Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Chemical Coordination Questions And Answers
Question 1. Why are the hormones considered as chemical messengers?
Answer:
Hormones are considered as chemical messengers because—
- Hormones are peptides or steroidal substances, secreted in very small quantities, from the endocrine glands.
- They are carried by blood to more than one target cell.
- They act as messengers i.e., transmit information and affect different physiological and metabolic processes of the target cells.
Question 2. Justify the same hormone being named vasopressin as well as ADH.
Answer: The ADH hormone has two names due to its different physiological functions.
They are as follows—
It helps to constrict the muscles of the blood vessels, mainly that of blood capillaries and arteries.
So, it increases the blood pressure. Hence, it has been rightly named vasopressin (vaso: blood vessel; pressin: pressure).
It increases water reabsorption in the DCT as well as the collecting duct, thereby releasing less amount of concentrated urine. This phenomenon is known as antidiuresis. Thus, it has been rightly named an Antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
Chemical coordination and integration questions and answers PDF
Question 3. Write down the characteristics of the neurohypophysis. or Name the hormone secreted by this region.
Answer:
The characteristics of the neurohypophysis
There are no endocrine cells present in the pars nervosa region of the neurohypophysis. The axons of the neurosecretory cells present in the adenohypophysis remain scattered over the neurohypophysis region.
Two neurohormones are secreted by the neurohypophysis region—ADH or antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
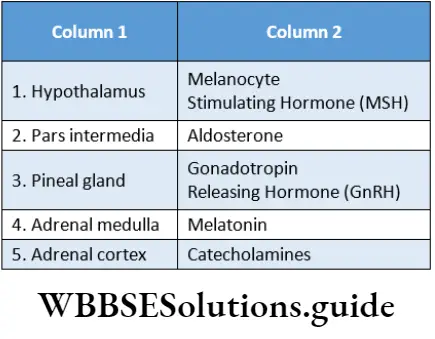
Question 4. What is the full form of HIOMT? or Which gland shows the presence of HIOMT?or Name one hormone secreted by this gland.
Answer:
HIOMT:
The full form of HIOMT is hydoxy-indolO-methyl transferase. It is a type of enzyme.
The pineal gland shows the presence of HIOMT.
Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland.
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 5. Mention the roles of the emergency hormone.
Answer:
The roles of the emergency hormone (adrenaline) are as follows—
- Pupillary dilation (varies the size of the pupil), piloerection, sweating, etc.
- Increase in rate of heartbeat, strength of heart contraction, rate of breathing, etc.
- Stimulates glycogenolysis and breaks down glycogen into glucose, thereby increasing its level in the blood.
Question 6. Which part of the body secretes aldosterone? Or why is it considered a mineralocorticoid? Mention the functions of aldosterone.
Answer:
Aldosterone is synthesized and secreted by the adrenal cortex.
It is considered a mineralocorticoid because it helps in the metabolism of the mineral salts within the body.
The functions of aldosterone are—
It regulates Na+ and water reabsorption in – the renal tubule.
It stimulates the removal of K+ and phosphate ions. Through this mechanism, it maintains electrolyte balance, volume of body fluids, osmotic pressure, and blood pressure.

Question 7. Name the endocrine regions of the pancreas. What percentage of the pancreas of a healthy human being, comprises the endocrine region?
Answer: Islets of Langerhans constitute the endocrine region of the pancreas.
About 1-2% of the pancreas of a healthy human being, comprises the endocrine region.
Question 8. Which hormone is known as the ‘hyperglycemia hormone’? Why? Mention its source.
Answer: Glucagon hormone is known as the ’hyperglycemia hormone’, because it stimulates the process of glycogenolysis within the hepatocytes. It helps to break down glycogen into glucose, thereby increasing its concentration in the blood.
Glucagon is synthesized and secreted by a-cells of the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas.
Question 9. What are the primary symptoms of the disease, diabetes mellitus?
Answer: The primary symptoms of diabetes mellitus are—
- Increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood of the patient, i.e, hyperglycemia.
- Glucosuria, i.e., release of glucose through urine.
- Release of excess ketone bodies through the urine, i.e., ketonuria, in case of hyperglycemia, that extends for a long period.
Question 10. Which cells secrete testosterone? Why is it known as ‘androgen’?
Answer:
- Interstitial cells or Leydig cells secrete testosterone.
- Testosterone is a sex steroid hormone, that carries out the following functions—
- It regulates the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics.
- It stimulates the production of sperm (spermatogenesis).
- It controls the male libido (desire for sexual activity). For carrying out these functions, it is known as an ‘androgen’ (Greek word ‘andro’, meaning masculine). Androgens are the male sex hormones.
