyte stage under the influence of LH, during ovulation. This stage is the result of
first meiotic division of primary oocyte into a large secondary oocyte and a small first polar body.
spermatogenesis takes place in
The secondary oocyte starts undergoing the second meiotic division which does not proceed beyond metaphase until a sperm enters it.
Question 102. Select the incorrect statement.
- Oogenesis is started inside ovary and is completed in oviduct
- Ovum is much larger than oogonium
- Oogonia form egg nest at the tips of egg tubes of pfluger during maturation phase
- Oogenesis is a discontinuous process
Answer: 3. Oogonia form egg nest at the tips of egg tubes of pfluger during maturation phase
Statement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as Oogonia form rounded masses or egg nest at the tip of egg tubes of pfluger during the growth phase of oogenesis. Rest all options are correct.
Question 103. Stroma is a term applied to
- Gall stone
- Ovarian follicles
- Connective tissue in which Graafian follicles are embedded
- Connective tissue surrounding the seminiferous tubules
Answer: 3. Connective tissue in which Graafian follicles are embedded
- The stroma of the ovary is a type of connective tissue, abundantly supplied with blood vessels in which Graafian follicular cells are embedded.
- The stroma also contains ordinary connective tissue such as reticular fibers and collagen.
Question 104. The tertiary follicle changes into
- Graafian follicle
- Oocyte
- Megaspore mother cell
- Ovum
Answer: 1. Graafian follicle
A tertiary follicle changes into the mature Graafian follicle. The secondary oocyte forms a new membrane called zona pellucida surrounding it.
Question 105. Transformation of a young follicle into Graafian follicle is controlled by
- Progesterone
- lactogenic hormone
- Follicular stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
Answer: 3. Follicular stimulating hormone
spermatogenesis takes place in
Follicle stimulating hormone stimulates the development of young follicle into the mature Graafian follicle.
Question 106. Cumulus oophorus is
- Mass of sperm embedded in Sertoli cells
- Heap of eggs
- Mass of epithelial cells in Graafian follicles
- Heap of maturing follicles
Answer: 3. Mass of epithelial cells in Graafian follicles
The cumulus oophorus or discus proligerus is a cluster of epithelial cells that surround the oocyte in the Graafian follicle.
Question 107. Assertion In Graafian follicles, the primary oocyte and the follicle cells may be regarded as sibling cells. Reason (R) Both arise from the same parent cell, the oogonium, by mitotic divisions.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Primary oocyte and follicle cells both arises from the oogonium by the mitosis cell division. Hence, they (Graafian follicle and primary oocytes) are regarded as the sibling cells.
Question 108. During multiplication phase of oogenesis,
- Oogonium grows and form primary oocyte
- Germinal cells undergo mitosis to form oogonia
- Primary oocyte undergoes maturation
- Secondary oocyte undergoes maturation
Answer: 2. Germinal cells undergo mitosis to form oogonia
During multiplication phase of oogenesis, germinal cells undergo mitosis to produce oogonia or egg mother cells. No more oogonia are formed after birth.
Question 109. During maturation phase of oogenesis,
- Primary oocyte undergoes meiotic division-I and shows equal nuclear division and unequal cytoplasmic division
- Haploid secondary oocyte undergo meiotic division-2 to form ovum
- Both 1 and 2
- Primary oocyte undergoes meiotic division-I which shows equal nuclear and cytoplasmic division
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
In maturation phase, the primary oocyte undergoes meiotic division-I and shows equal nuclear division and unequal cytoplasmic division. It results in the formation of haploid secondary oocyte and first polar body. The former further undergo meiotic division-2 to form ovum.
Question 110. Egg is liberated from ovary at the
- Secondary oocyte stage
- Primary oocyte stage
- Oogonial stage
- Mature ovum stage
Answer: 1. Secondary oocyte stage
Egg is liberated from the ovary (ovulation) at secondary oocyte stage when meiosis-2 is arrested in secondary oocyte.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 111. Which of the following has haploid chromosomes?
