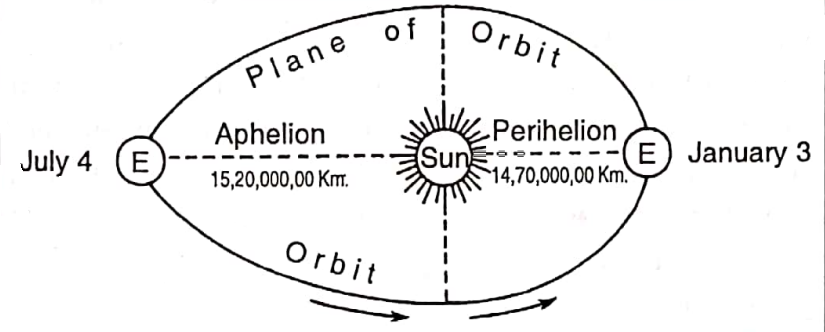
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earth’s Surface
The location of a place on the rotating earth is of vital importance. The most important aspect of Geography is to find out the location of a place on the earth’s surface. Because of the spherical shape of the earth, it is very difficult to fix the position of a point about the whole of the earth.
We know that the location or distance between two places on a flat surface is measured by a tape or rope in inch, foot mile etc. or cm, metre, km, etc. This is called ‘Linear distance’.
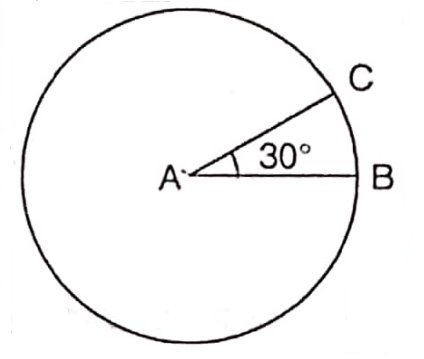
But the distance or location of a place on a spherical or curved surface is measured in seconds, minutes and degrees. This is called ‘Angular distance’.
“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 2 notes”
The distance between any two places on a curved earth’s surface is measured by the angle made by two straight lines that meet at the centre of the earth from the two places on the earth’s surface is called ‘Angular distance’.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes for Class 7 Middle Class Geography
So, the location of a place on the earth is determined by angular measurements. For e.g. Kolkata is located at 22°34′ north latitude and 88°24′ east longitude.
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earths Surface Determination Of The Location Of A Place On A Flat Or Plane Surface
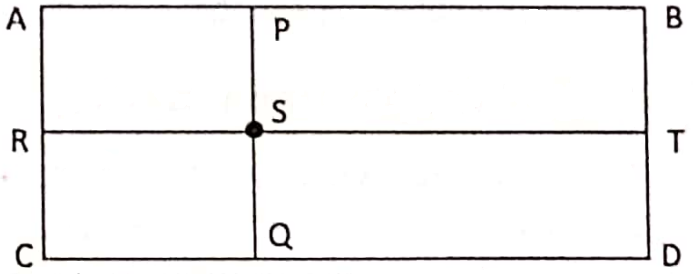
location of a student in the classroom can be marked by two reference lines namely the ‘rows from the teacher’s table and the number of seats from the entrance to the classroom.
Therefore to find out the location of student ‘S’ in the rectangular classroom ABCD, parallel lines are drawn from the sides of AB (Line of Teachers table), AC (Line of the entrance of the room) cl intersecting at ‘S’, ‘P’ i.e. R.T. and P.Q.
“class 7 social science geography “
Now the actual location of the student (S) in the classroom (ABCD rectangle) can be found by measuring the distance of ‘RS’ and ‘PS’.
Determination of the location of a place on a spherical or curved earth surface :
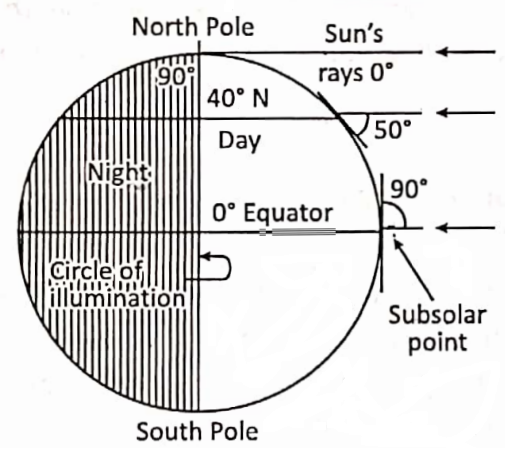
In order to locate each and every place on the earth’s surface correctly, a network of horizontal and vertical lines is drawn on the globe. This network of lines is called the ‘Earth Grid’.