NEET chemical coordination and integration important questions with answers
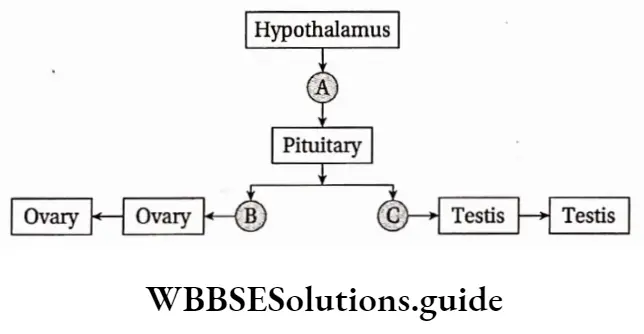
Question 11. Which hormone synthesises the placenta, in pregnant women? From where is it synthesized and secreted?
Answer: Progesterone is the hormone responsible for the synthesis of the placenta, in pregnant women. It is synthesized and secreted by the corpus luteum present in the ovaries of women. Some amount of progesterone is also secreted by the adrenal cortex (zona reticularis).
Question 12. Which hormone is known as ‘calorigenic hormone’? Why?
Answer: Triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4), secreted by thyroid follicles of the thyroid gland, are known as calorigenic hormones. They stimulate the oxidation of carbohydrates thereby releasing large amounts of energy. They increase BMR. Hence, they are known as ‘calorigenic hormones’.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Chemical Coordination Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Name the gland that requires iodine to produce most of its hormones.
Answer: Thyroid gland.
Question 2. Define hormone.
Answer:
Hormones
Hormones are biochemical substances synthesised and secreted by endocrine glands, which are transported by circulator)7 system to their target organs where they regulate various physiological processes.
Question 3. Name the two hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary.
Answer: ADH and oxytocin.
Question 4. What stimulates the release of epinephrine?
Answer: Stress, intense emotions like anger, fear, etc., stimulate the release of epinephrine.
Question 5. What is a mixed gland?
Answer:
Mixed gland
A mixed gland is a gland which has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
Question 6. Where are the adrenal glands located?
Answer: The adrenal glands are located at tire apex of the kidneys.
Class 11 biology chemical coordination and integration Q&A
Question 7. What are the hormones secreted by the adrenal medulla?
Answer: Epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Question 8. What are tropic hormones?
Answer:
Tropic hormones
Hormones that control the secretion of hormones from other glands are called tropic hormones.
Question 9. Mention one important function of the pineal gland.
Answer: An important function of pineal gland is to secrete melatonin. Melanin regulates body’s circadian rhythm.
Question 10. What is neurohypophysis?
Answer:
Neurohypophysis
Neurohypophysis is the posterior pituitary gland. It principally consists of the pars nervosa (neural lobe of hypophysis) and the infundibulum (stalk-like structure that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus).
Question 11. Name one steroid hormone in human and mention its source.
Answer: Aldosterone is a steroid hormone. Its source is the adrenal cortex.
Question 12. Which hormone is called stress hormone?
Answer: Cortisol.
Question 13. Write the full names of TSH and ADH.
Answer: TSH—Thyroid stimulating hormone, ADHAntidiuretic hormone.
Question 14. Which type of cell is stimulated by calcitonin?
Answer: Osteoblast cells
Question 15. Where are chromaffin cells located?
Answer:
Location of chromaffin cells
Adrenal medulla. terms italicised.
Question 16. Name that hormone that aids in sodium conservation and potassium excretion.
Answer: Aldosterone.
Question 17. Define the term erythropoiesis. Also name the hormone that stimulates it.
Answer: Erythropoiesis is the process of formation of RBC. The hormone erythropoietin, secreted by juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney, stimulate the process.
Question 18. Name the cells that produce testosterone.
Answer: Leydigcell.
Question 19. What is second messenger?
Answer:
Second messenger
Diffusible small signalling molecules, synthesisedin the target cells by those hormones or enzymes which are unable to enter the cells to bring about the biochemical changes, are known as second messengers.
Question 20. There are many endocrine glands in human body. Name the gland, which is absent in male and the one absent in female.
Answer: The two endocrine glands, ovary and testis are absent in male and female respectively.
Short answer questions on chemical coordination and integration
Question 21. Which of the two adrenocortical layers, zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis, lies outside enveloping the other?
Answer: Zona glomerulosa lies outer to zona reticularis.
Question 22. Name the only hormone secreted by pars intermedia of pituitary gland.
Answer: Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH).
Question 23. A patient was complaining of constant thirst, excessive passing of urine and low blood pressure. When the doctor checked the patient’s blood glucose and blood insulin level, the levels were normal or slightly low. The doctor diagnosed the condition as diabetes insipidus. To confirm his diagnosis, he decides to measure the concentration of a specific hormone in the patient’s blood. Which hormone does the doctor intend to measure?
Answer: ADH.