- Oogonia
- Primary oocyte
- Secondary oocyte
- Primary spermatocyte
Answer: 3. Secondary oocyte
Secondary oocyte has haploid set of chromosomes. Oogonia is a diploid mother cell. Primary oocyte is a diploid cell formed from oogonia Primary spermatocyte is formed from diploid spermatogonium.
Question 112. Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups.
- Primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, spermatid
- Secondary spermatocyte, first polar body, ovum
- Spermatogonia, primary spermatocyte, spermatid
- Primay spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, second polar body
Answer: 2. Secondary spermatocyte, first polar body, ovum
- Out of the given options, the haploid cells are secondary spermatocyte, first polar body, ovum secondary oocyte, spermatid and second polar body.
- The diploid cells are primary oocyte and primary spermatocyte. Thus, option is correct.
Question 113. Mature human ovum is
- Haploid
- Non-motile
- Spherical in shape
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Mature human ovum is generally haploid spherical, non-motile gamete with yolky cytoplasm and enclosed by one or more egg envelopes.
Question 114. Human egg is
- Alecithal
- Mesolecithal
- Telolecithal
- Centrolecithal
Answer: 1. Alecithal
Human egg is alecithal. In it, the amount of yolk is almost nill than the amount of cytoplasm.
Question 115. Select the correct statement.
- The nucleus of human ovum contains a prominent nucleolus
- The large nucleus of ovum is called germinal vesicle
- Primary egg membranes are secreted by ovum itself
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the given statements are correct.
Question 116. As compared to the sperm, the egg contains more
- Chromosomes
- Centrioles
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
An egg is larger than the sperm cell. Unlike a sperm cell, the egg contains a lot of cytoplasm however, the number of chromosomes is same.
Egg do not contain centriole and mitochondria.
Question 117. The size of the egg chiefly depends upon the
- Size of the animal
- Amount of yolk reserved in it
- Amount of food taken by the mother
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Amount of yolk reserved in it
The size of the egg chiefly depends upon the amount of yolk reserved in it.
Question 118. The side of ovum with nucleus and polar body is called
- Animal pole
- Vegetal pole
- Cumulus oophorus
- Ootid
Answer: 1. Animal pole
The animal pole is the point on the surface of an egg that is diametrically opposite to the vegetal pole and usually marks the most active part of the protoplasm or the part containing least yolk. This side contains nucleus and the polar body.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 119. The plasma membrane of human ovum is covered with
- Theca externa
- Corona radiata
- Zona pellucida
- Theca interna
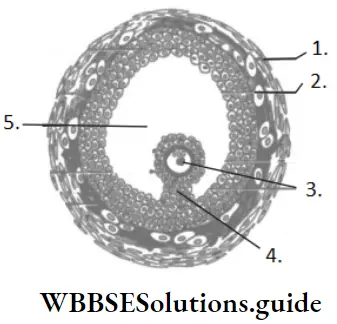
Answer: 3. Zona pellucida
The zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of mammalian ovum.
Question 120. The membrane that appear in mammalian egg immediately after ovulation is
- Chorion
- Zona pellucida
- Corona radiata
- Vitelline membrane
Answer: 3. Corona radiata
Just after ovulation, the layer formed around the ovum is called corona radiata. It is formed by the granulosa cells of cumulus oophorus. It probably increases the likelihood that the ovum will be picked up in the uterine tube.
Question 121. The layer of cells immediately surrounding the ovum, but outside the zona pellucida is called
- Corona radiata
- Membrana granulosa
- Theca interna
- Germinal epithelium
Answer: 1. Corona radiata
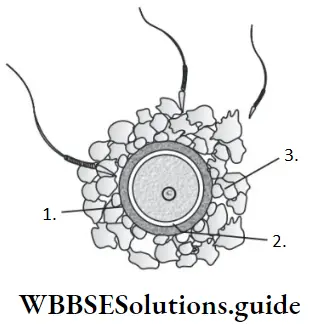
The ovum possesses three coverings, inner plasma membrane, middle glycoprotein zona pellucida and outer cellular corona radiata with
radially elongated scattered cells held in mucopolysaccharide.