The location of any place on the sphere is to be determined with the help of imaginary lines encircling the earth is an East-West and North-South direction.
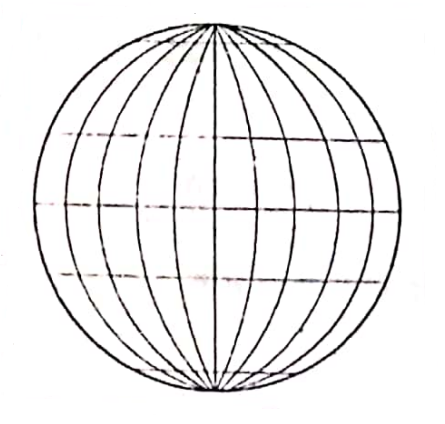
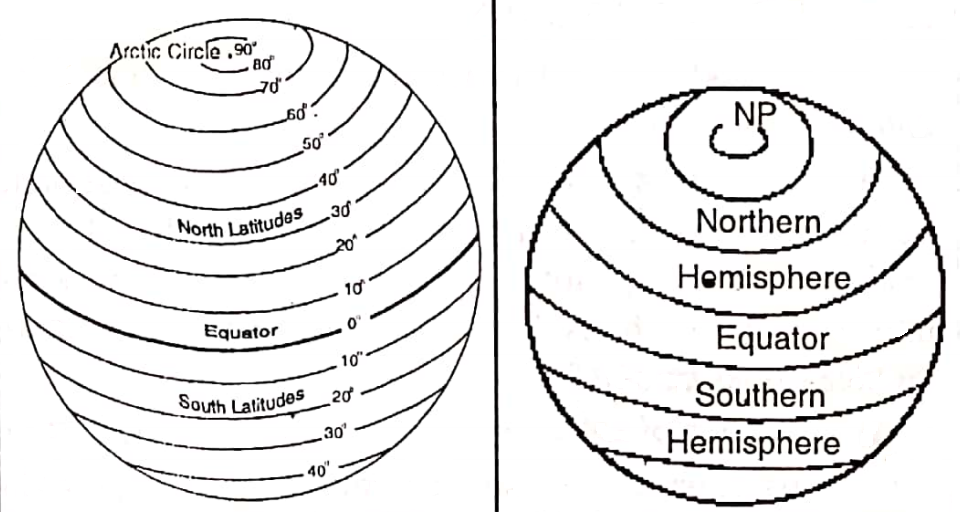
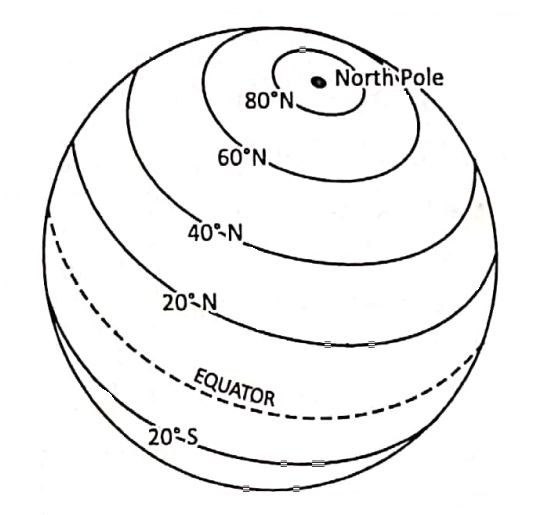
East-West Extended Lines Or Parallels Of Latitudes :
The imaginary East-West extended circles including the Equator and the two poles are known as parallels of Latitude. The parallels lying north of the Equator is know as the north parallels of latitude and the parallels south of the Equator as the south parallels of latitude.
