Tissues Long Answer Questions
Directions: Give answer in four to five sentences.
Question 1.
1. Which type of epithelium would you expect to find in blood vessels or in the capillaries?
Answer: Simple squamous epithelium is found in the blood capillaries.
Read And Learn More: NEET Class 9 Biology Long Question And Answers
2. What is the site of diffusion of substances between the blood and tissues?
Answer: It promotes the diffusion of gases and other substances between the blood and tissues surrounding the capillaries
3. What type of epithelium would you expect to find in the ducts of the pancreas?
Answer: Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in the lining of the ducts of the pancreas. Simple cuboidal epithelium is adapted for watery secretion.
4. What type of epithelium would you expect to find lining the mouth?
Answer: Stratified squamous epithelium protects against abrasion in the mouth.
“tissues extra questions class 9 “
Question 2. What is the role of dendrite versus axon in neuron function?
Answer: In simple terms, the dendrite is the neuron extension that receives signals at synapses and the axon is the neuron extension that transmits signals to other neurons or muscle cells. Typically each neuron has multiple dendrites that radiate out from the cell body and only one axon that extends from the cell body.

Question 3. With the help of diagrams (if required) describe the various kinds of connective tissues.
Answer:
The connective tissues are office major types:
Areolar tissue: The areolar tissue (Loose connective tissue) is the most widely distributed connective tissue in the animal body. It consists of a transparent, jelly-like sticky matrix containing numerous fires and cells and abundant mucin.
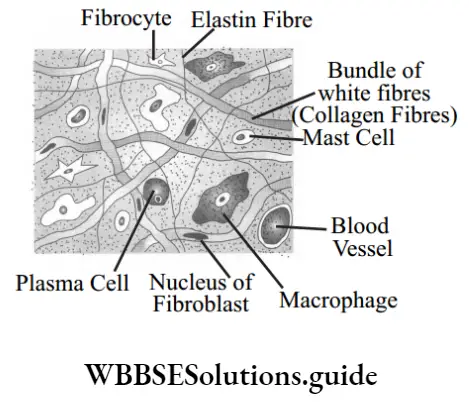
NEET Biology Tissues long questions and answers
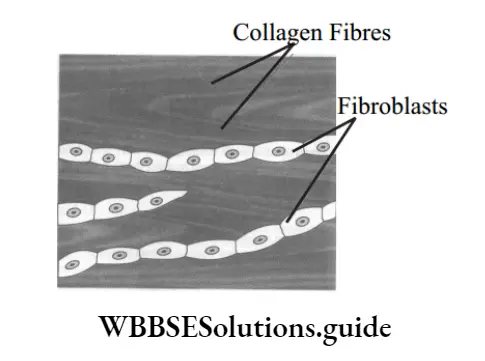
Dense regular connective tissue: It consists of ordered and densely packed fibers and cells. The fibers are loose and very elastic in nature. They are secreted by the surrounding connective tissue cells. This tissue is the principal component of tendons and ligaments.
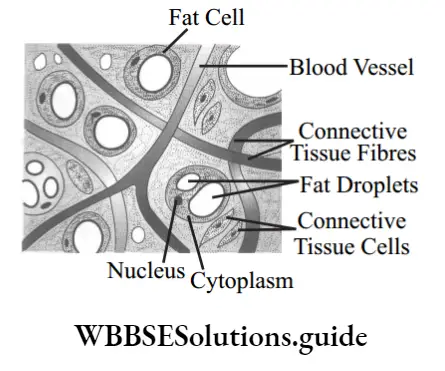
Adipose tissue: It is primarily a fat-storing tissue in which the matrix is packed with large, spherical or oval fat cells. The matrix also contains fibroblasts, macrophages, collagen fires, and elastic fires.
“class 9 biology chapter 2 tissue questions and answers “
Skeletal tissue: It forms the rigid skeleton that supports the vertebrate body, helps in locomotion and provides protection to many vital organs. Cartilage and bones are examples of skeletal tissues.
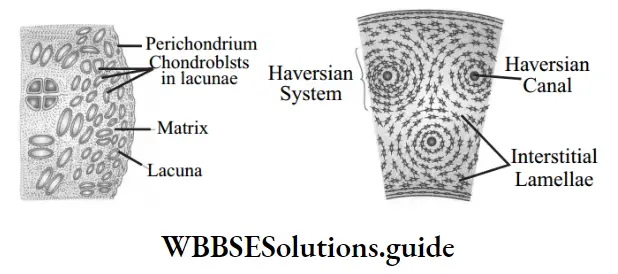
Important long questions from Tissues for NEET
Fluid tissue (Blood and lymph): Fluid tissue is also known as vascular tissue. It consists of the flown matrix in which free-floating cells are suspended. The matrix is devoid of fires, flows freely and is not secreted by the cells it contains. Fluid tissue includes blood and lymph.
Question 4. What is connective tissue? Explain tendons and ligaments.
Answer:
Connective tissues of animals serve the functions of binding and joining one tissue to another and form a protective sheath and pack material around the various organs separating them. They do not interfere with each other’s activities and carry materials from one part to another in the body and form a supporting framework of cartilage and bones for the body, etc.
Tendon: Tendons are cord-like, very tough, inelastic bundles of white collagen fires bound together by areolar tissue. The cells present in the tendons are elongated fibroblasts which lie in almost continuous rows here and there. The tendons connect the skeletal muscles with the bones.