Question 122. Corona radiata is made up of
- Vitelline membrane
- Zona pellucida around the oocyte
- Follicular cells around the oocyte
- Membrana granulosa
Answer: 3. Follicular cells around the oocyte
spermatogenesis takes place in
The corona radiata is the innermost layer of the cells of the cumulus oophorus. It is made up of follicular cells around the oocyte.
Question 123. Select the incorrect statement.
- Zona pellucida is secreted by the ovum itself
- Corona radiata is a primary egg membrane
- Hyaluronic acid which binds corona radiata cells is a mucopolysaccharide
- Zona pellucida is extracellular material that is composed of various glycoproteins
Answer: 2. Corona radiata is a primary egg membrane
Statement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as Corona radiata is a secondary egg membrane because it is not secreted by ovum itself. Zona pellucida is the primary egg membrane. Rest all options are correct.
Question 124. Consider the following statements.
- Corona radiata is non-cellular layer.
- Zona pellucida is a cellular layer.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 4. Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect and can be corrected as The corona radiata is cellular layer that forms around a developing oocyte
in the ovary and remain with it upon ovulation, whereas the zona pellucida is a non-cellular layer.
Question 125. There is no ………… in ovum.
- Nucleus
- Germinal vesicle
- Centriole
- Corona radiata
Answer: 3. Centriole
- There is no centriole in ovum or secondary oocyte because during fertilisation, sperm’s centrioles are recurited in zygote.
- Since, only one pair is needed in one cell, ovum looses its centriole along with second polar body during second maturation division.
Question 126. Layers of an ovum from outside to inside is
- Corona radiata, zona pellucida and vitelline membrane
- Zona pellucida, corona radiata and vitelline membrane
- Vitelline membrane, zona pellucida and corona radiata
- Zona pellucida, vitelline membrane and corona radiata
Answer: 1. Corona radiata, zona pellucida and vitelline membrane
Layers of an ovum from outside to inside are as follows Corona radiata → Zona pellucida → Vitelline membrane
NEET Gametogenesis Topic-wise Questions with Explanations
Question 127. Which activity occurs first during the development of an egg?
- Induction
- Differential growth
- Polarity
- Gastrulation
Answer: 3. Polarity
Polarity occurs during the first stage of egg development. The side of ovum which forms the extrudes polar bodies is called animal pole and the opposite side is called vegetal pole.
Question 128. A small space between ooplasm and vitelline membrane is called
- Lacunae
- Perivitelline space
- Intercellular space
- Stroma
Answer: 2. Perivitelline space
The perivitelline space is the space between the ooplasm and the vitelline membrane of an oocyte or fertilised ovum.
Question 129. Assertion Ovum retains most of the contents of the primary oocyte and is much larger than a spermatozoan. Reason (R) Ovum needs energy to go about in search of a spermatozoan for fertilisation.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Reason can be corrected as 3. A is true, but R is false. Reason can be corrected as
Question 130. Cumulus proligerus cells are found around
- Oviducal funnel
- Corpus albicans
- Ovum
- Ovary
Answer: 3. Ovum
Cumulus oophorus (discus proligerus) is a solid mass of follicular cells that surround the developing ovum. It projects into the antrum of the Graafian follicle.
Question 131. In human ovum, nucleus is eccentric called
- Ooplasm
- Germinal vesicle
- Oocyte
- Germinal layer
Answer: 2. Germinal vesicle.
In human ovum, the eccentric nucleus is known as germinal vesicle.
Question 132. An atretic follicle is
- Also known as corpus albicans
- Fails to mature and degenerates
- Released from the ovum
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Fails to mature and degenerates
An atretic follicle fails to mature and thus degenerates. It occurs continually throughout a women’s life as she is born with millions of follicles, but ovulate only around 400 times in her lifetime.