The Equator :
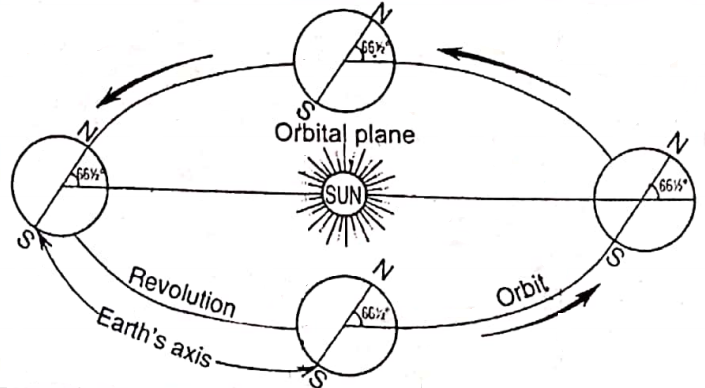
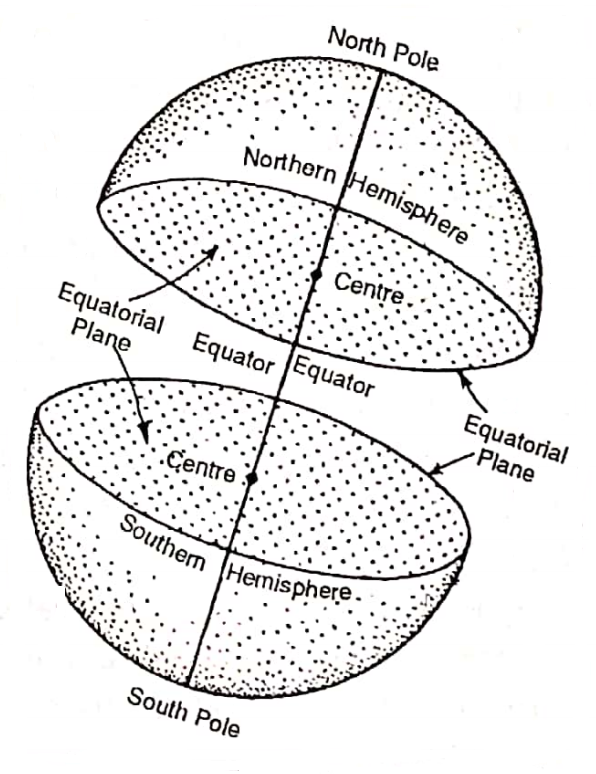
The Equator is an imaginary line on the globe passing through the midpoints between the North Pole and the South Pole. It is a circle whose centre is the centre of the globe. The Equator divides the globe into two hemispheres.
The hemisphere that lies north of the equator or that contains the North Pole is known as the Northern Hemisphere and the hemisphere south of the Equator or that contains the South Pole is the Southern Hemisphere. The word ‘hemisphere’ means half of a sphere or a globe.
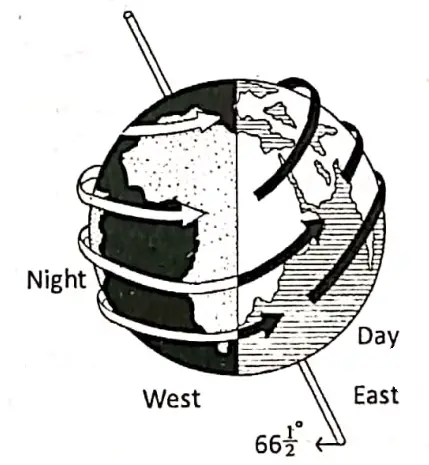
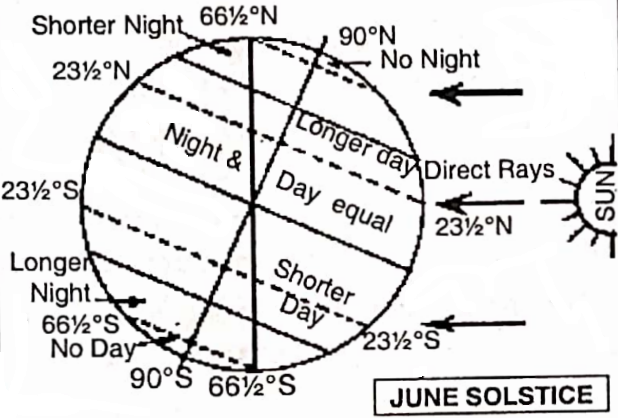
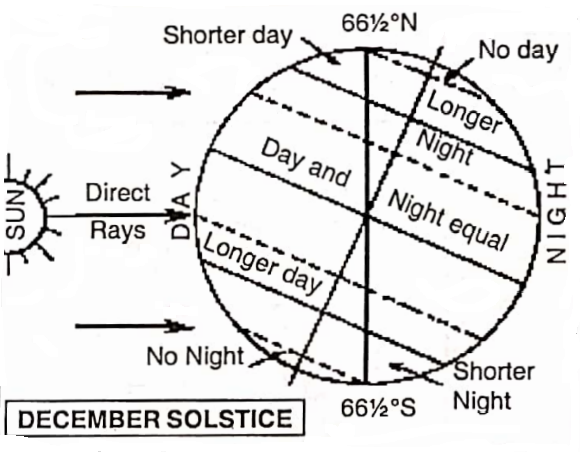
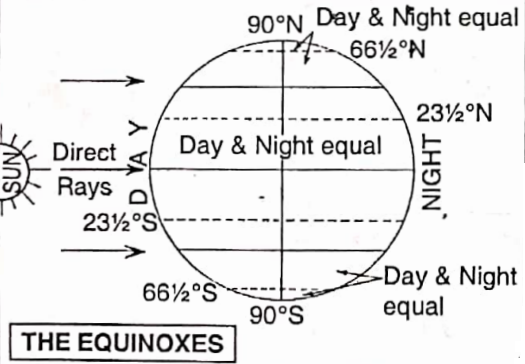
The Equator is also called the Great Circle because it is the greatest parallel and other parallels decrease in size gradually. Another name for the Equator is the Line of Equinox because throughout the year the equatorial region has equal lengths of day and night.