Ligaments: Ligaments are cords formed by yellow elastic tissue in which many collagen fires are bound together by areolar tissue. The firoblasts are irregularly scattered. This tissue combines strength with great flexibility. The ligaments serve to bind the bones together. Both tendons and ligaments are examples of dense regular connective tissue
Tissues Class 9 long answer questions with solutions
Question 5. Give reasons for
1. Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole.
Answer: Meristematic cells are actively dividing cells hence they contain dense cytoplasm and large prominent nucleus. Since, they are not storage cells therefore lack vacuoles.
2. Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
Answer: The cells of sclerenchymatous tissues are thick-walled due to the deposition of lignin along the cell wall. they are lignifid, intercellular spaces are absent.
3. We get a crunchy and granular feeling when we chew pear fruit.
Answer: The pulp of pear fruit contains stone cells or grit cells. These are highly lignified and dead sclerenchymatous cells. Because of the presence of stone cells pear fruit gives a crunchy and granular feeling on chewing.
“class 9th tissues chapter “
4. Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
Answer: Collenchyma provides elasticity to the plant organs. Due to its peripheral position in stem it helps to the branches of a tree to move and bend freely in high wind velocity. Hence, it provides flexibility to the tree.
5. It is difficult to pull out the husk ofa coconut tree.
Answer: The husk of a coconut is made of sclerenchymatous tissue which provides protection and rigidity to it. The lignin presentin sclerenchyma fires actas cement, that is why it is diffiult to pull out the husk ofa coconut.
Question 6.
1. Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
Answer: Differences between meristematic and permanent tissue Meristematic tissue Permanent tissue
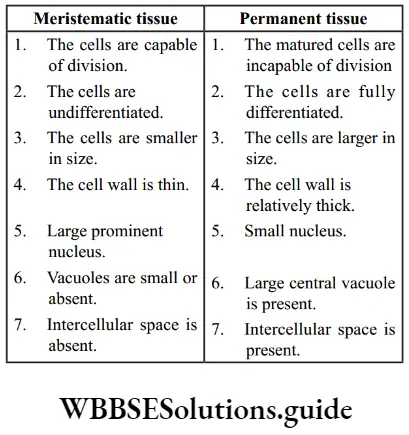
Types of plant tissues long answer questions NEET
2. Define the process of differentiation.
Answer: The process by which cells derived from meristematic tissues loose the ability to divide and acquires permanent shape, size and function to become permanent tissue is called differentiation.
3. Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
Simple tissue: Parenchyma/Collenchyma/sclerenchyma Complex tissue: Phloem/Xylem
Question 7. Explain the “Complex tissue” of plants.
Answer:
- Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these cells coordinate to perform common function are two types of complex tissues present in the plant. Xylem and Phloem are two types of complex tissues present in the plant. Both are conducting tissues and form a vascular bundle.
- Xylem consists of -Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem parenchyma and Xylem fires. Most of these cell are dead. These allow the water transportation, parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
- Phleom is made up of Sieve tubes, Companion cells, Phloem fires and phloem parenchyma. It helps in the transportation of food in both the directions from leaves to roots.
Difference between simple and complex tissues long questions
Question 8. Show the types of Animal tissues using flow chart.
Answer:
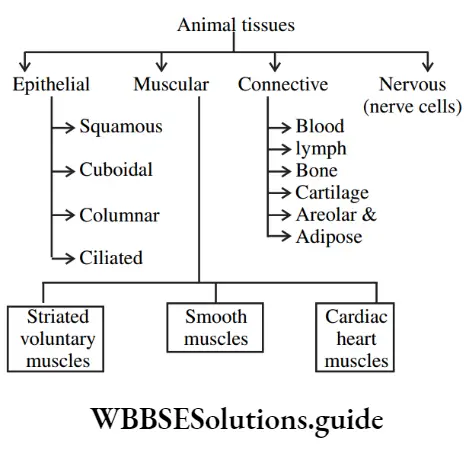
Question 9. Describe ‘epidermis’ in plants.
Answer:
- The Epidermis forms the outermost layer of plants present on entire outer surface of plant. It is made up of single cell layer. It protects all the internal parts of the plant.
- The epidermis secretes waxy, water-resistant layer on their outer surface.
- This helps in protection against loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion of parasitic fungi.
- In leaves epidermis consists of small pores called stomata. These pores helps in the transpiration and exchange of gases, like oxygen and carbondioxide for plants.
- The Epidermis helps in the water absorption in roots. In desert plants epidermis has a thick waxy coating of cutin acts as water proofig agent.
Animal tissues and their functions long answer questions NEET
Question 10. What is skeletal connective tissue? Give its functions.
Answer:
Skeletal connective tissue is that connective tissue in which the matrix is solid and the living cells occur inside flied filed spaces called lacunae. It is of two types, cartilage and bone.
“which tissue makes the plant hard and stiff “
Functions of Skeletal connective tissue:
- Endoskeleton: It forms the internal supporting framework of the animal body.
- Protection: The tissue protects the vital organs like brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, etc.
- Joints: The tissue forms joints which allow for growth and movement of body parts.
- Muscles: It provides a surface for attachement to muscles.
- Blood Cells: They form inside red marrow of bones.
- Minerals: Bony skeleton stores minerals, some of which are withdrawn by the body in case of emergency.