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 133. One of the minute cell which separates from the animal egg during maturation is known as
- Primary spermatogonia
- Secondary oogonia
- Primary oogonia
- Polar body
Answer: 4. Polar body
- During maturation phase, polar bodies are extruded. The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis-I producing two haploid cells (n), the larger one is secondary oocyte and the smaller one is a first polar body.
- Meiosis-2 of secondary oocyte further results in the formation of functional egg or ovum and a second polar body.
Question 134. Polar bodies formed during the formation of oocytes are
- Smaller cells formed due to unequal meiosis
- Structures which break off as bud during oogenesis
- Structures formed during spermatogenesis
- Daughter cells formed after mitosis
Answer: 1. Smaller cells formed due to unequal meiosis
- A polar body is a small haploid cell that is formed concomitantly as an egg cell during oogenesis. It generally does not have the ability to be fertilised.
- When certain diploid cells in animals undergo cytokinesis after meiosis to produce egg cells, they divide unevenly.
Question 135. Assertion One polar body is released by the oocyte during ovulation. Reason (R) When the oocyte is in Fallopian tube, it is in second metaphase state.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation A
- Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- The secondary oocyte that is released during ovulation has completed first meiotic division and released one polar body.
- The secondary oocyte get arrested at second metaphase stage of meiosis-2. This division resumes when the sperm penetrate it.
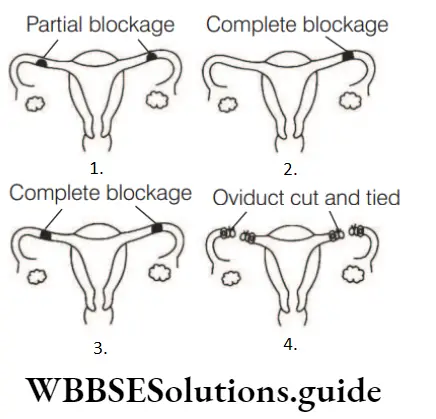
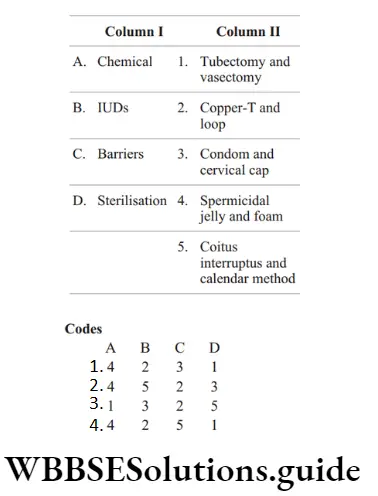
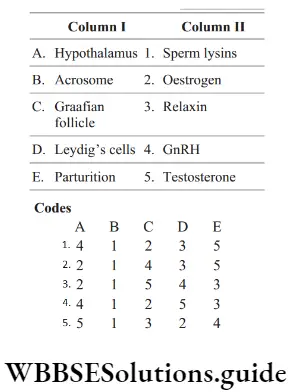
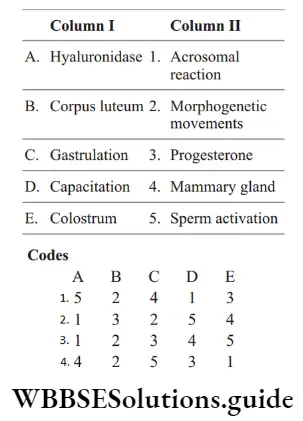
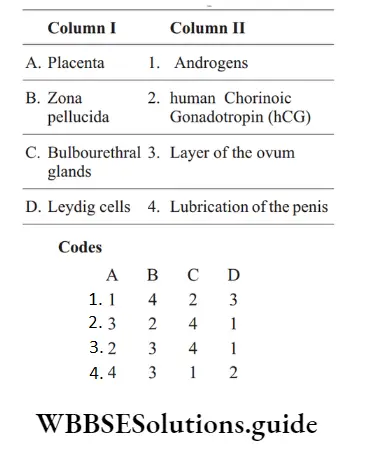
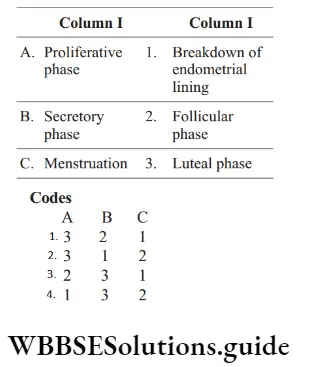
Question 136. Match the following columns.