“determination of the position of a place on the earth’s surface WBBSE”
Importance Of The Equator :
1. The Equator divides the earth into two hemispheres. It helps to know about the position of a place is how much north or south on the earth’s surface.
2. The Equator also helps to find out the latitude of a place on the earth’s surface.

The Equatorial Plane :
The plane bounded by the Equator of the earth is known as the Equatorial plane. If the earth could be sliced into two halves all along the Equator, the Equatorial plane could be seen and the earth could be divided into two halves.
Latitude :
The latitude of a place on the earth is the angular distance of that place north or south of the Equator. If a line is drawn from any place to the north or south of the Equator to the centre of the earth, the angle formed by the line with the equatorial plane is the angular distance of that place.
This angular distance is the latitude of that place.
“exercise 2 solved questions on determination of position class 7”
Example :
The Latitude of Kolkata is 22°34′ north. The word ‘North’ ‘means Kolkata is located in the northern hemisphere and 22°34’ indicates the angle produced by a straight line joining Kolkata and the centre of the earth and the Equator drawn on the Equatorial plane.
Based on latitude, we also describe different regions of the earth as under.
Low Latitude: The region between the Equator (000 and 30°N or S.
Mid-latitude : The region between 30° and 60° N and S
High Latitudes: The region between 60° and 90° N and S. (Polar region)
Importance Of Latitudes :
1. It helps in the location of a place for latitudes and shows how a place is north and south of the Equator.
2. Latitudes are used to divide the earth into temperature belts. Thus the latitude of a place gives an idea about climate.
Parallels Of Latitude Or Line Of Latitude
On either side of the Equator east-west extending imagináry circles, lying parallel to each other are called Lines of Latitude or Parallels of Latitude.
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earths Surface Difference Between Latitude And Parallels Of Latitude
Latitude is the angular distance of any place north or south of the Equator. Parallels of Latitude means an imaginary line joining an infinite number of places having the same angular distance from the Equator. They are mainly extensive east-west trending circles.
Characteristics of Parallels of Latitude :
- Parallels of Latitudes are imaginary full circles on the earth, all parallel to the Equator. i.e. they always remain an equal distance apart.
- All parallels represent true east-west lines.
- Parallels intersect meridians. at right angles. This fact holds true for any place on the globe, except the two poles.
- All parallels except the Equator are smaller circles.
- The Equator is a Great Circle and the only parallel drawn from the earth’s centre.
- An infinite number of parallels may be drawn on the globe. Therefore, every point on the globe, except the North Pole or the South Pole lies on a parallel.
- Latitudes are of the same value in both the northern and southern hemispheres. But more than one latitude of the same value does not exist in one hemisphere.
- The value of latitudes is measured from the Equator (0°) northwards to the point of the North pole (90°N) and southwards to the South Pole (90°S).
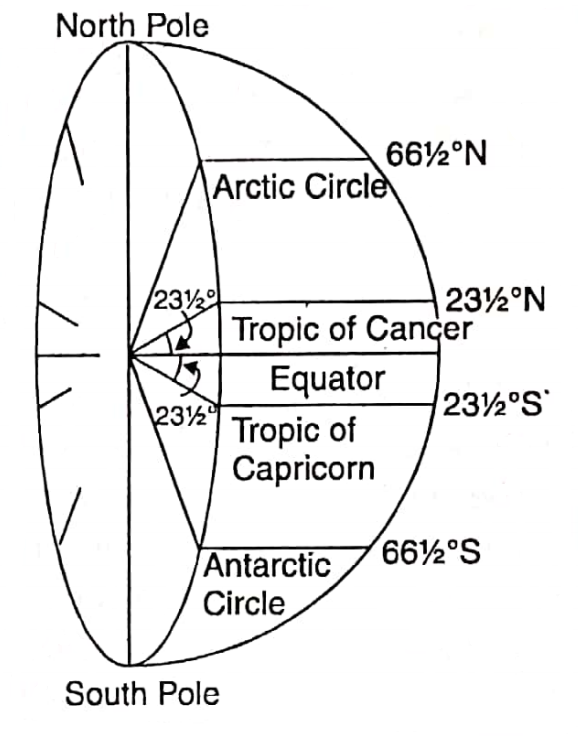
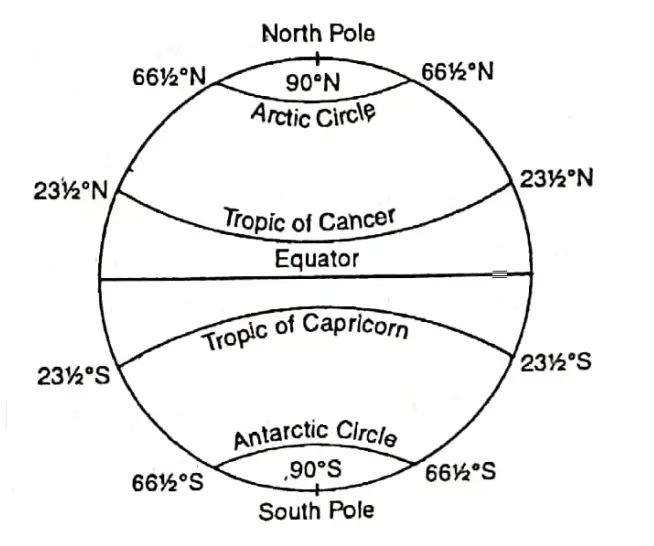
Important Parallels Of Latitude :
Important lines of Latitude and their distance from the Equator in degrees are given below.
The Equator = 0°
Tropic of cancer = 232 or 23°30′N, Tropic of Capricorn = 23°30’S.
Arctic Circle = 66°30′ N and Antarctic Circle = 66°30’S. North Pole 90°N, South Pole.= 90°S.
“what is terrarium class 7 “
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earths Surface North-South Extended Lines Or Meridians Of Longitude
Lines of longitude or Meridian of Longitude are imaginary lines joining places located at the same angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Prime Meridian :
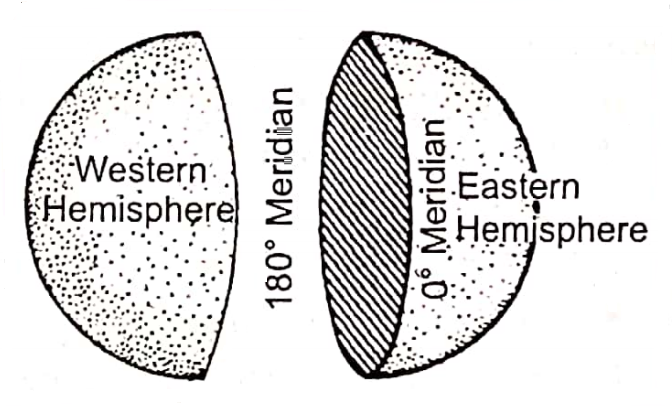
North-south extended semi- circular the particular imaginary line drawn along the Royal Observatory of Greenwich near London is called the Prime Meridian whose value is 0°. This is also known as Greenwich Meridian.
Importance Of Prime Meridian :
- The Prime. Meridian divides the earth into two equal halves or the eastern and western hemispheres.
- It helps us to know about the position of a place is how much east or west is on the earth’s surface.
- The local time of the prime meridian is known as Greenwich Mean Time or G.M.T. It is accepted all over the world as the standard time.
Longitude :
The longitude of a place on the earth is the angular distance of that place east or west of the Prime Meridian. The angle formed by the location of any place east or west of the Prime Meridian to the centre of the earth and the plane of the Prime Meridian is called the longitude.