Answer: 2. A–4, B–2, C–3, D–1
Question 137. What is the role of polar bodies during oogenesis?
- Polar bodies ensure that the ovum contain the most cytoplasm
- They rid the body of defective sets of chromosomes, leaving the ‘good’ set within the ovum
- They are merely the byproduct of meiosis and serve no function
- They prevent the development of most sets of multiple births
Answer: 1. Polar bodies ensure that the ovum contain the most cytoplasm
Polar bodies ensure that the ovum contains most of the cytoplasm during oogenesis due to the unequal division.
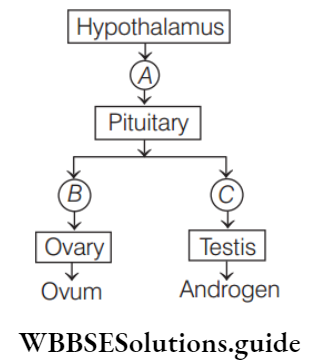
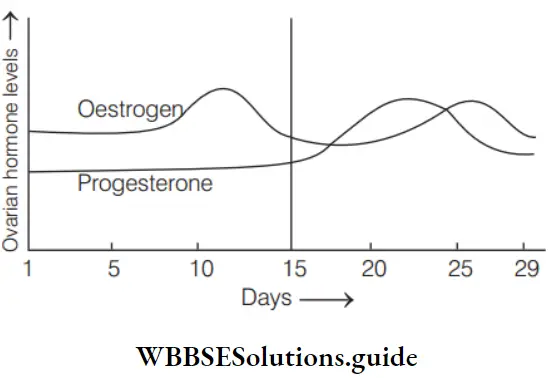
Question 138. Given below is a flowchart showing influence of hormones on gametogenesis in human females. Identify A, B, C and D form the options given below.

- A–GnRH, B–Oestrogen and progesterone, C–Ovary, D–FSH and LH
- A–GnRH, B–Progesterone and LH, C–Ovary, D–Oestrogen and FSH
- A–GnRH, B–FSH and estrogen, C–Ovary, D–LH and progesterone
- A–GnRH, B–FSH and LH, C–Ovary, D–Oestrogen and progesterone
Answer: 4. A–GnRH, B–FSH and LH, C–Ovary, D–Oestrogen and progesterone.
Question 139. 1st polar body is formed at which stage of oogenesis?
- 1st meiosis
- 2nd mitosis
- 1st mitosis
- Differentiation
Answer: 1. 1st meiosis
spermatogenesis takes place in
Question 140. The seminal plasma along with the sperm is called
- Spermatid
- Spermatozoa
- Semen
- All of these
Answer: 3. Semen
Question 141. The number of sperms produced from 24 secondary spermatocytes will be
- 24
- 48
- 12
- 96
Answer: 2. 48 sperms will be produced from 24 secondary spermatocytes.
Question 142. What do you mean by the term spermioteleosis ?
- Conversion of spermatids to sperm
- Conversion of spermatogonium to spermatid
- Conversion of spermatid to spermatogonium
- Conversion of primary spermatocyte to secondary spermatocyte
Answer: 1. Conversion of spermatids to sperm
Question 143. One million oocytes and one million secondary spermatocytes will form
- 2 million ova and 2 million sperms
- 1 million ova and 1 million sperms
- 2 million ova and I million sperms
- 1 million ova and 2 million sperms
Answer: 4. 1 million ova and 2 million sperm