Example :
The Longitude of Kolkata is 88°24′ east. The word ‘East’ means Kolkata is located in the eastern hemisphere and 88°24′ indicates the angular distance of Kolkata from the Prime Meridian.
Meridian Of Longitude :
A line of longitude passing from the North Pole to the South Pole and forming half of a Great Circle is called the Meridian of Longitude. From the Greenwich meridian (Prime Meridian), all other meridians are measured.
Difference between Longitude and Meridians of Longitude :
Longitude is the angular distance of a place east or west of the Prime Meridian. Meridians of longitude are imaginary semi or half-circles each of them joining all the places having the same longitudes either east or west of the Prime Meridian extending from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Features Of Meridians Of Longitudes :
- All lines of longitudes are semi-circular of equal length.
- All meridians of longitude are equal in length but not parallel to each other.
- The distance between two lines of longitude is maximum at the Equator and decreases gradually away from the Equator.
- The lines of longitudes converge at the two poles.
- Lines of longitudes are called ‘Meridians’ because all places along a longitude line have noon or midday at the same time.
- Value of the meridians of longitude increases from the Prime Meridian to the east and west up to 180°.
- The longitude of a meridian has a definite value.
- 180°E and 180°W meridian of longitude is one line.
- All meridians cut all latitudinal lines at right angles.
- All places on the same meridian have sunrise, noon and sunset at the same time.
Importance Of Meridians Of Longitude :
- The Meridians of longitudes show how a place is located to the east or west of the Prime Meridian.
- All places on the same longitude have sunrise, noon and sunset at the same time.
- It enables us to calculate time.
- With the help of meridians of longitudes the local time of a place is easily determined.
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earths Surface Relation Between Parallels Of Latitudes And Meridians Of Longitudes
- The Parallels of latitudes and meridians of longitude intersect at a right angle to each other.
- The meridians converge at both poles. This means the meridians together from the angle of 360° at each of the poles.
- The areas of the graticules demarcated by two adjacent parallels and two adjacent meridians diminishes gradually from the Equator to the poles.
Difference Between Parallels Of Latitude And Meridians Of Longitude :
| Parallels of Latitude | Meridians of Longitude |
| 1. The imaginary horizontal circular lines drawn by joining places having the same latitude are called Parallels of Latitude. | 1. The imaginary vertical semicircular lines drawn by joining places having the same longitude are called Meridian’ of longitude |
| 2. Parallels of latitude encircle the earth in an east-west direction. the earth. | 2. Meridians of longitude extend in a north-south direction on the earth. |
| 3. Each parallel is a complete circle. | 3. Each meridian is a semi or half-circle. |
| 4. Parallels of latitude are not equal in length. Their lengths decrease towards the poles. | 4. All meridians are of equal length. |
| 5. The linear distance between the parallels is equal to each other. | 5. The linear distance between the meridians decreases towards the poles. |
| 6. The parallel’s latitude is measured from the Equator. | 6. The Meridians of longitude are Measured From the Prime Meridian. |
| 7. These are divided into North and South parallels of latitude. | 7. These are divided into East and West meridians of longitude. |
| 8. In the same parallel at different places sunrise, noon and sunset occur at different times. | 8. All places on a particular meridian sunrise, noon and sunset occur at the same time. |
| 9. In the same parallel of latitude at different regions local time is different. Thus in determining the local time it has no role to play. | 9. In the same meridian of longitude has the same local time at all the regions along it. Thus, determining the local time has an important role. |
| 10. Parallels of latitude help in dividing the earth’s surface into heat belts or temperature zones. | 10. Meridians of longitude help in determining the time zones. |
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earths Surface Location Of A Place On The Earth’s Surface
On a spherical earth’s surface, the exact location of a place can be determined by latitude and longitude together.
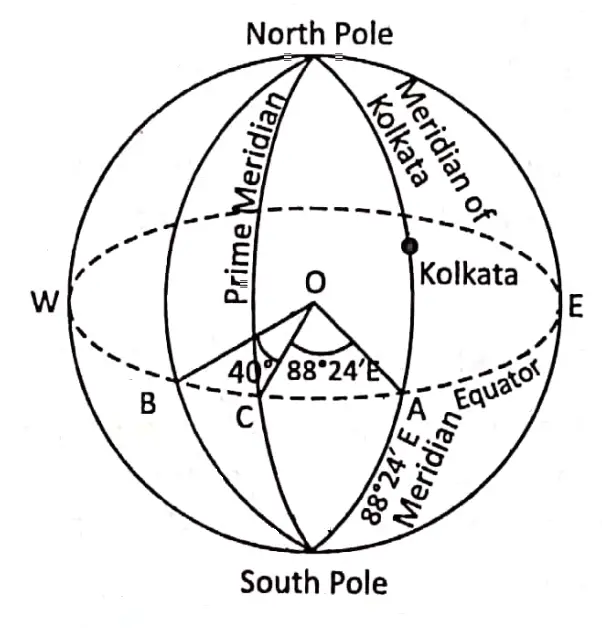
Example: The location of Kolkata is at 88°24′ east longitude and 22°34′ north latitude.
“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 2 important questions”
So, Kolkata is located at the point of intersection between 88°24′ east meridian of longitude and 22°34′ north parallel of latitude.
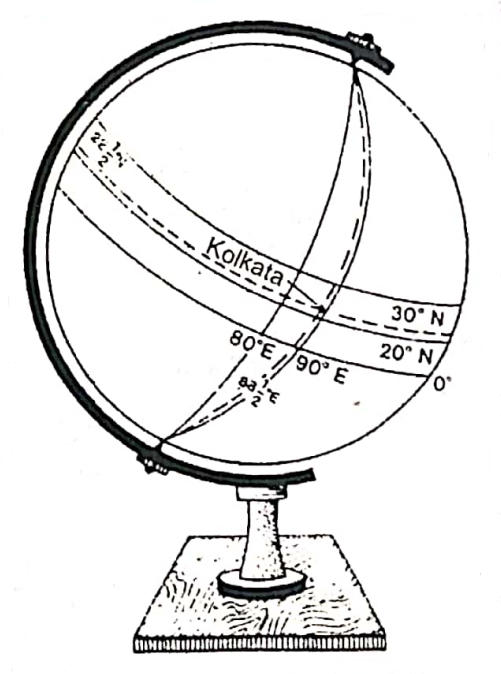
Location Of A Place On The Globe :
The Globe is a small-scale model of the Earth. So, the exact location of a place can be identified with the help of circles of parallel and half circles of meridian of longitudes drawn on the spherical Globe.
Kolkata is located at the point of intersection between 88°24′ (88) east meridian of longitude and 22°34′ (22) north parallel of latitude as shown on the diagram.
Chapter 2 Determination Of The Position Of A Place On The Earth’s SurfaceLocation Of A Place On The Wall Maps And Atlas
A map or Atlas is flat. Thus on a flat surface of paper of a map or an Atlas the circular shape of the latitudes cannot be drawn, they are shown as parallel straight lines Meridians of longitude also do not meet at the poles, they run in a north-south direction as straight lines.
Longitude And Time :
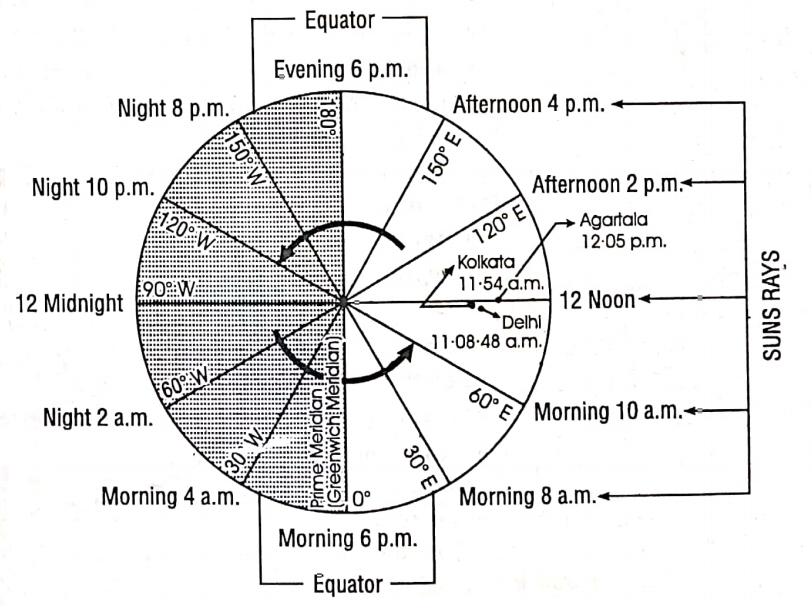
Longitude and time have a very close relationship. Longitudes help in the calculation of Noon and Local time. Each degree of longitude takes 4 minutes to rate. A difference of 1° of longitude has a time difference of 4 minutes. It must be remembered that a difference of 15° in longitudes causes a time of difference of 1 hour.
Local Time :
When a meridian comes in line with the centre of the sun local mid-day is said to have occurred at all places on the meridian. Fixing time on the basis of the local mid-day of a place is known as the local time of a place.
The for each degree o longitude local time varies by 4 minutes. This means that for cities like Delhi, London, New York etc. local time will differ from one point to another from place to place within a country or from country to country.
Standard Time :
In a country, local times of places at different longitudes differ from each other. If each place maintained its own time schedule based on its own local time much inconveniences would have been corrupted. To avoid such inconveniences the local time of a central place of a country or part of a country is generally selected for the time of the country (or selected region) as a whole. This time is known as a standard time of the country (or part of the country or a scheduled region).
“how to determine the location of a place on earth class 7”
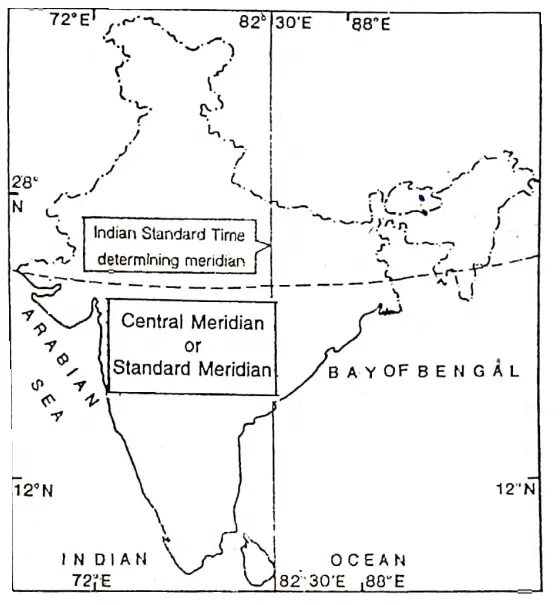
I. S. T.: The local time of 82°30′ E (Passing through near Allahabad) is selected as Indian Standard Time (I. S. T). I. S. T. is ahead of G.M.T by (5 hours 30 minutes) It is followed throughout the country.
G. M. T.: The local time of Greenwich (Prime Meridian or 0° meridian), is regarded as the standard time of the zone at 0° and this is called Greenwich Mean Time or G.M.T. Fig. 2.14: Meridian determining Indian Standard Time Astronomers call in universal times, and regarded Greenwich at the reference meridian for all calculation.
Time Zones: The surface of the earth has been divided into 24 time zones or as many hours in a day. The time from one zone to the next zone differs by one hour only.
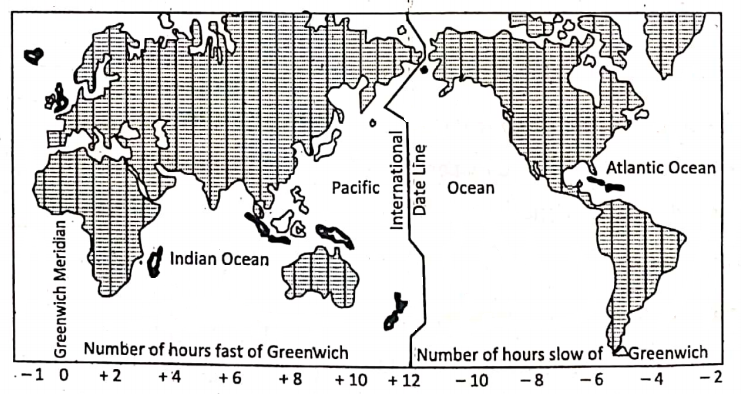
International Date Line: A line that roughly follows the 180° meridian, with some deviations to avoid land masses and groups of islands is called the International Date Line(I.D.L).
The date the Atlantic Ocean immediately off the line is one day earlier than to the West. This situation occurs because of the accumulated time change of one hour for each 15° of longitude West and East of the Greenwich Meridian (0°); i.e. 180° W of Greenwich is 12 hours slow but 180°E is 12 hours fast.
“latitude and longitude explanation WBBSE geography”
G.P.S. Or Global Positioning System :
Global positioning system or G.P.S. is a modern .technological system which helps to determine the latitude or longitude of a place on the earth. This system is performed by artificial satellites. This system is presently used in navigation, aviation and other modern transportation and communication systems.